DNA sequencing is the process of determining the
nucleic acid sequence
A nucleic acid sequence is a succession of Nucleobase, bases within the nucleotides forming alleles within a DNA (using GACT) or RNA (GACU) molecule. This succession is denoted by a series of a set of five different letters that indicate the orde ...
– the order of
nucleotides
Nucleotides are Organic compound, organic molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both o ...
in
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases:
adenine
Adenine (, ) (nucleoside#List of nucleosides and corresponding nucleobases, symbol A or Ade) is a purine nucleotide base that is found in DNA, RNA, and Adenosine triphosphate, ATP. Usually a white crystalline subtance. The shape of adenine is ...
,
thymine
Thymine () (symbol T or Thy) is one of the four nucleotide bases in the nucleic acid of DNA that are represented by the letters G–C–A–T. The others are adenine, guanine, and cytosine. Thymine is also known as 5-methyluracil, a pyrimidine ...
,
cytosine
Cytosine () (symbol C or Cyt) is one of the four nucleotide bases found in DNA and RNA, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine ( uracil in RNA). It is a pyrimidine derivative, with a heterocyclic aromatic ring and two substituents attac ...
, and
guanine
Guanine () (symbol G or Gua) is one of the four main nucleotide bases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine ( uracil in RNA). In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. The guanine nucleoside ...
. The advent of rapid DNA sequencing methods has greatly accelerated biological and medical research and discovery.
Knowledge of DNA sequences has become indispensable for basic biological research,
DNA Genographic Projects and in numerous applied fields such as
medical diagnosis
Medical diagnosis (abbreviated Dx, Dx, or Ds) is the process of determining which disease or condition explains a person's symptoms and signs. It is most often referred to as a diagnosis with the medical context being implicit. The information ...
,
biotechnology
Biotechnology is a multidisciplinary field that involves the integration of natural sciences and Engineering Science, engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms and parts thereof for products and services. Specialists ...
,
forensic biology,
virology
Virology is the Scientific method, scientific study of biological viruses. It is a subfield of microbiology that focuses on their detection, structure, classification and evolution, their methods of infection and exploitation of host (biology), ...
and biological
systematics
Systematics is the study of the diversification of living forms, both past and present, and the relationships among living things through time. Relationships are visualized as evolutionary trees (synonyms: phylogenetic trees, phylogenies). Phy ...
. Comparing healthy and mutated DNA sequences can diagnose different diseases including various cancers, characterize antibody repertoire,
and can be used to guide patient treatment. Having a quick way to sequence DNA allows for faster and more individualized medical care to be administered, and for more organisms to be identified and cataloged.
The rapid advancements in DNA sequencing technology have played a crucial role in sequencing complete genomes of various life forms, including humans, as well as numerous animal, plant, and microbial species.

The first DNA sequences were obtained in the early 1970s by academic researchers using laborious methods based on
two-dimensional chromatography. Following the development of
fluorescence
Fluorescence is one of two kinds of photoluminescence, the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. When exposed to ultraviolet radiation, many substances will glow (fluoresce) with colore ...
-based sequencing methods with a
DNA sequencer,
DNA sequencing has become easier and orders of magnitude faster.
Applications
DNA sequencing may be used to determine the sequence of individual
gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
s, larger genetic regions (i.e. clusters of genes or
operons), full chromosomes, or
entire genomes of any organism. DNA sequencing is also the most efficient way to indirectly sequence
RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself (non-coding RNA) or by forming a template for the production of proteins (messenger RNA). RNA and deoxyrib ...
or
protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s (via their
open reading frame
In molecular biology, reading frames are defined as spans of DNA sequence between the start and stop codons. Usually, this is considered within a studied region of a prokaryotic DNA sequence, where only one of the six possible reading frames ...
s). In fact, DNA sequencing has become a key technology in many areas of biology and other sciences such as medicine,
forensics
Forensic science combines principles of law and science to investigate criminal activity. Through crime scene investigations and laboratory analysis, forensic scientists are able to link suspects to evidence. An example is determining the time and ...
, and
anthropology
Anthropology is the scientific study of humanity, concerned with human behavior, human biology, cultures, society, societies, and linguistics, in both the present and past, including archaic humans. Social anthropology studies patterns of behav ...
.
Molecular biology
Sequencing is used in
molecular biology
Molecular biology is a branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecule, molecular basis of biological activity in and between Cell (biology), cells, including biomolecule, biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactio ...
to study genomes and the proteins they encode. Information obtained using sequencing allows researchers to identify changes in genes and noncoding DNA (including regulatory sequences), associations with diseases and phenotypes, and identify potential drug targets.
Evolutionary biology
Since DNA is an informative macromolecule in terms of transmission from one generation to another, DNA sequencing is used in
evolutionary biology
Evolutionary biology is the subfield of biology that studies the evolutionary processes such as natural selection, common descent, and speciation that produced the diversity of life on Earth. In the 1930s, the discipline of evolutionary biolo ...
to study how different organisms are related and how they evolved. In February 2021, scientists reported, for the first time, the sequencing of
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
from
animal remains, a
mammoth
A mammoth is any species of the extinct elephantid genus ''Mammuthus.'' They lived from the late Miocene epoch (from around 6.2 million years ago) into the Holocene until about 4,000 years ago, with mammoth species at various times inhabi ...
in this instance, over a million years old, the oldest DNA sequenced to date.
Metagenomics
The field of
metagenomics
Metagenomics is the study of all genetics, genetic material from all organisms in a particular environment, providing insights into their composition, diversity, and functional potential. Metagenomics has allowed researchers to profile the mic ...
involves identification of organisms present in a body of water,
sewage
Sewage (or domestic sewage, domestic wastewater, municipal wastewater) is a type of wastewater that is produced by a community of people. It is typically transported through a sewerage, sewer system. Sewage consists of wastewater discharged fro ...
, dirt, debris filtered from the air, or swab samples from organisms. Knowing which organisms are present in a particular environment is critical to research in
ecology
Ecology () is the natural science of the relationships among living organisms and their Natural environment, environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community (ecology), community, ecosystem, and biosphere lev ...
,
epidemiology
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and Risk factor (epidemiology), determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population, and application of this knowledge to prevent dise ...
,
microbiology
Microbiology () is the branches of science, scientific study of microorganisms, those being of unicellular organism, unicellular (single-celled), multicellular organism, multicellular (consisting of complex cells), or non-cellular life, acellula ...
, and other fields. Sequencing enables researchers to determine which types of microbes may be present in a
microbiome
A microbiome () is the community of microorganisms that can usually be found living together in any given habitat. It was defined more precisely in 1988 by Whipps ''et al.'' as "a characteristic microbial community occupying a reasonably wel ...
, for example.
Virology
As most viruses are too small to be seen by a light microscope, sequencing is one of the main tools in virology to identify and study the virus.
Viral genomes can be based in DNA or RNA. RNA viruses are more time-sensitive for genome sequencing, as they degrade faster in clinical samples.
Traditional
Sanger sequencing
Sanger sequencing is a method of DNA sequencing that involves electrophoresis and is based on the random incorporation of chain-terminating dideoxynucleotides by DNA polymerase during in vitro DNA replication. After first being developed by Fred ...
and next-generation sequencing are used to sequence viruses in basic and clinical research, as well as for the diagnosis of emerging viral infections,
molecular epidemiology Molecular epidemiology is a branch of epidemiology and medical science that focuses on the contribution of potential genetic and environmental risk factors, identified at the molecular level, to the etiology, distribution and prevention of disease w ...
of viral pathogens, and drug-resistance testing. There are more than 2.3 million unique viral sequences in
GenBank
The GenBank sequence database is an open access, annotated collection of all publicly available nucleotide sequences and their protein translations. It is produced and maintained by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI; a par ...
.
Recently, NGS has surpassed traditional Sanger as the most popular approach for generating viral genomes.
During the
1997 avian influenza outbreak, viral sequencing determined that the influenza sub-type originated through
reassortment
Reassortment is the mixing of the genetic material of a species into new combinations in different individuals. The product of reassortment is called a reassortant. It is particularly used when two similar viruses that are infecting the same cell ...
between
quail
Quail is a collective name for several genera of mid-sized birds generally placed in the order Galliformes. The collective noun for a group of quail is a flock, covey, or bevy.
Old World quail are placed in the family Phasianidae, and New ...
and poultry. This led to legislation in
Hong Kong
Hong Kong)., Legally Hong Kong, China in international treaties and organizations. is a special administrative region of China. With 7.5 million residents in a territory, Hong Kong is the fourth most densely populated region in the wor ...
that prohibited selling live quail and poultry together at market. Viral sequencing can also be used to estimate when a viral outbreak began by using a
molecular clock
The molecular clock is a figurative term for a technique that uses the mutation rate of biomolecules to deduce the time in prehistory when two or more life forms diverged. The biomolecular data used for such calculations are usually nucleot ...
technique.
Medicine
Medical technicians may sequence genes (or, theoretically, full genomes) from patients to determine if there is risk of genetic diseases. This is a form of
genetic testing
Genetic testing, also known as DNA testing, is used to identify changes in DNA sequence or chromosome structure. Genetic testing can also include measuring the results of genetic changes, such as RNA analysis as an output of gene expression, or ...
, though some genetic tests may not involve DNA sequencing.
As of 2013 DNA sequencing was increasingly used to diagnose and treat rare diseases. As more and more genes are identified that cause rare genetic diseases, molecular diagnoses for patients become more mainstream. DNA sequencing allows clinicians to identify genetic diseases, improve disease management, provide reproductive counseling, and more effective therapies. Gene sequencing panels are used to identify multiple potential genetic causes of a suspected disorder.
Also, DNA sequencing may be useful for determining a specific bacteria, to allow for more
precise antibiotics treatments, hereby reducing the risk of creating
antimicrobial resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR or AR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from antimicrobials, which are drugs used to treat infections. This resistance affects all classes of microbes, including bacteria (antibiotic resista ...
in bacteria populations.
Forensic investigation
DNA sequencing may be used along with
DNA profiling
DNA profiling (also called DNA fingerprinting and genetic fingerprinting) is the process of determining an individual's deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) characteristics. DNA analysis intended to identify a species, rather than an individual, is cal ...
methods for
forensic identification
Forensic identification is the application of forensic science, or "forensics", and technology to identify specific objects from the trace evidence they leave, often at a crime scene or the scene of an accident. Forensic means "for the courts".
Hu ...
and
paternity testing. DNA testing has evolved tremendously in the last few decades to ultimately link a DNA print to what is under investigation. The DNA patterns in fingerprint, saliva, hair follicles, etc. uniquely separate each living organism from another. Testing DNA is a technique which can detect specific genomes in a DNA strand to produce a unique and individualized pattern.
DNA sequencing may be used along with
DNA profiling
DNA profiling (also called DNA fingerprinting and genetic fingerprinting) is the process of determining an individual's deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) characteristics. DNA analysis intended to identify a species, rather than an individual, is cal ...
methods for
forensic identification
Forensic identification is the application of forensic science, or "forensics", and technology to identify specific objects from the trace evidence they leave, often at a crime scene or the scene of an accident. Forensic means "for the courts".
Hu ...
and
paternity testing, as it has evolved significantly over the past few decades to ultimately link a DNA print to what is under investigation. The DNA patterns in fingerprint, saliva, hair follicles, and other bodily fluids uniquely separate each living organism from another, making it an invaluable tool in the field of
forensic science
Forensic science combines principles of law and science to investigate criminal activity. Through crime scene investigations and laboratory analysis, forensic scientists are able to link suspects to evidence. An example is determining the time and ...
. The process of DNA testing involves detecting specific
genomes
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as ...
in a DNA strand to produce a unique and individualized pattern, which can be used to identify individuals or determine their relationships.
The advancements in DNA sequencing technology have made it possible to analyze and compare large amounts of
genetic data quickly and accurately, allowing investigators to gather evidence and solve crimes more efficiently. This technology has been used in various applications, including forensic identification, paternity testing, and human identification in cases where traditional identification methods are unavailable or unreliable. The use of DNA sequencing has also led to the development of new forensic techniques, such as
DNA phenotyping, which allows investigators to predict an individual's physical characteristics based on their genetic data.
In addition to its applications in forensic science, DNA sequencing has also been used in medical research and diagnosis. It has enabled scientists to identify genetic mutations and variations that are associated with certain diseases and disorders, allowing for more accurate diagnoses and targeted treatments. Moreover, DNA sequencing has also been used in conservation biology to study the genetic diversity of endangered species and develop strategies for their conservation.
Furthermore, the use of DNA sequencing has also raised important ethical and legal considerations. For example, there are concerns about the privacy and security of genetic data, as well as the potential for misuse or discrimination based on genetic information. As a result, there are ongoing debates about the need for regulations and guidelines to ensure the responsible use of DNA sequencing technology.
Overall, the development of DNA sequencing technology has revolutionized the field of forensic science and has far-reaching implications for our understanding of genetics, medicine, and conservation biology.
The four canonical bases
The canonical structure of DNA has four bases:
thymine
Thymine () (symbol T or Thy) is one of the four nucleotide bases in the nucleic acid of DNA that are represented by the letters G–C–A–T. The others are adenine, guanine, and cytosine. Thymine is also known as 5-methyluracil, a pyrimidine ...
(T),
adenine
Adenine (, ) (nucleoside#List of nucleosides and corresponding nucleobases, symbol A or Ade) is a purine nucleotide base that is found in DNA, RNA, and Adenosine triphosphate, ATP. Usually a white crystalline subtance. The shape of adenine is ...
(A),
cytosine
Cytosine () (symbol C or Cyt) is one of the four nucleotide bases found in DNA and RNA, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine ( uracil in RNA). It is a pyrimidine derivative, with a heterocyclic aromatic ring and two substituents attac ...
(C), and
guanine
Guanine () (symbol G or Gua) is one of the four main nucleotide bases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine ( uracil in RNA). In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. The guanine nucleoside ...
(G). DNA sequencing is the determination of the physical order of these bases in a molecule of DNA. However, there are many other bases that may be present in a molecule. In some viruses (specifically,
bacteriophage
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a phage (), is a virus that infects and replicates within bacteria. The term is derived . Bacteriophages are composed of proteins that Capsid, encapsulate a DNA or RNA genome, and may have structu ...
), cytosine may be replaced by hydroxy methyl or hydroxy methyl glucose cytosine. In mammalian DNA, variant bases with
methyl
In organic chemistry, a methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, having chemical formula (whereas normal methane has the formula ). In formulas, the group is often abbreviated as ...
groups or phosphosulfate may be found. Depending on the sequencing technique, a particular modification, e.g., the 5mC (
5-Methylcytosine
5-Methylcytosine (5mC) is a methylation, methylated form of the DNA base cytosine (C) that regulates gene Transcription (genetics), transcription and takes several other biological roles. When cytosine is methylated, the DNA maintains the same s ...
) common in humans, may or may not be detected.
In almost all organisms, DNA is synthesized in vivo using only the 4 canonical bases; modification that occurs post replication creates other bases like 5 methyl C. However, some bacteriophage can incorporate a non standard base directly.
In addition to modifications, DNA is under constant assault by environmental agents such as UV and Oxygen radicals. At the present time, the presence of such damaged bases is not detected by most DNA sequencing methods, although PacBio has published on this.
History
Discovery of DNA structure and function
Deoxyribonucleic acid (
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
) was first discovered and isolated by
Friedrich Miescher
Johannes Friedrich Miescher (13 August 1844 – 26 August 1895) was a Swiss physician and biologist. He was the first scientist to isolate nucleic acid in 1869. Miescher also identified protamine and made several other discoveries.
Miescher had ...
in 1869, but it remained under-studied for many decades because
protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s, rather than DNA, were thought to hold the genetic blueprint to life. This situation changed after 1944 as a result of some experiments by
Oswald Avery
Oswald Theodore Avery Jr. (October 21, 1877 – February 20, 1955) was a Canadian-American physician and medical researcher. The major part of his career was spent at the Rockefeller Hospital in New York City. Avery was one of the first molecu ...
,
Colin MacLeod, and
Maclyn McCarty
Maclyn McCarty (June 9, 1911 – January 2, 2005) was an American geneticist, a research scientist described in 2005 as "the last surviving member of a Manhattan scientific team that overturned medical dogma in the 1940s and became the first to ...
demonstrating that purified DNA could change one strain of bacteria into another. This was the first time that DNA was shown capable of transforming the properties of cells.
In 1953,
James Watson
James Dewey Watson (born April 6, 1928) is an American molecular biology, molecular biologist, geneticist, and zoologist. In 1953, he co-authored with Francis Crick the academic paper in ''Nature (journal), Nature'' proposing the Nucleic acid ...
and
Francis Crick
Francis Harry Compton Crick (8 June 1916 – 28 July 2004) was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist, and neuroscientist. He, James Watson, Rosalind Franklin, and Maurice Wilkins played crucial roles in deciphering the Nucleic acid doub ...
put forward their
double-helix
In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA. The double helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its secondary structure, a ...
model of DNA, based on
crystallized X-ray structures being studied by
Rosalind Franklin
Rosalind Elsie Franklin (25 July 192016 April 1958) was a British chemist and X-ray crystallographer. Her work was central to the understanding of the molecular structures of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), RNA (ribonucleic acid), viruses, coal ...
. According to the model, DNA is composed of two strands of nucleotides coiled around each other, linked together by hydrogen bonds and running in opposite directions. Each strand is composed of four complementary nucleotides – adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T) – with an A on one strand always paired with T on the other, and C always paired with G. They proposed that such a structure allowed each strand to be used to reconstruct the other, an idea central to the passing on of hereditary information between generations.

The foundation for sequencing proteins was first laid by the work of
Frederick Sanger
Frederick Sanger (; 13 August 1918 – 19 November 2013) was a British biochemist who received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry twice.
He won the 1958 Chemistry Prize for determining the amino acid sequence of insulin and numerous other prote ...
who by 1955 had completed the sequence of all the amino acids in
insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the insulin (''INS)'' gene. It is the main Anabolism, anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabol ...
, a small protein secreted by the pancreas. This provided the first conclusive evidence that proteins were chemical entities with a specific molecular pattern rather than a random mixture of material suspended in fluid. Sanger's success in sequencing insulin spurred on x-ray crystallographers, including Watson and Crick, who by now were trying to understand how DNA directed the formation of proteins within a cell. Soon after attending a series of lectures given by Frederick Sanger in October 1954, Crick began developing a theory which argued that the arrangement of nucleotides in DNA determined the sequence of amino acids in proteins, which in turn helped determine the function of a protein. He published this theory in 1958.
RNA sequencing
RNA sequencing
RNA-Seq (named as an abbreviation of RNA sequencing) is a technique that uses next-generation sequencing to reveal the presence and quantity of RNA molecules in a biological sample, providing a snapshot of gene expression in the sample, also kn ...
was one of the earliest forms of nucleotide sequencing. The major landmark of RNA sequencing is the sequence of the first complete gene and the complete genome of
Bacteriophage MS2
Bacteriophage MS2 (''Emesvirus zinderi''), commonly called MS2, is an icosahedral, positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus that infects the bacterium ''Escherichia coli'' and other members of the Enterobacteriaceae. MS2 is a member of a family ...
, identified and published by
Walter Fiers and his coworkers at the
University of Ghent
Ghent University (, abbreviated as UGent) is a Public university, public research university located in Ghent, in the East Flanders province of Belgium.
Located in Flanders, Ghent University is the second largest Belgian university, consisting o ...
(
Ghent
Ghent ( ; ; historically known as ''Gaunt'' in English) is a City status in Belgium, city and a Municipalities of Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the Provinces of Belgium, province ...
,
Belgium
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. Situated in a coastal lowland region known as the Low Countries, it is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeas ...
), in 1972 and 1976. Traditional RNA sequencing methods require the creation of a
cDNA
In genetics, complementary DNA (cDNA) is DNA that was reverse transcribed (via reverse transcriptase) from an RNA (e.g., messenger RNA or microRNA). cDNA exists in both single-stranded and double-stranded forms and in both natural and engin ...
molecule which must be sequenced.
Traditional RNA Sequencing Methods
Traditional RNA sequencing methods involve several steps:
1) ''Reverse Transcription'': The first step is to convert the RNA molecule into a complementary DNA (cDNA) molecule using an enzyme called
reverse transcriptase
A reverse transcriptase (RT) is an enzyme used to convert RNA genome to DNA, a process termed reverse transcription. Reverse transcriptases are used by viruses such as HIV and hepatitis B to replicate their genomes, by retrotransposon mobi ...
.
2) ''cDNA Synthesis'': The cDNA molecule is then synthesized through a process called PCR (
Polymerase Chain Reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to make millions to billions of copies of a specific DNA sample rapidly, allowing scientists to amplify a very small sample of DNA (or a part of it) sufficiently to enable detailed st ...
), which amplifies the cDNA to produce multiple copies.
3)''Sequencing'': The amplified cDNA is then sequenced using a technique such as
Sanger sequencing
Sanger sequencing is a method of DNA sequencing that involves electrophoresis and is based on the random incorporation of chain-terminating dideoxynucleotides by DNA polymerase during in vitro DNA replication. After first being developed by Fred ...
or
Maxam-Gilbert sequencing.
Challenges and Limitations
Traditional RNA sequencing methods have several limitations. For example:
They require the creation of a cDNA molecule, which can be time-consuming and labor-intensive.
They are prone to errors and biases, which can affect the accuracy of the sequencing results.
They are limited in their ability to detect rare or low-abundance transcripts.
