|
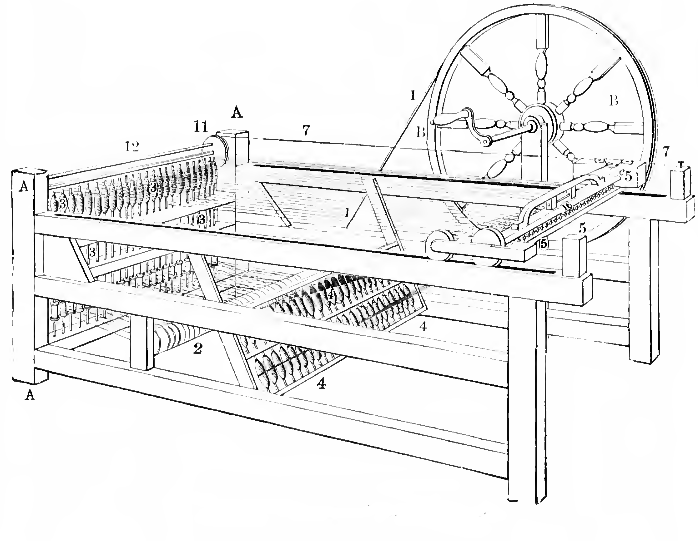
Spinning Jenny
The spinning jenny is a multi- spindle spinning frame, and was one of the key developments in the industrialisation of textile manufacturing during the early Industrial Revolution. It was invented in 1764–1765 by James Hargreaves in Stan Hill, Oswaldtwistle, Lancashire in England. The device reduced the amount of work needed to produce cloth, with a worker able to work eight or more spools at once. This grew to 120 as technology advanced. The yarn produced by the jenny was not very strong until Richard Arkwright invented the water-powered water frame. The spinning jenny helped to start the factory system of cotton manufacturing. History The spinning jenny was invented by James Hargreaves. He was born in Oswaldtwistle, near Blackburn, around 1720. Blackburn was a town with a population of about 5,000, known for the production of "Blackburn greys," cloths of linen warp and cotton weft initially imported from India. They were usually sent to London to be printed. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinning Jenny Improved 203 Marsden
Spin or spinning most often refers to: * Spin (physics) or particle spin, a fundamental property of elementary particles * Spin quantum number, a number which defines the value of a particle's spin * Spinning (textiles), the creation of yarn or thread by twisting fibers together, traditionally by hand spinning * Spin (geometry), the rotation of an object around an internal axis * Spin (propaganda), an intentionally biased portrayal of something Spin, spinning or spinnin may also refer to: Physics and mathematics * Spin group, Spin(''n''), a particular double cover of the special orthogonal group SO(''n'') ** the corresponding spin algebra, \mathfrak(n) * Spin tensor, a tensor quantity for describing spinning motion in special relativity and general relativity * Spin (aerodynamics), autorotation of an aerodynamically stalled aeroplane * SPIN bibliographic database, an indexing and abstracting service focusing on physics research Textile arts * Spinning (polymers), a proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Transport
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport using wheeled vehicles running in railway track, tracks, which usually consist of two parallel steel railway track, rails. Rail transport is one of the two primary means of land transport, next to road transport. It is used for about 8% of passenger and rail freight transport, freight transport globally, thanks to its Energy efficiency in transport, energy efficiency and potentially high-speed rail, high speed.Rolling stock on rails generally encounters lower friction, frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, allowing rail cars to be coupled into longer trains. Power is usually provided by Diesel locomotive, diesel or Electric locomotive, electric locomotives. While railway transport is capital intensity, capital-intensive and less flexible than road transport, it can carry heavy loads of passengers and cargo with greater energy efficiency and safety. Precursors of railways driven by human or an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canal
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface flow under atmospheric pressure, and can be thought of as artificial rivers. In most cases, a canal has a series of dams and locks that create reservoirs of low speed current flow. These reservoirs are referred to as ''slack water levels'', often just called ''levels''. A canal can be called a navigation canal when it parallels a natural river and shares part of the latter's discharges and drainage basin, and leverages its resources by building dams and locks to increase and lengthen its stretches of slack water levels while staying in its valley. A canal can cut across a drainage divide atop a ridge, generally requiring an external water source above the highest elevation. The best-known example of such a canal is the Panama Can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fustian
Fustian is a variety of heavy cloth woven from cotton, chiefly prepared for menswear. History and use Known in Late Latin as ''fustaneum'' or ''fustanum'' and in Medieval Latin as ''pannus fustāneus'' ('fustian cloth') or ''tela fustānea'' ('fustian mesh'), the cloth is possibly named after the Egyptian city of Fustat near Cairo that manufactured such a material. It embraces plain twilled cloth known as jean, and cut fabrics similar to velvet, known as velveteen, moleskin, corduroy etc. The original medieval fustian was a stout but respectable cloth with a cotton weft and a linen Warp (weaving), warp. The term seems to have quickly become less precise, and was applied to a coarse cloth made of wool and linen, and in the reign of Edward III of England, the name was given to a woollen fabric. By the early 20th century, fustians were usually of cotton dyed various colours. In a petition to Parliament of England, Parliament during the reign of Mary I of England, Mary I, "f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coventry
Coventry ( or rarely ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and metropolitan borough in the West Midlands (county), West Midlands county, in England, on the River Sherbourne. Coventry had been a large settlement for centuries. Founded in the early Middle Ages, its city status was formally recognised in a charter of 1345. The city is governed by Coventry City Council, and the West Midlands Combined Authority. Historic counties of England, Formerly part of Warwickshire until 1451, and again from 1842 to 1974, Coventry had a population of 345,324 at the 2021 census, making it the tenth largest city in England and the 13th largest in the United Kingdom. It is the second largest city in the West Midlands (region), West Midlands region, after Birmingham, from which it is separated by an area of Green belt (United Kingdom), green belt known as the Meriden Gap; it is the third largest in the wider Midlands after Birmingham and Leicester. The city is part of a larger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
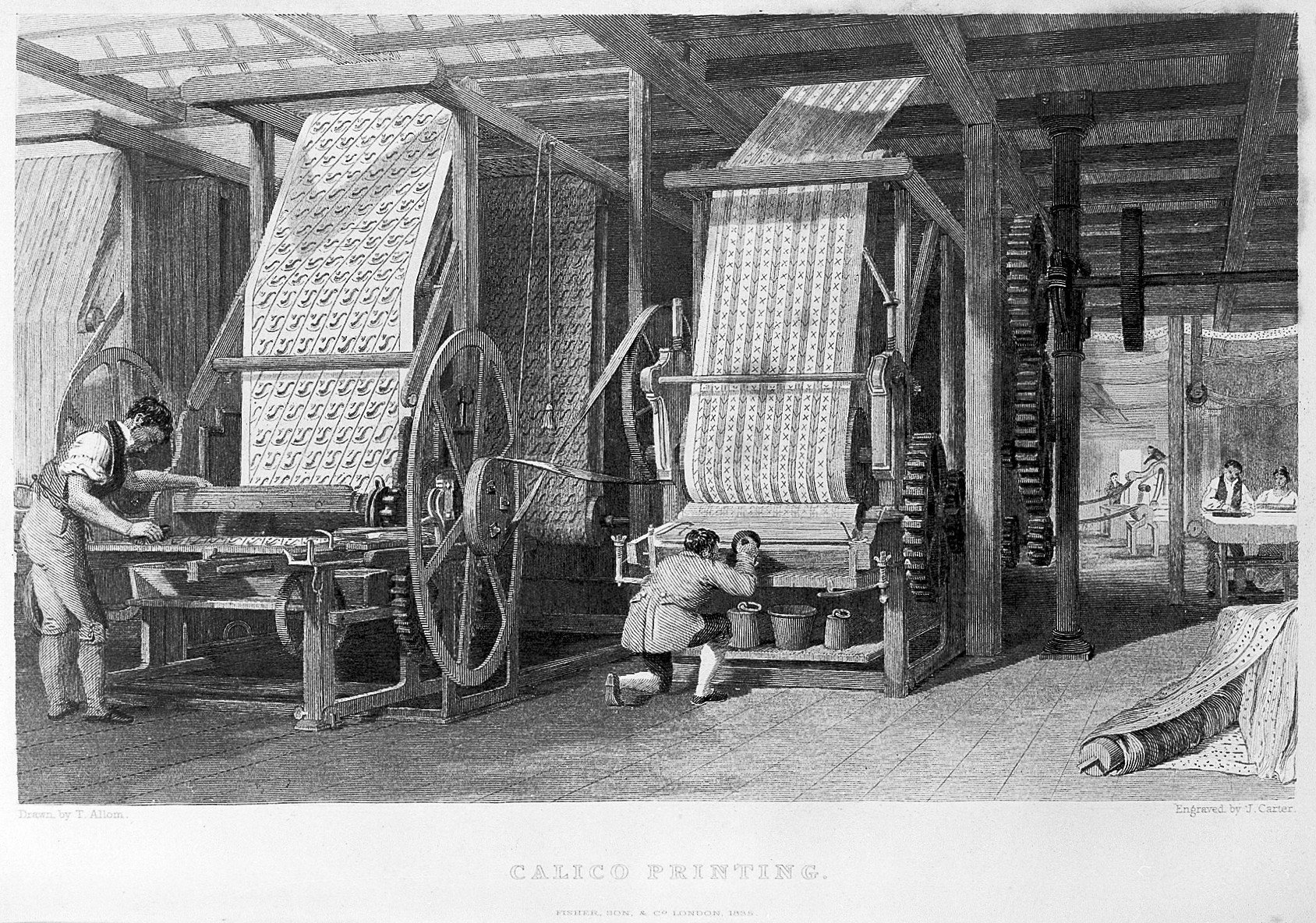
Calico
Calico (; in British usage since 1505) is a heavy plain-woven textile made from unbleached, and often not fully processed, cotton. It may also contain unseparated husk parts. The fabric is far coarser than muslin, but less coarse and thick than canvas or denim. However, it is still very cheap owing to its unfinished and undyed appearance. The fabric was originally from the city of Calicut in southwestern India. It was made by the traditional weavers called cāliyans. The raw fabric was dyed and printed in bright hues, and calico prints became popular in Europe. History Origins Calico originated in Calicut, from which the name of the textile came, in South India, now Kerala, during the 11th century, where the cloth was known as "chaliyan". It was mentioned in Indian literature by the 12th century when the polymath and writer Hemachandra described calico fabric prints with a lotus design.''Encyclopædia Britannica'' (2008)"calico" Calico was woven using Gujarati cotton from Su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindustan
''Hindūstān'' ( English: /ˈhɪndustæn/ or /ˈhɪndustɑn/, ; ) was a historical region, polity, and a name for India, historically used simultaneously for northern Indian subcontinent and the entire subcontinent, used in the modern day to refer to the Republic of India by some but not officially. Being the Iranic cognate of the Indic word ''Sindhu'', it originally referred to the land of lower Indus basin (present-day Sindh) during the ancient era, but was later extended to refer to northern Indian subcontinent. It finally referred to the entire subcontinent since the early modern period.: "They used the name ''Hindustan'' for India Intra Gangem or taking the latter expression rather loosely for the Indian subcontinent proper. The term ''Hindustan'', which in the "Naqsh-i-Rustam" inscription of Shapur I denoted India on the lower Indus, and which later gradually began to denote more or less the whole of the subcontinent, was used by some of the European authors concer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company that was founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to Indian Ocean trade, trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (South Asia and Southeast Asia), and later with East Asia. The company gained Company rule in India, control of large parts of the Indian subcontinent and British Hong Kong, Hong Kong. At its peak, the company was the largest corporation in the world by various measures and had its own armed forces in the form of the company's three presidency armies, totalling about 260,000 soldiers, twice the size of the British Army at certain times. Originally Chartered company, chartered as the "Governor and Company of Merchants of London Trading into the East-Indies," the company rose to account for half of the world's trade during the mid-1700s and early 1800s, particularly in basic commodities including cotton, silk, indigo dye, sugar, salt, spices, Potass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calico (textile)
Calico (; in British usage since 1505) is a heavy plain-woven textile made from unbleached, and often not fully processed, cotton. It may also contain unseparated husk parts. The fabric is far coarser than muslin, but less coarse and thick than canvas or denim. However, it is still very cheap owing to its unfinished and undyed appearance. The fabric was originally from the city of Calicut in southwestern India. It was made by the traditional weavers called cāliyans. The raw fabric was dyed and printed in bright hues, and calico prints became popular in Europe. History Origins Calico originated in Calicut, from which the name of the textile came, in South India, now Kerala, during the 11th century, where the cloth was known as "chaliyan". It was mentioned in Indian literature by the 12th century when the polymath and writer Hemachandra described calico fabric prints with a lotus design.''Encyclopædia Britannica'' (2008)"calico" Calico was woven using Gujarati cotton f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calico Acts
The Calico Acts (1700, 1721) were acts of the Parliament of England and the Parliament of Great Britain which banned the import of most cotton textiles into England, followed by the restriction of sale of most cotton textiles. It was a form of economic protectionism, largely in response to India (particularly Bengal), which dominated world cotton textile markets at the time. The acts were a precursor to the Industrial Revolution, when Britain eventually surpassed India as the world's leading textile manufacturer in the 19th century. Context The English East India Company introduced Britain to cheap calico and chintz cloth after the restoration of the monarchy in the 1660s. Initially imported as a novelty side line, from its spice trading posts in Asia, the cheap colourful cloth proved popular and overtook the EIC's spice trade by value in the late 17th century. The EIC embraced the demand, particularly for calico, by expanding its factories in Asia and producing and impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norwich
Norwich () is a cathedral city and district of the county of Norfolk, England, of which it is the county town. It lies by the River Wensum, about north-east of London, north of Ipswich and east of Peterborough. The population of the Norwich City Council local authority area was estimated to be 144,000 in 2021, which was an increase from 143,135 in 2019. The wider Norwich List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, built-up area had a population of 213,166 at the 2011 census. As the seat of the Episcopal see, See of Norwich, the city has one of the country's largest medieval cathedrals. For much of the second millennium, from medieval to just before Industrial Revolution, industrial times, Norwich was one of the most prosperous and largest towns of England; at one point, it was List of towns and cities in England by historical population, second only to London. Today, it is the largest settlement in East Anglia. Heritage and status Norwich claims to be the most complete medie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |