Indy Racing on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
American open-wheel car racing, generally and commonly known as Indy car racing, is a category of professional automobile racing in the

 The national championship was sanctioned by the Contest Board of the
The national championship was sanctioned by the Contest Board of the
 Prior to the start of the 2008 season, the CCWS Board authorized bankruptcy and Champ Car was absorbed into the IRL, creating a unified series for the national championship for the first time since 1978. The unified series competed under the name
Prior to the start of the 2008 season, the CCWS Board authorized bankruptcy and Champ Car was absorbed into the IRL, creating a unified series for the national championship for the first time since 1978. The unified series competed under the name
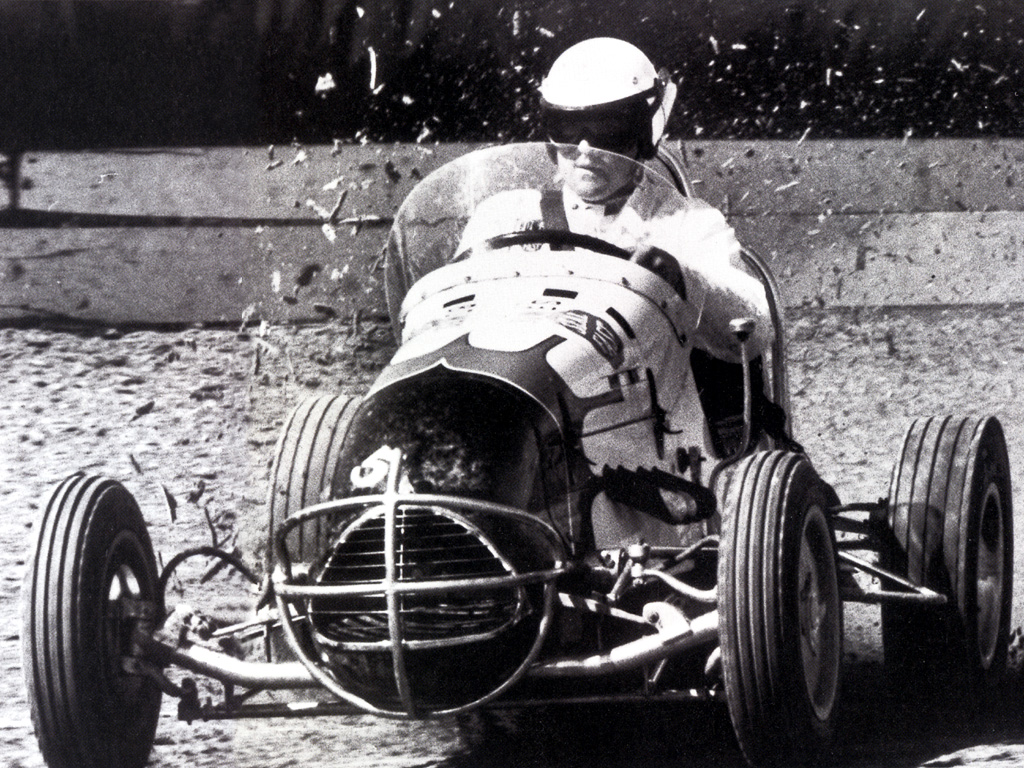
 The race cars participating in national championship events have been referred to by various names. Early nomenclature was to call the machines "Championship Cars", which was later shortened to "Champ Cars". This was a simple, yet descriptive term, which positively identified the machines as those that competed for the National ''Championship''. The term "Big Cars" saw some limited use; a term that identified the machines as larger and faster than junior formulae such as sprints and midgets. That term disappeared from use and was instead largely used for Sprint cars. However, some promoters continued to advertise their championship events with the term "Big Cars", which leads to some inconsistencies. In the post-
The race cars participating in national championship events have been referred to by various names. Early nomenclature was to call the machines "Championship Cars", which was later shortened to "Champ Cars". This was a simple, yet descriptive term, which positively identified the machines as those that competed for the National ''Championship''. The term "Big Cars" saw some limited use; a term that identified the machines as larger and faster than junior formulae such as sprints and midgets. That term disappeared from use and was instead largely used for Sprint cars. However, some promoters continued to advertise their championship events with the term "Big Cars", which leads to some inconsistencies. In the post-
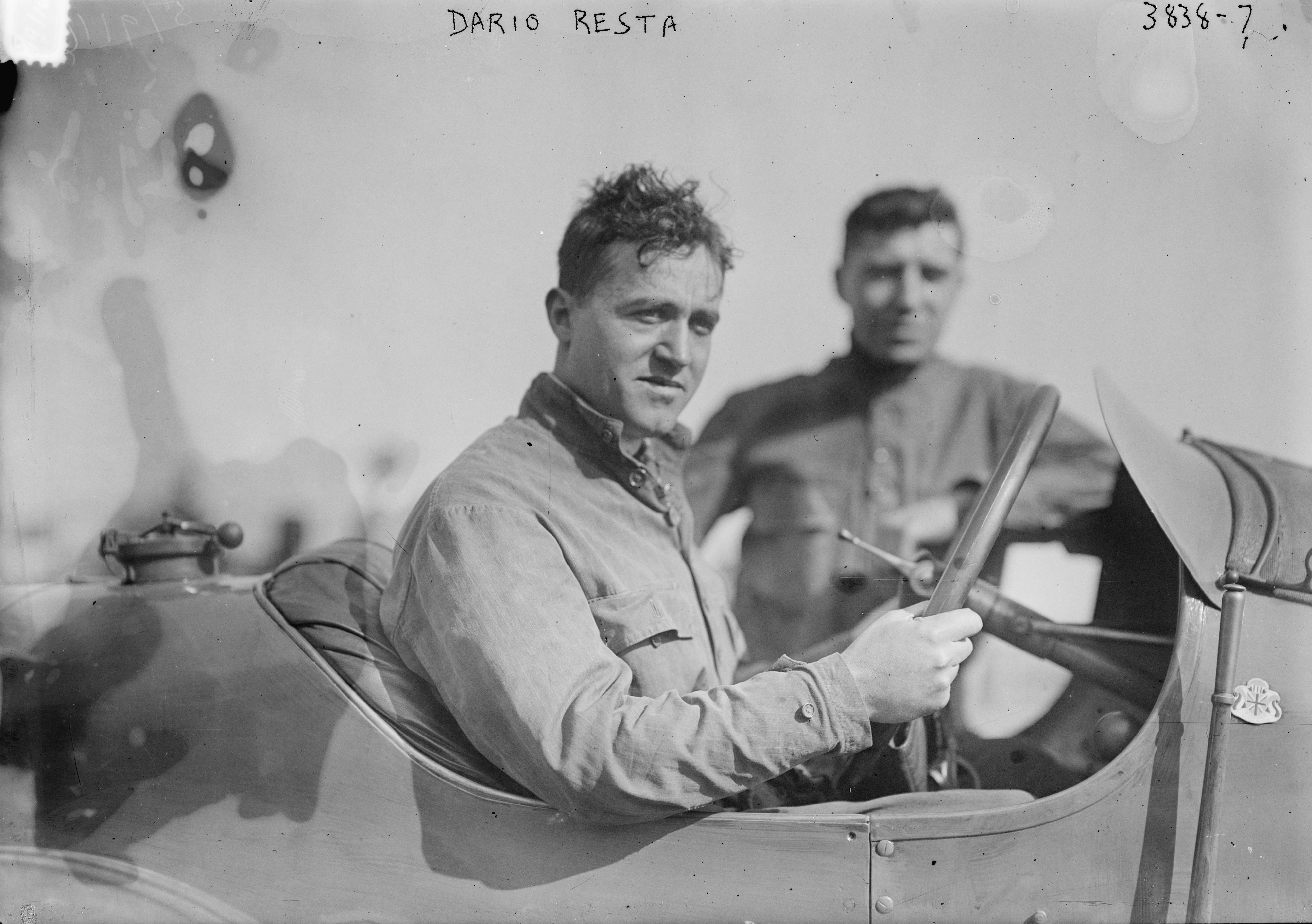
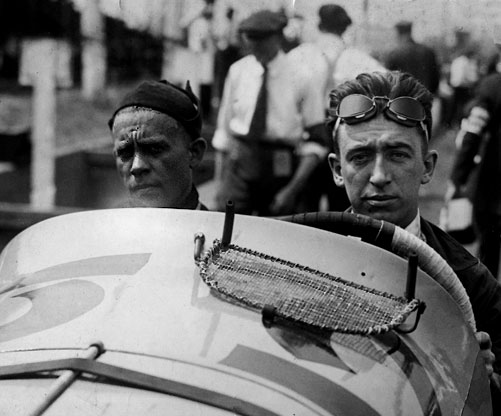





 : From 1979 to 1995 the Indianapolis 500 and the national championship were sanctioned by separate organizations, USAC and
: From 1979 to 1995 the Indianapolis 500 and the national championship were sanctioned by separate organizations, USAC and
ChampCarStats.com
complete AAA, USAC, CART, CCWS and IRL race results. {{Indy Racing League Seasons Open wheel racing Auto racing series in the United States
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
. As of 2025
So far, the year has seen the continuation of major armed conflicts, including the Russian invasion of Ukraine, the Sudanese civil war (2023–present), Sudanese civil war, and the Gaza war. Internal crises in Bangladesh post-resignation v ...
