|
Inactivated Vaccine
An inactivated vaccine (or killed vaccine) is a type of vaccine that contains pathogens (such as virus or bacteria) that have been killed or rendered inactive, so they cannot replicate or cause disease. In contrast, live vaccines use pathogens that are still alive (but are almost always attenuated, that is, weakened). Pathogens for inactivated vaccines are grown under controlled conditions and are killed as a means to reduce infectivity and thus prevent infection from the vaccine. Inactivated vaccines were first developed in the late 1800s and early 1900s for cholera, plague, and typhoid. In 1897, Japanese scientists developed an inactivated vaccine for the bubonic plague. In the 1950s, Jonas Salk created an inactivated vaccine for the poliovirus, creating the first vaccine that was both safe and effective against polio. Today, inactivated vaccines exist for many pathogens, including influenza, polio (IPV), rabies, hepatitis A, CoronaVac, Covaxin and pertussis. Because ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Health
Public health is "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals". Analyzing the determinants of health of a population and the threats it faces is the basis for public health. The ''public'' can be as small as a handful of people or as large as a village or an entire city; in the case of a pandemic it may encompass several continents. The concept of ''health'' takes into account physical, psychological, and Well-being, social well-being, among other factors.What is the WHO definition of health? from the Preamble to the Constitution of WHO as adopted by the Internationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Influenza Vaccine
Influenza vaccines, colloquially known as flu shots or the flu jab, are vaccines that protect against infection by influenza viruses. New versions of the vaccines are developed twice a year, as the influenza virus rapidly changes. While their effectiveness varies from year to year, most provide modest to high protection against influenza. Vaccination against influenza began in the 1930s, with large-scale availability in the United States beginning in 1945. Both the World Health Organization and the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend yearly vaccination for nearly all people over the age of six months, especially those at high risk, and the influenza vaccine is on the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines, World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. The European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) also recommends yearly vaccination of high-risk groups, particularly pregnant women, the elderly, children between six months and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epitope
An epitope, also known as antigenic determinant, is the part of an antigen that is recognized by the immune system, specifically by antibodies, B cells, or T cells. The part of an antibody that binds to the epitope is called a paratope. Although epitopes are usually non-self proteins, sequences derived from the host that can be recognized (as in the case of autoimmune diseases) are also epitopes. The epitopes of protein antigens are divided into two categories, conformational epitopes and linear epitopes, based on their structure and interaction with the paratope. Conformational and linear epitopes interact with the paratope based on the 3-D conformation adopted by the epitope, which is determined by the surface features of the involved epitope residues and the shape or tertiary structure of other segments of the antigen. A conformational epitope is formed by the 3-D conformation adopted by the interaction of discontiguous amino acid residues. In contrast, a linear epitope i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antigen-presenting Cell
An antigen-presenting cell (APC) or accessory cell is a Cell (biology), cell that displays an antigen bound by major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins on its surface; this process is known as antigen presentation. T cells may recognize these complexes using their T cell receptors (TCRs). APCs antigen processing, process antigens and present them to T cells. Almost all cell types can present antigens in some way. They are found in a variety of tissue types. Dedicated antigen-presenting cells, including macrophages, B cells and dendritic cells, present foreign antigens to T helper cell, helper T cells, while virus-infected cells (or cancer cells) can present antigens originating inside the cell to cytotoxic T cells. In addition to the MHC family of proteins, antigen presentation relies on other specialized signaling molecules on the surfaces of both APCs and T cells. Antigen-presenting cells are vital for effective Adaptive immune system, adaptive immune response, as the fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule, moiety, foreign particulate matter, or an allergen, such as pollen, that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response. Antigens can be proteins, peptides (amino acid chains), polysaccharides (chains of simple sugars), lipids, or nucleic acids. Antigens exist on normal cells, cancer cells, parasites, viruses, fungus, fungi, and bacteria. Antigens are recognized by antigen receptors, including antibodies and T-cell receptors. Diverse antigen receptors are made by cells of the immune system so that each cell has a specificity for a single antigen. Upon exposure to an antigen, only the lymphocytes that recognize that antigen are activated and expanded, a process known as clonal selection. In most cases, antibodies are ''antigen-specific'', meaning that an antibody can only react to and bind one specific antigen; in some instances, however, antibodies may cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunodeficiency
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromise, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that affect the patient's immune system. Examples of these extrinsic factors include HIV infection and environmental factors, such as nutrition. Immunocompromisation may also be due to genetic diseases/flaws such as SCID. In clinical settings, immunosuppression by some drugs, such as steroids, can either be an adverse effect or the intended purpose of the treatment. Examples of such use is in organ transplant surgery as an anti- rejection measure and in patients with an overactive immune system, as in autoimmune diseases. Some people are born with intrinsic defects in their immune system, or primary immunodeficiency. A person who has an immunodeficiency of any kind is said to be immunocompromised. An immunocompromised individual may par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Age
Old age is the range of ages for people nearing and surpassing life expectancy. People who are of old age are also referred to as: old people, elderly, elders, senior citizens, seniors or older adults. Old age is not a definite biological stage: the chronological age denoted as "old age" varies culturally and historically. Some disciplines and domains focus on the aging and the aged, such as the organic processes of aging (senescence), medical studies of the aging process (gerontology), diseases that afflict older adults (geriatrics), technology to support the aging society (gerontechnology), and leisure and sport activities adapted to older people (such as senior sport). Older people often have limited regenerative abilities and are more susceptible to illness and injury than younger adults. They face social problems related to retirement, loneliness, and ageism. In 2011, the United Nations proposed a human-rights convention to protect old people. History European The hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Booster Injection
A booster dose is an extra administration of a vaccine after an earlier ( primer) dose. After initial immunization, a booster provides a re-exposure to the immunizing antigen. It is intended to increase immunity against that antigen back to protective levels after memory against that antigen has declined through time. For example, tetanus shot boosters are often recommended every 10 years, by which point memory cells specific against tetanus lose their function or undergo apoptosis. The need for a booster dose following a primary vaccination is evaluated in several ways. One way is to measure the level of antibodies specific against a disease a few years after the primary dose is given. Anamnestic response, the rapid production of antibodies after a stimulus of an antigen, is a typical way to measure the need for a booster dose of a certain vaccine. If the anamnestic response is high after receiving a primary vaccine many years ago, there is most likely little to no need for a bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunologic Adjuvant
In immunology, an adjuvant is a substance that increases or modulates the immune response to a vaccine. The word "adjuvant" comes from the Latin word , meaning to help or aid. "An immunologic adjuvant is defined as any substance that acts to accelerate, prolong, or enhance antigen-specific immune responses when used in combination with specific vaccine antigens." In the early days of vaccine manufacture, significant variations in the efficacy of different batches of the same vaccine were correctly assumed to be caused by contamination of the reaction vessels. However, it was soon found that more scrupulous cleaning actually seemed to ''reduce'' the effectiveness of the vaccines, and some contaminants actually enhanced the immune response. There are many known adjuvants in widespread use, including potassium alum, various plant and animal derived oils and virosomes. Overview Adjuvants in immunology are often used to modify or augment the effects of a vaccine by stimulating the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pertussis Vaccine
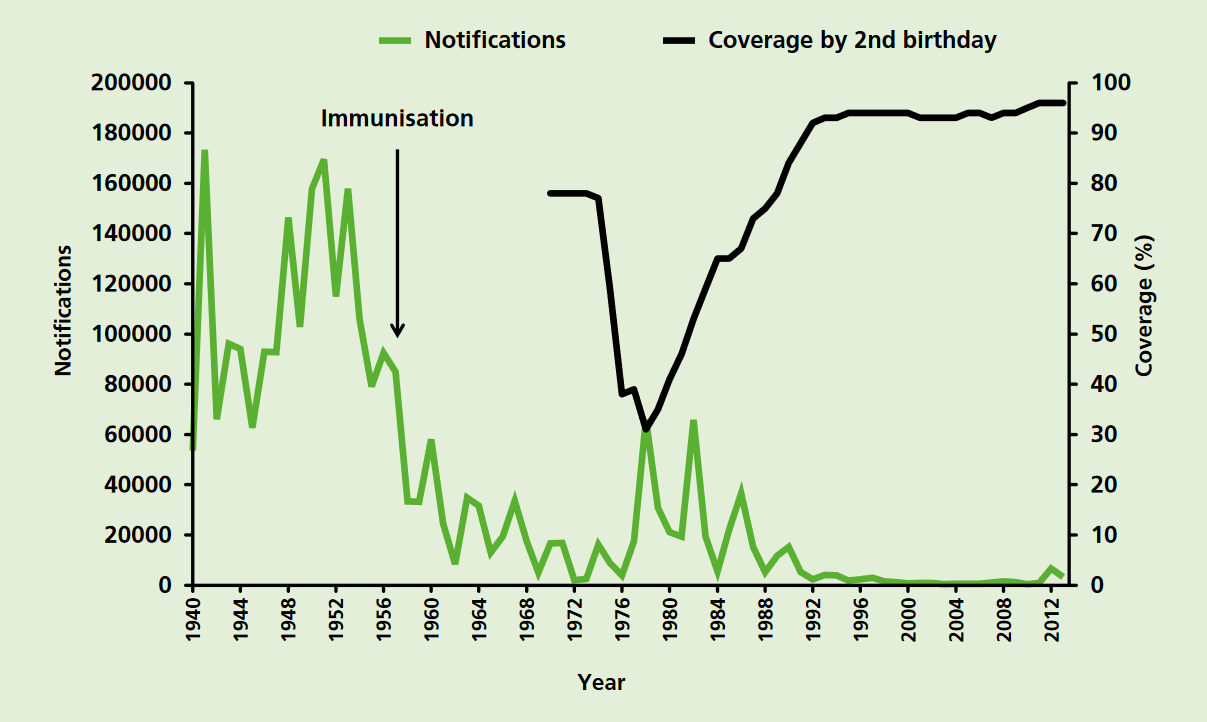
Pertussis vaccine is a vaccine that protects against whooping cough (pertussis). There are two main types: whole-cell vaccines and acellular vaccines. The whole-cell vaccine is about 78% effective while the acellular vaccine is 71–85% effective. The effectiveness of the vaccines appears to decrease by between 2 and 10% per year after vaccination, with a more rapid decrease with the acellular vaccines. The vaccine is only available in combination with tetanus and diphtheria vaccines (DPT vaccine). Pertussis vaccine is estimated to have saved over 500,000 lives in 2002. Vaccinating the mother during pregnancy may protect the baby. The World Health Organization and the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend all children be vaccinated for pertussis and that it be included in Vaccination schedule, routine vaccinations. Three doses starting at six weeks of age are typically recommended in young children. Additional doses may be given to older children and adults. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Covaxin
Covaxin (list of pharmaceutical compound number prefixes, development name, BBV152) is a Inactivated vaccine, whole inactivated virus-based COVID-19 vaccine developed by Bharat Biotech in collaboration with the Indian Council of Medical Research - National Institute of Virology. On 3 November 2021, the World Health Organization (WHO) validated the vaccine for emergency use, as the first Indian-developed covid vaccine to be approved. By 31 January 2022, Covaxin had been granted emergency use approval in 13 countries. Medical uses Effectiveness A vaccine is generally considered effective if the estimate is ≥50% with a >30% lower limit of the 95% confidence interval. Effectiveness is generally expected to slowly decrease over time. Efficacy A phase 3 clinical trial with 25,798 participants found that the vaccine is effective against asymptomatic cases, effective against symptomatic disease, effective against severe disease, and effective against the Delta variant. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CoronaVac
CoronaVac, also known as the Sinovac COVID-19 vaccine, was a whole inactivated virus COVID-19 vaccine developed by the Chinese company Sinovac Biotech. It was phase III clinically trialled in Brazil, Chile, Indonesia, the Philippines, and Turkey and relies on traditional technology similar to other inactivated-virus COVID-19 vaccines, such as the Sinopharm BIBP vaccine, another Chinese vaccine, and Covaxin, an Indian vaccine. CoronaVac does not need to be frozen, and both the final product and the raw material for formulating CoronaVac can be transported refrigerated at 2–8 °C (36–46 °F), the temperatures at which flu vaccines are kept. A real-world study of tens of millions of Chileans who received CoronaVac found it to be 66% effective against symptomatic COVID-19, 88% effective against hospitalization, 90% effective against ICU admissions, and 86% effective against deaths. In Brazil, after 75% of the population in Serrana, São Paulo, received CoronaVa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |