Graph Of A Function on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In 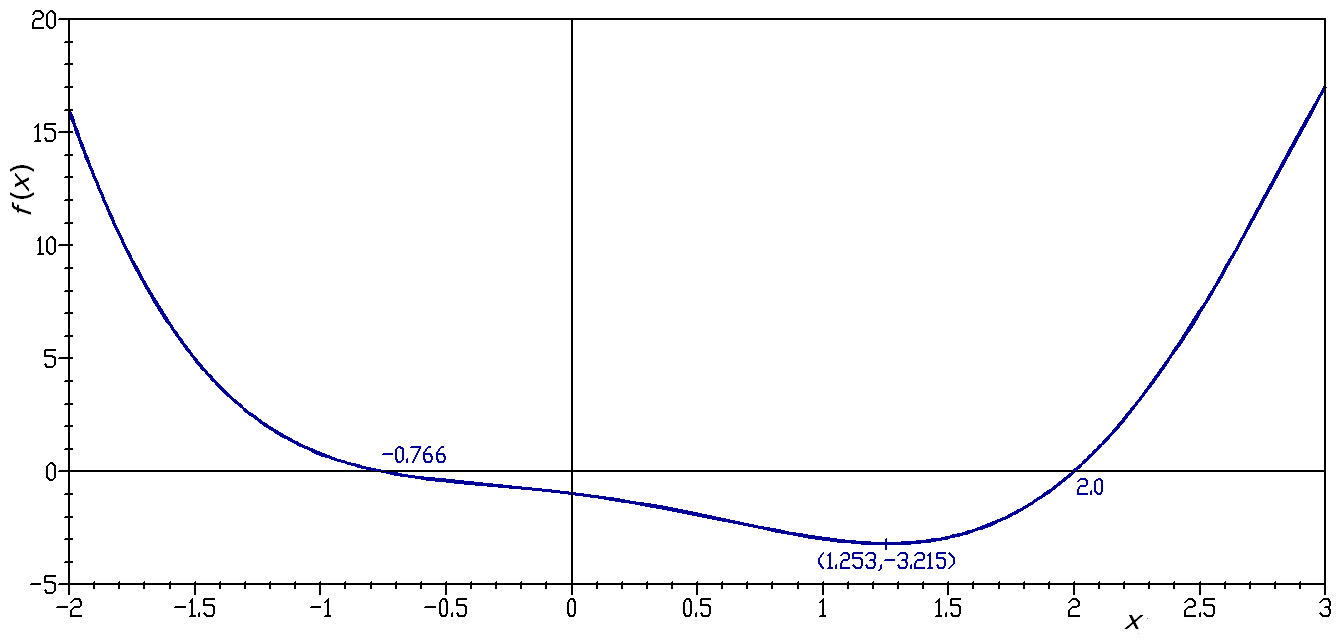
 The graph of the function defined by
is the subset of the set
From the graph, the domain is recovered as the set of first component of each pair in the graph .
Similarly, the
The graph of the function defined by
is the subset of the set
From the graph, the domain is recovered as the set of first component of each pair in the graph .
Similarly, the
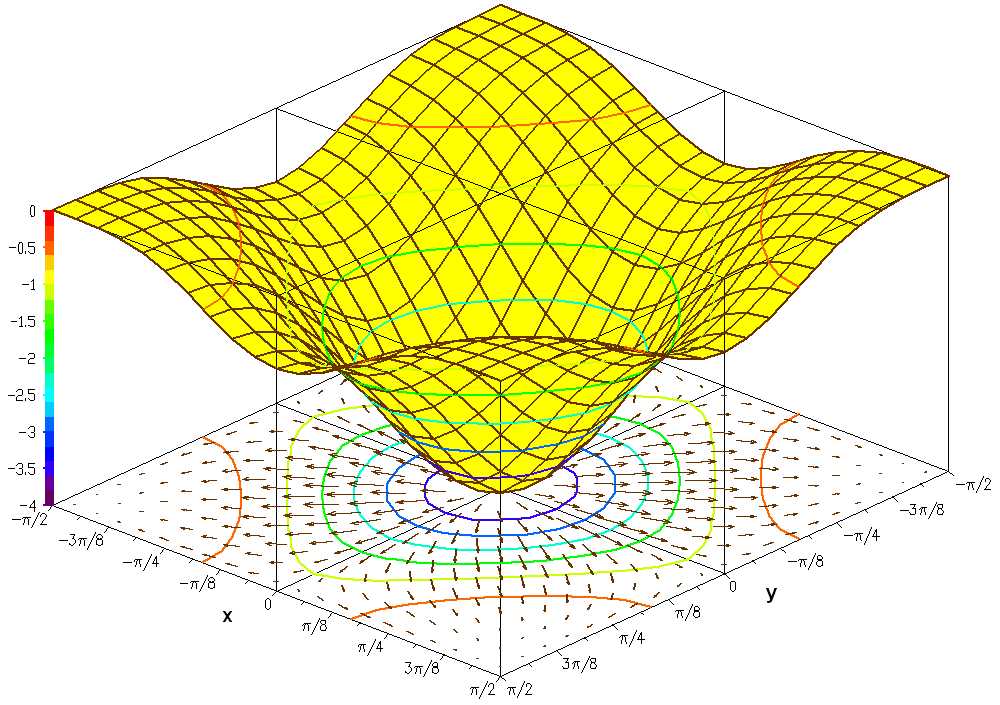 The graph of the trigonometric function
is
If this set is plotted on a three dimensional Cartesian coordinate system, the result is a surface (see figure).
Oftentimes it is helpful to show with the graph, the gradient of the function and several level curves. The level curves can be mapped on the function surface or can be projected on the bottom plane. The second figure shows such a drawing of the graph of the function:
The graph of the trigonometric function
is
If this set is plotted on a three dimensional Cartesian coordinate system, the result is a surface (see figure).