, the top-level American open-wheel racing championship is sanctioned by IndyCar
IndyCar, LLC (stylized as INDYCAR), is an auto racing sanctioning body for American open-wheel car racing headquartered in Indianapolis, Indiana. The organization sanctions two racing series: the premier IndyCar Series with the Indianapolis ...
and is known as the IndyCar Series
The IndyCar Series, officially known as the NTT IndyCar Series for sponsorship reasons, is the highest class of American open-wheel car racing in the United States, which has been conducted under the auspices of various sanctioning bodies sinc ...
. Competitive events for professional-level, open-wheel race cars have been conducted under the auspices of various sanctioning bodies, and traces it roots as far back as 1902. A season-long, points-based, ''National Championship'' of drivers has been officially recognized in 1905, 1916, and each year since 1920 (except for a hiatus during WWII
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
). As such, for many years, this discipline of motorsports was known as Championship car racing (or Champ car racing for short). That name has fallen from use, and the term ''Indy car'' racing (derived from the Indy 500) has become the preferred moniker.
The machines, typically referred to as "Indy cars", are a formula
In science, a formula is a concise way of expressing information symbolically, as in a mathematical formula or a ''chemical formula''. The informal use of the term ''formula'' in science refers to the general construct of a relationship betwe ...
of single-seat, open cockpit, open-wheel, purpose-built race cars. They compete on a variety of circuits, including ovals, road courses
Road racing is a North American term to describe motorsport racing held on a paved road surface. The races can be held on a race track, closed circuit—generally, a purpose-built racing facility—or on a street circuit that uses temporarily c ...
, street circuit
A street circuit is a motorsport race track, racing circuit composed of temporarily closed-off public roads of a city, town or village, used in motor racing, motor races. Airport Runway, runways and Taxiway, taxiways are also sometimes part of ...
s, and combined road courses. The most famous and most important event of the season is the Indianapolis 500
The Indianapolis 500, formally known as the Indianapolis 500-Mile Race, and commonly shortened to Indy 500, is an annual automobile race held at the Indianapolis Motor Speedway in Speedway, Indiana, United States, an enclave suburb of Indian ...
, held at the Indianapolis Motor Speedway
The Indianapolis Motor Speedway is a motor racing circuit located in Speedway, Indiana, United States, an enclave suburb of Indianapolis, Indiana. It is the home of the Indianapolis 500 and the Brickyard 400, and and formerly the home of the U ...
on Memorial Day
Memorial Day (originally known as Decoration Day) is a federal holiday in the United States for mourning the U.S. military personnel who died while serving in the United States Armed Forces. It is observed on the last Monday of May.
It i ...
weekend in late May. Over the decades, Indy cars have been generally similar to those in Formula One
Formula One (F1) is the highest class of worldwide racing for open-wheel single-seater formula Auto racing, racing cars sanctioned by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA). The FIA Formula One World Championship has been one ...
, though there are important differences. Though the IndyCar Series
The IndyCar Series, officially known as the NTT IndyCar Series for sponsorship reasons, is the highest class of American open-wheel car racing in the United States, which has been conducted under the auspices of various sanctioning bodies sinc ...
is American-based, international races have occasionally been held, in such places as Canada, Mexico, Brazil, Japan, Australia, as well as Europe.
This form of racing experienced considerable growth and popularity in the decades after World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
. The " Golden Era" of the front-engined roadsters was followed by a decade of innovation
Innovation is the practical implementation of ideas that result in the introduction of new goods or service (economics), services or improvement in offering goods or services. ISO TC 279 in the standard ISO 56000:2020 defines innovation as "a n ...
and transition in the 1960s. By the late-1960s and early-1970s, the cars had rapidly evolved to rear-engined, formula-style machines. Speeds climbed on the superspeedways to over , while international participation also increased. The sport saw much success, exposure, and popularity particularly during the 1980s–1990s under the sanctioning of Championship Auto Racing Teams
Championship Auto Racing Teams (CART) was a Governing body, sanctioning body for American open-wheel car racing that operated from 1979 until dissolving after the 2003 CART season, 2003 season. CART was founded in 1979 by team owners formerly ...
(CART). Organizational disputes in 1979
Events
January
* January 1
** United Nations Secretary-General Kurt Waldheim heralds the start of the ''International Year of the Child''. Many musicians donate to the ''Music for UNICEF Concert'' fund, among them ABBA, who write the song ...
and 1996
1996 was designated as:
* International Year for the Eradication of Poverty
Events January
* January 8 – A Zairean cargo plane crashes into a crowded market in the center of the capital city of the Democratic Republic of the Congo ...
split participants and the fanbase among two separate competing series. The sport was re-unified in 2008
2008 was designated as:
*International Year of Languages
*International Year of Planet Earth
*International Year of the Potato
*International Year of Sanitation
The Great Recession, a worldwide recession which began in 2007, continued throu ...
, and in late 2019, IndyCar and the Indianapolis Motor Speedway
The Indianapolis Motor Speedway is a motor racing circuit located in Speedway, Indiana, United States, an enclave suburb of Indianapolis, Indiana. It is the home of the Indianapolis 500 and the Brickyard 400, and and formerly the home of the U ...
were bought by Roger Penske
Roger Searle Penske (born February 20, 1937), also known as "the Captain", is an American auto racing team owner, businessman, and former professional driver. Penske is the owner of Team Penske, the Indianapolis Motor Speedway, IndyCar, and ...
and Penske Entertainment.
Sanctioning bodies
AAA (1902–1955)

 The national championship was sanctioned by the Contest Board of the
The national championship was sanctioned by the Contest Board of the American Automobile Association
American Automobile Association (AAA) is a federation of motor clubs throughout North America. AAA is a privately held not-for-profit national member association and service organization with over 60 million members in the United States and Cana ...
(AAA). The AAA first sanctioned automobile motorsports events in 1902. At first it used the rules of the Automobile Club of America (ACA), but it formed its own rules in 1903. It introduced the first track season championship for racing cars in 1905. Barney Oldfield
Berna Eli "Barney" Oldfield (January 29, 1878 – October 4, 1946) was a pioneer American racing driver. His name was "synonymous with speed in the first two decades of the 20th century". He was the winner of the inaugural List of American ope ...
was the first champion. No official season championship was recognized from 1906 to 1915, however, many races were held. Official records regard 1916 as the next contested championship season. Years later, retroactive titles were named back to 1902. These ''post factum'' seasons (1902–1904, 1906–1915, and 1917–1919) are considered unofficial and revisionist history by accredited historians.
Racing did not cease in the United States during WWI, but the official national championship was suspended. The Indianapolis 500
The Indianapolis 500, formally known as the Indianapolis 500-Mile Race, and commonly shortened to Indy 500, is an annual automobile race held at the Indianapolis Motor Speedway in Speedway, Indiana, United States, an enclave suburb of Indian ...
itself was voluntarily suspended for 1917–1918 due to the war. In 1920, the championship officially resumed, and despite the difficult economic climate that would later follow, ran continuously throughout the Depression. Shortly after Pearl Harbor
Pearl Harbor is an American lagoon harbor on the island of Oahu, Hawaii, west of Honolulu. It was often visited by the naval fleet of the United States, before it was acquired from the Hawaiian Kingdom by the U.S. with the signing of the Reci ...
, all auto racing was suspended during World War II. From 1942 to 1945 no events were contested, banned by the U.S. government primarily on account of rationing
Rationing is the controlled distribution (marketing), distribution of scarcity, scarce resources, goods, services, or an artificial restriction of demand. Rationing controls the size of the ration, which is one's allowed portion of the resourc ...
. Racing resumed in full in 1946. The 1946 season is unique, in that it included six Champ Car events, and 71 " Big Car" races, as organizers were initially unsure about the availability of cars and participation.
AAA ceased participation in auto racing at the end of the 1955 season. It cited a series of high-profile fatal accidents, namely Bill Vukovich during the 1955 Indianapolis 500, and the 1955 Le Mans disaster.
Through 1922 and again from 1930 to 1937, it was commonplace for the cars to be two-seaters, as opposed to the aforementioned standard single-seat form. The driver would be accompanied by a riding mechanic (or ''"mechanician"'').
USAC (1956–1978)
The national championship was taken over by theUnited States Auto Club
The United States Auto Club (USAC) is one of the sanctioning bodies of auto racing in the United States. From 1956 to 1979, USAC sanctioned the List of USAC Championship Car seasons, United States National Championship, and from 1956 to 1997 the ...
(USAC), a new sanctioning body formed by the then-owner of the Indianapolis Motor Speedway
The Indianapolis Motor Speedway is a motor racing circuit located in Speedway, Indiana, United States, an enclave suburb of Indianapolis, Indiana. It is the home of the Indianapolis 500 and the Brickyard 400, and and formerly the home of the U ...
, Tony Hulman. Championship racing continued to grow in popularity in a stabilized environment for over two decades, with the two traditional disciplines of paved oval tracks and dirt oval tracks. During the 1950s, front-engined "roadsters" became the dominant cars on the paved oval tracks, while "upright" Champ Dirt Cars continued to dominate on dirt tracks. In the 1960s, drivers and team owners with road racing backgrounds, both American and foreign, began creeping into the series and the paved oval track cars evolved from front-engine " roadsters" to rear-engine formula-style racers. Technology, speed, and expense climbed at a rapid rate. The schedule continued to be dominated by oval tracks, but a few road course races were added to assuage the newcomers. Dirt tracks were dropped from the national championship after 1970.
During the 1970s, the increasing costs began to drive some of the traditional USAC car owners out of the sport. The dominant teams became Penske, Patrick, Gurney, and McLaren, all run by people with road racing backgrounds. There was a growing dissent between these teams and USAC management. Events outside Indianapolis were suffering from low attendance, and poor promotion. The Indy 500 was televised on a same day tape delayed basis on ABC, however, most of the other races had little or no coverage on television.
Towards the end of the decade, the growing dissent prompted several car owners to consider creating a new sanctioning body to conduct the races. Meanwhile, two events had a concomitant effect on the situation. Tony Hulman, president of the Indianapolis Motor Speedway and founder of USAC, died in the fall of 1977. A few months later, eight key USAC officials were killed in a plane crash. By the end of 1978, the owners had broken away and founded Championship Auto Racing Teams (CART) to wrest control of Championship racing away from USAC.
CART & USAC (1979–1981): First open-wheel "split"
Championship Auto Racing Teams
Championship Auto Racing Teams (CART) was a Governing body, sanctioning body for American open-wheel car racing that operated from 1979 until dissolving after the 2003 CART season, 2003 season. CART was founded in 1979 by team owners formerly ...
(CART) was formed by most of the existing team owners, with some initial assistance from the SCCA (in order to be recognized by ACCUS). Therefore, there were two national championships run each by USAC and CART. The Indianapolis 500 remained under USAC sanction. The top teams allied to CART, and the CART championship quickly became the more prestigious national championship. USAC ran a "rump" 1979 season, with few big name drivers — the only exception being A. J. Foyt. In 1979, USAC denied several of the entries from the CART teams at the 1979 Indianapolis 500. The controversy saw a court injunction during the month, which allowed the CART-affiliated entrants to participate.
In 1980 USAC and CART jointly formed the Championship Racing League (CRL) to jointly run the national championship, but IMS management disliked the idea. USAC pulled out of the CRL arrangement in July. CART continued with the schedule for the remainder of the season. Both CART and USAC awarded separate national championship titles that year, and Johnny Rutherford happened to win both.
In 1981–1982, the Indianapolis 500 remained sanctioned by USAC. The preeminent national championship was now the one being sanctioned by CART. The Indy 500 field would consist largely of CART teams, as well as numerous independent, "Indy-only" teams. Indianapolis was not included as a points-paying round of the CART national championship. In addition, by that time USAC had designated Indianapolis an "invitational" race, offering entries only to invited teams. That moved in part to prevent the uproar over denied entries which occurred in 1979. One further race in 1981 was run by USAC at Pocono. This race was not supported by many CART teams, and featured a mixed field filled out by converted dirt track cars. USAC soon stopped sanctioning championship races outside the Indianapolis 500.
CART & USAC (1982–1995)
Stability returned and the national championship was now run by CART full-time. The Indianapolis 500 was sanctioned singly by USAC, but points were paid towards the CART season championship. The cars and engines used in the CART races and USAC-sanctioned Indy 500 were the same, with only relatively minor rules differences. The Indy 500 field would consist of the CART regulars, and numerous one-off ("Indy only") entries. On occasion, some of the "Indy only" entries also elected to participate in the Michigan 500 and Pocono 500 (both sanctioned by CART) given the increased stature and exposure of those two events. One of the more noticeable rule differences by USAC was allowing " stock block" engines a higher level ofturbocharger
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (also known as a turbo or a turbosupercharger) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake air, forcing more air into th ...
boost. While most full-time CART-based teams utilized their V-8 quadcam engines at Indy, some of the smaller and "Indy only" teams elected to run stock block engines at Indy, attracted by the boost rules.
USAC's Gold Crown Championship continued, settling into an unusual June through May schedule calendar. This provided that the Indianapolis 500 would be the final race of the respective season. However, between the 1984–85 season and the 1994–95 season (its final season), the USAC Gold Crown Championship only had one points-paying race: the Indianapolis 500
The Indianapolis 500, formally known as the Indianapolis 500-Mile Race, and commonly shortened to Indy 500, is an annual automobile race held at the Indianapolis Motor Speedway in Speedway, Indiana, United States, an enclave suburb of Indian ...
. As a result, during that timespan, the winner of the Indy 500 would win that year's USAC Gold Crown Championship by default.
CART & IRL (1996–2003): Second open-wheel "split"
In 1994, Tony Hulman's grandson,Tony George
Anton Hulman "Tony" George (born December 30, 1959) is the former Chairman, President, and CEO of the Indianapolis Motor Speedway and Hulman & Company, serving from 1989 to 2009. He was also formerly on the Board of Directors of both entities. ...
, president of the Indianapolis Motor Speedway, founded the Indy Racing League
IndyCar, LLC (stylized as INDYCAR), is an auto racing Governing body, sanctioning body for American open-wheel car racing headquartered in Indianapolis, Indiana. The organization sanctions two Auto racing, racing series: the premier IndyCar Serie ...
(IRL), to begin competition in 1996. It would exist as a separate championship, and leveraged the fame of the Indianapolis 500, which was placed as its centerpiece. After the IRL announced that 25 teams that competed in IRL races would get automatic qualifications to the race, making it impossible for the majority of the CART field to make the race, CART teams boycotted the 1996 Indy 500. It was the beginning of the second open-wheel "split". Initially, USAC sanctioned the IRL, however after officiating controversies in 1997 at Indianapolis and Texas
Texas ( , ; or ) is the most populous U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the we ...
, the USAC was replaced by the IRL's in-house officiating.
CART, which had been licensing the trademarked "IndyCar" name for several seasons, subsequently entered into a legal battle with the Indianapolis Motor Speedway (the trademark owner) over the use of the moniker. Eventually a settlement was reached in which CART gave up use of the name, but the IRL in turn could not use it until 2003. CART rebranded themselves with the CART name, and began referring to their machines as Champ Cars.
CART's existing national championship remained dominant after the split for some time, initially retaining the top drivers, teams, and sponsors. However, in 2000, CART teams began to return to the Indy 500, eventually defecting permanently to the IRL. For 2003, it lost title sponsor FedEx
FedEx Corporation, originally known as Federal Express Corporation, is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate holding company specializing in Package delivery, transportation, e-commerce, and ...
and engine providers Honda
commonly known as just Honda, is a Japanese multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate automotive manufacturer headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan.
Founded in October 1946 by Soichiro Honda, Honda has bee ...
and Toyota
is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational Automotive industry, automotive manufacturer headquartered in Toyota City, Aichi, Japan. It was founded by Kiichiro Toyoda and incorporated on August 28, 1937. Toyota is the List of manuf ...
to the IRL.
IRL IndyCar Series & Champ Car World Series (2004–2007)
After steadily losing teams and drivers, sponsors, and manufacturers, and after a series of major financial setbacks, CART filed for bankruptcy in 2003. The assets were purchased by a consortium called Open Wheel Racing Series (OWRS) in 2004 and the series was renamed the Champ Car Open Wheel Racing Series, later renaming it to theChamp Car World Series
Champ Car World Series (CCWS) was the series sanctioned by Open-Wheel Racing Series Inc., a sanctioning body for American open-wheel car racing that operated from 2004 to 2008. It was the successor to Championship Auto Racing Teams (CART), ...
. However, the sanctioning body continued to be plagued by financial difficulties, In 2007, CCWS's presenting sponsors Bridgestone
is a Japanese multinational manufacturing company founded in 1931 by Shojiro Ishibashi (18891976) in the city of Kurume, Fukuoka Prefecture, Fukuoka, Japan. The name Bridgestone comes from a calque translation and transposition of (), meaning ...
and Ford Motor Company
Ford Motor Company (commonly known as Ford) is an American multinational corporation, multinational automobile manufacturer headquartered in Dearborn, Michigan, United States. It was founded by Henry Ford and incorporated on June 16, 1903. T ...
withdrew.
During this time, the IRL was now operating under the moniker IndyCar Series, and slowly beginning to establish itself as the more preeminent national championship trail. In 2005, the IRL added road/street courses, and began picking up several former CART venues. And in 2007, Champ Car raced in Europe for the first time since 2003, with races in The Netherlands and Belgium and a planned round in Spain in 2008 before the unification.
IndyCar (2008–2019): Unification era
 Prior to the start of the 2008 season, the CCWS Board authorized bankruptcy and Champ Car was absorbed into the IRL, creating a unified series for the national championship for the first time since 1978. The unified series competed under the name
Prior to the start of the 2008 season, the CCWS Board authorized bankruptcy and Champ Car was absorbed into the IRL, creating a unified series for the national championship for the first time since 1978. The unified series competed under the name IndyCar Series
The IndyCar Series, officially known as the NTT IndyCar Series for sponsorship reasons, is the highest class of American open-wheel car racing in the United States, which has been conducted under the auspices of various sanctioning bodies sinc ...
. The two calendars were merged into one schedule, with the top Champ Car races such as Long Beach (which was a CCWS-sanctioned event with IRL points before being an official round of the IRL in 2009), Edmonton and Surfers Paradise in Australia surviving, later being replaced with an A1GP event in 2009 that never happened before the focus was changed to the Australian Supercars Championship in 2010. Some of the other races from the Champ Car schedule were dropped or put on hiatus for a few seasons. All historical record and property of CART/CCWS was assumed by the IRL.
Randy Bernard was announced as the new IRL CEO in February 2010. In 2011, the sanctioning body dropped the Indy Racing League name, becoming IndyCar to reflect the merged series. The new Dallara DW12 racecar was introduced for the 2012 season. Bernard was replaced by Mark Miles in 2012. The series operated under the name IZOD IndyCar Series from 2010 to 2013, then became known as the Verizon
Verizon Communications Inc. ( ), is an American telecommunications company headquartered in New York City. It is the world's second-largest telecommunications company by revenue and its mobile network is the largest wireless carrier in the ...
IndyCar Series from 2014 to 2018, and the NTT IndyCar Series since 2019.
IndyCar (2020–present): Penske era
In 2020, the IndyCar Series, as well as theIndianapolis Motor Speedway
The Indianapolis Motor Speedway is a motor racing circuit located in Speedway, Indiana, United States, an enclave suburb of Indianapolis, Indiana. It is the home of the Indianapolis 500 and the Brickyard 400, and and formerly the home of the U ...
and other holdings, was sold to Penske Entertainment Corp., a subsidiary of the Penske Corporation
Penske Corporation, Inc. () is an American diversified transportation services company based in Bloomfield Township, Oakland County, Michigan. Roger Penske is the founder and chairman of the privately held company, and Rob Kurnick is the pres ...
, owned by Roger Penske
Roger Searle Penske (born February 20, 1937), also known as "the Captain", is an American auto racing team owner, businessman, and former professional driver. Penske is the owner of Team Penske, the Indianapolis Motor Speedway, IndyCar, and ...
.
Car names and trademarks
 The race cars participating in national championship events have been referred to by various names. Early nomenclature was to call the machines "Championship Cars", which was later shortened to "Champ Cars". This was a simple, yet descriptive term, which positively identified the machines as those that competed for the National ''Championship''. The term "Big Cars" saw some limited use; a term that identified the machines as larger and faster than junior formulae such as sprints and midgets. That term disappeared from use and was instead largely used for Sprint cars. However, some promoters continued to advertise their championship events with the term "Big Cars", which leads to some inconsistencies. In the post-
The race cars participating in national championship events have been referred to by various names. Early nomenclature was to call the machines "Championship Cars", which was later shortened to "Champ Cars". This was a simple, yet descriptive term, which positively identified the machines as those that competed for the National ''Championship''. The term "Big Cars" saw some limited use; a term that identified the machines as larger and faster than junior formulae such as sprints and midgets. That term disappeared from use and was instead largely used for Sprint cars. However, some promoters continued to advertise their championship events with the term "Big Cars", which leads to some inconsistencies. In the post-World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
era, the term "Speedway Cars" saw limited use; a loosely descriptive term, distinguishing the machines as those driven at the Indianapolis Motor ''Speedway'' and other major ''speedways'', as opposed to those driven at smaller tracks, for instance. Nevertheless, the term "Championship/Champ Cars" prevailed as the preferred moniker.
In most years since the USAC era, the term "Indy cars" (after the Indy 500) has taken over as the preferred moniker. Apropos to that, when CART
A cart or dray (Australia and New Zealand) is a vehicle designed for transport, using two wheels and normally pulled by draught animals such as horses, donkeys, mules and oxen, or even smaller animals such as goats or large dogs.
A handcart ...
was founded in 1979, its acronym
An acronym is a type of abbreviation consisting of a phrase whose only pronounced elements are the initial letters or initial sounds of words inside that phrase. Acronyms are often spelled with the initial Letter (alphabet), letter of each wor ...
stood for ''Championship Auto Racing Teams'', a reflection of the historical use of the term "Championship Car". From its onset, CART started marketed itself with the two-word "Indy Car" term, advertising itself as the "CART Indy Car World Series".
Through the mid-1990s, the term "Indy car" referred to machines used to compete in events sanctioned by CART
A cart or dray (Australia and New Zealand) is a vehicle designed for transport, using two wheels and normally pulled by draught animals such as horses, donkeys, mules and oxen, or even smaller animals such as goats or large dogs.
A handcart ...
, as well as the machines competing in the Indianapolis 500
The Indianapolis 500, formally known as the Indianapolis 500-Mile Race, and commonly shortened to Indy 500, is an annual automobile race held at the Indianapolis Motor Speedway in Speedway, Indiana, United States, an enclave suburb of Indian ...
(sanctioned singly by USAC).
In 1992, the CamelCase term "IndyCar" was trademarked by IMS, Inc. It was licensed to CART from 1992 through 1996. After the inception of the Indy Racing League
IndyCar, LLC (stylized as INDYCAR), is an auto racing Governing body, sanctioning body for American open-wheel car racing headquartered in Indianapolis, Indiana. The organization sanctions two Auto racing, racing series: the premier IndyCar Serie ...
in 1996, the terms of the contract were voided after a lawsuit. As part of the settlement, the term was shelved by a six-year non-use agreement. Following the settlement, and the lack of connection to the Indy 500, CART decided to revert to the former term. It re-assumed the name CART
A cart or dray (Australia and New Zealand) is a vehicle designed for transport, using two wheels and normally pulled by draught animals such as horses, donkeys, mules and oxen, or even smaller animals such as goats or large dogs.
A handcart ...
, and the machines would be referred to again as "Champ cars". This continued after CART was reorganized into CCWS.
Complicating the situation resulting from the open-wheel split, CART/Champ Car races held outside the United States were still permitted to use the ''Indy'' moniker (e.g., Molson Indy Toronto and Lexmark Indy 300). Foreign venue promoters took advantage of the marketing power of the Indy 500 name for their events, even though the Champ Car series they were promoting no longer had any ties to that race. The exceptions created confusion, and Champ Car gradually phased out the usage to distance itself further from the IRL.
After the settlement expired in 2003, the term IndyCar was brought back. The Indy Racing League was re-branded as the "IRL IndyCar Series". The machines in the series were also referred to as "Indy cars". Despite the official acknowledgment, media and fans alike would continue to use the term "IRL" to describe the series, and to a lesser extent, "IRL cars" to describe the machines. Removing the "IRL" term from use proved difficult.
With two series (IndyCar
IndyCar, LLC (stylized as INDYCAR), is an auto racing sanctioning body for American open-wheel car racing headquartered in Indianapolis, Indiana. The organization sanctions two racing series: the premier IndyCar Series with the Indianapolis ...
and Champ Car
Champ Car World Series (CCWS) was the series sanctioned by Open-Wheel Racing Series Inc., a Governing body, sanctioning body for American open-wheel car racing that operated from 2004 to 2008. It was the successor to Championship Auto Racing T ...
) still competing in parallel, the umbrella terms "Open Wheel Cars" and "Open Wheel Racing" saw increased use during the split and post-split era. Many drivers had logged starts in both series at one time or another during their careers. The term was used as a way to combine a driver's career accomplishments without being series/machine specific. It also served to link the lineage of events, teams, drivers, etc., even as they switched sanctioning bodies.
In 2008, when Champ Car World Series
Champ Car World Series (CCWS) was the series sanctioned by Open-Wheel Racing Series Inc., a sanctioning body for American open-wheel car racing that operated from 2004 to 2008. It was the successor to Championship Auto Racing Teams (CART), ...
was merged into the Indy Racing League, the term "Champ Car" was permanently retired. The unified racing series fell under the "IndyCar" name, and the machines would be known as "Indy cars". On January 1, 2011, the names "Indy Racing League" and "IRL" were officially retired. The sanction body was re-branded as INDYCAR LLC, and the premier touring series was named the IndyCar Series
The IndyCar Series, officially known as the NTT IndyCar Series for sponsorship reasons, is the highest class of American open-wheel car racing in the United States, which has been conducted under the auspices of various sanctioning bodies sinc ...
(currently known as the NTT IndyCar Series for sponsorship reasons).
Comparison with Formula One
At first, American and European open-wheel racing were not distinct disciplines. Races on both continents were mostly point-to-point races, and large ovals tracks emerged on both continents. But in America, racing took off at horse-race tracks and at the Indianapolis Motor Speedway, while in Europe, racing from point to point and around large circuits gained in popularity. Grand Prix racing (which becameFormula One
Formula One (F1) is the highest class of worldwide racing for open-wheel single-seater formula Auto racing, racing cars sanctioned by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA). The FIA Formula One World Championship has been one ...
) and rallying
Rallying is a wide-ranging form of motorsport with various competitive motoring elements such as speed tests (sometimes called "rally racing" in United States), navigation tests, or the ability to reach waypoints or a destination at a prescribed ...
then diverged in Europe. Formula One was established after World War II as the World Championship for road racing, and F1 cars became increasingly specialized and high-tech.
In the 1960s, road racing gained popularity in North America, and Formula One-style design ideas changed IndyCars, which until then had all been classic-styled front-engined roadsters. When North America's road racing championship, Can-Am Challenge, collapsed in the 1970s, the IndyCars were ready to fill the void. IndyCar was a combination road- and oval-racing championship from this time until the Split. Compared to F1 cars, IndyCars were partly specialized for oval-racing: they were larger and had other safety features, and were designed to run at the higher speeds necessary for oval racing. Because IndyCars were usually "customer" cars that the teams purchased from constructors, and because of rules to contain costs, they were considerably less expensive than F1 cars, each model of which was designed by the team that used it. After the Split in the 1990s, CART maintained the old formula while the IRL drifted toward the "spec" design that has been the only IndyCar model since 2003 (which changed in 2012, with specialized aero kits available from 2015 to 2017).
As engine formulas have changed, and as engine technology has developed over time, F1 cars and IndyCars have each produced more power than the other at different times. But for the foreseeable future, F1 cars will have considerably more power than the spec IndyCar.
Alex Zanardi, who drove both in F1 and CART, said that the lighter, naturally aspirated F1 car was more responsive and accelerated off the turns faster, while the turbocharged CART car was more stable and accelerated to top speed faster.
More recently Formula 2
Formula Two (F2) is a type of open-wheel formula racing category first codified in 1948. It was replaced in 1985 by Formula 3000, but revived by the FIA from 2009 to 2012 in the form of the FIA Formula Two Championship. The name returned aga ...
drivers Callum Ilott and Christian Lundgaard, who are both also test and reserve drivers for Alpine F1 and Scuderia Ferrari
Scuderia Ferrari (; ), currently racing under Scuderia Ferrari HP, is the racing division of luxury Italian auto manufacturer Ferrari and the racing team that competes in Formula One racing. The team is also known by the nickname "the Pranc ...
respectively, have stated that the modern Dallara DW12 spec car used in the IndyCar Series sits in between a Formula 2 and a Formula One car on road and street courses in terms of performance. Both Ilott and Lundgaard have stated that the IndyCar's lack of power steering combined with the lower downforce levels and roughly 100 horsepower advantage make the IndyCar harder to drive than a Formula 2 car. Both noted however that around a road or street course the Formula One car would be significantly faster than an IndyCar.
There is debate on which series is more demanding. Some point out that champions that retired from F1 have won CART championships: e.g., Emerson Fittipaldi and Nigel Mansell. Drivers who did not excel in F1 have continued their careers in IndyCar with varying levels of success. Some successful IndyCar drivers have tried but failed to get a seat in even a low level Formula One team. A handful of notable IndyCar drivers, however, found subsequent success in F1, including Mario Andretti and Jacques Villeneuve, who became Formula One champions, and Juan Pablo Montoya, who won several F1 races. Conversely, some point to the different track designs of IndyCar (see below) as a bigger challenge to the drivers. Former Haas F1 driver Romain Grosjean stated in 2021 that a modern IndyCar is more physically exerting to drive than a modern Formula One car but that the Formula One car was more mentally taxing due to all its additional complexity, horsepower, and downforce levels compared to the IndyCar as well as the need to manage fuel levels given that Formula One cars do not refuel during the race while IndyCar racing allows refueling during races.
Open-wheel cars
* "Indy car" is a generic name for championship open-wheel auto racing in the United States. "Indy car" initially described anopen-wheel car
An open-wheel car is a car with the wheels outside the car's main body, and usually having only one seat. Open-wheel cars contrast with street cars, Sports car racing, sports cars, Stock car racing, stock cars, and Touring car racing, touring car ...
that participated in the Indianapolis 500-Mile Race. Originally, the cars were generally referred to as "Championship cars". However, as the result of the Indianapolis being the most notable race on the calendar, many people started to apply the "Indy car" designation for the entire American open-wheel class of cars in order to differentiate those from other types of open-wheel cars, such as those used in Formula One
Formula One (F1) is the highest class of worldwide racing for open-wheel single-seater formula Auto racing, racing cars sanctioned by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA). The FIA Formula One World Championship has been one ...
.
* In general, ''IndyCars'' of both CART
A cart or dray (Australia and New Zealand) is a vehicle designed for transport, using two wheels and normally pulled by draught animals such as horses, donkeys, mules and oxen, or even smaller animals such as goats or large dogs.
A handcart ...
and IndyCar
IndyCar, LLC (stylized as INDYCAR), is an auto racing sanctioning body for American open-wheel car racing headquartered in Indianapolis, Indiana. The organization sanctions two racing series: the premier IndyCar Series with the Indianapolis ...
are slower on street and road courses, being less expensive and technology-centric platforms than their Formula One counterparts. This was even the case during the CART PPG era during the mid to late 1990s. With the bid to keep costs down around teams in IndyCar, a competitive ''Indy car'' team like Newman/Haas Racing operated on approximately US$20 Million per season, while the McLaren
McLaren Racing Limited ( ) is a British auto racing, motor racing team based at the McLaren Technology Centre in Woking, Surrey, England. The team is a subsidiary of the McLaren Group, which owns a majority of the team. McLaren is best known a ...
- Mercedes F1 team had an annual budget of US$400 million in 2008. With the budget cap in Formula One which was introduced in 2021, a team now can spend a maximum of US$145 Million on developing their car.
* The Formula One chassis was required to be built by their respective team/constructor since 1981, whereas an ''Indy car'' chassis could be purchased. The dominance of a select few manufacturers has essentially turned the IndyCar Series
The IndyCar Series, officially known as the NTT IndyCar Series for sponsorship reasons, is the highest class of American open-wheel car racing in the United States, which has been conducted under the auspices of various sanctioning bodies sinc ...
into a spec series. CART/CCWS became a spec series more intentionally for cost savings purposes.
Racing description
* Indy car racing historically tended to take place on high speed ovals, while Formula One used primarily permanent road courses. However, Champ Car had no oval tracks for the 2007 season (which was its last), while the IRL added road/street courses to what was originally an all-oval series, and IndyCar has had a nearly equal balance of ovals and road/street courses in some years. Currently, the IndyCar Series has fewer ovals on its schedule than road/street courses due to safety concerns; the 2021 season had only four oval races, out of 16 overall. * Indy car racing was dominated by North American drivers until the 1980s and 1990s, which saw the debuts of drivers from Europe, South America, and Japan, many of whom had previously competed in Formula One. This led toTony George
Anton Hulman "Tony" George (born December 30, 1959) is the former Chairman, President, and CEO of the Indianapolis Motor Speedway and Hulman & Company, serving from 1989 to 2009. He was also formerly on the Board of Directors of both entities. ...
forming the IRL in order to promote American drivers. Conversely, American drivers have not found much success in Formula One
Formula One (F1) is the highest class of worldwide racing for open-wheel single-seater formula Auto racing, racing cars sanctioned by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA). The FIA Formula One World Championship has been one ...
since the 1970s; the last American driver to date to have won a Formula One race or the World Drivers' Championship was Mario Andretti
Mario Gabriele Andretti (born February 28, 1940) is an American former racing driver and businessman, who competed in Formula One from to , and American open-wheel racing, IndyCar from 1964 USAC Championship Car season, 1964 to 1994 IndyCar se ...
, who accomplished both in 1978. Andretti was born in Italy and later became an American citizen.
* Due partly to the lack of American drivers and teams, Formula One struggled to establish itself in that market, with the United States Grand Prix not being part of the Formula One season in some years. However, since the 2023 season, the Formula One calendar featured three Grands Prix taking place in the United States. In a parallel, Indy car racing has made little headway outside of the United States and Canada, despite occasionally having races overseas.
Types of circuits
The American National Championship is notable for the wide variety of racetracks it has used compared to other series, such asFormula One
Formula One (F1) is the highest class of worldwide racing for open-wheel single-seater formula Auto racing, racing cars sanctioned by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA). The FIA Formula One World Championship has been one ...
and the various forms of Endurance sports car racing
Sports car racing is a form of motorsport road racing that uses sports cars with two seats and enclosed wheels. They may be either purpose-built Sports prototype, sports prototypes, which are the highest level in sports car racing; or grand to ...
. The mainstays of the championship are as follows:
* Paved ovals and tri-oval
A tri-oval is a shape which derives its name from the two other shapes it most resembles, a triangle and an Oval (geometry), oval. Rather than meeting at sharp, definable angles as the sides of a triangle do, in a tri-oval these angles are instea ...
s (e.g. Indianapolis
Indianapolis ( ), colloquially known as Indy, is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Indiana, most populous city of the U.S. state of Indiana and the county seat of Marion County, Indiana, Marion ...
, Texas
Texas ( , ; or ) is the most populous U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the we ...
)
* Permanent (or "Natural") road courses
Road racing is a North American term to describe motorsport racing held on a paved road surface. The races can be held on a race track, closed circuit—generally, a purpose-built racing facility—or on a street circuit that uses temporarily c ...
(e.g. Barber
A barber is a person whose occupation is mainly to cut, dress, groom, style and shave hair or beards. A barber's place of work is known as a barbershop or the barber's. Barbershops have been noted places of social interaction and public discourse ...
, Mid-Ohio
Mid-Ohio Sports Car Course is a road course auto racing facility located in Troy Township, Morrow County, Ohio, United States, just outside the village of Lexington, Ohio, Lexington. It hosts a number of racing series such as IndyCar Series, Indy ...
)
* Temporary street circuits/courses (e.g. Long Beach
Long Beach is a coastal city in southeastern Los Angeles County, California, United States. It is the list of United States cities by population, 44th-most populous city in the United States, with a population of 451,307 as of 2022. A charter ci ...
, St. Pete)
* Combined road course (e.g. IndyCar Grand Prix)
Until 1970 the championship frequently raced on dirt and clay tracks, but all such tracks were removed permanently by USAC before the 1971 season.
From 1915 to 1931 board tracks were frequently used for championship races, however safety concerns and cost of maintenance, especially with the onset of the Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe global economic downturn from 1929 to 1939. The period was characterized by high rates of unemployment and poverty, drastic reductions in industrial production and international trade, and widespread bank and ...
, and nearly all were demolished in the 1930s.
The Pikes Peak Hillclimb was a round of the championship in the years 1947—1955 and 1965–1969.
In 1909 a point-to-point race from Los Angeles
Los Angeles, often referred to by its initials L.A., is the List of municipalities in California, most populous city in the U.S. state of California, and the commercial, Financial District, Los Angeles, financial, and Culture of Los Angeles, ...
to Phoenix was included in the championship.
Airport runways have also been used to create temporary circuits. The most notable used for open-wheel racing was the Cleveland Grand Prix at Burke Lakefront Airport. St. Pete and Edmonton also utilize airport runways for parts of the course, however, they lead back to streets for the rest of the lap.
Events outside the United States
For the majority of the national championship, the races have been held inside the United States. American championship cars raced at the Monza oval in 1957 and 1958 alongsideFormula One
Formula One (F1) is the highest class of worldwide racing for open-wheel single-seater formula Auto racing, racing cars sanctioned by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA). The FIA Formula One World Championship has been one ...
and sports cars
A sports car is a type of automobile that is designed with an emphasis on dynamic performance, such as handling, acceleration, top speed, the thrill of driving, and racing capability. Sports cars originated in Europe in the early 1910s and ar ...
in the non-championship Race of Two Worlds. Also, in 1966 there was a non-championship USAC race at Fuji Speedway
is a motorsport race track standing in the foothills of Mount Fuji, in Oyama, Shizuoka, Oyama, Suntō District, Shizuoka, Suntō District, Shizuoka Prefecture, Japan. It was built in the early 1960s. In the 1980s, Fuji Speedway was used for the ...
in Japan. The first championship events outside the U.S. took place in 1967
Events January
* January 1 – Canada begins a year-long celebration of the 100th anniversary of Canadian Confederation, Confederation, featuring the Expo 67 World's Fair.
* January 6 – Vietnam War: United States Marine Corps and Army of ...
at Mosport and Saint-Jovite in Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
. In 1971 *
The year 1971 had three partial solar eclipses (Solar eclipse of February 25, 1971, February 25, Solar eclipse of July 22, 1971, July 22 and Solar eclipse of August 20, 1971, August 20) and two total lunar eclipses (February 1971 lunar eclip ...
, the USAC season-opening race was held at Rafaela. In the autumn of 1978, two races were held in England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
, the first at Silverstone, then a week later at Brands Hatch
Brands Hatch is a motor racing circuit in West Kingsdown, Kent, England, United Kingdom. Originally used as a grasstrack motorcycle circuit on farmland, it hosted 12 runnings of the British Grand Prix between 1964 and 1986 and currently hosts ...
.
Beginning in the mid-1980s, CART expanded throughout North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
, venturing into Mexico (Mexico City
Mexico City is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Mexico, largest city of Mexico, as well as the List of North American cities by population, most populous city in North America. It is one of the most important cultural and finan ...
) and Canada ( Sanair, Toronto
Toronto ( , locally pronounced or ) is the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, most populous city in Canada. It is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Ontario. With a p ...
and Vancouver
Vancouver is a major city in Western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the List of cities in British Columbia, most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the cit ...
). In the 1990s and early 2000s, international expansion reached overseas with events at Surfer's Paradise, Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro, or simply Rio, is the capital of the Rio de Janeiro (state), state of Rio de Janeiro. It is the List of cities in Brazil by population, second-most-populous city in Brazil (after São Paulo) and the Largest cities in the America ...
, Motegi, Lausitz, and Rockingham.
Towards the end of its run, Champ Car ran races at European tracks such as TT Circuit Assen
The TT Circuit Assen is a motorsport race track built in 1955 and located in Assen, Netherlands. Host of the Dutch TT, it is popularly referred to as "The Cathedral of Speed" by motorcycle racing fans. The venue has the distinction of holding th ...
and Zolder Circuit, intentionally scheduled in regions and dates that would not compete with Formula One.
Trophies and awards
Astor Cup
In 2011 IndyCar revived the Astor Cup, first awarded in 1915 as the series championship trophy. A black granite base has been added displaying the names of all the American Championship car racing series winners since 1909.Vanderbilt Cup
The 1916, 1936 and 1937 Vanderbilt Cup races were included in the national championship. The 1909–1915 races were retrospectively added to the championship in 1926. CART resurrected the Cup in 1996 as the winner's trophy for the US500 race. When that race was discontinued in 2000, the Cup changed roles and became the championship trophy. Champ Car retained the rights to use the trophy after CART's bankruptcy, but use of the trophy was discontinued after Champ Car's merger with the Indy Racing League.Indianapolis 500 as part of the national championship
From its inception in 1911, theIndianapolis 500
The Indianapolis 500, formally known as the Indianapolis 500-Mile Race, and commonly shortened to Indy 500, is an annual automobile race held at the Indianapolis Motor Speedway in Speedway, Indiana, United States, an enclave suburb of Indian ...
has been considered the marquee event of Championship/Indy car racing. The race has been held every year from 1911, with the exception of 1917–1918 (World War I) and 1942–1945 (World War II). The Indianapolis 500 has been part of an official national championship in 1916, 1920–1941, and since 1946. In the years from 1911 to 1915, as well as 1919, the race was held as a formally sanctioned event, but an official national championship was not recognized in those years. Therefore, those six editions of the race were not attached to an officially recognized national championship.
Winning the Indianapolis 500 has frequently been considered at near or equal profile to winning the national championship. However, direct comparisons are difficult as many of the national champions are also Indy 500 winners in their own right. In many instances, drivers have won both the 500 and the championship in the same calendar year.
During the first USAC/CART
A cart or dray (Australia and New Zealand) is a vehicle designed for transport, using two wheels and normally pulled by draught animals such as horses, donkeys, mules and oxen, or even smaller animals such as goats or large dogs.
A handcart ...
open-wheel "split", which encompasses the period from 1979 to 1995, the status of the Indianapolis 500 as part of the national championship changed somewhat. The Indy 500 was sanctioned by USAC, and during that time, was officially part of the USAC Gold Crown Championship calendar. However, the bulk of the field was CART-based teams and drivers. The Indy 500 paid points to the CART title in 1979 and 1980, but did not count towards the CART title in 1981 and 1982. By 1983, an arrangement was made such that the Indy 500 would continue to be sanctioned singly by USAC, but be it would be recognized on the CART schedule, and pay championship points towards the CART title.
Starting in 1996, the Indianapolis 500 became part of the new Indy Racing League
IndyCar, LLC (stylized as INDYCAR), is an auto racing Governing body, sanctioning body for American open-wheel car racing headquartered in Indianapolis, Indiana. The organization sanctions two Auto racing, racing series: the premier IndyCar Serie ...
championship. All ties to the CART championship were severed. It was the beginning of the second open-wheel "split". In 2008, when the two series unified as IndyCar, ending the "split", the Indianapolis 500 was now part of the unified IndyCar Series national championship. Since 2014, the Indy 500 has paid double points towards the IndyCar Series points championship, and additional championship points are awarded based on Indy 500 qualifying results.
Notable drivers
* The driver with the most championship titles and race wins is A. J. Foyt. From 1959 to 1981 Foyt won 67 USAC championship races and seven USAC titles. *Mario Andretti
Mario Gabriele Andretti (born February 28, 1940) is an American former racing driver and businessman, who competed in Formula One from to , and American open-wheel racing, IndyCar from 1964 USAC Championship Car season, 1964 to 1994 IndyCar se ...
is the most successful driver born outside the United States with 52 total wins (33 USAC & 19 CART) and 4 titles (3 USAC & 1 CART).
* New Zealand's Scott Dixon is the most successful non-U.S. driver with 6 championship titles and holds the record for IndyCar race wins (49). He sits 3rd all time behind A. J. Foyt and Mario Andretti
Mario Gabriele Andretti (born February 28, 1940) is an American former racing driver and businessman, who competed in Formula One from to , and American open-wheel racing, IndyCar from 1964 USAC Championship Car season, 1964 to 1994 IndyCar se ...
with a total of 50 race wins (includes 1 CART/Champ Car win in 2001).
* Michael Andretti has won the most CART/Champ Car-sanctioned races (42).
* Tony Bettenhausen (19) is credited with the most AAA championship race wins.
* Danica Patrick
Danica Sue Patrick (; born March 25, 1982) is an American former professional racing driver and model. She is the most successful woman in the history of American open-wheel car racing—her victory in the 2008 Indy Japan 300 is the only win ...
is the only woman to ever win a national championship-level open-wheel race ( Motegi, 2008). Sarah Fisher was the first female driver to win a pole position (Kentucky
Kentucky (, ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north, West Virginia to the ...
, 2002).
* Four drivers have held the crowns of CART Champion and Formula One
Formula One (F1) is the highest class of worldwide racing for open-wheel single-seater formula Auto racing, racing cars sanctioned by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA). The FIA Formula One World Championship has been one ...
World Driving Champion.
** Mario Andretti
Mario Gabriele Andretti (born February 28, 1940) is an American former racing driver and businessman, who competed in Formula One from to , and American open-wheel racing, IndyCar from 1964 USAC Championship Car season, 1964 to 1994 IndyCar se ...
, Emerson Fittipaldi
Emerson Fittipaldi (; born 12 December 1946) is a Brazilian former racing driver and motorsport executive, who competed in Formula One from to . Fittipaldi won two Formula One World Drivers' Championship titles, which he won in and with Team ...
, Nigel Mansell
Nigel Ernest James Mansell (; born 8 August 1953) is a British former racing driver, who competed in Formula One from to . Mansell won the Formula One World Drivers' Championship in with Williams, and won 31 Grands Prix across 15 seasons ...
, Jacques Villeneuve
* Six other drivers have won both a national championship race as well as at least one Formula One Grand Prix. They are as follows:
** Peter Revson, Dan Gurney
Daniel Sexton Gurney (April 13, 1931 – January 14, 2018) was an American racing driver, engineer and motorsport executive, who competed in Formula One from to . Widely regarded as one of the most influential figures in the history of motorspo ...
, Jim Clark, Graham Hill, Juan Pablo Montoya
Juan Pablo Montoya Roldán (; born 20 September 1975) is a Colombian racing driver, who competed in Formula One from to , IndyCar between 1999 and 2022, and the NASCAR Cup Series between 2006 and 2024. Montoya won seven Formula One Grand ...
, Jackie Stewart
Notable fatalities in competition
* Jimmy Murphy, champion in 1922 and 1924, died after crashing at theSyracuse, New York
Syracuse ( ) is a City (New York), city in and the county seat of Onondaga County, New York, United States. With a population of 148,620 and a Syracuse metropolitan area, metropolitan area of 662,057, it is the fifth-most populated city and 13 ...
in September, 1924.
* Ted Horn, champion in 1946-1947-1948, died after crashing at the DuQuoin dirt track in late 1948.
* Defending Indianapolis 500 winners Floyd Roberts and Bill Vukovich were killed during the 1939
This year also marks the start of the World War II, Second World War, the largest and deadliest conflict in human history.
Events
Events related to World War II have a "WWII" prefix.
January
* January 1
** Coming into effect in Nazi Ger ...
and 1955 Indy 500s respectively.
* 1951 and 1958 champion Tony Bettenhausen was killed in a crash at Indianapolis in May 1961.
* Eddie Sachs and Dave MacDonald were killed during the 1964 Indianapolis 500.
* Art Pollard (practice) and Swede Savage (race) died of injuries suffered during the 1973 Indianapolis 500.
* Gordon Smiley was killed while attempting to qualify for the 1982 Indianapolis 500.
* 1996 Indianapolis 500
The 80th Indianapolis 500 was held at the Indianapolis Motor Speedway in Speedway, Indiana on Sunday, May 26, 1996. This was the first Indy 500 contested as part of the new Indy Racing League, under the overall sanctioning umbrella of USAC. It ...
pole-sitter Scott Brayton was killed May 17, 1996, during a practice session for the Indianapolis 500.
* Gonzalo Rodríguez was killed September 11, 1999, during a qualifying in the IndyCar Monterey Grand Prix at Laguna Seca
Laguna Seca Raceway (branded as WeatherTech Raceway Laguna Seca, and previously Mazda Raceway Laguna Seca for sponsorship reasons) is a paved Racing track#Motorsport, road racing track in central California used for both auto racing and Motorcyc ...
.
* Greg Moore died after an October 31, 1999, crash in the Marlboro 500 at Fontana.
* Paul Dana died during practice for the first race of the 2006 IndyCar Series season, at Homestead-Miami Speedway on March 26, 2006.
* 2005 IndyCar Series champion and two-time Indianapolis 500 champion Dan Wheldon died after a 15-car pile-up on the 11th lap of the IZOD IndyCar World Championships at Las Vegas
Las Vegas, colloquially referred to as Vegas, is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Nevada and the county seat of Clark County. The Las Vegas Valley metropolitan area is the largest within the greater Mojave Desert, and second-l ...
on October 16, 2011.
* Justin Wilson died on August 24, 2015, the day after a crash on lap 180 of the 2015 ABC Supply 500 at Pocono Raceway
Pocono Raceway (formerly known as the Pocono International Raceway in early years) is a tri-oval track in Blakeslee, Pennsylvania. The track has held a variety of events since its opening in 1969, including NASCAR, IndyCar Series, and IMSA GT ...
.
National champions





 : From 1979 to 1995 the Indianapolis 500 and the national championship were sanctioned by separate organizations, USAC and
: From 1979 to 1995 the Indianapolis 500 and the national championship were sanctioned by separate organizations, USAC and CART
A cart or dray (Australia and New Zealand) is a vehicle designed for transport, using two wheels and normally pulled by draught animals such as horses, donkeys, mules and oxen, or even smaller animals such as goats or large dogs.
A handcart ...
, respectively. USAC continued to sanction their own national championship series until 1981, when they formed the USAC Gold Crown Championship.
: From 1985 to 1995 the USAC Gold Crown Championship consisted solely of the Indianapolis 500, thus making such championship winners indistinguishable from Indianapolis winners. IndyCar
IndyCar, LLC (stylized as INDYCAR), is an auto racing sanctioning body for American open-wheel car racing headquartered in Indianapolis, Indiana. The organization sanctions two racing series: the premier IndyCar Series with the Indianapolis ...
does not recognize winners of the USAC Gold Crown Championship as full season champions.
In fiction
; Films * '' The Crowd Roars'' (1932) * ''Speed
In kinematics, the speed (commonly referred to as ''v'') of an object is the magnitude of the change of its position over time or the magnitude of the change of its position per unit of time; it is thus a non-negative scalar quantity. Intro ...
'' (1936)
* '' Indianapolis Speedway'' (1939)
* '' The Big Wheel'' (1949)
* '' To Please a Lady'' (1950)
* '' Roar of the Crowd'' (1953)
* ''Winning
Winning may refer to:
* Victory
Film
* Winning (film), ''Winning'' (film), a 1969 movie starring Paul Newman
* ''Winning: The Racing Life of Paul Newman'', a 2015 documentary by Adam Carolla and Nate Adams
Music
* ''Winning'', an album by Ten Fo ...
'' (1969)
* '' Super Speedway'' (1997)
* '' Driven'' (2001)
* ''Turbo
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (also known as a turbo or a turbosupercharger) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake air, forcing more air into the ...
'' (2013)
; Video games
See also
* List of American Championship Car winners * List of American Championship Car Rookie of the Year Winners * List of American Championship car racing point scoring systems * NASCAR Speedway Division * American Indycar SeriesReferences
External links
ChampCarStats.com
complete AAA, USAC, CART, CCWS and IRL race results. {{Indy Racing League Seasons Open wheel racing Auto racing series in the United States