Industrial and production engineering (IPE) is an interdisciplinary engineering discipline that includes
manufacturing
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of the
secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer ...
technology,
engineering
Engineering is the practice of using natural science, mathematics, and the engineering design process to Problem solving#Engineering, solve problems within technology, increase efficiency and productivity, and improve Systems engineering, s ...
sciences,
management science
Management science (or managerial science) is a wide and interdisciplinary study of solving complex problems and making strategic decisions as it pertains to institutions, corporations, governments and other types of organizational entities. It is ...
, and optimization of complex
processes,
system
A system is a group of interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its open system (systems theory), environment, is described by its boundaries, str ...
s, or
organizations
An organization or organisation ( Commonwealth English; see spelling differences) is an entity—such as a company, or corporation or an institution (formal organization), or an association—comprising one or more people and having a par ...
. It is concerned with the understanding and application of engineering procedures in manufacturing processes and production methods. Industrial engineering dates back all the way to the industrial revolution, initiated in 1700s by Sir
Adam Smith
Adam Smith (baptised 1723 – 17 July 1790) was a Scottish economist and philosopher who was a pioneer in the field of political economy and key figure during the Scottish Enlightenment. Seen by some as the "father of economics"——— or ...
,
Henry Ford
Henry Ford (July 30, 1863 – April 7, 1947) was an American Technological and industrial history of the United States, industrialist and business magnate. As the founder of the Ford Motor Company, he is credited as a pioneer in making automob ...
,
Eli Whitney
Eli Whitney Jr. (December 8, 1765January 8, 1825) was an American inventor, widely known for inventing the cotton gin in 1793, one of the key inventions of the Industrial Revolution that shaped the economy of the Antebellum South.
Whitney's ...
,
Frank Gilbreth
Frank Bunker Gilbreth (July 7, 1868 – June 14, 1924) was an American engineer, consultant, and author known as an early advocate of scientific management and a pioneer of time and motion study, and is perhaps best known as the father and c ...
and
Lilian Gilbreth,
Henry Gantt
Henry Laurence Gantt (; May 20, 1861 – November 23, 1919) was an American mechanical engineer and management consultant who is best known for his work in the development of scientific management. He created the Gantt chart in the 1910s.
Gant ...
,
F.W. Taylor, etc. After the 1970s, industrial and production engineering developed worldwide and started to widely use automation and robotics. Industrial and production engineering includes three areas:
Mechanical engineering
Mechanical engineering is the study of physical machines and mechanism (engineering), mechanisms that may involve force and movement. It is an engineering branch that combines engineering physics and engineering mathematics, mathematics principl ...
(where the production engineering comes from),
industrial engineering
Industrial engineering (IE) is concerned with the design, improvement and installation of integrated systems of people, materials, information, equipment and energy. It draws upon specialized knowledge and skill in the mathematical, physical, an ...
, and
management science
Management science (or managerial science) is a wide and interdisciplinary study of solving complex problems and making strategic decisions as it pertains to institutions, corporations, governments and other types of organizational entities. It is ...
.
The objective is to improve efficiency, drive up effectiveness of manufacturing, quality control, and to reduce cost while making their products more attractive and marketable. Industrial engineering is concerned with the development, improvement, and implementation of integrated systems of people, money, knowledge, information, equipment, energy, materials, as well as analysis and synthesis. The principles of IPE include mathematical, physical and
social sciences
Social science (often rendered in the plural as the social sciences) is one of the branches of science, devoted to the study of society, societies and the Social relation, relationships among members within those societies. The term was former ...
and methods of engineering design to specify, predict, and evaluate the results to be obtained from the systems or processes currently in place or being developed. The target of production engineering is to complete the production process in the smoothest, most-judicious and most-economic way. Production engineering also overlaps substantially with
manufacturing engineering
Manufacturing engineering or production engineering is a branch of professional engineering that shares many common concepts and ideas with other fields of engineering such as mechanical, chemical, electrical, and industrial engineering.
Manufac ...
and
industrial engineering
Industrial engineering (IE) is concerned with the design, improvement and installation of integrated systems of people, materials, information, equipment and energy. It draws upon specialized knowledge and skill in the mathematical, physical, an ...
. The concept of production engineering is interchangeable with manufacturing engineering.
As for education, undergraduates normally start off by taking courses such as physics, mathematics (calculus, linear analysis, differential equations), computer science, and chemistry. Undergraduates will take more major specific courses like production and inventory scheduling,
process management, CAD/CAM manufacturing,
ergonomics
Ergonomics, also known as human factors or human factors engineering (HFE), is the application of Psychology, psychological and Physiology, physiological principles to the engineering and design of products, processes, and systems. Primary goa ...
, etc., towards the later years of their undergraduate careers. In some parts of the world, universities will offer Bachelor's in Industrial and Production Engineering. However, most universities in the U.S. will offer them separately. Various career paths that may follow for industrial and production engineers include:
Plant Engineers,
Manufacturing Engineers,
Quality Engineers,
Process Engineers and industrial managers,
project management
Project management is the process of supervising the work of a Project team, team to achieve all project goals within the given constraints. This information is usually described in project initiation documentation, project documentation, crea ...
,
manufacturing
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of the
secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer ...
, production and distribution, From the various career paths people can take as an industrial and production engineer, most average a starting salary of at least $50,000.
History
Industrial Revolution
The roots of the industrial engineering profession date back to the
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
. The technologies that helped mechanize traditional manual operations in the textile industry including the
Flying shuttle
The flying shuttle is a type of weaving shuttle. It was a pivotal advancement in the mechanisation of weaving during the initial stages of the Industrial Revolution, and facilitated the weaving of considerably broader fabrics, enabling the p ...
, the
Spinning jenny
The spinning jenny is a multi- spindle spinning frame, and was one of the key developments in the industrialisation of textile manufacturing during the early Industrial Revolution. It was invented in 1764–1765 by James Hargreaves in Stan ...
, and perhaps most importantly the
Steam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs Work (physics), mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a Cylinder (locomotive), cyl ...
generated
Economies of scale
In microeconomics, economies of scale are the cost advantages that enterprises obtain due to their scale of operation, and are typically measured by the amount of Productivity, output produced per unit of cost (production cost). A decrease in ...
that made
Mass production
Mass production, also known as mass production, series production, series manufacture, or continuous production, is the production of substantial amounts of standardized products in a constant flow, including and especially on assembly lines ...
in centralized locations attractive for the first time. The concept of the production system had its genesis in the factories created by these innovations.
[Maynard & Zandin. Maynard's Industrial Engineering Handbook. McGraw Hill Professional 5th Edition. June 5, 2001. p. 1.4–1.6]
Specialization of labor

Adam Smith's concepts of
division of labour
The division of labour is the separation of the tasks in any economic system or organisation so that participants may specialise ( specialisation). Individuals, organisations, and nations are endowed with or acquire specialised capabilities, a ...
and the "invisible hand" of capitalism introduced in his treatise "
The Wealth of Nations
''An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations'', usually referred to by its shortened title ''The Wealth of Nations'', is a book by the Scottish people, Scottish economist and moral philosophy, moral philosopher Adam Smith; ...
" motivated many of the technological innovators of the Industrial Revolution to establish and implement factory systems. The efforts of James Watt and Matthew Boulton led to the first integrated machine manufacturing facility in the world, including the implementation of concepts such as cost control systems to reduce waste and increase productivity and the institution of skills training for craftsmen.
Charles Babbage
Charles Babbage (; 26 December 1791 – 18 October 1871) was an English polymath. A mathematician, philosopher, inventor and mechanical engineer, Babbage originated the concept of a digital programmable computer.
Babbage is considered ...
became associated with industrial engineering because of the concepts he introduced in his book "On the Economy of Machinery and Manufacturers" which he wrote as a result of his visits to factories in England and the United States in the early 1800s. The book includes subjects such as the time required to perform a specific task, the effects of subdividing tasks into smaller and less detailed elements, and the advantages to be gained from repetitive tasks.
Interchangeable parts
Eli Whitney
Eli Whitney Jr. (December 8, 1765January 8, 1825) was an American inventor, widely known for inventing the cotton gin in 1793, one of the key inventions of the Industrial Revolution that shaped the economy of the Antebellum South.
Whitney's ...
and
Simeon North
Simeon North (July 13, 1765 – August 25, 1852) was an American gun manufacturer, who developed one of America's first milling machines (possibly the very first) in 1818 and played an important role in the development of interchangeable parts ma ...
proved the feasibility of the notion of
interchangeable parts
Interchangeable parts are parts (wikt:component#Noun, components) that are identical for practical purposes. They are made to specifications that ensure that they are so nearly identical that they will fit into any assembly of the same type. One ...
in the manufacture of muskets and pistols for the US Government. Under this system, individual parts were mass-produced to tolerances to enable their use in any finished product. The result was a significant reduction in the need for skill from specialized workers, which eventually led to the industrial environment to be studied later.
Modern development
Industrial engineering
In 1960 to 1975, with the development of decision support systems in supply such as the
Material requirements planning
Material requirements planning (MRP) is a production planning, scheduling, and inventory control system used to manage manufacturing processes. Most MRP systems are software-based, but it is possible to conduct MRP by hand as well.
An MRP syst ...
(MRP), people can emphasize the timing issue (inventory, production, compounding, transportation, etc.) of industrial organization. Israeli scientist Dr.
Jacob Rubinovitz installed the CMMS program developed in IAI and Control-Data (Israel) in 1976 in South Africa and worldwide.
In the seventies, with the penetration of Japanese management theories such as
Kaizen
is a Japanese concept in business studies which asserts that significant positive results may be achieved due the cumulative effect of many, often small (and even trivial), improvements to all aspects of a company's operations. Kaizen is put ...
and
Kanban
Kanban ( meaning signboard) is a scheduling system for lean manufacturing (also called just-in-time manufacturing, abbreviated JIT). Taiichi Ohno, an industrial engineer at Toyota, developed kanban to improve manufacturing efficiency. The ...
, Japan realized very high levels of quality and productivity. These theories improved issues of quality, delivery time, and flexibility. Companies in the west realized the great impact of Kaizen and started implementing their own
Continuous improvement
A continual improvement process, also often called a continuous improvement process (abbreviated as CIP or CI), is an ongoing effort to improve products, services, or processes. These efforts can seek " incremental" improvement over time or "brea ...
programs.
In the nineties, following the global industry globalization process, the emphasis was on supply chain management, and customer-oriented business process design.
Theory of constraints
The theory of constraints (TOC) is a management paradigm that views any manageable system as being limited in achieving more of its goals by a very small number of constraints. There is always at least one constraint, and TOC uses a focusing p ...
developed by an Israeli scientist
Eliyahu M. Goldratt
Eliyahu Moshe Goldratt (; March 31, 1947 – June 11, 2011) was an Israeli business management guru. He was the originator of the Optimized Production Technique, the Theory of Constraints (TOC), the Thinking Processes (Theory of Constraints), Th ...
(1985) is also a significant milestone in the field.
Manufacturing (production) engineering
Modern manufacturing engineering studies include all intermediate processes required for the production and integration of a product's components.Some industries, such as
semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator. Its conductivity can be modified by adding impurities (" doping") to its crystal structure. When two regions with different doping level ...
and
steel
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon that demonstrates improved mechanical properties compared to the pure form of iron. Due to steel's high Young's modulus, elastic modulus, Yield (engineering), yield strength, Fracture, fracture strength a ...
manufacturers use the term "fabrication" for these processes.
Automation
Automation describes a wide range of technologies that reduce human intervention in processes, mainly by predetermining decision criteria, subprocess relationships, and related actions, as well as embodying those predeterminations in machine ...
is used in different processes of manufacturing such as machining and welding. Automated manufacturing refers to the application of automation to produce goods in a factory. The main advantages of automated manufacturing for the manufacturing process are realized with effective implementation of automation and include: higher consistency and quality, reduction of lead times, simplification of production, reduced handling, improved work flow, and improved worker morale.
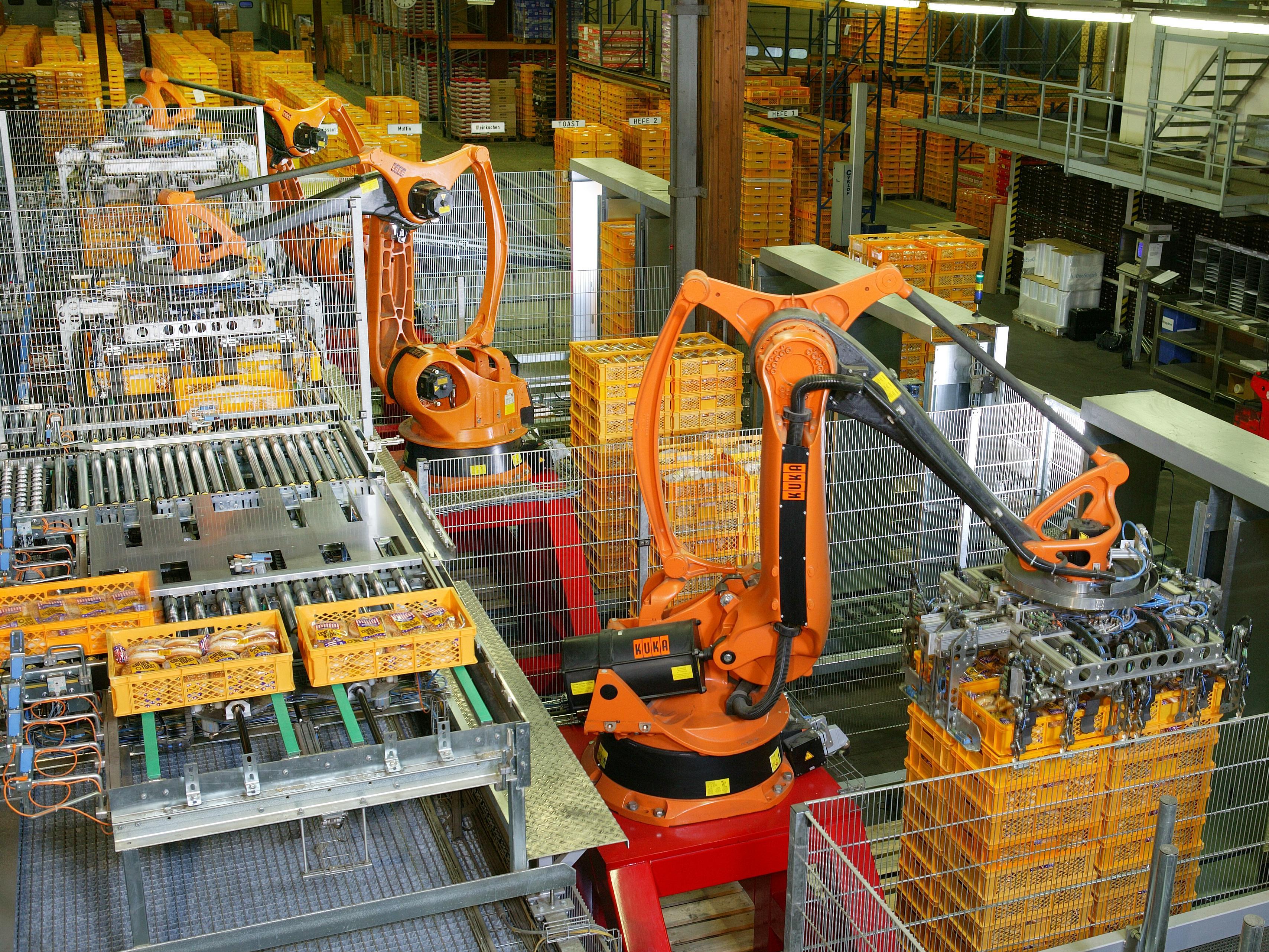

Robotics
Robotics is the interdisciplinary study and practice of the design, construction, operation, and use of robots.
Within mechanical engineering, robotics is the design and construction of the physical structures of robots, while in computer s ...
is the application of mechatronics and automation to create robots, which are often used in manufacturing to perform tasks that are dangerous, unpleasant, or repetitive. These robots may be of any shape and size, but all are preprogrammed and interact physically with the world. To create a robot, an engineer typically employs kinematics (to determine the robot's range of motion) and mechanics (to determine the stresses within the robot). Robots are used extensively in manufacturing engineering.
Robots allow businesses to save money on labor, perform tasks that are either too dangerous or too precise for humans to perform economically, and to ensure better quality. Many companies employ assembly lines of robots, and some factories are so robotized that they can run by themselves. Outside the factory, robots have been employed in bomb disposal, space exploration, and many other fields. Robots are also sold for various residential applications.
Overview
Industrial engineering
Industrial engineering is the branch of engineering that involves figuring out how to make or do things better. Industrial engineers are concerned with reducing production costs, increasing efficiency, improving the quality of products and services, ensuring worker health and safety, protecting the environment and complying with government regulations.
The various fields and topics that industrial engineers are involved with include:
*
Manufacturing engineering
Manufacturing engineering or production engineering is a branch of professional engineering that shares many common concepts and ideas with other fields of engineering such as mechanical, chemical, electrical, and industrial engineering.
Manufac ...
*
Engineering management
Engineering management is the application of engineering methods, tools, and techniques to business management systems. Engineering management is a career that brings together the technological problem-solving ability of engineering and the organi ...
*
Process engineering
Process engineering is a field of study focused on the development and optimization of industrial processes. It consists of the understanding and application of the fundamental principles and laws of nature to allow humans to transform raw mate ...
: design, operation, control, and optimization of chemical, physical, and biological processes.
*
Systems engineering
Systems engineering is an interdisciplinary field of engineering and engineering management that focuses on how to design, integrate, and manage complex systems over their Enterprise life cycle, life cycles. At its core, systems engineering uti ...
: an interdisciplinary field of engineering that focuses on how to design and manage complex engineering systems over their life cycles.
*
Software engineering
Software engineering is a branch of both computer science and engineering focused on designing, developing, testing, and maintaining Application software, software applications. It involves applying engineering design process, engineering principl ...
: an interdisciplinary field of engineering that focusing on design, development, maintenance, testing, and evaluation of the software that make computers or other devices containing software work
*
Safety engineering
Safety engineering is an engineering Branches of science, discipline which assures that engineered systems provide acceptable levels of safety. It is strongly related to industrial engineering/systems engineering, and the subset system safety en ...
: an engineering discipline which assures that engineered systems provide acceptable levels of safety.
*
Data science
Data science is an interdisciplinary academic field that uses statistics, scientific computing, scientific methods, processing, scientific visualization, algorithms and systems to extract or extrapolate knowledge from potentially noisy, stru ...
: the science of exploring, manipulating, analyzing, and visualizing data to derive useful insights and conclusions
*
Machine learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of study in artificial intelligence concerned with the development and study of Computational statistics, statistical algorithms that can learn from data and generalise to unseen data, and thus perform Task ( ...
: the automation of learning from data using models and algorithms
*
Analytics
Analytics is the systematic computational analysis of data or statistics. It is used for the discovery, interpretation, and communication of meaningful patterns in data, which also falls under and directly relates to the umbrella term, data sc ...
and
data mining
Data mining is the process of extracting and finding patterns in massive data sets involving methods at the intersection of machine learning, statistics, and database systems. Data mining is an interdisciplinary subfield of computer science and ...
: the discovery, interpretation, and extraction of patterns and insights from large quantities of data
*
Cost engineering
Cost engineering is "the engineering practice devoted to the management of project cost, involving such activities as estimating, cost control, cost forecasting, investment appraisal and risk analysis". "Cost Engineers budget, plan and monitor inv ...
: practice devoted to the management of project cost, involving such activities as cost- and control- estimating, which is cost control and cost forecasting, investment appraisal, and risk analysis.
*
Value engineering
Value engineering (VE) is a systematic analysis of the functions of various components and materials to lower the cost of goods, products and services with a tolerable loss of performance or functionality. Value, as defined, is the ratio of func ...
: a systematic method to improve the "value" of goods or products and services by using an examination of function.
*
Predetermined motion time system
A predetermined motion time system (PMTS) is frequently used to perform labor minute costing in order to set piece-rates, wage-rates or incentives in labor oriented industries by quantifying the amount of time required to perform specific tasks un ...
: a technique to quantify time required for repetitive tasks.
*
Quality engineering
Quality engineering is the discipline of engineering concerned with the principles and practice of product and service quality assurance and quality control, control. In software development, it is the management, development, operation and main ...
: a way of preventing mistakes or defects in manufactured products and avoiding problems when delivering solutions or services to customers.
*
Project management
Project management is the process of supervising the work of a Project team, team to achieve all project goals within the given constraints. This information is usually described in project initiation documentation, project documentation, crea ...
: is the process and activity of planning, organizing, motivating, and controlling resources, procedures and protocols to achieve specific goals in scientific or daily problems.
*
Supply chain management
In commerce, supply chain management (SCM) deals with a system of procurement (purchasing raw materials/components), operations management, logistics and marketing channels, through which raw materials can be developed into finished produc ...
: the management of the flow of goods. It includes the movement and storage of raw materials, work-in-process inventory, and finished goods from point of origin to point of consumption.
*
Ergonomics
Ergonomics, also known as human factors or human factors engineering (HFE), is the application of Psychology, psychological and Physiology, physiological principles to the engineering and design of products, processes, and systems. Primary goa ...
: the practice of designing products, systems or processes to take proper account of the interaction between them and the people that use them.
*
Operations research
Operations research () (U.S. Air Force Specialty Code: Operations Analysis), often shortened to the initialism OR, is a branch of applied mathematics that deals with the development and application of analytical methods to improve management and ...
, also known as
management science
Management science (or managerial science) is a wide and interdisciplinary study of solving complex problems and making strategic decisions as it pertains to institutions, corporations, governments and other types of organizational entities. It is ...
: discipline that deals with the application of advanced analytical methods to help make better decisions
*
Operations management
Operations management is concerned with designing and controlling the production (economics), production of good (economics), goods and service (economics), services, ensuring that businesses are efficiency, efficient in using resources to meet ...
: an area of management concerned with overseeing, designing, and controlling the process of production and redesigning business operations in the production of goods or services.
*
Job design
Work design (also referred to as job design or task design) is an area of research and practice within industrial and organizational psychology, and is concerned with the "content and organization of one's work tasks, activities, relationships, a ...
: the specification of contents, methods and relationship of jobs in order to satisfy technological and organizational requirements as well as the social and personal requirements of the job holder.
*
Financial engineering
Financial engineering is a multidisciplinary field involving financial theory, methods of engineering, tools of mathematics and the practice of programming. It has also been defined as the application of technical methods, especially from mathe ...
: the application of technical methods, especially from mathematical finance and computational finance, in the practice of finance
*
Industrial plant configuration: sizing of necessary infrastructure used in support and maintenance of a given facility.
*
Facility management
Facility management or facilities management (FM) is a professional discipline focused on coordinating the use of space, infrastructure, people, and organization. Facilities management ensures that physical assets and environments are managed effe ...
: an interdisciplinary field devoted to the coordination of space, infrastructure, people and organization
*
Engineering design process
The engineering design process, also known as the engineering method, is a common series of steps that engineers use in creating functional products and processes. The process is highly iterative – parts of the process often need to be repeat ...
: formulation of a plan to help an engineer build a product with a specified performance goal.
*
Logistics
Logistics is the part of supply chain management that deals with the efficient forward and reverse flow of goods, services, and related information from the point of origin to the Consumption (economics), point of consumption according to the ...
: the management of the flow of goods between the point of origin and the point of consumption in order to meet some requirements, of customers or corporations.
*
Accounting
Accounting, also known as accountancy, is the process of recording and processing information about economic entity, economic entities, such as businesses and corporations. Accounting measures the results of an organization's economic activit ...
: the measurement, processing and communication of financial information about economic entities
*
Capital projects: the management of activities in capital projects involves the flow of resources, or inputs, as they are transformed into outputs.
Many of the tools and principles of industrial engineering can be applied to the configuration of work activities within a project. The application of industrial engineering and operations management concepts and techniques to the execution of projects has been thus referred to as Project Production Management.
[ Traditionally, a major aspect of industrial engineering was planning the layouts of factories and designing assembly lines and other manufacturing paradigms. And now, in ]lean manufacturing
Lean manufacturing is a methods of production, method of manufacturing goods aimed primarily at reducing times within the Operations management#Production systems, production system as well as response times from suppliers and customers. It is ...
systems, industrial engineers work to eliminate wastes of time, money, materials, energy, and other resources.
Examples of where industrial engineering might be used include flow process charting, process mapping, designing an assembly workstation, strategizing for various operational logistics, consulting as an efficiency expert, developing a new financial algorithm or loan system for a bank, streamlining operation and emergency room location or usage in a hospital, planning complex distribution schemes for materials or products (referred to as supply-chain management), and shortening lines (or queues) at a bank, hospital, or a theme park.
Modern industrial engineers typically use predetermined motion time system
A predetermined motion time system (PMTS) is frequently used to perform labor minute costing in order to set piece-rates, wage-rates or incentives in labor oriented industries by quantifying the amount of time required to perform specific tasks un ...
, computer simulation
Computer simulation is the running of a mathematical model on a computer, the model being designed to represent the behaviour of, or the outcome of, a real-world or physical system. The reliability of some mathematical models can be determin ...
(especially discrete event simulation
A discrete-event simulation (DES) models the operation of a system as a (discrete) sequence of events in time. Each event occurs at a particular instant in time and marks a change of state in the system. Between consecutive events, no change in th ...
), along with extensive mathematical tools for modeling, such as mathematical optimization
Mathematical optimization (alternatively spelled ''optimisation'') or mathematical programming is the selection of a best element, with regard to some criteria, from some set of available alternatives. It is generally divided into two subfiel ...
and queueing theory
Queueing theory is the mathematical study of waiting lines, or queues. A queueing model is constructed so that queue lengths and waiting time can be predicted. Queueing theory is generally considered a branch of operations research because th ...
, and computational methods for system analysis, evaluation, and optimization. Industrial engineers also use the tools of data science
Data science is an interdisciplinary academic field that uses statistics, scientific computing, scientific methods, processing, scientific visualization, algorithms and systems to extract or extrapolate knowledge from potentially noisy, stru ...
and machine learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of study in artificial intelligence concerned with the development and study of Computational statistics, statistical algorithms that can learn from data and generalise to unseen data, and thus perform Task ( ...
in their work owing to the strong relatedness of these disciplines with the field and the similar technical background required of industrial engineers (including a strong foundation in probability theory
Probability theory or probability calculus is the branch of mathematics concerned with probability. Although there are several different probability interpretations, probability theory treats the concept in a rigorous mathematical manner by expre ...
, linear algebra
Linear algebra is the branch of mathematics concerning linear equations such as
:a_1x_1+\cdots +a_nx_n=b,
linear maps such as
:(x_1, \ldots, x_n) \mapsto a_1x_1+\cdots +a_nx_n,
and their representations in vector spaces and through matrix (mathemat ...
, and statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a s ...
, as well as having coding skills).
Manufacturing (production) engineering
Manufacturing Engineering is based on core industrial engineering
Industrial engineering (IE) is concerned with the design, improvement and installation of integrated systems of people, materials, information, equipment and energy. It draws upon specialized knowledge and skill in the mathematical, physical, an ...
and mechanical engineering
Mechanical engineering is the study of physical machines and mechanism (engineering), mechanisms that may involve force and movement. It is an engineering branch that combines engineering physics and engineering mathematics, mathematics principl ...
skills, adding important elements from mechatronics, commerce, economics and business management. This field also deals with the integration of different facilities and systems for producing quality products (with optimal expenditure) by applying the principles of physics and the results of manufacturing systems studies, such as the following:
* Craft
A craft or trade is a pastime or an occupation that requires particular skills and knowledge of skilled work. In a historical sense, particularly the Middle Ages and earlier, the term is usually applied to people occupied in small scale pr ...
or Guild
A guild ( ) is an association of artisans and merchants who oversee the practice of their craft/trade in a particular territory. The earliest types of guild formed as organizations of tradespeople belonging to a professional association. They so ...
* Putting-out system
The putting-out system is a means of subcontracting work, like a tailor. Historically, it was also known as the workshop system and the domestic system. In putting-out, work is contracted by a central agent to subcontractors who complete the p ...
* British factory system
The factory system is a method of manufacturing whereby workers and manufacturing equipment are centralized in a factory, the work is supervised and structured through a division of labor, and the manufacturing process is mechanized.
Because ...
* American system of manufacturing
The American system of manufacturing was a set of manufacturing methods that evolved in the 19th century. The two notable features were the extensive use of interchangeable parts and mechanization for production, which resulted in more efficient u ...
* Soviet collectivism in manufacturing
* Mass production
Mass production, also known as mass production, series production, series manufacture, or continuous production, is the production of substantial amounts of standardized products in a constant flow, including and especially on assembly lines ...
* Computer integrated manufacturing
* Computer-aided technologies in manufacturing
* Just in time manufacturing
* Lean manufacturing
Lean manufacturing is a methods of production, method of manufacturing goods aimed primarily at reducing times within the Operations management#Production systems, production system as well as response times from suppliers and customers. It is ...
* Flexible manufacturing
* Mass customization
Mass customization makes use of flexible computer-aided systems to produce custom products. Such systems combine the low unit costs of mass production processes with the flexibility of individual customization.
Mass customization is the new fro ...
* Agile manufacturing
* Rapid manufacturing
* Prefabrication
Prefabrication is the practice of assembling components of a structure in a factory or other manufacturing site, and transporting complete assemblies or sub-assemblies to the construction site where the structure is to be located. Some research ...
* Ownership
Ownership is the state or fact of legal possession and control over property, which may be any asset, tangible or intangible. Ownership can involve multiple rights, collectively referred to as '' title'', which may be separated and held by dif ...
* Fabrication
Fabrication may refer to:
* Manufacturing, specifically the crafting of individual parts as a solo product or as part of a larger combined product.
Processes in arts, crafts and manufacturing
*Semiconductor device fabrication, the process used t ...
* Publication
To publish is to make content available to the general public.[Berne Convention, articl ...](_blank)
 Manufacturing engineers develop and create physical artifacts, production processes, and technology. It is a very broad area which includes the design and development of products. Manufacturing engineering is considered to be a sub-discipline of
Manufacturing engineers develop and create physical artifacts, production processes, and technology. It is a very broad area which includes the design and development of products. Manufacturing engineering is considered to be a sub-discipline of industrial engineering
Industrial engineering (IE) is concerned with the design, improvement and installation of integrated systems of people, materials, information, equipment and energy. It draws upon specialized knowledge and skill in the mathematical, physical, an ...
/systems engineering
Systems engineering is an interdisciplinary field of engineering and engineering management that focuses on how to design, integrate, and manage complex systems over their Enterprise life cycle, life cycles. At its core, systems engineering uti ...
and has very strong overlaps with mechanical engineering
Mechanical engineering is the study of physical machines and mechanism (engineering), mechanisms that may involve force and movement. It is an engineering branch that combines engineering physics and engineering mathematics, mathematics principl ...
. Manufacturing engineers' success or failure directly impacts the advancement of technology and the spread of innovation. This field of manufacturing engineering emerged from tool and die discipline in the early 20th century. It expanded greatly from the 1960s when industrialized countries introduced factories with:
1. Numerical control
Computer numerical control (CNC) or CNC machining is the automated control of machine tools by a computer. It is an evolution of numerical control (NC), where machine tools are directly managed by data storage media such as punched cards or ...
machine tools and automated systems of production.
2. Advanced statistical methods of quality control
Quality control (QC) is a process by which entities review the quality of all factors involved in production. ISO 9000 defines quality control as "a part of quality management focused on fulfilling quality requirements".
This approach plac ...
: These factories were pioneered by the American electrical engineer William Edwards Deming
William Edwards Deming (October 14, 1900 – December 20, 1993) was an American business theorist, composer, economist, industrial engineer, management consultant, statistician, and writer. Educated initially as an electrical engineer and later ...
, who was initially ignored by his home country. The same methods of quality control later turned Japanese factories into world leaders in cost-effectiveness and production quality.
3. Industrial robots
An industrial robot is a robot system used for manufacturing. Industrial robots are automated, programmable and capable of movement on three or more axes.
Typical applications of robots include robot welding, welding, painting, assembly, Circu ...
on the factory floor, introduced in the late 1970s: These computer-controlled welding
Welding is a fabrication (metal), fabrication process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, primarily by using high temperature to melting, melt the parts together and allow them to cool, causing Fusion welding, fusion. Co ...
arms and grippers could perform simple tasks such as attaching a car door quickly and flawlessly 24 hours a day. This cut costs and improved production speed.
Education
Industrial engineering
Undergraduate curriculum
In the United States the undergraduate degree earned is the Bachelor of Science (B.S.) or Bachelor of Science and Engineering (B.S.E.) in Industrial Engineering (IE). Variations of the title include Industrial & Operations Engineering (IOE), and Industrial & Systems Engineering (ISE). The typical curriculum includes a broad math and science foundation spanning chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules a ...
, physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge whi ...
, mechanics (i.e., statics, kinematics, and dynamics), materials science, computer science, electronics/circuits, engineering design
The engineering design process, also known as the engineering method, is a common series of steps that engineers use in creating functional products and processes. The process is highly iterative – parts of the process often need to be repeat ...
, and the standard range of engineering mathematics (i.e. calculus
Calculus is the mathematics, mathematical study of continuous change, in the same way that geometry is the study of shape, and algebra is the study of generalizations of arithmetic operations.
Originally called infinitesimal calculus or "the ...
, linear algebra
Linear algebra is the branch of mathematics concerning linear equations such as
:a_1x_1+\cdots +a_nx_n=b,
linear maps such as
:(x_1, \ldots, x_n) \mapsto a_1x_1+\cdots +a_nx_n,
and their representations in vector spaces and through matrix (mathemat ...
, differential equations, statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a s ...
). For any engineering undergraduate program to be accredited, regardless of concentration, it must cover a largely similar span of such foundational work – which also overlaps heavily with the content tested on one or more engineering licensure exams in most jurisdictions.
The coursework specific to IE entails specialized courses in areas such as optimization
Mathematical optimization (alternatively spelled ''optimisation'') or mathematical programming is the selection of a best element, with regard to some criteria, from some set of available alternatives. It is generally divided into two subfiel ...
, applied probability
Applied probability is the application of probability theory to statistical problems and other scientific and engineering domains.
Scope
Much research involving probability is done under the auspices of applied probability. However, while such re ...
, stochastic Stochastic (; ) is the property of being well-described by a random probability distribution. ''Stochasticity'' and ''randomness'' are technically distinct concepts: the former refers to a modeling approach, while the latter describes phenomena; i ...
modeling, design of experiments
The design of experiments (DOE), also known as experiment design or experimental design, is the design of any task that aims to describe and explain the variation of information under conditions that are hypothesized to reflect the variation. ...
, statistical process control
Statistical process control (SPC) or statistical quality control (SQC) is the application of statistics, statistical methods to monitor and control the quality of a production process. This helps to ensure that the process operates efficiently, ...
, simulation
A simulation is an imitative representation of a process or system that could exist in the real world. In this broad sense, simulation can often be used interchangeably with model. Sometimes a clear distinction between the two terms is made, in ...
, manufacturing engineering
Manufacturing engineering or production engineering is a branch of professional engineering that shares many common concepts and ideas with other fields of engineering such as mechanical, chemical, electrical, and industrial engineering.
Manufac ...
, ergonomics
Ergonomics, also known as human factors or human factors engineering (HFE), is the application of Psychology, psychological and Physiology, physiological principles to the engineering and design of products, processes, and systems. Primary goa ...
/safety engineering
Safety engineering is an engineering Branches of science, discipline which assures that engineered systems provide acceptable levels of safety. It is strongly related to industrial engineering/systems engineering, and the subset system safety en ...
, and engineering economics
Engineering economics, previously known as engineering economy, is a subset of economics concerned with the use and "...application of economic principles"Dharmaraj, E.. Engineering Economics. Mumbai, IN: Himalaya Publishing House, 2009. ProQu ...
. Industrial engineering elective courses typically cover more specialized topics in areas such as manufacturing
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of the
secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer ...
, supply chains
A supply chain is a complex logistics system that consists of facilities that convert raw materials into finished products and distribute them to end consumers or end customers, while supply chain management deals with the flow of goods in distr ...
and logistics
Logistics is the part of supply chain management that deals with the efficient forward and reverse flow of goods, services, and related information from the point of origin to the Consumption (economics), point of consumption according to the ...
, analytics
Analytics is the systematic computational analysis of data or statistics. It is used for the discovery, interpretation, and communication of meaningful patterns in data, which also falls under and directly relates to the umbrella term, data sc ...
and machine learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of study in artificial intelligence concerned with the development and study of Computational statistics, statistical algorithms that can learn from data and generalise to unseen data, and thus perform Task ( ...
, production systems, human factors
Ergonomics, also known as human factors or human factors engineering (HFE), is the application of psychological and physiological principles to the engineering and design of products, processes, and systems. Primary goals of human factors eng ...
and industrial design
Industrial design is a process of design applied to physical Product (business), products that are to be manufactured by mass production. It is the creative act of determining and defining a product's form and features, which takes place in adva ...
, and service system
A service system (also customer service system (CSS)) is a configuration of technology and organizational networks designed to deliver services that satisfy the needs, wants, or aspirations of customers. "Service system" is a term used in the s ...
s.
Certain business schools may offer programs with some overlapping relevance to IE, but the engineering programs are distinguished by a much more intensely quantitative focus, required engineering science electives, and the core math and science courses required of all engineering programs.
Graduate curriculum
The usual graduate degree earned is the Master of Science (MS) or Master of Science and Engineering (MSE) in Industrial Engineering or various alternative related concentration titles. Typical MS curricula may cover:
* Operations research
Operations research () (U.S. Air Force Specialty Code: Operations Analysis), often shortened to the initialism OR, is a branch of applied mathematics that deals with the development and application of analytical methods to improve management and ...
and optimization
Mathematical optimization (alternatively spelled ''optimisation'') or mathematical programming is the selection of a best element, with regard to some criteria, from some set of available alternatives. It is generally divided into two subfiel ...
techniques
* Engineering economics
Engineering economics, previously known as engineering economy, is a subset of economics concerned with the use and "...application of economic principles"Dharmaraj, E.. Engineering Economics. Mumbai, IN: Himalaya Publishing House, 2009. ProQu ...
* Supply chain management
In commerce, supply chain management (SCM) deals with a system of procurement (purchasing raw materials/components), operations management, logistics and marketing channels, through which raw materials can be developed into finished produc ...
and logistics
Logistics is the part of supply chain management that deals with the efficient forward and reverse flow of goods, services, and related information from the point of origin to the Consumption (economics), point of consumption according to the ...
* Systems simulation and stochastic Stochastic (; ) is the property of being well-described by a random probability distribution. ''Stochasticity'' and ''randomness'' are technically distinct concepts: the former refers to a modeling approach, while the latter describes phenomena; i ...
processes
* Analytics
Analytics is the systematic computational analysis of data or statistics. It is used for the discovery, interpretation, and communication of meaningful patterns in data, which also falls under and directly relates to the umbrella term, data sc ...
and machine learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of study in artificial intelligence concerned with the development and study of Computational statistics, statistical algorithms that can learn from data and generalise to unseen data, and thus perform Task ( ...
* Manufacturing systems/manufacturing engineering
Manufacturing engineering or production engineering is a branch of professional engineering that shares many common concepts and ideas with other fields of engineering such as mechanical, chemical, electrical, and industrial engineering.
Manufac ...
* Human factors engineering and ergonomics (safety engineering
Safety engineering is an engineering Branches of science, discipline which assures that engineered systems provide acceptable levels of safety. It is strongly related to industrial engineering/systems engineering, and the subset system safety en ...
)
* Production planning and control
* System analysis and techniques
* Management science
Management science (or managerial science) is a wide and interdisciplinary study of solving complex problems and making strategic decisions as it pertains to institutions, corporations, governments and other types of organizational entities. It is ...
s
* Computer-aided manufacturing
Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) also known as computer-aided modeling or computer-aided machining is the use of software to control machine tools in the manufacturing of work pieces. This is not the only definition for CAM, but it is the most ...
* Lean Six Sigma
* Financial engineering
Financial engineering is a multidisciplinary field involving financial theory, methods of engineering, tools of mathematics and the practice of programming. It has also been defined as the application of technical methods, especially from mathe ...
* Facilities design and work-space design
* Quality engineering
Quality engineering is the discipline of engineering concerned with the principles and practice of product and service quality assurance and quality control, control. In software development, it is the management, development, operation and main ...
* Reliability engineering
Reliability engineering is a sub-discipline of systems engineering that emphasizes the ability of equipment to function without failure. Reliability is defined as the probability that a product, system, or service will perform its intended functi ...
and life testing
* Statistical process control
Statistical process control (SPC) or statistical quality control (SQC) is the application of statistics, statistical methods to monitor and control the quality of a production process. This helps to ensure that the process operates efficiently, ...
or quality control
Quality control (QC) is a process by which entities review the quality of all factors involved in production. ISO 9000 defines quality control as "a part of quality management focused on fulfilling quality requirements".
This approach plac ...
* Time and motion study
A time and motion study (or time–motion study) is a business efficiency technique combining the ''time study'' work of Frederick Winslow Taylor with the ''motion study'' work of Frank and Lillian Gilbreth (the same couple as is best known t ...
* Predetermined motion time system
A predetermined motion time system (PMTS) is frequently used to perform labor minute costing in order to set piece-rates, wage-rates or incentives in labor oriented industries by quantifying the amount of time required to perform specific tasks un ...
and computer use for IE
* Operations management
Operations management is concerned with designing and controlling the production (economics), production of good (economics), goods and service (economics), services, ensuring that businesses are efficiency, efficient in using resources to meet ...
* Project management
Project management is the process of supervising the work of a Project team, team to achieve all project goals within the given constraints. This information is usually described in project initiation documentation, project documentation, crea ...
* Productivity
Productivity is the efficiency of production of goods or services expressed by some measure. Measurements of productivity are often expressed as a ratio of an aggregate output to a single input or an aggregate input used in a production proce ...
improvement
* Materials management
Materials management is a core supply chain function and includes supply chain planning and supply chain execution capabilities. Specifically, materials management is the capability firms use to plan total material requirements. The material re ...
* Robotics
Robotics is the interdisciplinary study and practice of the design, construction, operation, and use of robots.
Within mechanical engineering, robotics is the design and construction of the physical structures of robots, while in computer s ...
* Product development
New product development (NPD) or product development in business and engineering covers the complete process of launching a new product to the market. Product development also includes the renewal of an existing product and introducing a product ...
* System dynamics
System dynamics (SD) is an approach to understanding the nonlinear behaviour of complex systems over time using stocks, flows, internal feedback loops, table functions and time delays.
Overview
System dynamics is a methodology and mathematical ...
and policy planning
Manufacturing (production) engineering
Degree certification programs
Manufacturing engineers possess an associate's or bachelor's degree in engineering with a major in manufacturing engineering. The length of study for such a degree is usually two to five years followed by five more years of professional practice to qualify as a professional engineer. Working as a manufacturing engineering technologist involves a more applications-oriented qualification path.
Academic degrees for manufacturing engineers are usually the Associate or Bachelor of Engineering, Eor Eng
Eng or ENG may refer to:
Language and linguistics
* Eng (letter), Ŋ ŋ
* En with descender, Ң ң
* eng, ISO 639-3 and ISO 639-2 code for English language
* Velar nasal, a phoneme
People
* Eng (name), a given name and surname in various cu ...
and the Associate or Bachelor of Science, Sor Sc For manufacturing technologists the required degrees are Associate or Bachelor of Technology .TECHor Associate or Bachelor of Applied Science AScin Manufacturing, depending upon the university. Master's degrees in engineering manufacturing include Master of Engineering Eor Eng
Eng or ENG may refer to:
Language and linguistics
* Eng (letter), Ŋ ŋ
* En with descender, Ң ң
* eng, ISO 639-3 and ISO 639-2 code for English language
* Velar nasal, a phoneme
People
* Eng (name), a given name and surname in various cu ...
in Manufacturing, Master of Science .Scin Manufacturing Management, Master of Science .Scin Industrial and Production Management, and Master of Science .Scas well as Master of Engineering Ein Design, which is a subdiscipline of manufacturing. Doctoral hDor Eng
Eng or ENG may refer to:
Language and linguistics
* Eng (letter), Ŋ ŋ
* En with descender, Ң ң
* eng, ISO 639-3 and ISO 639-2 code for English language
* Velar nasal, a phoneme
People
* Eng (name), a given name and surname in various cu ...
level courses in manufacturing are also available depending on the university.
The undergraduate degree curriculum generally includes courses in physics, mathematics, computer science, project management, and specific topics in mechanical and manufacturing engineering. Initially such topics cover most, if not all, of the subdisciplines of manufacturing engineering. Students then choose to specialize in one or more sub disciplines towards the end of their degree work.
Specific to Industrial Engineers, people will see courses covering ergonomics, scheduling, inventory management, forecasting, product development, and in general courses that focus on optimization. Most colleges breakdown the large sections of industrial engineering into Healthcare, Ergonomics, Product Development, or Consulting sectors. This allows for the student to get a good grasp on each of the varying sub-sectors so they know what area they are most interested about pursuing a career in.
Undergraduate curriculum
The Foundational Curriculum for a bachelor's degree of Manufacturing Engineering or Production Engineering includes below mentioned Syllabus. This Syllabus is closely related to Industrial Engineering and Mechanical Engineering. But it Differs by Placing more Emphasis on Manufacturing Science or Production Science. It includes following:
* Mathematics (Calculus, Differential Equations, Statistics and Linear Algebra)
* Mechanics (Statics & Dynamics)
* Solid Mechanics
* Fluid Mechanics
* Materials Science
* Strength of Materials
* Fluid Dynamics
* Hydraulics
* Pneumatics
* HVAC (Heating, Ventilation & Air Conditioning)
* Heat Transfer
* Applied Thermodynamics
* Energy conversion
Energy transformation, also known as energy conversion, is the process of changing energy from one form to another. In physics, energy is a quantity that provides the capacity to perform Work (physics), work (e.g. lifting an object) or provides ...
* Instrumentation and Measurement
* Engineering Drawing (Drafting) & Engineering Design
* Engineering Graphics
* Mechanism Design including Kinematics and Dynamics
* Manufacturing Processes
* Mechatronics
Mechatronics engineering, also called mechatronics, is the synergistic integration of mechanical, electrical, and computer systems employing mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, electronic engineering and computer engineering, and also ...
* Circuit analysis
In electrical engineering and electronics, a '' network'' is a collection of interconnected components. Network analysis is the process of finding the voltages across, and the currents through, all network components. There are many techniques ...
* Lean manufacturing
Lean manufacturing is a methods of production, method of manufacturing goods aimed primarily at reducing times within the Operations management#Production systems, production system as well as response times from suppliers and customers. It is ...
* Automation
* Reverse Engineering
* Quality Control
* CAD (Computer aided Design which includes Solid Modelling) and CAM (Computer aided Manufacturing)
A degree in Manufacturing Engineering versus Mechanical Engineering will typically differ only by a few specialized classes. Mechanical Engineering degree focuses more on the Product Design Process and on Complex Products which requires more Mathematics Expertise.
Manufacturing engineering certification
Professional engineering license
A Professional Engineer
A professional is a member of a profession or any person who works in a specified professional activity. The term also describes the standards of education and training that prepare members of the profession with the particular knowledge and ski ...
, PE, is a licensed engineer who is permitted to offer professional services to the public. Professional Engineers may prepare, sign, seal, and submit engineering plans to the public. Before a candidate can become a professional engineer, they will need to receive a bachelor's degree from an ABET
ABET (pronounced A-bet), formerly known as the Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology, Inc., is a non-governmental accreditation organization for post-secondary programs in engineering, engineering technology, computing, and applied ...
recognized university in the US, take and pass the Fundamentals of Engineering exam to become an "engineer-in-training", and work four years under the supervision of a professional engineer. After those tasks are complete the candidate will be able to take the PE exam. Upon receiving a passing score on the test, the candidate will receive their PE License .
Society of Manufacturing Engineers (SME) certifications (USA)
The SME (society)
SME, also known as the Society of Manufacturing Engineers, is a non-profit student and professional association for educating and advancing the manufacturing industry in North America.
History
SME was founded in January 1932 at the height of ...
administers qualifications specifically for the manufacturing industry. These are not degree level qualifications and are not recognized at the professional engineering level. The SME offers two certifications for Manufacturing engineers: Certified Manufacturing Technologist Certificate (CMfgT) and Certified Manufacturing Engineer (CMfgE).
Certified manufacturing technologist
Qualified candidates for the Certified Manufacturing Technologist Certificate (CMfgT) must pass a three-hour, 130-question multiple-choice exam. The exam covers math, manufacturing processes, manufacturing management, automation, and related subjects. A score of 60% or higher must be achieved to pass the exam. Additionally, a candidate must have at least four years of combined education and manufacturing-related work experience. The CMfgT certification must be renewed every three years in order to stay certified.
Certified manufacturing engineer
Certified Manufacturing Engineer (CMfgE) is an engineering qualification administered by the Society of Manufacturing Engineers, Dearborn, Michigan, USA. Candidates qualifying for a Certified Manufacturing Engineer credential must pass a four-hour, 180 question multiple-choice exam which covers more in-depth topics than does the CMfgT exam. A score of 60% or higher must be achieved to pass the exam. CMfgE candidates must also have eight years of combined education and manufacturing-related work experience, with a minimum of four years of work experience. The CMfgT certification must be renewed every three years in order to stay certified.
Research
Industrial engineering
Human factors
The human factors
Ergonomics, also known as human factors or human factors engineering (HFE), is the application of psychological and physiological principles to the engineering and design of products, processes, and systems. Primary goals of human factors eng ...
area specializes in exploring how systems fit the people who must operate them, determining the roles of people with the systems, and selecting those people who can best fit particular roles within these systems. Students who focus on Human Factors will be able to work with a multidisciplinary team of faculty with strengths in understanding cognitive behavior as it relates to automation, air and ground transportation, medical studies, and space exploration.
Production systems
The production systems area develops new solutions in areas such as engineering design, supply chain management (e.g. supply chain system design, error recovery, large scale systems), manufacturing (e.g. system design, planning and scheduling), and medicine (e.g. disease diagnosis, discovery of medical knowledge). Students who focus on production systems will be able to work on topics related to computational intelligence theories for applications in industry, healthcare, and service organizations.
Reliability systems
The objective of the reliability systems area is to provide students with advanced data analysis and decision making techniques that will improve quality and reliability of complex systems. Students who focus on system reliability and uncertainty will be able to work on areas related to contemporary reliability systems including integration of quality and reliability, simultaneous life cycle design for manufacturing systems, decision theory in quality and reliability engineering, condition-based maintenance and degradation modeling, discrete event simulation and decision analysis.
Wind power management
The Wind Power Management Program aims at meeting the emerging needs for graduating professionals involved in design, operations, and management of wind farm
A wind farm, also called a wind park or wind power plant, is a group of wind turbines in the same location used to produce electricity. Wind farms vary in size from a small number of turbines to several hundred wind turbines covering an exten ...
s deployed in massive numbers all over the country. The graduates will be able to fully understand the system and management issues of wind farms and their interactions with alternative and conventional power generation systems.
Production (manufacturing) engineering
Flexible manufacturing systems
 A
A flexible manufacturing system
A flexible manufacturing system (FMS) is a manufacturing system in which there is some amount of flexibility that allows the system to react in case of changes, whether predicted or unpredicted.
This flexibility is generally considered to fall ...
(FMS) is a manufacturing system in which there is some amount of flexibility that allows the system to react to changes, whether predicted or unpredicted. This flexibility is generally considered to fall into two categories, both of which have numerous subcategories. The first category, machine flexibility, covers the system's ability to be changed to produce new product types and the ability to change the order of operations executed on a part. The second category, called routing flexibility, consists of the ability to use multiple machines to perform the same operation on a part, as well as the system's ability to absorb large-scale changes, such as in volume, capacity, or capability.
Most FMS systems comprise three main systems. The work machines, which are often automated CNC machines, are connected by a material handling system to optimize parts flow, and to a central control computer, which controls material movements and machine flow. The main advantages of an FMS is its high flexibility in managing manufacturing resources like time and effort in order to manufacture a new product. The best application of an FMS is found in the production of small sets of products from a mass production.
Computer integrated manufacturing
Computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM) in engineering is a method of manufacturing in which the entire production process is controlled by computer. Traditionally separated process methods are joined through a computer by CIM. This integration allows the processes to exchange information and to initiate actions. Through this integration, manufacturing can be faster and less error-prone, although the main advantage is the ability to create automated manufacturing processes. Typically CIM relies on closed-loop control processes based on real-time input from sensors. It is also known as flexible design and manufacturing.
Friction stir welding
 Friction stir welding was discovered in 1991 by The Welding Institute (TWI). This innovative steady state (non-fusion) welding technique joins previously un-weldable materials, including several aluminum alloys. It may play an important role in the future construction of airplanes, potentially replacing rivets. Current uses of this technology to date include: welding the seams of the aluminum main space shuttle external tank, the Orion Crew Vehicle test article, Boeing Delta II and Delta IV Expendable Launch Vehicles and the SpaceX Falcon 1 rocket; armor plating for amphibious assault ships; and welding the wings and fuselage panels of the new Eclipse 500 aircraft from Eclipse Aviation, among an increasingly growing range of uses.
Friction stir welding was discovered in 1991 by The Welding Institute (TWI). This innovative steady state (non-fusion) welding technique joins previously un-weldable materials, including several aluminum alloys. It may play an important role in the future construction of airplanes, potentially replacing rivets. Current uses of this technology to date include: welding the seams of the aluminum main space shuttle external tank, the Orion Crew Vehicle test article, Boeing Delta II and Delta IV Expendable Launch Vehicles and the SpaceX Falcon 1 rocket; armor plating for amphibious assault ships; and welding the wings and fuselage panels of the new Eclipse 500 aircraft from Eclipse Aviation, among an increasingly growing range of uses.
Employment
Industrial engineering
The total number of engineers employed in the US in 2015 was roughly 1.6 million. Of these, 272,470 were industrial engineers (16.92%), the third most popular engineering specialty. The median salaries by experience level are $62,000 with 0–5 years experience, $75,000 with 5–10 years experience, and $81,000 with 10–20 years experience. The average starting salaries were $55,067 with a bachelor's degree, $77,364 with a master's degree, and $100,759 with a doctorate degree. This places industrial engineering at 7th of 15 among engineering bachelor's degrees, 3rd of 10 among master's degrees, and 2nd of 7 among doctorate degrees in average annual salary. The median annual income of industrial engineers in the U.S. workforce is $83,470.
Production (manufacturing) engineering
Manufacturing engineering is just one facet of the engineering industry. Manufacturing engineers enjoy improving the production process from start to finish. They have the ability to keep the whole production process in mind as they focus on a particular portion of the process. Successful students in manufacturing engineering degree programs are inspired by the notion of starting with a natural resource, such as a block of wood, and ending with a usable, valuable product, such as a desk, produced efficiently and economically.
Manufacturing engineers are closely connected with engineering and industrial design efforts. Examples of major companies that employ manufacturing engineers in the United States include General Motors Corporation
General Motors Company (GM) is an American multinational automotive manufacturing company headquartered in Detroit, Michigan, United States. The company is most known for owning and manufacturing four automobile brands: Chevrolet, Buick, GMC, ...
, Ford Motor Company, Chrysler
FCA US, LLC, Trade name, doing business as Stellantis North America and known historically as Chrysler ( ), is one of the "Big Three (automobile manufacturers), Big Three" automobile manufacturers in the United States, headquartered in Auburn H ...
, Boeing
The Boeing Company, or simply Boeing (), is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and product support s ...
, Gates Corporation
Gates Industrial Corporation plc, based in Denver, Colorado, is a manufacturer of power transmission belts and fluid power products, which are used in diverse industrial and automotive applications. The company employs over 15,000 and has sales ...
and Pfizer
Pfizer Inc. ( ) is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Pharmaceutical industry, pharmaceutical and biotechnology corporation headquartered at The Spiral (New York City), The Spiral in Manhattan, New York City. Founded in 184 ...
. Examples in Europe include Airbus
Airbus SE ( ; ; ; ) is a Pan-European aerospace corporation. The company's primary business is the design and manufacturing of commercial aircraft but it also has separate Airbus Defence and Space, defence and space and Airbus Helicopters, he ...
, Daimler, BMW
Bayerische Motoren Werke AG, trading as BMW Group (commonly abbreviated to BMW (), sometimes anglicised as Bavarian Motor Works), is a German multinational manufacturer of vehicles and motorcycles headquartered in Munich, Bavaria, Germany. Th ...
, Fiat
Fiat Automobiles S.p.A., commonly known as simply Fiat ( , ; ), is an Italian automobile manufacturer. It became a part of Fiat Chrysler Automobiles in 2014 and, in 2021, became a subsidiary of Stellantis through its Italian division, Stellant ...
, Navistar International
International Motors, LLC (formerly Navistar International Corporation) is an American manufacturer of commercial vehicles and engines, established in 1986 as a successor to the International Harvester company. International Motors produces ...
, and Michelin Tyre.
Related industries
Industries where industrial and production engineers are generally employed include:
* Aerospace industry
Aerospace is a term used to collectively refer to the atmosphere and outer space. Aerospace activity is very diverse, with a multitude of commercial, industrial, and military applications. Aerospace engineering consists of aeronautics and astr ...
* Automotive industry
The automotive industry comprises a wide range of company, companies and organizations involved in the design, Business development, development, manufacturing, marketing, selling, Maintenance, repairing, and Custom car, modification of motor ve ...
* Chemical industry
The chemical industry comprises the companies and other organizations that develop and produce industrial, specialty and other chemicals. Central to the modern world economy, the chemical industry converts raw materials ( oil, natural gas, air, ...
* Computer industry
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to automatically carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (''computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as ''programs'', ...
* Electronics industry
The electronics industry is the industry (economics), industry that produces electronic devices. It emerged in the 20th century and is today one of the largest global industries. Contemporary society uses a vast array of electronic devices that ar ...
* Food processing industry
* Garment industry
Clothing industry or garment industry summarizes the types of trade and industry along the production and value chain of clothing and garments, starting with the textile industry (producers of cotton, wool, fur, and synthetic fibre), embellishm ...
* Pharmaceutical industry
The pharmaceutical industry is a medical industry that discovers, develops, produces, and markets pharmaceutical goods such as medications and medical devices. Medications are then administered to (or self-administered by) patients for curing ...
* Plastic packaging
* Pulp and paper industry
The pulp and paper industry comprises companies that use wood, specifically pulpwood, as raw material and produce pulp, paper, paperboard, and other cellulose-based products.
Manufacturing process
In the manufacturing process, pulp is intr ...
* Toy industry
A toy or plaything is an object that is used primarily to provide entertainment. Simple examples include toy blocks, board games, and dolls. Toys are often designed for use by children, although many are designed specifically for adults and p ...
Modern tools
 Many manufacturing companies, especially those in industrialized nations, have begun to incorporate
Many manufacturing companies, especially those in industrialized nations, have begun to incorporate computer-aided engineering
Computer-aided engineering (CAE) is the general usage of technology to aid in tasks related to engineering analysis. Any use of technology to solve or assist engineering issues falls under this umbrella.
Overview
Following alongside the con ...
(CAE) programs, such as SolidWorks
SolidWorks (stylized as SOLIDWORKS) is a brand of software used for solid modeling computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided engineering (CAE). It was one of the first 3D CAD applications designed to run on a desktop PC.
The brand is owned ...
and AutoCAD
AutoCAD is a 2D and
3D computer-aided design (CAD) software application developed by Autodesk. It was first released in December 1982 for the CP/M and IBM PC platforms as a desktop app running on microcomputers with internal graphics control ...
, into their existing design and analysis processes, including 2D and 3D solid modeling computer-aided design
Computer-aided design (CAD) is the use of computers (or ) to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. This software is used to increase the productivity of the designer, improve the quality of design, improve c ...
(CAD). This method has many benefits, including easier and more exhaustive visualization of products, the ability to create virtual assemblies of parts, and ease of use in designing mating interfaces and tolerances.
SolidWorks
SolidWorks
SolidWorks (stylized as SOLIDWORKS) is a brand of software used for solid modeling computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided engineering (CAE). It was one of the first 3D CAD applications designed to run on a desktop PC.
The brand is owned ...
is an example of a CAD modeling computer program developed by Dassault Systèmes
Dassault Systèmes SE () (abbreviated 3DS) is a French Multinational corporation, multinational software corporation which develops software for 3D product design, simulation, manufacturing and other 3D related products.
Founded in 1981, it is ...
. SolidWorks is an industry standard for drafting designs and specifications for physical objects and has been used by more than 165,000 companies as of 2013.
AutoCAD
AutoCAD
AutoCAD is a 2D and
3D computer-aided design (CAD) software application developed by Autodesk. It was first released in December 1982 for the CP/M and IBM PC platforms as a desktop app running on microcomputers with internal graphics control ...
is an example of a CAD modeling computer program developed by Autodesk
Autodesk, Inc. is an American multinational software corporation that provides software products and services for the architecture, engineering, construction, manufacturing, media, education, and entertainment industries. Autodesk is headquarte ...
. AutoCad is also widely used for CAD modeling and CAE.finite element analysis
Finite element method (FEM) is a popular method for numerically solving differential equations arising in engineering and mathematical models, mathematical modeling. Typical problem areas of interest include the traditional fields of structural ...
(FEA), computational fluid dynamics
Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is a branch of fluid mechanics that uses numerical analysis and data structures to analyze and solve problems that involve fluid dynamics, fluid flows. Computers are used to perform the calculations required ...
(CFD), and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM). Using CAE programs, a mechanical design team can quickly and cheaply iterate the design process to develop a product that better meets cost, performance, and other constraints. There is no need to create a physical prototype until the design nears completion, allowing hundreds or thousands of designs to be evaluated, instead of relatively few. In addition, CAE analysis programs can model complicated physical phenomena which cannot be solved by hand, such as viscoelasticity
In materials science and continuum mechanics, viscoelasticity is the property of materials that exhibit both viscous and elastic characteristics when undergoing deformation. Viscous materials, like water, resist both shear flow and strain lin ...
, complex contact between mating parts, or non- Newtonian flows.
Just as manufacturing engineering is linked with other disciplines, such as mechatronics, multidisciplinary design optimization
Multi-disciplinary design optimization (MDO) is a field of engineering that uses optimization methods to solve design problems incorporating a number of disciplines. It is also known as multidisciplinary system design optimization (MSDO), and mul ...
(MDO) is also being used with other CAE programs to automate and improve the iterative design process.
Sub-disciplines
Mechanics
 Classical Mechanics, attempts to use Newtons basic laws of motion to describe how a body will react when that body undergoes a force. However modern
Classical Mechanics, attempts to use Newtons basic laws of motion to describe how a body will react when that body undergoes a force. However modern mechanics
Mechanics () is the area of physics concerned with the relationships between force, matter, and motion among Physical object, physical objects. Forces applied to objects may result in Displacement (vector), displacements, which are changes of ...
includes the rather recent quantum theory. Sub disciplines of mechanics include:
Classical Mechanics:
* Statics
Statics is the branch of classical mechanics that is concerned with the analysis of force and torque acting on a physical system that does not experience an acceleration, but rather is in mechanical equilibrium, equilibrium with its environment ...
, the study of non-moving bodies at equilibrium.
*Kinematics
In physics, kinematics studies the geometrical aspects of motion of physical objects independent of forces that set them in motion. Constrained motion such as linked machine parts are also described as kinematics.
Kinematics is concerned with s ...
, is the study of the motion of bodies (objects) and systems (groups of objects), while ignoring the forces that cause the motion.Fluid mechanics
Fluid mechanics is the branch of physics concerned with the mechanics of fluids (liquids, gases, and plasma (physics), plasmas) and the forces on them.
Originally applied to water (hydromechanics), it found applications in a wide range of discipl ...
, the study of how the principles of classical mechanics are observed with liquids and gases.
* Continuum mechanics
Continuum mechanics is a branch of mechanics that deals with the deformation of and transmission of forces through materials modeled as a ''continuous medium'' (also called a ''continuum'') rather than as discrete particles.
Continuum mec ...
, a method of applying mechanics that assumes that objects are continuous (rather than discrete)
Quantum:
*Quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics is the fundamental physical Scientific theory, theory that describes the behavior of matter and of light; its unusual characteristics typically occur at and below the scale of atoms. Reprinted, Addison-Wesley, 1989, It is ...
, the study of atoms, molecules, electrons, protons, and neutrons on a sub atomic scale. This type of mechanics attempts to explain their motion and physical properties within an atom.
If the engineering project were to design a vehicle, statics might be employed to design the frame of the vehicle in order to evaluate where the stresses will be most intense. Dynamics might be used when designing the car's engine to evaluate the forces in the pistons and cams as the engine cycles. Mechanics of materials might be used to choose appropriate materials for the manufacture of the frame and engine. Fluid mechanics might be used to design a ventilation system for the vehicle or to design the intake system for the engine.
Drafting
 Drafting or
Drafting or technical drawing
Technical drawing, drafting or drawing, is the act and discipline of composing drawings that visually communicate how something functions or is constructed.
Technical drawing is essential for communicating ideas in industry and engineering. ...
is the means by which manufacturers create instructions for manufacturing parts. A technical drawing can be a computer model or hand-drawn schematic showing all the dimensions necessary to manufacture a part, as well as assembly notes, a list of required materials, and other pertinent information. A skilled worker who creates technical drawings may be referred to as a drafter or draftsman
A drafter (also draughtsman / draughtswoman in British and Commonwealth English, draftsman / draftswoman, drafting technician, or CAD technician in American and Canadian English) is an engineering technician who makes detailed technical drawi ...
. Drafting has historically been a two-dimensional process, but computer-aided design (CAD) programs now allow the designer to create in three dimensions. Instructions for manufacturing a part must be fed to the necessary machinery, either manually, through programmed instructions, or through the use of a computer-aided manufacturing
Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) also known as computer-aided modeling or computer-aided machining is the use of software to control machine tools in the manufacturing of work pieces. This is not the only definition for CAM, but it is the most ...
(CAM) or combined CAD/CAM program. Programs such as SolidWorks
SolidWorks (stylized as SOLIDWORKS) is a brand of software used for solid modeling computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided engineering (CAE). It was one of the first 3D CAD applications designed to run on a desktop PC.
The brand is owned ...
and AutoCAD
AutoCAD is a 2D and
3D computer-aided design (CAD) software application developed by Autodesk. It was first released in December 1982 for the CP/M and IBM PC platforms as a desktop app running on microcomputers with internal graphics control ...
finite element analysis
Finite element method (FEM) is a popular method for numerically solving differential equations arising in engineering and mathematical models, mathematical modeling. Typical problem areas of interest include the traditional fields of structural ...
(FEA) and computational fluid dynamics
Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is a branch of fluid mechanics that uses numerical analysis and data structures to analyze and solve problems that involve fluid dynamics, fluid flows. Computers are used to perform the calculations required ...
(CFD).
Metal fabrication and machine tools
Metal fabrication
Metal fabrication is the creation of metal structures by cutting, bending and assembling processes. It is a value-added process involving the creation of machines, parts, and structures from various raw materials.
Typically, a fabrication shop ...
is the building of metal structures by cutting, bending, and assembling processes. Technologies such as electron beam melting, laser engineered net shape, and direct metal laser sintering has allowed for the production of metal structures to become much less difficult when compared to other conventional metal fabrication methods. These help to alleviate various issues when the idealized CAD structures do not align with the actual fabricated structure.
Machine tool
A machine tool is a machine for handling or machining metal or other rigid materials, usually by cutting, Boring (manufacturing), boring, grinding (abrasive cutting), grinding, shearing, or other forms of deformations. Machine tools employ some s ...
s employ many types of tools that do the cutting or shaping of materials. Machine tools usually include many components consisting of motors, levers, arms, pulleys, and other basic simple systems to create a complex system that can build various things. All of these components must work correctly in order to stay on schedule and remain on task. Machine tools aim to efficiently and effectively produce good parts at a quick pace with a small amount of error.
Computer integrated manufacturing
Computer-integrated manufacturing
Computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM) is the manufacturing approach of using computers to control the entire production process. This integration allows individual processes to exchange information with each part. Manufacturing can be faster a ...
(CIM) is the manufacturing approach of using computers to control the entire production process. Computer-integrated manufacturing is used in automotive, aviation, space, and ship building industries. Computer-integrated manufacturing allows for data, through various sensing mechanisms to be observed during manufacturing. This type of manufacturing has computers controlling and observing every part of the process. This gives CIM a unique advantage over other manufacturing processes.
Mechatronics
 Mechatronics is an engineering discipline that deals with the convergence of electrical, mechanical and manufacturing systems.
Mechatronics is an engineering discipline that deals with the convergence of electrical, mechanical and manufacturing systems.Microelectromechanical systems
MEMS (micro-electromechanical systems) is the technology of microscopic devices incorporating both electronic and moving parts. MEMS are made up of components between 1 and 100 micrometres in size (i.e., 0.001 to 0.1 mm), and MEMS devices ...
(MEMS), are used in automobiles to initiate the deployment of airbags, in digital projectors to create sharper images, and in inkjet printers to create nozzles for high-definition printing. In future it is hoped that such devices will be used in tiny implantable medical devices and to improve optical communication.
Textile engineering
Textile engineering courses deal with the application of scientific and engineering principles to the design and control of all aspects of fiber, textile, and apparel processes, products, and machinery. These include natural and man-made materials, interaction of materials with machines, safety and health, energy conservation, and waste and pollution control. Additionally, students are given experience in plant design and layout, machine and wet process design and improvement, and designing and creating textile products. Throughout the textile engineering curriculum, students take classes from other engineering and disciplines including: mechanical, chemical, materials and industrial engineering.
Advanced composite materials
Advanced composite materials (engineering)
In materials science, advanced composite materials (ACMs) are materials that are generally characterized by unusually high-strength fibres with unusually high stiffness, or modulus of elasticity characteristics, compared to other materials, whi ...
(ACMs) are also known as advanced polymer matrix composites. These are generally characterized or determined by unusually high strength fibres with unusually high stiffness, or modulus of elasticity characteristics, compared to other materials, while bound together by weaker matrices. Advanced composite materials have broad, proven applications, in the aircraft, aerospace, and sports equipment sectors. Even more specifically ACMs are very attractive for aircraft and aerospace structural parts. Manufacturing ACMs is a multibillion-dollar industry worldwide. Composite products range from skateboards to components of the space shuttle. The industry can be generally divided into two basic segments, industrial composites and advanced composites.
See also
* Washington Accord The Washington Agreement was a peace agreement that led to the modern Bosnia and Herzegovina, signed in 1994.
Washington Agreement or Washington Accords may also refer to:
* Washington Accords (1942), the Brazil-United States Political-Military ...
*Automotive engineering
Automotive engineering, along with aerospace engineering and naval architecture, is a branch of vehicle engineering, incorporating elements of Mechanical engineering, mechanical, Electrical engineering, electrical, Electronic engineering, electro ...
*Computer-aided design
Computer-aided design (CAD) is the use of computers (or ) to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. This software is used to increase the productivity of the designer, improve the quality of design, improve c ...
* Computer numerically controlled
*Engineering
Engineering is the practice of using natural science, mathematics, and the engineering design process to Problem solving#Engineering, solve problems within technology, increase efficiency and productivity, and improve Systems engineering, s ...
*Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
*Kinematics
In physics, kinematics studies the geometrical aspects of motion of physical objects independent of forces that set them in motion. Constrained motion such as linked machine parts are also described as kinematics.
Kinematics is concerned with s ...
*Manufacturing
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of the
secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer ...
* Manufacturing engineering education
*Mechatronics
Mechatronics engineering, also called mechatronics, is the synergistic integration of mechanical, electrical, and computer systems employing mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, electronic engineering and computer engineering, and also ...
*Mechanical engineering
Mechanical engineering is the study of physical machines and mechanism (engineering), mechanisms that may involve force and movement. It is an engineering branch that combines engineering physics and engineering mathematics, mathematics principl ...
*Mechanics
Mechanics () is the area of physics concerned with the relationships between force, matter, and motion among Physical object, physical objects. Forces applied to objects may result in Displacement (vector), displacements, which are changes of ...
* Occupational health and safety
* Package engineering
*Robotics
Robotics is the interdisciplinary study and practice of the design, construction, operation, and use of robots.
Within mechanical engineering, robotics is the design and construction of the physical structures of robots, while in computer s ...
*Second Industrial Revolution
The Second Industrial Revolution, also known as the Technological Revolution, was a phase of rapid Discovery (observation), scientific discovery, standardisation, mass production and industrialisation from the late 19th century into the early ...
*Surface-mount technology
Surface-mount technology (SMT), originally called planar mounting, is a method in which the electrical components are mounted directly onto the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB). An electrical component mounted in this manner is referred ...
*Technical drawing
Technical drawing, drafting or drawing, is the act and discipline of composing drawings that visually communicate how something functions or is constructed.
Technical drawing is essential for communicating ideas in industry and engineering. ...
Associations
* American Society for Engineering Education
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, ...
* American Society for Quality
The American Society for Quality (ASQ), formerly the American Society for Quality Control (ASQC), is a society of quality professionals, with more than 30,000 members, in more than 140 countries.
History
ASQC was established on 16 February ...
* European Students of Industrial Engineering and Management (ESTIEM)
* Indian Institution of Industrial Engineering
* Institute for Operations Research and the Management Sciences
The Institute for Operations Research and the Management Sciences (INFORMS) is an international society for practitioners in the fields of operations research
Operations research () (U.S. Air Force Specialty Code: Operations Analysis), often s ...
(INFORMS)
* Institute of Industrial Engineers
The Institute of Industrial and Systems Engineers (IISE), formerly the Institute of Industrial Engineers, is a professional society dedicated solely to the support of the industrial engineering profession and individuals involved with improving ...
* Institution of Electrical Engineers
The Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE) was a British professional organisation of electronics, electrical, manufacturing, and information technology professionals, especially electrical engineers. It began in 1871 as the Society of Tel ...
* Society of Manufacturing Engineers
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Industrial and Production Engineering
*
Engineering disciplines
Manufacturing
Management science
 Adam Smith's concepts of
Adam Smith's concepts of 
 Manufacturing engineers develop and create physical artifacts, production processes, and technology. It is a very broad area which includes the design and development of products. Manufacturing engineering is considered to be a sub-discipline of
Manufacturing engineers develop and create physical artifacts, production processes, and technology. It is a very broad area which includes the design and development of products. Manufacturing engineering is considered to be a sub-discipline of  A
A  Friction stir welding was discovered in 1991 by The Welding Institute (TWI). This innovative steady state (non-fusion) welding technique joins previously un-weldable materials, including several aluminum alloys. It may play an important role in the future construction of airplanes, potentially replacing rivets. Current uses of this technology to date include: welding the seams of the aluminum main space shuttle external tank, the Orion Crew Vehicle test article, Boeing Delta II and Delta IV Expendable Launch Vehicles and the SpaceX Falcon 1 rocket; armor plating for amphibious assault ships; and welding the wings and fuselage panels of the new Eclipse 500 aircraft from Eclipse Aviation, among an increasingly growing range of uses.
Friction stir welding was discovered in 1991 by The Welding Institute (TWI). This innovative steady state (non-fusion) welding technique joins previously un-weldable materials, including several aluminum alloys. It may play an important role in the future construction of airplanes, potentially replacing rivets. Current uses of this technology to date include: welding the seams of the aluminum main space shuttle external tank, the Orion Crew Vehicle test article, Boeing Delta II and Delta IV Expendable Launch Vehicles and the SpaceX Falcon 1 rocket; armor plating for amphibious assault ships; and welding the wings and fuselage panels of the new Eclipse 500 aircraft from Eclipse Aviation, among an increasingly growing range of uses.
 Drafting or
Drafting or