|
List Of Nutrition Guides
This is a list of nutrition guides. A nutrition guide is a reference that provides nutrition advice for general health, typically by dividing foods into food groups and recommending servings of each group. Nutrition guides can be presented in written or visual form, and are commonly published by government agencies, health associations and university health departments. Some countries also have nutrition facts labels which are not listed here; many of those reference specific target amounts for various nutrients. Historical guides Ancient Greece The Hippocratic Corpus of Ancient Greece contains one of the earliest known nutrition guides. It recommends a seasonal diet. For winter, it advises eating a heavy diet of bread and roasted meat and fish, while avoiding vegetables and restricting liquids to, if anything, strong wine. It then recommends a lighter summer diet of soft barley cake, vegetables, boiled meat, and large quantities of diluted wine. Gradual transitions between th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reference
A reference is a relationship between objects in which one object designates, or acts as a means by which to connect to or link to, another object. The first object in this relation is said to ''refer to'' the second object. It is called a ''name'' for the second object. The next object, the one to which the first object refers, is called the '' referent'' of the first object. A name is usually a phrase or expression, or some other symbolic representation. Its referent may be anything – a material object, a person, an event, an activity, or an abstract concept. References can take on many forms, including: a thought, a sensory perception that is audible ( onomatopoeia), visual (text), olfactory, or tactile, emotional state, relationship with other, spacetime coordinates, symbolic or alpha-numeric, a physical object, or an energy projection. In some cases, methods are used that intentionally hide the reference from some observers, as in cryptography. References feature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tang Dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, c=唐朝), or the Tang Empire, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907, with an Wu Zhou, interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. Historians generally regard the Tang as a high point in Chinese civilisation, and a Golden age (metaphor), golden age of cosmopolitan culture. Tang territory, acquired through the military campaigns of its early rulers, rivalled that of the Han dynasty. The House of Li, Li family founded the dynasty after taking advantage of a period of Sui decline and precipitating their final collapse, in turn inaugurating a period of progress and stability in the first half of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty was formally interrupted during 690–705 when Empress Wu Zetian seized the throne, proclaiming the Wu Zhou dynasty and becoming the only legitimate Chinese empress regnant. The An Lushan rebellion (755 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vegetables
Vegetables are edible parts of plants that are consumed by humans or other animals as food. This original meaning is still commonly used, and is applied to plants collectively to refer to all edible plant matter, including flowers, fruits, stems, leaves, roots, and seeds. An alternative definition is applied somewhat arbitrarily, often by culinary and cultural tradition; it may include savoury fruits such as tomatoes and courgettes, flowers such as broccoli, and seeds such as pulses, but exclude foods derived from some plants that are fruits, flowers, nuts, and cereal grains. Originally, vegetables were collected from the wild by hunter-gatherers and entered cultivation in several parts of the world, probably during the period 10,000 BC to 7,000 BC, when a new agricultural way of life developed. At first, plants that grew locally were cultivated, but as time went on, trade brought common and exotic crops from elsewhere to add to domestic types. Nowadays, most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
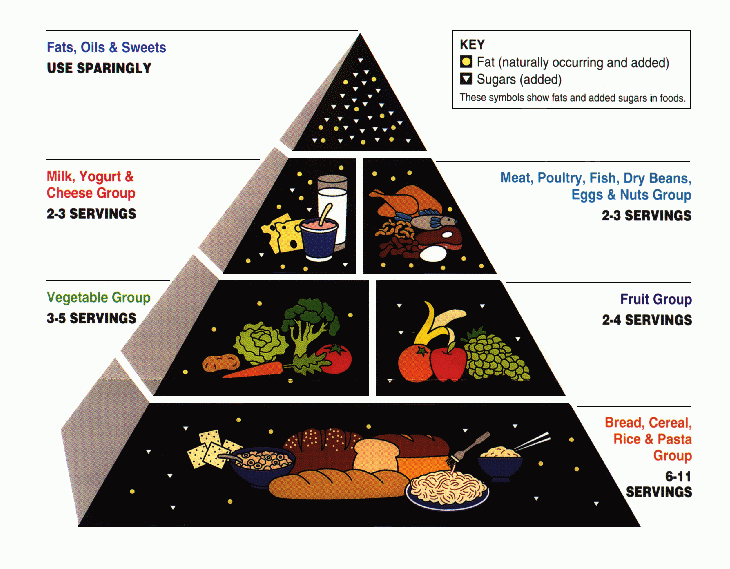
Food Guide Pyramid
A food pyramid is a representation of the optimal number of servings to be eaten each day from each of the basic food groups. The first pyramid was published in Sweden in 1974. The 1992 pyramid introduced by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) was called the "Food Guide Pyramid" or "Eating Right Pyramid". It was updated in 2005 to "MyPyramid", and then it was replaced by " MyPlate" in 2011. Swedish origin Amid high food prices in 1972, Sweden's National Board of Health and Welfare developed the idea of "basic foods" that were both cheap and nutritious, and "supplemental foods" that added nutrition missing from the basic foods. Anna-Britt Agnsäter, chief of the test kitchen for Kooperativa Förbundet (a cooperative Swedish retail chain), held a lecture the next year on how to illustrate these food groups. Attendee Fjalar Clemes suggested a triangle displaying basic foods at the base. Agnsäter developed the idea into the first food pyramid, which was introd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cooperative Federation
A cooperative federation or secondary cooperative is a cooperative in which all members are, in turn, cooperatives. Historically, cooperative federations have predominantly come in the form of cooperative wholesale societies and cooperative unions. Gide, Charles; as translated from French by the Cooperative Reference Library, Dublin, ''Consumers' Cooperative Societies'', Manchester: The Cooperative Union Limited, 1921, p. 122, Cooperative federations are a means through which cooperatives can fulfill the sixth Cooperative Principle, cooperation among cooperatives. The International Cooperative Alliance notes that ''“Cooperatives serve their members most effectively and strengthen the cooperative movement by working together through local, national, regional and international structures.”'' Retail According to cooperative economist Charles Gide, the aim of a cooperative wholesale society, which is owned by retail consumer cooperatives, is to arrange "bulk purchases, and, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kooperativa Förbundet
KF (, "Co-operative Union") is a federation of consumer co-operatives in Sweden and a retail group, with groceries as its core business. History KF was founded in 1899 by 41 local consumer co-operatives in order to support them with information and education of store managers and board members. Soon KF also became responsible for common procurement of goods. In the 1930s, KF expanded rapidly during the management of Albin Johansson, setting up various industries in order to support the co-operative grocery stores. From 1950 to 1970, KF was at the forefront of the Swedish retail trade by developing new and bigger store formats and it was one of the major business groups in Scandinavia. In the beginning of the 1990s, as a response to a financial crisis, KF decided to sell out all its industries and focus on retail trade only. Around the year 2000, KF formed the retail chain Coop Norden along with its Nordic co-operative counterparts, Danish FDB and Norwegian Coop NKL. In 2002, K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nutritious
Nutrition is the biochemical and physiological process by which an organism uses food and water to support its life. The intake of these substances provides organisms with nutrients (divided into macro- and micro-) which can be metabolized to create energy and chemical structures; too much or too little of an essential nutrient can cause malnutrition. Nutritional science, the study of nutrition as a hard science, typically emphasizes human nutrition. The type of organism determines what nutrients it needs and how it obtains them. Organisms obtain nutrients by consuming organic matter, consuming inorganic matter, absorbing light, or some combination of these. Some can produce nutrients internally by consuming basic elements, while some must consume other organisms to obtain pre-existing nutrients. All forms of life require carbon, energy, and water as well as various other molecules. Animals require complex nutrients such as carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins, obtaining the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Board Of Health And Welfare (Sweden)
The Swedish National Board of Health and Welfare () is a Swedish government agency. The agency was the result of a merger between the National Swedish Board of Health and the Swedish Royal Board of Social Affairs in 1968. , it is headed by director-general Björn Eriksson. The Board is the central national authority for social services and health services. The Board establishes norms by issuing provisions and general advice. It evaluates legislation and activities conducted by municipalities, county councils and local authorities. It also issues certificates of registration to 22 professional groups. Another responsibility are the official national statistics in the social services, medical care, and health and disease. Swedish Coronary Angiography and Angioplasty Register The Swedish Coronary Angiography and Angioplasty Register (SCAAR) is a national registry sponsored by the National Board of Health and Welfare that contains relevant medical data on consecutive pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic country by both area and population, and is the List of European countries by area, fifth-largest country in Europe. Its capital and largest city is Stockholm. Sweden has a population of 10.6 million, and a low population density of ; 88% of Swedes reside in urban areas. They are mostly in the central and southern half of the country. Sweden's urban areas together cover 1.5% of its land area. Sweden has a diverse Climate of Sweden, climate owing to the length of the country, which ranges from 55th parallel north, 55°N to 69th parallel north, 69°N. Sweden has been inhabited since Prehistoric Sweden, prehistoric times around 12,000 BC. The inhabitants emerged as the Geats () and Swedes (tribe), Swedes (), who formed part of the sea-faring peopl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beiji Qianjin Yaofang
''Beiji qianjin yaofang'' (), literally ''Essential Formulas Worth a Thousand in Gold for Emergencies'', is a Chinese medical text by Tang-dynasty physician Sun Simiao, first published in 652. A sequel was published in 682. Contents Comprising thirty '' juan'' or scrolls, the text is primarily focused on medical disorders and their remedies. The introduction discusses medical diagnosis and treatment, while laying out a moral code for physicians. The remaining twenty-nine ''juan'' pertain to, among other things, gynaecology; "wind-induced disorders"; diseases experienced by women and children; "disorders of the seven orifices"; disorders of '' qi''; "cold damage disorders"; "wasting thirst" and hemorrhoids; detoxification; acupuncture and moxibustion. Authorities cited in the text include Bian Que, Hua Tuo, Wang Shuhe, and Zhang Zhongjing. Uncharacteristically for medical texts of the time, ''Beiji qianjin yaofang'' also contains twenty-five case histories. According to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traditional Chinese Medicine
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is an alternative medicine, alternative medical practice drawn from traditional medicine in China. A large share of its claims are pseudoscientific, with the majority of treatments having no robust evidence of effectiveness or logical mechanism of action. Some TCM ingredients Traditional Chinese medicine#Safety, are known to be toxic and cause disease, including cancer. Medicine in traditional China encompassed a range of sometimes competing health and healing practices, folk beliefs, Scholar-official, literati theory and Confucianism, Confucian philosophy, Chinese herbology, herbal remedies, Chinese food therapy, food, diet, exercise, medical specializations, and schools of thought. TCM as it exists today has been described as a largely 20th century invention. In the early twentieth century, Chinese cultural and political modernizers worked to eliminate traditional practices as backward and unscientific. Traditional practitioners then selec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |