Heading (navigation) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
66
url=https://archive.org/details/weekendnavigator0000swee/page/66 Navigation
 In
In navigation
Navigation is a field of study that focuses on the process of monitoring and controlling the motion, movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another.Bowditch, 2003:799. The field of navigation includes four general categories: land navig ...
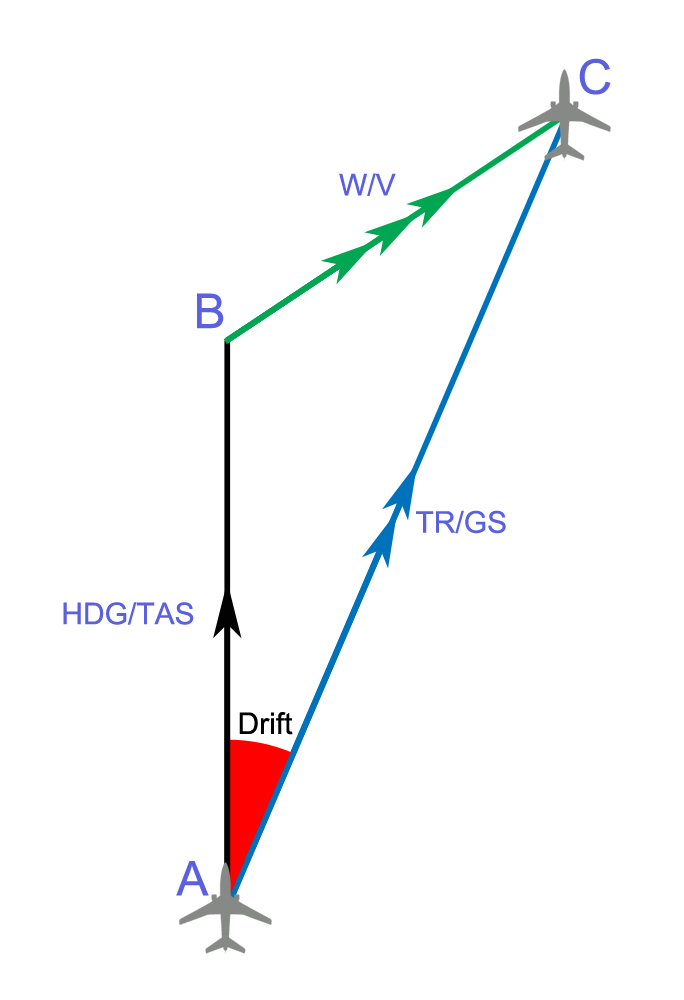
, the heading of a vessel or aircraft is the compass direction in which the craft's bow or nose is pointed. Note that the heading may not necessarily be the direction that the vehicle actually travels, which is known as its '' course''. Any difference between the heading and course is due to the motion of the underlying medium, the air or water, or other effects like skidding or slipping. The difference is known as the ''drift'', and can be determined by the ''wind triangle
In air navigation, the wind triangle is a graphical representation of the relationship between aircraft motion and wind. It is used extensively in dead reckoning navigation.
The wind triangle is a vector diagram, with three vectors.
*The air v ...
''. At least seven ways to measure the heading of a vehicle have been described.
Heading is typically based on cardinal direction
The four cardinal directions or cardinal points are the four main compass directions: north (N), south (S), east (E), and west (W). The corresponding azimuths ( clockwise horizontal angle from north) are 0°, 90°, 180°, and 270°.
The ...
s, so 0° (or 360°) indicates a direction toward true north
True north is the direction along Earth's surface towards the place where the imaginary rotational axis of the Earth intersects the surface of the Earth on its Northern Hemisphere, northern half, the True North Pole. True south is the direction ...
, 90° true east
East is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fact that ea ...
, 180° true south
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both west and east.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþa ...
, and 270° true west
West is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some Romance langu ...
.
TVMDC
TVMDC,AW is amnemonic
A mnemonic device ( ), memory trick or memory device is any learning technique that aids information retention or retrieval in the human memory, often by associating the information with something that is easier to remember.
It makes use of e ...
for converting from true heading, to magnetic and compass headings. TVMDC is a mnemonic initialism for true heading, variation, magnetic heading, deviation, compass heading, add westerly. The most common use of the TVMDC method is deriving compass courses during nautical navigation from maps. The inverse correction from compass heading to true heading is "CDMVTAE", with compass heading, deviation, magnetic heading, variation, true heading, add easterly The most common use of the CDMVTAE rule is to convert compass headings to map headings.
Background
The Geographic North Pole around which the Earth rotates is not in exactly the same position as the Magnetic North Pole. From any position on the globe, a direction can be determined to either the Geographic North Pole or to the Magnetic North Pole. These directions are expressed in degrees from 0–360°, and also fractions of a degree. The differences between these two directions at any point on the globe ismagnetic variation
Magnetic declination (also called magnetic variation) is the angle between magnetic north and true north at a particular location on the Earth's surface. The angle can change over time due to polar wandering.
Magnetic north is the direction that ...
(also known as magnetic declination
Magnetic declination (also called magnetic variation) is the angle between magnetic north and true north at a particular location on the Earth's surface. The angle can change over time due to polar wandering.
Magnetic north is the direction th ...
, but for the purposes of the mnemonic, the term 'variation' is preferred). When a compass is installed in a vehicle or vessel, local anomalies of the vessel can introduce error into the direction that the compass points. The difference between the local Magnetic North
The north magnetic pole, also known as the magnetic north pole, is a point on the surface of Earth's Northern Hemisphere at which the planet's magnetic field points vertically downward (in other words, if a magnetic compass needle is allowed t ...
and the direction that the compass indicates as north is known as magnetic deviation.
Determine variation in North America
Magnetic variation
Magnetic declination (also called magnetic variation) is the angle between magnetic north and true north at a particular location on the Earth's surface. The angle can change over time due to polar wandering.
Magnetic north is the direction that ...
(also known as magnetic declination
Magnetic declination (also called magnetic variation) is the angle between magnetic north and true north at a particular location on the Earth's surface. The angle can change over time due to polar wandering.
Magnetic north is the direction th ...
) is different depending on the geographic position on the globe. The Magnetic North Pole is currently in Northern Canada and is moving generally south. A straight line can be drawn from the Geographic North Pole, down to the Magnetic North Pole and then continued straight down to the equator. This line is known as the agonic line, and the line is also moving. In the year 1900, the agonic line passed roughly through Detroit and then was east of Florida. It currently passes roughly west of Chicago, IL, and through New Orleans, LA. If a navigator is located on the agonic line, then variation is zero: the Magnetic North Pole and the Geographic North Pole appear to be directly in line with each other. If a navigator is east of the agonic line, then the variation is westward; magnetic north appears slightly west of the Geographic North Pole. If a navigator is west of the agonic line, then the variation is eastward; the Magnetic North Pole appears to the east of the Geographic North Pole. The farther the navigator is from the agonic line, the greater the variation. The local magnetic variation is indicated on NOAA
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA ) is an American scientific and regulatory agency charged with forecasting weather, monitoring oceanic and atmospheric conditions, charting the seas, conducting deep-sea exploratio ...
nautical charts at the center of the compass rose
A compass rose or compass star, sometimes called a wind rose or rose of the winds, is a polar coordinates, polar diagram displaying the orientation of the cardinal directions (north, east, south, and west) and their points of the compass, inter ...
. The magnetic variation is indicated along with the year of that variation. The annual increase or decrease of the variation is also usually indicated, so that the variation for the current year can be calculated.
Determine deviation
A compass installed in a vehicle or vessel has a certain amount of error caused by the magnetic properties of the vessel. This error is known as compass deviation. The magnitude of the compass deviation varies greatly depending upon the local anomalies created by the vessel. Afiberglass
Fiberglass (American English) or fibreglass (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English) is a common type of fibre-reinforced plastic, fiber-reinforced plastic using glass fiber. The fibers may be randomly arranged, flattened i ...
recreational vessel will generally have much less compass deviation than a steel-hulled vessel. Electrical wires carrying current have a small magnetic field around them and can cause deviation. Any type of magnet, such as found in a speaker can also cause large magnitudes of compass deviation. The error can be corrected using a deviation table. Deviation tables are very difficult to create. Once a deviation table is established, it is only good for that particular vessel, with that particular configuration. If electrical wires are moved or anything else magnetic (speakers, electric motors, etc.) are moved, the deviation table will change. All deviations in the deviation table are indicated west or east. If the compass is pointing west of the Magnetic North Pole, then the deviation is westward. If the compass is pointing east of the Magnetic North Pole, then the deviation is eastward.
Formula
Calculating TVMDC is done with simple arithmetic. First arrange the values vertically: * True * Variation * Magnetic * Deviation * Compass The formula is always added moving down, and subtracted when moving up. The most complicated part is determining if the values are positive or negative. The True, Magnetic, and Compass values are directions on the compass, they must always be a positive number between 0–360. Variation and Deviation can be positive or negative. If either Variation or Deviation is westward, then the values are entered into the equation as positive. If the Variation or Deviation is eastward, then the values are entered into the formula as a negative. Some use themnemonic
A mnemonic device ( ), memory trick or memory device is any learning technique that aids information retention or retrieval in the human memory, often by associating the information with something that is easier to remember.
It makes use of e ...
: True Virgins Make Dull Companions - Going downward Add Whiskey (or West). An alternative, working the opposite direction: Can Dead Men Vote Twice.
Examples
True course is 120°, the Variation is 5° West, and the Deviation is 1° West. * T: 120° * V: +5° * M: 125° * D: +1° * C: 126° Therefore, to achieve a true course of 120°, one should follow a compass heading of 126°. True course is 120°, the Variation is 5° East and the Deviation is 1° East. * T: 120° * V: −5° * M: 115° * D: −1° * C: 114° True course is 035°, the Variation is 4° West and the Deviation is 1° East. * T: 035° * V: +4° * M: 039° * D: −1° * C: 038° True course is 306°, the Variation is 4° East and the Deviation is 11° West. * T: 306° * V: −4° * M: 302° * D: +11° * C: 313°Reverse
The formula can also be calculated in reverse. The formula is subtracted when moving up. Compass course is 093°, the Deviation is 4° West and the Variation is 3° West. * T: 086° * V: -3° * M: 089° * D: -4° * C: 093° Thus, when following a compass course of 093°, the true course is 086°.CDMVT
Aviation: CDMVT Can Dead Man Vote Twice: Mnemonic. Easy way to calculate compass magnetic or true north is maintaining the original signs for variation and deviation (+ for east and -for west): C+(Var)= M+(Dev)= T / T-(Dev)= M-(Var)= CSee also
*Bearing (navigation)
In navigation, bearing or azimuth is the horizontal angle between the direction of an object and north or another object. The angle value can be specified in various angular units, such as degrees, mils, or grad. More specifically:
* Absol ...
*Dead reckoning
In navigation, dead reckoning is the process of calculating the current position of a moving object by using a previously determined position, or fix, and incorporating estimates of speed, heading (or direction or course), and elapsed time. T ...
*Heading indicator
Heading can refer to:
* Heading (metalworking), a process which incorporates the extruding and upsetting processes
* Heading (navigation), the direction a person or vehicle is facing, usually similar to its course
** Aircraft heading, the dire ...
- Flight instrument
*Ship motions
Ship motions are the six degrees of freedom that a ship, boat, or other watercraft can experience.
Reference axes
The '' vertical/Z axis'', or ''yaw axis'', is an imaginary line running vertically through the ship and through its centre ...
Note
References
Bibliography
* Sea School (1977) True Virgins Make Dull Companions. Add Whiskey Going downward: Mnemonic * {{cite book, title=The Weekend Navigator: Simple Boat Navigation With GPS and Electronics, first=Robert J., last=Sweet, edition=Illustrated, publisher=McGraw-Hill Professional, year=2004, isbn=978-0-07-143035-7, pag66
url=https://archive.org/details/weekendnavigator0000swee/page/66 Navigation