I.C.I. on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI) was a British
 The company was founded in December 1926 from the merger of four companies:
The company was founded in December 1926 from the merger of four companies:
 In the 1940s and 1950s, the company established its
In the 1940s and 1950s, the company established its
 Dutch firm
Dutch firm
London
Pruteen had limited economic success but was followed by the much more successful development of Quorn. * Blackley (in Manchester) and Huddersfield: ICI used the sites to manufacture
chemical
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., wit ...
company. It was, for much of its history, the largest manufacturer in Britain.
It was formed by the merger of four leading British chemical companies in 1926.
Its headquarters were at Millbank
Millbank is an area of central London in the City of Westminster. Millbank is located by the River Thames, east of Pimlico and south of Westminster. Millbank is known as the location of major government offices, Burberry headquarters, the Mi ...
in London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
. ICI was a constituent of the FT 30
The FT 30 (''FT Ordinary Index'' or ''FTOI'', not "FTSE 30") is a now rarely used index that is similar to the Dow Jones Industrial Average. As an index of stocks to represent the real trends on the market, the FT 30 has been superseded by the FTS ...
and later the FTSE 100
The Financial Times Stock Exchange 100 Index, also called the FTSE 100 Index, FTSE 100, FTSE, or, informally, the "Footsie" , is a share index of the 100 companies listed on the London Stock Exchange with (in principle) the highest market ...
indices.
ICI made general chemicals, plastics, paints, pharmaceuticals and speciality products, including food ingredients, speciality polymer
A polymer (; Greek ''poly-'', "many" + '' -mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and ...
s, electronic materials, fragrances and flavourings.
In 2008, it was acquired by AkzoNobel
Akzo Nobel N.V., stylized as AkzoNobel, is a Dutch multinational company which creates paints and performance coatings for both industry and consumers worldwide. Headquartered in Amsterdam, the company has activities in more than 80 countries ...
,
which immediately sold parts of ICI to Henkel
AG & Co. KGaA, commonly known as Henkel, is a German multinational chemical and consumer goods company headquartered in Düsseldorf, Germany. It is active in both the consumer and industrial sectors. Founded in 1876, the DAX company is organ ...
and integrated ICI's remaining operations within its existing organisation.
History
Development of the business (1926–1944)
 The company was founded in December 1926 from the merger of four companies:
The company was founded in December 1926 from the merger of four companies: Brunner Mond Brunner may refer to:
Places
* Brunner, New Zealand
* Lake Brunner, New Zealand
* Brunner Mine, New Zealand
* Brunner, Houston, United States
* Brunner (crater), lunar crater
Other uses
* Brunner (surname)
* Brunner the Bounty Hunter, a character ...
, Nobel Explosives
Ardeer was a small town now officially incorporated into Stevenston on the Ardeer peninsula, in the parish of Stevenston, North Ayrshire, originally an island and later its extensive sand dune system became the site of Nobel Explosives, a domin ...
, the United Alkali Company
United Alkali Company Limited was a British chemical company formed in 1890, employing the Leblanc process to produce soda ash for the glass, textile, soap, and paper industries. It became one of the top four British chemical companies merged in 1 ...
, and British Dyestuffs Corporation
British Dyestuffs Corporation Ltd was a British company formed in 1919 from the merger of British Dyes Ltd with Levinstein Ltd. The British Government was the company's largest shareholder, and had two directors on the board.
Background
By 1913 ...
. It established its head office
Headquarters (commonly referred to as HQ) denotes the location where most, if not all, of the important functions of an organization are coordinated. In the United States, the corporate headquarters represents the entity at the center or the to ...
at Millbank in London in 1928.
Competing with DuPont and IG Farben
Interessengemeinschaft Farbenindustrie AG (), commonly known as IG Farben (German for 'IG Dyestuffs'), was a German chemical and pharmaceutical conglomerate. Formed in 1925 from a merger of six chemical companies— BASF, Bayer, Hoechst, Agfa ...
, the new company produced chemicals
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., wit ...
, explosives, fertiliser
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from ...
s, insecticides, dyestuff
A dye is a colored substance that chemically bonds to the substrate to which it is being applied. This distinguishes dyes from pigments which do not chemically bind to the material they color. Dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution and ...
s, non-ferrous
In metallurgy, non-ferrous metals are metals or alloys that do not contain iron ( allotropes of iron, ferrite, and so on) in appreciable amounts.
Generally more costly than ferrous metals, non-ferrous metals are used because of desirable prope ...
metals, and paints.
In its first year turnover was £27 million.
In the 1920s and 1930s, the company played a key role in the development of new chemical products, including the dyestuff phthalocyanine
Phthalocyanine () is a large, aromatic, macrocyclic, organic compound with the formula and is of theoretical or specialized interest in chemical dyes and photoelectricity.
It is composed of four isoindole units linked by a ring of nitrogen atom ...
(1929), the acrylic plastic Perspex
Poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) belongs to a group of materials called engineering plastics. It is a transparent thermoplastic. PMMA is also known as acrylic, acrylic glass, as well as by the trade names and brands Crylux, Plexiglas, Acrylite ...
(1932), Dulux
Dulux is an internationally available brand of architectural paint originated from the United Kingdom. The brand name Dulux has been used by both Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI) and DuPont since 1931 and was one of the first alkyd-based ...
paints (1932, co-developed with DuPont), polyethylene
Polyethylene or polythene (abbreviated PE; IUPAC name polyethene or poly(methylene)) is the most commonly produced plastic. It is a polymer, primarily used for packaging (plastic bags, plastic films, geomembranes and containers including ...
(1937), and polyethylene terephthalate fibre known as Terylene
Polyethylene terephthalate (or poly(ethylene terephthalate), PET, PETE, or the obsolete PETP or PET-P), is the most common thermoplastic polymer resin of the polyester family and is used in fibres for clothing, containers for liquids and foods ...
(1941).
In 1940, ICI started British Nylon Spinners
British Nylon Spinners (BNS) was a British company set up in 1940 by ICI and Courtaulds to produce nylon yarn. In 1964 it was taken over by ICI after ICI had tried and failed to take over Courtaulds.
Beginning
In 1939, ICI took out a licence ...
as a joint venture with Courtaulds
Courtaulds was a United Kingdom-based manufacturer of fabric, clothing, artificial fibres, and chemicals. It was established in 1794 and became the world's leading man-made fibre production company before being broken up in 1990 into Courtauld ...
.
ICI also owned the Sunbeam motorcycle business, which had come with Nobel Industries, and continued to build motorcycles until 1937.
During the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, ICI was involved with the United Kingdom's nuclear weapons programme codenamed Tube Alloys
Tube Alloys was the research and development programme authorised by the United Kingdom, with participation from Canada, to develop nuclear weapons during the Second World War. Starting before the Manhattan Project in the United States, the Bri ...
.
Postwar innovation (1945–1990)
 In the 1940s and 1950s, the company established its
In the 1940s and 1950s, the company established its pharmaceutical
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy ( pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field and ...
business and developed a number of key products, including Paludrine
Proguanil, also known as chlorguanide and chloroguanide, is a medication used to treat and prevent malaria. It is often used together with chloroquine or atovaquone. When used with chloroquine the combination will treat mild chloroquine resistan ...
(1940s, an anti-malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or deat ...
l drug), halothane
Halothane, sold under the brand name Fluothane among others, is a general anaesthetic. It can be used to induce or maintain anaesthesia. One of its benefits is that it does not increase the production of saliva, which can be particularly useful i ...
(1951, an inhalational anaesthetic
An inhalational anesthetic is a chemical compound possessing general anesthetic properties that can be delivered via inhalation. They are administered through a face mask, laryngeal mask airway or tracheal tube connected to an anesthetic vapori ...
agent), propofol
Propofol, marketed as Diprivan, among other names, is a short-acting medication that results in a decreased level of consciousness and a lack of memory for events. Its uses include the starting and maintenance of general anesthesia, sedation ...
(1977, an intravenous anaesthetic agent), Inderal
Propranolol, sold under the brand name Inderal among others, is a medication of the beta blocker class. It is used to treat high blood pressure, a number of types of irregular heart rate, thyrotoxicosis, capillary hemangiomas, performance anxi ...
(1965, a beta-blocker
Beta blockers, also spelled β-blockers, are a class of medications that are predominantly used to manage abnormal heart rhythms, and to protect the heart from a second heart attack after a first heart attack ( secondary prevention). They are a ...
), tamoxifen
Tamoxifen, sold under the brand name Nolvadex among others, is a selective estrogen receptor modulator used to prevent breast cancer in women and treat breast cancer in women and men. It is also being studied for other types of cancer. It has b ...
(1978, a frequently used drug for breast cancer),
and PEEK
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) is a colourless organic thermoplastic polymer in the polyaryletherketone (PAEK) family, used in engineering applications. The polymer was first developed in November 1978, later being introduced to the market by Vic ...
(1979, a high performance thermoplastic
A thermoplastic, or thermosoft plastic, is any plastic polymer material that becomes pliable or moldable at a certain elevated temperature and solidifies upon cooling.
Most thermoplastics have a high molecular weight. The polymer chains associat ...
). ICI formed ICI Pharmaceuticals in 1957.
ICI developed a fabric in the 1950s known as Crimplene
Crimplene is a texturised continuous fibre launched in 1959, produced by modifying Terylene. The patent was taken out by Mario Nava of Chesline and Crepes Ltd of Macclesfield, and sold to ICI Fibres. ICI licensed the product to various throwsters ...
, a thick polyester yarn used to make a fabric of the same name.
The resulting cloth is heavy and wrinkle-resistant, and retains its shape well.
The California-based fashion designer Edith Flagg
Edith Flagg (née Faierstein, also known as Feuerstein; November 1, 1919 – August 13, 2014) was an Austrian-born American fashion designer, fashion industry executive, and philanthropist. She was the first designer to import polyester as a fas ...
was the first to import this fabric from Britain to the United States.
During the first two years, ICI gave Flagg a large advertising budget to popularise the fabric across America.
In 1960, Paul Chambers
Paul Laurence Dunbar Chambers Jr. (April 22, 1935 – January 4, 1969) was an American jazz double bassist. A fixture of rhythm sections during the 1950s and 1960s, he has become one of the most widely-known jazz bassists of the hard bop era. H ...
became the first chairman appointed from outside the company.
Chambers employed the consultancy firm McKinsey
McKinsey & Company is a global management consulting firm founded in 1926 by University of Chicago professor James O. McKinsey, that offers professional services to corporations, governments, and other organizations. McKinsey is the oldest and ...
to help with reorganising the company. His eight-year tenure saw export sales double, but his reputation was severely damaged by a failed takeover bid for Courtaulds
Courtaulds was a United Kingdom-based manufacturer of fabric, clothing, artificial fibres, and chemicals. It was established in 1794 and became the world's leading man-made fibre production company before being broken up in 1990 into Courtauld ...
in 1961–62.
ICI was confronted with the nationalisation of its operations in Burma
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John C. Wells, Joh ...
on 1 August 1962 as a consequence of the military coup.
In 1964, ICI acquired British Nylon Spinners (BNS), the company it had jointly set up in 1940 with Courtaulds.
ICI surrendered its 37.5 per cent holding in Courtaulds and paid Courtaulds £2 million a year for five years, "to take account of the future development expenditure of Courtaulds in the nylon field."
In return, Courtaulds transferred to ICI their 50 per cent holding in BNS. BNS was absorbed into ICI's existing polyester operation, ICI Fibres. The acquisition included BNS production plants in Pontypool
Pontypool ( cy, Pont-y-pŵl ) is a town and the administrative centre of the county borough of Torfaen, within the historic boundaries of Monmouthshire in South Wales. It has a population of 28,970.
Location
It is situated on the Afon Lwyd ...
, Gloucester
Gloucester ( ) is a cathedral city and the county town of Gloucestershire in the South West of England. Gloucester lies on the River Severn, between the Cotswolds to the east and the Forest of Dean to the west, east of Monmouth and east of t ...
and Doncaster
Doncaster (, ) is a city in South Yorkshire, England. Named after the River Don, it is the administrative centre of the larger City of Doncaster. It is the second largest settlement in South Yorkshire after Sheffield. Doncaster is situated i ...
, together with research and development in Pontypool.
Early pesticide development under ICI Plant Protection Division, with its plant at Yalding
Yalding is a village and civil parish in the Borough of Maidstone in Kent, England. The village is situated south west of Maidstone at a point where the Rivers Teise and Beult join the River Medway. At the 2001 census, the parish, which incl ...
, Kent, research station at Jealott's Hill
Jealott's Hill is a village in the county of Berkshire, England, within the civil parish of Warfield. The settlement is on the A3095 road approximately north of Bracknell. The nearest railway station is in .
The name of the hill is reported to ...
and HQ at Fernhurst Research Station
The Fernhurst Research Station was a crop protection chemical research institute in West Sussex, mainly run by ICI, for the fruit industry. The site is to the east of the A286, around a mile south of the village of Fernhurst and a mile north of ...
included paraquat
Paraquat (trivial name; ), or ''N'',''N''′-dimethyl-4,4′-bipyridinium dichloride ( systematic name), also known as methyl viologen, is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H7N)2l2. It is classified as a viologen, a family of red ...
(1962, a herbicide), the insecticides pirimiphos-methyl
Pirimiphos-methyl, marketed as Actellic, and Sybol is a phosphorothioate used as an insecticide. It was originally developed by Imperial Chemical Industries Ltd., now Syngenta, at their Jealott's Hill
Jealott's Hill is a village in the cou ...
in 1967 and pirimicarb
Pirimicarb is a selective carbamate insecticide used to control aphids on vegetable, cereal and orchard crops by inhibiting acetylcholinesterase activity but does not affect useful predators such as ladybirds that eat them. It was originally dev ...
in 1970, brodifacoum
Brodifacoum is a highly lethal 4-hydroxycoumarin vitamin K antagonist anticoagulant poison. In recent years, it has become one of the world's most widely used pesticides. It is typically used as a rodenticide, but is also used to control larger pe ...
(a rodenticide
Rodenticides are chemicals made and sold for the purpose of killing rodents. While commonly referred to as "rat poison", rodenticides are also used to kill mice, squirrels, woodchucks, chipmunks, porcupines, nutria, beavers, and voles. Despite ...
) was developed in 1974; in the late 1970s, ICI was involved in the early development of synthetic pyrethroid
A pyrethroid is an organic compound similar to the natural pyrethrins, which are produced by the flowers of pyrethrums (''Chrysanthemum cinerariaefolium'' and '' C. coccineum''). Pyrethroids are used as commercial and household insecticides.
In ...
insecticides such as lambda-cyhalothrin
Cyhalothrin is the ISO common name for an organic compound that, in specific isomeric forms, is used as a pesticide.
It is a pyrethroid, a class of synthetic insecticides that mimic the structure and properties of the naturally occurring insecti ...
.
Peter Allen was appointed chairman between 1968 and 1971. He presided over the purchase of Viyella
Viyella is a blend of wool and cotton first woven in 1893 in England, and the "first branded fabric in the world".''Times'', 8 Sep 1987 It was made of 55% merino wool and 45% cotton in a twill weave, developed by James and Robert Sissons of ...
. Profits shrank under his tenure. During his tenure, ICI created the wholly owned subsidiary Cleveland Potash Ltd, for the construction of Boulby Mine in Redcar and Cleveland, North Yorkshire. The first shaft was dug in 1968, with full production from 1976. ICI jointly owned the mine with Anglo American, and then with De Beers, before complete ownership was transferred to Israel Chemicals Ltd in 2002.
Jack Callard was appointed chairman from 1971 to 1975. He almost doubled company profits between 1972 and 1974, and made ICI Britain's largest exporter. In 1971, the company acquired Atlas Chemical Industries Inc., a major American competitor.
In 1977, Imperial Metal Industries
IMI plc (), formerly Imperial Metal Industries, is a British-based engineering company headquartered in Birmingham, England. It is listed on the London Stock Exchange and is a constituent of the FTSE 250 Index.
History
The company was founded b ...
was divested as an independent quoted company.
From 1982 to 1987, the company was led by the charismatic John Harvey-Jones
Sir John Harvey-Jones MBE (16 April 1924 – 9 January 2008) was an English businessman. He was the chairman of Imperial Chemical Industries from 1982 to 1987. He was best known by the public for his BBC television show, '' Troubleshooter' ...
.
Under his leadership, the company acquired the Beatrice Chemical Division in 1985 and Glidden Coatings & Resins, a leading paint
Paint is any pigmented liquid, liquefiable, or solid mastic composition that, after application to a substrate in a thin layer, converts to a solid film. It is most commonly used to protect, color, or provide texture. Paint can be made in many ...
s business, in 1986.
Reorganisation of the business (1991–2007)
By the early 1990s, plans were carried out to demerge the company, as a result of increasing competition and internal complexity that caused heavy retrenchment and slowing innovation. In 1991, ICI sold the agricultural and merchandising operations of BritAg andScottish Agricultural Industries
Scottish usually refers to something of, from, or related to Scotland, including:
*Scottish Gaelic, a Celtic Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family native to Scotland
*Scottish English
*Scottish national identity, the Scottish ide ...
to Norsk Hydro
Norsk Hydro ASA (often referred to as just ''Hydro'') is a Norwegian aluminium and renewable energy company, headquartered in Oslo. It is one of the largest aluminium companies worldwide. It has operations in some 50 countries around the world ...
,
and fought off a hostile takeover bid from Hanson
Hanson or Hansson may refer to:
People
* Hanson (surname)
* Hansson (surname)
* Hanson (wrestler), ringname of an American professional wrestler
Musical groups
* Hanson (band), an American pop rock band
* Hanson (UK band), an English rock b ...
, who had acquired 2.8 percent of the company.
It also divested its soda ash
Sodium carbonate, , (also known as washing soda, soda ash and soda crystals) is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2CO3 and its various hydrates. All forms are white, odourless, water-soluble salts that yield moderately alkaline solutions ...
products arm to Brunner Mond Brunner may refer to:
Places
* Brunner, New Zealand
* Lake Brunner, New Zealand
* Brunner Mine, New Zealand
* Brunner, Houston, United States
* Brunner (crater), lunar crater
Other uses
* Brunner (surname)
* Brunner the Bounty Hunter, a character ...
, ending an association with the trade that had existed since the company's inception, one that had been inherited from the original Brunner, Mond & Co. Ltd.
In 1992, the company sold its nylon business to DuPont.
In 1993, the company de-merged its pharmaceutical bio-science businesses: pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals
An agrochemical or agrichemical, a contraction of ''agricultural chemical'', is a chemical product used in industrial agriculture. Agrichemical refers to biocides (pesticides including insecticides, herbicides, fungicides and nematicides) an ...
, specialities, seed
A seed is an embryonic plant enclosed in a protective outer covering, along with a food reserve. The formation of the seed is a part of the process of reproduction in seed plants, the spermatophytes, including the gymnosperm and angiosper ...
s and biological
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary ...
products were all transferred into a new and independent company called Zeneca
Zeneca (officially Zeneca Group PLC) was a British multinational pharmaceutical company headquartered in London, United Kingdom. It was formed in June 1993 by the demerger of the pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals businesses of Imperial Chemic ...
. Zeneca subsequently merged with Astra AB
Astra AB was a former international pharmaceutical company headquartered in Södertälje, Sweden. Astra was formed in 1913 and merged with the British Zeneca Group in 1999 to form AstraZeneca. Product development was focused on therapeutics for g ...
to form AstraZeneca
AstraZeneca plc () is a British-Swedish multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company with its headquarters at the Cambridge Biomedical Campus in Cambridge, England. It has a portfolio of products for major diseases in areas includ ...
.
Charles Miller Smith was appointed CEO in 1994, one of the few times that someone from outside ICI had been appointed to lead the company, Smith having previously been a director at Unilever
Unilever plc is a British multinational consumer goods company with headquarters in London, England. Unilever products include food, condiments, bottled water, baby food, soft drink, ice cream, instant coffee, cleaning agents, energy ...
.
Shortly afterwards, the company acquired a number of former Unilever businesses in an attempt to move away from its historical reliance on commodity
In economics, a commodity is an economic good, usually a resource, that has full or substantial fungibility: that is, the market treats instances of the good as equivalent or nearly so with no regard to who produced them.
The price of a co ...
chemicals.
In 1995, ICI acquired the American paint companies Devoe Paints, Fuller-O'Brien Paints and Grow Group. In 1997, ICI acquired National Starch & Chemical, Quest International
Quest International was a major producer of flavors, fragrances and food ingredients with sales of £560 million in 2005 before its acquisition by rival Givaudan. Quest created and marketed flavours and fragrance concepts and solutions for the ...
, Unichema, and Crosfield, the speciality chemicals
Speciality chemicals (also called specialties or effect chemicals) are particular chemical products which provide a wide variety of effects on which many other industry sectors rely. Some of the categories of speciality chemicals are adhesives, agr ...
businesses of Unilever
Unilever plc is a British multinational consumer goods company with headquarters in London, England. Unilever products include food, condiments, bottled water, baby food, soft drink, ice cream, instant coffee, cleaning agents, energy ...
for $8 billion.
This step was part of a strategy to move away from cyclical bulk chemicals and to progress up the value chain to become a higher growth, higher margin business.
Later that year it went on to buy Rutz & Huber, a Swiss paints business.
Having taken on some £4 billion of debt to finance these acquisitions, the company had to sell off its commodity chemicals businesses:
* Disposals of bulk chemicals businesses at that time included the sale of its Australian subsidiary, ICI Australia
Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI) was a British chemical company. It was, for much of its history, the largest manufacturer in Britain.
It was formed by the merger of four leading British chemical companies in 1926.
Its headquarters were at Mi ...
, for £1 billion in 1997, and of its polyester chemicals business to DuPont for $3 billion also in 1997.
* In 1998, it bought Acheson Industries Inc., an electronic chemicals business.
* In 2000, ICI sold its diisocyanate, advanced materials, and speciality chemicals businesses on Teesside
Teesside () is a built-up area around the River Tees in the north of England, split between County Durham and North Yorkshire. The name was initially used as a county borough in the North Riding of Yorkshire.
Historically a hub for heavy manu ...
and worldwide (including plants at Rozenburg
Rozenburg () is a town and former municipality in the western Netherlands, in the province of South Holland. The municipality had a population of 13,173 in 2004, and covers an area of 6.50 km² (of which 1.99 km² water). It was the s ...
in the Netherlands, and South Africa, Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
and Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northe ...
), and Tioxide, its titanium dioxide
Titanium dioxide, also known as titanium(IV) oxide or titania , is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula . When used as a pigment, it is called titanium white, Pigment White 6 (PW6), or CI 77891. It is a white solid that is insoluble ...
subsidiary, to Huntsman Corporation
Huntsman Corporation is an American multinational manufacturer and marketer of chemical products for consumers and industrial customers. Huntsman manufactures assorted polyurethanes, performance products, and adhesives for customers like BMW, ...
for £1.7 billion. It also sold the last of its industrial chemicals businesses to Ineos
INEOS Group Limited is a British multinational chemicals company headquartered and registered in London. , it is the fourth largest chemical company in the world.
Ineos is organised into about 20 standalone business units, each with its own b ...
for £325 million.
* In 2002, the ICI wholly transferred ownership of Boulby Mine to Israel Chemicals Ltd.
* In 2006, the Company sold Quest International, its flavour
Flavor or flavour is either the sensory perception of taste or smell, or a flavoring in food that produces such perception.
Flavor or flavour may also refer to:
Science
*Flavors (programming language), an early object-oriented extension to Lisp ...
s and fragrances business, to Givaudan
Givaudan () is a Swiss multinational manufacturer of flavours, fragrances and active cosmetic ingredients. As of 2008, it is the world's largest company in the flavour and fragrance industries.
Overview
The company's scents and flavours are de ...
, for £1.2 billion and Uniqema, its oleochemical business, to Croda International
Croda International plc is a British speciality chemicals company based at Snaith, England. It is listed on the London Stock Exchange.
History
The company was founded by George William Crowe and Henry James Dawe in 1925. Crowe bought an aband ...
, for £410 million.
Having sold much of its historically profitable commodities businesses, and many of the new speciality businesses which it had failed to integrate, the company consisted mainly of the Dulux paints business, which quickly found itself the subject of a takeover by AkzoNobel.
Takeover by AkzoNobel
 Dutch firm
Dutch firm AkzoNobel
Akzo Nobel N.V., stylized as AkzoNobel, is a Dutch multinational company which creates paints and performance coatings for both industry and consumers worldwide. Headquartered in Amsterdam, the company has activities in more than 80 countries ...
(owner of Crown Berger paints) bid £7.2 billion (€10.66 billion or $14.5 billion) for ICI in June 2007.
An area of concern about a potential deal was ICI's British pension fund
A pension fund, also known as a superannuation fund in some countries, is any plan, fund, or scheme which provides retirement income.
Pension funds typically have large amounts of money to invest and are the major investors in listed and priva ...
, which had a deficit of almost £700 million and future liabilities of more than £9 billion at the time.
Regulatory issues in the UK and other markets where Dulux
Dulux is an internationally available brand of architectural paint originated from the United Kingdom. The brand name Dulux has been used by both Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI) and DuPont since 1931 and was one of the first alkyd-based ...
and Crown Paints brands each have significant market share were also a cause for concern for the boards of ICI and AkzoNobel.
In the UK, any combined operation without divestment
In finance and economics, divestment or divestiture is the reduction of some kind of asset for financial, ethical, or political objectives or sale of an existing business by a firm. A divestment is the opposite of an investment. Divestiture is ...
s would have seen AkzoNobel have a 54 per cent market share in the paint market.
The initial bid was rejected by the ICI board and the majority of shareholders.
However, a subsequent bid for £8 billion (€11.82 billion) was accepted by ICI in August 2007, pending approval by regulators.
On 2 January 2008, completion of the takeover of ICI plc by AkzoNobel was announced.
Shareholders of ICI received either £6.70 in cash or AkzoNobel loan notes to the value of £6.70 per one nominal ICI share.
The adhesives business of ICI was transferred to Henkel
AG & Co. KGaA, commonly known as Henkel, is a German multinational chemical and consumer goods company headquartered in Düsseldorf, Germany. It is active in both the consumer and industrial sectors. Founded in 1876, the DAX company is organ ...
as a result of the deal,
while AkzoNobel agreed to sell its Crown Paints subsidiary to satisfy the concerns of the European Commissioner for Competition
The Commissioner for Competition is the member of the European Commission responsible for competition. The current commissioner is Margrethe Vestager ( ALDE).
Responsibilities
The portfolio has responsibility for such matters as commercial c ...
.
The areas of concern regarding the ICI UK pension scheme were addressed by ICI and AkzoNobel.
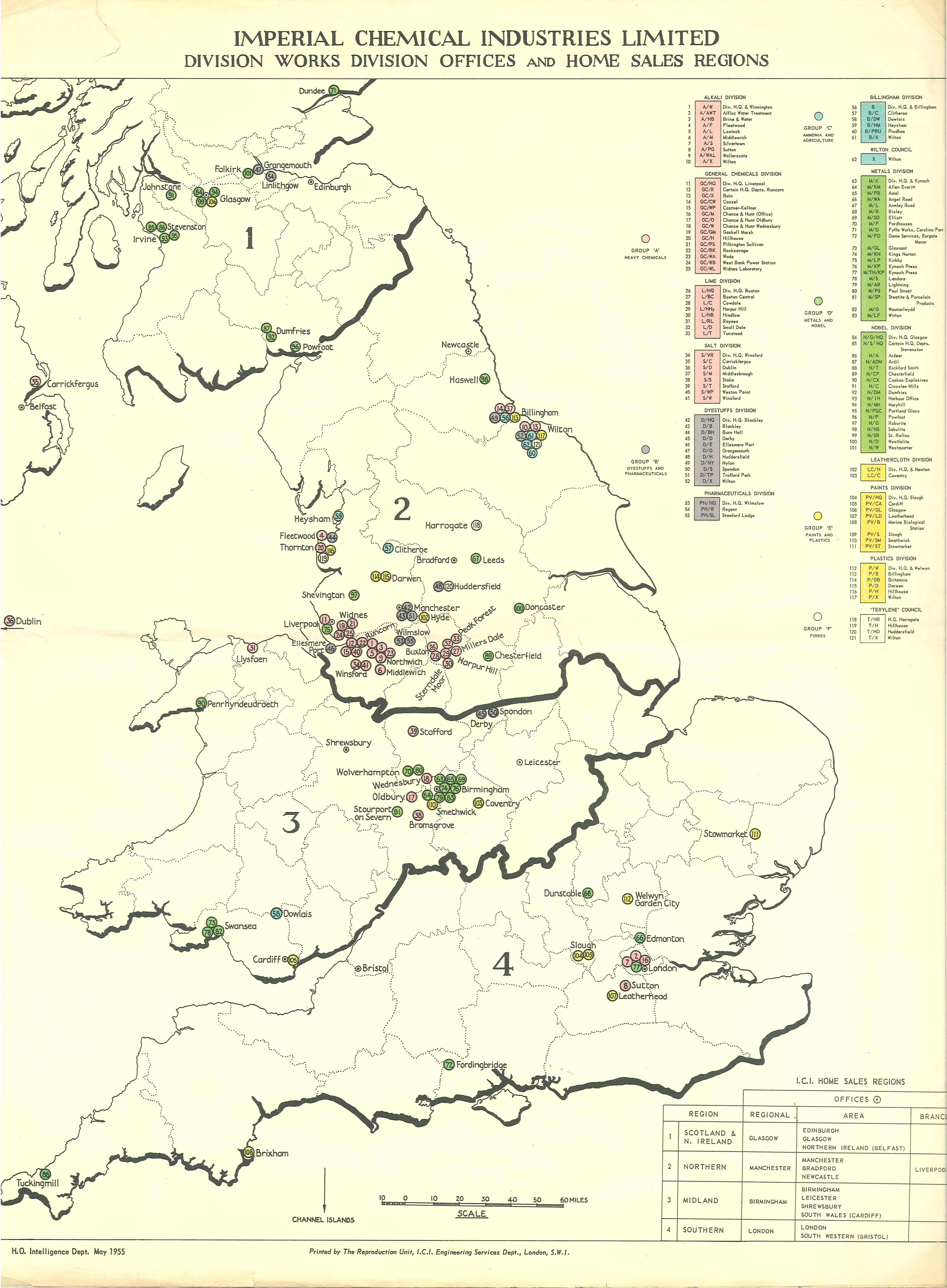
Operations
ICI operated a number of chemical sites around the world. In the UK, the main plants were as follows: * Billingham Manufacturing Plant (in Stockton-on-Tees) and Wilton, Redcar and Cleveland, Wilton (in present-day Redcar and Cleveland): ICI used the Billingham site to manufacturefertiliser
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from ...