Oftentimes it is helpful to show with the graph, the gradient of the function and several level curves. The level curves can be mapped on the function surface or can be projected on the bottom plane. The second figure shows such a drawing of the graph of the function:
Function Graph
" From MathWorld—A Wolfram Web Resource. {{Visualization Charts Functions and mappings Numerical function drawing
mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ...
, the graph of a function is the set of ordered pair
In mathematics, an ordered pair (''a'', ''b'') is a pair of objects. The order in which the objects appear in the pair is significant: the ordered pair (''a'', ''b'') is different from the ordered pair (''b'', ''a'') unless ''a'' = ''b''. (In con ...
s , where In the common case where and are real numbers, these pairs are Cartesian coordinates
A Cartesian coordinate system (, ) in a plane is a coordinate system that specifies each point uniquely by a pair of numerical coordinates, which are the signed distances to the point from two fixed perpendicular oriented lines, measured in t ...
of points in two-dimensional space and thus form a subset of this plane.
In the case of functions of two variables, that is functions whose domain
Domain may refer to:
Mathematics
*Domain of a function, the set of input values for which the (total) function is defined
**Domain of definition of a partial function
**Natural domain of a partial function
**Domain of holomorphy of a function
* Do ...
consists of pairs the graph usually refers to the set of ordered triple
In mathematics, a tuple is a finite ordered list (sequence) of elements. An -tuple is a sequence (or ordered list) of elements, where is a non-negative integer. There is only one 0-tuple, referred to as ''the empty tuple''. An -tuple is defi ...
s where instead of the pairs as in the definition above. This set is a subset of three-dimensional space; for a continuous real-valued function of two real variables, it is a surface.
In science, engineering, technology, finance
Finance is the study and discipline of money, currency and capital assets. It is related to, but not synonymous with economics, the study of production, distribution, and consumption of money, assets, goods and services (the discipline of fina ...
, and other areas, graphs are tools used for many purposes. In the simplest case one variable is plotted as a function of another, typically using rectangular axes; see ''Plot (graphics)
A plot is a graphical technique for representing a data set, usually as a graph showing the relationship between two or more variables. The plot can be drawn by hand or by a computer. In the past, sometimes mechanical or electronic plotters were u ...
'' for details.
A graph of a function is a special case of a relation
Relation or relations may refer to:
General uses
*International relations, the study of interconnection of politics, economics, and law on a global level
*Interpersonal relationship, association or acquaintance between two or more people
*Public ...
.
In the modern foundations of mathematics, and, typically, in set theory, a function is actually equal to its graph. However, it is often useful to see functions as mappings, which consist not only of the relation between input and output, but also which set is the domain, and which set is the codomain. For example, to say that a function is onto (surjective
In mathematics, a surjective function (also known as surjection, or onto function) is a function that every element can be mapped from element so that . In other words, every element of the function's codomain is the image of one element of i ...
) or not the codomain should be taken into account. The graph of a function on its own doesn't determine the codomain. It is common to use both terms ''function'' and ''graph of a function'' since even if considered the same object, they indicate viewing it from a different perspective.
Definition
Given a mapping in other words a function together with its domain and codomain the graph of the mapping is the set which is a subset of . In the abstract definition of a function, is actually equal to One can observe that, if, then the graph is a subset of (strictly speaking it is but one can embed it with the natural isomorphism).Examples
Functions of one variable
 The graph of the function defined by
is the subset of the set
From the graph, the domain is recovered as the set of first component of each pair in the graph .
Similarly, the
The graph of the function defined by
is the subset of the set
From the graph, the domain is recovered as the set of first component of each pair in the graph .
Similarly, the range
Range may refer to:
Geography
* Range (geographic), a chain of hills or mountains; a somewhat linear, complex mountainous or hilly area (cordillera, sierra)
** Mountain range, a group of mountains bordered by lowlands
* Range, a term used to i ...
can be recovered as .
The codomain , however, cannot be determined from the graph alone.
The graph of the cubic polynomial on the real line
In elementary mathematics, a number line is a picture of a graduated straight line (geometry), line that serves as visual representation of the real numbers. Every point of a number line is assumed to correspond to a real number, and every real ...
is
If this set is plotted on a Cartesian plane, the result is a curve (see figure).
Functions of two variables
See also
* Asymptote *Chart
A chart (sometimes known as a graph) is a graphical representation for data visualization, in which "the data is represented by symbols, such as bars in a bar chart, lines in a line chart, or slices in a pie chart". A chart can represent tabu ...
* Concave function
In mathematics, a concave function is the negative of a convex function. A concave function is also synonymously called concave downwards, concave down, convex upwards, convex cap, or upper convex.
Definition
A real-valued function f on an in ...
* Convex function
In mathematics, a real-valued function is called convex if the line segment between any two points on the graph of a function, graph of the function lies above the graph between the two points. Equivalently, a function is convex if its epigra ...
* Contour plot
* Critical point
* Derivative
* Epigraph
* Normal to a graph
* Slope
* Stationary point
* Tetraview A tetraview is an attempt to graph a complex function of a complex variable, by a method invented by Davide P. Cervone.
A graph of a real function of a real variable is the set of ordered pairs (x,y) such that y = f(x). This is the ordinary two- ...
* Vertical translation
* y-intercept
In analytic geometry, using the common convention that the horizontal axis represents a variable ''x'' and the vertical axis represents a variable ''y'', a ''y''-intercept or vertical intercept is a point where the graph of a function or relatio ...
References
*External links
* Weisstein, Eric W.Function Graph
" From MathWorld—A Wolfram Web Resource. {{Visualization Charts Functions and mappings Numerical function drawing