|
Periodontist
Periodontology or periodontics (from Ancient Greek , – 'around'; and , – 'tooth', genitive , ) is the specialty of dentistry that studies supporting structures of teeth, as well as diseases and conditions that affect them. The supporting tissues are known as the periodontium, which includes the gingiva (gums), alveolar bone, cementum, and the periodontal ligament. A periodontist is a dentist that specializes in the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of periodontal disease and in the placement of dental implants. The periodontium The term ''periodontium'' is used to describe the group of structures that directly surround, support and protect the teeth. The periodontium is composed largely of the gingival tissue and the supporting bone. Gingivae Normal gingiva may range in color from light coral pink to heavily pigmented. The soft tissues and connective fibres that cover and protect the underlying cementum, periodontal ligament and alveolar bone are known as the gingiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Degree
A number of professional degrees in dentistry are offered by dental schools in various countries around the world. Degrees Dental degrees may include: Bachelor's degree * Bachelor of Dental Surgery (BDS) * Bachelor's degree of Dentistry (BDS) * Bachelor of Dentistry (BDent) * Bachelor of Dental Science (BDSc) * Bachelor of Science in Dentistry (BScD) * Bachelor of Medicine in Dental Medicine (BM) * Baccalaureus Dentalis Chirurgiae (BChD) Master's degree * Master of Science (MS or MSc) * Master of Science in Dentistry (MSD or MScD) * Master of Medical Science (MMSc) * Master of Dentistry (MDent) * Master of Dental Surgery (MDS) * Master of Dental Science (MDentSci) * Master of Stomatology (MS) * Master of Clinical Stomatology (MCS) * Master of Stomatological Medicine (MSM) Doctorate * Doctor of Dental Surgery (DDS) * Doctor of Dental Medicine/Doctor of Medicine in Dentistry (DMD) * Doctor of Clinical Dentistry (DClinDent) * Doctor of Dental Science (DDSc) * Doctor of Sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specialty (dentistry)
In the United States and Canada, there are twelve recognized dental specialties in which some dentists choose to train and practice, in addition to or instead of general dentistry. In the United Kingdom and Australia, there are thirteen. To become a specialist requires training in a residency or advanced graduate training program. Once a residency is completed, the doctor is granted a certificate of specialty training. Many specialty programs have optional or required advanced degrees such as a master's degree, such as the Master of Science (MS or MSc), Master of Dental Surgery/Science (MDS/MDSc), Master of Dentistry (MDent), Master of Clinical Dentistry (MClinDent), Master of Philosophy (MPhil), Master of Medical Science (MMS or (MMSc); doctorate such as Doctor of Clinical Dentistry (DClinDent), Doctor of Medical Science/Sciences (DMSc), or PhD;or medical degree: Doctor of Medicine/Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery (MD/MBBS) specific to maxillofacial surgery and so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
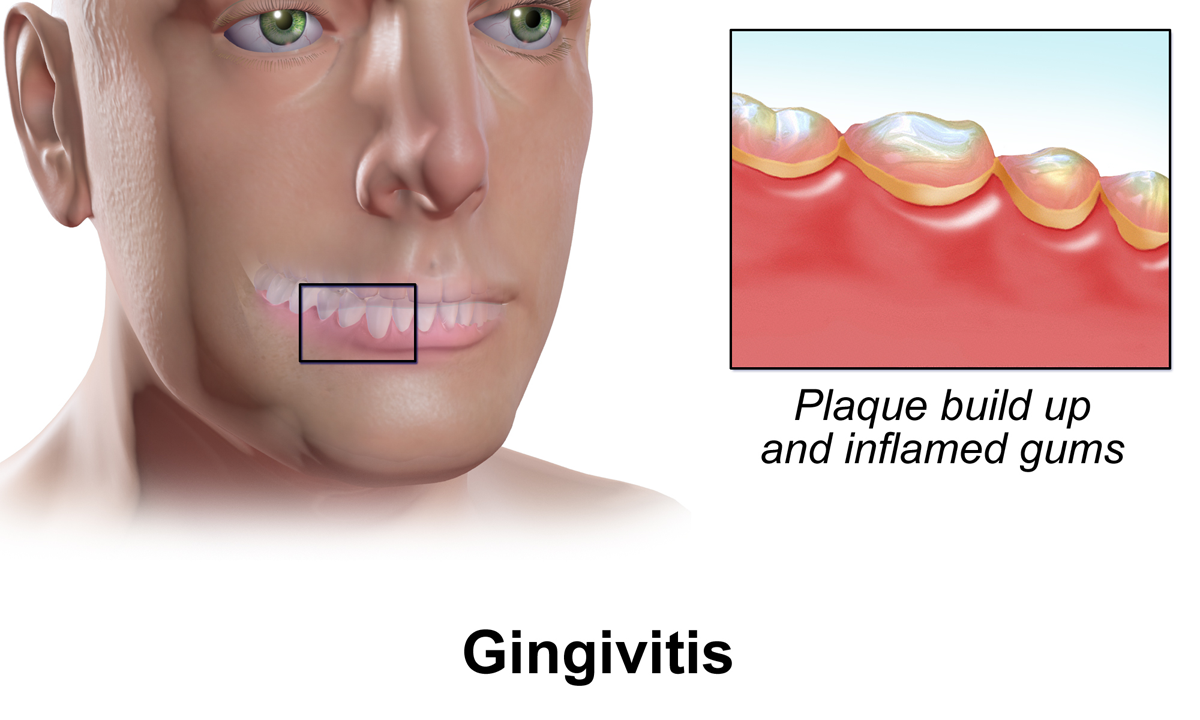
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is a non-destructive disease that causes inflammation of the gums; ulitis is an alternative term. The most common form of gingivitis, and the most common form of periodontal disease overall, is in response to bacterial biofilms (also called plaque) that are attached to tooth surfaces, termed ''plaque-induced gingivitis''. Most forms of gingivitis are plaque-induced. While some cases of gingivitis never progress to periodontitis, periodontitis is always preceded by gingivitis. Gingivitis is reversible with good oral hygiene; however, without treatment, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, in which the inflammation of the gums results in tissue destruction and bone resorption around the teeth. Periodontitis can ultimately lead to tooth loss. Signs and symptoms The symptoms of gingivitis are somewhat non-specific and manifest in the gum tissue as the classic signs of inflammation: *Swollen gums *Bright red gums *Gums that are tender or painful to the touch *B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a set of inflammatory conditions affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth. In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums become swollen and red and may bleed. It is considered the main cause of tooth loss for adults worldwide. In its more serious form, called periodontitis, the gums can pull away from the tooth, bone can be lost, and the teeth may loosen or fall out. Halitosis (bad breath) may also occur. Periodontal disease typically arises from the development of plaque biofilm, which harbors harmful bacteria such as ''Porphyromonas gingivalis'' and ''Treponema denticola''. These bacteria infect the gum tissue surrounding the teeth, leading to inflammation and, if left untreated, progressive damage to the teeth and gum tissue. Recent meta-analysis have shown that the composition of the oral microbiota and its response to periodontal disease differ between men and women. These differences are particularly notable in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gingival Sulcus
In dental anatomy, the gingival sulcus is an area of potential space between a tooth and the surrounding gingiva, gingival tissue and is lined by sulcular epithelium. The depth of the sulcus (Latin for ''groove'') is bounded by two entities: Commonly used terms of relationship and comparison in dentistry, apically by the gingival fibers of the connective tissue attachment and Commonly used terms of relationship and comparison in dentistry, coronally by the free gingival margin. A healthy sulcular depth is three millimeters or less, which is readily self-cleansable with a properly used toothbrush or the supplemental use of other oral hygiene aids. Anatomy The dentogingival tissues consist of many constituents, such as the enamel or cementum of the tooth and the connective tissue supporting epithelia like the junctional epithelium, the gingival epithelium and the sulcular epithelium. The junctional epithelium is developed during the eruption of teeth when the reduced enamel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Plaque
Dental plaque is a biofilm of microorganisms (mostly bacteria, but also fungi) that grows on surfaces within the mouth. It is a sticky colorless deposit at first, but when it forms Calculus (dental), tartar, it is often brown or pale yellow. It is commonly found between the teeth, on the front of teeth, behind teeth, on chewing surfaces, along the gums, gumline (supragingival), or below the gumline cervical margins (subgingival). Dental plaque is also known as microbial plaque, oral biofilm, dental biofilm, dental plaque biofilm or bacterial plaque biofilm. Bacterial plaque is one of the major causes for dental decay and gum disease. It has been observed that differences in the composition of dental plaque microbiota exist between men and women, particularly in the presence of periodontal disease, periodontitis. Progression and build-up of dental plaque can give rise to tooth decay – the localised destruction of the tissues of the tooth by acid produced from the bacterial degrad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Canaliculi
Dental may refer to: * Dental consonant, in phonetics * Dental Records, an independent UK record label * Dentistry Dentistry, also known as dental medicine and oral medicine, is the branch of medicine focused on the Human tooth, teeth, gums, and Human mouth, mouth. It consists of the study, diagnosis, prevention, management, and treatment of diseases, dis ..., oral medicine * Teeth See also * * Dental care (other) * Dentist (other) * Tooth (other) {{Disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentin
Dentin ( ) (American English) or dentine ( or ) (British English) () is a calcified tissue (biology), tissue of the body and, along with tooth enamel, enamel, cementum, and pulp (tooth), pulp, is one of the four major components of teeth. It is usually covered by enamel on the crown and cementum on the root and surrounds the entire pulp. By volume, 45% of dentin consists of the mineral hydroxyapatite, 33% is organic material, and 22% is water. Yellow in appearance, it greatly affects the color of a tooth due to the translucency of enamel. Dentin, which is less mineralized and less brittle than enamel, is necessary for the support of enamel. Dentin rates approximately 3 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness. There are two main characteristics which distinguish dentin from enamel: firstly, dentin forms throughout life; secondly, dentin is sensitive and can become hypersensitive to changes in temperature due to the sensory function of odontoblasts, especially when enamel recedes an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharpey's Fibres
