Gustaf III on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Gustav III (29 March 1792), also called ''Gustavus III'', was
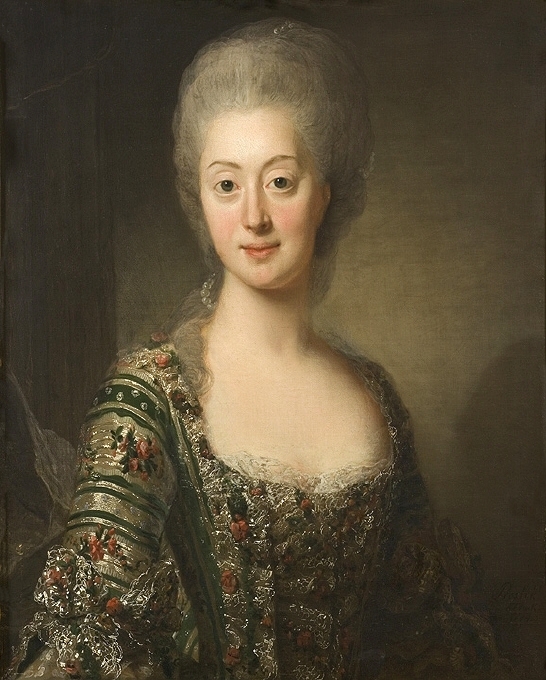 Gustav married Princess Sophia Magdalena, daughter of King
Gustav married Princess Sophia Magdalena, daughter of King
 Gustav first intervened actively in politics during the December Crisis (1768), when he compelled the dominant
Gustav first intervened actively in politics during the December Crisis (1768), when he compelled the dominant

 At the time of his accession, the Swedish
At the time of his accession, the Swedish  Gustav III was approached by
Gustav III was approached by
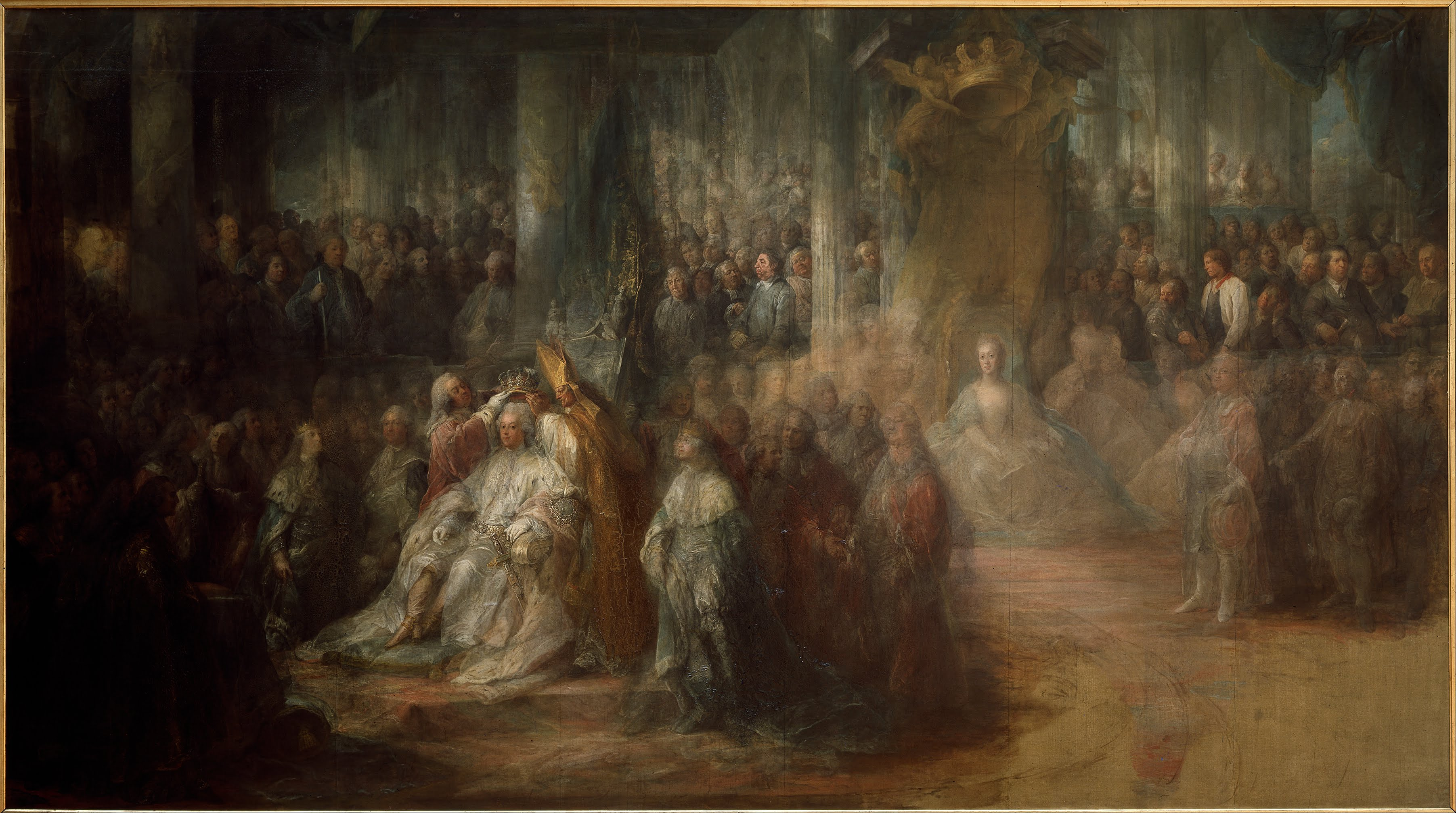
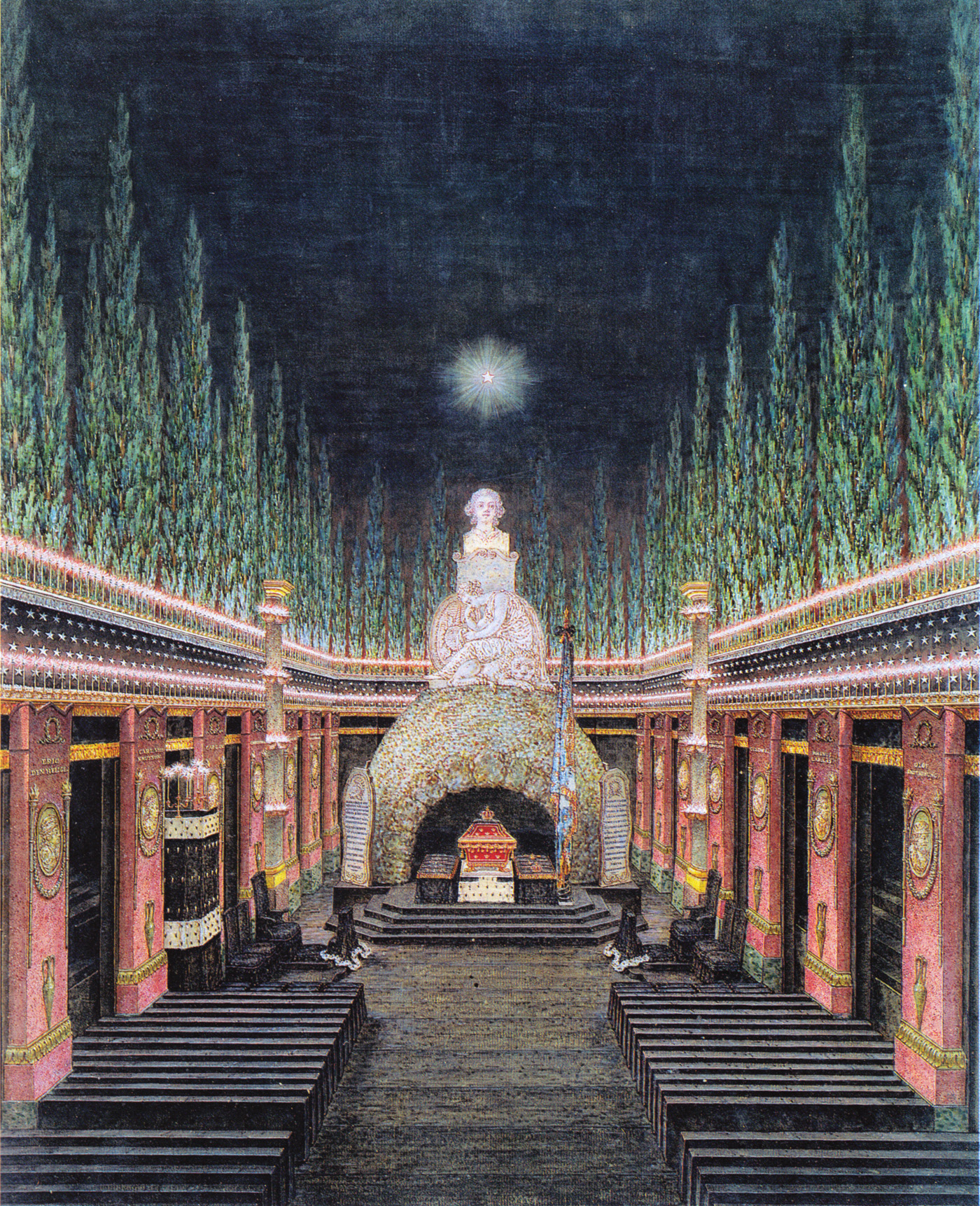 Gustav's funeral took place on 14 May 1792. It was held in
Gustav's funeral took place on 14 May 1792. It was held in
King of Sweden
The monarchy of Sweden is centred on the monarchical head of state of Sweden,See the #IOG, Instrument of Government, Chapter 1, Article 5. by law a constitutional monarchy, constitutional and hereditary monarchy with a parliamentary system.Parl ...
