Heloderma Texana on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Heloderma'' is a
 Family Helodermatidae
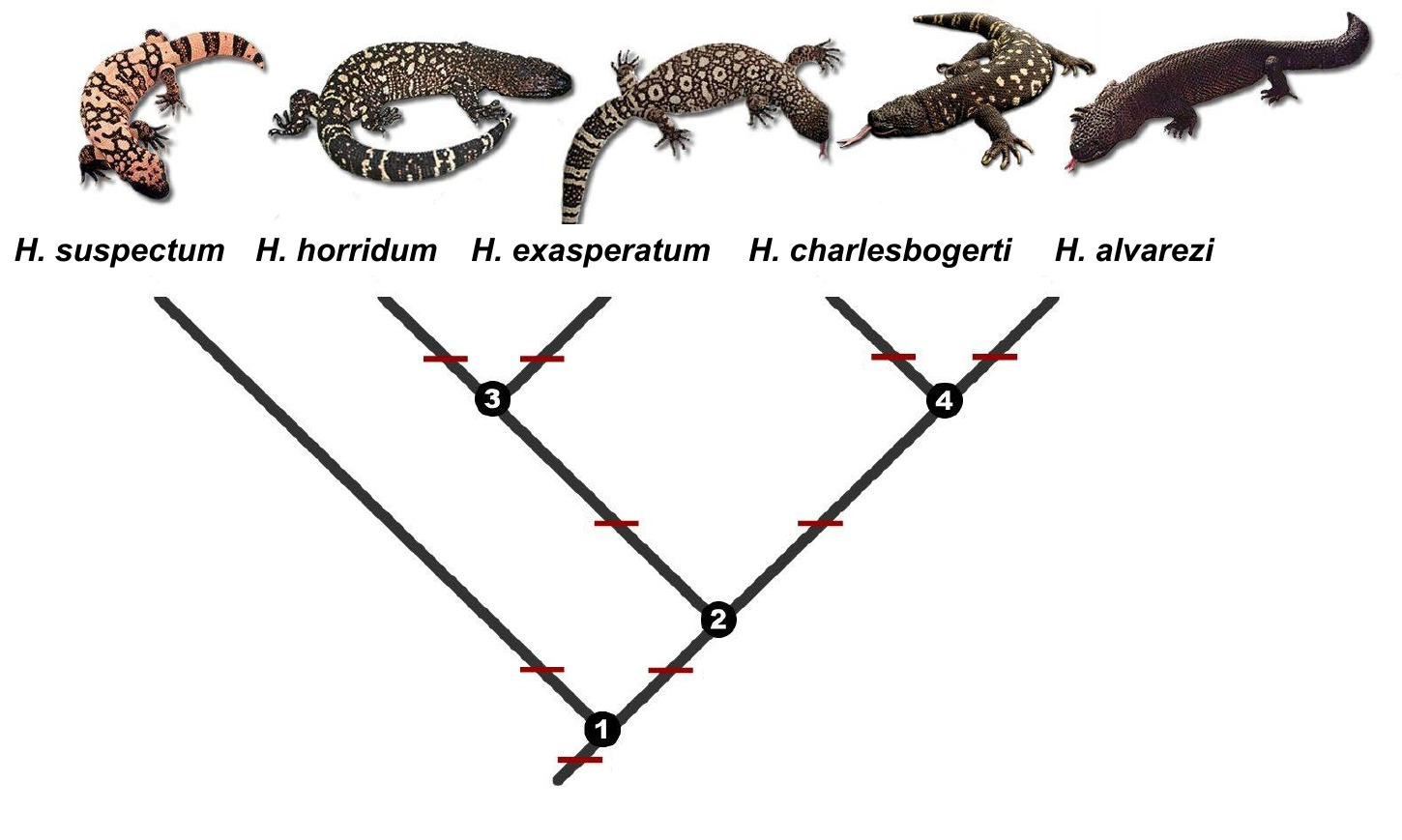
* Genus ''Heloderma''
** '' H. suspectum'' Cope, 1869; Gila monster
** '' H. horridum'' ( Wiegmann, 1829); Mexican beaded lizard
** '' H. exasperatum'' Bogert & Martin Del Campo, 1956; Rio Fuerte beaded lizard
** '' H. charlesbogerti'' Campbell & Vannini, 1988; Guatemalan beaded lizard
** '' H. alvarezi'' Bogert & Martin del Campo, 1956; Chiapan beaded lizard
Members of the genus ''Heloderma'' have many extinct relatives in the Helodermatidae whose evolutionary history may be traced back to the
Family Helodermatidae
* Genus ''Heloderma''
** '' H. suspectum'' Cope, 1869; Gila monster
** '' H. horridum'' ( Wiegmann, 1829); Mexican beaded lizard
** '' H. exasperatum'' Bogert & Martin Del Campo, 1956; Rio Fuerte beaded lizard
** '' H. charlesbogerti'' Campbell & Vannini, 1988; Guatemalan beaded lizard
** '' H. alvarezi'' Bogert & Martin del Campo, 1956; Chiapan beaded lizard
Members of the genus ''Heloderma'' have many extinct relatives in the Helodermatidae whose evolutionary history may be traced back to the  The
The

 ''H. horridum'', ''H. exasperatum'', and ''H. suspectum'' are frequently found in
''H. horridum'', ''H. exasperatum'', and ''H. suspectum'' are frequently found in
File:Heloderma Eiablage.jpg, alt=Helderema suspectum with 4 eggs, ''Heloderma suspectum'' with 4 eggs
File:Gila-monster-6-eggs.jpg, alt=Helderema suspectum with 6 eggs, ''Heloderma suspectum'' with 6 eggs
File:Schluepfendes-jungtier-OS6.jpg, alt=Gila monster hatching, Gila monster hatching
File:Group of young gila monster.jpg, alt=Group of young Gila monsters, Group of young Gila monsters


*Ariano-Sánchez, D. 2006. The Guatemalan beaded lizard: endangered inhabitant of a unique ecosystem. Iguana 13: 178–183
CONVENTION ON INTERNATIONAL TRADE IN ENDANGERED SPECIES OF WILD FAUNA AND FLORA
2007. Resume of the 14th Convention of the Parts. The Hague. The Netherlands.
www.heloderma.net
2006 in 6 languages
About Beaded Lizards
Family Helodermatidae (Gila Monsters)
{{Authority control Helodermatidae, * Extant Miocene first appearances Lizard genera Taxa named by Arend Friedrich August Wiegmann
genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial n ...
of toxicofera
Toxicofera (Greek for "those who bear toxins") is a proposed clade of scaled reptiles (squamates) that includes the Serpentes (snakes), Anguimorpha (monitor lizards, gila monster, and alligator lizards) and Iguania (iguanas, agamas, and cha ...
n lizards that contains five species, all of which are venom
Venom or zootoxin is a type of toxin produced by an animal that is actively delivered through a wound by means of a bite, sting, or similar action. The toxin is delivered through a specially evolved ''venom apparatus'', such as fangs or a ...
ous. It is the only extant genus of the family Helodermatidae
The Helodermatidae or beaded lizards are a small family of lizards endemic to North America today, but formerly more widespread in the ancient past. Traditionally, the Gila monster and the Mexican beaded lizard were the only species recognized, al ...
.
Description
The genus ''Heloderma'' contains theGila monster
The Gila monster (''Heloderma suspectum'', ) is a species of venomous lizard native to the Southwestern United States and the northwestern Mexican state of Sonora. It is a heavy, typically slow-moving reptile, up to long, and it is the only v ...
(''H. suspectum'') and four species of beaded lizards. The Gila monster is a large, stocky, most of the time slow-moving reptile that prefers arid deserts. Beaded lizards are seen to be more agile and seem to prefer more humid surroundings. The tails of all species of ''Heloderma'' are used as fat storage organs. The scales of the head, back and tail are bead-like, containing osteoderms
Osteoderms are bony deposits forming scales, plates, or other structures based in the dermis. Osteoderms are found in many groups of extant and extinct reptiles and amphibians, including lizards, crocodilians, frogs, temnospondyls (extinct ...
for better protection. The scales of the belly are free from osteoderms. Most species are dark in color, with yellowish or pinkish markings.
Venom
The venom glands of ''Heloderma'' are located at the end of the lower jaws, unlikesnake
Snakes are elongated, limbless, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more j ...
s' venom glands, which are located behind the eyes. Also, unlike snakes, the Gila monster and beaded lizards lack the musculature to inject venom immediately. They have to chew
Chewing or mastication is the process by which food is crushed and ground by teeth. It is the first step of digestion, and it increases the surface area of foods to allow a more efficient break down by enzymes. During the mastication process, th ...
the venom into the flesh of a victim. ''Heloderma'' venom is used only in defense. Venom glands are believed to have evolved early in the lineage leading to the modern helodermatids, as their presence is indicated even in the 65-million-year-old fossil genus ''Paraderma''. In general, one adult helodermatid has approximately 15 to 20 mg of venom, while the estimated lethal dose for humans is 5 to 8 mg.
Diet
Helodermatids arecarnivorous
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant whose food and energy requirements derive from animal tissues (mainly muscle, fat and other ...
, preying
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill th ...
on rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the Order (biology), order Rodentia (), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are roden ...
s and other small mammals, and eating the eggs
Humans and human ancestors have scavenged and eaten animal eggs for millions of years. Humans in Southeast Asia had domesticated chickens and harvested their eggs for food by 1,500 BCE. The most widely consumed eggs are those of fowl, especial ...
of bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
s and reptiles.
Reproduction
All species of ''Heloderma'' areoviparous
Oviparous animals are animals that lay their eggs, with little or no other embryonic development within the mother. This is the reproductive method of most fish, amphibians, most reptiles, and all pterosaurs, dinosaurs (including birds), a ...
. The Gila monster typically lays 6 eggs, the beaded lizards up to about 18 eggs . Comparing the different species, all eggs have a similar size, and the same holds true for their hatchlings.
Taxonomy
 Family Helodermatidae
* Genus ''Heloderma''
** '' H. suspectum'' Cope, 1869; Gila monster
** '' H. horridum'' ( Wiegmann, 1829); Mexican beaded lizard
** '' H. exasperatum'' Bogert & Martin Del Campo, 1956; Rio Fuerte beaded lizard
** '' H. charlesbogerti'' Campbell & Vannini, 1988; Guatemalan beaded lizard
** '' H. alvarezi'' Bogert & Martin del Campo, 1956; Chiapan beaded lizard
Members of the genus ''Heloderma'' have many extinct relatives in the Helodermatidae whose evolutionary history may be traced back to the
Family Helodermatidae
* Genus ''Heloderma''
** '' H. suspectum'' Cope, 1869; Gila monster
** '' H. horridum'' ( Wiegmann, 1829); Mexican beaded lizard
** '' H. exasperatum'' Bogert & Martin Del Campo, 1956; Rio Fuerte beaded lizard
** '' H. charlesbogerti'' Campbell & Vannini, 1988; Guatemalan beaded lizard
** '' H. alvarezi'' Bogert & Martin del Campo, 1956; Chiapan beaded lizard
Members of the genus ''Heloderma'' have many extinct relatives in the Helodermatidae whose evolutionary history may be traced back to the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
period, such as ''Estesia
''Estesia'' (in honour of Richard Estes) is an extinct genus of Late Cretaceous anguimorph lizard found in the Gobi Desert in Mongolia. It was discovered in June 1990 by a joint expedition made up of Mongolian and American palaeontologists, and ...
''. The genus ''Heloderma'' has existed since the Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" ...
, when ''H. texana'' lived, and fragments of osteoderm
Osteoderms are bony deposits forming scales, plates, or other structures based in the dermis. Osteoderms are found in many groups of extant and extinct reptiles and amphibians, including lizards, crocodilians, frogs, temnospondyls (extinc ...
s from the Gila monster have been found in late Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the '' Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed ...
(8,000-10,000 years ago) deposits near Las Vegas, Nevada
Las Vegas (; Spanish for "The Meadows"), often known simply as Vegas, is the 25th-most populous city in the United States, the most populous city in the state of Nevada, and the county seat of Clark County. The city anchors the Las Vega ...
. Because the helodermatids have remained relatively unchanged morphologically, they are occasionally regarded as living fossil
A living fossil is an extant taxon that cosmetically resembles related species known only from the fossil record. To be considered a living fossil, the fossil species must be old relative to the time of origin of the extant clade. Living foss ...
s. Although the beaded lizards and the Gila monster appear closely related to the monitor lizard
Monitor lizards are lizards in the genus ''Varanus,'' the only extant genus in the family Varanidae. They are native to Africa, Asia, and Oceania, and one species is also found in the Americas as an invasive species. About 80 species are reco ...
s (varanids) of Africa, Asia, and Australia, the wide geographical separation and unique features not found in the varanids indicates they are better placed in a separate family.
 The
The type species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen( ...
is ''Heloderma horridum'', which was first described in 1829 by Arend Wiegmann. Although he originally assigned it the generic name ''Trachyderma'', he changed it to ''Heloderma'' six months later, which means "studded skin", from the Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
words ''hêlos'' (ηλος)—the head of a nail or stud—and ''derma'' (δερμα), meaning skin.
Conrad, 2008 and Estes et al., 1988 (using morphological data) places Helodermatidae within Varanoidea
Varanoidea is a superfamily of lizards, including the well-known family Varanidae (the monitors and goannas). Also included in the Varanoidea are the Lanthanotidae ( earless monitor lizards), and the extinct Palaeovaranidae.
Throughout their lo ...
along with ''Lanthanotus borneensis'' and '' Varanus''. However, Estes et al., 1988 understood Helodermatidae as having split earlier from ''Lanthanotus'' and ''Varanus'', whereas Conrad, 2008 groups them at the same branch point.
In contrast, molecular studies have identified Heloderma as being within Anguioidea along with Anguidae and Xenosauridae, but specifically sister to Anguidae.
Venom
Venom production among lizards was long thought to be unique to this genus, but researchers studying venom production have proposed many others also produce some venom, all placed in the cladeToxicofera
Toxicofera (Greek for "those who bear toxins") is a proposed clade of scaled reptiles (squamates) that includes the Serpentes (snakes), Anguimorpha (monitor lizards, gila monster, and alligator lizards) and Iguania (iguanas, agamas, and cha ...
, which includes all snake
Snakes are elongated, limbless, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more j ...
s and 13 other families of lizards..
However, except for snakes, helodermatids, and possibly varanids, envenomation is not considered medically significant for humans

In captivity
 ''H. horridum'', ''H. exasperatum'', and ''H. suspectum'' are frequently found in
''H. horridum'', ''H. exasperatum'', and ''H. suspectum'' are frequently found in captivity
Captivity, or being held captive, is a state wherein humans or other animals are confined to a particular space and prevented from leaving or moving freely. An example in humans is imprisonment. Prisoners of war are usually held in captivity by a ...
and are well represented in zoo
A zoo (short for zoological garden; also called an animal park or menagerie) is a facility in which animals are kept within enclosures for public exhibition and often bred for conservation purposes.
The term ''zoological garden'' refers to zoo ...
s throughout much of the world. The other two species of ''Heloderma'', ''H. alvarezi'' and ''H. charlesbogerti'', are extremely rare, and only a few captive specimens are known.
Gallery

References

Notes
* *Ariano-Sánchez, D. & G. Salazar. 2007. Notes on the distribution of the endangered lizard, ''Heloderma horridum charlesbogerti'', in the dry forests of eastern Guatemala: an application of multi-criteria evaluation to conservation. Iguana 14: 152–158*Ariano-Sánchez, D. 2006. The Guatemalan beaded lizard: endangered inhabitant of a unique ecosystem. Iguana 13: 178–183
2007. Resume of the 14th Convention of the Parts. The Hague. The Netherlands.

External links
Schwandt, Hans- Joachiwww.heloderma.net
2006 in 6 languages
Further reading
* * * *About Beaded Lizards
Family Helodermatidae (Gila Monsters)
{{Authority control Helodermatidae, * Extant Miocene first appearances Lizard genera Taxa named by Arend Friedrich August Wiegmann