idolatory on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Idolatry is the
Idolatry is the
John Cort (2011), Jains in the World, Oxford University Press, , pages 80–85 In the traditional religions of
 The term ''idolatry'' comes from the
The term ''idolatry'' comes from the

 Idolatry is the
Idolatry is the worship
Worship is an act of religious devotion usually directed towards a deity or God. For many, worship is not about an emotion, it is more about a recognition of a God. An act of worship may be performed individually, in an informal or formal group, ...
of an idol as though it were a deity
A deity or god is a supernatural being considered to be sacred and worthy of worship due to having authority over some aspect of the universe and/or life. The ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' defines ''deity'' as a God (male deity), god or god ...
. In Abrahamic religions
The term Abrahamic religions is used to group together monotheistic religions revering the Biblical figure Abraham, namely Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. The religions share doctrinal, historical, and geographic overlap that contrasts them wit ...
(namely Judaism
Judaism () is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic, Monotheism, monotheistic, ethnic religion that comprises the collective spiritual, cultural, and legal traditions of the Jews, Jewish people. Religious Jews regard Judaism as their means of o ...
, Samaritanism
Samaritanism (; ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic ethnic religion. It comprises the collective spiritual, cultural, and legal traditions of the Samaritan people, who originate from the Hebrews and Israelites and began to emerge as a relative ...
, Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
, Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
, and the Baháʼí Faith
The Baháʼí Faith is a religion founded in the 19th century that teaches the Baháʼí Faith and the unity of religion, essential worth of all religions and Baháʼí Faith and the unity of humanity, the unity of all people. Established by ...
) idolatry connotes the worship of something or someone other than the Abrahamic God as if it were God. In these monotheistic religions, idolatry has been considered as the "worship of false gods" and is forbidden by texts such as the Ten Commandments
The Ten Commandments (), or the Decalogue (from Latin , from Ancient Greek , ), are religious and ethical directives, structured as a covenant document, that, according to the Hebrew Bible, were given by YHWH to Moses. The text of the Ten ...
. Other monotheistic religions may apply similar rules.
For instance, the phrase '' false god'' is a derogatory term used in Abrahamic religions to indicate cult image
In the practice of religion, a cult image is a Cultural artifact, human-made object that is venerated or worshipped for the deity, Spirit (supernatural entity), spirit or Daimon, daemon that it embodies or represents. In several traditions, incl ...
s or deities
A deity or god is a supernatural being considered to be sacred and worthy of worship due to having authority over some aspect of the universe and/or life. The ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' defines ''deity'' as a God (male deity), god or god ...
of non-Abrahamic Pagan religions, as well as other competing entities or objects to which particular importance is attributed. Conversely, followers of animistic
Animism (from meaning 'breath, Soul, spirit, life') is the belief that objects, places, and creatures all possess a distinct Spirituality, spiritual essence. Animism perceives all things—animals, plants, Rock (geology), rocks, rivers, Weather, ...
and polytheistic religions may regard the gods of various monotheistic religions as "false gods" because they do not believe that any real deity possesses the properties ascribed by monotheists to their sole deity. Atheists, who do not believe in any deities, do not usually use the term ''false god'' even though that would encompass all deities from the atheist viewpoint. Usage of this term is generally limited to theists, who choose to worship some deity or deities, but not others.
In many Indian religions
Indian religions, sometimes also termed Dharmic religions or Indic religions, are the religions that originated in the Indian subcontinent. These religions, which include Buddhism, Hinduism, Jainism, and Sikhism,Adams, C. J."Classification o ...
, which include Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified ...
, Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
, and Jainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religions, Indian religion whose three main pillars are nonviolence (), asceticism (), and a rejection of all simplistic and one-sided views of truth and reality (). Jainism traces its s ...
, idols (''murti
In the Hinduism, Hindu tradition, a ''murti'' (, ) is a devotional image, such as a statue or icon, of a Hindu deities, deity or Hindu saints, saint used during ''Puja (Hinduism), puja'' and/or in other customary forms of actively expressing d ...
'') are considered as symbolism for the Absolute but are not the Absolute itself, or icon
An icon () is a religious work of art, most commonly a painting, in the cultures of the Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox, Catholic Church, Catholic, and Lutheranism, Lutheran churches. The most common subjects include Jesus, Mary, mother of ...
s of spiritual ideas,Jeaneane D. Fowler (1996), Hinduism: Beliefs and Practices, Sussex Academic Press, , pages 41–45 or the embodiment of the divine. Klaus Klostermaier (2010), ''A Survey of Hinduism'', State University of New York Press, , pages 264–267 It is a means to focus one's religious pursuits and worship ('' bhakti'').Karel Werner (1995), Love Divine: Studies in Bhakti and Devotional Mysticism, Routledge, , pages 45-46;John Cort (2011), Jains in the World, Oxford University Press, , pages 80–85 In the traditional religions of
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower E ...
, Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
, Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
, Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
, Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which ...
, the Americas
The Americas, sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America and South America.''Webster's New World College Dictionary'', 2010 by Wiley Publishing, Inc., Cleveland, Ohio. When viewed as a sing ...
and elsewhere, the reverence of cult images or statues has been a common practice since antiquity, and idols have carried different meanings and significance in the history of religion
The history of religion is the written record of human religious feelings, thoughts, and ideas. This period of religious history begins with the invention of writing about 5,200 years ago (3200 BCE). The Prehistoric religion, prehistory of reli ...
. Moreover, the material depiction of a deity or more deities has always played an eminent role in all culture
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
s of the world.
The opposition to the use of any icon or image to represent ideas of reverence or worship is called aniconism
Aniconism is the cultural absence of artistic representations ('' icons'') of the natural and supernatural worlds, or it is the absence of representations of certain figures in religions. The prohibition of material representations may only extend ...
. The destruction of images as icons of veneration is called iconoclasm, and this has long been accompanied with violence between religious groups that forbid idol worship and those who have accepted icons, images and statues for veneration. The definition of idolatry has been a contested topic within Abrahamic religions, with many Muslims and most Protestant Christians condemning the Catholic and Eastern Orthodox practice of venerating the Virgin Mary in many churches as a form of idolatry.
The history of religions has been marked with accusations and denials of idolatry. These accusations have considered statues and images to be devoid of symbolism. Alternatively, the topic of idolatry has been a source of disagreements between many religions, or within denominations of various religions, with the presumption that icons of one's own religious practices have meaningful symbolism, while another person's different religious practices do not.
Etymology and nomenclature
 The term ''idolatry'' comes from the
The term ''idolatry'' comes from the Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
word ''eidololatria'' ( εἰδωλολατρία), which itself is a compound of two words: ''eidolon'' ( εἴδωλον "image/idol") and ''latreia'' (λατρεία "worship", related to λάτρις). The word ''eidololatria'' thus means "worship of idols", which in Latin appears first as ''idololatria'', then in Vulgar Latin as ''idolatria'', therefrom it appears in 12th century Old French as ''idolatrie'', which for the first time in mid 13th century English appears as "idolatry".
Although the Greek appears to be a loan translation of the Hebrew
Hebrew (; ''ʿÎbrit'') is a Northwest Semitic languages, Northwest Semitic language within the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family. A regional dialect of the Canaanite languages, it was natively spoken by the Israelites and ...
phrase ''avodat elilim'', (עבודת אלילים) which is attested in rabbinic literature
Rabbinic literature, in its broadest sense, is the entire corpus of works authored by rabbis throughout Jewish history. The term typically refers to literature from the Talmudic era (70–640 CE), as opposed to medieval and modern rabbinic ...
(e.g., bChul., 13b, Bar.), the Greek term itself is not found in the Septuagint
The Septuagint ( ), sometimes referred to as the Greek Old Testament or The Translation of the Seventy (), and abbreviated as LXX, is the earliest extant Greek translation of the Hebrew Bible from the original Biblical Hebrew. The full Greek ...
, Philo
Philo of Alexandria (; ; ; ), also called , was a Hellenistic Jewish philosopher who lived in Alexandria, in the Roman province of Egypt.
The only event in Philo's life that can be decisively dated is his representation of the Alexandrian J ...
, Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; , ; ), born Yosef ben Mattityahu (), was a Roman–Jewish historian and military leader. Best known for writing '' The Jewish War'', he was born in Jerusalem—then part of the Roman province of Judea—to a father of pr ...
, or in other Hellenistic Jewish writings. The original term used in early rabbinic writings is ''oved avodah zarah'' (''AAZ'', worship in strange service, or "pagan"), while ''avodat kochavim umazalot'' (''AKUM'', worship of planets and constellations) is not found in its early manuscripts. The later Jews used the term , ''avodah zarah'', meaning "foreign worship".
Idolatry has also been called idolism, iconolatry or idolodulia in historic literature.
Prehistoric and ancient civilizations
The earliest so-called Venus figurines have been dated to the prehistoricUpper Paleolithic
The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. Very broadly, it dates to between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago (the beginning of the Holocene), according to some theories ...
era (35–40 ka onwards). Archaeological evidence from the islands of the Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans and Anatolia, and covers an area of some . In the north, the Aegean is connected to the Marmara Sea, which in turn con ...
have yielded Neolithic era Cycladic figures from 4th and 3rd millennium BC, idols in ''namaste
''Namaste'' (, Devanagari: नमस्ते), sometimes called ''namaskār'' and ''namaskāram'', is a customary Hindu manner of respectfully greeting and honouring a person or group, used at any time of day. It is used worldwide among the ...
'' posture from Indus Valley civilization sites from the 3rd millennium BC, and much older petroglyph
A petroglyph is an image created by removing part of a rock surface by incising, picking, carving, or abrading, as a form of rock art. Outside North America, scholars often use terms such as "carving", "engraving", or other descriptions ...
s around the world show humans began producing sophisticated images. However, because of a lack of historic texts describing these, it is unclear what, if any connection with religious beliefs, these figures had, or whether they had other meaning and uses, even as toys.
The earliest historic records confirming idols are from the ancient Egyptian civilization, thereafter related to the Greek civilization. By the 2nd millennium BC two broad forms of cult image appear, in one images are zoomorphic (god in the image of animal or animal-human fusion) and in another anthropomorphic (god in the image of man). The former is more commonly found in ancient Egypt influenced beliefs, while the anthropomorphic images are more commonly found in Indo-European cultures. Symbols of nature, useful animals or feared animals may also be included by both. The stelae from 4,000 to 2,500 BC period discovered in France, Ireland through Ukraine, and in Central Asia through South Asia, suggest that the ancient anthropomorphic figures included zoomorphic motifs. In Nordic and Indian subcontinent, bovine (cow, ox, -*gwdus, -*g'ou) motifs or statues, for example, were common. In Ireland, iconic images included pigs.
The Ancient Egyptian religion
Ancient Egyptian religion was a complex system of Polytheism, polytheistic beliefs and rituals that formed an integral part of ancient Egyptian culture. It centered on the Egyptians' interactions with Ancient Egyptian deities, many deities belie ...
was polytheistic, with large idols that were either animals or included animal parts. Ancient Greek civilization preferred human forms, with idealized proportions, for divine representation. The Canaanites of West Asia incorporated a golden calf into their pantheon.
The ancient philosophy and practices of the Greeks, thereafter Romans, were imbued with polytheistic idolatry. They debate what is an image and if the use of image is appropriate. To Plato
Plato ( ; Greek language, Greek: , ; born BC, died 348/347 BC) was an ancient Greek philosopher of the Classical Greece, Classical period who is considered a foundational thinker in Western philosophy and an innovator of the writte ...
, images can be a remedy or poison to the human experience. To Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
, states Paul Kugler, an image is an appropriate mental intermediary that "bridges between the inner world of the mind and the outer world of material reality", the image is a vehicle between sensation and reason. Idols are useful psychological catalysts, they reflect sense data and pre-existing inner feelings. They are neither the origins nor the destinations of thought but the intermediary in the human inner journey. Fervid opposition to the idolatry of the Greeks and Romans was of Early Christianity
Early Christianity, otherwise called the Early Church or Paleo-Christianity, describes the History of Christianity, historical era of the Christianity, Christian religion up to the First Council of Nicaea in 325. Spread of Christianity, Christian ...
and later Islam, as evidenced by the widespread desecration and defacement of ancient Greek and Roman sculptures that have survived into the modern era.
Abrahamic religions
Judaism

Judaism
Judaism () is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic, Monotheism, monotheistic, ethnic religion that comprises the collective spiritual, cultural, and legal traditions of the Jews, Jewish people. Religious Jews regard Judaism as their means of o ...
prohibits any form of idolatry even if they are used to worship the one God of Judaism as occurred during the sin of the golden calf
According to the Torah, the Bible, and the Quran, the golden calf () was a cult image made by the Israelites when Moses went up to Mount Sinai (bible), Mount Sinai. In Hebrew, the incident is known as "the sin of the calf" (). It is first mentio ...
. According to the second word of the decalogue, Thou shalt not make unto thee any graven image. The worship of foreign gods in any form or through icons is not allowed.
Many Jewish scholars such as Rabbi Saadia Gaon
Saʿadia ben Yosef Gaon (892–942) was a prominent rabbi, Geonim, gaon, Jews, Jewish philosopher, and exegesis, exegete who was active in the Abbasid Caliphate.
Saadia is the first important rabbinic figure to write extensively in Judeo-Arabic ...
, Rabbi Bahya ibn Paquda, and Rabbi Yehuda Halevi have elaborated on the issues of idolatry. One of the oft-cited discussions is the commentary of Rabbi Moshe ben Maimon (Maimonides
Moses ben Maimon (1138–1204), commonly known as Maimonides (, ) and also referred to by the Hebrew acronym Rambam (), was a Sephardic rabbi and Jewish philosophy, philosopher who became one of the most prolific and influential Torah schola ...
) on idolatry. According to the Maimonidean interpretation, idolatry in itself is not a fundamental sin, but the grave sin is the denial of God's omnipresence that occurs with the belief that God can be corporeal. In the Jewish belief, the only image of God is man, one who lives and thinks; God has no visible shape, and it is absurd to make or worship images; instead man must worship the invisible God alone.
The commandments in the Hebrew Bible against idolatry forbade the practices and gods of ancient Akkad, Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
, and Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
. The Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
. '' polemics, states Naomi Janowitz, a professor of Religious Studies, has distorted the reality of Israelite religious practices and the historic use of images in Judaism. The direct material evidence is more reliable, such as that from the archaeological sites, and this suggests that the Jewish religious practices have been far more complex than what biblical polemics suggest. Judaism included images and cultic statues in the First Temple period, the Second Temple period, Late Antiquity (2nd to 8th century CE), and thereafter. Nonetheless, these sorts of evidence may be simply descriptive of Ancient Israelite practices in some—possibly deviant—circles, but cannot tell us anything about the mainstream religion of the Bible which proscribes idolatry. The history of Jewish religious practice has included idols and figurines made of ivory, terracotta,
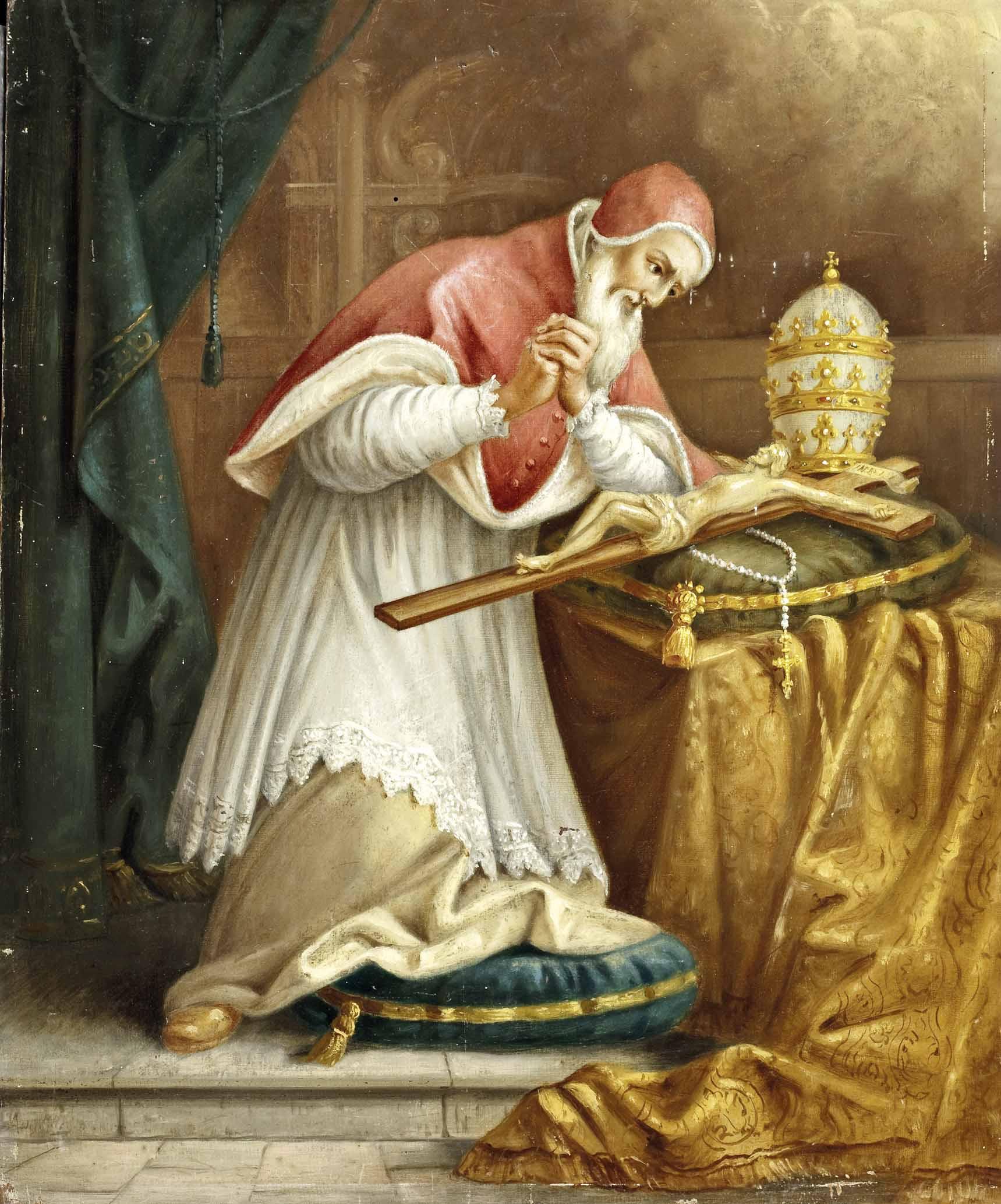 The early defense of images included exegesis of Old and New Testament. Evidence for the use of religious images is found in Early Christian art and documentary records. For example, the veneration of the tombs and statues of martyrs was common among early Christian communities. In 397 St.
The early defense of images included exegesis of Old and New Testament. Evidence for the use of religious images is found in Early Christian art and documentary records. For example, the veneration of the tombs and statues of martyrs was common among early Christian communities. In 397 St.
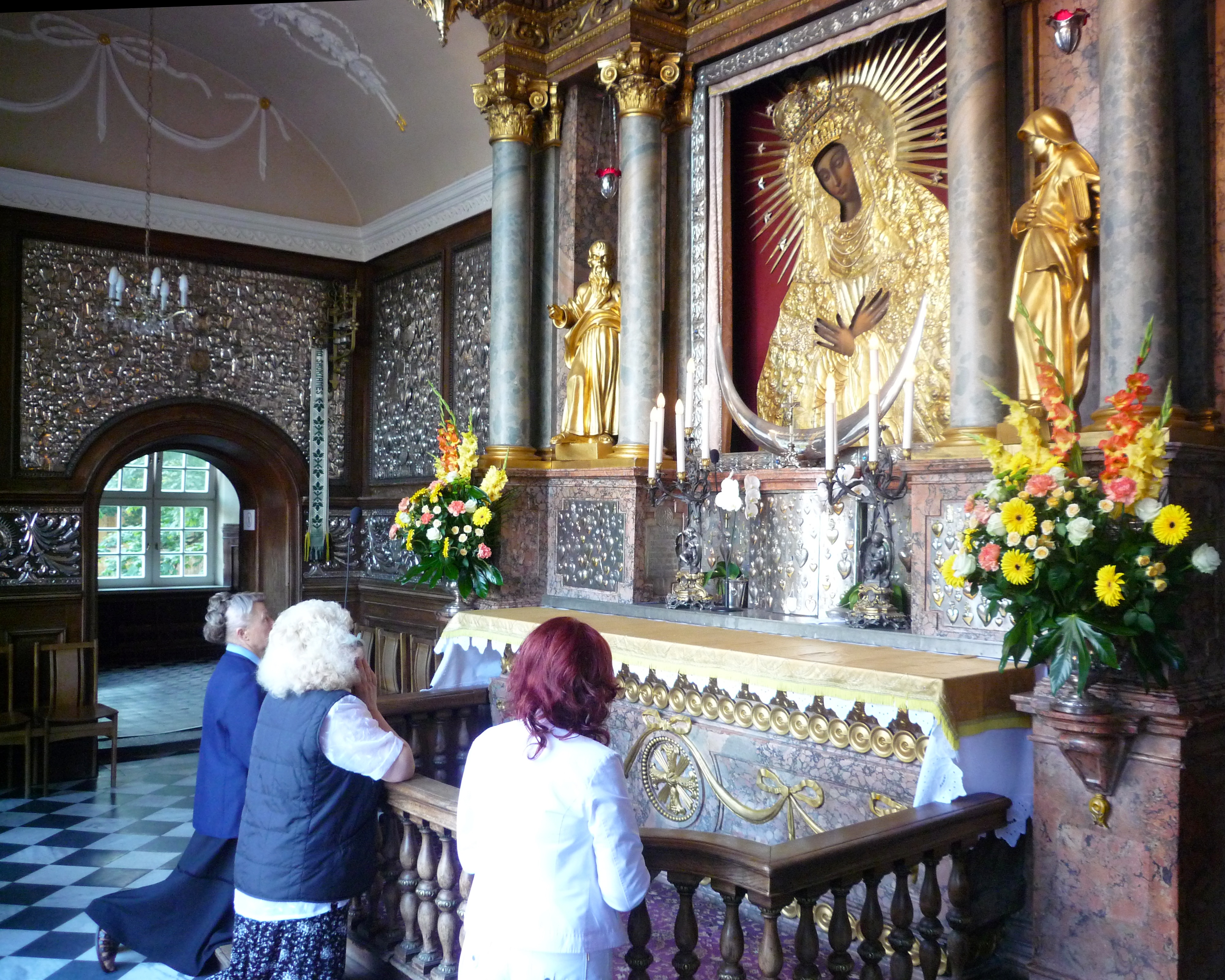 In Orthodox apologetic literature, the proper and improper use of images is extensively discussed. Exegetical Orthodox literature points to icons and the manufacture by Moses (under God's commandment) of the Bronze Snake in Numbers 21:9, which had the grace and power of God to heal those bitten by real snakes. Similarly, the
In Orthodox apologetic literature, the proper and improper use of images is extensively discussed. Exegetical Orthodox literature points to icons and the manufacture by Moses (under God's commandment) of the Bronze Snake in Numbers 21:9, which had the grace and power of God to heal those bitten by real snakes. Similarly, the
 Protestants did not abandon all icons and symbols of Christianity. They typically avoid the use of images, except the cross, in any context suggestive of veneration. The cross remained their central icon. Technically both major branches of Christianity have had their icons, states Carlos Eire, a professor of religious studies and history, but its meaning has been different to each and "one man's devotion was another man's idolatry". This was particularly true not only in the intra-Christian debate, states Eire, but also when soldiers of Catholic kings replaced "horrible
Protestants did not abandon all icons and symbols of Christianity. They typically avoid the use of images, except the cross, in any context suggestive of veneration. The cross remained their central icon. Technically both major branches of Christianity have had their icons, states Carlos Eire, a professor of religious studies and history, but its meaning has been different to each and "one man's devotion was another man's idolatry". This was particularly true not only in the intra-Christian debate, states Eire, but also when soldiers of Catholic kings replaced "horrible
Encyclopædia Britannica, Quote: "Shirk, (Arabic: "making a partner f someone), in Islam, idolatry, polytheism, and the association of God with other deities. The definition of Shirk differs in Islamic Schools, from Shiism and some classical Sunni Sufism accepting, sometimes, images, pilgrimage to shrines and veneration of relics and saints, to the more puritan Salafi-Wahhabi current, that condemns all the previous mentioned practices. The Quran stresses in many verses that God does not share his powers with any partner (sharik). It warns those who believe their idols will intercede for them that they, together with the idols, will become fuel for hellfire on the Day of Judgment ()." The concept of '' Within Islam, ''shirk'' is sin that can only be forgiven if the person who commits it asks God for forgiveness; if the person who committed it dies without repenting God may forgive any
Within Islam, ''shirk'' is sin that can only be forgiven if the person who commits it asks God for forgiveness; if the person who committed it dies without repenting God may forgive any
Devotionalism Reclaimed: Re-mapping Sacred Geography in Contemporary Korean Buddhism
Journal of Korean Religions, Vol. 3, No. 2, pages 153–171 The images or relics of Buddha are found in all Buddhist traditions, but they also feature gods and goddesses such as those in Tibetan Buddhism. Bhakti (called ''Bhatti'' in Pali) has been a common practice in Theravada Buddhism, where offerings and group prayers are made to Cetiya and particularly images of Buddha. Karel Werner notes that Bhakti has been a significant practice in Theravada Buddhism, and states, "there can be no doubt that deep devotion or ''bhakti / bhatti'' does exist in Buddhism and that it had its beginnings in the earliest days". According to Peter Harvey – a professor of Buddhist Studies, Buddha idols and idolatry spread into northwest Indian subcontinent (now Pakistan and Afghanistan) and into Central Asia with Buddhist Silk Road merchants. The Hindu rulers of different Indian dynasties patronized both Buddhism and Hinduism from 4th to 9th century, building Buddhist icons and cave temples such as the Ajanta Caves and Ellora Caves which featured Buddha idols., Quote: Hans Bakker's political history of the Vakataka dynasty observed that Ajanta caves belong to the Buddhist, not the Hindu tradition. That this should be so is already remarkable in itself. By all we know of Harisena he was a Hindu; (...). From the 10th century, states Harvey, the raids into northwestern parts of South Asia by Muslim Turks destroyed Buddhist idols, given their religious dislike for idolatry. The iconoclasm was so linked to Buddhism, that the Islamic texts of this era in India called all idols as ''Budd''. The desecration of idols in cave temples continued through the 17th century, states Geri Malandra, from the offense of "the graphic, anthropomorphic imagery of Hindu and Buddhist shrines". In East Asia and Southeast Asia, worship in Buddhist temples with the aid of icons and sacred objects has been historic. In Japanese Buddhism, for example, ''Butsugu'' (sacred objects) have been integral to the worship of the Buddha (''kuyo''), and such idolatry considered a part of the process of realizing one's Buddha nature. This process is more than meditation, it has traditionally included devotional rituals (''butsudo'') aided by the Buddhist clergy. These practices are also found in Korea and China.
 Statues, images and temples have been a part of the Traditional Religions of the indigenous people of the Americas. The Incan, Mayan and Aztec civilizations developed sophisticated religious practices that incorporated idols and religious arts. The Inca Empire, Inca culture, for example, has believed in ''Viracocha'' (also called ''Pachacutec'') as the
Statues, images and temples have been a part of the Traditional Religions of the indigenous people of the Americas. The Incan, Mayan and Aztec civilizations developed sophisticated religious practices that incorporated idols and religious arts. The Inca Empire, Inca culture, for example, has believed in ''Viracocha'' (also called ''Pachacutec'') as the  In Maya civilization, Mayan culture, ''Kukulkan'' has been the supreme
In Maya civilization, Mayan culture, ''Kukulkan'' has been the supreme
''Hombres ciegos, ídolos huecos: fetichismo y alteridad en la crítica de la idolatría del Apocalipsis de Abrahán''
(Medellín: Fondo Editorial Universidad Católica Luis Amigó) * Swagato Ganguly (2017).
Idolatry and The Colonial Idea of India: Visions of Horror, Allegories of Enlightenment
'. Routledge. * Reuven Chaim Klein (2018).
God versus Gods: Judaism in the Age of Idolatry
'. Mosaica Press. . * Yechezkel Kaufmann (1960)
''The Religion of Israel: From its Beginnings to the Babylonin Exile''
Univ. of Chicago Press. . * * * * * *
, Tufts University
Iconoclasm and idolatry
Columbia University {{Authority control Idolatry, Judeo-Christian topics Articles containing video clips
. '' polemics, states Naomi Janowitz, a professor of Religious Studies, has distorted the reality of Israelite religious practices and the historic use of images in Judaism. The direct material evidence is more reliable, such as that from the archaeological sites, and this suggests that the Jewish religious practices have been far more complex than what biblical polemics suggest. Judaism included images and cultic statues in the First Temple period, the Second Temple period, Late Antiquity (2nd to 8th century CE), and thereafter. Nonetheless, these sorts of evidence may be simply descriptive of Ancient Israelite practices in some—possibly deviant—circles, but cannot tell us anything about the mainstream religion of the Bible which proscribes idolatry. The history of Jewish religious practice has included idols and figurines made of ivory, terracotta,
faience
Faience or faïence (; ) is the general English language term for fine tin-glazed pottery. The invention of a white Ceramic glaze, pottery glaze suitable for painted decoration, by the addition of an stannous oxide, oxide of tin to the Slip (c ...
and seals. As more material evidence emerged, one proposal has been that Judaism oscillated between idolatry and iconoclasm. However, the dating of the objects and texts suggest that the two theologies and liturgical practices existed simultaneously. The claimed rejection of idolatry because of monotheism found in Jewish literature and therefrom in biblical Christian literature, states Janowitz, has been unreal abstraction and flawed construction of the actual history. The material evidence of images, statues and figurines taken together with the textual description of cherub and "wine standing for blood", for example, suggests that symbolism, making religious images, icon and index has been integral part of Judaism. Every religion has some objects that represent the divine and stand for something in the mind of the faithful, and Judaism too has had its holy objects and symbols such as Torah scrolls and holy books, Tefillin, the Menorah, mezuzah
A ''mezuzah'' ( "doorpost"; plural: ''mezuzot'') is a piece of parchment inscribed with specific Hebrew language, Hebrew verses from the Torah, which Jews affix in a small case to the doorposts of their homes. These verses are the Biblical pa ...
and many more.
Christianity
Ideas on idolatry in Christianity are based on the first ofTen Commandments
The Ten Commandments (), or the Decalogue (from Latin , from Ancient Greek , ), are religious and ethical directives, structured as a covenant document, that, according to the Hebrew Bible, were given by YHWH to Moses. The text of the Ten ...
.
This is expressed in the Bible in Exodus 20:3, Matthew 4:10, Luke 4:8 and elsewhere, e.g.:
The Christian view of idolatry may generally be divided into two general categories: the Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
and Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, otherwise known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity or Byzantine Christianity, is one of the three main Branches of Christianity, branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholic Church, Catholicism and Protestantism ...
view which accepts the use of religious images, and the views of many Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
churches that considerably restrict their use. However, many Protestants have used the image of the cross
A cross is a religious symbol consisting of two Intersection (set theory), intersecting Line (geometry), lines, usually perpendicular to each other. The lines usually run vertically and horizontally. A cross of oblique lines, in the shape of t ...
as a symbol.
Catholicism
The Catholic Church and the Orthodox Church have traditionally defended the use of icons. The debate on what images signify and whether reverence with the help of icons in church is equivalent to idolatry has lasted for many centuries, particularly from the 7th century until theReformation
The Reformation, also known as the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation, was a time of major Theology, theological movement in Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the p ...
in the 16th century. These debates have supported the inclusion of icons of Jesus Christ, the Virgin Mary, and the Apostles, the iconography expressed in stained glass, regional saints and other symbols of Christian faith. It has also supported the practices such as the Catholic mass, burning of candles before pictures, Christmas decorations and celebrations, and festive or memorial processions with statues of religious significance to Christianity.
St. John of Damascus
John of Damascus or John Damascene, born Yūḥana ibn Manṣūr ibn Sarjūn, was an Arab Christian monk, priest, hymnographer, and apologist. He was born and raised in Damascus or AD 676; the precise date and place of his death is not know ...
, in his "On the Divine Image", defended the use of icons and images, in direct response to the Byzantine iconoclasm
The Byzantine Iconoclasm () are two periods in the history of the Byzantine Empire when the use of religious images or icons was opposed by religious and imperial authorities within the Ecumenical Patriarchate (at the time still comprising the ...
that began widespread destruction of religious images in the 8th century, with support from emperor Leo III and continued by his successor Constantine V
Constantine V (; July 718 – 14 September 775) was Byzantine emperor from 741 to 775. His reign saw a consolidation of Byzantine security from external threats. As an able military leader, Constantine took advantage of Third Fitna, civil war ...
during a period of religious war with the invading Umayyads. John of Damascus wrote, "I venture to draw an image of the invisible God, not as invisible, but as having become visible for our sakes through flesh and blood", adding that images are expressions "for remembrance either of wonder, or an honor, or dishonor, or good, or evil" and that a book is also a written image in another form. He defended the religious use of images based on the Christian doctrine of Jesus as an incarnation
Incarnation literally means ''embodied in flesh'' or ''taking on flesh''. It is the Conception (biology), conception and the embodiment of a deity or spirit in some earthly form or an Anthropomorphism, anthropomorphic form of a god. It is used t ...
.
St. John the Evangelist
John the Evangelist ( – ) is the name traditionally given to the author of the Gospel of John. Christians have traditionally identified him with John the Apostle, John of Patmos, and John the Presbyter, although there is no consensus on how ...
cited John 1:14, stating that "the Word became flesh" indicates that the invisible God became visible, that God's glory manifested in God's one and only Son as Jesus Christ, and therefore God chose to make the invisible into a visible form, the spiritual incarnated into the material form.
 The early defense of images included exegesis of Old and New Testament. Evidence for the use of religious images is found in Early Christian art and documentary records. For example, the veneration of the tombs and statues of martyrs was common among early Christian communities. In 397 St.
The early defense of images included exegesis of Old and New Testament. Evidence for the use of religious images is found in Early Christian art and documentary records. For example, the veneration of the tombs and statues of martyrs was common among early Christian communities. In 397 St. Augustine of Hippo
Augustine of Hippo ( , ; ; 13 November 354 – 28 August 430) was a theologian and philosopher of Berber origin and the bishop of Hippo Regius in Numidia, Roman North Africa. His writings deeply influenced the development of Western philosop ...
, in his Confessions 6.2.2, tells the story of his mother making offerings for the tombs of martyrs and the oratories built in the memory of the saints.
The Catholic defense mentions textual evidence of external acts of honor towards icons, arguing that there are a difference between adoration and veneration and that the veneration shown to icons differs entirely from the adoration of God. Citing the Old Testament, these arguments present examples of forms of "veneration" such as in Genesis 33:3, with the argument that "adoration is one thing, and that which is offered in order to venerate something of great excellence is another". These arguments assert, "the honor given to the image is transferred to its prototype", and that venerating an image of Christ does not terminate at the image itself – the material of the image is not the object of worship – rather it goes beyond the image, to the prototype.
According to the ''Catechism of the Catholic Church
The ''Catechism of the Catholic Church'' (; commonly called the ''Catechism'' or the ''CCC'') is a reference work that summarizes the Catholic Church's doctrine. It was Promulgation (Catholic canon law), promulgated by Pope John Paul II in 1992 ...
'':
It also points out the following:
The manufacture of images of Jesus, the Virgin Mary and Christian saints, along with prayers directed to these has been widespread among the Catholic faithful.
Orthodox Church
TheEastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, officially the Orthodox Catholic Church, and also called the Greek Orthodox Church or simply the Orthodox Church, is List of Christian denominations by number of members, one of the three major doctrinal and ...
has differentiated between '' latria'' and '' dulia''. A ''latria'' is the worship
Worship is an act of religious devotion usually directed towards a deity or God. For many, worship is not about an emotion, it is more about a recognition of a God. An act of worship may be performed individually, in an informal or formal group, ...
due God, and ''latria'' to anyone or anything other than God is doctrinally forbidden by the Orthodox Church; however ''dulia'' has been defined as veneration of religious images, statues or icons which is not only allowed but obligatory. This distinction was discussed by Thomas Aquinas
Thomas Aquinas ( ; ; – 7 March 1274) was an Italian Dominican Order, Dominican friar and Catholic priest, priest, the foremost Scholasticism, Scholastic thinker, as well as one of the most influential philosophers and theologians in the W ...
in section 3.25 of ''Summa Theologiae''.
 In Orthodox apologetic literature, the proper and improper use of images is extensively discussed. Exegetical Orthodox literature points to icons and the manufacture by Moses (under God's commandment) of the Bronze Snake in Numbers 21:9, which had the grace and power of God to heal those bitten by real snakes. Similarly, the
In Orthodox apologetic literature, the proper and improper use of images is extensively discussed. Exegetical Orthodox literature points to icons and the manufacture by Moses (under God's commandment) of the Bronze Snake in Numbers 21:9, which had the grace and power of God to heal those bitten by real snakes. Similarly, the Ark of the Covenant
The Ark of the Covenant, also known as the Ark of the Testimony or the Ark of God, was a religious storage chest and relic held to be the most sacred object by the Israelites.
Religious tradition describes it as a wooden storage chest decorat ...
was cited as evidence of the ritual object above which Yahweh was present.
Veneration of icons through ''proskynesis
Proskynesis (), also called proscynesis () or proskinesis (; ; ), was a solemn gesture of respect towards gods and people in many societies. Among the Persians, it referred to a man prostrating himself and kissing the land or the limbs of a r ...
'' was codified in 787 AD by the Seventh Ecumenical Council. This was triggered by the Byzantine Iconoclasm controversy that followed raging Christian-Muslim wars and a period of iconoclasm in West Asia. The defense of images and the role of the Syrian scholar John of Damascus
John of Damascus or John Damascene, born Yūḥana ibn Manṣūr ibn Sarjūn, was an Arab Christian monk, priest, hymnographer, and apologist. He was born and raised in Damascus or AD 676; the precise date and place of his death is not know ...
was pivotal during this period. The Eastern Orthodox Church has ever since celebrated the use of icons and images. Eastern Rite Catholics also accepts icons in their Divine Liturgy
Divine Liturgy () or Holy Liturgy is the usual name used in most Eastern Christian rites for the Eucharistic service.
The Eastern Catholic Churches, Eastern Lutheranism, Eastern Lutheran Churches and the Eastern Orthodox Church believe the Divi ...
.
Protestantism
The idolatry debate has been one of the defining differences between papal Catholicism and anti-papal Protestantism. The anti-papal writers have prominently questioned the worship practices and images supported by Catholics, with many Protestant scholars listing it as the "one religious error larger than all others". The sub-list of erring practices have included among other things the veneration of Virgin Mary, the Catholic mass, the invocation of saints, and the reverence expected for and expressed to pope himself. The charges of supposed idolatry against the Roman Catholics were leveled by a diverse group of Protestants, fromAnglicans
Anglicanism, also known as Episcopalianism in some countries, is a Western Christianity, Western Christian tradition which developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the ...
to Calvinists
Reformed Christianity, also called Calvinism, is a major branch of Protestantism that began during the 16th-century Protestant Reformation. In the modern day, it is largely represented by the Continental Reformed Christian, Presbyterian, ...
in Geneva.
 Protestants did not abandon all icons and symbols of Christianity. They typically avoid the use of images, except the cross, in any context suggestive of veneration. The cross remained their central icon. Technically both major branches of Christianity have had their icons, states Carlos Eire, a professor of religious studies and history, but its meaning has been different to each and "one man's devotion was another man's idolatry". This was particularly true not only in the intra-Christian debate, states Eire, but also when soldiers of Catholic kings replaced "horrible
Protestants did not abandon all icons and symbols of Christianity. They typically avoid the use of images, except the cross, in any context suggestive of veneration. The cross remained their central icon. Technically both major branches of Christianity have had their icons, states Carlos Eire, a professor of religious studies and history, but its meaning has been different to each and "one man's devotion was another man's idolatry". This was particularly true not only in the intra-Christian debate, states Eire, but also when soldiers of Catholic kings replaced "horrible Aztec
The Aztecs ( ) were a Mesoamerican civilization that flourished in central Mexico in the Post-Classic stage, post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different Indigenous peoples of Mexico, ethnic groups of central ...
idols" in the American colonies with "beautiful crosses and images of Mary and the saints".
Protestants often accuse Catholics of idolatry, iconolatry, and even paganism
Paganism (, later 'civilian') is a term first used in the fourth century by early Christians for people in the Roman Empire who practiced polytheism, or ethnic religions other than Christianity, Judaism, and Samaritanism. In the time of the ...
; in the Protestant Reformation
The Reformation, also known as the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation, was a time of major theological movement in Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the papacy and ...
such language was common to all Protestants. In some cases, such as the Puritan
The Puritans were English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries who sought to rid the Church of England of what they considered to be Roman Catholic practices, maintaining that the Church of England had not been fully reformed and should b ...
groups denounced all forms of religious objects, regardless of whether it was a statue or sculpture, or image, including the Christian cross
The Christian cross, seen as representing the crucifixion of Jesus, is a religious symbol, symbol of Christianity. It is related to the crucifix, a cross that includes a ''corpus'' (a representation of Jesus' body, usually three-dimensional) a ...
. The Waldensians
The Waldensians, also known as Waldenses (), Vallenses, Valdesi, or Vaudois, are adherents of a church tradition that began as an ascetic movement within Western Christianity before the Reformation. Originally known as the Poor of Lyon in the l ...
were accused of idolatry by inquisitors.
The body of Christ on the cross is an ancient symbol used within the Catholic, Eastern Orthodox, Anglican, and Lutheran
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched ...
Churches, in contrast with some Protestant groups, which use only a simple cross. In Judaism, the reverence to the icon of Christ in the form of cross has been seen as idolatry. However, some Jewish scholars disagree and consider Christianity to be based on Jewish belief and not truly idolatrous., Quote: "Over time, however, new religions developed whose basis is in Jewish belief – such as Christianity and Islam – which are based on belief in the Creator and whose adherents follow commandments that are similar to some Torah laws (see the uncensored Rambam in his Mishneh Torah, Hilkhot Melakhim 11:4). All of the rishonim agree that adherents of these religions are not idol worshippers and should not be treated as the pagans described in the Torah."
Islam
In Islamic sources, the concept of '' shirk'' (triliteral root
The roots of verbs and most nouns in the Semitic languages are characterized as a sequence of consonants or " radicals" (hence the term consonantal root). Such abstract consonantal roots are used in the formation of actual words by adding the vowel ...
: ''sh-r-k'') can refer to "idolatry", though it is most widely used to denote "association of partners with God".ShirkEncyclopædia Britannica, Quote: "Shirk, (Arabic: "making a partner f someone), in Islam, idolatry, polytheism, and the association of God with other deities. The definition of Shirk differs in Islamic Schools, from Shiism and some classical Sunni Sufism accepting, sometimes, images, pilgrimage to shrines and veneration of relics and saints, to the more puritan Salafi-Wahhabi current, that condemns all the previous mentioned practices. The Quran stresses in many verses that God does not share his powers with any partner (sharik). It warns those who believe their idols will intercede for them that they, together with the idols, will become fuel for hellfire on the Day of Judgment ()." The concept of ''
Kufr
''Kāfir'' (; , , or ; ; or ) is an Arabic-language term used by Muslims to refer to a non-Muslim, more specifically referring to someone who disbelieves in the Islamic God, denies his authority, and rejects the message of Islam a ...
'' (k-f-r) can also include idolatry (among other forms of disbelief)., Quote: " afirThey included those who practiced idolatry, did not accept the absolute oneness of God, denied that Muhammad was a prophet, ignored God's commandments and signs (singular ''aya'') and rejected belief in a resurrection and final judgment." The one who practices ''shirk'' is called ''mushrik'' (plural ''mushrikun'') in the Islamic scriptures. The Quran forbids idolatry. Over 500 mentions of ''kufr'' and ''shirk'' are found in the Quran, and both concepts are strongly forbidden.
The Islamic concept of idolatry extends beyond polytheism, and includes some Christians and Jews as ''muširkūn'' (idolaters) and ''kafirun'' (infidels)., Quote: "in some verses it does appear to be suggested that Christians are guilty of both kufr and shirk. This is particularly the case in 5:72 ... In addition to 9:29, therefore, which has been discussed above and which refers to both Jews and Christians, other verses are extremely hostile to both Jews and Christians, other verses are extremely hostile to Christians in particular, suggesting that they both disbelieve (kafara) and are guilty of shirk." For example:
Shia classical theology differs in the concept of Shirk. According to Twelver theologians, the attributes and names of God have no independent and hypostatic existence apart from the being and essence of God. Any suggestion of these attributes and names being conceived of as separate is thought to entail polytheism. It would be even incorrect to say God knows by his knowledge which is in his essence but God knows by his knowledge which is his essence. Also God has no physical form and he is insensible. The border between theoretical Tawhid
''Tawhid'' () is the concept of monotheism in Islam, it is the religion's central and single most important concept upon which a Muslim's entire religious adherence rests. It unequivocally holds that God is indivisibly one (''ahad'') and s ...
and Shirk is to know that every reality and being in its essence, attributes and action are from him (from Him-ness), it is Tawhid
''Tawhid'' () is the concept of monotheism in Islam, it is the religion's central and single most important concept upon which a Muslim's entire religious adherence rests. It unequivocally holds that God is indivisibly one (''ahad'') and s ...
. Every supernatural action of the prophets is by God's permission as Quran points to it. The border between the Tawhid and Shirk in practice is to assume something as an end in itself, independent from God, not as a road to God (to Him-ness). Ismailis go deeper into the definition of ''Shirk'', declaring they don't recognize any sort of ''ground of being'' by the esoteric potential to have intuitive knowledge of the human being. Hence, most Shias
Shia Islam is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that Muhammad designated Ali ibn Abi Talib () as both his political successor (caliph) and as the spiritual leader of the Muslim community (imam). However, his right is understood to ...
have no problem with religious symbols
A religious symbol is an iconic representation intended to represent a specific religion, or a specific concept within a given religion.
Religious symbols have been used in the military in many countries, such as the United States military chap ...
and artworks, and with reverence for Wali
The term ''wali'' is most commonly used by Muslims to refer to a saint, or literally a "friend of God".John Renard, ''Friends of God: Islamic Images of Piety, Commitment, and Servanthood'' (Berkeley: University of California Press, 2008); John ...
s, Rasūl
Prophets in Islam () are individuals in Islam who are believed to spread God's message on Earth and serve as models of ideal human behaviour. Some prophets are categorized as messengers (; sing. , ), those who transmit divine revelation, most ...
s and Imams
Imam (; , '; : , ') is an Islamic leadership position. For Sunni Muslims, Imam is most commonly used as the title of a prayer leader of a mosque. In this context, imams may lead Islamic prayers, serve as community leaders, and provide relig ...
.
Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
strongly prohibits all form of idolatry, which is part of the sin of ''shirk'' (); ''širk'' comes from the Arabic root Š- R- K (), with the general meaning of "to share". In the context of the Qur'an, the particular sense of "sharing as an equal partner" is usually understood as "attributing a partner to Allah". ''Shirk'' is often translated as idolatry and polytheism. In the Qur'an, ''shirk'' and the related word (plural Stem IV active participle) ''mušrikūn'' (مشركون) "those who commit shirk" refers to the enemies of Islam (as in verse 9.1–15).
 Within Islam, ''shirk'' is sin that can only be forgiven if the person who commits it asks God for forgiveness; if the person who committed it dies without repenting God may forgive any
Within Islam, ''shirk'' is sin that can only be forgiven if the person who commits it asks God for forgiveness; if the person who committed it dies without repenting God may forgive any sin
In religious context, sin is a transgression against divine law or a law of the deities. Each culture has its own interpretation of what it means to commit a sin. While sins are generally considered actions, any thought, word, or act considered ...
except for committing ''shirk''. In practice, especially among strict conservative interpretations of Islam, the term has been greatly extended and means deification of anyone or anything other than the singular God. In Salafi-Wahhabi interpretation, it may be used very widely to describe behaviour that does not literally constitute worship, including use of images of sentient beings, building a structure over a grave, associating partners with God, giving his characteristics to others beside him, or not believing in his characteristics. 19th century Wahhabis regarded idolatry punishable with the death penalty, a practice that was "hitherto unknown" in Islam., Quote: "In reference to Wahhabi strictness in applying their moral code, Corancez writes that the distinguishing feature of the Wahhabis was their intolerance, which they pursued to hitherto unknown extremes, holding idolatry as a crime punishable by death". However, Classical Orthodox Sunni thought used to be rich in Relics and Saint veneration, as well as pilgrimage to their shrines. Ibn Taymiyya, a medieval theologian that influenced modern days Salafists, was put in prison for his negation of veneration of relics and Saints, as well as pilgrimage to Shrines, which was considered unorthodox by his contemporary theologians.
According to Islamic tradition, over the millennia after Ishmael
In the Bible, biblical Book of Genesis, Ishmael (; ; ; ) is the first son of Abraham. His mother was Hagar, the handmaiden of Abraham's wife Sarah. He died at the age of 137. Traditionally, he is seen as the ancestor of the Arabs.
Within Isla ...
's death, his progeny and the local tribes who settled around the oasis of Zam-Zam gradually turned to polytheism and idolatry. Several idols were placed within the Kaaba
The Kaaba (), also spelled Kaba, Kabah or Kabah, sometimes referred to as al-Kaba al-Musharrafa (), is a stone building at the center of Islam's most important mosque and Holiest sites in Islam, holiest site, the Masjid al-Haram in Mecca, Sa ...
representing deities of different aspects of nature and different tribes. Several heretical rituals were adopted in the Pilgrimage (''Hajj
Hajj (; ; also spelled Hadj, Haj or Haji) is an annual Islamic pilgrimage to Mecca, Saudi Arabia, the holiest city for Muslims. Hajj is a mandatory religious duty for capable Muslims that must be carried out at least once in their lifetim ...
'') including doing naked circumambulation.
In her book, ''Islam: A Short History'', Karen Armstrong
Karen Armstrong (born 14 November 1944) is a British author and commentator known for her books on comparative religion. A former Roman Catholic religious sister, she went from a conservative to a more liberal and Christian mysticism, mystical ...
asserts that the Kaaba was officially dedicated to Hubal
In Arabian mythology, Hubal () was a god worshipped in pre-Islamic Arabia, notably by the Quraysh at the Kaaba in Mecca. The god's icon was a human figure believed to control acts of divination, which was performed by tossing arrows before the ...
, a Nabatean
The Nabataeans or Nabateans (; Nabataean Aramaic: , , vocalized as ) were an ancient Arab people who inhabited northern Arabia and the southern Levant. Their settlements—most prominently the assumed capital city of Raqmu (present-day Petra ...
deity, and contained 360 idols that probably represented the days of the year. But by Muhammad's day, it seems that the Kaaba was venerated as the shrine of Allah
Allah ( ; , ) is an Arabic term for God, specifically the God in Abrahamic religions, God of Abraham. Outside of the Middle East, it is principally associated with God in Islam, Islam (in which it is also considered the proper name), althoug ...
, the High God. Allah was never represented by an idol. Once a year, tribes from all around the Arabian peninsula, whether Christian or pagan, would converge on Mecca to perform the ''Hajj'', marking the widespread conviction that Allah was the same deity worshipped by monotheists. Guillaume in his translation of Ibn Ishaq
Abu Abd Allah Muhammad ibn Ishaq ibn Yasar al-Muttalibi (; – , known simply as Ibn Ishaq, was an 8th-century Muslim historian and hagiographer who collected oral traditions that formed the basis of an important biography of the Islamic proph ...
, an early biographer of Muhammad, says the Ka'aba might have been itself addressed using a feminine grammatical form by the Quraysh. Circumambulation was often performed naked by men and almost naked by women. It is disputed whether al-Lat and Hubal were the same deity or different. Per a hypothesis by Uri Rubin
Uri Rubin (; 1944 – 26 October 2021) was an Israeli academic who was a professor in the Department of Arabic and Islamic Studies at Tel Aviv University. His areas of research were early Islam (with special emphasis on the ''Qur'an''), ''Qur'an ...
and Christian Robin, Hubal was only venerated by Quraysh and the Kaaba was first dedicated to al-Lat
Al-Lat (, ), also spelled Allat, Allatu, and Alilat, is a pre-Islamic Arabian goddess, at one time worshipped under various associations throughout the entire Arabian Peninsula, including Mecca, where she was worshipped alongside Al-Uzza and ...
, a supreme god of individuals belonging to different tribes, while the pantheon of the gods of Quraysh was installed in Kaaba after they conquered Mecca a century before Muhammad's time.
Indian religions
Provenance
The first attested date in peer-reviewed academic literature for the worship ofmurti
In the Hinduism, Hindu tradition, a ''murti'' (, ) is a devotional image, such as a statue or icon, of a Hindu deities, deity or Hindu saints, saint used during ''Puja (Hinduism), puja'' and/or in other customary forms of actively expressing d ...
(Sanskrit) or vigraha
In the Hindu tradition, a ''murti'' (, ) is a devotional image, such as a statue or icon, of a deity or saint used during '' puja'' and/or in other customary forms of actively expressing devotion or reverence – whether at Hindu temples or sh ...
(Sanskrit) in India is not clear, as different sources have different opinions and interpretations. However, the Indus Valley Civilization
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation, was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form from 2600 BCE ...
(circa 2500 - 1500 BCE) may have produced some of the earliest murtis or vigrahas in India, as evidenced by various terracotta and bronze figurines found in the archaeological sites. Some of these figurines have been interpreted as representations of deities, such as the so-called Pashupati seal, which depicts a horned figure surrounded by animals and possibly identified with Shiva
Shiva (; , ), also known as Mahadeva (; , , Help:IPA/Sanskrit, ɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐh and Hara, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the God in Hinduism, Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions w ...
. Another example is the bronze statuette of a Dancing Girl, which some scholars have associated with Parvati
Parvati (, , IPA: /Sanskrit phonology, pɑɾʋət̪iː/), also known as Uma (, , IPA: Sanskrit phonology, /ʊmɑː/) and Gauri (, , IPA: /Sanskrit phonology, gə͡ʊɾiː/), is one of the principal goddesses in Hinduism, revered as the Devi, ...
or Shakti
Shakti (Devanagari: शक्ति, IAST: Śakti; 'energy, ability, strength, effort, power, might, capability') in Hinduism, is the "Universal Power" that underlies and sustains all existence. Conceived as feminine in essence, Shakti refer ...
. However, these interpretations are not universally accepted, and some scholars have argued that the Indus Valley Civilization did not practice murti or vigraha worship, but rather used symbols and signs to express their religious beliefs.Source: https://www.oneindia.com/india/why-india-is-a-land-of-murti-and-vigraha-and-not-idols-and-idolators-as-perceived-by-the-west-3455405.html (accessed: Wednesday September 27, 2023)
The Vedic period
The Vedic period, or the Vedic age (), is the period in the late Bronze Age and early Iron Age of the history of India when the Vedic literature, including the Vedas (–900 BCE), was composed in the northern Indian subcontinent, between the e ...
(circa 1500 - 500 BCE) is traditionally considered as the origin of Hinduism proper, but it also did not emphasize murti or vigraha worship, as the Vedic religion was mainly focused on fire sacrifices and hymns to various gods and goddesses. However, some Vedic texts
upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the '' Atharvaveda''.
The Vedas ( or ; ), sometimes collectively called the Veda, are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed i ...
do mention the use of clay or wooden images for ritual purposes, such as the Shatapatha Brahmana
The Shatapatha Brahmana (, , abbreviated to 'SB') is a commentary on the Yajurveda, Śukla Yajurveda. It is attributed to the Vedic sage Yajnavalkya. Described as the most complete, systematic, and important of the Brahmanas (commentaries on the ...
(circa 8th - 6th century BCE), which describes how a clay image of Prajapati
Prajapati (, ) is a Vedas, Vedic deity of Hinduism. He is later identified with Brahma, the creator god.
Prajapati is a form of the creator-god Brahma, but the name is also the name of many different gods, in many Hindu scriptures, ranging f ...
(the creator god) was made and consecrated for the agnicayana ritual. Another example, is the Aitareya Brahmana (circa 8th - 6th century BCE), which mentions how a wooden image of Varuna
Varuna (; , ) is a Hindu god. He is one of the earliest deities in pantheon, whose role underwent a significant transformation from the Vedic to the Puranic periods. In the early Vedic era, Varuna is seen as the god-sovereign, ruling the sky ...
(the god of water and law) was installed in a temple and worshipped by the king. These examples suggest that murti or vigraha worship was not unknown in the Vedic period, but it was not widespread nor dominant.
The post-Vedic period (circa 500 BCE - 300 CE) witnessed the emergence and development of various religious movements and schools, such as Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
, Jainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religions, Indian religion whose three main pillars are nonviolence (), asceticism (), and a rejection of all simplistic and one-sided views of truth and reality (). Jainism traces its s ...
, Shaivism
Shaivism (, , ) is one of the major Hindu denominations, Hindu traditions, which worships Shiva as the Para Brahman, supreme being. It is the Hinduism#Demographics, second-largest Hindu sect after Vaishnavism, constituting about 385 million H ...
, Vaishnavism
Vaishnavism () ), also called Vishnuism, is one of the major Hindu denominations, Hindu traditions, that considers Vishnu as the sole Para Brahman, supreme being leading all other Hindu deities, that is, ''Mahavishnu''. It is one of the majo ...
, Shaktism
Shaktism () is a major Hindu denomination in which the God in Hinduism, deity or metaphysics, metaphysical reality is considered metaphorically to be a woman.
Shaktism involves a galaxy of goddesses, all regarded as different aspects, mani ...
and others. This period also saw the rise of murti or vigraha worship as a prominent feature of Hinduism, as evidenced by various literary and archaeological sources. For instance, the Ramayana
The ''Ramayana'' (; ), also known as ''Valmiki Ramayana'', as traditionally attributed to Valmiki, is a smriti text (also described as a Sanskrit literature, Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epic) from ancient India, one of the two important epics ...
(circa 5th - 4th century BCE) and the Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; , , ) is one of the two major Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epics of ancient India revered as Smriti texts in Hinduism, the other being the ''Ramayana, Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the events and aftermath of the Kuru ...
(circa 4th - 3rd century BCE) contain several references to murti or vigraha worship, such as Rama
Rama (; , , ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the seventh and one of the most popular avatars of Vishnu. In Rama-centric Hindu traditions, he is considered the Supreme Being. Also considered as the ideal man (''maryāda' ...
worshipping a Shiva linga
A lingam ( , lit. "sign, symbol or mark"), sometimes referred to as linga or Shiva linga, is an abstract or aniconic representation of the Hindu god Shiva in Shaivism. The word ''lingam'' is found in the Upanishads and epic literature, wher ...
at Rameshwaram, or Krishna
Krishna (; Sanskrit language, Sanskrit: कृष्ण, ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme God (Hinduism), Supreme God in his own right. He is the god of protection, c ...
installing an image of Vishnu
Vishnu (; , , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism, and the god of preservation ( ...
at Dwarka
Dwarka () is a town and municipality of Devbhumi Dwarka district in the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Gujarat. It is located on the western shore of the Okhamandal Peninsula on the right bank of the Gomti river at ...
. Another example, is the Buddhist text Lalitavistara Sutra (circa 3rd century BCE - 3rd century CE), which mentions how Buddha's mother Maya dreamt of a white elephant entering her womb, and how King Suddhodana made an image of this elephant and worshipped it. Moreover, many stone and metal sculptures of various deities and saints have been found from this period onwards, such as the famous Pancha Rathas at Mahabalipuram
Mamallapuram (also known as Mahabalipuram), is a town in Chengalpattu district in the southeastern Indian States and territories of India, state of Tamil Nadu, best known for the UNESCO World Heritage Site of 7th- and 8th-century Hindu Group of ...
(circa 7th century CE), which depict five chariots dedicated to different gods and goddesses.
General
The oldest forms of the ancient religions of India apparently made no use of idols. While theVedic literature
FIle:Atharva-Veda samhita page 471 illustration.png, upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the ''Atharvaveda''.
The Vedas ( or ; ), sometimes collectively called the Veda, are a large body of relig ...
leading up to Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified ...
is extensive, in the form of Samhita
Samhita (IAST: ''Saṃhitā'') literally means "put together, joined, union", a "collection", and "a methodical, rule-based combination of text or verses".
s, Brahmana
The Brahmanas (; Sanskrit: , International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration, IAST: ''Brāhmaṇam'') are Vedas, Vedic śruti works attached to the Samhitas (hymns and mantras) of the Rigveda, Rig, Samaveda, Sama, Yajurveda, Yajur, and Athar ...
s, Aranyaka
The ''Aranyakas'' (; ; IAST: ') are a part of the ancient Indian Vedas concerned with the meaning of ritual sacrifice, composed in about 700 BC. They typically represent the later sections of the Vedas, and are one of many layers of Vedic text ...
s and Upanishad
The Upanishads (; , , ) are late Vedic and post-Vedic Sanskrit texts that "document the transition from the archaic ritualism of the Veda into new religious ideas and institutions" and the emergence of the central religious concepts of Hind ...
s, and has been dated to have been composed over a period of centuries (1200 BC to 200 BC), historical Vedic religion
The historical Vedic religion, also called Vedism or Brahmanism, and sometimes ancient Hinduism or Vedic Hinduism, constituted the religious ideas and practices prevalent amongst some of the Indo-Aryan peoples of the northwest Indian subcontin ...
appears not to have used idols up to around 500 BC at least. The early Buddhist and Jain (pre-200 BC) traditions suggest no evidence of idolatry. The Vedic literature mentions many gods and goddesses, as well as the use of Homa (votive ritual using fire), but it does not mention images or their worship. The ancient Buddhist, Hindu and Jaina texts discuss the nature of existence, whether there is or is not a creator deity
A creator deity or creator god is a deity responsible for the creation of the Earth, world, and universe in human religion and mythology. In monotheism, the single God is often also the creator. A number of monolatristic traditions separate a ...
such as in the Nasadiya Sukta of the ''Rigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' (, , from wikt:ऋच्, ऋच्, "praise" and wikt:वेद, वेद, "knowledge") is an ancient Indian Miscellany, collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canoni ...
'', they describe meditation, they recommend the pursuit of simple monastic life and self-knowledge, they debate the nature of absolute reality as Brahman or Śūnyatā, yet the ancient Indian texts mention no use of images. Indologists such as the Max Muller, Jan Gonda, Pandurang Vaman Kane, Ramchandra Narayan Dandekar, Horace Hayman Wilson, Stephanie W. Jamison, Stephanie Jamison and other scholars state that "there is no evidence for icons or images representing god(s)" in the ancient religions of India. Use of idols developed among the Indian religions later, perhaps first in Buddhism, where large images of the Buddha appear by the 1st century AD.
According to John Grimes, a professor of Indian philosophy, Indian thought denied even dogmatic idolatry of its scriptures. Everything has been left to challenge, arguments and enquiry, with the medieval Indian scholar Vācaspati Miśra stating that not all scripture is authoritative, only scripture which "reveals the identity of the individual self and the supreme self as the non-dual Absolute".
Buddhism
According to Eric Reinders, icons and idolatry have been an integral part of Buddhism throughout its later history. Buddhists, from Korea to Vietnam, Thailand to Tibet, Central Asia to South Asia, have long produced temples and idols, altars and malas, relics to amulets, images to ritual implements.Pori Park (2012)Devotionalism Reclaimed: Re-mapping Sacred Geography in Contemporary Korean Buddhism
Journal of Korean Religions, Vol. 3, No. 2, pages 153–171 The images or relics of Buddha are found in all Buddhist traditions, but they also feature gods and goddesses such as those in Tibetan Buddhism. Bhakti (called ''Bhatti'' in Pali) has been a common practice in Theravada Buddhism, where offerings and group prayers are made to Cetiya and particularly images of Buddha. Karel Werner notes that Bhakti has been a significant practice in Theravada Buddhism, and states, "there can be no doubt that deep devotion or ''bhakti / bhatti'' does exist in Buddhism and that it had its beginnings in the earliest days". According to Peter Harvey – a professor of Buddhist Studies, Buddha idols and idolatry spread into northwest Indian subcontinent (now Pakistan and Afghanistan) and into Central Asia with Buddhist Silk Road merchants. The Hindu rulers of different Indian dynasties patronized both Buddhism and Hinduism from 4th to 9th century, building Buddhist icons and cave temples such as the Ajanta Caves and Ellora Caves which featured Buddha idols., Quote: Hans Bakker's political history of the Vakataka dynasty observed that Ajanta caves belong to the Buddhist, not the Hindu tradition. That this should be so is already remarkable in itself. By all we know of Harisena he was a Hindu; (...). From the 10th century, states Harvey, the raids into northwestern parts of South Asia by Muslim Turks destroyed Buddhist idols, given their religious dislike for idolatry. The iconoclasm was so linked to Buddhism, that the Islamic texts of this era in India called all idols as ''Budd''. The desecration of idols in cave temples continued through the 17th century, states Geri Malandra, from the offense of "the graphic, anthropomorphic imagery of Hindu and Buddhist shrines". In East Asia and Southeast Asia, worship in Buddhist temples with the aid of icons and sacred objects has been historic. In Japanese Buddhism, for example, ''Butsugu'' (sacred objects) have been integral to the worship of the Buddha (''kuyo''), and such idolatry considered a part of the process of realizing one's Buddha nature. This process is more than meditation, it has traditionally included devotional rituals (''butsudo'') aided by the Buddhist clergy. These practices are also found in Korea and China.
Hinduism
In Hinduism, an icon, image or statue is called ''murti
In the Hinduism, Hindu tradition, a ''murti'' (, ) is a devotional image, such as a statue or icon, of a Hindu deities, deity or Hindu saints, saint used during ''Puja (Hinduism), puja'' and/or in other customary forms of actively expressing d ...
'' or ''pratima''. Major Hindu traditions such as Vaishnavism
Vaishnavism () ), also called Vishnuism, is one of the major Hindu denominations, Hindu traditions, that considers Vishnu as the sole Para Brahman, supreme being leading all other Hindu deities, that is, ''Mahavishnu''. It is one of the majo ...
, Shaivism
Shaivism (, , ) is one of the major Hindu denominations, Hindu traditions, which worships Shiva as the Para Brahman, supreme being. It is the Hinduism#Demographics, second-largest Hindu sect after Vaishnavism, constituting about 385 million H ...
, Shaktism
Shaktism () is a major Hindu denomination in which the God in Hinduism, deity or metaphysics, metaphysical reality is considered metaphorically to be a woman.
Shaktism involves a galaxy of goddesses, all regarded as different aspects, mani ...
, and Smarta Tradition, Smartism favor the use of a ''murti'' (idol). These traditions suggest that it is easier to dedicate time and focus on Spirituality#Hinduism, spirituality through anthropomorphic or non-anthropomorphic icons. The ''Bhagavad Gita'' – a Hindu scripture, in verse 12.5, states that only a few have the time and mind to ponder and fix on the unmanifested Absolute (abstract formless Brahman), and it is much easier to focus on qualities, virtues, aspects of a manifested representation of god, through one's senses, emotions and heart, because the way human beings naturally are.
A ''murti'' in Hinduism, states Jeaneane Fowler – a professor of Religious Studies specializing on Indian Religions, is itself not god, it is an "image of god" and thus a symbol and representation. A ''murti'' is a form and manifestation, states Fowler, of the formless Absolute. Thus a literal translation of ''murti'' as idol is incorrect, when idol is understood as superstitious end in itself. Just like the photograph of a person is not the real person, a ''murti'' is an image in Hinduism but not the real thing, but in both cases the image reminds of something of emotional and real value to the viewer. When a person worships a ''murti'', it is assumed to be a manifestation of the essence or spirit of the deity, the worshipper's spiritual ideas and needs are meditated through it, yet the idea of ultimate reality – called Brahman in Hinduism – is not confined in it.
Devotional (''bhakti movement'') practices centered on cultivating a deep and personal bond of love with God, often expressed and facilitated with one or more murti, and includes individual or community hymns, japa or singing (''bhajan'', ''kirtana,'' or ''Arti (Hinduism), arati''). Acts of devotion, in major temples particularly, are structured on treating the ''murti'' as the manifestation of a revered guest, and the daily routine can include awakening the ''murti'' in the morning and making sure that it "is washed, dressed, and garlanded."Klaus Klostermaier (2007) Hinduism: A Beginner's Guide, 2nd Edition, Oxford: OneWorld Publications, , pages 63–65
In Vaishnavism, the building of a temple for the ''murti'' is considered an act of devotion, but non-murti symbolism is also common wherein the aromatic Tulsi, tulasi plant or Shaligram, ''shaligrama'' is an aniconic reminder of the spiritualism in Vishnu. In the Shaivism
Shaivism (, , ) is one of the major Hindu denominations, Hindu traditions, which worships Shiva as the Para Brahman, supreme being. It is the Hinduism#Demographics, second-largest Hindu sect after Vaishnavism, constituting about 385 million H ...
tradition of Hinduism, Shiva
Shiva (; , ), also known as Mahadeva (; , , Help:IPA/Sanskrit, ɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐh and Hara, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the God in Hinduism, Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions w ...
may be represented as a masculine idol, or half-man half woman Ardhanarishvara form, in an anicon Lingam, linga-yoni form. The worship rituals associated with the ''murti'', correspond to ancient cultural practices for a beloved guest, and the ''murti'' is welcomed, taken care of, and then requested to retire.Michael Willis (2009), The Archaeology of Hindu Ritual, Cambridge University Press, , pages 96–112, 123–143, 168–172
Christopher John Fuller states that an image in Hinduism cannot be equated with a deity and the object of worship is the divine whose power is inside the image, and the image is not the object of worship itself, Hindus believe everything is worthy of worship as it contains divine energy. The idols are neither random nor intended as superstitious objects, rather they are designed with embedded symbolism and iconographic rules which sets the style, proportions, the colors, the nature of items the images carry, their ''mudra'' and the legends associated with the deity. The ''Vāstusūtra Upaniṣad'' states that the aim of the ''murti'' art is to inspire a devotee towards contemplating the Ultimate Supreme Principle (Brahman).Alice Boner, Sadāśiva Rath Śarmā and Bettina Bäumer (2000), Vāstusūtra Upaniṣad, Motilal Banarsidass, , pages 7–9, for context see 1–10 This text adds (abridged):
Some Hindu movements founded during the Colonial India, colonial era, such as the Arya Samaj and Satya Mahima Dharma reject idolatry.
Jainism
Devotional idolatry has been a prevalent ancient practice in various Jaina sects, wherein learned Tirthankara (''Jina'') and human ''gurus'' have been venerated with offerings, songs and Aarti, Āratī prayers.John Cort, Jains in the World : Religious Values and Ideology in India, Oxford University Press, ISBN, pages 64–68, 86–90, 100–112 Like other major Indian religions, Jainism has premised its spiritual practices on the belief that "all knowledge is inevitably mediated by images" and human beings discover, learn and know what is to be known through "names, images and representations". Thus, idolatry has been a part of the major sects of Jainism such as Digambara and Shvetambara. The earliest archaeological evidence of the idols and images in Jainism is from Mathura, and has been dated to be from the first half of the 1st millennium AD. The creation of idols, their consecration, the inclusion of Jaina layperson in idols and temples of Jainism by the Jaina monks has been a historic practice. However, during the iconoclastic era of Islamic rule, between the 15th and 17th century, a Lonka sect of Jainism emerged that continued pursuing their traditional spirituality but without the Jaina arts, images and idols.Sikhism
Sikhism is a monotheistic Indian religion, and Sikh temples are devoid of idols and icons for God. Yet, Sikhism strongly encourages devotion to God.S Deol (1998), Japji: The Path of Devotional Meditation, , page 11HS Singha (2009), The Encyclopedia of Sikhism, Hemkunt Press, , page 110 Some scholars call Sikhism a Bhakti movement, Bhakti sect of Indian traditions.David Lorenzen (1995), Bhakti Religion in North India: Community Identity and Political Action, State University of New York Press, , pages 1–3 In Sikhism, "Nirguni Bhakti" is emphasised – devotion to a divine without Gunas (qualities or form),Hardip Syan (2014), in The Oxford Handbook of Sikh Studies (Editors: Pashaura Singh, Louis E. Fenech), Oxford University Press, , page 178 but its scripture also accepts representations of God with formless (''nirguni'') and with form (''saguni''), as stated in Adi Granth 287. Sikhism condemns worshipping images or statues as if it were God, but have historically challenged the iconoclastic policies and Hindu temple destruction activities of Islamic rulers in India. Sikhs house their scripture and revere the Guru Granth Sahib as the final Sikh gurus, Guru of Sikhism. It is installed in Sikh ''Gurdwara'' (temple), many Sikhs bow or prostrate before it on entering the gurdwara. Guru Granth Sahib is ritually installed every morning, and put to bed at night in many ''Gurdwaras''. In the Dasam Granth, Dasam Bani, Guru Gobind Singh wrote "I am idol-breaker" on line 95 of his Zafarnama (letter), Zafarnamah.Chinese and Sinosphere Traditions
Japan
In Japan, there are images of some kami (i.e. deities) such as those of Fūjin and Raijin at the Buddhist temple Sanjūsangen-dō.North Korean Juche
Kim Il-Sung, Kim Il Sung instituted North Korean cult of personality, worship of himself amongst the citizens of North Korea, and this act is considered the only instance of a modern country deifying its ruler. As many citizens frequently bow before statues and portraits of him, scholars have considered the Juche state religion to be a form of idolatry.Traditional religions
Africa
Africa has numerous ethnic groups, and their diverse religious idea have been grouped as African Traditional Religions, sometimes abbreviated to ATR. These religions typically believe in a Supreme Being which goes by different regional names, as well as spirit world often linked to ancestors, and mystical magical powers through divination. Idols and their worship have been associated with all three components in the African Traditional Religions. According to J.O. Awolalu, proselytizing Christians and Muslims have mislabelled idol to mean false god, when in the reality of most traditions of Africa, the object may be a piece of wood or iron or stone, yet it is "symbolic, an emblem and implies the spiritual idea which is worshipped".J. O. Awolalu (1976), What is African Traditional Religion?, Studies in Comparative Religion, Vol. 10, No. 2, pages 8, 1–10 The material objects may decay or get destroyed, the emblem may crumble or substituted, but the spiritual idea that it represents to the heart and mind of an African traditionalist remains unchanged. Sylvester Johnson – a professor of African American and Religious Studies, concurs with Awolalu, and states that the colonial era missionaries who arrived in Africa, neither understood the regional languages nor the African theology, and interpreted the images and ritualism as "epitome of idolatry", projecting the iconoclastic controversies in Europe they grew up with, onto Africa. First with the arrival of Islam in Africa, then during the Christian colonial efforts, the religiously justified wars, the colonial portrayal of idolatry as proof of savagery, the destruction of idols and the seizure of idolaters as slaves marked a long period of religious intolerance, which supported religious violence and demeaning caricature of the African Traditional Religionists. The violence against idolaters and idolatry of Traditional Religion practicers of Africa started in the medieval era and continued into the modern era. The charge of idolatry by proselytizers, state Michael Wayne Cole and Rebecca Zorach, served to demonize and dehumanize local African populations, and justify their enslavement and abuse locally or far off plantations, settlements or for forced domestic labor., Quote: "By negating African religious practices, the pejorative characterizations of these works as objects of idolatry served in vital ways to both demonize and dehumanize local populations, thereby providing a moral buttress for European religious and human trade practices on the continent".Americas
 Statues, images and temples have been a part of the Traditional Religions of the indigenous people of the Americas. The Incan, Mayan and Aztec civilizations developed sophisticated religious practices that incorporated idols and religious arts. The Inca Empire, Inca culture, for example, has believed in ''Viracocha'' (also called ''Pachacutec'') as the
Statues, images and temples have been a part of the Traditional Religions of the indigenous people of the Americas. The Incan, Mayan and Aztec civilizations developed sophisticated religious practices that incorporated idols and religious arts. The Inca Empire, Inca culture, for example, has believed in ''Viracocha'' (also called ''Pachacutec'') as the creator deity
A creator deity or creator god is a deity responsible for the creation of the Earth, world, and universe in human religion and mythology. In monotheism, the single God is often also the creator. A number of monolatristic traditions separate a ...
and nature deities such as ''Inti'' (Solar deity, sun deity), and ''Mama Cocha'' the goddess of the sea, lakes, rivers and waters.
 In Maya civilization, Mayan culture, ''Kukulkan'' has been the supreme
In Maya civilization, Mayan culture, ''Kukulkan'' has been the supreme creator deity
A creator deity or creator god is a deity responsible for the creation of the Earth, world, and universe in human religion and mythology. In monotheism, the single God is often also the creator. A number of monolatristic traditions separate a ...
, also revered as the god of reincarnation, water, fertility and wind. The Mayan people built Mesoamerican pyramids, step pyramid temples to honor ''Kukulkan'', aligning them to the Sun's position on the spring equinox. Other deities found at Mayan archaeological sites include ''Chac-Xib-Chac, Xib Chac'' – the benevolent male rain deity, and ''Ixchel'' – the benevolent female earth, weaving and pregnancy goddess. A deity with aspects similar to ''Kulkulkan'' in the Aztec culture has been called ''Quetzalcoatl''.
Missionaries came to the Americas with the start of Spanish colonial era, and the Catholic Church did not tolerate any form of native idolatry, preferring that the icons and images of Jesus and Mary replace the native idols. Aztec, for example, had a written history which included those about their Traditional Religion, but the Spanish colonialists destroyed this written history in their zeal to end what they considered as idolatry, and to convert the Aztecs to Catholicism. The Aztec Indians, however, preserved their religion and religious practices by burying their idols under the crosses, and then continuing their idol worship rituals and practices, aided by the syncretic composite of atrial crosses and their idols as before.
During and after the imposition of Catholic Christianity during Spanish Empire, Spanish colonialism, the Incan people retained their original beliefs in deities through syncretism, where they overlay the Christian God and teachings over their original beliefs and practices. The male deity ''Inti'' became accepted as the Christian God, but the Andean rituals centered around idolatry of Incan deities have been retained and continued thereafter into the modern era by the Incan people.
Philippines
Anito in modern Filipino context can mean idolatry or an idol of heathen deity Anito and Diwata, Anito worship in ancient Philippines involves venerating carved images often made from wood that represent ancestral spirits and ancestral deities. These wooden figures, known as anito or sometimes bulul among certain groups like the Ifugao, were believed to embody the presence or power of the spirits they represent. Indigenous Filipinos offered prayers, food, and rituals to these images, treating them not merely as symbols but as actual vessels or manifestations of the supernatural. This act of directing devotion and reverence toward physical objects, as though the spirit resided within or could be influenced through them, classifies the practice as idolatry in many theological frameworks, particularly those that distinguish between worship of a supreme being and veneration of material representations.Polynesia
The Polynesians, Polynesian people have had a range of polytheistic theologies found across the Pacific Ocean. The Polynesian people produced idols from wood, and congregated around these idols for worship. The Christian missionaries, particularly from the London Missionary Society such as John Williams, and others such as the Methodist Missionary Society, characterized these as idolatry, in the sense of islanders worshipping false gods. They sent back reports which primarily focussed on "overthrow of pagan idolatry" as evidence of their Christian sects triumph, with fewer mentions of actual converts and baptism.Religious tolerance and intolerance
The term ''false god'' is often used throughout the Abrahamic scriptures (Torah, Tanakh, Bible, and Quran) to single out Yahweh (interpreted by Jews, Samaritans, and Christians) or Elohim/Allah
Allah ( ; , ) is an Arabic term for God, specifically the God in Abrahamic religions, God of Abraham. Outside of the Middle East, it is principally associated with God in Islam, Islam (in which it is also considered the proper name), althoug ...
(interpreted by Muslims) as the only true God. Nevertheless, the Hebrew Bible/Old Testament itself recognizes and reports that originally the Israelites were not monotheists but actively engaged in idolatry and worshipped many foreign, non-Jewish Gods besides Yahweh and/or instead of him, such as Baal, Astarte, Asherah, Chemosh, Dagon, Moloch, Tammuz (mythology), Tammuz, and more, and continued to do so until their return from the Babylonian exile (see Ancient Hebrew religion). Judaism, the oldest Abrahamic religion, eventually shifted into a strict, exclusive monotheism, based on the Yahwism, sole veneration of Yahweh, the predecessor to the Abrahamic conception of God.
The History of religion, vast majority of religions in history have been and/or are still polytheistic, worshipping many diverse deities. Moreover, the material depiction of a deity or more deities has always played an eminent role in all culture
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
s of the world. The claim to worship the "one and only true God" came to most of the world with the arrival of Abrahamic religions and is the distinguishing characteristic of their monotheistic worldview, whereas virtually all the other religions in the world have been and/or are still animistic
Animism (from meaning 'breath, Soul, spirit, life') is the belief that objects, places, and creatures all possess a distinct Spirituality, spiritual essence. Animism perceives all things—animals, plants, Rock (geology), rocks, rivers, Weather, ...
and Polytheism, polytheistic. Some Neopagan religions such as Wicca utilize statues of deities within their worship experience.
The accusations and presumption that all idols and images are devoid of symbolism, or that icons of one's own religion are "true, healthy, uplifting, beautiful symbolism, mark of devotion, divine", while of other person's religion are "false, an illness, superstitious, grotesque madness, evil addiction, satanic, and cause of all incivility" is more a matter of subjective personal interpretation, rather than objective impersonal truth. Regina Schwartz and some other contemporary scholars state allegations that idols only represent false gods, followed by iconoclastic destruction is only little more than religious intolerance. The Scottish Enlightenment philosopher David Hume wrote in his essay ''Dialogues Concerning Natural Religion'' (1779) that the worship of different gods and idols in Pagan religions is premised on religious pluralism, tolerance, and acceptance of diverse representations of the divine. In contrast, Abrahamic monotheistic religions are intolerant, have attempted to destroy freedom of expression and have Forced conversion, violently forced others to accept and worship their conception of God.
Gallery
See also
* Buddhist devotion – prayer ritual in Buddhism * Dambana * Kemetism * Deity * El Tío * Fetishism * Jezebel * Perceptions of religious imagery in natural phenomena * Puja (Hinduism) – prayer ritual in HinduismNotes
References
Further reading
*Juan Sebastián Hernández Valencia (2023)''Hombres ciegos, ídolos huecos: fetichismo y alteridad en la crítica de la idolatría del Apocalipsis de Abrahán''
(Medellín: Fondo Editorial Universidad Católica Luis Amigó) * Swagato Ganguly (2017).
Idolatry and The Colonial Idea of India: Visions of Horror, Allegories of Enlightenment
'. Routledge. * Reuven Chaim Klein (2018).
God versus Gods: Judaism in the Age of Idolatry
'. Mosaica Press. . * Yechezkel Kaufmann (1960)
''The Religion of Israel: From its Beginnings to the Babylonin Exile''
Univ. of Chicago Press. . * * * * * *
External links
, Tufts University
Iconoclasm and idolatry
Columbia University {{Authority control Idolatry, Judeo-Christian topics Articles containing video clips