History Of USDA Nutrition Guides on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The history of USDA nutrition guidelines includes over 100 years of
 In 1943, during
In 1943, during
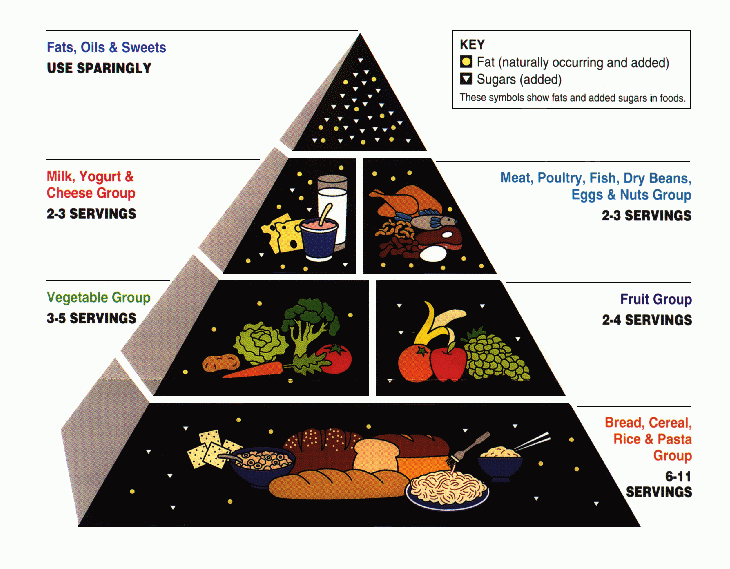 The introduction of the USDA's food guide pyramid in 1992 attempted to express the recommended servings of each food group, which previous guides did not do. 6 to 11 servings of bread, cereal, rice and pasta occupied the large base of the pyramid; followed by 3 to 5 servings of vegetables; then fruits (2 to 4); then milk, yogurt and cheese (2 to 3); followed by meat, poultry, fish, dry beans, eggs, and nuts (2 to 3); and finally fats, oils and sweets in the small apex (to be used sparingly). Inside each group were several images of representative foods, as well as symbols representing the fat and sugar contents of the foods.
A modified food pyramid was proposed for adults aged over 70. This "Modified Food Pyramid for 70+ Adults" accounted for changing diets with age by emphasizing water consumption as well as nutrient-dense and high-fiber foods.
The introduction of the USDA's food guide pyramid in 1992 attempted to express the recommended servings of each food group, which previous guides did not do. 6 to 11 servings of bread, cereal, rice and pasta occupied the large base of the pyramid; followed by 3 to 5 servings of vegetables; then fruits (2 to 4); then milk, yogurt and cheese (2 to 3); followed by meat, poultry, fish, dry beans, eggs, and nuts (2 to 3); and finally fats, oils and sweets in the small apex (to be used sparingly). Inside each group were several images of representative foods, as well as symbols representing the fat and sugar contents of the foods.
A modified food pyramid was proposed for adults aged over 70. This "Modified Food Pyramid for 70+ Adults" accounted for changing diets with age by emphasizing water consumption as well as nutrient-dense and high-fiber foods.
 In 2005, the USDA updated its guide with
In 2005, the USDA updated its guide with
 MyPlate is the current nutrition guide published by the
MyPlate is the current nutrition guide published by the
nutrition
Nutrition is the biochemistry, biochemical and physiology, physiological process by which an organism uses food and water to support its life. The intake of these substances provides organisms with nutrients (divided into Macronutrient, macro- ...
advice promulgated by the USDA (United States Department of Agriculture
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is an executive department of the United States federal government that aims to meet the needs of commercial farming and livestock food production, promotes agricultural trade and producti ...
). The guidelines have been updated over time, to adopt new scientific findings and new public health marketing techniques. The current guidelines are the Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2020–2025. The 2015–2020 guidelines were criticized as not accurately representing scientific information about optimal nutrition, and as being overly influenced by the agricultural industries the USDA promotes.
Earliest guides
The USDA's first nutrition guidelines were published in 1894 by Dr. Wilbur Olin Atwater as a farmers' bulletin. In Atwater's 1904 publication titled ''Principles of Nutrition and Nutritive Value of Food,'' he advocated variety, proportionality and moderation; measuringcalories
The calorie is a unit of energy that originated from the caloric theory of heat. The large calorie, food calorie, dietary calorie, kilocalorie, or kilogram calorie is defined as the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of one liter o ...
; and an efficient, affordable diet that focused on nutrient-rich foods and less fat, sugar and starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diet ...
. This information preceded the discovery of individual vitamin
Vitamins are Organic compound, organic molecules (or a set of closely related molecules called vitamer, vitamers) that are essential to an organism in small quantities for proper metabolism, metabolic function. Nutrient#Essential nutrients, ...
s beginning in 1910.
A new guide in 1916, ''Food for Young Children'' by nutritionist Caroline Hunt, categorized foods into milk and meat; cereals; vegetables and fruits; fats and fatty foods; and sugars and sugary foods. ''How to Select Food'' in 1917 promoted these five food groups to adults, and the guidelines remained in place through the 1920s. In 1933, the USDA introduced food plans at four different cost levels in response to the Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe global economic downturn from 1929 to 1939. The period was characterized by high rates of unemployment and poverty, drastic reductions in industrial production and international trade, and widespread bank and ...
.
In 1941, the first Recommended Dietary Allowances were created, listing specific intakes for calories
The calorie is a unit of energy that originated from the caloric theory of heat. The large calorie, food calorie, dietary calorie, kilocalorie, or kilogram calorie is defined as the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of one liter o ...
, protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
, iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
, calcium
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to it ...
, and vitamins A, B1, B2 B3, C and D.
Basic 7
 In 1943, during
In 1943, during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, the USDA introduced a nutrition guide promoting the "Basic 7" food groups to help maintain nutritional standards under wartime food rationing. The Basic 7 food groups were:
# Green and yellow vegetables (some raw; some cooked, frozen or canned)
# Oranges, tomatoes, grapefruit
The grapefruit (''Citrus'' × ''paradisi'') is a subtropical citrus tree known for its relatively large, sour to semi-sweet, somewhat bitter fruit. The flesh of the fruit is segmented and varies in color from pale yellow to dark red.
Grapefru ...
(or raw cabbage
Cabbage, comprising several cultivars of '' Brassica oleracea'', is a leafy green, red (purple), or white (pale green) biennial plant grown as an annual vegetable crop for its dense-leaved heads. It is descended from the wild cabbage ( ''B.& ...
or salad greens)
# Potatoes and other vegetables and fruits (raw, dried, cooked, frozen or canned)
# Milk and milk products (fluid, evaporated, dried milk, or cheese)
# Meat, poultry, fish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ...
, or eggs (or dried bean
A bean is the seed of some plants in the legume family (Fabaceae) used as a vegetable for human consumption or animal feed. The seeds are often preserved through drying (a ''pulse''), but fresh beans are also sold. Dried beans are traditi ...
s, peas, nuts, or peanut butter
Peanut butter is a food Paste (food), paste or Spread (food), spread made from Grinding (abrasive cutting), ground, dry roasting, dry-roasted peanuts. It commonly contains additional ingredients that modify the taste or texture, such as salt, ...
)
# Bread, flour, and cereals (natural whole grain
A whole grain is a grain of any cereal and pseudocereal that contains the endosperm, germ, and bran, in contrast to refined grains, which retain only the endosperm.
As part of a general healthy diet, consumption of whole grains is associated ...
, or enriched or restored)
# Butter and fortified margarine
Margarine (, also , ) is a Spread (food), spread used for flavoring, baking, and cooking. It is most often used as a substitute for butter. Although originally made from animal fats, most margarine consumed today is made from vegetable oil. The ...
(with added Vitamin A)
Basic Four
From 1956 until 1992 the United States Department of Agriculture recommended its "Basic Four" food groups. These food groups were: * milk * meat * fruit and vegetables * bread and cereals "Other foods" were said to round out meals and satisfy appetites. These included additional servings from the Basic Four, or foods such as butter, margarine, salad dressing andcooking oil
Cooking oil (also known as edible oil) is a plant or animal liquid fat used in frying, baking, and other types of cooking. Oil allows higher cooking temperatures than water, making cooking faster and more flavorful, while likewise distributing h ...
, sauce
In cooking, a sauce is a liquid, cream, or semi- solid food, served on or used in preparing other foods. Most sauces are not normally consumed by themselves; they add flavour, texture, and visual appeal to a dish. ''Sauce'' is a French wor ...
s, jellies and syrup
In cooking, syrup (less commonly sirup; from ; , beverage, wine and ) is a condiment that is a thick, viscous liquid consisting primarily of a Solution (chemistry), solution of sugar in water, containing a large amount of dissolved sugars but ...
s.
The Basic Four guide was omnipresent in nutrition education in the United States
The United States does not have a national or federal educational system. Although there are more than fifty independent systems of education (one run by each U.S. state, state and Territories of the United States, territory, the Bureau of In ...
. A notable example is the 1972 series ''Mulligan Stew'', providing nutrition education for schoolchildren in reruns until 1981.
Food Guide Pyramid
 The introduction of the USDA's food guide pyramid in 1992 attempted to express the recommended servings of each food group, which previous guides did not do. 6 to 11 servings of bread, cereal, rice and pasta occupied the large base of the pyramid; followed by 3 to 5 servings of vegetables; then fruits (2 to 4); then milk, yogurt and cheese (2 to 3); followed by meat, poultry, fish, dry beans, eggs, and nuts (2 to 3); and finally fats, oils and sweets in the small apex (to be used sparingly). Inside each group were several images of representative foods, as well as symbols representing the fat and sugar contents of the foods.
A modified food pyramid was proposed for adults aged over 70. This "Modified Food Pyramid for 70+ Adults" accounted for changing diets with age by emphasizing water consumption as well as nutrient-dense and high-fiber foods.
The introduction of the USDA's food guide pyramid in 1992 attempted to express the recommended servings of each food group, which previous guides did not do. 6 to 11 servings of bread, cereal, rice and pasta occupied the large base of the pyramid; followed by 3 to 5 servings of vegetables; then fruits (2 to 4); then milk, yogurt and cheese (2 to 3); followed by meat, poultry, fish, dry beans, eggs, and nuts (2 to 3); and finally fats, oils and sweets in the small apex (to be used sparingly). Inside each group were several images of representative foods, as well as symbols representing the fat and sugar contents of the foods.
A modified food pyramid was proposed for adults aged over 70. This "Modified Food Pyramid for 70+ Adults" accounted for changing diets with age by emphasizing water consumption as well as nutrient-dense and high-fiber foods.
MyPyramid
MyPyramid
MyPyramid, released by the United States Department of Agriculture, USDA Center for Nutrition Policy and Promotion on April 19, 2005, was an update on the earlier American food guide pyramid. It was used until June 2, 2011, when the USDA's MyPla ...
, which replaced the hierarchical levels of the Food Guide Pyramid with colorful vertical wedges, often displayed without images of foods, creating a more abstract design. Stairs were added up the left side of the pyramid with an image of a climber to represent a push for exercise. The share of the pyramid allotted to grains now only narrowly edged out vegetables and milk, which were of equal proportions. Fruits were next in size, followed by a narrower wedge for protein and a small sliver for oils. An unmarked white tip represented discretionary calories for items such as candy, alcohol, or additional food from any other group.
MyPlate
United States Department of Agriculture
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is an executive department of the United States federal government that aims to meet the needs of commercial farming and livestock food production, promotes agricultural trade and producti ...
, consisting of a diagram of a plate and glass divided into five food groups. It replaced the USDA's MyPyramid
MyPyramid, released by the United States Department of Agriculture, USDA Center for Nutrition Policy and Promotion on April 19, 2005, was an update on the earlier American food guide pyramid. It was used until June 2, 2011, when the USDA's MyPla ...
diagram on June 2, 2011, ending 19 years of food pyramid iconography. The diagram shows a plate divided into four wedges, with the two slightly larger ones representing vegetables and grains and the two slightly smaller ones representing protein and fruits, and with a circle adjacent to represent dairy (e.g. a glass of milk). The guide is displayed on food packaging and used in nutritional education in the United States.
Dietary Guidelines
The Center for Nutrition Policy and Promotion in the USDA and theUnited States Department of Health and Human Services
The United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) is a cabinet-level executive branch department of the US federal government created to protect the health of the US people and providing essential human services. Its motto is ...
jointly release a longer textual document called '' Dietary Guidelines for Americans. The first edition was published in 1980, and since 1985 has been updated every five years by the Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee. Like the USDA Food Pyramid, these guidelines have been criticized as being overly influenced by the agriculture industry.
These criticisms of the Dietary Guidelines arose due to the omission of high-quality evidence that the Public Health Service decided to exclude. The phrasing of recommendations was extremely important and widely affected everyone who read it. The wording had to be changed constantly as there were protests due to comments such as "cut down on fatty meats", which led to the U.S Department of Agriculture having to stop the publication of the USDA Food Book. Slight alterations of various dietary guidelines had to be made throughout the 1970s and 1980s in an attempt to calm down the protests emerged. As a compromise, the phrase was changed to "choose lean meat" but did not result in a better situation. In 2015 the committee factored in environmental sustainability for the first time in its recommendations. The committee's 2015 report found that a healthy diet should comprise higher plant based foods and lower animal based foods. It also found that a plant food based diet was better for the environment than one based on meat and dairy.
In 2013 and again in 2015, Edward Archer and colleagues published a series of research articles in PlosOne and Mayo Clinic Proceedings demonstrating that the dietary data used to develop the US Dietary Guidelines were physiologically implausible (i.e., incompatible with survival) and therefore these data were "inadmissible" as scientific evidence and should not be used to inform public policy.
The 2020–2025 guidelines were to be released in spring 2020.
Criticism and controversy
Overview of controversies
The USDA's Food Pyramid has been a focal point of contention, significantly highlighted in April 1991 when the publication of the "Eating Right Pyramid" was halted. This interruption came as a result of objections from meat and dairy lobbying groups displeased with the guide’s portrayal of their products. Although the USDA cited a need for further research and testing, it wasn't until a year later, backed by additional research, that the Eating Right Pyramid saw the light of day. Even then, adjustments were made to the guide’s graphic design to address industry concerns. This episode serves as a prime example of numerous instances where the food industry endeavored to modify federal dietary recommendations to suit their economic interests.Industry influence
The extent of industry influence over the years is well documented. The lobbying from meat and dairy industries has had a pronounced impact on the formulation and representation of the Food Pyramid. Instances where the design or content of the Food Pyramid was tweaked to assuage industry concerns are discussed in Marion Nestle's "Food Politics". The alteration of federal dietary guidelines to cater to industry interests highlights a long-standing issue of industry influence over public health recommendations.Impact on public perception
These controversies and the ensuing adjustments to the Food Pyramid have arguably cast a shadow on the public’s trust in USDA dietary guidelines. The ambiguity in the recommended quantities for different food types in the old pyramid also garnered criticism for lack of clarity. The transition from the Food Pyramid to MyPlate in 2011 could be seen as an attempt to mitigate these concerns and realign federal dietary guidelines with current nutritional science, although criticisms persist.Evolving guidelines
The controversies surrounding the Food Pyramid prompted the creation of alternative pyramids, like the Vegetarian Diet Pyramid. The successor to the Food Pyramid, MyPlate, also faced its share of criticisms, albeit it hasn't reached the same level of public recognition as the Food Pyramid, with a significant number of Americans unaware of the MyPlate dietary guideSee also
* List of nutrition guides * 5 A Day * Fruits & Veggies – More Matters *Nutrition facts label
The nutrition facts label (also known as the nutrition information panel, and other slight variations) is a label required on most convenience food, packaged food in many countries, showing what nutrients and other ingredients (to limit and get e ...
References
{{reflist Nutrition guides United States Department of Agriculture Publications of the United States government