Gum inflammation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Gingivitis is a non-destructive disease that causes
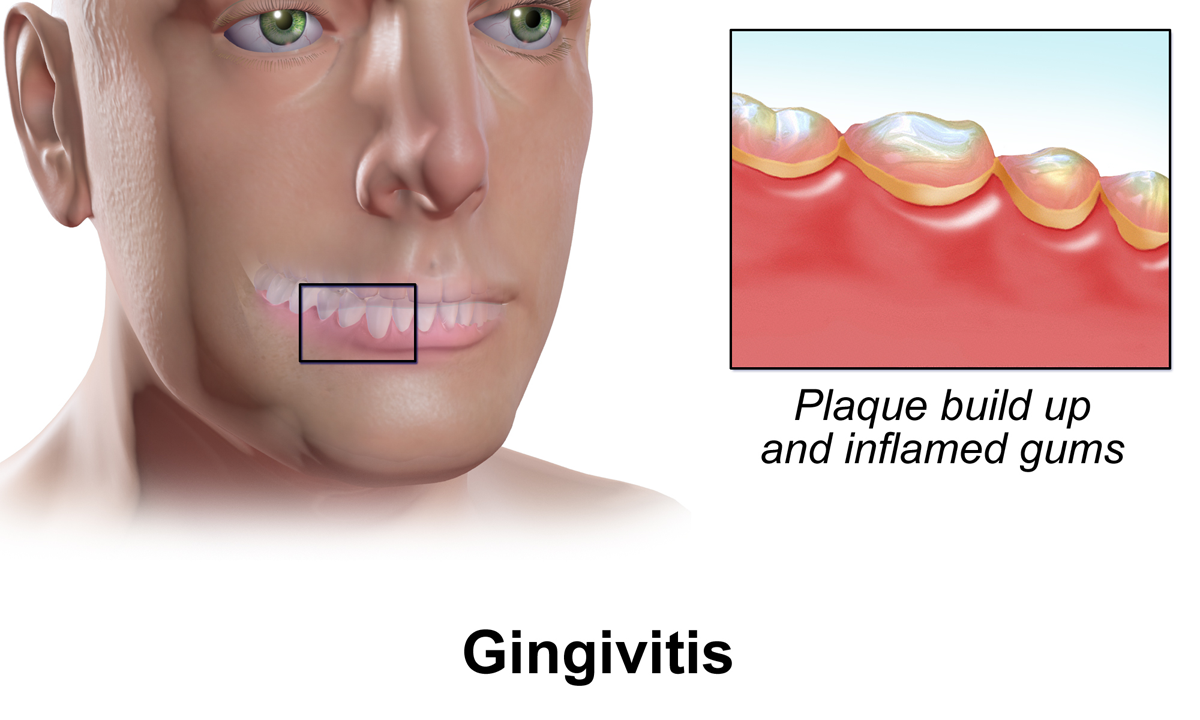 The symptoms of gingivitis are somewhat non-specific and manifest in the gum tissue as the classic signs of inflammation:
*Swollen gums
*Bright red gums
*Gums that are tender or painful to the touch
*Bleeding gums or bleeding after brushing and/or flossing
*Bad breath (
The symptoms of gingivitis are somewhat non-specific and manifest in the gum tissue as the classic signs of inflammation:
*Swollen gums
*Bright red gums
*Gums that are tender or painful to the touch
*Bleeding gums or bleeding after brushing and/or flossing
*Bad breath (

 The focus of treatment is to remove plaque. Therapy is aimed at the reduction of oral bacteria and may take the form of regular periodic visits to a dental professional together with adequate oral hygiene home care. Thus, several of the methods used in the prevention of gingivitis can also be used for the treatment of manifest gingivitis, such as scaling, root planing, curettage, mouth washes containing
The focus of treatment is to remove plaque. Therapy is aimed at the reduction of oral bacteria and may take the form of regular periodic visits to a dental professional together with adequate oral hygiene home care. Thus, several of the methods used in the prevention of gingivitis can also be used for the treatment of manifest gingivitis, such as scaling, root planing, curettage, mouth washes containing
inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
of the gums
The gums or gingiva (: gingivae) consist of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health.
Structure
The gums are part of the soft tissue lining of the ...
; ulitis is an alternative term. The most common form of gingivitis, and the most common form of periodontal disease
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a set of inflammatory conditions affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth. In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums become swollen and red and may bleed. It is considered the main c ...
overall, is in response to bacterial biofilms
A biofilm is a syntrophic community of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular polymer ...
(also called plaque) that are attached to tooth surfaces, termed ''plaque-induced gingivitis''. Most forms of gingivitis are plaque-induced.
While some cases of gingivitis never progress to periodontitis
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a set of inflammatory conditions affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth. In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums become swollen and red and may bleed. It is considered the main c ...
, periodontitis is always preceded by gingivitis.
Gingivitis is reversible with good oral hygiene; however, without treatment, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, in which the inflammation of the gums
The gums or gingiva (: gingivae) consist of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health.
Structure
The gums are part of the soft tissue lining of the ...
results in tissue destruction and bone resorption
Bone resorption is resorption of bone tissue, that is, the process by which osteoclasts break down the tissue in bones and release the minerals, resulting in a transfer of calcium from bone tissue to the blood.
The osteoclasts are multi-nuclea ...
around the teeth. Periodontitis can ultimately lead to tooth loss
Tooth loss is a process in which one or more teeth come loose and fall out. Tooth loss is normal for deciduous teeth, deciduous teeth (baby teeth), when they are replaced by a person's permanent teeth, adult teeth. Otherwise, losing teeth is unde ...
.
Signs and symptoms
 The symptoms of gingivitis are somewhat non-specific and manifest in the gum tissue as the classic signs of inflammation:
*Swollen gums
*Bright red gums
*Gums that are tender or painful to the touch
*Bleeding gums or bleeding after brushing and/or flossing
*Bad breath (
The symptoms of gingivitis are somewhat non-specific and manifest in the gum tissue as the classic signs of inflammation:
*Swollen gums
*Bright red gums
*Gums that are tender or painful to the touch
*Bleeding gums or bleeding after brushing and/or flossing
*Bad breath (halitosis
Bad breath, also known as halitosis, is a symptom in which a noticeably unpleasant breath odour is present. It can result in anxiety among those affected. It is also associated with depression and symptoms of obsessive compulsive disorder.
Th ...
)
Additionally, the stippling
Stippling is the creation of a pattern simulating varying Grayscale, degrees of solidity or shading by using small dots. Such a pattern may occur in nature and these effects are frequently emulated by artists.
Art
In printmaking, stipple ...
that normally exists in the gum tissue of some individuals will often disappear and the gums may appear shiny when the gum tissue becomes swollen and stretched over the inflamed underlying connective tissue. The accumulation may also emit an unpleasant odor. When the gingiva are swollen, the epithelial
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of man ...
lining of the gingival crevice becomes ulcer
An ulcer is a discontinuity or break in a bodily membrane that impedes normal function of the affected organ. According to Robbins's pathology, "ulcer is the breach of the continuity of skin, epithelium or mucous membrane caused by sloughin ...
ated and the gums will bleed more easily with even gentle brushing, and especially when flossing.
Complications
* Recurrence of gingivitis * Periodontitis * Infection orabscess
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body, usually caused by bacterial infection. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pre ...
of the gingiva or the jaw bones
* Trench mouth (bacterial infection and ulceration
An ulcer is a discontinuity or break in a bodily membrane that impedes normal function of the affected Organ (biology), organ. According to Robbins's pathology, "ulcer is the breach of the continuity of skin, epithelium or mucous membrane caus ...
of the gums)
* Swollen lymph nodes
* Associated with premature birth
Preterm birth, also known as premature birth, is the birth of a baby at fewer than 37 weeks gestational age, as opposed to full-term delivery at approximately 40 weeks. Extreme preterm is less than 28 weeks, very early preterm birth is betwee ...
and low birth weight
Alzheimer's and dementia
A study from 2018 found evidence that gingivitis bacteria may be linked toAlzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease and the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems wit ...
. Scientists agree that more research is needed to prove a cause and effect link. "Studies have also found that the bacteria '' P. gingivalis'' – which are responsible for many forms of gum disease – can migrate from the mouth to the brain in mice. And on entry to the brain, ''P. gingivalis'' can reproduce all of the characteristic features of Alzheimer's disease."
Cause
The cause of plaque-induced gingivitis is bacterial plaque, which acts to initiate the body's host response. This, in turn, can lead to destruction of the gingival tissues, which may progress to destruction of the periodontal attachment apparatus. The plaque accumulates in the small gaps between teeth, in the gingival grooves and in areas known as ''plaque traps'': locations that serve to accumulate and maintain plaque. Examples of plaque traps include bulky and overhanging restorative margins, clasps ofremovable partial denture
A removable partial denture (RPD) is a dentures, denture for a partially Edentulism, edentulous patient who desires to have replacement teeth for functional or aesthetic reasons and who cannot have a bridge (dentistry), bridge (a fixed prosthodont ...
s and calculus
Calculus is the mathematics, mathematical study of continuous change, in the same way that geometry is the study of shape, and algebra is the study of generalizations of arithmetic operations.
Originally called infinitesimal calculus or "the ...
(tartar) that forms on teeth. Although these accumulations may be tiny, the bacteria in them produce chemicals, such as degradative enzymes, and toxins, such as lipopolysaccharide
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), now more commonly known as endotoxin, is a collective term for components of the outermost membrane of the cell envelope of gram-negative bacteria, such as '' E. coli'' and ''Salmonella'' with a common structural archit ...
(LPS, otherwise known as endotoxin
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), now more commonly known as endotoxin, is a collective term for components of the outermost membrane of the cell envelope of gram-negative bacteria, such as '' E. coli'' and ''Salmonella'' with a common structural archit ...
) or lipoteichoic acid Lipoteichoic acid (LTA) is a major constituent of the cell wall of gram-positive bacteria. These organisms have an inner (or cytoplasmic) membrane and, external to it, a thick (up to 80 nanometer) peptidoglycan layer. The structure of LTA varies b ...
(LTA), that promote an inflammatory response in the gum tissue. This inflammation can cause an enlargement of the gingiva and subsequent formation. Early plaque in health consists of a relatively simple bacterial community dominated by Gram-positive
In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall.
The Gram stain is ...
cocci and rods. As plaque matures and gingivitis develops, the communities become increasingly complex with higher proportions of Gram-negative
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that, unlike gram-positive bacteria, do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. Their defining characteristic is that their cell envelope consists ...
rods, fusiforms, filaments, spirilla and spirochetes. Later experimental gingivitis studies, using culture, provided more information regarding the specific bacterial species present in plaque. Taxa associated with gingivitis included ''Fusobacterium nucleatum
''Fusobacterium nucleatum'' is a Gram-negative bacteria, Gram-negative, Anaerobic organism, anaerobic Bacteria, bacterium, Commensalism, commensal to the human oral cavity, that plays a role in periodontal disease. This organism is commonly reco ...
'' subspecies ''polymorphum'', '' Lachnospiraceae'' -2species HOT100, '' Lautropia'' species HOTA94, and '' Prevotella oulorum'' (a species of '' Prevotella'' bacterium), whilst '' Rothia dentocariosa'' was associated with periodontal health. Further study of these taxa is warranted and may lead to new therapeutic approaches to prevent periodontal disease including systemic health.
Risk factors
Risk factors associated with gingivitis include the following: *age *osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to more porous bone, and consequent increase in Bone fracture, fracture risk.
It is the most common reason f ...
*low dental care utilization
*poor oral hygiene
*overly aggressive oral hygiene such as brushing with stiff bristles
* mouth breathing during sleep
*orthodontic braces
*medications and conditions that dry the mouth
*cigarette smoking
Tobacco smoking is the practice of burning tobacco and ingesting the resulting smoke. The smoke may be inhaled, as is done with cigarettes, or released from the mouth, as is generally done with pipes and cigars. The practice is believed to hav ...
*genetic factors
*stress
*mental health issues such as depression
*pre-existing conditions such as diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of th ...
*drinking
*obesity.
Diagnosis
Gingivitis is a category of periodontal disease in which there is no loss of bone but inflammation and bleeding are present. Each tooth is divided into four gingival units (mesial, distal, buccal, and lingual) and given a score from 0–3 based on the gingival index. The four scores are then averaged to give each tooth a single score. The diagnosis of the periodontal disease gingivitis is done by a dentist. The diagnosis is based on clinical assessment data acquired during a comprehensive periodontal exam. Either a registered dental hygienist or a dentist may perform the comprehensive periodontal exam but the data interpretation and diagnosis are done by the dentist. The comprehensive periodontal exam consists of a visual exam, a series of radiographs, probing of the gingiva, determining the extent of current or past damage to the periodontium and a comprehensive review of the medical and dental histories. Current research shows that activity levels of the following enzymes in saliva samples are associated with periodontal destruction: aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), gamma glutamyl transferase (GGT),alkaline phosphatase
The enzyme alkaline phosphatase (ALP, alkaline phenyl phosphatase, also abbreviated PhoA) is a phosphatase with the physiological role of dephosphorylating compounds. The enzyme is found across a multitude of organisms, prokaryotes and eukaryo ...
(ALP), and acid phosphatase
Acid phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.2, systematic name ''phosphate-monoester phosphohydrolase (acid optimum)'') is an enzyme that frees attached phosphoryl groups from other molecules during digestion. It can be further classified as a phosphoric monoeste ...
(ACP). Therefore, these enzyme biomarkers may be used to aid in the diagnosis and treatment of gingivitis and periodontitis.
A dental hygienist or dentist will check for the symptoms of gingivitis, and may also examine the amount of plaque in the oral cavity. A dental hygienist or dentist will also look for signs of periodontitis
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a set of inflammatory conditions affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth. In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums become swollen and red and may bleed. It is considered the main c ...
using X-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
s or periodontal probing as well as other methods.
If gingivitis is not responsive to treatment, referral to a periodontist (a specialist in diseases of the gingiva and bone around teeth and dental implants) for further treatment may be necessary.
Classification
1999 Classification
As defined by the 1999 World Workshop in Clinical Periodontics, there are two primary categories of gingival diseases, each with numerous subgroups: # Dental plaque-induced gingival diseases. ## Gingivitis associated with plaque only ## Gingival diseases modified by systemic factors ## Gingival diseases modified by medications ## Gingival diseases modified by malnutrition # Non-plaque-induced gingival lesions ## Gingival diseases of specific bacterial origin ## Gingival diseases of viral origin ## Gingival diseases of fungal origin ## Gingival diseases of genetic origin ## Gingival manifestations of systemic conditions ## Traumatic lesions ## Foreign body reactions ## Not otherwise specified2017 Classification
As defined by the 2017 World Workshop, periodontal health, gingival diseases/ conditions have been categorised into the following: # Periodontal health and gingival health ## Clinical gingival health on an intact periodontium ## Clinical gingival health on a reduced periodontium ### Stable periodontitis patient ### Non-periodontitis patient # Gingivitis – dental biofilm-induced ## Associated with dental biofilm alone ## Mediated by systemic or local risk factors ## Drug-influenced gingival enlargement # Gingival diseases – non-dental biofilm induced ## Genetic/ developmental disorders ## Specific infections ## Inflammatory and immune conditions ## Reactive processes ## Neoplasms ## Endocrine, nutritional & metabolic diseases ## Traumatic lesions ## Gingival pigmentationPrevention
Gingivitis can be prevented through regularoral hygiene
Oral hygiene is the practice of keeping one's oral cavity clean and free of disease and other problems (e.g. bad breath) by regular brushing of the teeth (dental hygiene) and adopting good hygiene habits. It is important that oral hygiene be carr ...
that includes daily brushing and flossing
Dental floss is a cord of thin filaments, typically made of nylon or silk, used in interdental cleaning to remove food and dental plaque from between teeth or places a toothbrush has difficulty reaching or is unable to reach. Its regular use as ...
. Hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscosity, viscous than Properties of water, water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usua ...
, saline, alcohol
Alcohol may refer to:
Common uses
* Alcohol (chemistry), a class of compounds
* Ethanol, one of several alcohols, commonly known as alcohol in everyday life
** Alcohol (drug), intoxicant found in alcoholic beverages
** Alcoholic beverage, an alco ...
or chlorhexidine
Chlorhexidine is a disinfectant and antiseptic which is used for skin disinfection before surgery and to disinfect surgical instruments. It is also used for cleaning wounds, preventing dental plaque, treating yeast infections of the mouth, and ...
mouth washes may also be employed. In a 2004 clinical study, the beneficial effect of hydrogen peroxide on gingivitis has been highlighted. The use of oscillation type brushes might reduce the risk of gingivitis compared to manual brushing.
Rigorous plaque control programs along with periodontal scaling and curettage also have proved to be helpful, although according to the American Dental Association
The American Dental Association (ADA) is an American professional dental association. Established in 1859 and with over 159,000 current members, ADA is the world's largest and oldest national dental association. The organization lobbies on behal ...
, periodontal scaling and root planing are considered as a treatment for periodontal disease, not as a preventive treatment for periodontal disease. In a 1997 review of effectiveness data, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respo ...
(FDA) found clear evidence showing that toothpaste containing triclosan
Triclosan (sometimes abbreviated as TCS) is an antibacterial and antifungal agent present in some consumer products, including toothpaste, soaps, detergents, toys, and surgical cleaning treatments. It is similar in its uses and mechanism of act ...
was effective in preventing gingivitis. In 2017 the FDA banned triclosan in many consumer products but allowed it to remain in toothpaste because of its effectiveness against gingivitis. In 2019, Colgate, under pressure from health advocates, removed triclosan from the last toothpaste on the market containing it, Colgate Total.
Treatment

 The focus of treatment is to remove plaque. Therapy is aimed at the reduction of oral bacteria and may take the form of regular periodic visits to a dental professional together with adequate oral hygiene home care. Thus, several of the methods used in the prevention of gingivitis can also be used for the treatment of manifest gingivitis, such as scaling, root planing, curettage, mouth washes containing
The focus of treatment is to remove plaque. Therapy is aimed at the reduction of oral bacteria and may take the form of regular periodic visits to a dental professional together with adequate oral hygiene home care. Thus, several of the methods used in the prevention of gingivitis can also be used for the treatment of manifest gingivitis, such as scaling, root planing, curettage, mouth washes containing chlorhexidine
Chlorhexidine is a disinfectant and antiseptic which is used for skin disinfection before surgery and to disinfect surgical instruments. It is also used for cleaning wounds, preventing dental plaque, treating yeast infections of the mouth, and ...
or hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscosity, viscous than Properties of water, water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usua ...
, and flossing. Interdental brushes also help remove any causative agents.
Powered toothbrushes work better than manual toothbrushes in reducing the disease.
The active ingredients that "reduce plaque and demonstrate effective reduction of gingival inflammation over a period of time" are triclosan
Triclosan (sometimes abbreviated as TCS) is an antibacterial and antifungal agent present in some consumer products, including toothpaste, soaps, detergents, toys, and surgical cleaning treatments. It is similar in its uses and mechanism of act ...
, chlorhexidine digluconate, and a combination of thymol
Thymol (also known as 2-isopropyl-5-methylphenol, IPMP), , is a toxic monoterpenoid phenol derivative of ''p''-Cymene, isomeric with carvacrol. It occurs naturally in the oil of thyme, and it is extracted from ''Thymus vulgaris'' (common thy ...
, menthol
Menthol is an organic compound, specifically a Monoterpene, monoterpenoid, that occurs naturally in the oils of several plants in the Mentha, mint family, such as Mentha arvensis, corn mint and peppermint. It is a white or clear waxy crystallin ...
, eucalyptol, and methyl salicylate
Methyl salicylate (oil of wintergreen or wintergreen oil) is an organic compound with the formula C8H8O3. It is the methyl ester of salicylic acid. It is a colorless, viscous liquid with a sweet, fruity odor reminiscent of root beer (in which it ...
. These ingredients are found in toothpaste and mouthwash. Hydrogen peroxide was long considered a suitable over-the-counter agent to treat gingivitis. There has been evidence to show the positive effect on controlling gingivitis in short-term use. A study indicates the fluoridated hydrogen peroxide-based mouth rinse can remove teeth stain and reduce gingivitis.
Based on a limited evidence, mouthwashes with essential oils may also be useful, as they contain ingredients with anti-inflammatory properties, such as thymol, menthol and eucalyptol.
The bacteria that causes gingivitis can be controlled by using an oral irrigator daily with a mouthwash containing an antibiotic. Either amoxicillin, cephalexin, or minocycline in 500 grams of a non-alcoholic fluoride mouthwash is an effective mixture.
Overall, intensive oral hygiene care has been shown to improve gingival health in individuals with well-controlled type 2 diabetes. Periodontal destruction is also slowed due to the extensive oral care. Intensive oral hygiene care (oral health education plus supra-gingival scaling) without any periodontal therapy improves gingival health, and may prevent progression of gingivitis in well-controlled diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of th ...
.
See also
* Pericoronitis * " Full width gingivitis" of orofacial granulomatosis * Desquamative gingivitisReferences
External links
{{Authority control Inflammations Periodontal disorders