Sharpey's fibres (bone fibres, or perforating fibres) are a matrix of connective tissue consisting of bundles of strong predominantly type I collagen fibres connecting periosteum to bone. They are part of the outer fibrous layer of periosteum, entering into the outer circumferential and interstitial lamellae of bone tissue. Sharpey's fibres also attach muscle to the periosteum of bone by merging with the fibrous periosteum and underlying bone as well. A good example is the attachment of the rotator cuff muscles to the blade of the scapula. In the teeth, Sharpey's fibres are the terminal ends of principal fibres (of the periodontal ligament) that insert into the cementum and into the periosteum of the alveolar bone. A study on rats suggests that the three-dimensional structure of Sharpey's fibres intensifies the continuity between the periodontal ligament fibre and the alveolar bone (tooth socket), and acts as a buffer medium against stress. Sharpey's fibres in the pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periodontal Fiber
The periodontal ligament, commonly abbreviated as the PDL, are a group of specialized connective tissue fibers that essentially attach a tooth to the alveolar bone within which they sit. It inserts into root cementum on one side and onto alveolar bone on the other. Structure The PDL consists of principal fibers, loose connective tissue, blast and clast cells, oxytalan fibers and cell rest of Malassez. Alveolodental ligament The main principal fiber group is the alveolodental ligament, which consists of five fiber subgroups: alveolar crest, horizontal, oblique, apical, and interradicular on multirooted teeth. Principal fibers other than the alveolodental ligament are the transseptal fibers. All these fibers help the tooth withstand the naturally substantial compressive forces that occur during chewing and remain embedded in the bone. The ends of the principal fibers that are within either cementum or alveolar bone proper are considered Sharpey fibers. * Alveolar crest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interdental Gingiva
The interdental papilla, also known as the interdental gingiva, is the part of the gums (gingiva) that exists coronal to the free gingival margin on the mesial and distal surfaces of the teeth. The interdental papillae fill in the area between the teeth apical to their contact areas to prevent food impaction; they assume a conical shape for the anterior teeth and a blunted shape buccolingually for the posterior teeth. A missing papilla is often visible as a small triangular gap between adjacent teeth. Dentists will sometimes refer to this gap as a 'black triangle'. It can sometimes be corrected with orthodontic treatment. The relationship of interdental bone to the interproximal contact point between adjacent teeth is a determining factor in whether the interdental papilla will be present. If a distance greater than 8 mm exists between the interdental bone and the interproximal contact, usually no papilla will be present. If the distance is 5 mm or less, then a papilla wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chewing
Chewing or mastication is the process by which food is crushed and ground by the teeth. It is the first step in the process of digestion, allowing a greater surface area for digestive enzymes to break down the foods. During the mastication process, the food is positioned by the cheek and tongue between the teeth for grinding. The muscles of mastication move the jaws to bring the teeth into intermittent contact, repeatedly occluding and opening. As chewing continues, the food is made softer and warmer, and the enzymes in saliva begin to break down carbohydrates in the food. After chewing, the food (now called a bolus) is swallowed. It enters the esophagus and via peristalsis continues on to the stomach, where the next step of digestion occurs. Increasing the number of chews per bite stimulates the production of digestive enzymes and peptides and has been shown to increase diet-induced thermogenesis (DIT) by activating the sympathetic nervous system. Studies suggest that thoroug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |