|
General Anesthetic
General anaesthetics (or anesthetics) are often defined as compounds that induce a loss of consciousness in humans or loss of righting reflex in animals. Clinical definitions are also extended to include an induced coma that causes lack of awareness to painful stimuli, sufficient to facilitate surgical applications in clinical and veterinary practice. General anaesthetics do not act as analgesics and should also not be confused with sedatives. General anaesthetics are a structurally diverse group of compounds whose mechanisms encompass multiple biological targets involved in the control of neuronal pathways. The precise workings are the subject of some debate and ongoing research. General anesthetics elicit a state of general anesthesia. It remains somewhat controversial regarding how this state should be defined. General anesthetics, however, typically elicit several key reversible effects: immobility, analgesia, amnesia, unconsciousness, and reduced autonomic responsiveness to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sleep Medicine
Sleep medicine is a medical specialty or subspecialty devoted to the diagnosis and therapy of sleep disturbances and disorders. From the middle of the 20th century, research has provided increasing knowledge of, and answered many questions about, sleep–wake functioning. The rapidly evolving field has become a recognized medical subspecialty in some countries. Dental sleep medicine also qualifies for board certification in some countries. Properly organized, minimum 12-month, postgraduate training programs are still being defined in the United States. In some countries, the sleep researchers and the physicians who treat patients may be the same people. The first sleep clinics in the United States were established in the 1970s by interested physicians and technicians; the study, diagnosis and treatment of obstructive sleep apnea were their first tasks. As late as 1999, virtually any American physician, with no specific training in sleep medicine, could open a sleep laborator ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sevoflurane
Sevoflurane, sold under the brand name Sevorane, among others, is a sweet-smelling, nonflammable, highly fluorinated methyl isopropyl ether used as an inhalational anaesthetic for induction and maintenance of general anesthesia. After desflurane, it is the volatile anesthetic with the fastest onset. While its offset may be faster than agents other than desflurane in a few circumstances, its offset is more often similar to that of the much older agent isoflurane. While sevoflurane is only half as soluble as isoflurane in blood, the tissue blood partition coefficients of isoflurane and sevoflurane are quite similar. For example, in the muscle group: isoflurane 2.62 vs. sevoflurane 2.57. In the fat group: isoflurane 52 vs. sevoflurane 50. As a result, the longer the case, the more similar will be the emergence times for sevoflurane and isoflurane. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical uses It is one of the most commonly used volatile a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
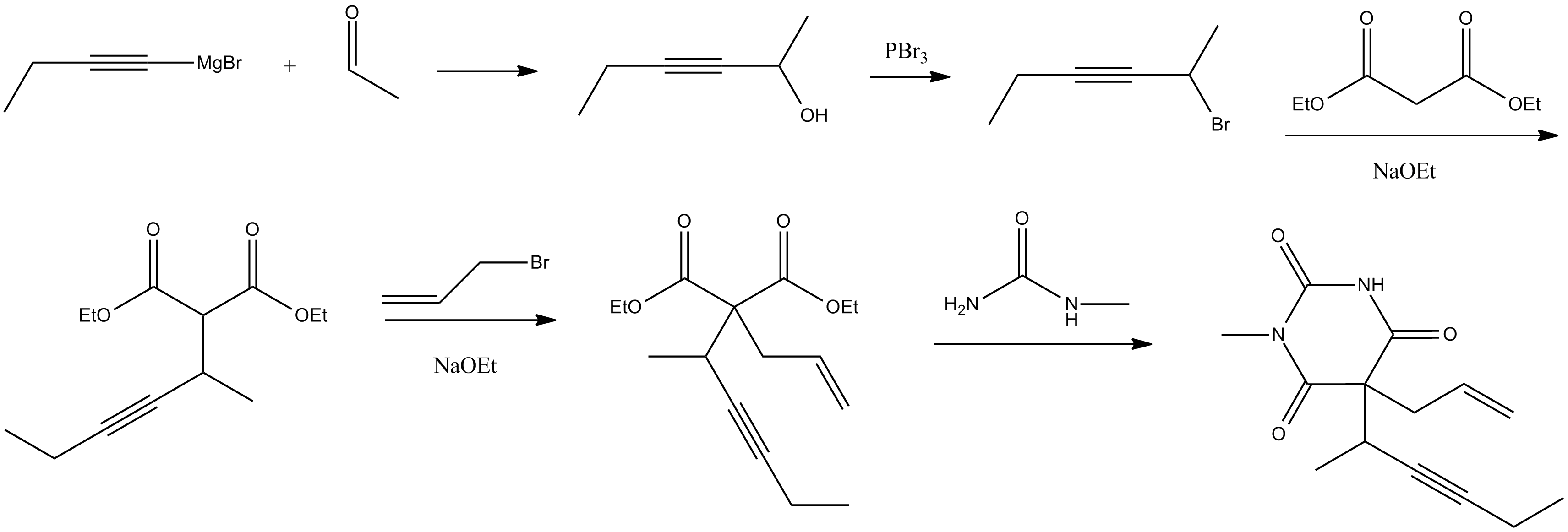
Thiopentone
Sodium thiopental, also known as Sodium Pentothal (a trademark of Abbott Laboratories), thiopental, thiopentone, or Trapanal (also a trademark), is a rapid-onset short-acting barbiturate general anesthetic. It is the thiobarbiturate analog of pentobarbital, and an analog of thiobarbital. Sodium thiopental was a core medicine in the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, but was supplanted by propofol. Despite this, thiopental is listed as an acceptable alternative to propofol, depending on local availability and cost of these agents. It was the first of three drugs administered during most lethal injections in the United States until the US division of Hospira objected and stopped manufacturing the drug in 2011, and the European Union banned the export of the drug for this purpose. Although thiopental abuse carries a dependency risk, its recreational use is rare. Sodium thiopental is well-known in popular culture, especially under the name "sodium pent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methohexital
Methohexital or methohexitone (marketed under the brand names Brevital and Brietal) is a drug which is a barbiturate derivative. It is classified as short-acting, and has a rapid onset of action. It is similar in its effects to sodium thiopental, a drug with which it competed in the market for anesthetics. Pharmacology Methohexital binds to a distinct site which is associated with Cl− ionophores at GABAA receptors. This increases the length of time which the Cl− ionopores are open, thus causing an Inhibitory postsynaptic potential, inhibitory effect. Metabolism of methohexital is primarily hepatic via demethylation and oxidation. Side-chain oxidation is the primary means of metabolism involved in the termination of the drug's biological activity. Indications Methohexital is primarily used to induce anesthesia, and is generally provided as a sodium salt (i.e. methohexital sodium). It is only used in hospital or similar settings, under strict supervision. It has been commonl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbiturate
Barbiturates are a class of depressant, depressant drugs that are chemically derived from barbituric acid. They are effective when used medication, medically as anxiolytics, hypnotics, and anticonvulsants, but have physical and psychological addiction potential as well as overdose potential among other possible adverse effects. They have been recreational drug use, used recreationally for their anti-anxiety and sedative effects, and are thus prohibition of drugs, controlled in most countries due to the risks associated with such use. Barbiturates have largely been replaced by benzodiazepines and nonbenzodiazepines ("Z-drugs") in routine medical practice, particularly in the treatment of anxiety disorders and insomnia, because of the significantly lower risk of overdose, and the lack of an antidote for barbiturate overdose. Despite this, barbiturates are still in use for various purposes: in general anesthesia, epilepsy, treatment of acute migraines or cluster headaches, acute t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etomidate
Etomidate (United States Adopted Name, USAN, International Nonproprietary Name, INN, British Approved Name, BAN; marketed as Amidate) is a short-acting intravenous anaesthetic agent used for the induction of general anaesthesia and sedation for short procedures such as reduction of dislocated joints, tracheal intubation, cardioversion and electroconvulsive therapy. It was developed at Janssen Pharmaceutica in 1964 and was introduced as an intravenous agent in 1972 in Europe and in 1983 in the United States. The most common side effects include venous pain on injection and skeletal muscle movements. Medical uses Sedation and anesthesia In emergency settings, etomidate can be used as a sedative hypnotic agent. It is used for conscious sedation and as a part of a rapid sequence induction to induce anaesthesia. It is used as an anaesthetic agent since it has a rapid onset of action and a safe cardiovascular risk profile, and therefore is less likely to cause a significant drop in b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propofol
Propofol is the active component of an intravenous anesthetic formulation used for induction and maintenance of general anesthesia. It is chemically termed 2,6-diisopropylphenol. The formulation was approved under the brand name Diprivan. Numerous generic versions have since been released. Intravenous administration is used to induce unconsciousness after which anesthesia may be maintained using a combination of medications. It is manufactured as part of a sterile injectable emulsion formulation using soybean oil and lecithin, giving it a white milky coloration. Recovery from propofol-induced anesthesia is generally rapid and associated with less frequent side effects (e.g., drowsiness, nausea, vomiting) compared to other anesthetic agents. Propofol may be used prior to diagnostic procedures requiring anesthesia, in the management of refractory status epilepticus, and for induction or maintenance of anesthesia prior to and during surgeries. It may be administered as a bolus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subcutaneous Injection
Subcutaneous administration is the insertion of medications beneath the skin either by injection or infusion. A subcutaneous injection is administered as a bolus (medicine), bolus into the subcutis, the layer of skin directly below the dermis and Epidermis (skin), epidermis, collectively referred to as the Cutis (anatomy), cutis. The instruments are usually a hypodermic needle and a syringe. Subcutaneous injections are highly effective in administering medications such as insulin, morphine, heroin, diacetylmorphine and goserelin. Subcutaneous administration may be List of medical abbreviations, abbreviated as SC, SQ, subcu, sub-Q, SubQ, or subcut. Subcut is the preferred abbreviation to reduce the risk of misunderstanding and potential errors. Subcutaneous tissue has few blood vessels and so drugs injected into it are intended for slow, sustained rates of absorption, often with some amount of depot injection, depot effect. Compared with other route of administration, routes of ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intravenous Injection
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrients for those who cannot, or will not—due to reduced mental states or otherwise—consume food or water by mouth. It may also be used to administer medications or other medical therapy such as blood products or electrolytes to correct electrolyte imbalances. Attempts at providing intravenous therapy have been recorded as early as the 1400s, but the practice did not become widespread until the 1900s after the development of techniques for safe, effective use. The intravenous route is the fastest way to deliver medications and fluid replacement throughout the body as they are introduced directly into the circulatory system and thus quickly distributed. For this reason, the intravenous route of administration is also used for the consump ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenon
Xenon is a chemical element; it has symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is a dense, colorless, odorless noble gas found in Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts. Although generally unreactive, it can undergo a few chemical reactions such as the formation of xenon hexafluoroplatinate, the first noble gas compound to be synthesized. Xenon is used in flash lamps and arc lamps, and as a general anesthetic. The first excimer laser design used a xenon dimer molecule (Xe2) as the lasing medium, and the earliest laser designs used xenon flash lamps as pumps. Xenon is also used to search for hypothetical weakly interacting massive particles and as a propellant for ion thrusters in spacecraft. Naturally occurring xenon consists of seven stable isotopes and two long-lived radioactive isotopes. More than 40 unstable xenon isotopes undergo radioactive decay, and the isotope ratios of xenon are an important tool for studying the early history of the Solar System. Radioactive xe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methoxyflurane
Methoxyflurane, sold under the brand name Penthrox among others, is an inhaled medication primarily used to reduce pain following trauma. It may also be used for short episodes of pain as a result of medical procedures. Onset of pain relief is rapid and of a short duration. Use is only recommended with direct medical supervision. Common side effects include anxiety, headache, sleepiness, cough, and nausea. Serious side effects may include kidney problems, liver problems, low blood pressure, and malignant hyperthermia. It is unclear if it is safe in either pregnancy or breastfeeding. It is only recommended in those who have a normal level of consciousness and stable blood pressure and heart rate. It is classified as a volatile anaesthetic. It was first made in 1948 by William T. Miller and came into medical use in the 1960s. It was used as a general anesthetic from its introduction in 1960 until the late 1970s. In 1999, the manufacturer discontinued methoxyflurane in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enflurane
Enflurane (2-chloro-1,1,2-trifluoroethyl difluoromethyl ether) is a halogenated ether. Developed by Ross Terrell in 1963, it was first used clinically in 1966. It was increasingly used for inhalational anesthesia during the 1970s and 1980s but is no longer in common use. Enflurane is a structural isomer of isoflurane. It vaporizes readily, but is a liquid at room temperature. Physical properties Pharmacology The exact mechanism of the action of general anaesthetics has not been delineated. Enflurane acts as a positive allosteric modulator of the GABAA, glycine, and 5-HT3 receptors, and as a negative allosteric modulator of the AMPA, kainate, and NMDA receptors, as well as of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Side effects Clinically, enflurane produces a dose-related depression of myocardial contractility with an associated decrease in myocardial oxygen consumption. Between 2% and 5% of the inhaled dose is oxidised in the liver, producing fluoride ions and difluoro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |