|
Dead Reckoning
In navigation, dead reckoning is the process of calculating the current position of a moving object by using a previously determined position, or fix, and incorporating estimates of speed, heading (or direction or course), and elapsed time. The corresponding term in biology, to describe the processes by which animals update their estimates of position or heading, is path integration. Advances in navigational aids that give accurate information on position, in particular satellite navigation using the Global Positioning System, have made simple dead reckoning by humans obsolete for most purposes. However, inertial navigation systems, which provide very accurate directional information, use dead reckoning and are very widely applied. Etymology Contrary to myth, the term "dead reckoning" was not originally used to abbreviate "deduced reckoning", nor is it a misspelling of the term "ded reckoning". The use of "ded" or "deduced reckoning" is not known to have appeared earlier th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocean Current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of seawater generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, shoreline configurations, and interactions with other currents influence a current's direction and strength. Ocean currents move both horizontally, on scales that can span entire oceans, as well as vertically, with vertical currents (upwelling and downwelling) playing an important role in the movement of nutrients and gases, such as carbon dioxide, between the surface and the deep ocean. Ocean currents flow for great distances and together they create the global conveyor belt, which plays a dominant role in determining the climate of many of Earth's regions. More specifically, ocean currents influence the temperature of the regions through which they travel. For example, warm currents traveling along more temperate coasts increase the temper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus (; between 25 August and 31 October 1451 – 20 May 1506) was an Italians, Italian explorer and navigator from the Republic of Genoa who completed Voyages of Christopher Columbus, four Spanish-based voyages across the Atlantic Ocean sponsored by the Catholic Monarchs, opening the way for the widespread European Age of Discovery, exploration and colonization of the Americas. His expeditions were the first known European contact with the Caribbean and Central and South America. The name ''Christopher Columbus'' is the Anglicisation (linguistics), anglicization of the Latin . Growing up on the coast of Liguria, he went to sea at a young age and traveled widely, as far north as the British Isles and as far south as what is now Ghana. He married Portuguese noblewoman Filipa Moniz Perestrelo, who bore a son, Diego Columbus, Diego, and was based in Lisbon for several years. He later took a Castilian mistress, Beatriz Enríquez de Arana, who bore a son, Ferdinand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east- west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek letter lambda (λ). Meridians are imaginary semicircular lines running from pole to pole that connect points with the same longitude. The prime meridian defines 0° longitude; by convention the International Reference Meridian for the Earth passes near the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, south-east London on the island of Great Britain. Positive longitudes are east of the prime meridian, and negative ones are west. Because of the Earth's rotation, there is a close connection between longitude and time measurement. Scientifically precise local time varies with longitude: a difference of 15° longitude corresponds to a one-hour difference in local time, due to the differing position in relation to the Sun. Comparing local time to an absol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Distance (navigation)
In celestial navigation, lunar distance, also called a ''lunar'', is the angular distance between the Moon and another celestial body. The lunar distances method uses this angle and a nautical almanac to calculate Greenwich time if so desired, or by extension any other time. That calculated time can be used in solving a spherical triangle. The theory was first published by Johannes Werner in 1524, before the necessary almanacs had been published. A fuller method was published in 1763 and used until about 1850 when it was superseded by the marine chronometer. A similar method uses the positions of the Galilean moons of Jupiter. Purpose In celestial navigation, knowledge of the time at Greenwich (or another known place) and the measured positions of one or more celestial objects allows the navigator to calculate longitude. Reliable marine chronometers were unavailable until the late 18th century and not affordable until the 19th century. After the method was firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Harrison
John Harrison ( – 24 March 1776) was an English carpenter and clockmaker who invented the marine chronometer, a long-sought-after device for solving the History of longitude, problem of how to calculate longitude while at sea. Harrison's solution revolutionized navigation and greatly increased the safety of long-distance sea travel. The problem he solved had been considered so important following the Scilly naval disaster of 1707 that the Parliament of Great Britain, British Parliament was offering financial rewards of up to £20,000 (equivalent to £ in ) under the 1714 Longitude Act, though Harrison never received the full reward due to political rivalries. He presented his first design in 1730, and worked over many years on improved designs, making several advances in time-keeping technology, finally turning to what were called sea watches. Harrison gained support from the Board of Longitude, Longitude Board in building and testing his designs. Towards the end of his life, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Chronometer
A marine chronometer is a precision timepiece that is carried on a ship and employed in the determination of the ship's position by celestial navigation. It is used to determine longitude by comparing Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), and the time at the current location found from observations of celestial bodies. When first developed in the 18th century, it was a major technical achievement, as accurate knowledge of the time over a long sea voyage was vital for effective navigation, lacking electronic or communications aids. The first true chronometer was the life work of one man, John Harrison, spanning 31 years of persistent experimentation and testing that revolutionized naval (and later aerial) navigation. The term ''wikt:chronometer, chronometer'' was coined from the Greek words () (meaning time) and (meaning measure). The 1713 book ''Physico-Theology'' by the English cleric and scientist William Derham includes one of the earliest theoretical descriptions of a marine chronome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
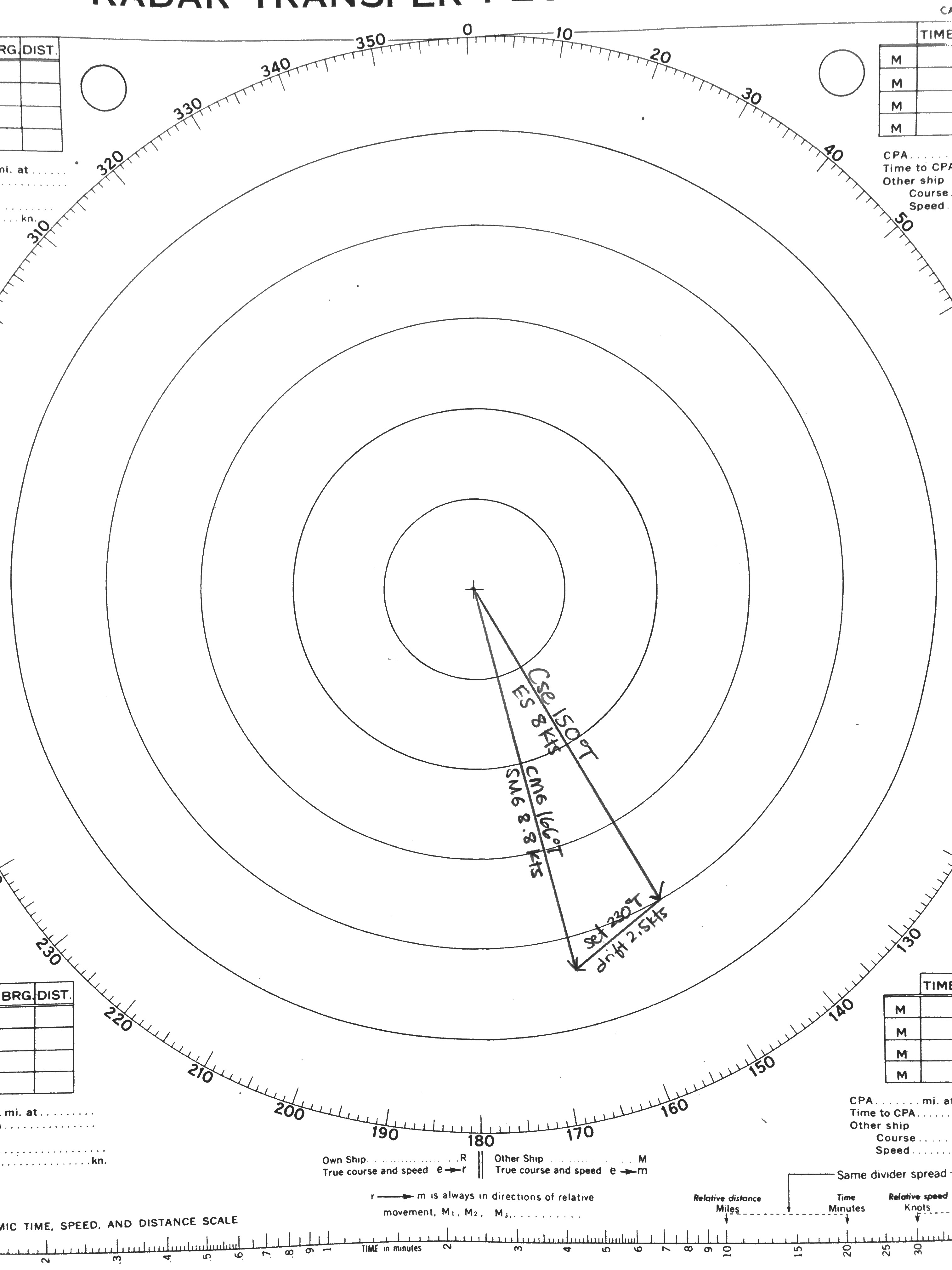
Set And Drift
The term “set and drift” is used to describe external forces that affect a boat and keep it from following an intended course. To understand and calculate set and drift, one needs to first understand currents. Ocean currents are the horizontal movements of water from one location to another. The movement of water is impacted by: meteorological effects, wind, temperature differences, gravity, and on occasion earthquakes. Set is the current's direction, expressed in true degrees. Drift is the current's speed, which is usually measured in knots. “Leeway” refers to the amount of sidewards translation of a vessel drifting off of or away from the intended course of travel (with no correction or compensation by altering the heading of the vessel such as pointing her into the wind.) Ignoring set and drift can cause a mariner to get off their desired course, sometimes by hundreds of miles. A mariner needs to be able to steer the ship and compensate for the effects of set and drift ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pit Sword
The pit sword (also known as a rodmeter) is a blade of metal or plastic that extends into the water beneath the hull of a ship. It is part of the pitometer log, a device for measuring the ship's speed through the water. See also * Electromagnetic log *Pitot tube A pitot tube ( ; also pitot probe) measures fluid flow velocity. It was invented by French engineer Henri Pitot during his work with aqueducts and published in 1732, and modified to its modern form in 1858 by Henry Darcy. It is widely use ... References External links Historical site with information on US Navy submarine pitometer log systems during World War II. This site shows the pit sword or rodmeter as it is deployed. {{DEFAULTSORT:Pit Sword Measuring instruments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equivalent Airspeed
In aviation, equivalent airspeed (EAS) is calibrated airspeed (CAS) corrected for the compressibility of air at a non-trivial Mach number. It is also the airspeed at sea level in the International Standard Atmosphere at which the dynamic pressure is the same as the dynamic pressure at the true airspeed (TAS) and altitude at which the aircraft is flying. In low-speed flight, it is the speed which would be shown by an airspeed indicator with zero error.Houghton, E.L. and Carpenter, P.W. (1993), ''Aerodynamics for Engineering Students'', Section 2.3.3, Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford UK. It is useful for predicting aircraft handling, aerodynamic loads, stalling etc. \mathrm = \mathrm \times \sqrt where is actual air density and is standard sea level density (1.225 kg/m3 or 0.00237 slug/ft3). is a function of dynamic pressure: \mathrm = \sqrt where is the dynamic pressure q = \tfrac12\, \rho\, v^. EAS can also be obtained from the aircraft Mach number and static pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitot Tube
A pitot tube ( ; also pitot probe) measures fluid flow velocity. It was invented by French engineer Henri Pitot during his work with aqueducts and published in 1732, and modified to its modern form in 1858 by Henry Darcy. It is widely used to determine the airspeed of aircraft; the water speed of boats; and the flow velocity of liquids, air, and gases in industry. Theory of operation The basic pitot tube consists of a tube pointing directly into the oncoming fluid flow. Pressure in the tube can be measured as the moving fluid cannot escape and stagnates. This pressure is the stagnation pressure of the fluid, also known as the total pressure or (particularly in aviation) the pitot pressure. The measured stagnation pressure cannot just by itself be used to determine the fluid flow velocity (airspeed in aviation) directly. However, with a measured static pressure as well it can be determined by the use of Bernoulli's equation which states: :Stagnation pressure = static pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolutions Per Minute
Revolutions per minute (abbreviated rpm, RPM, rev/min, r/min, or r⋅min−1) is a unit of rotational speed (or rotational frequency) for rotating machines. One revolution per minute is equivalent to hertz. Standards ISO 80000-3:2019 defines a physical quantity called ''rotation'' (or ''number of revolutions''), dimensionless, whose instantaneous rate of change is called ''rotational frequency'' (or ''rate of rotation''), with units of reciprocal seconds (s−1). A related but distinct quantity for describing rotation is ''angular frequency'' (or ''angular speed'', the magnitude of angular velocity), for which the SI unit is the radian per second (rad/s). Although they have the same dimensions (reciprocal time) and base unit (s−1), the hertz (Hz) and radians per second (rad/s) are special names used to express two different but proportional ISQ quantities: frequency and angular frequency, respectively. The conversions between a frequency and an angular frequency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |