food guide pyramid on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A food pyramid is a representation of the optimal number of servings to be eaten each day from each of the basic food groups. The first pyramid was published in Sweden in 1974. The 1992 pyramid introduced by the
A food pyramid is a representation of the optimal number of servings to be eaten each day from each of the basic food groups. The first pyramid was published in Sweden in 1974. The 1992 pyramid introduced by the
 Amid high
Amid high
 All percentages are ''percentages of
All percentages are ''percentages of
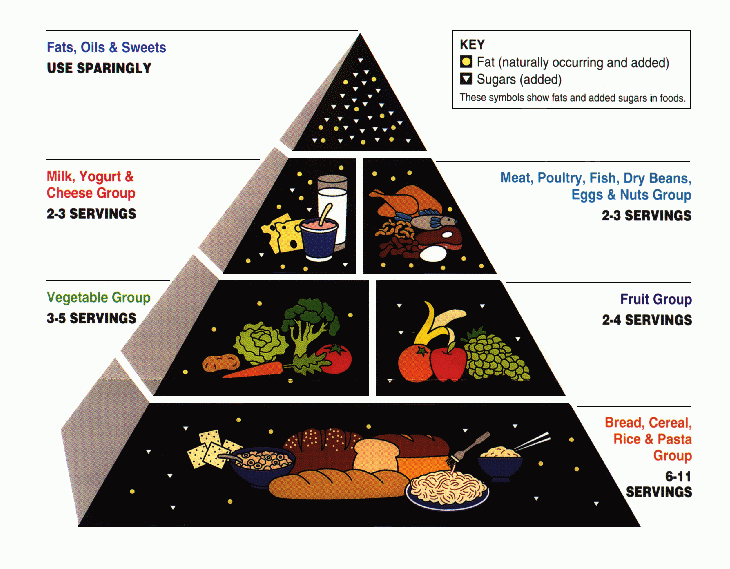
 The USDA food pyramid was created in 1992 and divided into six horizontal sections containing depictions of foods from each section's food group. It was updated in 2005 with black and white vertical wedges replacing the horizontal sections and renamed
The USDA food pyramid was created in 1992 and divided into six horizontal sections containing depictions of foods from each section's food group. It was updated in 2005 with black and white vertical wedges replacing the horizontal sections and renamed

 Certain dietary choices that have been linked to heart disease, such as an serving of hamburger daily, were technically permitted under the pyramid. The pyramid also lacked differentiation within the protein-rich group ("Meat, Poultry, Fish, Dry Beans, Eggs, and Nuts"). The development of the US food pyramid has been influenced by food lobbyists undermining its credibility.
In April 1991, the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) halted publication of its Eating Right Pyramid, due to objections raised by meat and dairy lobbying groups concerning the guide’s display of their products. Despite the USDA’s explanations that the guide required further research and testing, it was not until one year later—after its content was supported by additional research—that the Eating Right Pyramid was officially released. This time, even the guide’s graphic design was altered to appease industry concerns. This incident was only one of many in which the food industry attempted to alter federal dietary recommendations in their own economic self-interest.
Some of the recommended quantities for the different types of food in the old pyramid have also come under criticism for lack of clarity. For instance, the pyramid recommends two to three servings from the protein-rich group, but this is intended to be a maximum. The pyramid recommends two to four fruit servings, but this is intended to be the minimum.
The fats group as a whole have been put at the tip of the pyramid, under the direction to eat as little as possible, which some people have considered problematic. The guide instructs people to limit fat intake as much as possible, which can cause health problems because fat is essential to overall health. Research suggests that
Certain dietary choices that have been linked to heart disease, such as an serving of hamburger daily, were technically permitted under the pyramid. The pyramid also lacked differentiation within the protein-rich group ("Meat, Poultry, Fish, Dry Beans, Eggs, and Nuts"). The development of the US food pyramid has been influenced by food lobbyists undermining its credibility.
In April 1991, the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) halted publication of its Eating Right Pyramid, due to objections raised by meat and dairy lobbying groups concerning the guide’s display of their products. Despite the USDA’s explanations that the guide required further research and testing, it was not until one year later—after its content was supported by additional research—that the Eating Right Pyramid was officially released. This time, even the guide’s graphic design was altered to appease industry concerns. This incident was only one of many in which the food industry attempted to alter federal dietary recommendations in their own economic self-interest.
Some of the recommended quantities for the different types of food in the old pyramid have also come under criticism for lack of clarity. For instance, the pyramid recommends two to three servings from the protein-rich group, but this is intended to be a maximum. The pyramid recommends two to four fruit servings, but this is intended to be the minimum.
The fats group as a whole have been put at the tip of the pyramid, under the direction to eat as little as possible, which some people have considered problematic. The guide instructs people to limit fat intake as much as possible, which can cause health problems because fat is essential to overall health. Research suggests that
 MyPlate is the current nutrition guide published by the United States Department of Agriculture, depicting a place setting with a plate and glass divided into five food groups. It replaced the USDA's
MyPlate is the current nutrition guide published by the United States Department of Agriculture, depicting a place setting with a plate and glass divided into five food groups. It replaced the USDA's
USDA Dietary Guidelines
Tufts Researchers Update Their Food Guide Pyramid for Older Adults
U.S. Food Guide Pyramid Compared to Others
{{DEFAULTSORT:Food Guide Pyramid Symbols introduced in 1974
 A food pyramid is a representation of the optimal number of servings to be eaten each day from each of the basic food groups. The first pyramid was published in Sweden in 1974. The 1992 pyramid introduced by the
A food pyramid is a representation of the optimal number of servings to be eaten each day from each of the basic food groups. The first pyramid was published in Sweden in 1974. The 1992 pyramid introduced by the United States Department of Agriculture
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is an executive department of the United States federal government that aims to meet the needs of commercial farming and livestock food production, promotes agricultural trade and producti ...
(USDA) was called the "Food Guide Pyramid" or "Eating Right Pyramid". It was updated in 2005 to "MyPyramid
MyPyramid, released by the United States Department of Agriculture, USDA Center for Nutrition Policy and Promotion on April 19, 2005, was an update on the earlier American food guide pyramid. It was used until June 2, 2011, when the USDA's MyPla ...
", and then it was replaced by " MyPlate" in 2011.
Swedish origin
 Amid high
Amid high food prices
Food prices refer to the average price level for food across countries, regions and on a global scale. Food prices affect producers and consumers of food. Price levels depend on the food production process, including food marketing and food di ...
in 1972, Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
's National Board of Health and Welfare developed the idea of "basic foods" that were both cheap and nutritious, and "supplemental foods" that added nutrition missing from the basic foods. Anna-Britt Agnsäter, chief of the test kitchen for Kooperativa Förbundet
KF (, "Co-operative Union") is a federation of consumer co-operatives in Sweden and a retail group, with groceries as its core business.
History
KF was founded in 1899 by 41 local consumer co-operatives in order to support them with informatio ...
(a cooperative Swedish retail chain), held a lecture the next year on how to illustrate these food groups. Attendee Fjalar Clemes suggested a triangle displaying basic foods at the base. Agnsäter developed the idea into the first food pyramid, which was introduced to the public in 1974 in KF's '' Vi'' magazine. The pyramid was divided into basic foods at the base, including milk
Milk is a white liquid food produced by the mammary glands of lactating mammals. It is the primary source of nutrition for young mammals (including breastfeeding, breastfed human infants) before they are able to digestion, digest solid food. ...
, cheese
Cheese is a type of dairy product produced in a range of flavors, textures, and forms by coagulation of the milk protein casein. It comprises proteins and fat from milk (usually the milk of cows, buffalo, goats or sheep). During prod ...
, margarine
Margarine (, also , ) is a Spread (food), spread used for flavoring, baking, and cooking. It is most often used as a substitute for butter. Although originally made from animal fats, most margarine consumed today is made from vegetable oil. The ...
, bread
Bread is a baked food product made from water, flour, and often yeast. It is a staple food across the world, particularly in Europe and the Middle East. Throughout recorded history and around the world, it has been an important part of many cu ...
, cereals
A cereal is a grass cultivated for its edible grain. Cereals are the world's largest crops, and are therefore staple foods. They include rice, wheat, rye, oats, barley, millet, and maize (Corn). Edible grains from other plant families, suc ...
and potato
The potato () is a starchy tuberous vegetable native to the Americas that is consumed as a staple food in many parts of the world. Potatoes are underground stem tubers of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'', a perennial in the nightshade famil ...
; a large section of supplemental vegetables and fruit; and an apex of supplemental meat
Meat is animal Tissue (biology), tissue, often muscle, that is eaten as food. Humans have hunted and farmed other animals for meat since prehistory. The Neolithic Revolution allowed the domestication of vertebrates, including chickens, sheep, ...
, fish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ...
and egg
An egg is an organic vessel grown by an animal to carry a possibly fertilized egg cell (a zygote) and to incubate from it an embryo within the egg until the embryo has become an animal fetus that can survive on its own, at which point the ...
. The pyramid competed with the National Board's "dietary circle", which KF saw as problematic for resembling a cake divided into seven slices, and for not indicating how much of each food should be eaten. While the Board distanced itself from the pyramid, KF continued to promote it.
Food pyramids were developed in other Scandinavia
Scandinavia is a subregion#Europe, subregion of northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. It can sometimes also ...
n countries, as well as West Germany
West Germany was the common English name for the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) from its formation on 23 May 1949 until German reunification, its reunification with East Germany on 3 October 1990. It is sometimes known as the Bonn Republi ...
, Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
and Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
. The United States later developed its first food pyramid in 1992.
Food pyramid published by the WHO and FAO
TheWorld Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
, in conjunction with the Food and Agriculture Organization, published guidelines that can be effectively represented in a food pyramid relating to objectives in order to prevent obesity, improper nutrition, chronic diseases and dental caries based on meta-analysis though they represent it as a table rather than as a "pyramid". The structure is similar in some respects to the USDA food pyramid, but there are clear distinctions between types of fats, and a more dramatic distinction where carbohydrates are categorized on the basis of free sugars versus sugars in their natural form. Some food substances are singled out due to the impact on the target issues that the "pyramid" is meant to address. In a later revision, however, some recommendations are omitted as they automatically follow other recommendations while other sub-categories are added. The reports quoted here explain that where there is no stated lower limit in the table below, there is ''no'' requirement for that nutrient in the diet.
 All percentages are ''percentages of
All percentages are ''percentages of calories
The calorie is a unit of energy that originated from the caloric theory of heat. The large calorie, food calorie, dietary calorie, kilocalorie, or kilogram calorie is defined as the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of one liter o ...
'', not of weight or volume. To understand why, consider the determination of an amount of "10% free sugar" to include in a day's worth of calories. For the same amount of calories, free sugars take up less volume and weight, being refined and extracted ''from the competing carbohydrates in their natural form''. In a similar manner, all the items are in competition for various categories of calories.
The representation as a pyramid is not precise, and involves variations due to the alternative percentages of different elements, but the main sections can be represented.
USDA food pyramid
History
MyPyramid
MyPyramid, released by the United States Department of Agriculture, USDA Center for Nutrition Policy and Promotion on April 19, 2005, was an update on the earlier American food guide pyramid. It was used until June 2, 2011, when the USDA's MyPla ...
. MyPyramid was often displayed with the food images absent, creating a more abstract design.
In an effort to restructure food nutrition guidelines, the USDA rolled out its new MyPlate program in June 2011. My Plate is divided into four slightly different sized quadrants, with fruits and vegetables taking up half the space, and grains and protein making up the other half. The vegetables and grains portions are the largest of the four.
A modified food pyramid was proposed in 1999 for adults aged over 70.
Vegetables
Avegetable
Vegetables are edible parts of plants that are consumed by humans or other animals as food. This original meaning is still commonly used, and is applied to plants collectively to refer to all edible plant matter, including edible flower, flo ...
is a part of a plant consumed by humans that is generally savory but is not sweet. A vegetable is not considered a grain, fruit, nut, spice
In the culinary arts, a spice is any seed, fruit, root, Bark (botany), bark, or other plant substance in a form primarily used for flavoring or coloring food. Spices are distinguished from herbs, which are the leaves, flowers, or stems of pl ...
, or herb
Herbs are a widely distributed and widespread group of plants, excluding vegetables, with savory or aromatic properties that are used for flavoring and garnishing food, for medicinal purposes, or for fragrances. Culinary use typically distingu ...
. For example, the stem
Stem or STEM most commonly refers to:
* Plant stem, a structural axis of a vascular plant
* Stem group
* Science, technology, engineering, and mathematics
Stem or STEM can also refer to:
Language and writing
* Word stem, part of a word respon ...
, root
In vascular plants, the roots are the plant organ, organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often bel ...
, flower
Flowers, also known as blooms and blossoms, are the reproductive structures of flowering plants ( angiosperms). Typically, they are structured in four circular levels, called whorls, around the end of a stalk. These whorls include: calyx, m ...
, etc., may be eaten as vegetables. Vegetables contain many vitamin
Vitamins are Organic compound, organic molecules (or a set of closely related molecules called vitamer, vitamers) that are essential to an organism in small quantities for proper metabolism, metabolic function. Nutrient#Essential nutrients, ...
s and minerals
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid substance with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2011): M ...
; however, different vegetables contain different balances of micronutrients, so it is important to eat a wide variety of types. For example, orange and dark green vegetables typically contain vitamin A
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin that is an essential nutrient. The term "vitamin A" encompasses a group of chemically related organic compounds that includes retinol, retinyl esters, and several provitamin (precursor) carotenoids, most not ...
, dark green vegetables contain vitamin C
Vitamin C (also known as ascorbic acid and ascorbate) is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits, berries and vegetables. It is also a generic prescription medication and in some countries is sold as a non-prescription di ...
, and vegetables like broccoli and related plants contain iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
and calcium
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to it ...
. Vegetables are very low in fat
In nutrition science, nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such chemical compound, compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.
The term often refers specif ...
s and calorie
The calorie is a unit of energy that originated from the caloric theory of heat. The large calorie, food calorie, dietary calorie, kilocalorie, or kilogram calorie is defined as the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of one liter o ...
s, but ingredients added in preparation can often add them.
Grains
These foods provide complexcarbohydrates
A carbohydrate () is a biomolecule composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms. The typical hydrogen-to-oxygen atomic ratio is 2:1, analogous to that of water, and is represented by the empirical formula (where ''m'' and ''n'' ma ...
, which are the body's primary source of energy and provide quality nutrition in any case. Examples include corn
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout Poaceae, grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples of Mexico, indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago ...
, wheat
Wheat is a group of wild and crop domestication, domesticated Poaceae, grasses of the genus ''Triticum'' (). They are Agriculture, cultivated for their cereal grains, which are staple foods around the world. Well-known Taxonomy of wheat, whe ...
, pasta
Pasta (, ; ) is a type of food typically made from an Leavening agent, unleavened dough of wheat flour mixed with water or Eggs as food, eggs, and formed into sheets or other shapes, then cooked by boiling or baking. Pasta was originally on ...
, and rice
Rice is a cereal grain and in its Domestication, domesticated form is the staple food of over half of the world's population, particularly in Asia and Africa. Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice)—or, much l ...
. Grains, when digested, break down into glucose, the body's preferred energy source. Complex carbohydrates also provide dietary fiber
Dietary fiber (fibre in English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English) or roughage is the portion of plant-derived food that cannot be completely broken down by human digestive enzymes. Dietary fibers are diverse in chemical co ...
, which supports digestive health and lowers the risk of heart disease.
Fruits
In terms of food (rather than botany),fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants (angiosperms) that is formed from the ovary after flowering.
Fruits are the means by which angiosperms disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particular have long propaga ...
s are the sweet-tasting seed
In botany, a seed is a plant structure containing an embryo and stored nutrients in a protective coat called a ''testa''. More generally, the term "seed" means anything that can be Sowing, sown, which may include seed and husk or tuber. Seeds ...
-bearing parts of plants, or occasionally sweet parts of plants which do not bear seeds.
These include apple
An apple is a round, edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus'' spp.). Fruit trees of the orchard or domestic apple (''Malus domestica''), the most widely grown in the genus, are agriculture, cultivated worldwide. The tree originated ...
s, oranges, grape
A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus ''Vitis''. Grapes are a non- climacteric type of fruit, generally occurring in clusters.
The cultivation of grapes began approximately 8,0 ...
s, banana
A banana is an elongated, edible fruit – botanically a berry – produced by several kinds of large treelike herbaceous flowering plants in the genus '' Musa''. In some countries, cooking bananas are called plantains, distinguishing the ...
s, etc. Fruits are low in calories and fat and are a source of natural sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecul ...
s, fiber
Fiber (spelled fibre in British English; from ) is a natural or artificial substance that is significantly longer than it is wide. Fibers are often used in the manufacture of other materials. The strongest engineering materials often inco ...
and vitamins. Processing fruit when canning
Canning is a method of food preservation in which food is processed and sealed in an airtight container (jars like Mason jars, and steel and tin cans). Canning provides a shelf life that typically ranges from one to five years, although under ...
or making into juice
Juice is a drink made from the extraction or Cold-pressed juice, pressing of the natural liquid contained in fruit and vegetables. It can also refer to liquids that are flavored with concentrate or other biological food sources, such as meat ...
s may add sugars and remove nutrients. The fruit food group is sometimes combined with the vegetable food group. Note that a massive number of different plant species produce seed pods which are considered fruits in botany, and there are a number of botanical fruits which are conventionally not considered fruits in cuisine
A cuisine is a style of cooking characterized by distinctive ingredients, List of cooking techniques, techniques and Dish (food), dishes, and usually associated with a specific culture or geographic region. Regional food preparation techniques, ...
because they lack the characteristic sweet taste, e.g., tomato
The tomato (, ), ''Solanum lycopersicum'', is a plant whose fruit is an edible Berry (botany), berry that is eaten as a vegetable. The tomato is a member of the nightshade family that includes tobacco, potato, and chili peppers. It originate ...
es or avocado
The avocado, alligator pear or avocado pear (''Persea americana'') is an evergreen tree in the laurel family (Lauraceae). It is native to Americas, the Americas and was first domesticated in Mesoamerica more than 5,000 years ago. It was priz ...
s.
Dairy
Dairy product
Dairy products or milk products are food products made from (or containing) milk. The most common dairy animals are cow, water buffalo, goat, nanny goat, and Sheep, ewe. Dairy products include common grocery store food around the world such as y ...
s are produced from the milk
Milk is a white liquid food produced by the mammary glands of lactating mammals. It is the primary source of nutrition for young mammals (including breastfeeding, breastfed human infants) before they are able to digestion, digest solid food. ...
of animals, usually but not exclusively cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, bovid ungulates widely kept as livestock. They are prominent modern members of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus '' Bos''. Mature female cattle are calle ...
. They include milk, yogurt
Yogurt (; , from , ; also spelled yoghurt, yogourt or yoghourt) is a food produced by bacterial Fermentation (food), fermentation of milk. Fermentation of sugars in the milk by these bacteria produces lactic acid, which acts on milk protein to ...
and cheese
Cheese is a type of dairy product produced in a range of flavors, textures, and forms by coagulation of the milk protein casein. It comprises proteins and fat from milk (usually the milk of cows, buffalo, goats or sheep). During prod ...
. Milk and its derivative products are a rich source of dietary calcium and also provide protein, phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol P and atomic number 15. All elemental forms of phosphorus are highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive and are therefore never found in nature. They can nevertheless be prepared ar ...
, vitamin A, and vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of structurally related, fat-soluble compounds responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, along with numerous other biological functions. In humans, the most important compo ...
. However, many dairy products are high in saturated fat and cholesterol compared to vegetables, fruits and whole grains, which is why skimmed products are available as an alternative.
Historically, adults were recommended to consume three cups of dairy products per day. More recently, evidence is mounting that dairy products have greater levels of negative effects on health than previously thought and confer fewer benefits. For example, recent research has shown that dairy products are not related to stronger bones or less fractures; on the contrary, another study showed that milk (and yogurt) consumption results in higher bone mineral density in the hip. Overall, the majority of research suggests that dairy has some beneficial effects on bone health, in part because of milk's other nutrients.
Meat and beans
Meat
Meat is animal Tissue (biology), tissue, often muscle, that is eaten as food. Humans have hunted and farmed other animals for meat since prehistory. The Neolithic Revolution allowed the domestication of vertebrates, including chickens, sheep, ...
is the tissue—usually muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contra ...
—of an animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, ...
consumed by humans. Since most parts of many animals are edible, there is a vast variety of meats. Meat is a major source of protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
, as well as iron, zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
, and vitamin B12
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin involved in metabolism. One of eight B vitamins, it serves as a vital cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor in DNA synthesis and both fatty acid metabolism, fatty acid and amino a ...
. The category of meats, poultry, and fish include beef
Beef is the culinary name for meat from cattle (''Bos taurus''). Beef can be prepared in various ways; Cut of beef, cuts are often used for steak, which can be cooked to varying degrees of doneness, while trimmings are often Ground beef, grou ...
, chicken
The chicken (''Gallus gallus domesticus'') is a domesticated subspecies of the red junglefowl (''Gallus gallus''), originally native to Southeast Asia. It was first domesticated around 8,000 years ago and is now one of the most common and w ...
, pork
Pork is the culinary name for the meat of the pig (''Sus domesticus''). It is the most commonly consumed meat worldwide, with evidence of pig animal husbandry, husbandry dating back to 8000–9000 BCE.
Pork is eaten both freshly cooke ...
, salmon
Salmon (; : salmon) are any of several list of commercially important fish species, commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the genera ''Salmo'' and ''Oncorhynchus'' of the family (biology), family Salmonidae, native ...
, tuna
A tuna (: tunas or tuna) is a saltwater fish that belongs to the tribe Thunnini, a subgrouping of the Scombridae ( mackerel) family. The Thunnini comprise 15 species across five genera, the sizes of which vary greatly, ranging from the bul ...
, shrimp
A shrimp (: shrimp (American English, US) or shrimps (British English, UK)) is a crustacean with an elongated body and a primarily Aquatic locomotion, swimming mode of locomotion – typically Decapods belonging to the Caridea or Dendrobranchi ...
, and eggs.
The meat group is one of the major compacted food groups in the food guide pyramid. Since many of the same nutrients found in meat can also be found in foods like eggs, dry bean
A bean is the seed of some plants in the legume family (Fabaceae) used as a vegetable for human consumption or animal feed. The seeds are often preserved through drying (a ''pulse''), but fresh beans are also sold. Dried beans are traditi ...
s, and nuts, such foods are typically placed in the same category as meats, as meat alternatives. These include tofu
or bean curd is a food prepared by Coagulation (milk), coagulating soy milk and then pressing the resulting curds into solid white blocks of varying softness: ''silken'', ''soft'', ''firm'', and ''extra (or super) firm''. It originated in Chin ...
, products that resemble meat or fish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ...
but are made with soy, eggs, and cheese
Cheese is a type of dairy product produced in a range of flavors, textures, and forms by coagulation of the milk protein casein. It comprises proteins and fat from milk (usually the milk of cows, buffalo, goats or sheep). During prod ...
s. For those who do not consume meat or animal products (''see Vegetarianism
Vegetarianism is the practice of abstaining from the Eating, consumption of meat (red meat, poultry, seafood, insects as food, insects, and the flesh of any other animal). It may also include abstaining from eating all by-products of animal slau ...
, veganism
Veganism is the practice of abstaining from the use of animal products and the consumption of animal source foods, and an associated philosophy that rejects the commodity status of animals. A person who practices veganism is known as a vega ...
and Taboo food and drink''), meat analogs, tofu
or bean curd is a food prepared by Coagulation (milk), coagulating soy milk and then pressing the resulting curds into solid white blocks of varying softness: ''silken'', ''soft'', ''firm'', and ''extra (or super) firm''. It originated in Chin ...
, beans, lentils, chickpeas, nuts and other high-protein vegetables are also included in this group. The food guide pyramid suggests that adults eat 2–3 servings per day. One serving of meat is , about the size of a deck of cards.
Oils and sweets
A food pyramid's tip is the smallest part, so the fats and sweets in the top of the Food Pyramid should comprise the smallest percentage of the diet. The foods at the top of the food pyramid should be eaten sparingly because they provide calories, but not much in the way of nutrition. These foods include salad dressings, oils, cream, butter, margarine, sugars, soft drinks, candies, and sweet desserts. On the 1992–2005 pyramid, the fat circle and sugar triangle are scattered throughout the pyramid to represent the naturally-occurring fats and sugars in various foods. The idea of this is to reduce the temptation to eat so much junk food and excessive fats and sugars, as there is already enough fat and sugar in the rest of the diet. For example, the triangles in the Fruit Group represent the fact that sugar is inevitable in that group.Criticism and controversy


unsaturated fat
An unsaturated fat is a fat or fatty acid in which there is at least one double bond within the fatty acid chain. A fatty acid chain is Monounsaturated fat, monounsaturated if it contains one double bond, and polyunsaturated fat, polyunsaturated i ...
s aid in weight loss, reduce heart disease risk, lower blood sugar, and even lower cholesterol. Also, they are very long sustaining, and help keep blood sugar at a steady level. On top of that, these fats help brain function as well.
Several researchers have said that food and agricultural associations exert undue political power on the USDA. Food industries, such as milk companies, have been accused of influencing the United States Department of Agriculture into making the colored spots on the newly created food pyramid larger for their particular product. The milk section has been described as the easiest to see out of the six sections of the pyramid, making individuals believe that more milk should be consumed on a daily basis compared to the others.. Joel Fuhrman says in his book '' Eat to Live'' that U.S. taxpayers must contribute 20 billion on price support
In economics, a price support may be either a subsidy, a production quota, or a price floor, each with the intended effect of keeping the market price of a good higher than the competitive equilibrium level.
In the case of a price control, a pri ...
s to artificially reduce the price of cattle feed to benefit the dairy, beef and veal industries, and then pay the medical bills for an overweight population. He asks if the USDA is under the influence of the food industry
The food industry is a complex, global network of diverse businesses that supplies most of the food consumed by the world's population. The food industry today has become highly diversified, with manufacturing ranging from small, traditional, ...
, because a food pyramid based on science would have vegetables at its foundation.
These controversies prompted the creation of pyramids for specific audiences, including a Vegetarian Diet Pyramid.
The successor to the Food Pyramid called MyPlate has also received numerous criticisms, but unlike the Food Pyramid, which was very well known, the MyPlate program has yet to become publicly well known, with as many as "3 out of 4 Americans avingno idea what the government's MyPlate dietary guide ven
Venezuela, officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea. It comprises an area of , and its popul ...
is."
MyPlate
MyPyramid
MyPyramid, released by the United States Department of Agriculture, USDA Center for Nutrition Policy and Promotion on April 19, 2005, was an update on the earlier American food guide pyramid. It was used until June 2, 2011, when the USDA's MyPla ...
guide on June 2, 2011, concluding 19 years of USDA food pyramid diagrams.
See also
*Food and Nutrition Service
The Food and Nutrition Service (FNS) is an agency of the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). The FNS is the federal agency responsible for administering the nation’s domestic nutrition assistance programs. The service helps to add ...
* Fruits & Veggies – More Matters
*Healthy diet
A healthy diet is a diet that maintains or improves overall health. A healthy diet provides the body with essential nutrition: fluid, macronutrients such as protein, micronutrients such as vitamins, and adequate fibre and food energy.
A he ...
* Healthy eating pyramid
* History of USDA nutrition guides
* Human nutrition
Human nutrition deals with the provision of essential nutrients in food that are necessary to support human life and good health. Poor nutrition is a chronic problem often linked to poverty, food security, or a poor understanding of nutrition ...
* List of nutrition guides
This is a list of nutrition guides. A nutrition guide is a reference that provides nutrition advice for general health, typically by dividing foods into food groups and recommending servings of each group. Nutrition guides can be presented in wri ...
* Nutrition education
* Overall nutritional quality index
References
External links
USDA Dietary Guidelines
Tufts Researchers Update Their Food Guide Pyramid for Older Adults
U.S. Food Guide Pyramid Compared to Others
{{DEFAULTSORT:Food Guide Pyramid Symbols introduced in 1974