In Ovo on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In ovo is Latin for in the egg. In medical usage it refers to the growth of live virus in chicken egg embryos for vaccine development for human use, as well as an effective method for vaccination of poultry against various
In ovo is Latin for in the egg. In medical usage it refers to the growth of live virus in chicken egg embryos for vaccine development for human use, as well as an effective method for vaccination of poultry against various
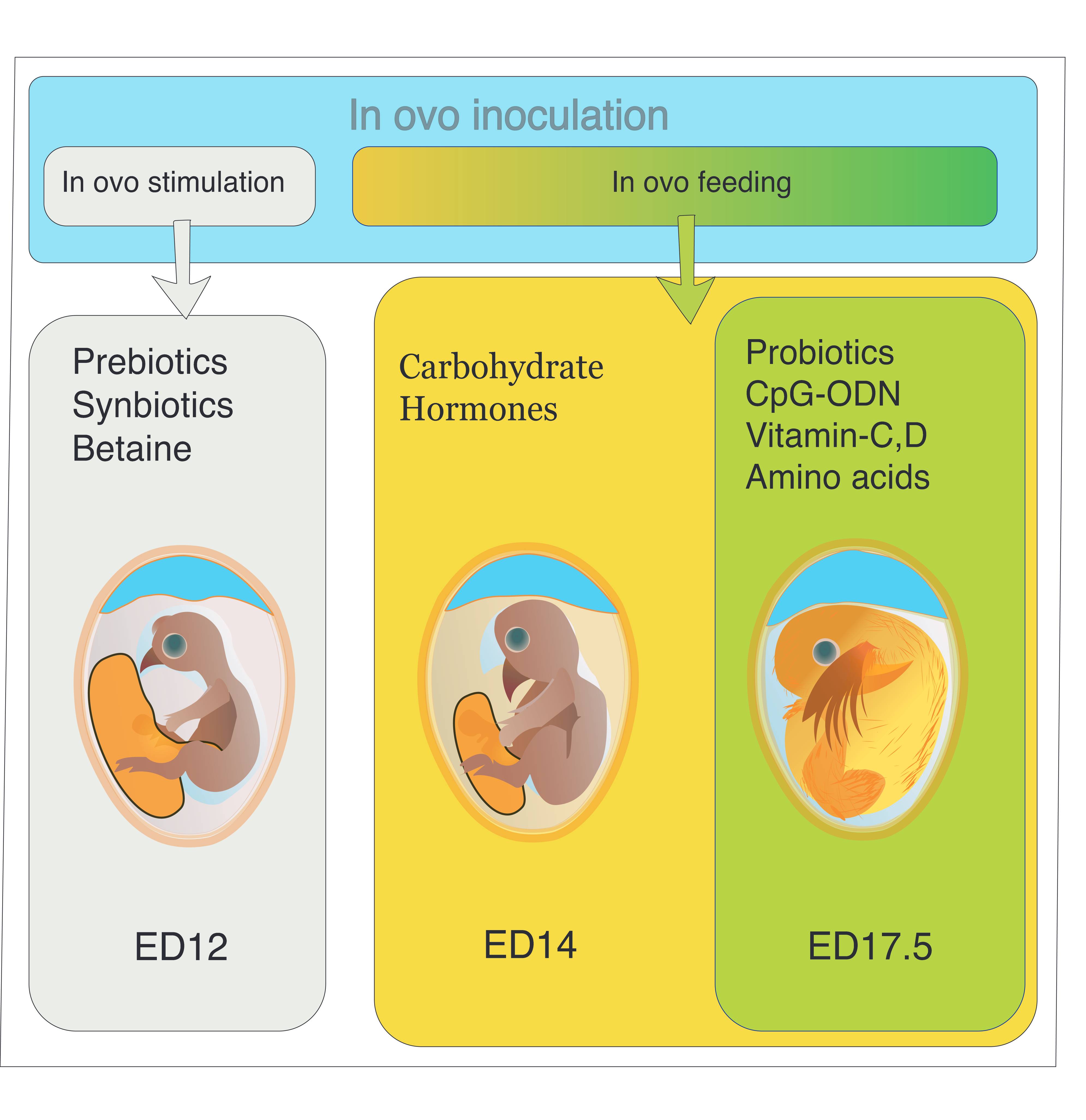 ''In ovo'' feeding is a considered as a potential tool to provide nutrient to embryo as well as to modulate performance and gut health of pre and post hatched chicks. Based on the purpose the ''in ovo'' injection could be considered as ''in ovo'' stimulation or ''in ovo'' feeding.
