Hex bolt on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
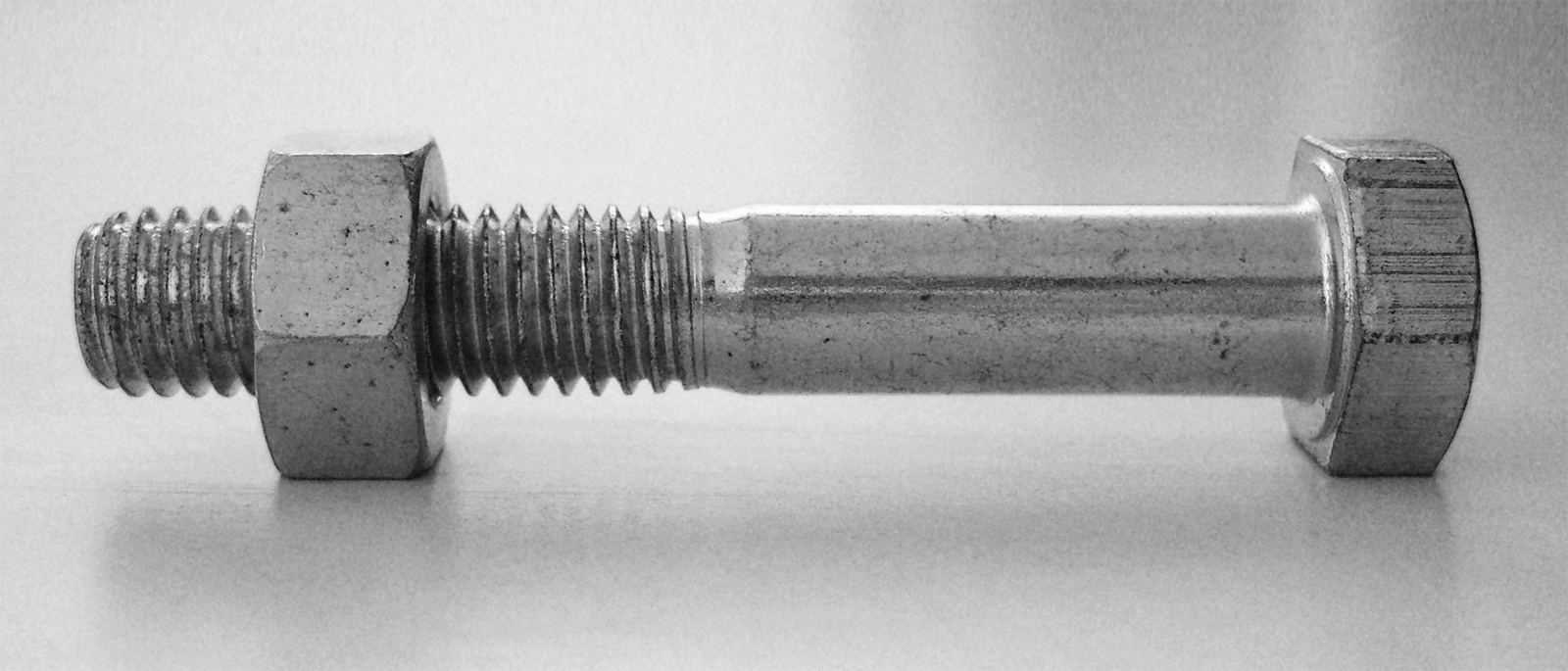 A bolt is an externally
A bolt is an externally

 The distinction between a bolt and a screw is poorly defined. The academic distinction, per ''
The distinction between a bolt and a screw is poorly defined. The academic distinction, per ''
 The American Institute of Steel Construction (
The American Institute of Steel Construction (
FOREIGN TECHNOLOGY DIVISION USSR STATE STANDARD BOLTS, SCREWS, STUDS AND NUTS. TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS GOST 1759-70
{{Authority control Fasteners Screws Threaded fasteners
 A bolt is an externally
A bolt is an externally helical thread
A screw thread is a helical structure used to convert between rotational and linear movement or force. A screw thread is a ridge wrapped around a cylinder or cone in the form of a helix, with the former being called a ''straight'' thread and th ...
ed fastener
A fastener (US English) or fastening (UK English) is a hardware device that mechanically joins or affixes two or more objects together. In general, fasteners are used to create non-permanent joints; that is, joints that can be removed or disman ...
capable of being tightened or released by a twisting force (torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational analogue of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). The symbol for torque is typically \boldsymbol\tau, the lowercase Greek letter ''tau''. Wh ...
) to a matching nut. The bolt has an external male thread requiring a matching nut with a pre-formed female thread.
History
Nuts and bolts were originally hand-crafted together, so that each nut matched its own bolt, but they were not interchangeable. This made it virtually impossible to replace lost or damaged fixers, as they were all different.Joseph Whitworth
Sir Joseph Whitworth, 1st Baronet (21 December 1803 – 22 January 1887) was an English engineer, entrepreneur, inventor and philanthropist. In 1841, he devised the British Standard Whitworth system, which created an accepted standard for screw ...
in 1841 proposed that a standard should be set, but it did not happen immediately.
In 1851 the Great Exhibition of the Works of Industry of All Nations
The Great Exhibition of the Works of Industry of All Nations, also known as the Great Exhibition or the Crystal Palace Exhibition (in reference to the temporary structure in which it was held), was an international exhibition that took ...
was to be held in Hyde Park, London, England, and it was decided to build the Crystal Palace
The Crystal Palace was a cast iron and plate glass structure, originally built in Hyde Park, London, to house the Great Exhibition of 1851. The exhibition took place from 1 May to 15 October 1851, and more than 14,000 exhibitors from around ...
as part; this had to be done in 190 days, and at reasonable cost. Research into the remains of the destroyed building in 2024 revealed a major innovation that made this possible. The construction firm responsible, Fox Henderson, decided to use nuts and bolts, but to use standardised sizes, a revolutionary method at the time. This enabled the building to be completed in time. The use of interchangeable nuts and bolts was so successful that the Whitworth standard was widely adopted. A British standard
British Standards (BS) are the standards produced by the BSI Group which is incorporated under a royal charter and which is formally designated as the national standards body (NSB) for the UK. The BSI Group produces British Standards under th ...
was not formally adopted until 1905.
Bolts vs. screws
Machinery's Handbook
''Machinery's Handbook'' ''for machine shop and drafting-room; a reference book on machine design and shop practice for the mechanical engineer, draftsman, toolmaker, and machinist'' (the full title of the 1st edition) is a classic reference ...
'', is in their intended purpose: bolts are designed to pass through an unthreaded hole in a component and be fastened with the aid of a nut. Screws in contrast are used in components which contain their own thread, or to cut its own internal thread into them. This definition allows ambiguity in the description of a fastener depending on the application it is actually used for, and the terms screw and bolt are widely used by different people or in different countries to apply to the same or varying fastener. In British terminology, a ''cap screw'' is a bolt that has threads all the way to the head.
Bolts are often used to make a bolted joint
A bolted joint is one of the most common elements in construction and machine design. It consists of a male threaded fastener (e. g., a Bolt (fastener), bolt) that captures and joins other parts, secured with a matching female screw thread. Ther ...
. This is a combination of the nut applying an axial clamping force and also the shank of the bolt acting as a dowel
The dowel is a cylindrical shape made of wood, plastic, or metal. In its original manufactured form, a dowel is long and called a ''dowel rod'', which are often cut into shorter ''dowel pins''. Dowels are commonly used as structural reinforceme ...
, pinning the joint against sideways shear force
In solid mechanics, shearing forces are unaligned forces acting on one part of a Rigid body, body in a specific direction, and another part of the body in the opposite direction. When the forces are Collinearity, collinear (aligned with each ot ...
s. For this reason, many bolts have a plain unthreaded shank (called the ), as this makes for a better, stronger dowel. The presence of the unthreaded shank has often been given as characteristic of bolts vs. screws,. but this is incidental to its use, rather than defining.
Where a fastener forms its own thread in the component being fastened, it is called a screw. This is most obviously so when the thread is tapered (i.e. traditional wood screws), precluding the use of a nut, or when a sheet metal screw or other thread-forming screw is used. A screw must always be turned to assemble the joint. Many bolts are held fixed in place during assembly, either by a tool or by a design of non-rotating bolt, such as a carriage bolt
A carriage bolt (also called coach bolt and round-head square-neck bolt) is a type of Bolt (fastener), bolt. It is also known as a cup head bolt in Australia and New Zealand.
It is distinguished from other bolts by its shallow Screw#Truss head, ...
, and only the corresponding nut is turned.
Bolt heads
Bolts use a wide variety of head designs, as do screws. These are designed to engage with the tool used to tighten them. Some bolt heads instead lock the bolt in place, so that it does not move and a tool is only needed for the nut end. Common bolt heads include hex, slotted hex washer, and socket cap. The first bolts had square heads, formed byforging
Forging is a manufacturing process involving the shaping of metal using localized compression (physics), compressive forces. The blows are delivered with a hammer (often a power hammer) or a die (manufacturing), die. Forging is often classif ...
. These are still found, although much more common today is the hexagonal head. These are held and turned by a spanner
A wrench or spanner is a tool used to provide grip and mechanical advantage in applying torque to turn objects—usually rotary fasteners, such as Nut (hardware), nuts and screw, bolts—or keep them from turning.
In the United Kingdom, UK, ...
or socket
Socket may refer to:
Mechanics
* Socket wrench, a type of wrench that uses separate, removable sockets to fit different sizes of nuts and bolts
* Socket head screw, a screw (or bolt) with a cylindrical head containing a socket into which the hexag ...
, of which there are many forms. Most are held from the side, some from in-line with the bolt. Other bolts have T-heads and slotted heads.
Many bolts use a screwdriver head fitting, rather than an external wrench. Screwdrivers are applied in-line with the fastener, rather than from the side. These are smaller than most wrench heads and cannot usually apply the same amount of torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational analogue of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). The symbol for torque is typically \boldsymbol\tau, the lowercase Greek letter ''tau''. Wh ...
. It is sometimes assumed that screwdriver heads imply a screw and wrenches imply a bolt, although this is incorrect. Coach screws, or lag screws, for example, are large square-headed screws with a tapered wood screw thread, used for attaching ironwork to timber. Head designs that overlap both bolts and include the Allen, Torx
Torx (pronounced ) is a trademark for a type of screw drive characterized by a 6-point star-shaped pattern, developed in 1967, Bernard F. Reiland, "Coupling arrangement and tools for same", filed 1967-03-21 by Camcar Textron. A popular gener ...
, hexagonal and splined heads. These modern designs span a large range of sizes and can carry a considerable torque. Threaded fasteners with screwdriver-style heads are often referred to as machine screw
A screw is an externally helical threaded fastener capable of being tightened or released by a twisting force (torque) to the head. The most common uses of screws are to hold objects together and there are many forms for a variety of materi ...
s whether they are being used with a nut or not.
Bolt types
*Anchor bolt
Anchor bolts are used to connect structural and non-structural elements to concrete.. The connection can be made by a variety of different components: anchor bolts (also named fasteners), steel plates, or stiffeners. Anchor bolts transfer diffe ...
- Bolt designed to allow objects to be attached to concrete. The bolt head is usually placed in concrete before it has cured or placed before the concrete is poured, leaving the threaded end exposed.
* Arbor bolt - Bolt with a washer permanently attached and reversed threading. Designed for use in miter saw
A miter saw or mitre saw is a saw used to make accurate crosscuts and miters in a workpiece by positioning a mounted blade onto a board. A miter saw in its earliest form was composed of a back saw in a miter box, but in modern implementation ...
and other tools to auto tighten during use to prevent blade fall out.
* Carriage bolt
A carriage bolt (also called coach bolt and round-head square-neck bolt) is a type of Bolt (fastener), bolt. It is also known as a cup head bolt in Australia and New Zealand.
It is distinguished from other bolts by its shallow Screw#Truss head, ...
- Bolt with a smooth rounded head and a square section to prevent turning followed with a threaded section for a nut.
* Elevator bolt - Bolt with a large flat head used in conveyor system setups.
* Hanger bolt - Bolt that has no head, machine threaded body followed by a wood threaded screw tip. Allow nuts to be attached to what is really a screw.
* Hex bolt - Bolt with a hexagonal head and threaded shank. Section immediately under head may be unthreaded for fastening thicker materials.
* J bolt - Bolt shaped like the letter J, used for tie downs. Only the straight section is threaded for a nut.
* Rock bolt - Used in tunnel construction to stabilize walls.
* Sex bolt or Chicago bolt - Bolt that has a male and female part with interior threads and bolt heads on either end. Commonly used in paper binding.
* Shoulder bolt or stripper bolt - Bolt with a broad smooth shank and small threaded section at the end used as a pivot pin or attachment point.
* U-bolt - Bolt shaped like the letter U where the two straight sections are threaded. A straight metal plate with two bolt holes is used with nuts to hold pipes or other round objects to the U-bolt.
Bolt materials
Depending on required strength and circumstances, there are several material types can be used for fasteners. *Steel
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon that demonstrates improved mechanical properties compared to the pure form of iron. Due to steel's high Young's modulus, elastic modulus, Yield (engineering), yield strength, Fracture, fracture strength a ...
fasteners (grade 2,5,8) - the level of strength
* Stainless steel
Stainless steel, also known as inox, corrosion-resistant steel (CRES), or rustless steel, is an iron-based alloy that contains chromium, making it resistant to rust and corrosion. Stainless steel's resistance to corrosion comes from its chromi ...
fasteners (martensitic stainless steel, austenitic stainless steel),
* Bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals (such as phosphorus) or metalloid ...
and brass
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc, in proportions which can be varied to achieve different colours and mechanical, electrical, acoustic and chemical properties, but copper typically has the larger proportion, generally copper and zinc. I ...
fasteners - water proof usage
* Nylon
Nylon is a family of synthetic polymers characterised by amide linkages, typically connecting aliphatic or Polyamide#Classification, semi-aromatic groups.
Nylons are generally brownish in color and can possess a soft texture, with some varieti ...
fasteners - used for the light material and water proof usage.
In general, steel is the most commonly used material of all fasteners: 90% or more.
Bolted joints
 The American Institute of Steel Construction (
The American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC
The American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC) is a not-for-profit technical institute and trade association for the use of structural steel in the construction industry of the United States.
AISC publishes the Steel Construction Manual, a ...
) 13th Edition Steel Design Manual section 16.1 chapter J-3 specifies the requirements for bolted structural connections. Structural bolts replaced rivets due to the decreasing cost and increasing strength of structural bolts in the 20th century. Connections are formed with two types of joints: slip-critical connections and bearing connections. In slip-critical connections, movement of the connected parts is a serviceability condition and bolts are tightened to a minimum required pre-tension. Slip is prevented through friction of the "faying" surface, that is the plane of shear for the bolt and where two members make contact. Because friction is proportional to the normal force
In mechanics, the normal force F_n is the component of a contact force that is perpendicular to the surface that an object contacts. In this instance '' normal'' is used in the geometric sense and means perpendicular, as opposed to the meanin ...
, connections must be sized with bolts numerous and large enough to provide the required load capacity. However, this greatly decreases the shear capacity of each bolt in the connection. The second (and more common type) of connection is a bearing connection. In this type of connection, the bolts carry the load through shear and are only tightened to a "snug-fit". These connections require fewer bolts than slip-critical connections and therefore are a less expensive alternative. Slip-critical connections are more common on flange plates for beam and column splices and moment critical connections. Bearing type connections are used in lightweight structures and in member connections where slip is not important and prevention of structural failure
Structural integrity and failure is an aspect of engineering that deals with the ability of a structure to support a designed structural load (weight, force, etc.) without breaking and includes the study of past structural failures in order to ...
is the design constraint. Common bearing type connections include: shear tabs, beam supports, gusset plate
In structural engineering and construction, a gusset plate is a plate for connecting Beam (structure), beams and girders to columns. A gusset plate can be fastened to a permanent member either by Bolted joint, bolts, rivets or welding or a combi ...
s in truss
A truss is an assembly of ''members'' such as Beam (structure), beams, connected by ''nodes'', that creates a rigid structure.
In engineering, a truss is a structure that "consists of two-force members only, where the members are organized so ...
es.
Spy bolt
The use of industrial bolts were used in espionage organizations as hidden containers for clandestine operations. They were used during WW2 by the SOE, OSS and underground resistance groups. The bolt would be stashed in for example a farm gate or almost anywhere, and used as a drop box for messages and microfilm etc. This consisted of a hollowed out bolt with a reverse threaded screw cap to prevent accidental opening.https://www.itstactical.com/gear/pass-information-like-a-spy-with-dead-drops/See also
* ASTM A325, standard for bolts to inches () in diameter * ISO 898, standard for metric bolts * Mechanical joint *Screw thread
A screw thread is a helical structure used to convert between rotational and linear movement or force. A screw thread is a ridge wrapped around a cylinder or cone in the form of a helix, with the former being called a ''straight'' thread and t ...
* Socket wrench
A socket wrench (or socket spanner) is a type of spanner (or wrench in North American English) that uses a closed ''socket'' format, rather than a typical open wrench/spanner to turn a fastener, typically in the form of a nut or bolt.
The most ...
* Thread angle
In mechanical engineering, the thread angle of a screw is the included angle between the Threading (manufacturing), thread flanks, measured in a plane containing the thread axis.. This is a defining factor for the shape of a screw thread. Standar ...
* Thread-locking compound
* Thread pitch gauge
* Torque wrench
A torque wrench is a tool used to apply a specific torque to a fastener such as a nut, bolt, or lag screw. It is usually in the form of a socket wrench with an indicating scale, or an internal mechanism which will indicate (as by 'clicking', ...
References
External links
FOREIGN TECHNOLOGY DIVISION USSR STATE STANDARD BOLTS, SCREWS, STUDS AND NUTS. TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS GOST 1759-70
{{Authority control Fasteners Screws Threaded fasteners