Ice Skater on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ice skating is the
 Research suggests that the earliest ice skating happened in southern
Research suggests that the earliest ice skating happened in southern
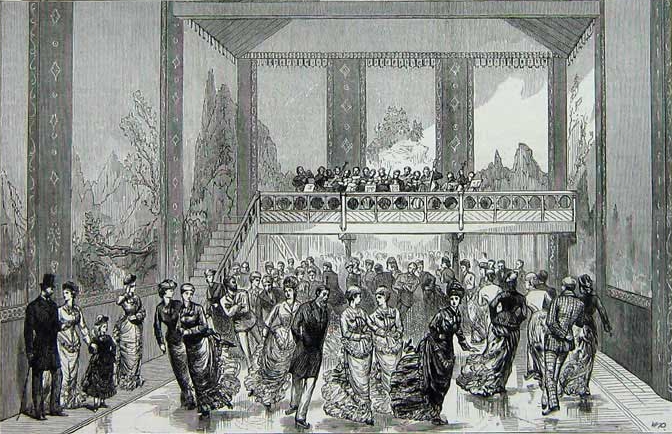 Early attempts at the construction of artificial ice rinks were made during the "rink mania" of 1841–44. As the technology for the maintenance of natural ice did not exist, these early rinks used a substitute consisting of a mixture of hog's
Early attempts at the construction of artificial ice rinks were made during the "rink mania" of 1841–44. As the technology for the maintenance of natural ice did not exist, these early rinks used a substitute consisting of a mixture of hog's
 Skating became popular as a recreation, a means of transport and spectator sport in
Skating became popular as a recreation, a means of transport and spectator sport in  In the Fens, skates were called
In the Fens, skates were called

 The first instructional book concerning ice skating was published in London in 1772. The book titled ''The Art of Figure Skating'', written by a British artillery lieutenant, Robert Jones, describes basic
The first instructional book concerning ice skating was published in London in 1772. The book titled ''The Art of Figure Skating'', written by a British artillery lieutenant, Robert Jones, describes basic
Team L.T.D. Cruising to Victory (16227312684).jpg,
(Individual) File:Kim 2010 Olympic FS.jpg,
(Individual, Pairs) File:Team amber WSSC.jpg,
(Team) File:Bandy game 1.jpg,
(Team) File:УФХМР 2013.jpg,
(Team) File:Stephen Weiss.jpg,
(Team) File:Atlantic Attack Ringette Team.jpg,
(Team) File:Langfardsskridskoakning.jpg,
(Individual) File:Fenskaters ronden ton.jpg, Fen skating
(Individual) Paulien van Deutekom (08-12-2007).jpg,
(Individual) File:Saguenay 500m.jpg,
(Individual, Team Relay) File:Black Forest Village (NBY 417446).jpg,
(Individual)
File:Eislaufen 01.ogg, Ice skater on
Skating and Science
(a bibliography) * {{Authority control Skating Winter Olympic sports Articles containing video clips
self-propulsion
Self-propulsion is the autonomous displacement of nano-, micro- and macroscopic natural and artificial objects, containing their own means of motion. Self-propulsion is driven mainly by interfacial phenomena. Various mechanisms of self-propelling ...
and gliding of a person across an ice
Ice is water that is frozen into a solid state, typically forming at or below temperatures of 0 ° C, 32 ° F, or 273.15 K. It occurs naturally on Earth, on other planets, in Oort cloud objects, and as interstellar ice. As a naturally oc ...
surface, using metal-bladed ice skate
Ice skates are metal blades attached underfoot and used to propel the bearer across a sheet of ice while ice skating.
The first ice skates were made from leg bones of horse, ox or deer, and were attached to feet with leather straps. These skates ...
s. People skate for various reasons, including recreation (fun), exercise, competitive sports, and commuting
Commuting is periodically recurring travel between a place of residence and place of work or study, where the traveler, referred to as a commuter, leaves the boundary of their home community. By extension, it can sometimes be any regular o ...
. Ice skating may be performed on naturally frozen bodies of water, such as ponds, lakes, canals, and rivers, and on human-made ice surfaces both indoors and outdoors.
Natural ice surfaces used by skaters can accommodate a variety of winter sports which generally require an enclosed area, but are also used by skaters who need ice tracks and trails for distance skating and speed skating
Speed skating is a competitive form of ice skating in which the competitors race each other in travelling a certain distance on skates. Types of speed skating are long-track speed skating, short-track speed skating, and marathon speed skat ...
. Man-made ice surfaces include ice rink
An ice rink (or ice skating rink) is a frozen body of water or an artificial sheet of ice where people can ice skate or play winter sports. Ice rinks are also used for exhibitions, contests and ice shows. The growth and increasing popularity of ...
s, ice hockey rink
An ice hockey rink is an ice rink that is specifically designed for ice hockey, a competitive team sport. Alternatively it is used for other sports such as broomball, ringette, rinkball, and rink bandy. It is a rectangle with rounded corners and ...
s, bandy field
A bandy field or bandy rink is a large ice rink used for playing the team winter sport of bandy. Being about the size of a football pitch, it is substantially larger than an ice hockey rink.
History
Originally, bandy was played on naturally froz ...
s, ice tracks required for the sport of ice cross downhill
Ice cross downhill is a winter extreme sporting event which involves direct competitive downhill skating on a walled track featuring sharp turns and high vertical drops. Ice cross downhill is similar to ski cross and boardercross, except with ...
, and arena
An arena is a large enclosed venue, often circular or oval-shaped, designed to showcase theatre, Music, musical performances or Sport, sporting events. It comprises a large open space surrounded on most or all sides by tiered seating for specta ...
s.
Various formal sports involving ice skating have emerged since the 19th century. Ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey in North America) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an Ice rink, ice skating rink with Ice hockey rink, lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. Tw ...
, bandy
Bandy is a winter sport and ball sport played by two team sport, teams wearing Ice skates#Bandy skates, ice skates on a large ice surface (either indoors or outdoors) while using sticks to direct a ball into the opposing team's goal.
The playin ...
, rinkball
Rinkball is a winter team sport played on ice with ice skates and is most popular in Finland, where it is known as ''kaukalopallo''. This ball sport originated in Sweden in the 1960s and from there landed in Finland in the 1970s.
The objective ...
, and ringette
Ringette is a winter team sport played on an ice rink using ice hockey skates, straight sticks with drag-tips, and a blue, rubber, pneumatic ring designed for use on ice surfaces. While the sport was originally created exclusively for female c ...
are team sports played with, respectively, a flat sliding puck, a ball, and a rubber ring. Synchronized skating
Synchronized skating, often called synchro, is an ice skating sport where between 8 and 20 skaters perform together as a team. They move as a flowing unit at high speed over the ice, while performing elements and footwork.
This complex sport orig ...
is a unique artistic team sport derived from figure skating
Figure skating is a sport in which individuals, pairs, or groups perform on figure skates on ice. It was the first winter sport to be included in the Olympic Games, with its introduction occurring at the Figure skating at the 1908 Summer Olympi ...
. Figure skating, ice cross downhill
Ice cross downhill is a winter extreme sporting event which involves direct competitive downhill skating on a walled track featuring sharp turns and high vertical drops. Ice cross downhill is similar to ski cross and boardercross, except with ...
, speed skating
Speed skating is a competitive form of ice skating in which the competitors race each other in travelling a certain distance on skates. Types of speed skating are long-track speed skating, short-track speed skating, and marathon speed skat ...
, and barrel jumping (a discipline of speed skating) are among the sporting disciplines for individuals.
History
Early history of ice skating
 Research suggests that the earliest ice skating happened in southern
Research suggests that the earliest ice skating happened in southern Finland
Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland to the south, ...
more than 4,000 years ago. This was done to save energy during winter journeys. True skating emerged when a steel blade with sharpened edges was used. Skates now cut into the ice instead of gliding on top of it. The Dutch
Dutch or Nederlands commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
** Dutch people as an ethnic group ()
** Dutch nationality law, history and regulations of Dutch citizenship ()
** Dutch language ()
* In specific terms, i ...
added edges to ice skate
Ice skates are metal blades attached underfoot and used to propel the bearer across a sheet of ice while ice skating.
The first ice skates were made from leg bones of horse, ox or deer, and were attached to feet with leather straps. These skates ...
s in the 13th or 14th century. These ice skates were made of steel, with sharpened edges on the bottom to aid movement.
The fundamental construction of modern ice skates has stayed largely the same since then, although differing greatly in the details, particularly in the method of binding and the shape and construction of the steel blades. In the Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
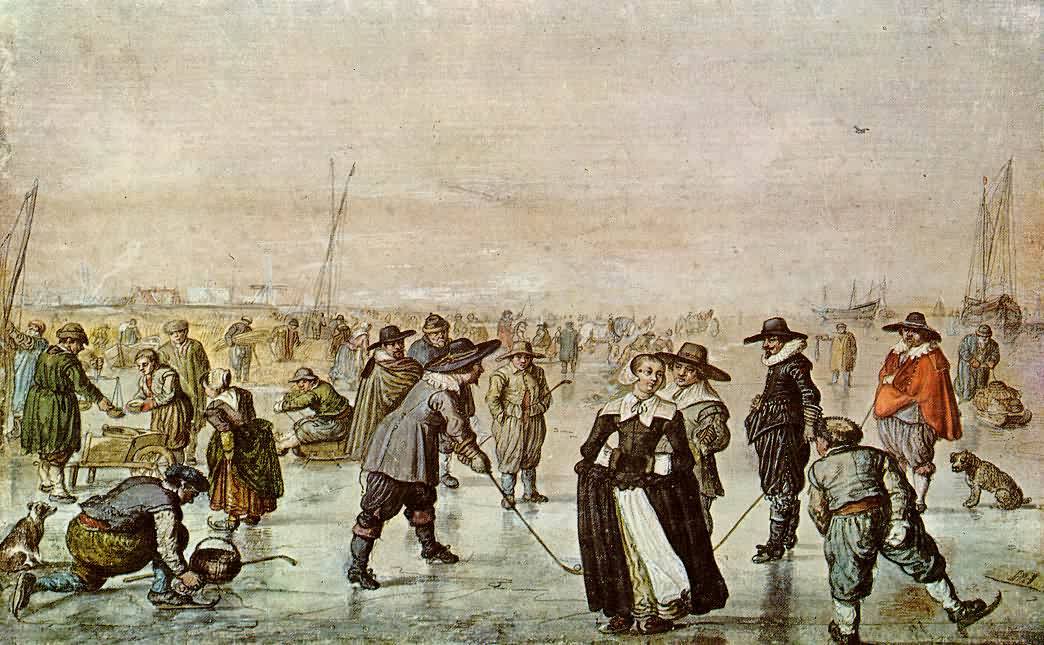
, ice skating was considered proper for all classes of people, as shown in many pictures from Dutch Golden Age painter
Dutch Golden Age painting is the painting of the Dutch Golden Age, a period in Dutch history roughly spanning the 17th century, during and after the later part of the Eighty Years' War (1568–1648) for Dutch independence.
The new Dutch Republi ...
s.
Ice skating was also practiced in China during the Song dynasty
The Song dynasty ( ) was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 960 to 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song, who usurped the throne of the Later Zhou dynasty and went on to conquer the rest of the Fiv ...
, and became popular among the ruling family of the Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the ...
. Ancient ice skates, made of animal bones, were found at the bronze age Gaotai Ruins in north west China
Northwestern China () is a region in the People's Republic of China. It consists of five provincial administrative regions, namely Shaanxi, Gansu, Qinghai, Ningxia, and Xinjiang.
The region is characterized by a (semi-)arid continental climate. ...
, and are estimated to be likely 3,500 years old. Archeologists say these ancient skates are "clear evidence for communication between China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
and Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
" in the Bronze Age era, as they are very similar to bone skates unearthed in Europe.
Rising popularity and first clubs
In England "the London boys" had improvised butcher's bones as skates since the 12th century. Skating on metal skates seems to have arrived in England at the same time as the garden canal, with theEnglish Restoration
The Stuart Restoration was the reinstatement in May 1660 of the Stuart monarchy in Kingdom of England, England, Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland, and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland. It replaced the Commonwealth of England, established in January 164 ...
in 1660, after the king and court returned from an exile largely spent in the Netherlands. In London the ornamental "canal" in St James's Park
St James's Park is a urban park in the City of Westminster, central London. A Royal Park, it is at the southernmost end of the St James's area, which was named after a once isolated medieval hospital dedicated to St James the Less, now the ...
was the main centre until the 19th century. Both Samuel Pepys
Samuel Pepys ( ; 23 February 1633 – 26 May 1703) was an English writer and Tories (British political party), Tory politician. He served as an official in the Navy Board and Member of Parliament (England), Member of Parliament, but is most r ...
and John Evelyn
John Evelyn (31 October 162027 February 1706) was an English writer, landowner, gardener, courtier and minor government official, who is now best known as a diary, diarist. He was a founding Fellow of the Royal Society.
John Evelyn's Diary, ...
, the two leading diarists of the day, saw it on the "new canal" there on 1 December 1662, the first time Pepys had ever seen it ("a very pretty art"). Then it was "performed before their Majesties and others, by diverse gentlemen and others, with scheets after the manner of the Hollanders". Two weeks later, on 15 December 1662, Pepys accompanied the Duke of York, later King James II, on a skating outing: "To the Duke, and followed him in the Park, when, though the ice was broken, he would go slide upon his skates, which I did not like; but he slides very well." In 1711 Jonathan Swift
Jonathan Swift (30 November 1667 – 19 October 1745) was an Anglo-Irish writer, essayist, satirist, and Anglican cleric. In 1713, he became the Dean (Christianity), dean of St Patrick's Cathedral, Dublin, and was given the sobriquet "Dean Swi ...
still thinks the sport might be unfamiliar to his "Stella", writing to her: "Delicate walking weather; and the Canal and Rosamund's Pond full of the rabble and with skates, ''if you know what that is''."
The first organised skating club was the Edinburgh Skating Club, formed in the 1740s; some claim the club was established as early as 1642."In The Beginning...", ''Skating'' magazine, Jun 1970An early contemporary reference to the club appeared in the second edition (1783) of the Encyclopædia Britannica
The is a general knowledge, general-knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It has been published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. since 1768, although the company has changed ownership seven times. The 2010 version of the 15th edition, ...
:
From this description and others, it is apparent that the form of skating practiced by club members was indeed an early form of figure skating
Figure skating is a sport in which individuals, pairs, or groups perform on figure skates on ice. It was the first winter sport to be included in the Olympic Games, with its introduction occurring at the Figure skating at the 1908 Summer Olympi ...
rather than speed skating
Speed skating is a competitive form of ice skating in which the competitors race each other in travelling a certain distance on skates. Types of speed skating are long-track speed skating, short-track speed skating, and marathon speed skat ...
. For admission to the club, candidates had to pass a skating test where they performed a complete circle on either foot (e.g., a figure eight), and then jumped over first one hat, then two and three, placed over each other on the ice.
On the Continent
A continent is any of several large geographical regions. Continents are generally identified by convention (norm), convention rather than any strict criteria. A continent could be a single large landmass, a part of a very large landmass, as ...
, participation in ice skating was limited to members of the upper classes. Emperor Rudolf II
Rudolf II (18 July 1552 – 20 January 1612) was Holy Roman Emperor (1576–1612), King of Hungary and Croatia (as Rudolf I, 1572–1608), King of Bohemia (1575–1608/1611) and Archduke of Austria (1576–1608). He was a member of the H ...
of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
enjoyed ice skating so much, he had a large ice carnival constructed in his court in order to popularise the sport. King Louis XVI
Louis XVI (Louis-Auguste; ; 23 August 1754 – 21 January 1793) was the last king of France before the fall of the monarchy during the French Revolution. The son of Louis, Dauphin of France (1729–1765), Louis, Dauphin of France (son and heir- ...
of France brought ice skating to Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
during his reign. Madame de Pompadour
Jeanne Antoinette Poisson, Marquise de Pompadour (, ; 29 December 1721 – 15 April 1764), commonly known as Madame de Pompadour, was a member of the French court. She was the official chief mistress of King Louis XV from 1745 to 1751, and rema ...
, Napoleon I
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career ...
, Napoleon III
Napoleon III (Charles-Louis Napoléon Bonaparte; 20 April 18089 January 1873) was President of France from 1848 to 1852 and then Emperor of the French from 1852 until his deposition in 1870. He was the first president, second emperor, and last ...
, and the House of Stuart
The House of Stuart, originally spelled Stewart, also known as the Stuart dynasty, was a dynasty, royal house of Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland, Kingdom of England, England, Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland and later Kingdom of Great Britain, Great ...
were, among others, royal and upper-class fans of ice skating.
The next skating club to be established was in London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
and was not founded until 1830. Members wore a silver skate hanging from their buttonhole and met on The Serpentine, Hyde Park on 27 December 1830.
By the mid-19th century, ice skating was a popular pastime among the British upper and middle classes. Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in January 1901. Her reign of 63 year ...
became acquainted with her future husband, Prince Albert
Prince Albert most commonly refers to:
*Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha (1819–1861), consort of Queen Victoria
*Albert II, Prince of Monaco (born 1958), present head of state of Monaco
Prince Albert may also refer to:
Royalty
* Alb ...
, through a series of ice skating trips. Albert continued to skate after their marriage and on falling through the ice was once rescued by Victoria and a lady in waiting from a stretch of water in the grounds of Buckingham Palace
Buckingham Palace () is a royal official residence, residence in London, and the administrative headquarters of the monarch of the United Kingdom. Located in the City of Westminster, the palace is often at the centre of state occasions and r ...
.
 Early attempts at the construction of artificial ice rinks were made during the "rink mania" of 1841–44. As the technology for the maintenance of natural ice did not exist, these early rinks used a substitute consisting of a mixture of hog's
Early attempts at the construction of artificial ice rinks were made during the "rink mania" of 1841–44. As the technology for the maintenance of natural ice did not exist, these early rinks used a substitute consisting of a mixture of hog's lard
Lard is a Quasi-solid, semi-solid white fat product obtained by rendering (animal products), rendering the adipose tissue, fatty tissue of a domestic pig, pig.
and various salts. An item in the 8 May 1844 issue of Littell's 'Living Age' headed the ' Glaciarium' reported that "This establishment, which has been removed to Grafton Street East' Tottenham Court Road
Tottenham Court Road (occasionally abbreviated as TCR) is a major road in Central London, almost entirely within the London Borough of Camden.
The road runs from Euston Road in the north to St Giles Circus in the south; Tottenham Court Road tu ...
, was opened on Monday afternoon. The area of artificial ice is extremely convenient for such as may be desirous of engaging in the graceful and manly pastime of skating."
Emergence as a sport
 Skating became popular as a recreation, a means of transport and spectator sport in
Skating became popular as a recreation, a means of transport and spectator sport in The Fens
The Fens or Fenlands in eastern England are a naturally marshy region supporting a rich ecology and numerous species. Most of the fens were drained centuries ago, resulting in a flat, dry, low-lying agricultural region supported by a system o ...
in England for people from all walks of life. Racing was the preserve of workers, most of them agricultural labourers. It is not known when the first skating matches were held, but by the early nineteenth century racing was well established and the results of matches were reported in the press. Skating as a sport developed on the lakes of Scotland and the canals of the Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
. In the 13th and 14th centuries wood was substituted for bone in skate blades, and in 1572 the first iron skates were manufactured. When the waters froze, skating matches were held in towns and villages all over the Fens. In these local matches men (or sometimes women or children) would compete for prizes of money, clothing, or food.''Cycling'', 19 January 1895, p 19.
The winners of local matches were invited to take part in the grand or championship matches, in which skaters from across the Fens would compete for cash prizes in front of crowds of thousands. The championship matches took the form of a Welsh main or "last man standing" contest (single-elimination tournament
A single-elimination knockout, or sudden-death tournament is a type of elimination tournament where the loser of a match-up is immediately eliminated from the tournament. Each winner will play another in the next round, until the final match-up, ...
). The competitors, 16 or sometimes 32, were paired off in heats and the winner of each heat went through to the next round. A course of 660 yards was measured out on the ice, and a barrel with a flag on it placed at either end. For a one-and-a-half-mile race the skaters completed two rounds of the course, with three barrel turns.
 In the Fens, skates were called
In the Fens, skates were called pattens
Pattens, also known by other names, are protective overshoes that were worn in Europe from the Middle Ages until the early 20th century. In appearance, they sometimes resembled contemporary clogs or sandals. Pattens were worn outdoors over a no ...
, fen runners, or Whittlesey
Whittlesey (also Whittlesea) is a market town and civil parish in the Fenland District, Fenland district of Cambridgeshire, England. Whittlesey is east of Peterborough. The population of the parish was 17,667 at the 2021 Census.
Toponymy
W ...
runners. The footstock was made of beechwood
Beechwood may refer to:
Plants
* Beech wood, the wood from any of ten species of beech trees
* Malay beechwood, tree ''Gmelina arborea'', and its wood
* Willow beechwood '' Faurea saligna'', and its wood
Places Canada
* Beechwood, Ontario ...
. A screw at the back was screwed into the heel of the boot, and three small spikes at the front kept the skate steady. There were holes in the footstock for leather straps to fasten it to the foot. The metal blades were slightly higher at the back than the front. In the 1890s, fen skaters started to race in Norwegian style skates.
On Saturday 1 February 1879, a number of professional ice skaters from Cambridgeshire
Cambridgeshire (abbreviated Cambs.) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in the East of England and East Anglia. It is bordered by Lincolnshire to the north, Norfolk to the north-east, Suffolk to the east, Essex and Hertfor ...
and Huntingdonshire
Huntingdonshire (; abbreviated Hunts) is a local government district in Cambridgeshire, England, which was historically a county in its own right. It borders Peterborough to the north, Fenland to the north-east, East Cambridgeshire to the e ...
met in the Guildhall, Cambridge, to set up the National Skating Association, the first national ice skating body in the world. The founding committee consisted of several landowners, a vicar, a fellow of Trinity College Trinity College may refer to:
Australia
* Trinity Anglican College, an Anglican coeducational primary and secondary school in , New South Wales
* Trinity Catholic College, Auburn, a coeducational school in the inner-western suburbs of Sydney, New ...
, a magistrate, two members of parliament, the mayor of Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a List of cities in the United Kingdom, city and non-metropolitan district in the county of Cambridgeshire, England. It is the county town of Cambridgeshire and is located on the River Cam, north of London. As of the 2021 Unit ...
, the Lord Lieutenant of Cambridge, journalist James Drake Digby, the president of Cambridge University
The University of Cambridge is a Public university, public collegiate university, collegiate research university in Cambridge, England. Founded in 1209, the University of Cambridge is the List of oldest universities in continuous operation, wo ...
Skating Club, and Neville Goodman, a graduate of Peterhouse, Cambridge
Peterhouse is the oldest Colleges of the University of Cambridge, constituent college of the University of Cambridge in England, founded in 1284 by Hugh de Balsham, Bishop of Ely. Peterhouse has around 300 undergraduate and 175 graduate stud ...
(and son of Potto Brown
Potto Brown (1797–1871) was a miller and nonconformist philanthropist in Huntingdonshire, England. He is commemorated by a statue in the village of Houghton where he was born, lived and died. Local schools and churches are a monument to his p ...
's milling partner, Joseph Goodman).DL Bird 1979 ''Our Skating Heritage''. London. The newly formed Association held their first one-and-a-half-mile British professional championship at Thorney in December 1879.
Figure skating

 The first instructional book concerning ice skating was published in London in 1772. The book titled ''The Art of Figure Skating'', written by a British artillery lieutenant, Robert Jones, describes basic
The first instructional book concerning ice skating was published in London in 1772. The book titled ''The Art of Figure Skating'', written by a British artillery lieutenant, Robert Jones, describes basic figure skating
Figure skating is a sport in which individuals, pairs, or groups perform on figure skates on ice. It was the first winter sport to be included in the Olympic Games, with its introduction occurring at the Figure skating at the 1908 Summer Olympi ...
forms such as circles and figure eights. The book was written solely for men, as women did not normally ice skate in the late 18th century. It was with the publication of this manual that ice skating split into its two main disciplines, speed skating and figure skating.
The founder of modern figure skating as it is known today was Jackson Haines, an American. He was the first skater to incorporate ballet and dance movements into his skating, as opposed to focusing on tracing patterns on the ice. Haines also invented the sit spin
The sit spin (also known as the Jackson Haines spin) is one of the oldest elements in figure skating
Figure skating is a sport in which individuals, pairs, or groups perform on figure skates on ice. It was the first winter sport to be included ...
and developed a shorter, curved blade for figure skating that allowed for easier turns. He was also the first to wear blades that were permanently attached to the boot.
The International Skating Union
The International Skating Union (ISU) is the international sport governing body, governing body for competitive ice skating disciplines, including figure skating, synchronized skating, speed skating, and short track speed skating. It was founded ...
was founded in 1892 as the first international ice skating organisation in Scheveningen
Scheveningen () is one of the eight districts of The Hague, Netherlands, as well as a subdistrict () of that city. Scheveningen is a modern seaside resort with a long, sandy beach, an esplanade, a pier, and a lighthouse. The beach is popular ...
, in the Netherlands. The Union created the first codified set of figure skating rules and governed international competition in speed and figure skating. The first Championship, known as the Championship of the Internationale Eislauf-Vereinigung, was held in Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg, formerly known as Petrograd and later Leningrad, is the List of cities and towns in Russia by population, second-largest city in Russia after Moscow. It is situated on the Neva, River Neva, at the head of the Gulf of Finland ...
in 1896. The event had four competitors and was won by Gilbert Fuchs
Gilbert Fuchs (1871–1952) was a German figure skater who won the first World Figure Skating Championships, held in St. Petersburg, Russia, in 1896. He recaptured the world title ten years later in Munich.
Relations with his constant rival ...
.
Physical mechanics of skating
A skate can glide over ice because there is a layer of ice molecules on the surface that are not as tightly bound as the molecules of the mass of ice beneath. These molecules are in a semiliquid state, providing lubrication. The molecules in this "quasi-fluid" or "water-like" layer are less mobile than liquid water, but are much more mobile than the molecules deeper in the ice. At about the slippery layer is one molecule thick; as the temperature increases the slippery layer becomes thicker. It had long been believed that ice is slippery because the pressure of an object in contact with it causes a thin layer to melt. The hypothesis was that the blade of an ice skate, exerting pressure on the ice, melts a thin layer, providing lubrication between the ice and the blade. This explanation, called " pressure melting", originated in the 19th century. (SeeRegelation
Regelation is the phenomenon of ice melting under pressure and refreezing when the pressure is reduced. This can be demonstrated by looping a fine wire around a block of ice, with a heavy weight attached to it. The pressure exerted on the ice s ...
.) Pressure melting could not account for skating on ice temperatures lower than −3.5 °C, whereas skaters often skate on lower-temperature ice.
In the 20th century, an alternative explanation, called "friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. Types of friction include dry, fluid, lubricated, skin, and internal -- an incomplete list. The study of t ...
melting", proposed by Lozowski, Szilder, Le Berre, Pomeau, and others showed that because of the viscous
Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's rate-dependent resistance to a change in shape or to movement of its neighboring portions relative to one another. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of ''thickness''; for example, syrup h ...
frictional heating, a macroscopic layer of melt ice is in-between the ice and the skate. With this they fully explained the low friction with nothing else but macroscopic physics, whereby the frictional heat generated between skate and ice melts a layer of ice. This is a self-stabilizing mechanism of skating. If by fluctuation the friction gets high, the layer grows in thickness and lowers the friction, and if it gets low, the layer decreases in thickness and increases the friction. The friction generated in the sheared layer of water between skate and ice grows as ''√V'' with ''V'' the velocity of the skater, such that for low velocities the friction is also low.
Whatever the origin of the water layer, skating is more destructive than simply gliding. A skater leaves a visible trail behind on virgin ice and skating rinks have to be regularly resurfaced to improve the skating conditions. It means that the deformation caused by the skate is plastic rather than elastic. The skate ploughs through the ice in particular due to the sharp edges. Van Leeuwen proposed that another component has to be added to the friction: the "ploughing friction". The calculated frictions are of the same order as the measured frictions in real skating in a rink. The ploughing friction decreases with the velocity ''V'', since the pressure in the water layer increases with V and lifts the skate (aquaplaning
Aquaplaning or hydroplaning by the tires of a road vehicle, aircraft or other wheeled vehicle occurs when a layer of water builds between the wheels of the vehicle and the road surface, leading to a loss of traction that prevents the vehicle ...
). As a result the sum of the water-layer friction and the ploughing friction only increases slightly with ''V'', making skating at high speeds (>90 km/h) possible.
Inherent safety risks
A person's ability to ice skate depends on the roughness of the ice, the design of the ice skate, and the skill and experience of the skater. While serious injury is rare, a number of short track speed skaters have beenparalysed
Paralysis (: paralyses; also known as plegia) is a loss of motor function in one or more muscles. Paralysis can also be accompanied by a loss of feeling (sensory loss) in the affected area if there is sensory damage. In the United States, r ...
after a heavy fall when they collided with the boarding. A fall can be fatal if a helmet
A helmet is a form of protective gear worn to protect the head. More specifically, a helmet complements the skull in protecting the human brain. Ceremonial or symbolic helmets (e.g., a policeman's helmet in the United Kingdom) without protecti ...
is not worn to protect against severe head injury
A head injury is any injury that results in trauma to the skull or brain. The terms ''traumatic brain injury'' and ''head injury'' are often used interchangeably in the medical literature. Because head injuries cover such a broad scope of inju ...
. Accidents are rare but there is a risk of injury from collisions, particularly during hockey games or in pair skating
Pair skating is a figure skating discipline defined by the International Skating Union (ISU) as "the skating of two persons in unison who perform their movements in such harmony with each other as to give the impression of genuine Pair Skating ...
.
A significant danger when skating outdoors on a frozen body of water is falling through the ice into the freezing water underneath. Death can result from shock
Shock may refer to:
Common uses
Healthcare
* Acute stress reaction, also known as psychological or mental shock
** Shell shock, soldiers' reaction to battle trauma
* Circulatory shock, a medical emergency
** Cardiogenic shock, resulting from ...
, hypothermia
Hypothermia is defined as a body core temperature below in humans. Symptoms depend on the temperature. In mild hypothermia, there is shivering and mental confusion. In moderate hypothermia, shivering stops and confusion increases. In severe ...
, or drowning
Drowning is a type of Asphyxia, suffocation induced by the submersion of the mouth and nose in a liquid. Submersion injury refers to both drowning and near-miss incidents. Most instances of fatal drowning occur alone or in situations where othe ...
. It is often difficult or impossible for the skater to climb out of the water, due to the weight of their ice skates and thick winter clothing, and the ice repeatedly breaking as they struggle to get back onto the surface. Also, if the skater becomes disoriented under the water, they might not be able to find the hole in the ice through which they have fallen. Although this can prove fatal, it is also possible for the rapid cooling to produce a condition in which a person can be revived up to hours after falling into the water. Experts have warned not to ice skate alone, and also warned parents not to leave children unattended on a frozen body of water.
Communal activities on ice
A number of recreational and sporting activities take place on ice:Ice skating
* Fen skating – a traditional form of ice skating in the Fenland of England which involved skating races and matches held in towns and villages all over the Fens *Tour skating
Tour skating is recreational long distance ice skating on natural ice. It is particularly popular in the Netherlands and the Nordic countries. It is becoming more popular in areas of North America such as New England, Southcentral Alaska, and Nov ...
– recreational and competitive long-distance skating outdoors on open areas of natural ice
* Speed skating
Speed skating is a competitive form of ice skating in which the competitors race each other in travelling a certain distance on skates. Types of speed skating are long-track speed skating, short-track speed skating, and marathon speed skat ...
– competitive form of ice skating in which contenders race over fixed distances, short track and long track versions
* Barrel jumping
Barrel jumping is a discipline of speed skating, where ice skaters build up speed to jump over a length of multiple barrels lined up, usually side by side like rollers. Occasionally barrels would also be stacked pyramid-style for height. The obj ...
– a speed skating discipline in which skaters jump over a length of multiple barrels
* Figure skating
Figure skating is a sport in which individuals, pairs, or groups perform on figure skates on ice. It was the first winter sport to be included in the Olympic Games, with its introduction occurring at the Figure skating at the 1908 Summer Olympi ...
– winter sport with multiple disciplines: men's singles, ladies' singles, pair skating, ice dance, and synchronized skating
Synchronized skating, often called synchro, is an ice skating sport where between 8 and 20 skaters perform together as a team. They move as a flowing unit at high speed over the ice, while performing elements and footwork.
This complex sport orig ...
* Bandy
Bandy is a winter sport and ball sport played by two team sport, teams wearing Ice skates#Bandy skates, ice skates on a large ice surface (either indoors or outdoors) while using sticks to direct a ball into the opposing team's goal.
The playin ...
– non-contact team sport similar to ice hockey, but using a bandy ball and played on a large ice field
* Ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey in North America) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an Ice rink, ice skating rink with Ice hockey rink, lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. Tw ...
– fast-paced contact team sport, using a vulcanized rubber puck, usually played on a special ice hockey rink
* Rink bandy
Rink bandy is a variant of the larger sport of bandy. Unlike bandy which is played on a large bandy field, rink bandy is played on significantly smaller ice hockey-sized ice rinks.
While a bandy field is about the same size as a football pi ...
– a form of bandy that can be played on a standard ice hockey rink
* Rinkball
Rinkball is a winter team sport played on ice with ice skates and is most popular in Finland, where it is known as ''kaukalopallo''. This ball sport originated in Sweden in the 1960s and from there landed in Finland in the 1970s.
The objective ...
– non-contact team sport using a bandy ball with combined elements from bandy and ice hockey
* Ringette
Ringette is a winter team sport played on an ice rink using ice hockey skates, straight sticks with drag-tips, and a blue, rubber, pneumatic ring designed for use on ice surfaces. While the sport was originally created exclusively for female c ...
– non-contact team sport using a rubber pneumatic ring instead of a ball or puck
* Ice cross downhill
Ice cross downhill is a winter extreme sporting event which involves direct competitive downhill skating on a walled track featuring sharp turns and high vertical drops. Ice cross downhill is similar to ski cross and boardercross, except with ...
– competitive extreme sport featuring downhill skating on a walled track
No skating
The following sports and games are also played on ice, but players are not required to wear ice skates. * Ice cricket - a variant of the English game of cricket played in harsh wintry conditions *Spongee
Spongee or sponge hockey is a winter sport and a variant of ice hockey that is played on outdoor ice rinks without ice hockey skates. It is played almost exclusively in Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada, and has been played by thousands of players in ...
– an outdoor team sport which is a non-contact variant of ice hockey played on outdoor ice hockey rinks
* Broomball
Broomball is a both a recreational and organized competitive winter sport, winter and ball sport played on ice or snow. It is played either indoors or outdoors, depending on the climate and location. It is most popularly played in Canada and the ...
– a team sport played on ice hockey rinks using sticks with paddles to propel a ball into the opposing team's net
* Moscow broomball
Broomball is a both a recreational and organized competitive winter and ball sport played on ice or snow. It is played either indoors or outdoors, depending on the climate and location. It is most popularly played in Canada and the United States. ...
– an outdoor team game played using ice hockey equipment and a ball played at the Russian embassy on frozen outdoor courts flooded with water
* Curling
Curling is a sport in which players slide #Curling stone, stones on a sheet of ice toward a target area that is segmented into four concentric circles. It is related to bowls, boules, and shuffleboard. Two teams, each with four players, take t ...
– a team sport using "rocks" and lanes and a target
* Ice stock – a team sport using lanes and a target
* Crokicurl
Crokicurl is a Canadian winter sport invented by Liz Wreford and Leanne Muir of Public City Architecture in 2016 and first played in Winnipeg, Canada. The game is a large scale hybrid of curling and the board game Crokinole.
The related game of ...
– an outdoor team sport using "rocks" on an octagonal playing area with posts and a target
Gallery
Ice cross downhill
Ice cross downhill is a winter extreme sporting event which involves direct competitive downhill skating on a walled track featuring sharp turns and high vertical drops. Ice cross downhill is similar to ski cross and boardercross, except with ...
(Individual) File:Kim 2010 Olympic FS.jpg,
Figure skating
Figure skating is a sport in which individuals, pairs, or groups perform on figure skates on ice. It was the first winter sport to be included in the Olympic Games, with its introduction occurring at the Figure skating at the 1908 Summer Olympi ...
(Individual, Pairs) File:Team amber WSSC.jpg,
Synchronized skating
Synchronized skating, often called synchro, is an ice skating sport where between 8 and 20 skaters perform together as a team. They move as a flowing unit at high speed over the ice, while performing elements and footwork.
This complex sport orig ...
(Team) File:Bandy game 1.jpg,
Bandy
Bandy is a winter sport and ball sport played by two team sport, teams wearing Ice skates#Bandy skates, ice skates on a large ice surface (either indoors or outdoors) while using sticks to direct a ball into the opposing team's goal.
The playin ...
(Team) File:УФХМР 2013.jpg,
Rink bandy
Rink bandy is a variant of the larger sport of bandy. Unlike bandy which is played on a large bandy field, rink bandy is played on significantly smaller ice hockey-sized ice rinks.
While a bandy field is about the same size as a football pi ...
(Team) File:Stephen Weiss.jpg,
Ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey in North America) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an Ice rink, ice skating rink with Ice hockey rink, lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. Tw ...
(Team) File:Atlantic Attack Ringette Team.jpg,
Ringette
Ringette is a winter team sport played on an ice rink using ice hockey skates, straight sticks with drag-tips, and a blue, rubber, pneumatic ring designed for use on ice surfaces. While the sport was originally created exclusively for female c ...
(Team) File:Langfardsskridskoakning.jpg,
Tour skating
Tour skating is recreational long distance ice skating on natural ice. It is particularly popular in the Netherlands and the Nordic countries. It is becoming more popular in areas of North America such as New England, Southcentral Alaska, and Nov ...
(Individual) File:Fenskaters ronden ton.jpg, Fen skating
(Individual) Paulien van Deutekom (08-12-2007).jpg,
Speed skating
Speed skating is a competitive form of ice skating in which the competitors race each other in travelling a certain distance on skates. Types of speed skating are long-track speed skating, short-track speed skating, and marathon speed skat ...
(Individual) File:Saguenay 500m.jpg,
Short track speed skating
Short-track speed skating is a form of competitive ice skating, ice speed skating. In competitions, multiple skaters (typically between four and six) skate on an oval ice track with a length of . The rink itself is long by wide, which is the s ...
(Individual, Team Relay) File:Black Forest Village (NBY 417446).jpg,
Barrel jumping
Barrel jumping is a discipline of speed skating, where ice skaters build up speed to jump over a length of multiple barrels lined up, usually side by side like rollers. Occasionally barrels would also be stacked pyramid-style for height. The obj ...
(Individual)
Videos
Lake Neusiedl
Lake Neusiedl (, ; or ; ; ; ), or Fertő (), is the largest endorheic lake in Central Europe, straddling the Austrian– Hungarian border. The lake covers , of which is on the Austrian side and on the Hungarian side. The lake's drainage basi ...
.
File:Skating in Central Park Frank-S.-Armitage-American-Mutoscope-And-Biograph-1900.ogv, ''Skating in Central Park'' (1900), one minute silent film by Frank S. Armitage. EYE Film Institute Netherlands
Eye Filmmuseum is a film archive, museum, and cinema in Amsterdam that preserves and presents both Dutch and foreign films screened in the Netherlands.
Location and history
Eye Filmmuseum is located in the Overhoeks neighborhood of Amsterdam in ...
.
File:Wereldkampioenschappen schaatsen.ogv, Documentary on the World Championship Skating for Women at Helsinki
Helsinki () is the Capital city, capital and most populous List of cities and towns in Finland, city in Finland. It is on the shore of the Gulf of Finland and is the seat of southern Finland's Uusimaa region. About people live in the municipali ...
in 1971.
See also
* Fen skating *Ice resurfacer
An ice resurfacer is a vehicle or hand-pushed device for cleaning and smoothing the surface of a sheet of ice, usually in an ice rink. The first ice resurfacer was developed by American inventor and engineer Frank Zamboni in 1949 in Paramount, C ...
* Kite ice skating
Kite ice skating, sometimes referred to as ice kiting, ice kite skating, para-skating or para ice skating, is a sport practised on ice skates using a large controllable kite to propel across frozen rivers, frozen lakes and other frozen surfaces. ...
* Lidwina
Lidwina (Lydwine, Lydwid, Lidwid, Liduina of Schiedam) (1380–1433) was a Dutch people, Dutch mystic who is honored as a saint by the Catholic Church. She is the patroness saint of the town of Schiedam, of chronic pain, and of ice skating.
Lid ...
, patron saint
A patron saint, patroness saint, patron hallow or heavenly protector is a saint who in Catholicism, Anglicanism, Eastern Orthodoxy or Oriental Orthodoxy is regarded as the heavenly advocate of a nation, place, craft, activity, class, clan, fa ...
of ice skaters
References
External links
Skating and Science
(a bibliography) * {{Authority control Skating Winter Olympic sports Articles containing video clips