''In ovo'' feeding is a considered as a potential tool to provide nutrient to embryo as well as to modulate performance and gut health of pre and post hatched chicks. Based on the purpose the ''in ovo'' injection could be considered as ''in ovo'' stimulation or ''in ovo'' feeding.
 In ovo is Latin for in the egg. In medical usage it refers to the growth of live virus in chicken egg embryos for vaccine development for human use, as well as an effective method for vaccination of poultry against various
In ovo is Latin for in the egg. In medical usage it refers to the growth of live virus in chicken egg embryos for vaccine development for human use, as well as an effective method for vaccination of poultry against various Avian influenza
Avian influenza, also known as avian flu or bird flu, is a disease caused by the influenza A virus, which primarily affects birds but can sometimes affect mammals including humans. Wild aquatic birds are the primary host of the influenza A viru ...
and coronavirus
Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the comm ...
es. During the incubation period
Incubation period (also known as the latent period or latency period) is the time elapsed between exposure to a pathogenic organism, a chemical, or ionizing radiation, radiation, and when symptoms and signs are first apparent. In a typical infect ...
, the virus replicates in the cells that make up the chorioallantoic membrane
The chorioallantoic membrane (CAM), also known as the chorioallantois, is a highly vascularized membrane found in the eggs of certain amniotes like birds and reptiles. It is formed by the fusion of the mesodermal layers of two extra-embryonic memb ...
.
Advantages
In human vaccine development, the main advantage is rapid propagation, and high yield, of viruses for vaccine production. This method is most commonly used for growth of influenza virus, bothattenuated vaccine
An attenuated vaccine (or a live attenuated vaccine, LAV) is a vaccine created by reducing the virulence of a pathogen, but still keeping it viable (or "live"). Attenuation takes an infectious agent and alters it so that it becomes harmless or le ...
and inactivated vaccine
An inactivated vaccine (or killed vaccine) is a type of vaccine that contains pathogens (such as virus or bacteria) that have been killed or rendered inactive, so they cannot replicate or cause disease. In contrast, live vaccines use pathogens ...
forms. It is recommended by the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
in managing influenza pandemics because it is high-yield and cost effective.
In poultry, In ovo vaccination improves hatchability and efficient protection against Avian influenza
Avian influenza, also known as avian flu or bird flu, is a disease caused by the influenza A virus, which primarily affects birds but can sometimes affect mammals including humans. Wild aquatic birds are the primary host of the influenza A viru ...
(AI), Newcastle disease
Virulent Newcastle disease (VND), formerly exotic Newcastle disease, is a contagious viral avian disease affecting many domestic and wild bird species; it is transmissible to humans. Though it can infect humans, most cases are non-symptomati ...
(ND) and Coronavirus
Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the comm ...
es (Av-CoV). Seroconversion rates of chickens vaccinated as embryos ranged from 27% to 100% with ND vaccination and 85% to 100% for AI vaccination. The birds are protected before delivery to a commercial operation such as a farm, thus preventing the spread of Avian viruses.
Vaccination
In ovo vaccination is carried out by machines. These machines perform a number of actions to ensure good vaccination of the chick inside the egg. Benefits of In ovo vaccination include avoidance of bird stress, controlled hygienic conditions, and earlier immunity with less interference from maternal antibodies.Feeding
 ''In ovo'' feeding is a considered as a potential tool to provide nutrient to embryo as well as to modulate performance and gut health of pre and post hatched chicks. Based on the purpose the ''in ovo'' injection could be considered as ''in ovo'' stimulation or ''in ovo'' feeding.
''In ovo'' feeding is a considered as a potential tool to provide nutrient to embryo as well as to modulate performance and gut health of pre and post hatched chicks. Based on the purpose the ''in ovo'' injection could be considered as ''in ovo'' stimulation or ''in ovo'' feeding.
See also
*Vaccine
A vaccine is a biological Dosage form, preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious disease, infectious or cancer, malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verifi ...
* Polio vaccine
Polio vaccines are vaccines used to prevent poliomyelitis (polio). Two types are used: an inactivated vaccine, inactivated poliovirus given by injection (IPV) and a attenuated vaccine, weakened poliovirus given by mouth (OPV). The World Healt ...
* List of vaccine ingredients
This is a list of excipients per vaccine, as published by the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control. Vaccine ingredients and production in other nations are substantially the same. Also listed are s ...
* List of vaccine topics
* Virosome
References
{{Vaccines, state=expanded Vaccination