from 1771 until his assassination in 1792. He was the eldest son of King Adolf Frederick and Queen Louisa Ulrika of Sweden.
Gustav was a vocal opponent of what he saw as the abuse of political privileges seized by the nobility
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy. It is normally appointed by and ranked immediately below royalty. Nobility has often been an estate of the realm with many exclusive functions and characteristics. T ...
since the death of King Charles XII
Charles XII, sometimes Carl XII () or Carolus Rex (17 June 1682 – 30 November 1718 Old Style and New Style dates, O.S.), was King of Sweden from 1697 to 1718. He belonged to the House of Palatinate-Zweibrücken, a branch line of the House of ...
in the Great Northern War
In the Great Northern War (1700–1721) a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in Northern Europe, Northern, Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the ant ...
. Seizing power from the government in a coup d'état
A coup d'état (; ; ), or simply a coup
, is typically an illegal and overt attempt by a military organization or other government elites to unseat an incumbent leadership. A self-coup is said to take place when a leader, having come to powe ...
, called the Swedish Revolution, in 1772, that ended the Age of Liberty
In Swedish history, the Age of Liberty () was a period that saw parliamentary governance, increasing civil rights, and the decline of the Swedish Empire that began with the adoption of the Instrument of Government in 1719 and ended with Gustav ...
, he initiated a campaign to restore a measure of royal autocracy
Autocracy is a form of government in which absolute power is held by the head of state and Head of government, government, known as an autocrat. It includes some forms of monarchy and all forms of dictatorship, while it is contrasted with demo ...
. This was completed by the Union and Security Act of 1789, which swept away most of the powers exercised by the Swedish Riksdag of the estates
Riksdag of the Estates (; informally ) was the name used for the Estates of Sweden when they were assembled. Until its dissolution in 1866, the institution was the highest authority in Sweden next to the King. It was a Diet made up of the Fou ...
during the Age of Liberty, but at the same time it opened up the government for all citizens, thereby breaking the privileges of the nobility.
A believer in enlightened absolutism
Enlightened absolutism, also called enlightened despotism, refers to the conduct and policies of European absolute monarchs during the 18th and early 19th centuries who were influenced by the ideas of the Enlightenment, espousing them to enhanc ...
, Gustav spent considerable public funds on cultural ventures, which were controversial among his critics, as well as military attempts to seize Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of the Kingdom of ...
with Russian aid, then a series of attempts to re-capture the Swedish Baltic dominions lost during the Great Northern War
In the Great Northern War (1700–1721) a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in Northern Europe, Northern, Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the ant ...
through the failed war with Russia. Nonetheless, his successful leadership in the Battle of Svensksund
The Second Battle of Svensksund (; ) was a naval battle fought in the Gulf of Finland outside the present day city of Kotka on 9 and 10 July 1790. The Swedish Empire, Swedish naval forces dealt the Imperial Russia, Russian fleet a devastatin ...
averted a complete military defeat and signified that Swedish military might was to be countenanced after its major defeats earlier in the century.
An admirer of Voltaire
François-Marie Arouet (; 21 November 169430 May 1778), known by his ''Pen name, nom de plume'' Voltaire (, ; ), was a French Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment writer, philosopher (''philosophe''), satirist, and historian. Famous for his wit ...
, Gustav legalised Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
and Jewish
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
presence in Sweden, and enacted wide-ranging reforms aimed at economic liberalism
Economic liberalism is a political and economic ideology that supports a market economy based on individualism and private property in the means of production. Adam Smith is considered one of the primary initial writers on economic liberalism ...
, social reform and the restriction, in many cases, of torture
Torture is the deliberate infliction of severe pain or suffering on a person for reasons including corporal punishment, punishment, forced confession, extracting a confession, interrogational torture, interrogation for information, or intimid ...
and capital punishment
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty and formerly called judicial homicide, is the state-sanctioned killing of a person as punishment for actual or supposed misconduct. The sentence (law), sentence ordering that an offender b ...
. The much-praised Freedom of the Press Act of 1766 was severely curtailed, however, by amendments in 1774 and 1792, effectively extinguishing independent media.
Following the uprising against the French monarchy in 1789, Gustav pursued an alliance of princes aimed at crushing the insurrection and re-instating his French counterpart, King Louis XVI
Louis XVI (Louis-Auguste; ; 23 August 1754 – 21 January 1793) was the last king of France before the fall of the monarchy during the French Revolution. The son of Louis, Dauphin of France (1729–1765), Louis, Dauphin of France (son and heir- ...
, offering Swedish military assistance as well as his leadership. In 1792 he was mortally wounded
:
A mortal wound is an injury that will ultimately lead to a person's death. ''Mortal'' refers to the mortality of a human: whether they are going to live or die."mortal_adjective." Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary. 2018. Oxford University ...
by a gunshot in the lower back during a masquerade ball as part of an aristocratic-parliamentary coup attempt, but managed to assume command and quell the uprising before succumbing to sepsis
Sepsis is a potentially life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs.
This initial stage of sepsis is followed by suppression of the immune system. Common signs and s ...
13 days later, a period during which he received apologies from many of his political enemies. Gustav's immense powers were placed in the hands of a regency
In a monarchy, a regent () is a person appointed to govern a state because the actual monarch is a minor, absent, incapacitated or unable to discharge their powers and duties, or the throne is vacant and a new monarch has not yet been dete ...
under his brother Prince Carl and Gustaf Adolf Reuterholm
Baron Gustaf Adolf Reuterholm (7 July 1756 in Sjundeå, Nyland, Sweden (now Finland) – 27 December 1813 in Schleswig), was a Swedish statesman. He acted as the de facto regent of Sweden during the minor regency of Gustav IV Adolf of Sweden ...
until his son and successor Gustav IV Adolf
Gustav IV Adolf or Gustav IV Adolph (1 November 1778 – 7 February 1837) was King of Sweden from 1792 until he was deposed in a coup in 1809. He was also the last Swedish monarch to be the ruler of Finland.
The occupation of Finland in 180 ...
reached adulthood in 1796. The Gustavian autocracy thus survived until 1809, when his son was ousted in another coup d'état, which definitively established parliament as the dominant political power; this has lasted until the modern day, where the Riksdag
The Riksdag ( , ; also or , ) is the parliament and the parliamentary sovereignty, supreme decision-making body of the Kingdom of Sweden. Since 1971, the Riksdag has been a unicameral parliament with 349 members (), elected proportional rep ...
is Sweden's supreme legislature.
A patron of the arts and benefactor of arts and literature, Gustav founded the Swedish Academy
The Swedish Academy (), founded in 1786 by King Gustav III, is one of the Royal Academies of Sweden. Its 18 members, who are elected for life, comprise the highest Swedish language authority. Outside Scandinavia, it is best known as the body t ...
, created a national costume
Folk costume, traditional dress, traditional attire or folk attire, is clothing of an ethnic group, nation or region, and expresses cultural, religious or national identity. An ethnic group's clothing may also be called ethnic clothing or ethnic ...
and had the Royal Swedish Opera
Royal Swedish Opera () is an opera and ballet company based in Stockholm, Sweden.
Location and environment
The building is located in the centre of Sweden's capital, Stockholm, in the borough of Norrmalm (borough), Norrmalm, on the eastern si ...
and Royal Dramatic Theatre
The Royal Dramatic Theatre (, colloquially ''Dramaten'') is Sweden's national stage for "spoken drama", founded in 1788. Around one thousand shows are put on annually on the theatre's five running stages.
The theatre has been at its present lo ...
built. In 1772 he founded the Royal Order of Vasa
The Royal Order of Vasa () is a Swedish order of chivalry founded on 29 May 1772 by Gustav III, King Gustav III. It is awarded to Swedish citizens for service to state and society especially in the fields of agriculture, mining and commerce.
His ...
to acknowledge and reward those Swedes who had contributed to advances in the fields of agriculture, mining and commerce. He was also a patron of many cultural figures, including Alexander Roslin
Alexander Roslin (; spelled Alexandre in French, ; 15 July 17185 July 1793) was a Swedish painter who worked in Scania, Bayreuth, Paris, Italy, Warsaw and St. Petersburg, primarily for members of aristocratic families. He combined insightful psyc ...
and Carl Michael Bellman, and is often considered one of the most important figures in the history of Swedish art, music and architecture. Gustav III was well liked by the Swedish population and was mourned upon his death.
In 1777, Gustav III was the first formally neutral head of state in the world to recognise the United States during its war for independence from Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-west coast of continental Europe, consisting of the countries England, Scotland, and Wales. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the List of European ...
. Swedish military forces were engaged by the thousands on the side of the colonists, largely through the French expedition force. Through the acquisition of Saint Barthélemy
Saint Barthélemy, officially the Collectivité territoriale de Saint-Barthélemy, also known as St. Barts (English) or St. Barth (French), is an overseas collectivity of France in the Caribbean. The island lies about southeast of the island ...
in 1784, Gustav enabled the restoration, if symbolic, of Swedish overseas colonies
Swedish overseas colonies () consisted of the overseas colonies controlled by Sweden. Sweden possessed overseas colonies from 1638 to 1663, in 1733 and from 1784 to 1878. Sweden possessed five colonies, four of which were short lived. The colon ...
in America, as well as great personal profits from the transatlantic slave trade
The Atlantic slave trade or transatlantic slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of Slavery in Africa, enslaved African people to the Americas. European slave ships regularly used the triangular trade route and its Middle Pass ...
.
Royal title
Gustav III was known in Sweden and abroad by his royal titles, or styles:Early life and education
Gustav was born inStockholm
Stockholm (; ) is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in Sweden by population, most populous city of Sweden, as well as the List of urban areas in the Nordic countries, largest urban area in the Nordic countries. Approximately ...
. He was placed under the tutelage of Hedvig Elisabet Strömfelt
Hedvig Elisabet Strömfelt (née Wrangel; 1687 — 8 March 1751) was a Swedish courtier. She served as överhovmästarinna to two queens of Sweden, Ulrika Eleonora of Sweden and Louisa Ulrika of Prussia, and as Royal Governess to the royal child ...
until the age of five, then educated under the care of two governors who were among the most eminent Swedish statesmen of the day: Carl Gustaf Tessin
Count Carl Gustaf Tessin (5 September 1695 – 7 January 1770) was a Swedish Count and politician and son of architect Nicodemus Tessin the Younger and Hedvig Eleonora Stenbock. He was one of the most brilliant personages of his day, and the mo ...
and Carl Fredrik Scheffer. Nonetheless, he perhaps owed most of what shaped him during his early education to the poet and historian Olof von Dalin
Olof von Dalin (29 August 1708 – 12 August 1763) was a Swedish nobleman, poet, historian and courtier. He was an influential literary figure of the Swedish Enlightenment.
Background
Olof Dalin was born in the parish of Vinberg in Hallan ...
.
State interference with his education as a young child caused significant political disruptions within the royal family. Gustav's parents taught him to despise the governors imposed upon him by the Riksdag, and the atmosphere of intrigue and duplicity in which he grew up made him precociously experienced in the art of dissimulation.
Even his most hostile teachers were amazed by his combination of natural gifts.
Marriage and sons
 Gustav married Princess Sophia Magdalena, daughter of King
Gustav married Princess Sophia Magdalena, daughter of King Frederick V of Denmark
Frederick V (Danish language, Danish and Norwegian language, Norwegian: ''Frederik V''; 31 March 1723 – 14 January 1766) was King of Denmark–Norway, Denmark and Norway and Duke of Schleswig-Holstein from 6 August 1746 until his death in 1766. ...
, by proxy in Christiansborg Palace
Christiansborg Palace (, ) is a palace and government building on the islet of Slotsholmen in central Copenhagen, Denmark. It is the seat of the Danish Parliament (), the Danish Prime Minister's Office, and the Supreme Court of Denmark. Also ...
, Copenhagen, on 1 October 1766 and in person in Stockholm on 4 November 1766. Gustav was first impressed by Sophia Magdalena's beauty, but her silent nature made her a disappointment in court life. The match was not a happy one, owing partly to an incompatibility of temperament, but still more to the interference of Gustav's jealous mother, Queen Louisa Ulrika.
The marriage produced two children: Crown Prince Gustav Adolf (1778–1837), and Prince Carl Gustav, Duke of Småland (1782–1783). For the consummation of the marriage, the king and queen requested actual physical instruction by Count Adolf Munck, reportedly because of anatomical problems of both spouses. There were also rumors that the queen was made pregnant by Munck, who would then be the true father of the heir Prince Gustav Adolf. Gustav's mother supported rumors that he was not the father of his first son and heir. It was rumored at the time that Gustav was homosexual
Homosexuality is romantic attraction, sexual attraction, or sexual behavior between people of the same sex or gender. As a sexual orientation, homosexuality is "an enduring pattern of emotional, romantic, and/or sexual attractions" exc ...
, a possibility asserted by some writers. The close personal relationships that he formed with two of his courtiers, Count Axel von Fersen and Baron Gustav Armfelt, were alluded to in that regard. His sister-in-law Charlotte implied as much in her famous diary.
Professor Erik Lönnroth of the Swedish Academy
The Swedish Academy (), founded in 1786 by King Gustav III, is one of the Royal Academies of Sweden. Its 18 members, who are elected for life, comprise the highest Swedish language authority. Outside Scandinavia, it is best known as the body t ...
, who described the assistance provided by Munck, asserted that there is no factual basis for the assumption that Gustav III was homosexual. When his second son was born, there was no doubt as to his legitimacy, and the boy was strong and healthy. King Gustav was especially fond of him and suffered obvious and severe mental and physical reactions to the baby's illness and death. The spring of 1783 has been considered a turning point in the king's personality. After his controversial mother's death in 1782, he found consolation in the birth of the Duke of Småland, but this was followed by severe grief when the child died the following year.
Politics of an heir apparent
 Gustav first intervened actively in politics during the December Crisis (1768), when he compelled the dominant
Gustav first intervened actively in politics during the December Crisis (1768), when he compelled the dominant Cap
A cap is a flat headgear, usually with a visor. Caps have crowns that fit very close to the head. They made their first appearance as early as 3200 BC. The origin of the word "cap" comes from the Old French word "chapeau" which means "head co ...
faction, which mainly represented the interests of the peasantry and clergy, to summon an extraordinary diet
Diet may refer to:
Food
* Diet (nutrition), the sum of the food consumed by an organism or group
* Dieting, the deliberate selection of food to control body weight or nutrient intake
** Diet food, foods that aid in creating a diet for weight loss ...
from which he hoped for the reform of the constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organization or other type of entity, and commonly determines how that entity is to be governed.
When these pri ...
in a way that would increase the power of the crown. But the victorious Hat party, which mainly represented the interests of the aristocracy and military establishment, refused to redeem the pledges that they had given before the previous elections. "That we should have lost the constitutional battle does not distress us so much", wrote Gustav, in the bitterness of his heart; "but what does dismay me is to see my poor nation so sunk in corruption as to place its own felicity in absolute anarchy
Anarchy is a form of society without rulers. As a type of stateless society, it is commonly contrasted with states, which are centralized polities that claim a monopoly on violence over a permanent territory. Beyond a lack of government, it can ...
."
Gustav found greater success abroad. From 4 February to 25 March 1771, Gustav was in Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
, where he carried both the court and the city by storm. The poets and the philosophers paid him enthusiastic homage, and distinguished women testified to his superlative merits. With many of them he maintained a lifelong correspondence. His visit to the French capital was, however, no mere pleasure trip; it was also a political mission. Confidential agents from the Swedish court had already prepared the way for him, and the Duke of Choiseul, the retired Chief Minister, resolved to discuss with him the best method of bringing about a revolution in France's ally, Sweden. Before he departed, the French government undertook to pay the outstanding subsidies to Sweden unconditionally, at the rate of one and a half million livres annually. Count de Vergennes, one of the most prominent French diplomats, was transferred from Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
to Stockholm
Stockholm (; ) is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in Sweden by population, most populous city of Sweden, as well as the List of urban areas in the Nordic countries, largest urban area in the Nordic countries. Approximately ...
.
On his way home, Gustav paid a short visit to his uncle, Frederick the Great
Frederick II (; 24 January 171217 August 1786) was the monarch of Prussia from 1740 until his death in 1786. He was the last Hohenzollern monarch titled ''King in Prussia'', declaring himself ''King of Prussia'' after annexing Royal Prussia ...
, at Potsdam
Potsdam () is the capital and largest city of the Germany, German States of Germany, state of Brandenburg. It is part of the Berlin/Brandenburg Metropolitan Region. Potsdam sits on the Havel, River Havel, a tributary of the Elbe, downstream of B ...
. Frederick bluntly informed his nephew that, in concert with Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
and Denmark
Denmark is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe. It is the metropole and most populous constituent of the Kingdom of Denmark,, . also known as the Danish Realm, a constitutionally unitary state that includes the Autonomous a ...
, he had guaranteed the integrity of the existing Swedish constitution; he advised the young monarch to play the part of mediator and abstain from violence.
Reign and coup d'état

 At the time of his accession, the Swedish
At the time of his accession, the Swedish Riksdag
The Riksdag ( , ; also or , ) is the parliament and the parliamentary sovereignty, supreme decision-making body of the Kingdom of Sweden. Since 1971, the Riksdag has been a unicameral parliament with 349 members (), elected proportional rep ...
held more power than the monarchy, but the Riksdag was bitterly divided between rival parties, the Hats and Caps. On his return to Sweden, Gustav III tried unsuccessfully to mediate between the two groups. On 21 June 1771, he opened his first Riksdag with a speech that aroused powerful emotions. It was the first time in more than a century that a Swedish king had addressed a Swedish Riksdag in its native tongue. He stressed the need for all parties to sacrifice their animosities for the common good, and volunteered, as "the first citizen of a free people," to be the mediator between the contending factions. A composition committee was actually formed, but it proved illusory from the first: the patriotism
Patriotism is the feeling of love, devotion, and a sense of attachment to one's country or state. This attachment can be a combination of different feelings for things such as the language of one's homeland, and its ethnic, cultural, politic ...
of neither faction was sufficient for the smallest act of self-denial. The subsequent attempts of the dominant Caps to reduce him to a ''roi fainéant'' (a powerless king), encouraged him to consider a ''coup d'état''.
Under the sway of the Cap faction, Sweden seemed in danger of falling prey to the political ambitions of Russia. It appeared on the point of being absorbed into the Northern Accord sought by the Russian vice-chancellor, Count Nikita Panin
Count Nikita Ivanovich Panin (; ) was an influential Russian statesman and political mentor to Catherine the Great for the first 18 years of her reign (1762–1780). In that role, he advocated the Northern Alliance, closer ties with Frederick the ...
. It seemed to many that only a swift and sudden coup d'état could preserve Sweden's independence.
 Gustav III was approached by
Gustav III was approached by Jacob Magnus Sprengtporten
Baron Jacob Magnus Sprengtporten (10 November 1727 – 2 April 1786) was a Swedish-Finnish army officer and politician, and half-brother of Georg Magnus Sprengtporten. He is most famous as one of the leaders of the Revolution of 1772, the ''co ...
, a Finnish nobleman, who had incurred the enmity of the Caps, with the prospect of a revolution. He undertook to seize the fortress of Sveaborg in Finland by a ''coup de main
A ''coup de main'' (, : , ) is a swift attack that relies on speed and surprise to accomplish its objectives in a single blow.
Definition
The United States Department of Defense defines it as
"An offensive operation that capitalizes on surprise ...
''. Once Finland was secured, he intended to embark for Sweden, join up with the king and his friends near Stockholm
Stockholm (; ) is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in Sweden by population, most populous city of Sweden, as well as the List of urban areas in the Nordic countries, largest urban area in the Nordic countries. Approximately ...
, and force the estates to accept a new constitution dictated by the king.
At this juncture, the plotters were reinforced by Johan Christopher Toll
Count Johan Christopher Toll (1 February 1743 – 21 May 1817) was a Swedish statesman and soldier.
Early life
He was born in Mölleröd, Scania (now part of Hässleholm Municipality, Skåne County). Toll came of from an old family of Dutc ...
, another victim of Cap oppression. Toll proposed to raise a second revolt in the province of Scania
Scania ( ), also known by its native name of Skåne (), is the southernmost of the historical provinces of Sweden, provinces () of Sweden. Located in the south tip of the geographical region of Götaland, the province is roughly conterminous w ...
, and to secure the southern fortress of Kristianstad
Kristianstad ( , ) is a Urban areas in Sweden, city and the seat of Kristianstad Municipality, Scania County, Sweden with 41,198 inhabitants in 2023. Since the 1990s, the city has gone from being a garrison town to a developed commercial city, ...
. After some debate, it was agreed that Kristianstad should openly declare against the government a few days after the Finnish revolt had begun. Duke Charles (Karl), the eldest of the king's brothers, would thereupon be forced to mobilize the garrisons of all the southern fortresses hastily, ostensibly to crush the revolt at Kristianstad, but on arriving in front of the fortress, he was to make common cause with the rebels and march upon the capital from the south while Sprengtporten attacked it simultaneously from the east.
The entire revolutionary enterprise was underwritten with loans procured from the French financier Nicolas Beaujon, arranged by the Swedish ambassador to France, Count Creutz.
On 6 August 1772, Toll succeeded in winning the fortress of Kristianstad by sheer bluff, and on 16 August, Sprengtporten succeeded in surprising Sveaborg, but contrary winds prevented him from crossing to Stockholm. Events soon occurred there that made his presence unnecessary in any case.
On 16 August, the Cap leader, Ture Rudbeck, arrived at Stockholm with news of the insurrection in the south, and Gustav found himself isolated in the midst of enemies. Sprengtporten lay weather-bound in Finland, Toll was away, the Hat leaders were in hiding. Gustav thereupon resolved to strike the decisive blow without waiting for Sprengtporten's arrival.
He acted promptly. On the evening of 18 August, all the officers whom he thought he could trust received secret instructions to assemble in the great square facing the arsenal on the following morning. At ten o'clock on 19 August, Gustav mounted his horse and rode to the arsenal. On the way, his adherents joined him in little groups, as if by accident, so that by the time he reached his destination he had about two hundred officers in his suite.
After parade he reconducted them to the guard-room in the north western wing of the palace where the Guard of Honour had its headquarters and unfolded his plans to them. He told the assembled officers,
:"If you follow me, just like your ancestors followed Gustav Vasa
Gustav Eriksson Vasa (12 May 1496 – 29 September 1560), also known as Gustav I, was King of Sweden from 1523 until his death in 1560. He was previously self-recognised Protector of the Realm (''Reichsverweser#Sweden, Riksföreståndare'') fr ...
and Gustavus Adolphus
Gustavus Adolphus (9 December N.S 19 December">Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="/nowiki>Old Style and New Style dates">N.S 19 December15946 November Old Style and New Style dates">N.S 16 November] 1632), also known in English as ...
, then I will risk my life and blood for you and the salvation of the fatherland!"
A young ensign then spoke up:
:"We are willing to sacrifice both blood and life in Your Majesty's service!"
Gustav then dictated a new oath of allegiance
An oath of allegiance is an oath whereby a subject or citizen acknowledges a duty of allegiance and swears loyalty to a monarch or a country. In modern republics, oaths are sworn to the country in general, or to the country's constitution. For ...
, and everyone signed it without hesitation. It absolved them from their allegiance to the estates, and bound them solely to obey "their lawful king, Gustav III".
Meanwhile, the Privy Council and its president, Rudbeck, had been arrested and the fleet secured. Then Gustav made a tour of the city and was everywhere received by enthusiastic crowds, who hailed him as a deliverer. A song was composed by Carl Michael Bellman called the " Toast to King Gustav!"
On the evening of 20 August, heralds roamed the streets proclaiming that the estates were to meet at the palace on the following day; every deputy absenting himself would be regarded as the enemy of his country and his king. On 21 August, the king appeared in full regalia. Taking his seat on the throne, he delivered his famous philippic
A philippic () is a fiery, damning speech, or tirade, delivered to condemn a particular political actor. The term is most famously associated with three noted orators of the ancient world: Demosthenes of ancient Athens, Cato the Elder and Cic ...
, viewed as one of the masterpieces of Swedish oratory, in which he reproached the estates for their unpatriotic venality and license in the past.
Part of the speech by Gustav III to the Estates:...has given birth to hatred, hatred to revenge, revenge to persecution, persecution to new revolutions which finally have passed into a period of disease, which has wounded and degraded the whole nation. Ambition and lust for glory on the part of a few people have damaged the realm, and blood has been shed by both parties, and the result of this has been the suffering of the people. The establishment of their own power base has been the sole goal of those ruling, often at the cost of other citizens, and always at the cost of the nation. In times when the law was clear, the law was distorted, and when that was not possible, it was broken. Nothing has been sacred to a populace bent on hatred and revenge, and lunacy has finally reached so far, that it has been assumed that members of parliament are above the law, their not having any other guidance than their own consciences. By this Freedom, the most noble of human rights have been transformed by an unbearable aristocratic despotism in the hands of the ruling party, which in itself has been subdued by few...A new constitution, the
Instrument of Government
The Instrument of Government was the first constitution of the Commonwealth of England, Scotland and Ireland and was also the first codified and written constitution in England. It was drafted by Major-General John Lambert in 1653.
Anteced ...
, was read to the estates and unanimously accepted by them. The diet was then dissolved.
Between constitutionalism and absolutism
Gustav worked towards reform in the same direction as other contemporary sovereigns of theAge of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment (also the Age of Reason and the Enlightenment) was a Europe, European Intellect, intellectual and Philosophy, philosophical movement active from the late 17th to early 19th century. Chiefly valuing knowledge gained th ...
. Criminal justice became more lenient, the death penalty
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty and formerly called judicial homicide, is the state-sanctioned killing of a person as punishment for actual or supposed misconduct. The sentence ordering that an offender be punished in s ...
was restricted to a relatively short list of crimes (including murder), and torture was abolished in order to gain confessions, although the "strict death penalty", with torture-like corporal punishment
A corporal punishment or a physical punishment is a punishment which is intended to cause physical pain to a person. When it is inflicted on Minor (law), minors, especially in home and school settings, its methods may include spanking or Padd ...
preceding the execution, was maintained.
Gustav took an active part in every department of business, but relied heavily on extra-official counsellors of his own choosing rather than upon the Privy Council of Sweden
The Council of the Realm, or simply The Council ( or : sometimes in ), was a cabinet of medieval origin, consisting of magnates () which advised, and at times co-ruled with, the King of Sweden.
The 1634 Instrument of Government, Sweden's fir ...
. The effort to remedy the widespread corruption that had flourished under the Hats and Caps engaged a considerable share of his time and he even found it necessary to put on trial the entire Göta Hovrätt, the superior court of justice, in Jönköping
Jönköping (, ) is a Urban areas in Sweden, city in southern Sweden with 112,766 inhabitants (2022). Jönköping is situated on the southern shore of Sweden's second largest lake, Vättern, in the province of Småland.
The city is the seat o ...
.
Measures were also taken to reform the administration and judicial procedures. In 1774, an ordinance was proclaimed providing for the liberty of the press, though "within certain limits". The national defences were raised to a "Great Power" scale, and the navy was so enlarged as to become one of the most formidable in Europe. The dilapidated finances were set in good order by the " currency realization ordinance" of 1776.
Gustav also introduced new national economic policies. In 1775, free trade in grain was promoted and several oppressive export tolls were abolished. The poor law
In English and British history, poor relief refers to government and ecclesiastical action to relieve poverty. Over the centuries, various authorities have needed to decide whose poverty deserves relief and also who should bear the cost of hel ...
was amended, and limited religious liberty
Freedom of religion or religious liberty, also known as freedom of religion or belief (FoRB), is a principle that supports the freedom of an individual or community, in public or private, to manifest religion or belief in teaching, practice ...
was proclaimed for both Roman Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institut ...
s and Jew
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, religion, and community are highly inte ...
s. Gustav even designed and popularized a Swedish national costume, which was in general use among the upper classes from 1778 until his death (and it is still worn by the ladies of the court on state occasions). The king's one great economic blunder was his attempt in 1775 to make the sale of alcoholic spirits a government monopoly, through the establishment of a network of crown distilleries. These proved to be unprofitable, and moreover the monopoly was hugely unpopular among the common people, and so Gustav was forced to abolish it in 1786.
Gustav's foreign policy, in contrast, was at first both restrained and cautious. Thus, when the king summoned the estates to assemble at Stockholm on 3 September 1778, he could give a highly positive account of his six years' stewardship. The Riksdag was quite obsequious
In modern English, sycophant denotes an "insincere flatterer" and is used to refer to someone practising sycophancy (i.e., insincere flattery to gain advantage).
The word has its origin in the legal system of Classical Athens, where it had a d ...
towards the king. "There was no room for a single question during the whole session."
Short as the session was, it was long enough for the deputies to realize that their political supremacy was over. They had changed places with the king. He was now indeed their sovereign lord. For all his gentleness, he guarded the royal prerogative fiercely and plainly showed that he would continue to do so.
Even those who were prepared to acquiesce in the change by no means liked it. If the Riksdag of 1778 had been docile, the Riksdag of 1786 was mutinous. The consequence was that nearly all the royal propositions were either rejected outright or so modified that Gustav himself withdrew them.
Earlier in foreign affairs, however, and privately, Gustav had shown considerable interest in the American Revolution
The American Revolution (1765–1783) was a colonial rebellion and war of independence in which the Thirteen Colonies broke from British America, British rule to form the United States of America. The revolution culminated in the American ...
and had this to say about it in October 1776:It is such an interesting drama to see a nation create itself, that I – if I now had not been who I am – would go to America to follow up close every phase in the emergence of this new republic. – This perhaps is America's century. The new republic, which hardly has a population put together better than Rome had to begin with, may perhaps take advantage of Europe some day, in the same manner as Europe has taken advantage of America for two centuries. No matter what, I cannot help but admire their courage and enthusiastically appreciate their daring.
Increased royal power
The Riksdag of 1786 marks a turning-point in Gustav's history. Henceforth he showed a growing determination to rule without a parliament, a cautious and gradual passage from semi-constitutionalism to semi-absolutism. At the same time, his foreign policy became more adventurous. At first he sought to gain Russian support to acquire Norway from Denmark. WhenCatherine the Great
Catherine II. (born Princess Sophie of Anhalt-Zerbst; 2 May 172917 November 1796), most commonly known as Catherine the Great, was the reigning empress of Russia from 1762 to 1796. She came to power after overthrowing her husband, Peter I ...
refused to abandon her ally Denmark, Gustav declared war on Russia in June 1788, while it was deeply engaged in a war with the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
to the south. In embarking on a war of aggression without the consent of the estates, Gustav violated his own constitution of 1772, which led to a serious mutiny, the Anjala Conspiracy
The Anjala conspiracy (, ) of 1788 was a scheme by disgruntled Swedish officers to end Gustav III's Russian War of 1788–1790. Declaring Finland an independent state was not a part of the original plot, but one of the conspirators Johan Ande ...
, among his aristocratic officers in Finland. Denmark declared war in support of its Russian ally, but was soon persuaded to sign a ceasefire through British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
and Prussian
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, the House of Hohenzoll ...
diplomacy.
Returning to Sweden, Gustav aroused popular indignation against the mutinous aristocratic officers. Ultimately, he quelled their rebellion and arrested its leaders. Capitalizing on the powerful anti-aristocratic passions thus aroused, Gustav summoned a Riksdag early in 1789, at which he put through an Act of Union and Security on 17 February 1789 with the backing of the three lower estates. This reinforced monarchical authority significantly, although the estates retained the power of the purse
The power of the purse is the ability of one group to control the actions of another group by withholding funding, or putting stipulations on the use of funds. The power of the purse can be used positively (e.g. awarding extra funding to programs ...
. In return, Gustav abolished most of the old privileges of the nobility.
Russo-Swedish War (1788–1790)
Throughout 1789 and 1790, Gustav conducted a war with Russia known as the Russo-Swedish War of 1788–1790. At first, the venture seemed headed for disaster before the Swedes successfully broke a blockade by the Russian fleet at theBattle of Svensksund
The Second Battle of Svensksund (; ) was a naval battle fought in the Gulf of Finland outside the present day city of Kotka on 9 and 10 July 1790. The Swedish Empire, Swedish naval forces dealt the Imperial Russia, Russian fleet a devastatin ...
on 9 July 1790. This is regarded as the greatest naval victory ever achieved by the Swedish Navy
The Swedish Navy () is the maritime service branch of the Swedish Armed Forces. It is composed of surface and submarine naval units – the Fleet (), formally sometimes referred to as the Royal Navy () – as well as marine units, the Amph ...
. The Russians lost one-third of their fleet and 7,000 men. A month later, on 14 August 1790, a peace treaty was signed between Russia and Sweden: the Treaty of Värälä. Only eight months before, Catherine had declared that "the odious and revolting aggression" of the king of Sweden would be "forgiven" only if he "testified his repentance" by agreeing to a peace granting a general and unlimited amnesty to all his rebels and consenting to a guarantee by the Swedish Riksdag for the observance of peace in the future ("as it would be imprudent to confide in his good faith alone"). The Treaty of Värälä spared Sweden from any such humiliating concession, and in October 1791, Gustav concluded an eight years' defensive alliance with the empress, who thereby bound herself to pay her new ally an annual subsidy of 300,000 rubles.
Gustav next aimed at forming a league of princes against the revolutionary government in France, and subordinated every other consideration to this goal. His profound knowledge of popular assemblies enabled him, alone among contemporary sovereigns, to gauge the scope of the French Revolution accurately from the first. He was hampered, however, by financial restrictions and lack of support from the other European powers. Then, after the brief Diet of Gävle
Gävle ( ; ) is a Urban areas in Sweden, city in Sweden, the seat of Gävle Municipality and the capital of Gävleborg County. It had 79,004 inhabitants in 2020, which makes it the List of cities in Sweden, 13th-most-populated city in Sweden. I ...
on 22 January – 24 February 1792, he fell victim to a widespread political conspiracy among his aristocratic enemies.
Assassination
Gustav III's war against Russia and his implementation of the Union and Security Act of 1789 helped increase hatred of the king amongst the nobility, which had been growing ever since the coup d'état of 1772. In the winter of 1791–92, members of the nobility began a conspiracy to assassinate the king and reform the constitution. The conspirators includedJacob Johan Anckarström
Jacob Johan Anckarström (11 May 1762 – 27 April 1792) was a Swedish people, Swedish military officer who is known as the assassination, assassin of King Gustav III of Sweden. He was convicted and executed for regicide.
Life
He was the son of ...
, Adolph Ribbing, Claes Fredrik Horn, Carl Pontus Lilliehorn and Carl Fredrik Pechlin. Anckarström was chosen to carry out the murder with pistols and knives, but there has also been evidence suggesting that Ribbing was the one who actually shot Gustav.
The assassination of the king was enacted at a masked ball at the Royal Opera House
The Royal Opera House (ROH) is a theatre in Covent Garden, central London. The building is often referred to as simply Covent Garden, after a previous use of the site. The ROH is the main home of The Royal Opera, The Royal Ballet, and the Orch ...
in Stockholm at midnight on 16 March 1792. Gustav had arrived earlier that evening to enjoy a dinner in the company of friends. During dinner, he received an anonymous letter that described a threat to his life (written by the colonel of the Life Guards Carl Pontus Lilliehorn), but, as the king had received numerous threatening letters in the past, he chose to ignore it. The letter was written in French, and in translation it stated:
To dare any possible assassins, the King went out into an open box facing the opera stage. And after roughly ten minutes he said "this would have been an opportunity to shoot. Come, let us go down. The ball seems to be merry and bright." The King with Baron Hans Henrik von Essen by his right arm went around the theatre once and then into the foyer where they met Captain Carl Fredrik Pollet.
The King, von Essen and Pollet continued through a corridor leading from the foyer towards the opera stage where the dancing took place. On the stage several masked men – some witnesses talked of 20 or 30 men – made it impossible for the king to proceed. Due to the crowd, Pollet receded behind the King, who bent backwards to talk to Pollet.''High Court protocols, 1792''
Anckarström stood with Ribbing next to him at the entrance to the corridor holding a knife in his left hand and carrying one pistol in his left inner pocket and another pistol in his right back pocket. They edged themselves behind the King, Anckarström took out the pistol from his left inner pocket, then either he or Ribbing pulled the trigger with the gun in Anckarström's hand. Because of the King turning backwards the shot went in at an angle from the third lumbar vertebra towards the hip region.
The King twitched and said "aee" without falling. Anckarström then lost courage, dropped the pistol and knife and shouted fire. People from the King's lifeguard stood some meters away. When they reached the King, they heard him say in French "" (Ouch, I am wounded).
The king was carried back to his quarters, and the exits of the Opera were sealed. Anckarström was arrested the following morning and immediately confessed to the murder, although he denied a conspiracy until informed that Horn and Ribbing had also been arrested and had confessed in full.
The king had not been shot dead; he was alive and continued to function as head of state. The coup was a failure in the short run. However, the wound became infected, and on 29 March 1792, the king finally died with these last words
Last words are the final utterances before death. The meaning is sometimes expanded to somewhat earlier utterances.
Last words of famous or infamous people are sometimes recorded (although not always accurately), which then became a historical an ...
:
:''Jag känner mig sömnig, några ögonblicks vila skulle göra mig gott'' ("I feel sleepy, a few moments' rest would do me good")
Gustav's gunshot wound was not initially considered life-threatening; reexamined evidence allows that the sudden serious infection that killed him almost immediately, 13 days into his convalescence, may have been caused chemically by attending surgeon who was his known adversary.
Ulrica Arfvidsson, the famous medium
Medium may refer to:
Aircraft
*Medium bomber, a class of warplane
* Tecma Medium, a French hang glider design Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* ''The Medium'' (1921 film), a German silent film
* ''The Medium'' (1951 film), a film vers ...
of the Gustavian era, had told him something that could be interpreted as a prediction of his assassination in 1786, when he visited her anonymously – a coincidence – but she was known to have a large network of informers all over town to help her with her predictions, and she was in fact interrogated about the murder.
Funeral
 Gustav's funeral took place on 14 May 1792. It was held in
Gustav's funeral took place on 14 May 1792. It was held in Riddarholmskyrkan
Riddarholmen Church () is the Church (building), church of the former medieval Greyfriars Monastery, Stockholm, Greyfriars Monastery in Stockholm, Sweden. The church serves as the final resting place of most Monarchs of Sweden, Swedish monarchs.
...
, which had been decorated in a grand manner.
For the funeral, Joseph Martin Kraus composed a funeral march to a text of Carl Gustaf af Leopold that was performed by the solo singers Caroline Müller, Franziska Stading, Kristofer Kristian Karsten and Carl Stenborg
Carl Stenborg (8 September 1752 – 1 August 1813) was a Swedish opera singer, composer and theatre director. He belonged to the pioneer generation of the Royal Swedish Opera and was regarded as one of the leading opera singers of the Gustavian e ...
, choir and orchestra from the Royal Swedish Opera
Royal Swedish Opera () is an opera and ballet company based in Stockholm, Sweden.
Location and environment
The building is located in the centre of Sweden's capital, Stockholm, in the borough of Norrmalm (borough), Norrmalm, on the eastern si ...
under the direction of the composer himself.
Contributions to culture
Although he may be charged with many foibles and extravagances, Gustav III is regarded one of the leading sovereigns of the 18th century for patronage of the arts. He was very fond of the performing and visual arts, as well as literature. Gustav was also active as a playwright. He is largely credited with creating the ''Royal Theatre'' ''(Kungliga Teatern)'', where his own historical dramas were performed, and he promoted the careers of many native singers and actors, among them the dramatic stars Fredrique Löwen and Lars Hjortsberg and the operatic starsElisabeth Olin
Elisabeth Olin née ''Lillström'' (December 1740 – 26 March 1828) was a Swedish opera singer and a music composer. She performed the leading female role in the inauguration performance of the Royal Swedish Opera in 1773, and is referred to ...
and Christoffer Christian Karsten, by letting them perform in his plays or in his commissioned operas, respectively. In 1773 he founded the Royal Swedish Opera
Royal Swedish Opera () is an opera and ballet company based in Stockholm, Sweden.
Location and environment
The building is located in the centre of Sweden's capital, Stockholm, in the borough of Norrmalm (borough), Norrmalm, on the eastern si ...
and the Royal Swedish Ballet
The Royal Swedish Ballet is one of the oldest ballet companies in Europe. Based in Stockholm, Sweden, Gustav III of Sweden, King Gustav III founded the ballet in 1773 as a part of his national cultural project in response to the French and Italian ...
under the umbrella of his ''Royal Theatre''. A new opera house was built in 1775 and inaugurated in 1782, connected to the Stockholm Palace
Stockholm Palace, or the Royal Palace, ( or ) is the official residence and major royal palace of the Swedish monarch (King Carl XVI Gustaf and Queen Silvia use Drottningholm Palace as their usual residence). Stockholm Palace is in Stadsholm ...
by the '' Norrbro'' bridge. Until 1788, spoken drama was also performed in the opera house. Gustav then founded a separate entity for spoken drama, the Royal Dramatic Theatre
The Royal Dramatic Theatre (, colloquially ''Dramaten'') is Sweden's national stage for "spoken drama", founded in 1788. Around one thousand shows are put on annually on the theatre's five running stages.
The theatre has been at its present lo ...
, with a new building behind the Royal Swedish Opera
Royal Swedish Opera () is an opera and ballet company based in Stockholm, Sweden.
Location and environment
The building is located in the centre of Sweden's capital, Stockholm, in the borough of Norrmalm (borough), Norrmalm, on the eastern si ...
house.
He became a Freemason
Freemasonry (sometimes spelled Free-Masonry) consists of fraternal groups that trace their origins to the medieval guilds of stonemasons. Freemasonry is the oldest secular fraternity in the world and among the oldest still-existing organizati ...
in 1780, and introduced the Rite of Strict Observance
The Rite of Strict Observance was a Rite of Freemasonry, a series of progressive degrees that were conferred by the Order of Strict Observance, a Masonic body of the 18th century.
History
Baron Karl Gotthelf von Hund (1722–1776) introduced ...
into Sweden. That year, he named his brother, the Duke of Södermanland
Södermanland ( ), locally Sörmland, sometimes referred to under its Latinisation of names, Latinized form Sudermannia or Sudermania, is a Provinces of Sweden, historical province (or ) on the south eastern coast of Sweden. It borders Österg� ...
(later Charles XIII
Charles XIII or Carl XIII (; 7 October 1748 – 5 February 1818) was King of Sweden from 1809 and King of Norway from 1814 to his death. He was the second son (and younger brother to King Gustav III) of King Adolf Frederick of Sweden and Louisa ...
), to the office of Grand Master for the Grand Lodge of Sweden. The Grand Lodge conferred upon him the title "Vicarius Salomonis" (Vicar of Solomon).
Opera
Notable opera composers under Gustav's reign were three artists originally from Germany:Johann Gottlieb Naumann
Johann Gottlieb Naumann (17 April 1741 – 23 October 1801) was a German composer, conductor, and Kapellmeister.
Life
Johann Gottlieb Naumann was born in Blasewitz and received his musical training from the teachers at his town school, where h ...
, Georg Joseph Vogler
Georg Joseph Vogler, also known as Abbé Vogler (15 June 1749 – 6 May 1814), was a German composer, organist, teacher and theorist. In a long and colorful career extending over many more nations and decades than was usual at the time, Vogler e ...
and Joseph Martin Kraus. All of them succeeded in adapting their musical origins to Swedish national dramatic style, a process sometimes overseen by the king (notably in the layout of the libretto
A libretto (From the Italian word , ) is the text used in, or intended for, an extended musical work such as an opera, operetta, masque, oratorio, cantata or Musical theatre, musical. The term ''libretto'' is also sometimes used to refer to th ...
for the opera ''Gustav Wasa'' from 1786).
It was in the foyer of the opera house that King Gustav III was assassinated. This incident became the basis of an opera libretto by Eugène Scribe
Augustin Eugène Scribe (; 24 December 179120 February 1861) was a French dramatist and librettist. He is known for writing "well-made plays" ("pièces bien faites"), a mainstay of popular theatre for over 100 years, and as the librettist of man ...
set by Daniel Auber
Daniel-François-Esprit Auber (; 29 January 178212 May 1871) was a French composer and director of the Paris Conservatoire.
Born into an artistic family, Auber was at first an amateur composer before he took up writing operas professionally whe ...
in 1833 under the title '' Gustave III,'' by Saverio Mercadante
Giuseppe Saverio Raffaele Mercadante (baptised 17 September 179517 December 1870) was an Italian composer, particularly of operas. While Mercadante may not have retained the international celebrity of Vincenzo Bellini, Gaetano Donizetti or Gioa ...
in 1843 as ''Il Reggente'', and by Giuseppe Verdi
Giuseppe Fortunino Francesco Verdi ( ; ; 9 or 10 October 1813 – 27 January 1901) was an Italian composer best known for List of compositions by Giuseppe Verdi, his operas. He was born near Busseto, a small town in the province of Parma ...
in 1859 as '' Un ballo in maschera'' (A Masked Ball), with the specifics changed under the pressure of censorship.
It is widely agreed that the contribution and dedication of Gustav III to the performing arts in Sweden, notably the building of the theatre houses and the founding of a national theatre company, has been crucial to the Swedish culture. The era of opera during his time is referred to today as the ''Gustavian Opera''.
Balloon
Following Gustav III's visit toLyon
Lyon (Franco-Provençal: ''Liyon'') is a city in France. It is located at the confluence of the rivers Rhône and Saône, to the northwest of the French Alps, southeast of Paris, north of Marseille, southwest of Geneva, Switzerland, north ...
, the aeronautics pioneers Montgolfier brothers
The Montgolfier brothers – Joseph-Michel Montgolfier (; 26 August 1740 – 26 June 1810) and Jacques-Étienne Montgolfier (; 6 January 1745 – 2 August 1799) – were aviation pioneers, balloonists and paper manufacturers from the Communes o ...
in June 1784 launched a new hot air balloon called the '' Gustave'' in honor of the Swedish King, in which the first ever female aeronaut, singer Élisabeth Thible, took to the air.
Saint-Barthélemy and Gustavia
It was under King Gustav III that Sweden gained the smallCaribbean
The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America ...
island of Saint-Barthélemy from France in 1785 (in exchange for French trading rights in Gothenburg
Gothenburg ( ; ) is the List of urban areas in Sweden by population, second-largest city in Sweden, after the capital Stockholm, and the fifth-largest in the Nordic countries. Situated by the Kattegat on the west coast of Sweden, it is the gub ...
).
The island's capital still bears the name Gustavia in honour of Gustav III. Though it was sold back to France in 1878, many streets and locations there still carry Swedish names, including the airport
An airport is an aerodrome with extended facilities, mostly for commercial Aviation, air transport. They usually consist of a landing area, which comprises an aerially accessible open space including at least one operationally active surf ...
which was named after him. Also, the Swedish national arms, the three crowns
Three Crowns () is the national emblem of Sweden, present in the coat of arms of Sweden, and composed of three yellow or Gilding, gilded coronets ordered two above and one below, placed on a blue background. Similar designs are found on a numbe ...
, appear in the island's coat of arms along with insignia of the island's two other previous owners: three fleurs-de-lis representing France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
and a Maltese cross
The Maltese cross is a cross symbol, consisting of four " V" or arrowhead shaped concave quadrilaterals converging at a central vertex at right angles, two tips pointing outward symmetrically.
It is a heraldic cross variant which develope ...
representing the Knights of Saint John.
Plan to colonise Australia 1786–1787
While the British were preparing to establish a colony inBotany Bay
Botany Bay (Dharawal language, Dharawal: ''Kamay'') is an open oceanic embayment, located in Sydney, New South Wales, Australia, south of the Sydney central business district. Its source is the confluence of the Georges River at Taren Point a ...
, the Government of Gustav III agreed to sponsor William Bolts
William Bolts (7 February 1739 – 1808) was a Dutch-born British merchant active in India. He began his career as an employee of the East India Company, and subsequently became an independent merchant. He is best known today for his 1772 book, ' ...
' proposal for an equivalent venture in Nuyts Land (part of the south-western coast of Australia). The war with Russia caused this venture to be abandoned."W. Bolts' forslag till kolonisation af en ö….1786–1790", Rigsarkivet, Handel och Sjöfart, 193; cited in Åke W. Essén, "Wilhelm Bolts und die schwedischen Kolonisierungspläne in Asien", ''Bijdragen voor vaderlandsche Geschiedenis en Oudheidkunde,'' Bd.7 (6), 1935, pp. 83–101. See also Clas Theodor Odhner, ''Sveriges Politiska Historia under Konung Gustaf III:s Regering,'' Stockholm, Norstedt, 1885–1905, Del. 2, pp. 492–8; cited in Carl Sprinchorn, "Sjuttonhundratalets och förslag till Svensk Kolonisation i främmande världsdelar", ''Historisk Tidskrift'', årg.43, 1923, pp. 153–4; and Robert J. King, "Gustaf III’s Australian Colony", ''The Great Circle,'' vol. 27, no. 2, 2005, pp. 3–20
Ancestors
See also
* Absolute Monarchy in Sweden * '' Anno 1790'' (Swedish 2011 television series set in Stockholm in 1790–1792) *Culture of Sweden
The Culture of Sweden is characterised by its art, music, dance, literature, traditions, religious practices and more. It is similar to but distinct from the cultures of neighboring countries. Sweden's modern history has a well-established tradi ...
* The Funeral of Gustav III
* Gustav III of Sweden's coffee experiment
Gustav III of Sweden's coffee experiment was a purported twin study ordered by the king to study the health effects of coffee. The authenticity of the event has been questioned. The primitive medical study, supposedly conducted in the second h ...
* Gustavian era
* Gustavians
* Gustavian style
* History of Sweden
The history of Sweden can be traced back to the melting of the Northern polar ice cap. From as early as 12000 BC, humans have inhabited this area. Throughout the Stone Age, between 8000 BC and 6000 BC, early inhabitants used sto ...
* List of coups d'état and coup attempts by country
* Marstrand Free Port
The Marstrand Free Port () was a largely autonomous island territory of Sweden, during the Gustavian Era of the late 18th century, which effectively functioned as a merchant republic. As a free port designed with inspiration from the Italian ' ...
* Swedish slave trade
* Swedish-Algerian War (1791–1792)
Notes
References
References
* * * * * ch 37 pp 203–19 * * * *External links
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Gustav III 1746 births 1792 deaths 18th-century Swedish monarchs 18th-century murdered monarchs * Assassinated Swedish politicians Burials at Riddarholmen Church Crown princes of Sweden Deaths by firearm in Sweden Deaths from sepsis Early modern history of Sweden Honorary members of the Saint Petersburg Academy of Sciences House of Holstein-Gottorp Royalty from Stockholm People murdered in Sweden People of the Russo-Swedish War (1788–1790) Swedish Freemasons Swedish monarchs of German descent 1770s in Sweden 1780s in Sweden 1790s in Sweden Sons of kings 18th-century murders in Sweden People murdered in the 1790s Politicians assassinated in the 18th century