Advances in RNA Sequencing Technology
In recent years, advances in RNA sequencing technology have addressed some of these limitations. New methods such as
next-generation sequencing
Massive parallel sequencing or massively parallel sequencing is any of several high-throughput approaches to DNA sequencing using the concept of massively parallel processing; it is also called next-generation sequencing (NGS) or second-generation ...
(NGS) and
single-molecule real-time (SMRT) sequencing have enabled faster, more accurate, and more cost-effective sequencing of RNA molecules. These advances have opened up new possibilities for studying gene expression, identifying new genes, and understanding the regulation of gene expression.
Early DNA sequencing methods
The first method for determining
DNA sequences
A nucleic acid sequence is a succession of bases within the nucleotides forming alleles within a DNA (using GACT) or RNA (GACU) molecule. This succession is denoted by a series of a set of five different letters that indicate the order of the ...
involved a location-specific primer extension strategy established by
Ray Wu, a geneticist, at
Cornell University
Cornell University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university based in Ithaca, New York, United States. The university was co-founded by American philanthropist Ezra Cornell and historian and educator Andrew Dickson W ...
in 1970. DNA polymerase catalysis and specific nucleotide labeling, both of which figure prominently in current sequencing schemes, were used to sequence the cohesive ends of lambda phage DNA.
Between 1970 and 1973, Wu, scientist Radha Padmanabhan and colleagues demonstrated that this method can be employed to determine any DNA sequence using synthetic location-specific primers.
Walter Gilbert
Walter Gilbert (born March 21, 1932) is an American biochemist, physicist, molecular biology pioneer, and Nobel laureate.
Education and early life
Walter Gilbert was born in Boston, Massachusetts, on March 21, 1932, into a Jewish family, the so ...
, a biochemist, and
Allan Maxam, a molecular geneticist, at
Harvard
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Founded in 1636 and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher lear ...
also developed sequencing methods, including one for "DNA sequencing by chemical degradation".
In 1973, Gilbert and Maxam reported the sequence of 24 basepairs using a method known as wandering-spot analysis. Advancements in sequencing were aided by the concurrent development of
recombinant DNA
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) molecules are DNA molecules formed by laboratory methods of genetic recombination (such as molecular cloning) that bring together genetic material from multiple sources, creating sequences that would not otherwise be fo ...
technology, allowing DNA samples to be isolated from sources other than viruses.
Two years later in 1975,
Frederick Sanger
Frederick Sanger (; 13 August 1918 – 19 November 2013) was a British biochemist who received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry twice.
He won the 1958 Chemistry Prize for determining the amino acid sequence of insulin and numerous other prote ...
, a biochemist, and
Alan Coulson, a genome scientist, developed a method to sequence DNA. The
technique
Technique or techniques may refer to:
Music
* The Techniques, a Jamaican rocksteady vocal group of the 1960s
* Technique (band), a British female synth pop band in the 1990s
* ''Technique'' (album), by New Order, 1989
* ''Techniques'' (album), by ...
known as the "Plus and Minus" method, involved supplying all the components of the DNA but excluding the reaction of one of the four bases needed to complete the DNA.
In 1976, Gilbert and Maxam, invented a method for rapidly sequencing DNA while at Harvard, known as the Maxam–Gilbert sequencing. The technique involved treating radiolabelled DNA with a chemical and using a polyacrylamide gel to determine the sequence.
In 1977, Sanger then adopted a primer-extension strategy to develop more rapid DNA sequencing methods at the
MRC Centre,
Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a List of cities in the United Kingdom, city and non-metropolitan district in the county of Cambridgeshire, England. It is the county town of Cambridgeshire and is located on the River Cam, north of London. As of the 2021 Unit ...
, UK. This technique was similar to his "Plus and Minus" strategy, however, it was based upon the selective incorporation of chain-terminating dideoxynucleotides (ddNTPs) by
DNA polymerase
A DNA polymerase is a member of a family of enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of DNA molecules from nucleoside triphosphates, the molecular precursors of DNA. These enzymes are essential for DNA replication and usually work in groups to create t ...
during in vitro
DNA replication
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all life, living organisms, acting as the most essential part of heredity, biolog ...
. Sanger published this method in the same year.
Sequencing of full genomes
The first full DNA genome to be sequenced was that of
bacteriophage φX174 in 1977.
Medical Research Council scientists deciphered the complete DNA sequence of the
Epstein-Barr virus in 1984, finding it contained 172,282 nucleotides. Completion of the sequence marked a significant turning point in DNA sequencing because it was achieved with no prior genetic profile knowledge of the virus.
A non-radioactive method for transferring the DNA molecules of sequencing reaction mixtures onto an immobilizing matrix during
electrophoresis
Electrophoresis is the motion of charged dispersed particles or dissolved charged molecules relative to a fluid under the influence of a spatially uniform electric field. As a rule, these are zwitterions with a positive or negative net ch ...
was developed by Herbert Pohl and co-workers in the early 1980s. Followed by the commercialization of the DNA sequencer "Direct-Blotting-Electrophoresis-System GATC 1500" by
GATC Biotech, which was intensively used in the framework of the EU genome-sequencing programme, the complete DNA sequence of the yeast ''
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' () (brewer's yeast or baker's yeast) is a species of yeast (single-celled fungal microorganisms). The species has been instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have be ...
'' chromosome II.
's laboratory at the
California Institute of Technology
The California Institute of Technology (branded as Caltech) is a private research university in Pasadena, California, United States. The university is responsible for many modern scientific advancements and is among a small group of institutes ...
announced the first semi-automated DNA sequencing machine in 1986. This was followed by
Applied Biosystems
Applied Biosystems is one of various brands under the Life Technologies brand of Thermo Fisher Scientific corporation. The brand is focused on integrated systems for genetic analysis, which include computerized machines and the consumables used ...
' marketing of the first fully automated sequencing machine, the ABI 370, in 1987 and by Dupont's Genesis 2000 which used a novel fluorescent labeling technique enabling all four
dideoxynucleotides to be identified in a single lane. By 1990, the U.S.
National Institutes of Health
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and public health research. It was founded in 1887 and is part of the United States Department of Health and Human Service ...
(NIH) had begun large-scale sequencing trials on ''
Mycoplasma capricolum'', ''
Escherichia coli
''Escherichia coli'' ( )Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Escherichia'' that is commonly fo ...
'', ''
Caenorhabditis elegans
''Caenorhabditis elegans'' () is a free-living transparent nematode about 1 mm in length that lives in temperate soil environments. It is the type species of its genus. The name is a Hybrid word, blend of the Greek ''caeno-'' (recent), ''r ...
'', and ''
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' () (brewer's yeast or baker's yeast) is a species of yeast (single-celled fungal microorganisms). The species has been instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have be ...
'' at a cost of US$0.75 per base. Meanwhile, sequencing of human
cDNA
In genetics, complementary DNA (cDNA) is DNA that was reverse transcribed (via reverse transcriptase) from an RNA (e.g., messenger RNA or microRNA). cDNA exists in both single-stranded and double-stranded forms and in both natural and engin ...
sequences called
expressed sequence tag
In genetics, an expressed sequence tag (EST) is a short sub-sequence of a cDNA sequence. ESTs may be used to identify gene transcripts, and were instrumental in gene discovery and in gene-sequence determination. The identification of ESTs has pro ...
s began in
Craig Venter
John Craig Venter (born October 14, 1946) is an American scientist. He is known for leading one of the first draft sequences of the human genome and led the first team to transfect a cell with a synthetic chromosome. Venter founded Celera Geno ...
's lab, an attempt to capture the coding fraction of the
human genome
The human genome is a complete set of nucleic acid sequences for humans, encoded as the DNA within each of the 23 distinct chromosomes in the cell nucleus. A small DNA molecule is found within individual Mitochondrial DNA, mitochondria. These ar ...
.
In 1995, Venter,
Hamilton Smith, and colleagues at
The Institute for Genomic Research
The J. Craig Venter Institute (JCVI) is a non-profit genomics research institute founded by J. Craig Venter, Ph.D. in October 2006. The institute was the result of consolidating four organizations: the Center for the Advancement of Ge ...
(TIGR) published the first complete genome of a free-living organism, the bacterium ''
Haemophilus influenzae
''Haemophilus influenzae'' (formerly called Pfeiffer's bacillus or ''Bacillus influenzae'') is a Gram-negative, Motility, non-motile, Coccobacillus, coccobacillary, facultative anaerobic organism, facultatively anaerobic, Capnophile, capnophili ...
''. The circular chromosome contains 1,830,137 bases and its publication in the journal Science marked the first published use of whole-genome shotgun sequencing, eliminating the need for initial mapping efforts.
By 2003, the Human Genome Project's shotgun sequencing methods had been used to produce a draft sequence of the human genome; it had a 92% accuracy.
In 2022, scientists successfully sequenced the last 8% of the human genome. The fully sequenced standard reference gene is called GRCh38.p14, and it contains 3.1 billion base pairs.
High-throughput sequencing (HTS) methods

Several new methods for DNA sequencing were developed in the mid to late 1990s and were implemented in commercial
DNA sequencers by 2000. Together these were called the "next-generation" or "second-generation" sequencing (NGS) methods, in order to distinguish them from the earlier methods, including
Sanger sequencing
Sanger sequencing is a method of DNA sequencing that involves electrophoresis and is based on the random incorporation of chain-terminating dideoxynucleotides by DNA polymerase during in vitro DNA replication. After first being developed by Fred ...
. In contrast to the first generation of sequencing, NGS technology is typically characterized by being highly scalable, allowing the entire genome to be sequenced at once. Usually, this is accomplished by fragmenting the genome into small pieces, randomly sampling for a fragment, and sequencing it using one of a variety of technologies, such as those described below. An entire genome is possible because multiple fragments are sequenced at once (giving it the name "massively parallel" sequencing) in an automated process.
NGS technology has tremendously empowered researchers to look for insights into health, anthropologists to investigate human origins, and is catalyzing the "
Personalized Medicine" movement. However, it has also opened the door to more room for error. There are many software tools to carry out the computational analysis of NGS data, often compiled at online platforms such as CSI NGS Portal, each with its own algorithm. Even the parameters within one software package can change the outcome of the analysis. In addition, the large quantities of data produced by DNA sequencing have also required development of new methods and programs for sequence analysis. Several efforts to develop standards in the NGS field have been attempted to address these challenges, most of which have been small-scale efforts arising from individual labs. Most recently, a large, organized, FDA-funded effort has culminated in the
BioCompute standard.
On 26 October 1990,
Roger Tsien, Pepi Ross, Margaret Fahnestock and Allan J Johnston filed a patent describing stepwise ("base-by-base") sequencing with removable 3' blockers on DNA arrays (blots and single DNA molecules).
In 1996,
Pål Nyrén
Pål Nyrén (born 1955) is a biochemistry professor at the Royal Institute of Technology (KTH), Stockholm. He is most famous for developing the pyrosequencing method for DNA sequencing.
Career
*1999 Professor in Biochemistry, KTH, Stockholm
*19 ...
and his student
Mostafa Ronaghi at the Royal Institute of Technology in
Stockholm
Stockholm (; ) is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in Sweden by population, most populous city of Sweden, as well as the List of urban areas in the Nordic countries, largest urban area in the Nordic countries. Approximately ...
published their method of
pyrosequencing
Pyrosequencing is a method of DNA sequencing (determining the order of nucleotides in DNA) based on the "sequencing by synthesis" principle, in which the sequencing is performed by detecting the nucleotide incorporated by a DNA polymerase. Pyrosequ ...
.
On 1 April 1997,
Pascal Mayer and Laurent Farinelli submitted patents to the World Intellectual Property Organization describing DNA colony sequencing.
The DNA sample preparation and random surface-
polymerase chain reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to make millions to billions of copies of a specific DNA sample rapidly, allowing scientists to amplify a very small sample of DNA (or a part of it) sufficiently to enable detailed st ...
(PCR) arraying methods described in this patent, coupled to Roger Tsien et al.'s "base-by-base" sequencing method, is now implemented in
Illumina's Hi-Seq genome sequencers.
In 1998, Phil Green and Brent Ewing of the University of Washington described their
phred quality score for sequencer data analysis, a landmark analysis technique that gained widespread adoption, and which is still the most common metric for assessing the accuracy of a sequencing platform.
Lynx Therapeutics published and marketed
massively parallel signature sequencing
Massive parallel signature sequencing (MPSS) is a procedure that is used to identify and quantify mRNA transcripts, resulting in data similar to serial analysis of gene expression (SAGE), although it employs a series of biochemical and sequencing ...
(MPSS), in 2000. This method incorporated a parallelized, adapter/ligation-mediated, bead-based sequencing technology and served as the first commercially available "next-generation" sequencing method, though no
DNA sequencers were sold to independent laboratories.
Basic methods
Maxam-Gilbert sequencing
Allan Maxam and
Walter Gilbert
Walter Gilbert (born March 21, 1932) is an American biochemist, physicist, molecular biology pioneer, and Nobel laureate.
Education and early life
Walter Gilbert was born in Boston, Massachusetts, on March 21, 1932, into a Jewish family, the so ...
published a DNA sequencing method in 1977 based on chemical modification of DNA and subsequent cleavage at specific bases.
Also known as chemical sequencing, this method allowed purified samples of double-stranded DNA to be used without further cloning. This method's use of radioactive labeling and its technical complexity discouraged extensive use after refinements in the Sanger methods had been made.
Maxam-Gilbert sequencing requires radioactive labeling at one 5' end of the DNA and purification of the DNA fragment to be sequenced. Chemical treatment then generates breaks at a small proportion of one or two of the four nucleotide bases in each of four reactions (G, A+G, C, C+T). The concentration of the modifying chemicals is controlled to introduce on average one modification per DNA molecule. Thus a series of labeled fragments is generated, from the radiolabeled end to the first "cut" site in each molecule. The fragments in the four reactions are electrophoresed side by side in denaturing
acrylamide
Acrylamide (or acrylic amide) is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH2=CHC(O)NH2. It is a white odorless solid, soluble in water and several organic solvents. From the chemistry perspective, acrylamide is a vinyl-substituted primary ...
gels for size separation. To visualize the fragments, the gel is exposed to X-ray film for autoradiography, yielding a series of dark bands each corresponding to a radiolabeled DNA fragment, from which the sequence may be inferred.
This method is mostly obsolete as of 2023.
Chain-termination methods
The
chain-termination method developed by
Frederick Sanger
Frederick Sanger (; 13 August 1918 – 19 November 2013) was a British biochemist who received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry twice.
He won the 1958 Chemistry Prize for determining the amino acid sequence of insulin and numerous other prote ...
and coworkers in 1977 soon became the method of choice, owing to its relative ease and reliability.
When invented, the chain-terminator method used fewer toxic chemicals and lower amounts of radioactivity than the Maxam and Gilbert method. Because of its comparative ease, the Sanger method was soon automated and was the method used in the first generation of
DNA sequencers.
Sanger sequencing is the method which prevailed from the 1980s until the mid-2000s. Over that period, great advances were made in the technique, such as fluorescent labelling, capillary electrophoresis, and general automation. These developments allowed much more efficient sequencing, leading to lower costs. The Sanger method, in mass production form, is the technology which produced the
first human genome in 2001, ushering in the age of
genomics
Genomics is an interdisciplinary field of molecular biology focusing on the structure, function, evolution, mapping, and editing of genomes. A genome is an organism's complete set of DNA, including all of its genes as well as its hierarchical, ...
. However, later in the decade, radically different approaches reached the market, bringing the cost per genome down from $100 million in 2001 to $10,000 in 2011.
Sequencing by synthesis
The objective for sequential sequencing by synthesis (SBS) is to determine the sequencing of a
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
sample by detecting the incorporation of a
nucleotide
Nucleotides are Organic compound, organic molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both o ...
by a
DNA polymerase
A DNA polymerase is a member of a family of enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of DNA molecules from nucleoside triphosphates, the molecular precursors of DNA. These enzymes are essential for DNA replication and usually work in groups to create t ...
. An engineered polymerase is used to synthesize a copy of a single strand of DNA and the incorporation of each nucleotide is monitored. The principle of real-time sequencing by synthesis was first described in 1993 with improvements published some years later. The key parts are highly similar for all embodiments of SBS and includes (1)
amplification of DNA (to enhance the subsequent signal) and attach the DNA to be sequenced to a solid support, (2) generation of single stranded DNA on the solid support, (3) incorporation of nucleotides using an engineered polymerase and (4) real-time detection of the incorporation of nucleotide The steps 3-4 are repeated and the sequence is assembled from the signals obtained in step 4. This principle of real-time sequencing-by-synthesis has been used for almost all
massive parallel sequencing
Massive parallel sequencing or massively parallel sequencing is any of several high-throughput approaches to DNA sequencing using the concept of massively parallel processing; it is also called next-generation sequencing (NGS) or second-generation ...
instruments, including
454,
PacBio,
IonTorrent,
Illumina and
MGI.
Large-scale sequencing and ''de novo'' sequencing

Large-scale sequencing often aims at sequencing very long DNA pieces, such as whole
chromosome
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most import ...
s, although large-scale sequencing can also be used to generate very large numbers of short sequences, such as found in
phage display
Phage display is a laboratory technique for the study of protein–protein, protein–peptide, and protein–DNA interactions that uses bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria) to connect proteins with the genetic information that encodes ...
. For longer targets such as chromosomes, common approaches consist of cutting (with
restriction enzyme
A restriction enzyme, restriction endonuclease, REase, ENase or'' restrictase '' is an enzyme that cleaves DNA into fragments at or near specific recognition sites within molecules known as restriction sites. Restriction enzymes are one class o ...
s) or shearing (with mechanical forces) large DNA fragments into shorter DNA fragments. The fragmented DNA may then be
cloned into a
DNA vector and amplified in a bacterial host such as ''
Escherichia coli
''Escherichia coli'' ( )Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Escherichia'' that is commonly fo ...
''. Short DNA fragments purified from individual bacterial colonies are individually sequenced and
assembled electronically into one long, contiguous sequence. Studies have shown that adding a size selection step to collect DNA fragments of uniform size can improve sequencing efficiency and accuracy of the genome assembly. In these studies, automated sizing has proven to be more reproducible and precise than manual gel sizing.
The term "''de novo'' sequencing" specifically refers to methods used to determine the sequence of DNA with no previously known sequence. ''De novo'' translates from Latin as "from the beginning". Gaps in the assembled sequence may be filled by
primer walking. The different strategies have different tradeoffs in speed and accuracy;
shotgun methods are often used for sequencing large genomes, but its assembly is complex and difficult, particularly with
sequence repeats often causing gaps in genome assembly.
Most sequencing approaches use an ''in vitro'' cloning step to amplify individual DNA molecules, because their molecular detection methods are not sensitive enough for single molecule sequencing. Emulsion PCR
isolates individual DNA molecules along with primer-coated beads in aqueous droplets within an oil phase. A
polymerase chain reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to make millions to billions of copies of a specific DNA sample rapidly, allowing scientists to amplify a very small sample of DNA (or a part of it) sufficiently to enable detailed st ...
(PCR) then coats each bead with clonal copies of the DNA molecule followed by immobilization for later sequencing. Emulsion PCR is used in the methods developed by Marguilis et al. (commercialized by
454 Life Sciences
454 Life Sciences was a biotechnology company based in Branford, Connecticut that specialized in high-throughput DNA sequencing. It was acquired by Roche in 2007 and shut down by Roche in 2013 when its technology became noncompetitive, although ...
), Shendure and Porreca et al. (also known as "
polony sequencing") and
SOLiD sequencing, (developed by
Agencourt, later
Applied Biosystems
Applied Biosystems is one of various brands under the Life Technologies brand of Thermo Fisher Scientific corporation. The brand is focused on integrated systems for genetic analysis, which include computerized machines and the consumables used ...
, now
Life Technologies).
Emulsion PCR is also used in the GemCode and Chromium platforms developed by
10x Genomics.
Shotgun sequencing
Shotgun sequencing is a sequencing method designed for analysis of DNA sequences longer than 1000 base pairs, up to and including entire chromosomes. This method requires the target DNA to be broken into random fragments. After sequencing individual fragments using the
chain termination method
Sanger sequencing is a method of DNA sequencing that involves electrophoresis and is based on the random incorporation of chain-terminating dideoxynucleotides by DNA polymerase during in vitro DNA replication. After first being developed by Fred ...
, the sequences can be reassembled on the basis of their overlapping regions.
High-throughput methods
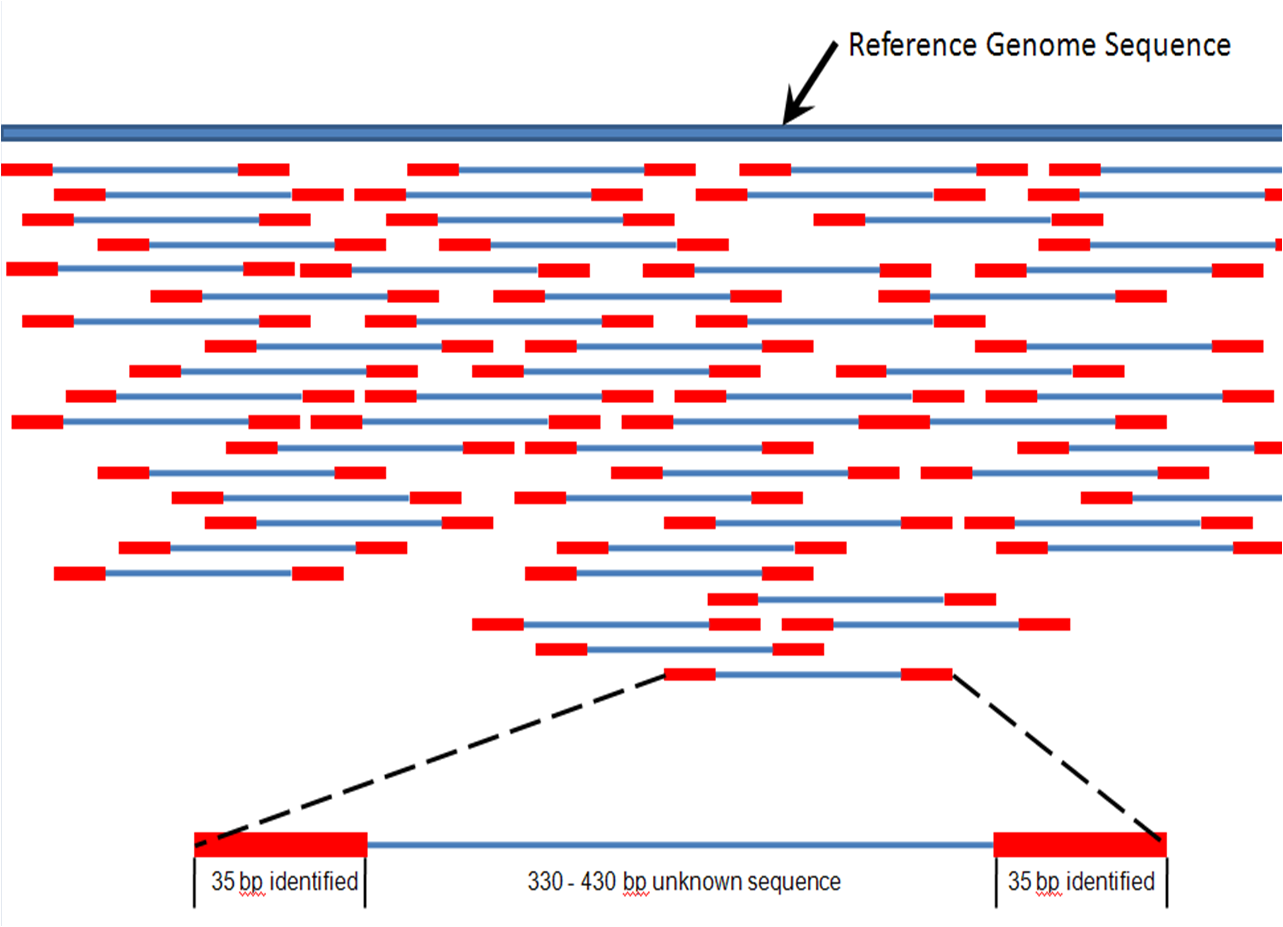
High-throughput sequencing, which includes next-generation "short-read" and third-generation "long-read" sequencing methods,
["Next-generation" remains in broad use as of 2019. For instance, ] applies to
exome sequencing
Exome sequencing, also known as whole exome sequencing (WES), is a genomic technique for sequencing all of the protein-coding regions of genes in a genome (known as the exome). It consists of two steps: the first step is to select only the subs ...
, genome sequencing, genome resequencing,
transcriptome
The transcriptome is the set of all RNA transcripts, including coding and non-coding, in an individual or a population of cells. The term can also sometimes be used to refer to all RNAs, or just mRNA, depending on the particular experiment. The ...
profiling (
RNA-Seq
RNA-Seq (named as an abbreviation of RNA sequencing) is a technique that uses next-generation sequencing to reveal the presence and quantity of RNA molecules in a biological sample, providing a snapshot of gene expression in the sample, also k ...
), DNA-protein interactions (
ChIP-sequencing
ChIP-sequencing, also known as ChIP-seq, is a method used to analyze protein interactions with DNA. ChIP-seq combines chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) with massively parallel DNA sequencing to identify the binding sites of DNA-associated prote ...
), and
epigenome
In biology, the epigenome of an organism is the collection of chemical changes to its DNA and histone proteins that affects when, where, and how the DNA is expressed; these changes can be passed down to an organism's offspring via transgenerat ...
characterization.
The high demand for low-cost sequencing has driven the development of high-throughput sequencing technologies that
parallelize the sequencing process, producing thousands or millions of sequences concurrently.
High-throughput sequencing technologies are intended to lower the cost of DNA sequencing beyond what is possible with standard dye-terminator methods.
In ultra-high-throughput sequencing as many as 500,000 sequencing-by-synthesis operations may be run in parallel.
Such technologies led to the ability to sequence an entire human genome in as little as one day.
, corporate leaders in the development of high-throughput sequencing products included
Illumina,
Qiagen
QIAGEN N.V. is a German-founded multinational provider of sample and assay technologies for molecular diagnostics, applied testing, academic research, and pharmaceutical research. The company operates in more than 35 offices in over 25 countries ...
and
ThermoFisher Scientific.
Long-read sequencing methods
Single molecule real time (SMRT) sequencing
SMRT sequencing is based on the sequencing by synthesis approach. The DNA is synthesized in zero-mode wave-guides (ZMWs) – small well-like containers with the capturing tools located at the bottom of the well. The sequencing is performed with use of unmodified polymerase (attached to the ZMW bottom) and fluorescently labelled nucleotides flowing freely in the solution. The wells are constructed in a way that only the fluorescence occurring by the bottom of the well is detected. The fluorescent label is detached from the nucleotide upon its incorporation into the DNA strand, leaving an unmodified DNA strand. According to
Pacific Biosciences
Pacific Biosciences of California, Inc. (aka PacBio) is an American biotechnology company founded in 2004 that develops and manufactures systems for gene sequencing and some novel real time biological observation. PacBio has two principal sequ ...
(PacBio), the SMRT technology developer, this methodology allows detection of nucleotide modifications (such as cytosine methylation). This happens through the observation of polymerase kinetics. This approach allows reads of 20,000 nucleotides or more, with average read lengths of 5 kilobases.
In 2015, Pacific Biosciences announced the launch of a new sequencing instrument called the Sequel System, with 1 million ZMWs compared to 150,000 ZMWs in the PacBio RS II instrument. SMRT sequencing is referred to as "
third-generation" or "long-read" sequencing.
Nanopore DNA sequencing
The DNA passing through the nanopore changes its ion current. This change is dependent on the shape, size and length of the DNA sequence. Each type of the nucleotide blocks the ion flow through the pore for a different period of time. The method does not require modified nucleotides and is performed in real time. Nanopore sequencing is referred to as "
third-generation" or "long-read" sequencing, along with SMRT sequencing.
Early industrial research into this method was based on a technique called 'exonuclease sequencing', where the readout of electrical signals occurred as nucleotides passed by
alpha(α)-hemolysin pores covalently bound with
cyclodextrin
Cyclodextrins are a family of cyclic oligosaccharides, consisting of a macrocycle, macrocyclic ring of glucose subunits joined by α-1,4 glycosidic bonds. Cyclodextrins are produced from starch by enzyme, enzymatic conversion. They are used in ...
. However the subsequent commercial method, 'strand sequencing', sequenced DNA bases in an intact strand.
Two main areas of nanopore sequencing in development are solid state nanopore sequencing, and protein based nanopore sequencing. Protein nanopore sequencing utilizes membrane protein complexes such as α-hemolysin, MspA (''
Mycobacterium smegmatis
''Mycobacterium smegmatis'' is an acid-fast bacterium, bacterial species in the phylum ''Actinomycetota'' and the genus ''Mycobacterium''. It is 3.0 to 5.0 μm long with a bacillus (shape), bacillus shape and can be stained by Ziehl–Neels ...
'' Porin A) or CssG, which show great promise given their ability to distinguish between individual and groups of nucleotides.
In contrast, solid-state nanopore sequencing utilizes synthetic materials such as silicon nitride and aluminum oxide and it is preferred for its superior mechanical ability and thermal and chemical stability.
The fabrication method is essential for this type of sequencing given that the nanopore array can contain hundreds of pores with diameters smaller than eight nanometers.
The concept originated from the idea that single stranded DNA or RNA molecules can be electrophoretically driven in a strict linear sequence through a biological pore that can be less than eight nanometers, and can be detected given that the molecules release an ionic current while moving through the pore. The pore contains a detection region capable of recognizing different bases, with each base generating various time specific signals corresponding to the sequence of bases as they cross the pore which are then evaluated.
Precise control over the DNA transport through the pore is crucial for success. Various enzymes such as exonucleases and polymerases have been used to moderate this process by positioning them near the pore's entrance.
Short-read sequencing methods
Massively parallel signature sequencing (MPSS)
The first of the high-throughput sequencing technologies,
massively parallel signature sequencing
Massive parallel signature sequencing (MPSS) is a procedure that is used to identify and quantify mRNA transcripts, resulting in data similar to serial analysis of gene expression (SAGE), although it employs a series of biochemical and sequencing ...
(or MPSS, also called next generation sequencing), was developed in the 1990s at Lynx Therapeutics, a company founded in 1992 by
Sydney Brenner
Sydney Brenner (13 January 1927 – 5 April 2019) was a South African biologist. In 2002, he shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine with H. Robert Horvitz and Sir John E. Sulston. Brenner made significant contributions to wo ...
and
Sam Eletr. MPSS was a bead-based method that used a complex approach of adapter ligation followed by adapter decoding, reading the sequence in increments of four nucleotides. This method made it susceptible to sequence-specific bias or loss of specific sequences. Because the technology was so complex, MPSS was only performed 'in-house' by Lynx Therapeutics and no DNA sequencing machines were sold to independent laboratories. Lynx Therapeutics merged with Solexa (later acquired by
Illumina) in 2004, leading to the development of sequencing-by-synthesis, a simpler approach acquired from
Manteia Predictive Medicine, which rendered MPSS obsolete. However, the essential properties of the MPSS output were typical of later high-throughput data types, including hundreds of thousands of short DNA sequences. In the case of MPSS, these were typically used for sequencing
cDNA
In genetics, complementary DNA (cDNA) is DNA that was reverse transcribed (via reverse transcriptase) from an RNA (e.g., messenger RNA or microRNA). cDNA exists in both single-stranded and double-stranded forms and in both natural and engin ...
for measurements of
gene expression
Gene expression is the process (including its Regulation of gene expression, regulation) by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, proteins or non-coding RNA, ...
levels.
Polony sequencing
The
polony sequencing method, developed in the laboratory of
George M. Church at Harvard, was among the first high-throughput sequencing systems and was used to sequence a full ''
E. coli
''Escherichia coli'' ( )Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus ''Escherichia'' that is commonly foun ...
'' genome in 2005.
It combined an in vitro paired-tag library with emulsion PCR, an automated microscope, and ligation-based sequencing chemistry to sequence an ''E. coli'' genome at an accuracy of >99.9999% and a cost approximately 1/9 that of Sanger sequencing.
The technology was licensed to Agencourt Biosciences, subsequently spun out into Agencourt Personal Genomics, and eventually incorporated into the
Applied Biosystems
Applied Biosystems is one of various brands under the Life Technologies brand of Thermo Fisher Scientific corporation. The brand is focused on integrated systems for genetic analysis, which include computerized machines and the consumables used ...
SOLiD platform. Applied Biosystems was later acquired by
Life Technologies, now part of
Thermo Fisher Scientific
Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. is an American life science and clinical research company. It is a global supplier of analytical instruments, clinical development solutions, specialty diagnostics, laboratory, pharmaceutical and biotechnology s ...
.
454 pyrosequencing
A parallelized version of
pyrosequencing
Pyrosequencing is a method of DNA sequencing (determining the order of nucleotides in DNA) based on the "sequencing by synthesis" principle, in which the sequencing is performed by detecting the nucleotide incorporated by a DNA polymerase. Pyrosequ ...
was developed by
454 Life Sciences
454 Life Sciences was a biotechnology company based in Branford, Connecticut that specialized in high-throughput DNA sequencing. It was acquired by Roche in 2007 and shut down by Roche in 2013 when its technology became noncompetitive, although ...
, which has since been acquired by
Roche Diagnostics. The method amplifies DNA inside water droplets in an oil solution (emulsion PCR), with each droplet containing a single DNA template attached to a single primer-coated bead that then forms a clonal colony. The sequencing machine contains many
picoliter-volume wells each containing a single bead and sequencing enzymes. Pyrosequencing uses
luciferase
Luciferase is a generic term for the class of oxidative enzymes that produce bioluminescence, and is usually distinguished from a photoprotein. The name was first used by Raphaël Dubois who invented the words ''luciferin'' and ''luciferase'' ...
to generate light for detection of the individual nucleotides added to the nascent DNA, and the combined data are used to generate sequence
reads.
This technology provides intermediate read length and price per base compared to Sanger sequencing on one end and Solexa and SOLiD on the other.
Illumina (Solexa) sequencing
Solexa, now part of
Illumina, was founded by
Shankar Balasubramanian and
David Klenerman in 1998, and developed a sequencing method based on reversible dye-terminators technology, and engineered polymerases.
The reversible terminated chemistry concept was invented by Bruno Canard and Simon Sarfati at the Pasteur Institute in Paris. It was developed internally at Solexa by those named on the relevant patents. In 2004, Solexa acquired the company
Manteia Predictive Medicine in order to gain a massively parallel sequencing technology invented in 1997 by
Pascal Mayer and Laurent Farinelli.
It is based on "DNA clusters" or "DNA colonies", which involves the clonal amplification of DNA on a surface. The cluster technology was co-acquired with Lynx Therapeutics of California. Solexa Ltd. later merged with Lynx to form Solexa Inc.


In this method, DNA molecules and primers are first attached on a slide or flow cell and amplified with
polymerase
In biochemistry, a polymerase is an enzyme (Enzyme Commission number, EC 2.7.7.6/7/19/48/49) that synthesizes long chains of polymers or nucleic acids. DNA polymerase and RNA polymerase are used to assemble DNA and RNA molecules, respectively, by ...
so that local clonal DNA colonies, later coined "DNA clusters", are formed. To determine the sequence, four types of reversible terminator bases (RT-bases) are added and non-incorporated nucleotides are washed away. A camera takes images of the
fluorescently labeled nucleotides. Then the dye, along with the terminal 3' blocker, is chemically removed from the DNA, allowing for the next cycle to begin. Unlike pyrosequencing, the DNA chains are extended one nucleotide at a time and image acquisition can be performed at a delayed moment, allowing for very large arrays of DNA colonies to be captured by sequential images taken from a single camera.

Decoupling the enzymatic reaction and the image capture allows for optimal throughput and theoretically unlimited sequencing capacity. With an optimal configuration, the ultimately reachable instrument throughput is thus dictated solely by the analog-to-digital conversion rate of the camera, multiplied by the number of cameras and divided by the number of pixels per DNA colony required for visualizing them optimally (approximately 10 pixels/colony). In 2012, with cameras operating at more than 10 MHz A/D conversion rates and available optics, fluidics and enzymatics, throughput can be multiples of 1 million nucleotides/second, corresponding roughly to 1 human genome equivalent at 1x
coverage per hour per instrument, and 1 human genome re-sequenced (at approx. 30x) per day per instrument (equipped with a single camera).
Combinatorial probe anchor synthesis (cPAS)
This method is an upgraded modification to combinatorial probe anchor ligation technology (cPAL) described by
Complete Genomics which has since become part of Chinese genomics company
BGI in 2013. The two companies have refined the technology to allow for longer read lengths, reaction time reductions and faster time to results. In addition, data are now generated as contiguous full-length reads in the standard FASTQ file format and can be used as-is in most short-read-based bioinformatics analysis pipelines.
The two technologies that form the basis for this high-throughput sequencing technology are
DNA nanoballs (DNB) and patterned arrays for nanoball attachment to a solid surface.
DNA nanoballs are simply formed by denaturing double stranded, adapter ligated libraries and ligating the forward strand only to a splint oligonucleotide to form a ssDNA circle. Faithful copies of the circles containing the DNA insert are produced utilizing Rolling Circle Amplification that generates approximately 300–500 copies. The long strand of ssDNA folds upon itself to produce a three-dimensional nanoball structure that is approximately 220 nm in diameter. Making DNBs replaces the need to generate PCR copies of the library on the flow cell and as such can remove large proportions of duplicate reads, adapter-adapter ligations and PCR induced errors.

The patterned array of positively charged spots is fabricated through photolithography and etching techniques followed by chemical modification to generate a sequencing flow cell. Each spot on the flow cell is approximately 250 nm in diameter, are separated by 700 nm (centre to centre) and allows easy attachment of a single negatively charged DNB to the flow cell and thus reducing under or over-clustering on the flow cell.
Sequencing is then performed by addition of an oligonucleotide probe that attaches in combination to specific sites within the DNB. The probe acts as an anchor that then allows one of four single reversibly inactivated, labelled nucleotides to bind after flowing across the flow cell. Unbound nucleotides are washed away before laser excitation of the attached labels then emit fluorescence and signal is captured by cameras that is converted to a digital output for base calling. The attached base has its terminator and label chemically cleaved at completion of the cycle. The cycle is repeated with another flow of free, labelled nucleotides across the flow cell to allow the next nucleotide to bind and have its signal captured. This process is completed a number of times (usually 50 to 300 times) to determine the sequence of the inserted piece of DNA at a rate of approximately 40 million nucleotides per second as of 2018.
SOLiD sequencing

Applied Biosystems
Applied Biosystems is one of various brands under the Life Technologies brand of Thermo Fisher Scientific corporation. The brand is focused on integrated systems for genetic analysis, which include computerized machines and the consumables used ...
' (now a
Life Technologies brand) SOLiD technology employs
sequencing by ligation. Here, a pool of all possible oligonucleotides of a fixed length are labeled according to the sequenced position. Oligonucleotides are annealed and ligated; the preferential ligation by
DNA ligase
DNA ligase is a type of enzyme that facilitates the joining of DNA strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond. It plays a role in repairing single-strand breaks in duplex DNA in living organisms, but some forms (such ...
for matching sequences results in a signal informative of the nucleotide at that position. Each base in the template is sequenced twice, and the resulting data are decoded according to the
2 base encoding scheme used in this method. Before sequencing, the DNA is amplified by emulsion PCR. The resulting beads, each containing single copies of the same DNA molecule, are deposited on a glass slide.
The result is sequences of quantities and lengths comparable to Illumina sequencing.
This
sequencing by ligation method has been reported to have some issue sequencing palindromic sequences.
Ion Torrent semiconductor sequencing
Ion Torrent Systems Inc. (now owned by
Life Technologies) developed a system based on using standard sequencing chemistry, but with a novel, semiconductor-based detection system. This method of sequencing is based on the detection of
hydrogen ion
A hydrogen ion is created when a hydrogen atom loses or gains an electron. A positively charged hydrogen ion (or proton) can readily combine with other particles and therefore is only seen isolated when it is in a gaseous state or a nearly particl ...
s that are released during the
polymerisation
In polymer chemistry, polymerization (American English), or polymerisation (British English), is a process of reacting monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to form polymer chains or three-dimensional networks. There are many form ...
of
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
, as opposed to the optical methods used in other sequencing systems. A microwell containing a template DNA strand to be sequenced is flooded with a single type of
nucleotide
Nucleotides are Organic compound, organic molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both o ...
. If the introduced nucleotide is
complementary to the leading template nucleotide it is incorporated into the growing complementary strand. This causes the release of a hydrogen ion that triggers a hypersensitive ion sensor, which indicates that a reaction has occurred. If
homopolymer repeats are present in the template sequence, multiple nucleotides will be incorporated in a single cycle. This leads to a corresponding number of released hydrogens and a proportionally higher electronic signal.
DNA nanoball sequencing
DNA nanoball sequencing is a type of high throughput sequencing technology used to determine the entire
genomic sequence
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as ...
of an organism. The company
Complete Genomics uses this technology to sequence samples submitted by independent researchers. The method uses
rolling circle replication
Rolling circle replication (RCR) is a process of unidirectional nucleic acid replication that can rapidly synthesize multiple copies of circular molecules of DNA or RNA, such as plasmids, the genomes of bacteriophages, and the circular RNA genom ...
to amplify small fragments of genomic DNA into DNA nanoballs. Unchained sequencing by ligation is then used to determine the nucleotide sequence.
This method of DNA sequencing allows large numbers of DNA nanoballs to be sequenced per run and at low
reagent
In chemistry, a reagent ( ) or analytical reagent is a substance or compound added to a system to cause a chemical reaction, or test if one occurs. The terms ''reactant'' and ''reagent'' are often used interchangeably, but reactant specifies a ...
costs compared to other high-throughput sequencing platforms. However, only short sequences of DNA are determined from each DNA nanoball which makes mapping the short reads to a
reference genome
A reference genome (also known as a reference assembly) is a digital nucleic acid sequence database, assembled by scientists as a representative example of the genome, set of genes in one idealized individual organism of a species. As they are a ...
difficult.
Heliscope single molecule sequencing
Heliscope sequencing is a method of
single-molecule sequencing developed by
Helicos Biosciences. It uses DNA fragments with added poly-A tail adapters which are attached to the flow cell surface. The next steps involve extension-based sequencing with cyclic washes of the flow cell with fluorescently labeled nucleotides (one nucleotide type at a time, as with the Sanger method). The reads are performed by the Heliscope sequencer. The reads are short, averaging 35 bp. What made this technology especially novel was that it was the first of its class to sequence non-amplified DNA, thus preventing any read errors associated with amplification steps. In 2009 a human genome was sequenced using the Heliscope, however in 2012 the company went bankrupt.
Microfluidic Systems
There are two main microfluidic systems that are used to sequence DNA;
droplet based microfluidics and
digital microfluidics. Microfluidic devices solve many of the current limitations of current sequencing arrays.
Abate et al. studied the use of droplet-based microfluidic devices for DNA sequencing.
These devices have the ability to form and process picoliter sized droplets at the rate of thousands per second. The devices were created from
polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) and used Forster resonance energy transfer,
FRET assays to read the sequences of DNA encompassed in the droplets. Each position on the array tested for a specific 15 base sequence.
Fair et al. used digital microfluidic devices to study DNA
pyrosequencing
Pyrosequencing is a method of DNA sequencing (determining the order of nucleotides in DNA) based on the "sequencing by synthesis" principle, in which the sequencing is performed by detecting the nucleotide incorporated by a DNA polymerase. Pyrosequ ...
.
Significant advantages include the portability of the device, reagent volume, speed of analysis, mass manufacturing abilities, and high throughput. This study provided a proof of concept showing that digital devices can be used for pyrosequencing; the study included using synthesis, which involves the extension of the enzymes and addition of labeled nucleotides.
Boles et al. also studied pyrosequencing on digital microfluidic devices.
They used an electro-wetting device to create, mix, and split droplets. The sequencing uses a three-enzyme protocol and DNA templates anchored with magnetic beads. The device was tested using two protocols and resulted in 100% accuracy based on raw pyrogram levels. The advantages of these digital microfluidic devices include size, cost, and achievable levels of functional integration.
DNA sequencing research, using microfluidics, also has the ability to be applied to the
sequencing of RNA, using similar droplet microfluidic techniques, such as the method, inDrops. This shows that many of these DNA sequencing techniques will be able to be applied further and be used to understand more about genomes and transcriptomes.
Methods in development
DNA sequencing methods currently under development include reading the sequence as a DNA strand transits through
nanopores (a method that is now commercial but subsequent generations such as solid-state nanopores are still in development),
and microscopy-based techniques, such as
atomic force microscopy
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) or scanning force microscopy (SFM) is a very-high-resolution type of scanning probe microscopy (SPM), with demonstrated resolution on the order of fractions of a nanometer, more than 1000 times better than the opti ...
or
transmission electron microscopy
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is a microscopy technique in which a beam of electrons is transmitted through a specimen to form an image. The specimen is most often an ultrathin section less than 100 nm thick or a suspension on a g ...
that are used to identify the positions of individual nucleotides within long DNA fragments (>5,000 bp) by nucleotide labeling with heavier elements (e.g., halogens) for visual detection and recording.
Third generation technologies aim to increase throughput and decrease the time to result and cost by eliminating the need for excessive reagents and harnessing the processivity of DNA polymerase.
Tunnelling currents DNA sequencing
Another approach uses measurements of the electrical tunnelling currents across single-strand DNA as it moves through a channel. Depending on its electronic structure, each base affects the tunnelling current differently, allowing differentiation between different bases.
The use of tunnelling currents has the potential to sequence orders of magnitude faster than ionic current methods and the sequencing of several DNA oligomers and micro-RNA has already been achieved.
Sequencing by hybridization
''
Sequencing by hybridization'' is a non-enzymatic method that uses a
DNA microarray
A DNA microarray (also commonly known as a DNA chip or biochip) is a collection of microscopic DNA spots attached to a solid surface. Scientists use DNA microarrays to measure the expression levels of large numbers of genes simultaneously or t ...
. A single pool of DNA whose sequence is to be determined is fluorescently labeled and hybridized to an array containing known sequences. Strong hybridization signals from a given spot on the array identifies its sequence in the DNA being sequenced.
This method of sequencing utilizes binding characteristics of a library of short single stranded DNA molecules (oligonucleotides), also called DNA probes, to reconstruct a target DNA sequence. Non-specific hybrids are removed by washing and the target DNA is eluted.
Hybrids are re-arranged such that the DNA sequence can be reconstructed. The benefit of this sequencing type is its ability to capture a large number of targets with a homogenous coverage.
A large number of chemicals and starting DNA is usually required. However, with the advent of solution-based hybridization, much less equipment and chemicals are necessary.
Sequencing with mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a ''mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is used ...
may be used to determine DNA sequences. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry, or
MALDI-TOF MS, has specifically been investigated as an alternative method to gel electrophoresis for visualizing DNA fragments. With this method, DNA fragments generated by chain-termination sequencing reactions are compared by mass rather than by size. The mass of each nucleotide is different from the others and this difference is detectable by mass spectrometry. Single-nucleotide mutations in a fragment can be more easily detected with MS than by gel electrophoresis alone. MALDI-TOF MS can more easily detect differences between RNA fragments, so researchers may indirectly sequence DNA with MS-based methods by converting it to RNA first.
The higher resolution of DNA fragments permitted by MS-based methods is of special interest to researchers in forensic science, as they may wish to find
single-nucleotide polymorphisms
In genetics and bioinformatics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP ; plural SNPs ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in ...
in human DNA samples to identify individuals. These samples may be highly degraded so forensic researchers often prefer
mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA and mDNA) is the DNA located in the mitochondrion, mitochondria organelles in a eukaryotic cell that converts chemical energy from food into adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is a small portion of the D ...
for its higher stability and applications for lineage studies. MS-based sequencing methods have been used to compare the sequences of human mitochondrial DNA from samples in a
Federal Bureau of Investigation
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is the domestic Intelligence agency, intelligence and Security agency, security service of the United States and Federal law enforcement in the United States, its principal federal law enforcement ag ...
database and from bones found in mass graves of World War I soldiers.
Early chain-termination and TOF MS methods demonstrated read lengths of up to 100 base pairs. Researchers have been unable to exceed this average read size; like chain-termination sequencing alone, MS-based DNA sequencing may not be suitable for large ''de novo'' sequencing projects. Even so, a recent study did use the short sequence reads and mass spectroscopy to compare single-nucleotide polymorphisms in pathogenic ''
Streptococcus
''Streptococcus'' is a genus of gram-positive spherical bacteria that belongs to the family Streptococcaceae, within the order Lactobacillales (lactic acid bacteria), in the phylum Bacillota. Cell division in streptococci occurs along a sing ...
'' strains.
Microfluidic Sanger sequencing
In microfluidic
Sanger sequencing
Sanger sequencing is a method of DNA sequencing that involves electrophoresis and is based on the random incorporation of chain-terminating dideoxynucleotides by DNA polymerase during in vitro DNA replication. After first being developed by Fred ...
the entire thermocycling amplification of DNA fragments as well as their separation by electrophoresis is done on a single glass wafer (approximately 10 cm in diameter) thus reducing the reagent usage as well as cost. In some instances researchers have shown that they can increase the throughput of conventional sequencing through the use of microchips. Research will still need to be done in order to make this use of technology effective.
Microscopy-based techniques
This approach directly visualizes the sequence of DNA molecules using electron microscopy. The first identification of DNA base pairs within intact DNA molecules by enzymatically incorporating modified bases, which contain atoms of increased atomic number, direct visualization and identification of individually labeled bases within a synthetic 3,272 base-pair DNA molecule and a 7,249 base-pair viral genome has been demonstrated.
RNAP sequencing
This method is based on use of
RNA polymerase
In molecular biology, RNA polymerase (abbreviated RNAP or RNApol), or more specifically DNA-directed/dependent RNA polymerase (DdRP), is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactions that synthesize RNA from a DNA template.
Using the e ...
(RNAP), which is attached to a
polystyrene
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin per unit weight. It i ...
bead. One end of DNA to be sequenced is attached to another bead, with both beads being placed in optical traps. RNAP motion during transcription brings the beads in closer and their relative distance changes, which can then be recorded at a single nucleotide resolution. The sequence is deduced based on the four readouts with lowered concentrations of each of the four nucleotide types, similarly to the Sanger method. A comparison is made between regions and sequence information is deduced by comparing the known sequence regions to the unknown sequence regions.
''In vitro'' virus high-throughput sequencing
A method has been developed to analyze full sets of
protein interactions using a combination of 454 pyrosequencing and an ''in vitro'' virus
mRNA display method. Specifically, this method covalently links proteins of interest to the mRNAs encoding them, then detects the mRNA pieces using reverse transcription
PCRs. The mRNA may then be amplified and sequenced. The combined method was titled IVV-HiTSeq and can be performed under cell-free conditions, though its results may not be representative of ''in vivo'' conditions.
Market share
While there are many different ways to sequence DNA, only a few dominate the market. In 2022, Illumina had about 80% of the market; the rest of the market is taken by only a few players (PacBio, Oxford, 454, MGI)
Sample preparation
The success of any DNA sequencing protocol relies upon the DNA or RNA sample extraction and preparation from the biological material of interest.
* A successful DNA extraction will yield a DNA sample with long, non-degraded strands.
* A successful RNA extraction will yield a RNA sample that should be converted to complementary DNA (cDNA) using reverse transcriptase—a DNA polymerase that synthesizes a complementary DNA based on existing strands of RNA in a PCR-like manner. Complementary DNA can then be processed the same way as genomic DNA.
After DNA or RNA extraction, samples may require further preparation depending on the sequencing method. For Sanger sequencing, either cloning procedures or PCR are required prior to sequencing. In the case of next-generation sequencing methods, library preparation is required before processing. Assessing the quality and quantity of nucleic acids both after extraction and after library preparation identifies degraded, fragmented, and low-purity samples and yields high-quality sequencing data.
Development initiatives

In October 2006, the
X Prize Foundation established an initiative to promote the development of
full genome sequencing
Whole genome sequencing (WGS), also known as full genome sequencing or just genome sequencing, is the process of determining the entirety of the DNA sequence of an organism's genome at a single time. This entails sequencing all of an organism's ...
technologies, called the
Archon X Prize
The Archon Genomics X PRIZE presented by Express Scripts for Genomics, the second X Prize offered by the X Prize Foundation, based in Playa Vista, California, was announced on October 4, 2006 stating that the prize of "$10 million will be awarded ...
, intending to award $10 million to "the first Team that can build a device and use it to sequence 100 human genomes within 10 days or less, with an accuracy of no more than one error in every 100,000 bases sequenced, with sequences accurately covering at least 98% of the genome, and at a recurring cost of no more than $10,000 (US) per genome."
Each year the
National Human Genome Research Institute
The National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI) is an institute of the National Institutes of Health, located in Bethesda, Maryland.
NHGRI began as the Office of Human Genome Research in The Office of the Director in 1988. This Office transi ...
, or NHGRI, promotes grants for new research and developments in
genomics
Genomics is an interdisciplinary field of molecular biology focusing on the structure, function, evolution, mapping, and editing of genomes. A genome is an organism's complete set of DNA, including all of its genes as well as its hierarchical, ...
. 2010 grants and 2011 candidates include continuing work in microfluidic, polony and base-heavy sequencing methodologies.
Computational challenges
The sequencing technologies described here produce raw data that needs to be assembled into longer sequences such as complete genomes (
sequence assembly
In bioinformatics, sequence assembly refers to aligning and merging fragments from a longer DNA sequence in order to reconstruct the original sequence. This is needed as DNA sequencing technology might not be able to 'read' whole genomes in one g ...
). There are many computational challenges to achieve this, such as the evaluation of the raw sequence data which is done by programs and algorithms such as
Phred and
Phrap. Other challenges have to deal with
repetitive sequences that often prevent complete genome assemblies because they occur in many places of the genome. As a consequence, many sequences may not be assigned to particular
chromosome
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most import ...
s. The production of raw sequence data is only the beginning of its detailed
bioinformatical analysis.
Yet new methods for sequencing and correcting sequencing errors were developed.
Read trimming
Sometimes, the raw reads produced by the sequencer are correct and precise only in a fraction of their length. Using the entire read may introduce artifacts in the downstream analyses like genome assembly, SNP calling, or gene expression estimation. Two classes of trimming programs have been introduced, based on the window-based or the running-sum classes of algorithms. This is a partial list of the trimming algorithms currently available, specifying the algorithm class they belong to:
Ethical issues
Human genetics have been included within the field of
bioethics
Bioethics is both a field of study and professional practice, interested in ethical issues related to health (primarily focused on the human, but also increasingly includes animal ethics), including those emerging from advances in biology, me ...
since the early 1970s
and the growth in the use of DNA sequencing (particularly high-throughput sequencing) has introduced a number of ethical issues. One key issue is the ownership of an individual's DNA and the data produced when that DNA is sequenced.
Regarding the DNA molecule itself, the leading legal case on this topic, ''
Moore v. Regents of the University of California
''Moore v. Regents of the University of California'' was a landmark Supreme Court of California decision. Filed on July 9, 1990, it dealt with the issue of property rights to one's own cells taken in samples by doctors or researchers.
In 1976, ...
'' (1990) ruled that individuals have no property rights to discarded cells or any profits made using these cells (for instance, as a patented
cell line
An immortalised cell line is a population of cells from a multicellular organism that would normally not proliferate indefinitely but, due to mutation, have evaded normal cellular senescence and instead can keep undergoing division. The cells ...
). However, individuals have a right to informed consent regarding removal and use of cells. Regarding the data produced through DNA sequencing, ''Moore'' gives the individual no rights to the information derived from their DNA.
As DNA sequencing becomes more widespread, the storage, security and sharing of genomic data has also become more important.
For instance, one concern is that insurers may use an individual's genomic data to modify their quote, depending on the perceived future health of the individual based on their DNA.
In May 2008, the
Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act
The Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act of 2008 (, GINA ), is an Act of Congress in the United States designed to prohibit some types of genetic discrimination. The act bars the use of genetic information in health insurance and employm ...
(GINA) was signed in the United States, prohibiting discrimination on the basis of genetic information with respect to health insurance and employment.
[Statement of Administration policy](_blank)
Executive Office of the President, Office of Management and Budget, 27 April 2007 In 2012, the US
Presidential Commission for the Study of Bioethical Issues
The Presidential Commission for the Study of Bioethical Issues (the Bioethics Commission) was created by on November 24, 2009.s:Executive Order 13521, Executive Order 13521 - ''Establishing the Presidential Commission for the Study of Bioethical ...
reported that existing privacy legislation for DNA sequencing data such as GINA and the
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA or the Ted Kennedy, Kennedy–Nancy Kassebaum, Kassebaum Act) is a United States Act of Congress enacted by the 104th United States Congress and signed into law by President ...
were insufficient, noting that whole-genome sequencing data was particularly sensitive, as it could be used to identify not only the individual from which the data was created, but also their relatives.
In most of the United States, DNA that is "abandoned", such as that found on a licked stamp or envelope, coffee cup, cigarette, chewing gum, household trash, or hair that has fallen on a public sidewalk, may legally be collected and sequenced by anyone, including the police, private investigators, political opponents, or people involved in paternity disputes. As of 2013, eleven states have laws that can be interpreted to prohibit "DNA theft".
Ethical issues have also been raised by the increasing use of genetic variation screening, both in newborns, and in adults by companies such as
23andMe
23andMe Holding Co. is an American personal genomics and biotechnology company based in South San Francisco, California. It is best known for providing a direct-to-consumer genetic testing service in which customers provide a saliva testing, sali ...
.
It has been asserted that screening for genetic variations can be harmful, increasing
anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion characterised by an unpleasant state of inner wikt:turmoil, turmoil and includes feelings of dread over Anticipation, anticipated events. Anxiety is different from fear in that fear is defined as the emotional response ...
in individuals who have been found to have an increased risk of disease.
For example, in one case noted in ''
Time
Time is the continuous progression of existence that occurs in an apparently irreversible process, irreversible succession from the past, through the present, and into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequ ...
'', doctors screening an ill baby for genetic variants chose not to inform the parents of an unrelated variant linked to
dementia
Dementia is a syndrome associated with many neurodegenerative diseases, characterized by a general decline in cognitive abilities that affects a person's ability to perform activities of daily living, everyday activities. This typically invo ...
due to the harm it would cause to the parents.
However, a 2011 study in ''
The New England Journal of Medicine
''The New England Journal of Medicine'' (''NEJM'') is a weekly medical journal published by the Massachusetts Medical Society. Founded in 1812, the journal is among the most prestigious peer-reviewed medical journals. Its 2023 impact factor w ...
'' has shown that individuals undergoing disease risk profiling did not show increased levels of anxiety.
Also, the development of Next Generation sequencing technologies such as Nanopore based sequencing has also raised further ethical concerns.
See also
*
*
*
Circular consensus sequencing
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Linked-read sequencing
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Notes
References
External links
* A
wikibook on next generation sequencing
{{DEFAULTSORT:Dna Sequencing
Genetic mapping
Molecular biology techniques
1970 introductions
1970 in biology
1970 in biotechnology
1970 in science
1998 in technology
 The first DNA sequences were obtained in the early 1970s by academic researchers using laborious methods based on two-dimensional chromatography. Following the development of
The first DNA sequences were obtained in the early 1970s by academic researchers using laborious methods based on two-dimensional chromatography. Following the development of  The foundation for sequencing proteins was first laid by the work of
The foundation for sequencing proteins was first laid by the work of  Several new methods for DNA sequencing were developed in the mid to late 1990s and were implemented in commercial DNA sequencers by 2000. Together these were called the "next-generation" or "second-generation" sequencing (NGS) methods, in order to distinguish them from the earlier methods, including
Several new methods for DNA sequencing were developed in the mid to late 1990s and were implemented in commercial DNA sequencers by 2000. Together these were called the "next-generation" or "second-generation" sequencing (NGS) methods, in order to distinguish them from the earlier methods, including  Large-scale sequencing often aims at sequencing very long DNA pieces, such as whole
Large-scale sequencing often aims at sequencing very long DNA pieces, such as whole  High-throughput sequencing, which includes next-generation "short-read" and third-generation "long-read" sequencing methods,"Next-generation" remains in broad use as of 2019. For instance, applies to
High-throughput sequencing, which includes next-generation "short-read" and third-generation "long-read" sequencing methods,"Next-generation" remains in broad use as of 2019. For instance, applies to 
 In this method, DNA molecules and primers are first attached on a slide or flow cell and amplified with
In this method, DNA molecules and primers are first attached on a slide or flow cell and amplified with  Decoupling the enzymatic reaction and the image capture allows for optimal throughput and theoretically unlimited sequencing capacity. With an optimal configuration, the ultimately reachable instrument throughput is thus dictated solely by the analog-to-digital conversion rate of the camera, multiplied by the number of cameras and divided by the number of pixels per DNA colony required for visualizing them optimally (approximately 10 pixels/colony). In 2012, with cameras operating at more than 10 MHz A/D conversion rates and available optics, fluidics and enzymatics, throughput can be multiples of 1 million nucleotides/second, corresponding roughly to 1 human genome equivalent at 1x coverage per hour per instrument, and 1 human genome re-sequenced (at approx. 30x) per day per instrument (equipped with a single camera).
Decoupling the enzymatic reaction and the image capture allows for optimal throughput and theoretically unlimited sequencing capacity. With an optimal configuration, the ultimately reachable instrument throughput is thus dictated solely by the analog-to-digital conversion rate of the camera, multiplied by the number of cameras and divided by the number of pixels per DNA colony required for visualizing them optimally (approximately 10 pixels/colony). In 2012, with cameras operating at more than 10 MHz A/D conversion rates and available optics, fluidics and enzymatics, throughput can be multiples of 1 million nucleotides/second, corresponding roughly to 1 human genome equivalent at 1x coverage per hour per instrument, and 1 human genome re-sequenced (at approx. 30x) per day per instrument (equipped with a single camera).
 The patterned array of positively charged spots is fabricated through photolithography and etching techniques followed by chemical modification to generate a sequencing flow cell. Each spot on the flow cell is approximately 250 nm in diameter, are separated by 700 nm (centre to centre) and allows easy attachment of a single negatively charged DNB to the flow cell and thus reducing under or over-clustering on the flow cell.
Sequencing is then performed by addition of an oligonucleotide probe that attaches in combination to specific sites within the DNB. The probe acts as an anchor that then allows one of four single reversibly inactivated, labelled nucleotides to bind after flowing across the flow cell. Unbound nucleotides are washed away before laser excitation of the attached labels then emit fluorescence and signal is captured by cameras that is converted to a digital output for base calling. The attached base has its terminator and label chemically cleaved at completion of the cycle. The cycle is repeated with another flow of free, labelled nucleotides across the flow cell to allow the next nucleotide to bind and have its signal captured. This process is completed a number of times (usually 50 to 300 times) to determine the sequence of the inserted piece of DNA at a rate of approximately 40 million nucleotides per second as of 2018.
The patterned array of positively charged spots is fabricated through photolithography and etching techniques followed by chemical modification to generate a sequencing flow cell. Each spot on the flow cell is approximately 250 nm in diameter, are separated by 700 nm (centre to centre) and allows easy attachment of a single negatively charged DNB to the flow cell and thus reducing under or over-clustering on the flow cell.
Sequencing is then performed by addition of an oligonucleotide probe that attaches in combination to specific sites within the DNB. The probe acts as an anchor that then allows one of four single reversibly inactivated, labelled nucleotides to bind after flowing across the flow cell. Unbound nucleotides are washed away before laser excitation of the attached labels then emit fluorescence and signal is captured by cameras that is converted to a digital output for base calling. The attached base has its terminator and label chemically cleaved at completion of the cycle. The cycle is repeated with another flow of free, labelled nucleotides across the flow cell to allow the next nucleotide to bind and have its signal captured. This process is completed a number of times (usually 50 to 300 times) to determine the sequence of the inserted piece of DNA at a rate of approximately 40 million nucleotides per second as of 2018.