Haploinsufficiency Graph Only on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Haploinsufficiency in
Haploinsufficiency in
 Haploinsufficiency in
Haploinsufficiency in genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinians, Augustinian ...
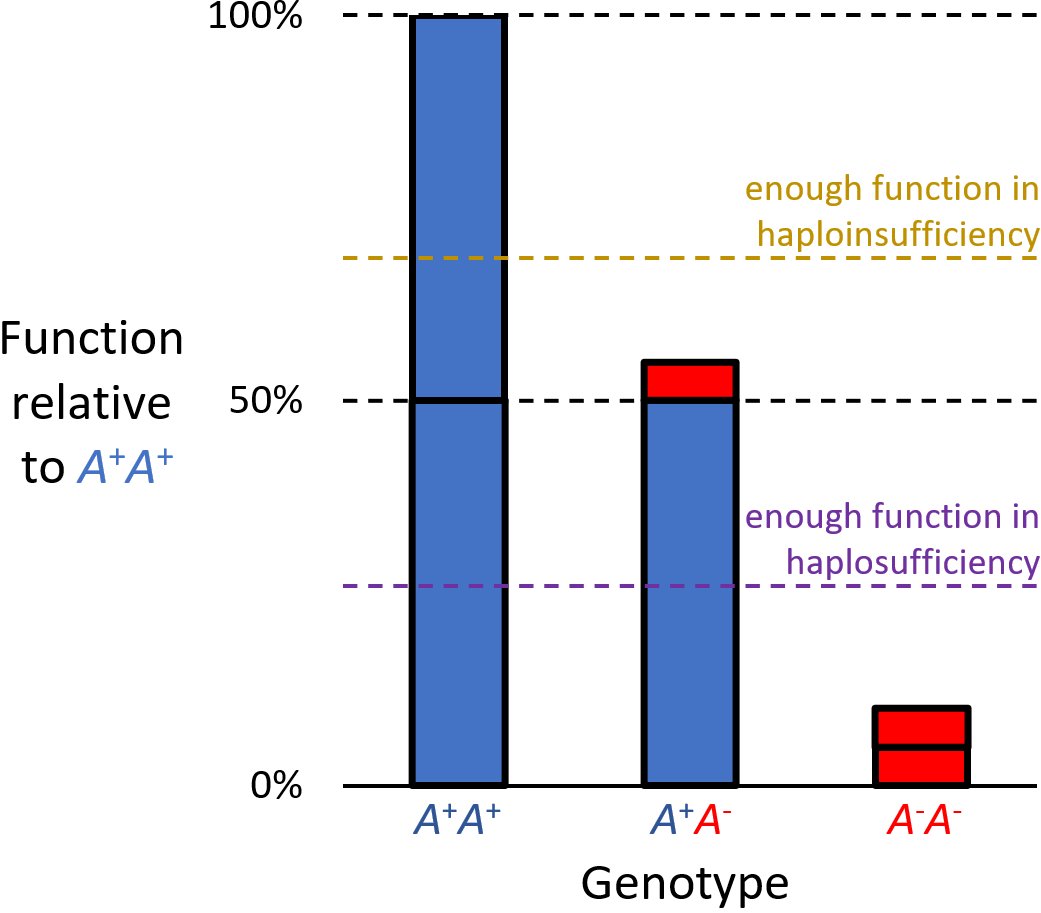
describes a model of dominant gene action in diploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, ...
organisms, in which a single copy of the wild-type
The wild type (WT) is the phenotype of the typical form of a species as it occurs in nature. Originally, the wild type was conceptualized as a product of the standard "normal" allele at a locus, in contrast to that produced by a non-standard, " ...
allele
An allele is a variant of the sequence of nucleotides at a particular location, or Locus (genetics), locus, on a DNA molecule.
Alleles can differ at a single position through Single-nucleotide polymorphism, single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP), ...
at a locus in heterozygous
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism.
Mos ...
combination with a variant allele is insufficient to produce the wild-type phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology (physical form and structure), its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological propert ...
. Haploinsufficiency may arise from a ''de novo'' or inherited loss-of-function mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosis ...
in the variant allele, such that it yields little or no gene product (often a protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
). Although the other, standard allele still produces the standard amount of product, the total product is insufficient to produce the standard phenotype. This heterozygous
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism.
Mos ...
genotype
The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. Genotype can also be used to refer to the alleles or variants an individual carries in a particular gene or genetic location. The number of alleles an individual can have in a ...
may result in a non- or sub-standard, deleterious, and (or) disease phenotype. Haploinsufficiency is the standard explanation for dominant deleterious alleles.
In the alternative case of haplosufficiency, the loss-of-function allele behaves as above, but the single standard allele in the heterozygous
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism.
Mos ...
genotype produces sufficient gene product to produce the same, standard phenotype as seen in the homozygote
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism.
Mos ...
. Haplosufficiency accounts for the typical dominance of the "standard" allele over variant alleles, where the phenotypic identity of genotypes heterozygous and homozygous for the allele defines it as dominant, ''versus'' a variant phenotype produced only by the genotype homozygous for the alternative allele, which defines it as recessive.
Mechanism
The alteration in the gene dosage, which is caused by the loss of a functional allele, is also called allelic insufficiency.Haploinsufficiency in humans
About 3,000 human genes cannot tolerate loss of one of the two alleles. An example of this is seen in the case ofWilliams syndrome
Williams syndrome (WS), also Williams–Beuren syndrome (WBS), is a genetic disorder that affects many parts of the body. Facial features frequently include a broad forehead, underdeveloped chin, short nose, and full cheeks. Mild to moderate int ...
, a neurodevelopmental disorder caused by the haploinsufficiency of genes at 7q11.23. The haploinsufficiency is caused by the copy-number variation
Copy number variation (CNV) is a phenomenon in which sections of the genome are repeated and the number of repeats in the genome varies between individuals. Copy number variation is a type of structural variation: specifically, it is a type of ...
(CNV) of 28 genes led by the deletion of ~1.6 Mb. These dosage-sensitive genes are vital for human language and constructive cognition.
Another example is the haploinsufficiency of telomerase reverse transcriptase
Telomerase reverse transcriptase (abbreviated to TERT, or hTERT in humans) is a catalytic subunit of the enzyme telomerase, which, together with the telomerase RNA component (TERC), comprises the most important unit of the telomerase complex.
...
which leads to anticipation in autosomal dominant dyskeratosis congenita
Dyskeratosis congenita (DKC), also known as Zinsser-Engman-Cole syndrome, is a rare progressive congenital disorder with a highly variable phenotype. The entity was classically defined by the triad of abnormal skin pigmentation, nail dystrophy, an ...
. It is a rare inherited disorder characterized by abnormal skin manifestations, which results in bone marrow failure, pulmonary fibrosis
Pulmonary fibrosis is a condition in which the lungs become scarred over time. Symptoms include shortness of breath, a dry cough, feeling tired, weight loss, and nail clubbing. Complications may include pulmonary hypertension, respiratory ...
and an increased predisposition to cancer. A null mutation
A null allele is a nonfunctional allele (a variant of a gene) caused by a genetic mutation. Such mutations can cause a complete lack of production of the associated gene product or a product that does not function properly; in either case, the al ...
in motif D of the reverse transcriptase domain of the telomerase protein, hTERT, leads to this phenotype. Thus telomerase dosage is important for maintaining tissue proliferation.
A variation of haploinsufficiency exists for mutations in the gene '' PRPF31'', a known cause of autosomal dominant
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the Phenotype, effect of a different variant of the same gene on Homologous chromosome, the other copy of the chromosome. The firs ...
retinitis pigmentosa
Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) is a member of a group of genetic disorders called inherited retinal dystrophy (IRD) that cause loss of vision. Symptoms include trouble seeing at night and decreasing peripheral vision (side and upper or lower visua ...
. There are two wild-type alleles of this gene—a high- expressivity allele and a low-expressivity allele. When the mutant gene is inherited with a high-expressivity allele, there is no disease phenotype. However, if a mutant allele and a low-expressivity allele are inherited, the residual protein levels falls below that required for normal function, and disease phenotype is present.
Copy number variation
Copy number variation (CNV) is a phenomenon in which sections of the genome are repeated and the number of repeats in the genome varies between individuals. Copy number variation is a type of structural variation: specifically, it is a type of ...
(CNV) refers to the differences in the number of copies of a particular region of the genome. This leads to too many or too few of the dosage sensitive genes. The genomic rearrangements, that is, deletions or duplications, are caused by the mechanism of non-allelic homologous recombination Non-allelic homologous recombination (NAHR) is a form of homologous recombination that occurs between two lengths of DNA that have high sequence similarity, but are not alleles.
It usually occurs between sequences of DNA that have been previously ...
(NAHR). In the case of the Williams Syndrome, the microdeletion includes the '' ELN'' gene. The hemizygosity of the elastin is responsible for supravalvular aortic stenosis, the obstruction in the left ventricular outflow of blood in the heart.
Other examples include:
* Some cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
s
* 1q21.1 deletion syndrome
* 5q- syndrome in myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS)
* 22q11.2 deletion syndrome
DiGeorge syndrome, also known as 22q11.2 deletion syndrome, is a syndrome caused by a microdeletion on the long arm of chromosome 22. While the symptoms can vary, they often include congenital heart problems, specific facial features, frequent i ...
* CHARGE syndrome
CHARGE syndrome (formerly known as CHARGE association) is a rare syndrome caused by a genetic disorder. First described in 1979, the acronym "CHARGE" came into use for newborn children with the congenital features of coloboma of the eye, heart ...
* Cleidocranial dysostosis
Cleidocranial dysostosis (CCD), also called cleidocranial dysplasia, is a congenital disorder, birth defect that mostly affects the bones and teeth. The collarbones are typically either poorly developed or absent, which allows the shoulders to be ...
* Ehlers–Danlos syndrome
Ehlers–Danlos syndromes (EDS) is a group of 14 genetic connective-tissue disorders. Symptoms often include loose joints, joint pain, stretchy velvety skin, and abnormal scar formation. These may be noticed at birth or in early childhood. Co ...
* Frontotemporal dementia
Frontotemporal dementia (FTD), also called frontotemporal degeneration disease or frontotemporal neurocognitive disorder, encompasses several types of dementia involving the progressive degeneration of the brain's frontal lobe, frontal and tempor ...
caused by mutations in progranulin
* GLUT1 deficiency (DeVivo syndrome)
* Haploinsufficiency of A20
* Haploinsufficiency of PRR12
* Holoprosencephaly
Holoprosencephaly (HPE) is a cephalic disorder in which the prosencephalon (the forebrain of the embryo) fails to Prenatal development, develop into two Cerebral hemisphere, hemispheres, typically occurring between the 18th and 28th day of gestati ...
caused by haploinsufficiency in the Sonic Hedgehog gene
* Holt–Oram syndrome
Holt–Oram syndrome (also called atrio-digital syndrome, atriodigital dysplasia, cardiac-limb syndrome, heart-hand syndrome type 1, HOS, ventriculo-radial syndrome) is an autosomal dominant disorder that affects bones in the arms and hands (th ...
* Marfan syndrome
Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a multi-systemic genetic disorder that affects the connective tissue. Those with the condition tend to be tall and thin, with dolichostenomelia, long arms, legs, Arachnodactyly, fingers, and toes. They also typically ha ...
* Phelan–McDermid syndrome
* Polydactyly
Polydactyly is a birth defect that results in extra fingers or toes. The hands are more commonly involved than the feet. Extra fingers may be painful, affect self-esteem, or result in clumsiness.
It is associated with at least 39 genetic mut ...
* Dravet Syndrome
Dravet syndrome (DS), previously known as severe myoclonic epilepsy of infancy (SMEI), is an autosomal dominant genetic disorder which causes a catastrophic form of epilepsy, with prolonged seizures that are often triggered by hot temperatures o ...
* ZTTK
* FOXP1
Forkhead box protein P1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''FOXP1'' gene. FOXP1 is necessary for the proper development of the brain, heart, and lung in mammals. It is a member of the large FOX proteins, FOX family of transcription f ...
Syndrome
* NR4A2-related syndrome
Methods of detection
The most direct method to detect haploinsufficiency is theheterozygous
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism.
Mos ...
deletion of one allele
An allele is a variant of the sequence of nucleotides at a particular location, or Locus (genetics), locus, on a DNA molecule.
Alleles can differ at a single position through Single-nucleotide polymorphism, single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP), ...
in a model organism. This can be done in tissue culture cells or in single-celled organisms such as yeast (''Saccharomyces cerevisiae
''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' () (brewer's yeast or baker's yeast) is a species of yeast (single-celled fungal microorganisms). The species has been instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have be ...
'').
References
Further reading
* * {{Commons category, Haploinsufficiency Genetics Rare diseases