HIV Rev Response Element on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The 
 The HIV-1 genome contains a single promoter and uses multiple reading frames and alternative splicing to encode 15 proteins from a single pre-mRNA species. Transcription from an integrated HIV-1 provirus generates a single 9 kilobase (kb) pre-mRNA containing multiple splice sites and nuclear retention signals. In the early phase of the viral life cycle, this pre-RNA is completely spliced to RRE-free, 2 kb messages. These smaller messages are then transported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm via standard mRNA nuclear export pathways (see Figure). One of these small, 2kb messages encodes the HIV-1 Rev protein which is imported into the nucleus via its
The HIV-1 genome contains a single promoter and uses multiple reading frames and alternative splicing to encode 15 proteins from a single pre-mRNA species. Transcription from an integrated HIV-1 provirus generates a single 9 kilobase (kb) pre-mRNA containing multiple splice sites and nuclear retention signals. In the early phase of the viral life cycle, this pre-RNA is completely spliced to RRE-free, 2 kb messages. These smaller messages are then transported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm via standard mRNA nuclear export pathways (see Figure). One of these small, 2kb messages encodes the HIV-1 Rev protein which is imported into the nucleus via its
HIV-1
The subtypes of HIV include two main subtypes, known as HIV type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV type 2 (HIV-2). These subtypes have distinct genetic differences and are associated with different epidemiological patterns and clinical characteristics.
HIV-1 e ...
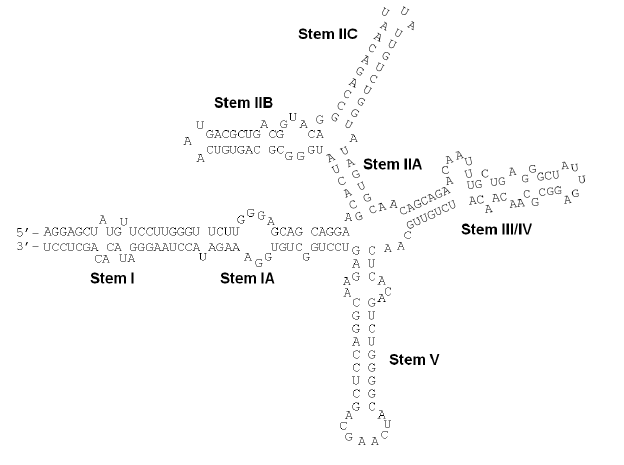
Rev response element (RRE) is a highly structured, ~350 nucleotide RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself (non-coding RNA) or by forming a template for the production of proteins (messenger RNA). RNA and deoxyrib ...
segment present in the Env coding region of unspliced and partially spliced viral mRNAs. In the presence of the HIV-1
The subtypes of HIV include two main subtypes, known as HIV type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV type 2 (HIV-2). These subtypes have distinct genetic differences and are associated with different epidemiological patterns and clinical characteristics.
HIV-1 e ...
accessory protein Rev, HIV-1 m RNAs that contain the RRE can be exported from the nucleus
Nucleus (: nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucleu ...
to the cytoplasm
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell a ...
for downstream events such as translation
Translation is the communication of the semantics, meaning of a #Source and target languages, source-language text by means of an Dynamic and formal equivalence, equivalent #Source and target languages, target-language text. The English la ...
and virion packaging.

RRE and HIV-1 biology
Early phase
 The HIV-1 genome contains a single promoter and uses multiple reading frames and alternative splicing to encode 15 proteins from a single pre-mRNA species. Transcription from an integrated HIV-1 provirus generates a single 9 kilobase (kb) pre-mRNA containing multiple splice sites and nuclear retention signals. In the early phase of the viral life cycle, this pre-RNA is completely spliced to RRE-free, 2 kb messages. These smaller messages are then transported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm via standard mRNA nuclear export pathways (see Figure). One of these small, 2kb messages encodes the HIV-1 Rev protein which is imported into the nucleus via its
The HIV-1 genome contains a single promoter and uses multiple reading frames and alternative splicing to encode 15 proteins from a single pre-mRNA species. Transcription from an integrated HIV-1 provirus generates a single 9 kilobase (kb) pre-mRNA containing multiple splice sites and nuclear retention signals. In the early phase of the viral life cycle, this pre-RNA is completely spliced to RRE-free, 2 kb messages. These smaller messages are then transported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm via standard mRNA nuclear export pathways (see Figure). One of these small, 2kb messages encodes the HIV-1 Rev protein which is imported into the nucleus via its nuclear localization sequence
A nuclear localization signal ''or'' sequence (NLS) is an amino acid sequence that 'tags' a protein for import into the cell nucleus by nuclear transport. Typically, this signal consists of one or more short sequences of positively charged lysines ...
. This phase of the virus life cycle is both Rev and RRE independent.
Late phase
The late phase of the viral life cycle is characterized by the expression of viral proteins that are encoded on the long, unspliced (9kb) or partially spliced (4 kb) messages containing the RRE. Because of their retention and splicing signals, these intron-containing RNAs are initially retained in the nucleus for splicing/degradation. However, after a sufficient level of Rev has been produced by the 2 kb messages, these longer messages can be exported to the cytoplasm via a Rev dependent export pathway. Nuclear export of these RNAs is achieved by a specific, co-operative assembly of multiple Rev molecules on the RRE. Assembly of this Rev-RRE complex is followed by the recruitment of a human protein complex containing the proteins exportin-1 (XPO1/CRM1) and Ran-GTP. Rev recruits this export machinery via a nuclear export sequence (NES) present in Rev. This Rev-RRE-Xpo1/RanGTP complex is then transported to the cytoplasm. In the cytoplasm, these messages are translated to produce all the remaining viral proteins or packaged as genomes for newly budding virions (see Figure).Secondary Structure and Rev Recognition
The RRE is a highly structured RNA element. Computational predictions, later verified by chemical and enzymatic probing, indicate that RRE contains multiple stem loops and bulges (see Figure). Rev binds to RRE in a sequence specific manner with Rev-RNA recognition mediated by a 17-residue a-helical stretch on Rev, the Arginine-Rich-Motif (ARM).
Stem IIB: a high-affinity binding site
Stem IIB is a site on the RRE which Rev binds with high affinity and specificity. The structure of an isolated stem IIB bound to a peptide corresponding to a Rev-ARM has been solved byNMR
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a physical phenomenon in which atomic nucleus, nuclei in a strong constant magnetic field are disturbed by a weak oscillating magnetic field (in the near and far field, near field) and respond by producing ...
. This structure reveals an RNA A-form major groove widened by purine-purine base pairs at the purine-rich bulge to accommodate the a-helical Rev-ARM. Binding is achieved through a combination of base-specific contacts and electrostatic contacts with the phosphate backbone (see figure). More recent studies have identified another region on the RRE, stem IA, that binds Rev in a specific manner, but with a 5-fold weaker affinity than stem IIB. Recent crystal structure of RRE stem-loop II shows that stem IIB is incorporated into the three-way junction of stem-loop II.
Co-operative Rev assembly required for RRE function
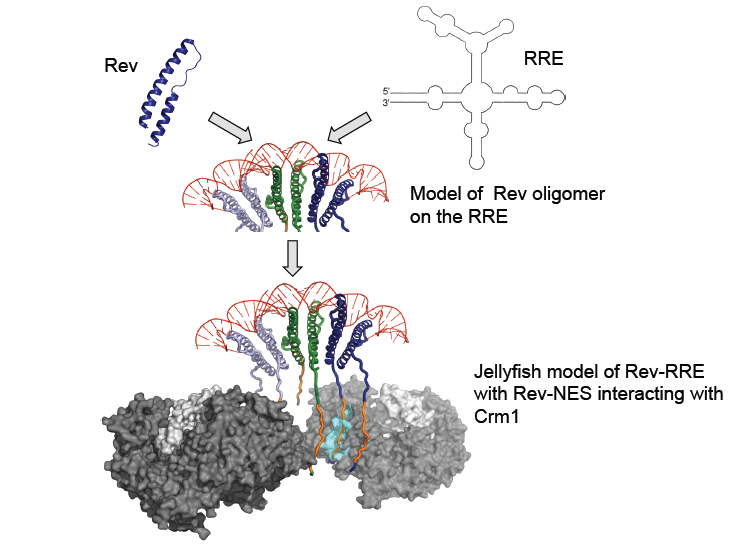
Although Stems IIB and IA can bind Rev in isolation, a full-length RRE (at least ~250 nt) is required for viral function. Multiple molecules of Rev bind to the full RRE in a specific and co-operative manner through a combination of Rev-RNA and Rev-Rev interactions. It is believed that IIB acts as an "anchor point", with the Rev molecules bound at secondary sites (such as IA) stabilized by protein-protein interactions with other Rev molecules (in addition to the RNA-protein interactions). Biochemical studies on a 242-nucleotide RRE have established a ratio of 6 Rev monomers to each RRE. In a sense, the RRE acts as a scaffolding platform onto which a specific and co-operative complex of Revs (and eventually cellular export machinery) assembles. This cooperativity that is dictated by RRE structure and sequence is required for the formation of a high affinity, export-competent complex. Current models of Rev assembly on the RRE suggest an initial Rev nucleation event at stem IIB followed by progressive addition of Rev molecules to form the full complex.Rev-RRE Complexes recruit additional partners
After assembly of a Rev-RRE complex, cellular export machinery must be added to guide the RNA through thenuclear pore
The nuclear pore complex (NPC), is a large protein complex giving rise to the nuclear pore. A great number of nuclear pores are studded throughout the nuclear envelope that surrounds the eukaryote cell nucleus. The pores enable the nuclear tran ...
. Nuclear export of Rev-RRE containing mRNAs is achieved using the human Crm1- RanGTP nuclear export pathway. Rev contains a nuclear export sequence (NES) that binds Crm1, and Crm1 guides the entire complex out of the nucleus.
Recent crystal structures of Rev, the Rev-ARM/Stem IIB structure and the information on Rev-RRE stoichiometry have led to the proposal of a jelly-fish model for a functionally active complex. In this model, The RRE provides a structural scaffold to assemble a Rev hexamer, and this assembly forms the head of the jelly-fish. The NESs from the 6 Rev monomers form the jelly-fish "tentacles" that could interact with the host Crm1-RanGTP proteins. This entire "jellyfish" would then be exported to the cytoplasm (see Figure).

Tertiary structure
Images of thetertiary structure
Protein tertiary structure is the three-dimensional shape of a protein. The tertiary structure will have a single polypeptide chain "backbone" with one or more protein secondary structures, the protein domains. Amino acid side chains and the ...
of RRE (and the Rev-RRE complex) have been captured using atomic force microscopy
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) or scanning force microscopy (SFM) is a very-high-resolution type of scanning probe microscopy (SPM), with demonstrated resolution on the order of fractions of a nanometer, more than 1000 times better than the opti ...
. These images show a globular "head" with a long stalk extending from it and are in accordance with 3D predictions from computer models, as well as electron microscope (EM) images of assembled Rev-RRE complexes.
Rev-RRE as a Drug Target
As the export of RRE-containing RNAs is essential for HIV replication, the association of RRE and Rev is an attractive therapeutic target. Various RNA cleavage methods and small molecule screens have been implemented in an effort to designantiviral drug
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Antiviral drugs are a class of antimicrobials ...
s to treat HIV infection by metallopeptide structures. Rev and RRE are particularly attractive drug targets as both elements exist in reading frames
In molecular biology, a reading frame is a specific choice out of the possible ways to read the sequence of nucleotides in a nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) molecule as a sequence of triplets. Where these triplets equate to amino acids or stop signals ...
that code other proteins (Tat and Env for Rev, Env for RRE), theoretically restricting potential escape mutations. However, to date there are no clinically approved therapies that target Rev-RRE.
Relationship to Other Viruses
All complex retroviruses face the problem of exporting unspliced and partially spliced mRNAs. Some use systems similar to Rev/RRE; these include HIV-2 and SIV (Simian Immunodeficiency Virus) which use their own Rev-RRE systems, some betaretroviruses, which use a Rem/RmRE system, and all deltaretroviruses which use a Rex/RxRRE systems. Many simple retroviruses, most notably Mason–Pfizer monkey virus (MPMV), do not encode a Rev-like protein, but instead have evolved a cis-acting RNA element, the constitutive transport element (CTE), that directly binds to components of the host mRNA export machinery. The MPMV CTE is ~220 nucleotides and consists of two identical binding sites for the cellular export protein Tap. Tap directly binds the viral RNA and exports it to the cytoplasm.See also
* HIV Ribosomal frameshift signal * Retrovirus direct repeat 1 (dr1)References
External links
* * http://www.scripps.edu/mb/millar/research/rev.htm{{Dead link, date=July 2024 , bot=InternetArchiveBot , fix-attempted=yes Cis-regulatory RNA elements