s in the 1920s and went on to produce plastics at Billingham in 1934. During World War II it manufactured Synthonia, a Organic compound#Synthetic compounds, synthetic ammonia for explosives. The Wilton R&D site was built to support the plastics division with R&D and chemical engineering facilities. The ICI Billingham Division was split into the ICI Heavy Organic Chemicals Division and ICI Agricultural Division in the 1960s. From 1971 to 1988 ICI Physics and Radioisotopes Section (later known as Tracerco) operated a small General Atomics TRIGA Mark I nuclear reactor at its Billingham factory for the production of radioisotopes used in the manufacture of flow and level instruments, among other products. The Agricultural Division was noted for the development of the world's largest bioreactor at the time – the 1.5 million litre Pruteen Reactor, used for the cultivation of animal feed. Engineering models of components and the builder's model of the complete plant are now in the collection of the Science Museum, London, Science Museum]London
Pruteen had limited economic success but was followed by the much more successful development of Quorn. * Blackley (in Manchester) and Huddersfield: ICI used the sites to manufacture
dyestuff
A dye is a colored substance that chemically bonds to the substrate to which it is being applied. This distinguishes dyes from pigments which do not chemically bind to the material they color. Dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution and ...
s. The dye business, known as the ICI Dyestuffs Division in the 1960s, went through several reorganisations. Huddersfield was tied in with Wilton with the production of nitrobenzene and nitrotoluene. Huddersfield also produced insecticides. (Syngenta still manufacture insecticides at Huddersfield). Proxel Biocide was made at Huddersfield from the 80's onwards. Additives also made at Huddersield. Huddersfield became Zeneca then AstraZeneca, in 2004 Huddersfield was Syngenta, Avecia, Arch and Lubrizol running what were all ICI plants at one time. Through the years it was combined with other speciality chemicals
Speciality chemicals (also called specialties or effect chemicals) are particular chemical products which provide a wide variety of effects on which many other industry sectors rely. Some of the categories of speciality chemicals are adhesives, agr ...
businesses and became Organics Division. Then became ICI Colours and Fine Chemicals and then ICI Specialties.
* Runcorn (in Cheshire): ICI operated a number of separate sites within the Runcorn area, including the Castner-Kellner site, where ICI manufactured chlorine and sodium hydroxide (caustic soda). Adjacent to the Castner-Kellner site was Rocksavage works, where a variety of chemicals based on chlorine products were manufactured, including Chloromethanes, Arklone dry cleaning fluid, Trichloethylene degreasing fluid and the Arcton range of CFCs. Also on that site were PVC manufacture and HF (Hydrogen fluoride) manufacture. At Runcorn Heath Research Laboratories, technical support, research and development for Mond Division products was carried out, and the support sections included chemical plan design and engineering sections. Just to the north of Runcorn, on an island between the Manchester Ship Canal and the River Mersey could be found the Wigg Works, which had been erected originally for producing poison gas in wartime. In Widnes could also be found several factories producing weedkillers and other products. For many years it was known as ICI Mond Division but later became part of the ICI Chemicals and Polymers Division. The Runcorn site was also responsible for the development of the HiGEE and Spinning Disc Reactor concepts. These were originated by Professor Colin Ramshaw and led to the concept of Micro process engineering, Process Intensification; research into these novel technologies is now being pursued by the Process Intensification Group at Newcastle University.
* Winnington and Wallerscote (in Northwich, Cheshire): It was here that ICI manufactured sodium carbonate (soda ash) and its various by-products such as sodium bicarbonate (bicarbonate of soda), and sodium sesquicarbonate. The Winnington site, built in 1873 by the entrepreneurs John Tomlinson Brunner and Ludwig Mond, was also the base for the former company Brunner, Mond & Co. Ltd. and, after the merger which created ICI, the powerful and influential Alkali Division. It was at the Winnington Laboratory, laboratories on this site that polythene was discovered by accident in 1933 during experiments into high pressure reactions. Wallerscote was built in 1926, its construction delayed by the First World War, and became one of the largest factories devoted to a single product (soda ash) in the world. However, the decreasing importance of the soda ash trade to ICI in favour of newer products such as paints and plastics, meant that in 1984 the Wallerscote site was closed, and thereafter mostly demolished. The laboratory where polythene was discovered was sold off and the building became home to a variety of businesses including a go-kart track and paintballing, and the Winnington Works were divested to the newly formed company, Brunner Mond Brunner may refer to:
Places
* Brunner, New Zealand
* Lake Brunner, New Zealand
* Brunner Mine, New Zealand
* Brunner, Houston, United States
* Brunner (crater), lunar crater
Other uses
* Brunner (surname)
* Brunner the Bounty Hunter, a character ...
, in 1991. It was again sold in 2006, to Tata (an Indian-based company) and in 2011 was re branded as Tata Chemicals Europe. The Winnington plant closed in February 2014, with the last shift on 2 February bringing to a close 140 years of soda ash production in this Northwich site.
* Ardeer, Scotland, Ardeer (in Stevenston, Ayrshire): ICI Nobel used the site to manufacture dynamite and other explosives and nitrocellulose-based products. For a time, the site also produced nylon and nitric acid. Nobel Enterprises was sold in 2002 to Inabata & Co., Ltd., Inabata.
*Penrhyndeudraeth (Gwynedd, North Wales): Gwaith Powdwr, Cooke’s Works, part of ICI’s Nobel’s Explosives Company division produced nitroglycerine-based explosives up until the site’s closure in 1995.
* Slough (in Berkshire): Headquarters of ICI Paints Division.
* Welwyn Garden City (in Hertfordshire): Headquarters of ICI Plastics Division until the early 1990s.
Argentina
An ICI subsidiary called Duperial operated in Argentine from 1928 to 1995, when it was renamed ICI. Established in the city of San Lorenzo, Santa Fe, it operates an integrated production site with commercial offices in Buenos Aires. Since 2009 it has made sulphuric acid with ISO certification under the company name Akzo Nobel Functional Chemicals S.A. It also had an operation at Palmira, Mendoza, for its Wine Chemicals Division, that manufactured tartaric acid, wine alcohol and grapeseed oil from natural raw material coming from the wine industry in the provinces of Mendoza and San Juan. This operation held 10% world market share for tartaric acid. It was sold in 2008 and currently operates as Derivados Vínicos S.A. (DERVINSA).Australia
The subsidiary ICI Australia Ltd established the Adelaide International Bird Sanctuary, Dry Creek Saltfields at Dry Creek, South Australia, Dry Creek north of Adelaide, South Australia, in 1940, with an associatedsoda ash
Sodium carbonate, , (also known as washing soda, soda ash and soda crystals) is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2CO3 and its various hydrates. All forms are white, odourless, water-soluble salts that yield moderately alkaline solutions ...
plant at nearby Osborne, South Australia, Osborne.
In 1989, these operations were sold to Penrice Soda Products.
An ICI plant was built at Botany Bay in New South Wales in the 1940s and was sold to Orica in 1997.
The plant once manufactured paints, plastics and industrial chemicals such as solvents. It was responsible for the Botany Bay Groundwater Plume contamination of a local aquifer.
Bangladesh
In 1968 a subsidiary of Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI) was established in then-East Pakistan. After Bangladesh gained independence in 1971, the company was incorporated on 24 January 1973 as ICI Bangladesh Manufacturers Limited and also as Public Limited Company. The company divested its investment in Bangladesh and was renamed as ACI Limited, Advanced Chemical Industries Limited (ACI Limited) on 5 May 1992. The company sold its insect control, air care and toilet care brands to S. C. Johnson & Son, SC Johnson & Son in 2015. Currently Advanced Chemical Industries (ACI) Limited is one of the largest conglomerates in Bangladesh with a multinational heritage operating across the country. The company operates through three reporting divisions: Pharmaceuticals, Consumer Brands and Agribusiness.Sri Lanka
ICI maintained offices in Colombo importing and supplying chemicals for manufacturers in Ceylon. In 1964, following import restrictions that allowed only locally owned subsidiaries of multinational companies to gain import licenses, CIC Holdings, Chemical Industries (Colombo) Limited was formed as an ICI subsidiary with 49% ICI ownership and remaining held public.New Zealand
The subsidiary ICI New Zealand provided substantial quantities of chemical products – including swimming pool chemicals, commercial healthcare products, herbicides and pesticides for use within New Zealand and the neighbouring Pacific Islands. A Structure fire, fire at the ICI New Zealand store in Mount Wellington, New Zealand, Mount Wellington, Auckland, on 21 December 1984, killed an ICI employee and caused major health concerns. Over 200 firefighters were exposed to toxic smoke and effluents during the firefighting efforts. Six firefighters retired for medical reasons as a result of the fire. This incident was a major event in the history of the New Zealand Fire Service and subject to a formal investigation, led by future Chief Justice of New Zealand, Chief Justice Sian Elias. The fire was a trigger for major reforms of the service; direct consequences included improved protective clothing for firefighters, a standard safety protocol for major incidents, the introduction of dedicated fireground safety officers, and changes to occupational health regulations.See also
* Imperial Chemical House * IMI plc (formerly Imperial Metal Industries) * Pharmaceutical industry in the United KingdomReferences
Further reading
* * {{Authority control Imperial Chemical Industries, AstraZeneca British companies established in 1926 British companies disestablished in 2008 Chemical companies established in 1926 Chemical companies of the United Kingdom Former defence companies of the United Kingdom Companies formerly listed on the London Stock Exchange Paint and coatings companies of the United Kingdom 1926 establishments in England 2008 mergers and acquisitions