Hamstring on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
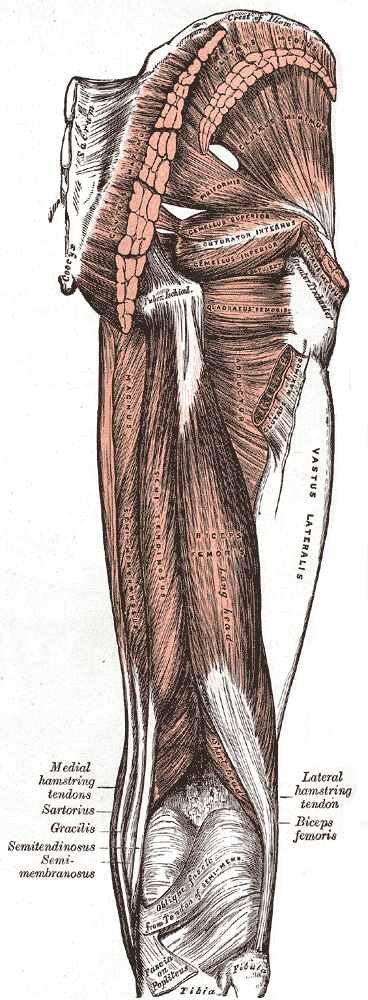
A hamstring () is any one of the three posterior thigh muscles in human anatomy between the hip and the knee: from medial to lateral, the semimembranosus, semitendinosus and biceps femoris.
The adductor magnus reaches only up to the adductor tubercle of the femur, but it is included amongst the hamstrings because the tibial collateral ligament of the knee joint morphologically is the degenerated tendon of this muscle. The ligament is attached to the medial epicondyle, two millimeters from the adductor tubercle.
Etymology
The word " ham" is derived from the Old English “ham” or “hom” meaning the hollow or bend of the knee, from a Germanic base where it meant "crooked". It gained the meaning of the leg of an animal around the 15th century. ''String'' refers to tendons, and thus the hamstrings' string-like tendons felt on either side of the back of the knee.Criteria
The common criteria of any hamstring muscles are: # Muscles should originate from ischial tuberosity. # Muscles should be inserted over the knee joint, in the tibia or in the fibula. # Muscles will be innervated by the tibial branch of the sciatic nerve. # Muscle will participate in flexion of the knee joint and extension of the hip joint. Those muscles which fulfill all of the four criteria are called true hamstrings.The adductor magnus reaches only up to the adductor tubercle of the femur, but it is included amongst the hamstrings because the tibial collateral ligament of the knee joint morphologically is the degenerated tendon of this muscle. The ligament is attached to the medial epicondyle, two millimeters from the adductor tubercle.
Structure
The three muscles of the posterior thigh (semitendinosus, semimembranosus, biceps femoris) flex (bend) the knee, while all but the biceps femoris extend (straighten) the hip. The three 'true' hamstrings cross both the hip and the knee joint and are therefore involved in knee flexion and hip extension. The short head of the biceps femoris crosses only one joint (knee) and is therefore not involved in hip extension. With its divergent origin and innervation, it is sometimes excluded from the 'hamstring' characterization. A portion of the adductor magnus is sometimes considered a part of the hamstrings.
Function
The hamstrings cross and act upon two joints – the hip and the knee – and as such they are termed biarticular muscles. The hamstrings contract when the knee is bent, and lengthen when the knee is extended, and when the hips are extended Semitendinosus and semimembranosus extend the hip when the trunk is fixed; they also flex the knee and medially (inwardly) rotate the lower leg when the knee is bent. The long head of the biceps femoris extends the hip, as when beginning to walk; both short and long heads flex the knee and laterally (outwardly) rotate the lower leg when the knee is bent. The hamstrings play a crucial role in many daily activities such as walking, running, jumping, and controlling some movement in the gluteus. In walking, they are most important as anantagonist
An antagonist is a character in a story who is presented as the main enemy or rival of the protagonist and is often depicted as a villain.quadriceps in the deceleration of knee extension.
 Imaging the hamstring muscles is usually performed with an ultrasound and/or MRI. The biceps femoris is most commonly injured, followed by semitendinosus. Semimembranosus injury is rare. Imaging is useful in differentiating the grade of strain, especially if the muscle is completely torn. In this setting, the level and degree of retraction can be determined, serving as a useful roadmap prior to any surgery. Those with a hamstring strain of greater than in length have a greater risk of recurrence.
Imaging the hamstring muscles is usually performed with an ultrasound and/or MRI. The biceps femoris is most commonly injured, followed by semitendinosus. Semimembranosus injury is rare. Imaging is useful in differentiating the grade of strain, especially if the muscle is completely torn. In this setting, the level and degree of retraction can be determined, serving as a useful roadmap prior to any surgery. Those with a hamstring strain of greater than in length have a greater risk of recurrence.
MRI Images demonstrating avulsion fracture of the hamstring muscle origin
{{Muscles of lower limb Hip extensors Knee flexors Muscles of the lower limb Posterior compartment of thigh Hamstring
Clinical significance
Sports running injuries
A common running injury in several sports, excessive stretch of a hamstring results from extensive hip flexion while the knee is extended. During sprinting, a hamstring injury may occur from excessive muscle strain during eccentric contraction late in the leg swing phase. The overall incidence of a hamstring injury in sports and professional dancers is about two per 1000 hours of performance. In some sports, a hamstring injury occurs at the incidence of 19% of all sports injuries, and results in an average time loss from competition of 24 days.Imaging
 Imaging the hamstring muscles is usually performed with an ultrasound and/or MRI. The biceps femoris is most commonly injured, followed by semitendinosus. Semimembranosus injury is rare. Imaging is useful in differentiating the grade of strain, especially if the muscle is completely torn. In this setting, the level and degree of retraction can be determined, serving as a useful roadmap prior to any surgery. Those with a hamstring strain of greater than in length have a greater risk of recurrence.
Imaging the hamstring muscles is usually performed with an ultrasound and/or MRI. The biceps femoris is most commonly injured, followed by semitendinosus. Semimembranosus injury is rare. Imaging is useful in differentiating the grade of strain, especially if the muscle is completely torn. In this setting, the level and degree of retraction can be determined, serving as a useful roadmap prior to any surgery. Those with a hamstring strain of greater than in length have a greater risk of recurrence.
Use in surgery
The distal semitendinosus tendon is one of the tendons that can be used in the surgical procedure ACL reconstruction. In this procedure, a piece of it is used to replace the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). The ACL is one of the four major ligaments in the knee, which also include the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), medial collateral ligament (MCL), and lateral collateral ligament (LCL).See also
* Hamstringing * Hamstring curl * Lombard's paradox * Popliteal fossa * Pulled hamstringReferences
External links
MRI Images demonstrating avulsion fracture of the hamstring muscle origin
{{Muscles of lower limb Hip extensors Knee flexors Muscles of the lower limb Posterior compartment of thigh Hamstring