Himalayish on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Tibeto-Burman languages are the non-
 During the 18th century, several scholars noticed parallels between Tibetan and Burmese, both languages with extensive literary traditions.
In the following century,
During the 18th century, several scholars noticed parallels between Tibetan and Burmese, both languages with extensive literary traditions.
In the following century,
 The southernmost group is the
The southernmost group is the  The Tibeto-Burman languages of south-west China have been heavily influenced by Chinese over a long period, leaving their affiliations difficult to determine. The grouping of the
The Tibeto-Burman languages of south-west China have been heavily influenced by Chinese over a long period, leaving their affiliations difficult to determine. The grouping of the
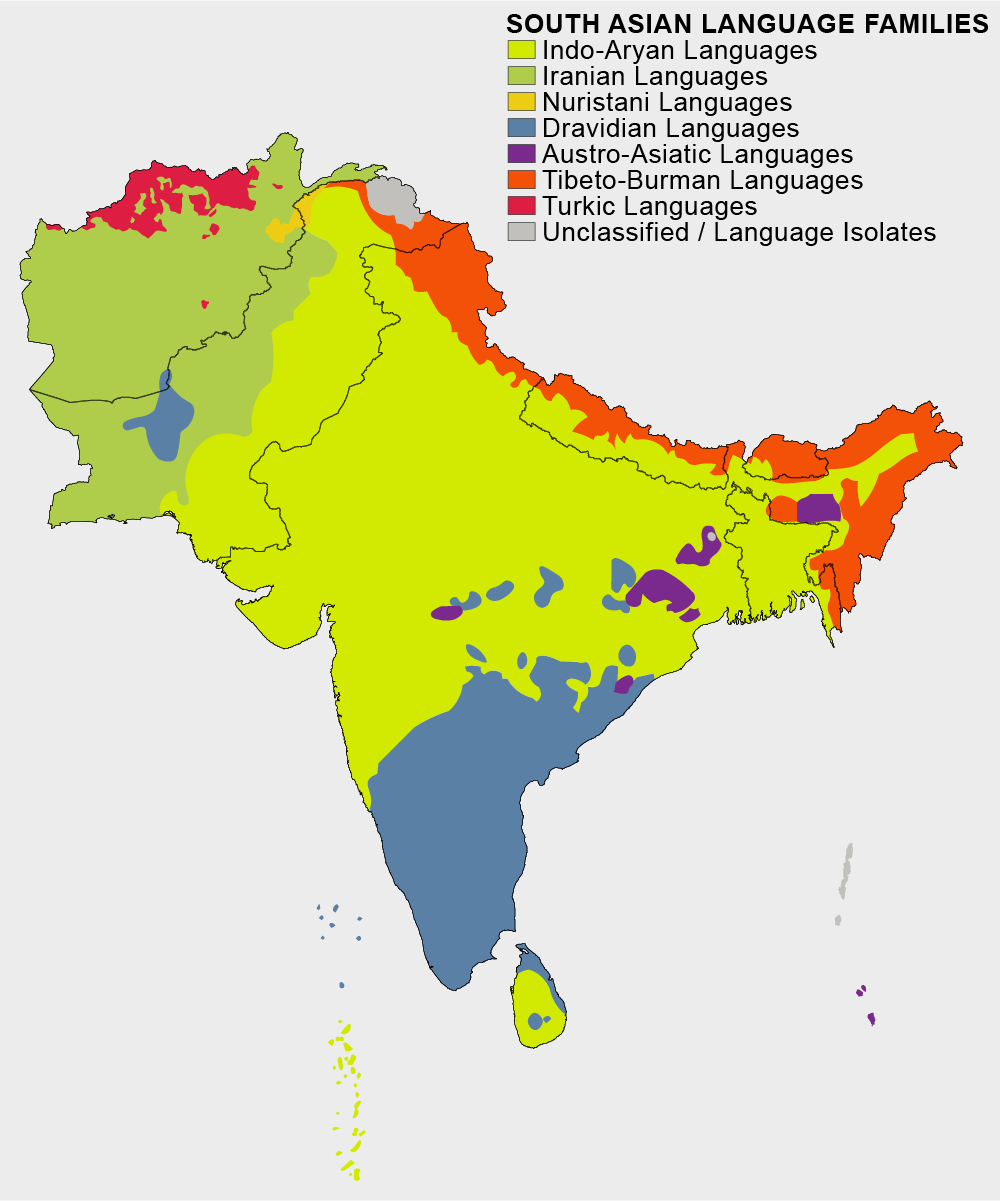 Over eight million people in the
Over eight million people in the
''The Sino-Tibetan Etymological Dictionary and Thesaurus''
Berkeley: University of California.
PDF
Bruhn, Daniel; Lowe, John; Mortensen, David; Yu, Dominic (2015). ''Sino-Tibetan Etymological Dictionary and Thesaurus Database Software''. Software, UC Berkeley Dash. *Tibeto-Burman **Northeast Indian areal group ***"North Assam" **** Tani ****
A phonological reconstruction of Proto Northern Burmic
'. Unpublished thesis. Arlington: The University of Texas. *
Sino-Tibetan Etymological Dictionary and Thesaurus (STEDT)
''Linguistics of the Tibeto-Burman Area''
(journal) * (by
Sino-Tibetan Branches Project (STBP)
Tibeto-Burman bibliography website
{{Authority control Languages of Tibet Languages of Myanmar
Sinitic
The Sinitic languages (), often synonymous with the Chinese languages, are a group of East Asian analytic languages that constitute a major branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family. It is frequently proposed that there is a primary split be ...
members of the Sino-Tibetan language family
Sino-Tibetan (also referred to as Trans-Himalayan) is a language family, family of more than 400 languages, second only to Indo-European languages, Indo-European in number of native speakers. Around 1.4 billion people speak a Sino-Tibetan languag ...
, over 400 of which are spoken throughout the Southeast Asian Massif
The term Southeast Asian Massif was proposed in 1997 by anthropologist Jean Michaud to discuss the human societies inhabiting the lands above an elevation of approximately in the southeastern portion of the Asian landmass, thus not merely in the ...
("Zomia") as well as parts of East Asia
East Asia is a geocultural region of Asia. It includes China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan, plus two special administrative regions of China, Hong Kong and Macau. The economies of Economy of China, China, Economy of Ja ...
and South Asia
South Asia is the southern Subregion#Asia, subregion of Asia that is defined in both geographical and Ethnicity, ethnic-Culture, cultural terms. South Asia, with a population of 2.04 billion, contains a quarter (25%) of the world's populatio ...
. Around 60 million people speak Tibeto-Burman languages. The name derives from the most widely spoken of these languages, Burmese and the Tibetic languages
The Tibetic languages form a well-defined group of languages descending from Old Tibetan.Tournadre, Nicolas. 2014. "The Tibetic languages and their classification." In ''Trans-Himalayan linguistics, historical and descriptive linguistics of the ...
, which also have extensive literary traditions, dating from the 12th and 7th centuries respectively. Most of the other languages are spoken by much smaller communities, and many of them have not been described in detail.
Though the division of Sino-Tibetan into Sinitic and Tibeto-Burman branches (e.g. Benedict, Matisoff) is widely used, some historical linguists criticize this classification, as the non-Sinitic Sino-Tibetan languages lack any shared innovation
In linguistics, the comparative method is a technique for studying the development of languages by performing a feature-by-feature comparison of two or more languages with common descent from a shared ancestor and then extrapolating backwards ...
s in phonology
Phonology (formerly also phonemics or phonematics: "phonemics ''n.'' 'obsolescent''1. Any procedure for identifying the phonemes of a language from a corpus of data. 2. (formerly also phonematics) A former synonym for phonology, often pre ...
or morphology
Morphology, from the Greek and meaning "study of shape", may refer to:
Disciplines
*Morphology (archaeology), study of the shapes or forms of artifacts
*Morphology (astronomy), study of the shape of astronomical objects such as nebulae, galaxies, ...
to show that they comprise a clade
In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach t ...
of the phylogenetic tree
A phylogenetic tree or phylogeny is a graphical representation which shows the evolutionary history between a set of species or taxa during a specific time.Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA. In ...
.
History
 During the 18th century, several scholars noticed parallels between Tibetan and Burmese, both languages with extensive literary traditions.
In the following century,
During the 18th century, several scholars noticed parallels between Tibetan and Burmese, both languages with extensive literary traditions.
In the following century, Brian Houghton Hodgson
Brian Houghton Hodgson (1 February 1801 – 23 May 1894) was a pioneer natural history, naturalist and ethnologist working in India and Nepal where he was a British Resident (title), Resident. He described numerous species of birds and mammals fr ...
collected a wealth of data on the non-literary languages of the Himalayas and northeast India, noting that many of these were related to Tibetan and Burmese.
Others identified related languages in the highlands of Southeast Asia and south-west China.
The name "Tibeto-Burman" was first applied to this group in 1856 by James Logan, who added Karen
Karen may refer to:
* Karen (name), a given name and surname
* Karen (slang), a term and meme for a demanding white woman displaying certain behaviors
People
* Karen people, an ethnic group in Myanmar and Thailand
* House of Karen, a historic ...
in 1858.
Charles Forbes viewed the family as uniting the Gangetic and Lohitic branches of Max Müller
Friedrich Max Müller (; 6 December 1823 – 28 October 1900) was a German-born British comparative philologist and oriental studies, Orientalist. He was one of the founders of the Western academic disciplines of Indology and religious s ...
's Turanian
Turanian is a term that has been used in reference to diverse groups of people.
Many of the uses of the word are obsolete. It may refer to:
*An Iranic ethnic group mentioned in the Avesta
**See Turanian (Avesta)
**See Turan
*The Turanid race
*Any ...
, a huge family consisting of all the Eurasian languages except the Semitic, "Aryan" (Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the northern Indian subcontinent, most of Europe, and the Iranian plateau with additional native branches found in regions such as Sri Lanka, the Maldives, parts of Central Asia (e. ...
) and Chinese languages.
The third volume of the ''Linguistic Survey of India
The Linguistic Survey of India (LSI) is a comprehensive survey of the languages of British India, describing 364 languages and dialects. The Survey was first proposed by George Abraham Grierson, a member of the Indian Civil Service and a lingu ...
'' was devoted to the Tibeto-Burman languages of British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance in South Asia. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another ...
.
Julius Klaproth
Heinrich Julius Klaproth (11 October 1783 – 28 August 1835) was a German linguist, historian, ethnographer, author, orientalist and explorer. As a scholar, he is credited along with Jean-Pierre Abel-Rémusat with being instrumental in turning ...
had noted in 1823 that Burmese, Tibetan and Chinese all shared common basic vocabulary
A vocabulary (also known as a lexicon) is a set of words, typically the set in a language or the set known to an individual. The word ''vocabulary'' originated from the Latin , meaning "a word, name". It forms an essential component of languag ...
, but that Thai, Mon
Mon, MON or Mon. may refer to:
Places
* Mon State, a subdivision of Myanmar
* Mon, India, a town in Nagaland
* Mon district, Nagaland
* Mon, Raebareli, a village in Uttar Pradesh, India
* Mon, Switzerland, a village in the Canton of Grisons
* A ...
and Vietnamese
Vietnamese may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Vietnam, a country in Southeast Asia
* Vietnamese people, or Kinh people, a Southeast Asian ethnic group native to Vietnam
** Overseas Vietnamese, Vietnamese people living outside Vietna ...
were quite different.
Several authors, including Ernst Kuhn in 1883 and August Conrady
August Conrady (Chi. 孔好古) (28 April 1864, Wiesbaden – 4 June 1925, Leipzig) was a German sinologist and linguist. From 1897 he was professor at the University of Leipzig.
Conrady first studied classical philology, comparative linguistics ...
in 1896, described an "Indo-Chinese" family consisting of two branches, Tibeto-Burman and Chinese-Siamese.
The Tai languages
The Tai, Zhuang–Tai, or Daic languages (Ahom language, Ahom: 𑜁𑜪𑜨 𑜄𑜩 or 𑜁𑜨𑜉𑜫 𑜄𑜩 ; ; or , ; , ) are a branch of the Kra–Dai languages, Kra–Dai language family. The Tai languages include the most widely spo ...
were included on the basis of vocabulary and typological features shared with Chinese.
Jean Przyluski introduced the term ''sino-tibétain'' (Sino-Tibetan) as the title of his chapter on the group in Antoine Meillet
Paul Jules Antoine Meillet (; 11 November 1866 – 21 September 1936) was one of the most important French linguists of the early 20th century. He began his studies at the Sorbonne University, where he was influenced by Michel Bréal, the Swiss l ...
and Marcel Cohen
Marcel Samuel Raphaël Cohen (February 6, 1884 – November 5, 1974) was a French linguist. He was an important scholar of Semitic languages and especially of Ethiopian languages. He studied the French language and contributed much to general lin ...
's ''Les Langues du Monde'' in 1924.
The Tai languages have not been included in most Western accounts of Sino-Tibetan since the Second World War, though many Chinese linguists still include them.
The link between Tibeto-Burman and Chinese is now accepted by most linguists, with a few exceptions such as Roy Andrew Miller
Roy Andrew Miller (September 5, 1924 – August 22, 2014) was an American linguist best known as the author of several books on Japanese language and linguistics, and for his advocacy of Korean and Japanese as members of the proposed Alta ...
and Christopher Beckwith
Christopher I. Beckwith (born October 23, 1945) is an American philologist and distinguished professor in the Department of Central Eurasian Studies at Indiana University Bloomington, Indiana.
He has a Bachelor of Arts in Chinese from Ohio Stat ...
.
More recent controversy has centred on the proposed primary branching of Sino-Tibetan into Chinese and Tibeto-Burman subgroups.
In spite of the popularity of this classification, first proposed by Kuhn and Conrady, and also promoted by Paul Benedict
Paul Bernard Benedict (September 17, 1938 – December 1, 2008) was an American actor who made numerous appearances in television and films, beginning in 1965. He was known for his roles as The Number Painter on the PBS children's show ''Sesame ...
(1972) and later James Matisoff
James Alan Matisoff ( zh, , t=馬蒂索夫, s=马蒂索夫, p=Mǎdìsuǒfū or zh, , t=馬提索夫, s=马提索夫, p=Mǎtísuǒfū; born July 14, 1937) is an American linguist. He is a professor emeritus of linguistics at the University of Cal ...
, Tibeto-Burman has not been demonstrated to be a valid subgroup in its own right.
Overview
Most of the Tibeto-Burman languages are spoken in remote mountain areas, which has hampered their study. Many lack a written standard. It is generally easier to identify a language as Tibeto-Burman than to determine its precise relationship with other languages of the group. The subgroupings that have been established with certainty number several dozen, ranging from well-studied groups of dozens of languages with millions of speakers to several isolates, some only discovered in the 21st century but in danger of extinction. These subgroups are here surveyed on a geographical basis.Southeast Asia and southwest China
Karen languages
The Karen () or Karenic languages are tonal languages spoken by some 4.5 million Karen people. They are of unclear affiliation within the Sino-Tibetan languages. The Karen languages are written using the Karen script. The three main branches a ...
, spoken by three million people on both sides of the Burma–Thailand border. They differ from all other Tibeto-Burman languages (except Bai) in having a subject–verb–object word order, attributed to contact with Tai–Kadai and Austroasiatic languages
The Austroasiatic languages ( ) are a large language family spoken throughout Mainland Southeast Asia, South Asia and East Asia. These languages are natively spoken by the majority of the population in Vietnam and Cambodia, and by minority popu ...
.
The most widely spoken Tibeto-Burman language is Burmese, the national language of Myanmar, with over 32 million speakers and a literary tradition dating from the early 12th century. It is one of the Lolo-Burmese languages
The Lolo-Burmese languages (also Burmic languages) of Burma and Southern China form a coherent branch of the Sino-Tibetan languages, Sino-Tibetan family.
Names
Until ca. 1950, the endonym ''Lolo'' was written with Graphic pejoratives in written C ...
, an intensively studied and well-defined group comprising approximately 100 languages spoken in Myanmar and the highlands of Thailand, Laos, Vietnam, and southwest China
Southwestern China () is a region in the People's Republic of China. It consists of five provincial administrative regions, namely Chongqing, Sichuan, Guizhou, Yunnan, and Xizang.
Geography
Southwestern China is a rugged and mountainous region, ...
. Major languages include the Loloish languages
The Loloish languages, also known as Yi (like the Yi people) and occasionally Ngwi or Nisoic, are a family of 50–100 Tibeto-Burman languages spoken primarily in the Yunnan province of Southwestern China. They are most closely related to Bur ...
, with two million speakers in western Sichuan
Sichuan is a province in Southwestern China, occupying the Sichuan Basin and Tibetan Plateau—between the Jinsha River to the west, the Daba Mountains to the north, and the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau to the south. Its capital city is Cheng ...
and northern Yunnan
Yunnan; is an inland Provinces of China, province in Southwestern China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 47.2 million (as of 2020). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the Chinese provinces ...
, the Akha language
Akha is the language spoken by the Akha people of southern China (Yunnan Province), eastern Burma (Shan State), northern Laos, and northern Thailand.
Western scholars group Akha, Hani and Honi into the Hani languages, treating all three as sep ...
and Hani language
The Hani language (Hani: or '; ; ) is a language of the Loloish (Yi) branch of the Tibeto-Burman linguistic group spoken in China, Laos, Myanmar, and Vietnam by the Hani people.
Distribution
In China, Hani is spoken mostly in areas to the e ...
s, with two million speakers in southern Yunnan, eastern Myanmar, Laos and Vietnam, and Lisu
Lisu may refer to:
*Lisu people, an ethnic group of the mountainous regions of Yunnan (China), Arunachal Pradesh (India), northern Myanmar and Thailand
*Lisu language, Tibeto-Burman language spoken by the Lisu people
**Fraser script or Old Lisu A ...
and Lahu in Yunnan, northern Myanmar and northern Thailand. All languages of the Loloish subgroup show significant Austroasiatic influence.
The Pai-lang songs, transcribed in Chinese characters in the 1st century, appear to record words from a Lolo-Burmese language, but arranged in Chinese order.
 The Tibeto-Burman languages of south-west China have been heavily influenced by Chinese over a long period, leaving their affiliations difficult to determine. The grouping of the
The Tibeto-Burman languages of south-west China have been heavily influenced by Chinese over a long period, leaving their affiliations difficult to determine. The grouping of the Bai language
Bai (Bai: ; ) is a Sino-Tibetan language spoken in China, primarily in Yunnan Province, by the Bai people. The language has over a million speakers and is divided into three or four main dialects. Bai syllables are always open, with a rich set ...
, with one million speakers in Yunnan, is particularly controversial, with some workers suggesting that it is a sister language to Chinese. The Naxi language
Naxi (), also known as ''Nakhi'', ''Nasi'', ''Lomi'', ''Moso'', or ''Mo-su'', is a Sino-Tibetan language or group of languages spoken by approximately 310,000 Nakhi people, most of whom live in or around Yulong Naxi Autonomous County in the pr ...
of northern Yunnan is usually included in Lolo-Burmese, though other scholars prefer to leave it unclassified. The hills of northwestern Sichuan are home to the small Qiangic and Rgyalrongic groups of languages, which preserve many archaic features. The most easterly Tibeto-Burman language is Tujia Tujia may refer to:
*the Tujia people
*the Tujia language
The Tujia language (; zh, s=土家语 , t=土家語 , p=Tǔjiāyǔ) is a Sino-Tibetan language spoken natively by the Tujia people in Hunan Province, China. It is unclassified within t ...
, spoken in the Wuling Mountains
The Wuling Mountains () are a mountain range located in Central China, running from Chongqing Municipality and East Guizhou to West Hunan. They are home to many ethnic groups, including the Tujia, Han, Miao, Dong, and Bai.
Wulingyuan
T ...
on the borders of Hunan, Hubei, Guizhou and Chongqing.
Two historical languages are believed to be Tibeto-Burman, but their precise affiliation is uncertain. The Pyu language of central Myanmar in the first centuries is known from inscriptions using a variant of the Gupta script
The Gupta script (sometimes referred to as Gupta Brahmi script or Late Brahmi script)Sharma, Ram. '' 'Brahmi Script' ''. Delhi: BR Publishing Corp, 2002 was used for writing Sanskrit and is associated with the Gupta Empire of the Indian subcon ...
. The Tangut language
Tangut (Tangut: ; ) is an extinct language in the Sino-Tibetan language family.
Tangut was one of the official languages of the Western Xia, Western Xia dynasty, founded by the Tangut people in northwestern China. The Western Xia was annihilate ...
of the 12th century Western Xia
The Western Xia or the Xi Xia ( zh, c=, w=Hsi1 Hsia4, p=Xī Xià), officially the Great Xia ( zh, c=大夏, w=Ta4 Hsia4, p=Dà Xià, labels=no), also known as the Tangut Empire, and known as Stein (1972), pp. 70–71. to the Tanguts ...
of northern China is preserved in numerous texts written in the Chinese-inspired Tangut script
The Tangut script ( Tangut: ; ) is a logographic writing system, formerly used for writing the extinct Tangut language of the Western Xia dynasty. According to the latest count, 5863 Tangut characters are known, excluding variants. The Tangut ch ...
.
Tibet and South Asia
 Over eight million people in the
Over eight million people in the Tibetan Plateau
The Tibetan Plateau, also known as the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau or Qingzang Plateau, is a vast elevated plateau located at the intersection of Central Asia, Central, South Asia, South, and East Asia. Geographically, it is located to the north of H ...
and neighbouring areas in Baltistan
Baltistan (); also known as Baltiyul or Little Tibet, is a mountainous region in the Pakistani-administered territory of Gilgit-Baltistan and constitutes a northern portion of the larger Kashmir region that has been the subject of a dispute bet ...
, Ladakh
Ladakh () is a region administered by India as a union territory and constitutes an eastern portion of the larger Kashmir region that has been the subject of a Kashmir#Kashmir dispute, dispute between India and Pakistan since 1947 and India an ...
, Nepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China Ch ...
, Sikkim
Sikkim ( ; ) is a States and union territories of India, state in northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Koshi Province of Nepal in the west, and West Bengal in the ...
and Bhutan
Bhutan, officially the Kingdom of Bhutan, is a landlocked country in South Asia, in the Eastern Himalayas between China to the north and northwest and India to the south and southeast. With a population of over 727,145 and a territory of , ...
speak one of several related Tibetic languages
The Tibetic languages form a well-defined group of languages descending from Old Tibetan.Tournadre, Nicolas. 2014. "The Tibetic languages and their classification." In ''Trans-Himalayan linguistics, historical and descriptive linguistics of the ...
. There is an extensive literature in Classical Tibetan
Classical Tibetan refers to the language of any text written in Tibetic after the Old Tibetan period. Though it extends from the 7th century until the modern day (along with Arabic, Ge'ez, and New Persian, it is one of the handful of 'living' ...
dating from the 8th century. The Tibetic languages are usually grouped with the smaller East Bodish languages
The East Bodish languages are a small group of non-Tibetic Bodish languages spoken in eastern Bhutan and adjacent areas of Tibet and India. They include:
* Dakpa (Tawang Monpa)
* Dzala
* Nyen, including Mangde and Phobjib
* Chali
* Bumthang
...
of Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh
Arunachal Pradesh (; ) is a States and union territories of India, state in northeast India. It was formed from the North-East Frontier Agency (NEFA) region, and India declared it as a state on 20 February 1987. Itanagar is its capital and la ...
as the Bodish group.
Many diverse Tibeto-Burman languages are spoken on the southern slopes of the Himalayas.
Sizable groups that have been identified are the West Himalayish languages
The West Himalayish languages, also known as Almora and Kanauric, are a family of Sino-Tibetan languages centered in Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand and across the border into Nepal. LaPolla (2003) proposes that the West Himalayish languages may b ...
of Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh (; Sanskrit: ''himācāl prādes;'' "Snow-laden Mountain Province") is a States and union territories of India, state in the northern part of India. Situated in the Western Himalayas, it is one of the thirteen Indian Himalayan ...
and western Nepal, the Tamangic languages
The Tamangic languages, TGTM languages, or West Bodish languages or Kaike-Ghale-Tamangic languages (Glottolog), are a family of Sino-Tibetan languages spoken in the Himalayas of Nepal. They are called "West Bodish" by Bradley (1997), from ''Bod' ...
of western Nepal, including Tamang with one million speakers, and the Kiranti languages
The Kiranti languages are a major family of Sino-Tibetan languages spoken in Nepal and India (notably Sikkim, Darjeeling, Kalimpong, and Bhutan) by the Kirati people.
External relationships
George van Driem had formerly proposed that the K ...
of eastern Nepal.
The remaining groups are small, with several isolates.
The Newar language
Newar (; , ) is a Sino-Tibetan languages, Sino-Tibetan language spoken by the Newar people, the indigenous inhabitants of Nepal Mandala, which consists of the Kathmandu Valley and surrounding regions in Nepal. The language is known officially ...
(Nepal Bhasa) of central Nepal has a million speakers and literature dating from the 12th century, and nearly a million people speak Magaric languages
The Magar languages (or Magaric languages) are a small proposed family of Sino-Tibetan languages spoken in Nepal, notably including Magar and Kham. ''(Ethnologue'' considers each to be a cluster of languages.) They are often classified as part o ...
, but the rest have small speech communities.
Other isolates and small groups in Nepal are Dura, Raji–Raute, Chepangic and Dhimalish.
Lepcha is spoken in an area from eastern Nepal to western Bhutan.
Most of the languages of Bhutan are Bodish, but it also has three small isolates, 'Ole ("Black Mountain Monpa"), Lhokpu and Gongduk
Gongduk or Gongdu (, it is also known as Gongdubikha) is an endangered Sino-Tibetan language spoken by about 1,000 people in a few inaccessible villages located near the Kuri Chhu river in the Gongdue Gewog of Mongar District in eastern Bhutan. ...
and a larger community of speakers of Tshangla
Tshangla is a Sino-Tibetan language of the Bodish branch closely related to the Tibetic languages. Tshangla is primarily spoken in Eastern Bhutan and acts as a lingua franca in the region; it is also spoken in the adjoining Tawang tract in the ...
.
The Tani languages
The Tani language, often referred to as Tani languages, encompasses a group of closely related languages spoken by the Tani people in the northeastern region of India, primarily in the Indian states of Arunachal Pradesh and Assam. These language ...
include most of the Tibeto-Burman languages of Arunachal Pradesh and adjacent areas of Tibet.
The remaining languages of Arunachal Pradesh are much more diverse, belonging to the small Siangic, Kho-Bwa (or Kamengic), Hruso, Miju and Digaro languages
The Digaro (Digarish), Northern Mishmi (Mishmic), or Kera'a–Tawrã languages are a possible small family of possibly Sino-Tibetan languages spoken by the Mishmi people of southeastern Tibet and Arunachal Pradesh.
The languages are Idu language ...
(or Mishmic) groups.
These groups have relatively little Tibeto-Burman vocabulary, and Bench and Post dispute their inclusion in Sino-Tibetan.
The greatest variety of languages and subgroups is found in the highlands stretching from northern Myanmar to northeast India.
Northern Myanmar is home to the small Nungish group, as well as the Jingpho–Luish languages
The Jingpho-Luish, Jingpho-Asakian, Kachin–Luic, or Kachinic languages are a group of Sino-Tibetan languages belonging the Sal branch. They are spoken in northeastern India, Bangladesh and Myanmar, and consist of the Jingpho (also known as Ka ...
, including Jingpho with nearly a million speakers.
The Brahmaputran or Sal languages
The Sal languages, also known as the Brahmaputran languages, are a branch of Tibeto-Burman languages spoken in northeast India, as well as parts of Bangladesh, Myanmar (Burma), and China.
Alternative names
''Ethnologue'' calls the group "Jingpho ...
include at least the Boro–Garo and Konyak languages
The Konyak languages, or alternatively the Konyakian, Northern Naga, or Patkaian languages, is a branch of Sino-Tibetan languages spoken by various Naga peoples in southeastern Arunachal Pradesh and northeastern Nagaland states of northeastern ...
, spoken in an area stretching from northern Myanmar through the Indian states of Nagaland
Nagaland () is a States and union territories of India, state in the northeast India, north-eastern region of India. It is bordered by the Indian states of Arunachal Pradesh to the north, Assam to the west, Manipur to the south, and the Naga Sel ...
, Meghalaya
Meghalaya (; "the abode of clouds") is a states and union territories of India, state in northeast India. Its capital is Shillong. Meghalaya was formed on 21 January 1972 by carving out two districts from the Assam: the United Khasi Hills an ...
, and Tripura
Tripura () is a States and union territories of India, state in northeastern India. The List of states and union territories of India by area, third-smallest state in the country, it covers ; and the seventh-least populous state with a populat ...
, and are often considered to include the Jingpho–Luish group.
The border highlands of Nagaland
Nagaland () is a States and union territories of India, state in the northeast India, north-eastern region of India. It is bordered by the Indian states of Arunachal Pradesh to the north, Assam to the west, Manipur to the south, and the Naga Sel ...
, Manipur
Manipur () is a state in northeastern India with Imphal as its capital. It borders the Indian states of Assam to the west, Mizoram to the south, and Nagaland to the north and shares the international border with Myanmar, specifically t ...
and western Myanmar are home to the small Ao, Angami–Pochuri, Tangkhulic
The Tangkhulic and Tangkhul languages are a group of Sino-Tibetan languages spoken mostly in northeastern Manipur, India. Conventionally classified as "Naga," they are not clearly related to other Naga languages, and (with Maringic) are conservat ...
, and Zeme groups of languages, as well as the Karbi language
The Karbi language () is a Tibeto-Burman language spoken by the Karbi (also known as Mikir or Arlêng) people of Northeastern India. It is also called Hills Karbi to differentiate it from Plains Karbi (Amri Karbi) which is variously treated a ...
.
Meithei, the main language of Manipur with 1.4 million speakers, is sometimes linked with the 50 or so Kuki-Chin languages
The Kuki-Chin languages (also called Kukish or South-Central Tibeto-Burman languages) are a branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family spoken in northeastern India, western Myanmar and southeastern Bangladesh. Most notable Kuki-Chin-speaking ...
are spoken in Mizoram
Mizoram is a states and union territories of India, state in northeastern India, with Aizawl as its Capital city, capital and largest city. It shares 722-kilometres (449 miles) of international borders with Bangladesh to the west, and Myanmar t ...
and the Chin State
Chin State (, ) is a state in western Myanmar. Chin State is bordered by Sagaing Division and Magway Division to the east, Rakhine State to the south, the Chattogram Division of Bangladesh to the west, and the Indian states of Mizoram to th ...
of Myanmar.
The Mru language
Mru, also known as Mrung (Murung), is a Sino-Tibetan languages, Sino-Tibetan language of Bangladesh and Myanmar. It is spoken by a community of Mru people, Mrus (Mros) inhabiting the Chittagong Hill Tracts of Bangladesh with a population of 22 ...
is spoken by a small group in the Chittagong Hill Tracts
The Chittagong Hill Tracts (), often shortened to simply the Hill Tracts and abbreviated to CHT, refers to the three hilly districts within the Chittagong Division in southeastern Bangladesh, bordering India and Myanmar (Burma) in the east: Kh ...
between Bangladesh and Myanmar.
Classification
There have been two milestones in the classification of Sino-Tibetan and Tibeto-Burman languages, and , which were actually produced in the 1930s and 1940s respectively.Shafer (1955)
Shafer's tentative classification took an agnostic position and did not recognize Tibeto-Burman, but placed Chinese (Sinitic) on the same level as the other branches of a Sino-Tibetan family. He retained Tai–Kadai (Daic) within the family, allegedly at the insistence of colleagues, despite his personal belief that they were not related. * Sino-Tibetan ** ''Sinitic
The Sinitic languages (), often synonymous with the Chinese languages, are a group of East Asian analytic languages that constitute a major branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family. It is frequently proposed that there is a primary split be ...
''
** ?? '' Daic''
** ''Bodic''
*** Bodish (Gurung
Gurung (exonym; ) or Tamu (endonym; Gurung language, Gurung: ) are a Tibetan people, Tibetan ethnic group living in the hills and mountains of Gandaki Province of Nepal. Gurungs speak Tamu kyi which is a Sino-Tibetan language derived from the ...
, Tshangla
Tshangla is a Sino-Tibetan language of the Bodish branch closely related to the Tibetic languages. Tshangla is primarily spoken in Eastern Bhutan and acts as a lingua franca in the region; it is also spoken in the adjoining Tawang tract in the ...
, Gyarong, Tibetic
The Tibetic languages form a well-defined group of languages descending from Old Tibetan.Tournadre, Nicolas. 2014. "The Tibetic languages and their classification." In ''Trans-Himalayan linguistics, historical and descriptive linguistics of the H ...
)
*** West Himalayish
The West Himalayish languages, also known as Almora and Kanauric, are a family of Sino-Tibetan languages centered in Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand and across the border into Nepal. LaPolla (2003) proposes that the West Himalayish languages may b ...
(incl. Kinnauri
Kinnauri is the most widely used language in Kinnaur. The languages have seen different nomenclatures in written literature. Kinnauri was mentioned as Kunawaree (Gerard 1842, Cunninham 1844), Kanauri (Konow 1905), Kanawari (Bailey 1909) and ...
, Baram, Thangmi)
*** West Central Himalayish ( Magar, Chepang, Hayu
The Hayus () are a member of the Kirat tribe speaking their own language, Wayu or Hayu. Little is known about them. They are Hindus by religion. According to the 2001 Nepal census, there are 1821 Hayu in the country, of which 70.29% were Hind ...
)
*** East Himalayish
*** Newarish (Newar
Newar (; , endonym: Newa; , Pracalit script: ), or Nepami, are primarily inhabitants in Kathmandu Valley of Nepal and its surrounding areas, and the creators of its historic heritage and civilisation. Page 15. Newars are a distinct linguisti ...
, Pahari)
*** Digarish
*** Midźuish
*** Hrusish
*** Dhimalish
*** Miśingish
*** Dzorgaish
** ''Burmic''
*** Burmish
The Burmish languages are a subgroup of the Sino-Tibetan languages consisting of Burmese (including Standard Burmese, Arakanese, and other Burmese dialects such as the Tavoyan dialects) as well as non-literary languages spoken across Myanmar an ...
*** Mruish
*** Nungish
*** Katśinish ( Jingpho)
*** Tśairelish
*** Luish
*** Taman
*** Kukish
** ''Baric''
*** Barish
*** Nagish
** ''Karenic
The Karen () or Karenic languages are tonal languages spoken by some 4.5 million Karen people. They are of unclear affiliation within the Sino-Tibetan languages. The Karen languages are written using the Karen script. The three main branches a ...
''
Benedict (1972)
A very influential, although also tentative, classification is that of , which was actually written around 1941. Like Shafer's work, this drew on the data assembled by the Sino-Tibetan Philology Project, which was directed by Shafer and Benedict in turn. Benedict envisaged Chinese as the first family to branch off, followed by Karen. *Sino-Tibetan ** Chinese ** Tibeto-Karen *** Karen *** Tibeto-Burman The Tibeto-Burman family is then divided into seven primary branches: * Tibeto-Burman ** '' Tibetan–Kanauri'' (a.k.a. Bodish–Himalayish) *** Bodish **** (Tibetic
The Tibetic languages form a well-defined group of languages descending from Old Tibetan.Tournadre, Nicolas. 2014. "The Tibetic languages and their classification." In ''Trans-Himalayan linguistics, historical and descriptive linguistics of the H ...
, Gyarung, Takpa
The Takpa is a sub-group of the Monpa people, while the southern sub-group is identified as the Tshangla. Monpas of the Takpa group are found in Tawang and Dirang of Arunachal Pradesh, Cuona of Tibet as well as Trashigang in Bhutan
Bhu ...
, Tsangla, Murmi & Gurung)
*** Himalayish
**** "major" Himalayish
The Tibeto-Burman languages are the non-Sinitic languages, Sinitic members of the Sino-Tibetan languages, Sino-Tibetan language family, over 400 of which are spoken throughout the Southeast Asian Massif ("Zomia") as well as parts of East Asia and ...
**** "minor" Himalayish
The Tibeto-Burman languages are the non-Sinitic languages, Sinitic members of the Sino-Tibetan languages, Sino-Tibetan language family, over 400 of which are spoken throughout the Southeast Asian Massif ("Zomia") as well as parts of East Asia and ...
***** (Rangkas, Darmiya, Chaudangsi, Byangsi)
*** (perhaps also Dzorgai, Lepcha, Magari)
** '' Bahing–Vayu''
*** Bahing (Sunuwar
The Sunuwar or Koinch are a Tibeto-Burman ethnic group. ( Nepali:सुनुवार जाति, ''Sunuwār Jāti'') a Kirati tribe native to Nepal, parts of India (West Bengal and Sikkim) and southern Bhutan. They speak the Sunuwar languag ...
, Khaling)
*** Sampang, Rungchenbung, Yakha, and Limbu
Limbu may refer to:
* Limbu people, an indigenous tribe living in Nepal, Sikkim (India) and Bhutan
** Limbu language, their Sino-Tibetan language
*** Limbu script
**** Limbu (Unicode block)
* Rambahadur Limbu
Rambahadur Limbu, (; 8 July 1939 � ...
*** Vayu
Vayu (; ), also known as Vata () and Pavana (), is the Hindu deities, Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine messenger of the gods. In the ''Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king o ...
– Chepang
*** (perhaps also Newar
Newar (; , endonym: Newa; , Pracalit script: ), or Nepami, are primarily inhabitants in Kathmandu Valley of Nepal and its surrounding areas, and the creators of its historic heritage and civilisation. Page 15. Newars are a distinct linguisti ...
)
** '' Abor–Miri–Dafla''
*** (perhaps also Aka, Digaro, Miju, and Dhimal
The Dhimal or Dhemal () are ethnic group residing in the eastern Terai of Nepal and West Bengal of India. They are a Sino-Tibetan-speaking ethnic group of the eastern Terai. They mainly reside in Morang and Jhapa districts of Nepal and Darjee ...
)
** '' Kachin''
*** (perhaps including Luish)
** '' Burmese–Lolo''
*** Burmese–Maru
*** Southern Lolo
*** Northern Lolo
*** Kanburi Lawa
*** Moso
*** Hsi-fan ( Qiangic and Jiarongic languages
The Gyalrongic languages (also known as Rgyalrongic or Jiarongic) constitute a branch of the Qiangic languages of Sino-Tibetan, but some propose that it may be part of a larger Rung languages group and do not consider it to be particularly clos ...
apart from Qiang and Gyarung themselves)
*** Tangut
Tangut may refer to:
*Tangut people, an ancient ethnic group in Northwest China
*Tangut language, the extinct language spoken by the Tangut people
*Tangut script, the writing system used to write the Tangut language
*Tangut (Unicode block)
*Wester ...
*** (perhaps also Nung)
** '' Boro-Garo''
*** Boro
*** Garo ( A·chik)
*** Tripuri (Kokborok)
*** Dimasa
*** Deori
*** Mech
*** Rava (Koch
Koch may refer to:
People
* Koch (surname), people with this surname
* Koch dynasty, a dynasty in Assam and Bengal, north east India
* Koch family
* Koch people (or Koche), an ethnic group originally from the ancient Koch kingdom in north east In ...
)
*** Tiwa
Tiwa and Tigua may refer to:
* Tiwa Puebloans, an ethnic group of New Mexico, US
* Tiwa (Lalung), an ethnic group of north-eastern India
* Tiwa language (India), a Sino-Tibetan language of India
* Tiwa languages, a group of Tanoan languages of the ...
(Lalung)
*** Sutiya
*** Saraniya
*** Moran
*** Sonowal
*** Thengal
*** (Perhaps also " Naked Naga" a.k.a. Konyak)
** '' Kuki–Naga'' (a.k.a. Kukish)
*** (perhaps also Karbi, Meithei, Mru)
Matisoff (1978)
James Matisoff
James Alan Matisoff ( zh, , t=馬蒂索夫, s=马蒂索夫, p=Mǎdìsuǒfū or zh, , t=馬提索夫, s=马提索夫, p=Mǎtísuǒfū; born July 14, 1937) is an American linguist. He is a professor emeritus of linguistics at the University of Cal ...
proposes a modification of Benedict that demoted Karen but kept the divergent position of Sinitic. Of the 7 branches within Tibeto-Burman, 2 branches (Baic and Karenic) have SVO-order languages, whereas all the other 5 branches have SOV-order languages.
* Sino-Tibetan
** Chinese
** Tibeto-Burman
Tibeto-Burman is then divided into several branches, some of them geographic conveniences rather than linguistic proposals:
*Tibeto-Burman
**Kamarupan (geographic)
*** Kuki-Chin–Naga (geographic)
*** Abor–Miri–Dafla
*** Boro–Garo
**Himalayish
The Tibeto-Burman languages are the non-Sinitic languages, Sinitic members of the Sino-Tibetan languages, Sino-Tibetan language family, over 400 of which are spoken throughout the Southeast Asian Massif ("Zomia") as well as parts of East Asia and ...
(geographic)
*** Mahakiranti (includes Newar
Newar (; , endonym: Newa; , Pracalit script: ), or Nepami, are primarily inhabitants in Kathmandu Valley of Nepal and its surrounding areas, and the creators of its historic heritage and civilisation. Page 15. Newars are a distinct linguisti ...
, Magar, Kiranti
The Kirati people, also spelled as Kirat or Kirant or Kiranti, are Tibeto-Burman ethnolinguistic groups living in the Himalayas, mostly the Eastern Himalaya extending eastward from Nepal to North East India (predominantly in the Indian state ...
)
*** Tibeto-Kanauri (includes Lepcha)
** Qiangic
**Jingpho–Nungish–Luish
*** Jingpho
*** Nungish
*** Luish
**Lolo–Burmese
The Lolo-Burmese languages (also Burmic languages) of Burma and Southern China form a coherent branch of the Sino-Tibetan family.
Names
Until ca. 1950, the endonym ''Lolo'' was written with derogatory characters in Chinese, and for this reason ...
– Naxi
**Karenic
The Karen () or Karenic languages are tonal languages spoken by some 4.5 million Karen people. They are of unclear affiliation within the Sino-Tibetan languages. The Karen languages are written using the Karen script. The three main branches a ...
** Baic
**Tujia Tujia may refer to:
*the Tujia people
*the Tujia language
The Tujia language (; zh, s=土家语 , t=土家語 , p=Tǔjiāyǔ) is a Sino-Tibetan language spoken natively by the Tujia people in Hunan Province, China. It is unclassified within t ...
(unclassified)
Matisoff makes no claim that the families in the Kamarupan or Himalayish branches have a special relationship to one another other than a geographic one. They are intended rather as categories of convenience pending more detailed comparative work.
Matisoff also notes that Jingpho–Nungish–Luish is central to the family in that it contains features of many of the other branches, and is also located around the center of the Tibeto-Burman-speaking area.
Bradley (2002)
Since Benedict (1972), many languages previously inadequately documented have received more attention with the publication of new grammars, dictionaries, and wordlists. This new research has greatly benefited comparative work, andBradley
Bradley may refer to:
People
* Bradley (given name)
* Bradley (surname)
Places
In the United Kingdom
In England:
* Bradley, Cheshire
* Bradley, Derbyshire
* Bradley (house), a manor in Kingsteignton, Devon
* Bradley, Gloucestershire
* ...
(2002) incorporates much of the newer data.
* Tibeto-Burman
** Western (= Bodic
The Tibeto-Kanauri languages, also called Bodic, Bodish–Himalayish, and Western Tibeto-Burman, are a proposed intermediate level of classification of the Sino-Tibetan languages, centered on the Tibetic languages and the Kinnauri dialect cluste ...
)
*** Tibetan–Kanauri
**** Tibetic
The Tibetic languages form a well-defined group of languages descending from Old Tibetan.Tournadre, Nicolas. 2014. "The Tibetic languages and their classification." In ''Trans-Himalayan linguistics, historical and descriptive linguistics of the H ...
**** Gurung
Gurung (exonym; ) or Tamu (endonym; Gurung language, Gurung: ) are a Tibetan people, Tibetan ethnic group living in the hills and mountains of Gandaki Province of Nepal. Gurungs speak Tamu kyi which is a Sino-Tibetan language derived from the ...
**** East Bodic (incl. Tsangla)
**** Kanauri
*** Himalayan
**** Eastern (Kiranti
The Kirati people, also spelled as Kirat or Kirant or Kiranti, are Tibeto-Burman ethnolinguistic groups living in the Himalayas, mostly the Eastern Himalaya extending eastward from Nepal to North East India (predominantly in the Indian state ...
)
**** Western (Newar
Newar (; , endonym: Newa; , Pracalit script: ), or Nepami, are primarily inhabitants in Kathmandu Valley of Nepal and its surrounding areas, and the creators of its historic heritage and civilisation. Page 15. Newars are a distinct linguisti ...
, Chepang, Magar, Thangmi, Baram)
** '' Sal''
*** Baric ( Boro–Garo–Northern Naga
The Konyak languages, or alternatively the Konyakian, Northern Naga, or Patkaian languages, is a branch of Sino-Tibetan languages spoken by various Naga peoples in southeastern Arunachal Pradesh and northeastern Nagaland states of northeastern I ...
)
*** Jinghpaw
*** Luish (incl. Pyu
Pyu, also spelled Phyu or Phyuu, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency. is a town in Taungoo District, Bago Region in Myanmar
Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar; and also referred to as Burma (th ...
)
*** Kuki-Chin
The Kuki-Chin languages (also called Kukish or South-Central Tibeto-Burman languages) are a branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family spoken in northeastern India, western Myanmar and southeastern Bangladesh. Most notable Kuki-Chin-speaking ...
(incl. Meithei and Karbi)
** ''Central'' (perhaps a residual group, not actually related to each other. Lepcha may also fit here.)
*** Adi–Galo–Mishing–Nishi
*** Mishmi ( Digarish and Keman
(Japanese phoneticization from the Sanskrit ''kusumamālā'' "Garland of Flowers"), is a Buddhist ritual decoration, placed hanging on the beam of the inner sanctuary before the enshrined Buddha, in the main hall of the temple. (revised editio ...
)
*** Rawang
** ''North-Eastern''
*** Qiangic
*** Naxi– Bai
*** Tujia Tujia may refer to:
*the Tujia people
*the Tujia language
The Tujia language (; zh, s=土家语 , t=土家語 , p=Tǔjiāyǔ) is a Sino-Tibetan language spoken natively by the Tujia people in Hunan Province, China. It is unclassified within t ...
*** Tangut
Tangut may refer to:
*Tangut people, an ancient ethnic group in Northwest China
*Tangut language, the extinct language spoken by the Tangut people
*Tangut script, the writing system used to write the Tangut language
*Tangut (Unicode block)
*Wester ...
** ''South-Eastern''
*** Burmese–Lolo (incl. Mru)
*** Karen
Karen may refer to:
* Karen (name), a given name and surname
* Karen (slang), a term and meme for a demanding white woman displaying certain behaviors
People
* Karen people, an ethnic group in Myanmar and Thailand
* House of Karen, a historic ...
van Driem
George van Driem
George "Sjors" van Driem (born 1957) is a Dutch professor emeritus of linguistics at the University of Bern. He studied East Asian languages and is known for the father tongue hypothesis.
Education
* Leiden University, 1983–1987 (PhD, ''A Gra ...
rejects the primary split of Sinitic, making Tibeto-Burman synonymous with Sino-Tibetan.
Matisoff (2015)
The internal structure of Tibeto-Burman is tentatively classified as follows by Matisoff (2015: xxxii, 1123–1127) in the final release of the ''Sino-Tibetan Etymological Dictionary and Thesaurus
The ''Sino-Tibetan Etymological Dictionary and Thesaurus'' (commonly abbreviated ''STEDT'') was a linguistics research project hosted at the University of California at Berkeley. The project, which focused on Sino-Tibetan languages, Sino-Tibetan hi ...
'' (STEDT).Matisoff, James A. 2015''The Sino-Tibetan Etymological Dictionary and Thesaurus''
Berkeley: University of California.
Bruhn, Daniel; Lowe, John; Mortensen, David; Yu, Dominic (2015). ''Sino-Tibetan Etymological Dictionary and Thesaurus Database Software''. Software, UC Berkeley Dash. *Tibeto-Burman **Northeast Indian areal group ***"North Assam" **** Tani ****
Deng Deng may refer to:
People and ethnic groups
* Deng (Chinese surname), including a list of people with the name
**Deng Sui, empress dowager of the Eastern Han Dynasty.
** Deng Xiaoping, leader of China 1978–1989
** Honghao Deng (born 1994), Chines ...
***Kuki-Chin
The Kuki-Chin languages (also called Kukish or South-Central Tibeto-Burman languages) are a branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family spoken in northeastern India, western Myanmar and southeastern Bangladesh. Most notable Kuki-Chin-speaking ...
***"Naga
Naga or NAGA may refer to:
Mythology
* Nāga, a serpentine deity or race in Hindu, Buddhist and Jain traditions
** Phaya Naga, mythical creatures believed to live in the Laotian stretch of the Mekong River
** Naga, another name for Bakunawa, an ...
" areal group
****Central Naga ( Ao group)
**** Angami–Pochuri group
**** Zeme group
****Tangkhulic
The Tangkhulic and Tangkhul languages are a group of Sino-Tibetan languages spoken mostly in northeastern Manipur, India. Conventionally classified as "Naga," they are not clearly related to other Naga languages, and (with Maringic) are conservat ...
*** Meithei
***Mikir / Karbi
*** Mru
*** Sal
**** Boro–Garo
****Northern Naga / Konyakian
**** Jingpho–Asakian
**Himalayish
*** Tibeto-Kanauri
**** Western Himalayish
****Bodic
The Tibeto-Kanauri languages, also called Bodic, Bodish–Himalayish, and Western Tibeto-Burman, are a proposed intermediate level of classification of the Sino-Tibetan languages, centered on the Tibetic languages and the Kinnauri dialect cluste ...
**** Lepcha
**** Tamangish
****Dhimal
The Dhimal or Dhemal () are ethnic group residing in the eastern Terai of Nepal and West Bengal of India. They are a Sino-Tibetan-speaking ethnic group of the eastern Terai. They mainly reside in Morang and Jhapa districts of Nepal and Darjee ...
***Newar
Newar (; , endonym: Newa; , Pracalit script: ), or Nepami, are primarily inhabitants in Kathmandu Valley of Nepal and its surrounding areas, and the creators of its historic heritage and civilisation. Page 15. Newars are a distinct linguisti ...
***Kiranti
The Kirati people, also spelled as Kirat or Kirant or Kiranti, are Tibeto-Burman ethnolinguistic groups living in the Himalayas, mostly the Eastern Himalaya extending eastward from Nepal to North East India (predominantly in the Indian state ...
***Kham
Kham (; ) is one of the three traditional Tibet, Tibetan regions, the others being Domey also known as Amdo in the northeast, and Ü-Tsang in central Tibet. The official name of this Tibetan region/province is Dotoe (). The original residents of ...
- Magar- Chepang
**Tangut-Qiang
***Tangut
Tangut may refer to:
*Tangut people, an ancient ethnic group in Northwest China
*Tangut language, the extinct language spoken by the Tangut people
*Tangut script, the writing system used to write the Tangut language
*Tangut (Unicode block)
*Wester ...
*** Qiangic
*** rGyalrongic
** Nungic
**Tujia Tujia may refer to:
*the Tujia people
*the Tujia language
The Tujia language (; zh, s=土家语 , t=土家語 , p=Tǔjiāyǔ) is a Sino-Tibetan language spoken natively by the Tujia people in Hunan Province, China. It is unclassified within t ...
**Lolo-Burmese–Naxi
*** Lolo-Burmese
*** Naxi
**Karenic
The Karen () or Karenic languages are tonal languages spoken by some 4.5 million Karen people. They are of unclear affiliation within the Sino-Tibetan languages. The Karen languages are written using the Karen script. The three main branches a ...
** Bai
Other languages
The classification ofTujia Tujia may refer to:
*the Tujia people
*the Tujia language
The Tujia language (; zh, s=土家语 , t=土家語 , p=Tǔjiāyǔ) is a Sino-Tibetan language spoken natively by the Tujia people in Hunan Province, China. It is unclassified within t ...
is difficult due to extensive borrowing. Other unclassified Tibeto-Burman languages include Basum and the Songlin and Chamdo languages
The Chamdo languages are a group of recently discovered, closely related Sino-Tibetan languages spoken in Chamdo Prefecture, Tibet.Suzuki, Hiroyuki and Tashi Nyima. 2018Historical relationship among three non-Tibetic languages in Chamdo, TAR ''Pro ...
, both of which were only described in the 2010s. New Tibeto-Burman languages continue to be recognized, some not closely related to other languages. Distinct languages only recognized in the 2010s include Koki Naga.
Randy LaPolla
Randy John LaPolla () is a professor and former Head of Division at thDivision of Linguistics and Multilingual Studiesin Nanyang Technological University. He is also a Fellow of the Australian Academy of the Humanities, elected 2008. He is current ...
(2003) proposed a Rung branch of Tibeto-Burman, based on morphological evidence, but this is not widely accepted.
Scott DeLancey
Scott DeLancey (born 1949) is an American linguist from the University of Oregon. His work focuses on typology and historical linguistics of Tibeto-Burman languages as well as Indigenous languages of the Americas, North American indigenous languag ...
(2015)DeLancey, Scott. 2015. "Morphological Evidence for a Central Branch of Trans-Himalayan (Sino-Tibetan)." ''Cahiers de linguistique – Asie oriental'' 44(2):122–149. December 2015. proposed a Central branch of Tibeto-Burman based on morphological evidence.
Roger Blench and Mark Post (2011) list a number of divergent languages of Arunachal Pradesh
Arunachal Pradesh (; ) is a States and union territories of India, state in northeast India. It was formed from the North-East Frontier Agency (NEFA) region, and India declared it as a state on 20 February 1987. Itanagar is its capital and la ...
, in northeastern India, that might have non-Tibeto-Burman substrates, or could even be non-Tibeto-Burman language isolate
A language isolate is a language that has no demonstrable genetic relationship with any other languages. Basque in Europe, Ainu and Burushaski in Asia, Sandawe in Africa, Haida and Zuni in North America, Kanoê in South America, and Tiwi ...
s:
** Kamengic
*** Bugun (Khowa)
*** Mey (Sherdukpen) of Shergaon
*** Mey (Sherdukpen) of Rupa
*** Sartang
*** Chug and Lish
Lish () is a village in Tutaki Rural District of the Central District of Siahkal County, Gilan province, Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Ira ...
** orthernMishmi (Digarish)
*** Idu (Luoba)
*** Taraon (Digaru)
** Siangic
***Koro Koro may refer to:
Geography
*Koro Island, a Fijian island
* Koro Sea, in the Pacific Ocean
* Koro, Ivory Coast
*Koro, Mali
*Koro, Wisconsin, United States, an unincorporated community
Languages
*Koro language (India), an endangered language spok ...
*** Milang
** Puroik (Sulung) – East Kameng District
East Kameng district is one of districts of Arunachal Pradesh state in northeastern, India. It shares an international border with China in the north and district borders with West Kameng district to the west, Pakke-Kessang district to the south ...
** Hruso (Aka) – Thrizino Circle, West Kameng District
West Kameng (pronounced ) is a district of Arunachal Pradesh in northeastern India. It accounts for 8.86% of the total area of the state. The name is derived from the Kameng river, a tributary of the Brahmaputra, that flows through the distri ...
** Miji (Sajolang, Dimai, Dhimmai)
** Miju
Blench and Post believe the remaining languages with these substratal characteristics are more clearly Sino-Tibetan:
**East Bodish
*** Meyor (Zakhring)
*** Monpa of Tawang – Tawang District
Tawang district (Pron:/tɑ:ˈwæŋ or təˈwæŋ/) is the smallest of the 26 Districts of Arunachal Pradesh, administrative districts of Arunachal Pradesh state in northeastern India. With a population of 49,977, it is the eighth least populous ...
*** Monpa of Kalaktang (Tshangla)
*** Monpa of Zemithang
***Monpa of Mago-Thingbu
**Tani: Nah
Sodium hydride is the chemical compound with the empirical formula Na H. This alkali metal hydride is primarily used as a strong yet combustible base in organic synthesis. NaH is a saline (salt-like) hydride, composed of Na+ and H− ions, in con ...
Notes
References
Notes Bibliography * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * **Further reading
* Mann, Noel Walter (1998).A phonological reconstruction of Proto Northern Burmic
'. Unpublished thesis. Arlington: The University of Texas. *
External links
Sino-Tibetan Etymological Dictionary and Thesaurus (STEDT)
''Linguistics of the Tibeto-Burman Area''
(journal) * (by
George van Driem
George "Sjors" van Driem (born 1957) is a Dutch professor emeritus of linguistics at the University of Bern. He studied East Asian languages and is known for the father tongue hypothesis.
Education
* Leiden University, 1983–1987 (PhD, ''A Gra ...
)
Sino-Tibetan Branches Project (STBP)
Tibeto-Burman bibliography website
{{Authority control Languages of Tibet Languages of Myanmar