Gotland Sheep Breeders Association Of North America on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Gotland (; ; ''Gutland'' in
Distinguishing bone fat exploitation from other taphonomic processes: what caused the high level of bone fragmentation at the Middle Neolithic site of Ajvide, Gotland?
, pp. 32–43. In Mulville, J and Outram, A (eds). ''The Zooarchaeology of Milk and Fats''. Oxford: Oxbow Books. A DNA study conducted on the 5,000-year-old skeletal remains of three Middle Neolithic seal hunters from Gotland showed that they were related to modern-day
Gutnish
Gutnish ( ), or rarely Gutnic ( or ), is a North Germanic language spoken sporadically on the islands of Gotland and Fårö. The different dialects of Gutnish, while stemming from the Old Gutnish () variety of Old Norse, are sometimes considere ...
), also historically spelled Gottland or Gothland (), is Sweden's largest island. It is also a province
A province is an administrative division within a country or sovereign state, state. The term derives from the ancient Roman , which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire, Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
/county
A county () is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesL. Brookes (ed.) '' Chambers Dictionary''. Edinburgh: Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, 2005. in some nations. The term is derived from the Old French denoti ...
(Swedish län), municipality
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having municipal corporation, corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality' ...
, and diocese
In Ecclesiastical polity, church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided Roman province, prov ...
. The province includes the islands of Fårö
Fårö () or in Gutnish is a Baltic Sea island just north of the island of Gotland, itself off mainland Sweden's southeastern coast. It is the second-largest island in the county and it is a popular summer resort. It has its own language, Fårö ...
and Gotska Sandön
Gotska Sandön (literally translated as "The Gotlandic Sand Island") is an uninhabited Swedish island north of Gotland in the Baltic Sea. It has been a national park since 1909.
Geography
Sandön is situated north of Fårö in the Baltic Se ...
to the north, as well as the Karlsö Islands ( Lilla and Stora
Stora Enso Oyj (from and ) is a Finnish and Swedish forest industry company. It develops and produces various materials, mostly based on wood, for a range of industries and applications worldwide. It has headquarters in Helsinki, Finland, an ...
) to the west. The population is 61,023 (2024) of which about 23,600 live in Visby
Visby () is an urban areas in Sweden, urban area in Sweden and the seat of Gotland Municipality in Gotland County on the island of Gotland with 24,330 inhabitants . Visby is also the episcopal see for the Diocese of Visby. The Hanseatic League, ...
, the main town. Outside Visby, there are minor settlements and a mainly rural population. The island of Gotland and the other areas of the province of Gotland make up less than one percent of Sweden's total land area. The county formed by the archipelago is the second smallest by area and is the least populated in Sweden. In spite of the small size due to its narrow width, the driving distance between the furthermost points of the populated islands is about .
Gotland is a fully integrated part of Sweden with no particular autonomy, unlike several other offshore island groups in Europe. Historically, there was a linguistic difference between the archipelago and the mainland with Gutnish
Gutnish ( ), or rarely Gutnic ( or ), is a North Germanic language spoken sporadically on the islands of Gotland and Fårö. The different dialects of Gutnish, while stemming from the Old Gutnish () variety of Old Norse, are sometimes considere ...
being the native language. In recent centuries, Swedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
took over almost entirely and the island is virtually monolingually Swedish in modern times. The archipelago is a very popular domestic tourist destination for mainland Swedes, with the population rising to very high numbers during summers. Some of the reasons are the sunny climate and the extensive shoreline bordering mild waters. During summer, Visby hosts the political event Almedalen Week
The Almedalen Week (, ), also known as Politician's Week in Almedalen () is an annual event taking place in week 26 in and around Almedalen, a park in the city of Visby, Gotland, Sweden.
With speeches, seminars and other political activities, ...
, followed by the Medieval Week, further boosting visitor numbers. In winter, Gotland usually remains surrounded by ice-free water and has mild weather.
Gotland has been inhabited since approximately 7200 BCE. The island's main sources of income are agriculture, food processing, tourism, information technology services, design, and some heavy industry such as concrete production from locally mined limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science) ...
. From a military standpoint, it occupies a strategic location at the center of the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
and is home to the Gotland Regiment
The Gotland Regiment (, P 18) is a Swedish Army armoured warfare, armoured regiment which has been active in various forms between 1963–1994 and 2000–2005, when it was disbanded. The regiment was re-established on 1 January 2018. The regiment ...
which was re-established in 2018.
Etymology
The name of Gotland is closely related to that of theGeats
The Geats ( ; ; ; ), sometimes called ''Geats#Goths, Goths'', were a large North Germanic peoples, North Germanic tribe who inhabited ("land of the Geats") in modern southern Sweden from antiquity until the Late Middle Ages. They are one of ...
and Goths
The Goths were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe. They were first reported by Graeco-Roman authors in the 3rd century AD, living north of the Danube in what is ...
.
History
Prehistoric time to Viking Age
The island was the home of theGutes
The Gutes ( Old West Norse: ''Gotar'', Old Gutnish: ''Gutar'') were a North Germanic tribe inhabiting the island of Gotland. The ethnonym is related to that of the ''Goths'' (''Gutans''), and both names were originally Proto-Germanic *''Gutan ...
, and sites such as the Ajvide Settlement
The Ajvide Settlement () is located in Ajvide, Eksta, on the western coast of Gotland, Sweden. It covers an area of and was occupied from the Late Mesolithic through to the mid Bronze Age. The majority of the activity on the site took place du ...
show that it has been occupied since prehistory
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use ...
.Outram, A. K. 2006Distinguishing bone fat exploitation from other taphonomic processes: what caused the high level of bone fragmentation at the Middle Neolithic site of Ajvide, Gotland?
, pp. 32–43. In Mulville, J and Outram, A (eds). ''The Zooarchaeology of Milk and Fats''. Oxford: Oxbow Books. A DNA study conducted on the 5,000-year-old skeletal remains of three Middle Neolithic seal hunters from Gotland showed that they were related to modern-day
Finns
Finns or Finnish people (, ) are a Baltic Finns, Baltic Finnic ethnic group native to Finland. Finns are traditionally divided into smaller regional groups that span several countries adjacent to Finland, both those who are native to these cou ...
, while a farmer from Gökhem
Gökhem in Västergötland was originally part of Vilske härad and is since 1974, a part of the Falköping Municipality
Falköping Municipality () is a municipalities of Sweden, municipality in Västra Götaland County in western Sweden. Its se ...
parish in Västergötland
Västergötland (), also known as West Gothland or the Latinized version Westrogothia in older literature, is one of the 25 traditional non-administrative provinces of Sweden (''landskap'' in Swedish), situated in the southwest of Sweden.
Vä ...
on the mainland was found to be more closely related to modern-day Mediterraneans. This is consistent with the spread of agricultural peoples from the Middle East at about that time.
Gutasaga
Gutasaga (''Gutasagan'') is a saga regarding the history of Gotland before its Christianization. It was recorded in the 13th century and survives in only a single manuscript, the Codex Holm. B 64, dating to , kept at the National Library of Sweden ...
contains legends of how the island was settled by Þieluar and populated by his descendants. It also tells that a third of the population had to emigrate and settle in southern Europe, a tradition associated with the migration of the Goths
The Goths were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe. They were first reported by Graeco-Roman authors in the 3rd century AD, living north of the Danube in what is ...
, whose name has the same origin as ''Gutes'', the native name of the people of the island. It later tells that the Gutes voluntarily submitted to the king of Sweden and asserts that the submission was based on mutual agreement, and notes the duties and obligations of the Swedish King and Bishop in relationship to Gotland. According to some historians, it is therefore an effort not only to write down the history of Gotland, but also to assert Gotland's independence from Sweden.
It gives Awair Strabain
Awair Strabain or ''Avar Stråben'' ("straw-legs") was according to the Gutasaga a chieftain from Alva socken on Gotland and a wise and able man.
The Gutasaga relates how many kinds attacked the island of Gotland in heathen times, but the gute ...
as the name of the man who arranged the mutually beneficial agreement with the king of Sweden; the event would have taken place before the end of the ninth century, when Wulfstan of Hedeby
Wulfstan of Hedeby was a late ninth-century traveller and trader. His travel accounts, as well as those of another trader, Ohthere of Hålogaland, were included in the ''Old English Orosius''. It is unclear if Wulfstan was England, English or in ...
reported that the island was subject to the Swedes:
The number of Arab dirham
The dirham, dirhem or drahm is a unit of currency and of mass. It is the name of the currencies of Moroccan dirham, Morocco, the United Arab Emirates dirham, United Arab Emirates and Armenian dram, Armenia, and is the name of a currency subdivisi ...
s discovered on the island of Gotland alone is astoundingly high. In the various hoard
A hoard or "wealth deposit" is an archaeological term for a collection of valuable objects or artifacts, sometimes purposely buried in the ground, in which case it is sometimes also known as a cache. This would usually be with the intention of ...
s located around the island, there are more of these silver coins than at any other site in Western Eurasia. The total sum is almost as great as the number that has been unearthed in the entire Muslim world. These coins moved north through trade between Rus
Rus or RUS may refer to:
People
* East Slavic historical peoples (). See Names of Rus', Russia and Ruthenia
** Rus' people, the people of Rus'
** Rus, a legendary eponymous ancestor, see Lech, Czech and Rus
* Rus (surname), a surname found in Ro ...
merchants and the Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate or Abbasid Empire (; ) was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib (566–653 CE), from whom the dynasty takes ...
, along the Silver-Fur Road, and the money made by Scandinavian merchants would help northern Europe, especially Viking Scandinavia and the Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–887) was a Franks, Frankish-dominated empire in Western and Central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as List of Frankish kings, kings of the Franks since ...
, as major commercial centers for the next several centuries.
The Berezan' Runestone
The Berezan' Runestone (rundata, X UaFv1914;47) was discovered in 1905 by Ernst von Stern, professor at Odessa, on Berezan Island, Berezan' Island (also known as the Island of St Aitherios) where the Dnieper River meets the ...
, discovered in 1905 in Ukraine, was made by a Varangian
The Varangians ( ; ; ; , or )Varangian
," Online Etymology Dictionary were
 The
The
 Early on, Gotland became a commercial center, with the town of Visby the most important
Early on, Gotland became a commercial center, with the town of Visby the most important
 Since the Treaty of Brömsebro in 1645, the island has remained under Swedish rule.
On 19 September 1806,
Since the Treaty of Brömsebro in 1645, the island has remained under Swedish rule.
On 19 September 1806,  On 22 April 1808, during the
On 22 April 1808, during the
 Gotland was granted its arms in about 1560. The
Gotland was granted its arms in about 1560. The


 Gotland is Sweden's largest island, and it is the largest island fully encompassed by the Baltic Sea (with Denmark's
Gotland is Sweden's largest island, and it is the largest island fully encompassed by the Baltic Sea (with Denmark's
helagotland.se alternatively referred to in other reports as a "modular-structured rapid response Army battalion". A later report claimed that plans were at an advanced stage for a support helicopter squadron and an Air Force "fast response Gripen jet squadron" to also be based on the island to support the new garrison and further reinforce the defences. Prior to the disbandment of the original garrison, there had been a continuous Swedish military presence on Gotland in one form or another, for nearly 200 years. After the standing down of the original garrison, a battalion of the Gotland currently has no local air defence capability. Despite its importance as a naval base in the past, , there are no naval units based on Gotland. The Tofta firing range itself (also known as the Tofta Tank firing range), is a military training ground which is located south of Visby. Another less common name for the range is the Toftasjön firing range. Tracing its origins back to 1898, the range extended over . It was a major training and storage facility for the Gotland garrison during its existence, and was still occasionally used for training by various elements of the
Gotland currently has no local air defence capability. Despite its importance as a naval base in the past, , there are no naval units based on Gotland. The Tofta firing range itself (also known as the Tofta Tank firing range), is a military training ground which is located south of Visby. Another less common name for the range is the Toftasjön firing range. Tracing its origins back to 1898, the range extended over . It was a major training and storage facility for the Gotland garrison during its existence, and was still occasionally used for training by various elements of the

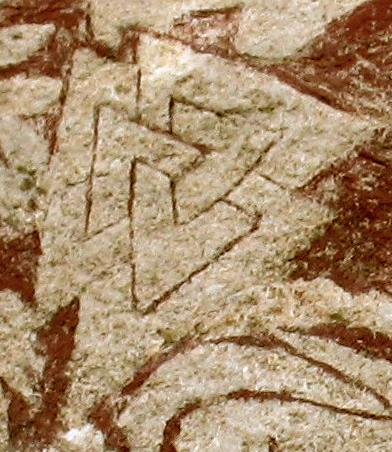 The Medieval town of Visby has been entered as a site of the
The Medieval town of Visby has been entered as a site of the
 In 2012, there were 171 registered sports organizations on Gotland.
Gotland has two senior women's sport teams playing in the first tiers:
In 2012, there were 171 registered sports organizations on Gotland.
Gotland has two senior women's sport teams playing in the first tiers:
 A number of
A number of
LIBRIS
''Gotland, facts and statistics 2013'', pdf, Gotland County.
Important years in Gotland' s history
''GotslandsResor'' tourist website
Official portal for Gotland County
Gotland administrative portal
Swedish Radio on Gotland, P4
Portal on Gotland with detailed facts about everything on the island
Commercial portal on Gotland
Official Gotland Tourist Association
Famous footprints – traveling on Gotland
Portal for eastern Gotland – Östergarnslandet
Portal for eastern Gotland – Ljugarn
Interactive map of Gotland
A short video (with music) with footage of the Gotland Grand National 2007
Gotland Grand National (GGN) webpage
(''Nordic Sport & Event'') {{Authority control Islands of Gotland County Important Bird Areas of Sweden Important Bird Areas of Baltic islands Swedish islands in the Baltic Ramsar sites in Sweden Provinces of Sweden
," Online Etymology Dictionary were
Viking
Vikings were seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway, and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded, and settled throughout parts of Europe.Roesdahl, pp. 9� ...
) trader named Grani in memory of his business partner
A business partner is a commercial entity with which another commercial entity has some form of alliance. This relationship may be a contractual, exclusive bond in which both entities commit not to ally with third parties. Alternatively, it may be ...
Karl. It is assumed that they were from Gotland.
Notable archaeological findings
 The
The Mästermyr chest
The Mästermyr chest is a Viking Age (789–1066) tool chest found in the Mästermyr mire west of Hemse on the island of Gotland, Sweden. It is the largest tool find from that era in Europe.
History
During the Viking Age, the area where Mäster ...
, an important artefact from the Viking Age
The Viking Age (about ) was the period during the Middle Ages when Norsemen known as Vikings undertook large-scale raiding, colonising, conquest, and trading throughout Europe and reached North America. The Viking Age applies not only to their ...
, was found in Gotland.
On 16July 1999, the world's largest Viking silver treasure, the Spillings Hoard
The Spillings Hoard () is the world's largest Viking silver treasure, found on Friday 16July 1999 in a field at the Spilling farm northwest of Slite, on northern Gotland, Sweden. The silver hoard consisted of two parts with a total weight of bef ...
, was found in a field at Spillings farm northwest of Slite
Slite is a locality situated in Gotland Municipality, Gotland County, on the island of Gotland, Sweden with 1,500 inhabitants in 2014.
Geography
Slite is situated on the northern east coast of Gotland. The town is divided by the Sjuströmmar in ...
. The silver treasure was divided into two parts weighing a total of ( and ) and consisted mostly of coins, about 14,000, from foreign countries, mostly Islamic. It also contained about of bronze objects along with numerous everyday objects such as nails, glass beads, parts of tools, pottery, iron bands and clasps. The treasure was found by using a metal detector, and the finders fee, given to the farmer who owned the land, was over 2 million kronor (about US$308,000). The treasure was found almost by accident while filming a news report for TV4 TV4 or TV 4 may refer to:
*TV4 (Polish TV channel), a private Polish television station
*TV4 (Swedish TV channel), a Swedish television network
**TV4 AB, owners of the Swedish television station
*SABC TV4, a channel operated by the South African st ...
about illegal treasure hunting on Gotland.
Middle Ages
 Early on, Gotland became a commercial center, with the town of Visby the most important
Early on, Gotland became a commercial center, with the town of Visby the most important Hanseatic
The Hanseatic League was a Middle Ages, medieval commercial and defensive network of merchant guilds and market towns in Central Europe, Central and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Growing from a few Northern Germany, North German towns in the ...
city in the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
. In late medieval times, the island had twenty district courts ( tings), each represented by its elected judge at the island-ting, called ''landsting''. New laws were decided at the landsting, which also took other decisions regarding the island as a whole. The earliest recorded law for the island is Gutalagen
Gutalagen (or Guta lag; "The law of the Gotlanders") is the earliest preserved law book for Gotland. The laws were likely first written down around 1220 CE but there is evidence for the laws being older than this, with some aspects likely being ...
, which was written around 1220 CE and remained in use until 1645 when Sweden regained control of the island from Denmark.
The city of Visby and rest of the island were governed separately, and a civil war caused by conflicts between the German merchants in Visby and the peasants they traded with in the countryside had to be put down by King Magnus III of Sweden
Magnus, meaning "Great" in Latin, was used as cognomen of Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus in the first century BC. The best-known use of the name during the Roman Empire is for the fourth-century Western Roman Emperor Magnus Maximus. The name gained wid ...
in 1288. In 1361, Valdemar Atterdag of Denmark invaded the island. About 1,500 Gotlandic farmers were killed by the Danish invaders after massing for the Battle of Mästerby
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force co ...
. The Victual Brothers
The Victual Brothers () were a loosely organized guild of privateers who later turned to piracy. They affected maritime history, maritime trade during the 14th century in both the North Sea, North and Baltic Sea, Baltic Seas.
They were initially ...
occupied the island in 1394 to set up a stronghold as a headquarters of their own in Visby. At last, Gotland became a fief
A fief (; ) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form of feudal alle ...
of the Teutonic Knights
The Teutonic Order is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem was formed to aid Christians on their pilgrimages to t ...
, awarded to them on the condition that they expel the piratical Victual Brothers from their fortified sanctuary
A sanctuary, in its original meaning, is a sacred space, sacred place, such as a shrine, protected by ecclesiastical immunity. By the use of such places as a haven, by extension the term has come to be used for any place of safety. This seconda ...
. An invading army of Teutonic Knights conquered the island in 1398, destroying Visby and driving the Victual Brothers from Gotland. In 1409, Grand Master Ulrich von Jungingen
Ulrich von Jungingen (1360 – 15 July 1410) was the 26th Grand Master of the Teutonic Knights, serving from 1407 to 1410. His policy of confrontation with the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Kingdom of Poland would spark the Polish–Lithuan ...
of the Teutonic Knights guaranteed peace with the Kalmar Union
The Kalmar Union was a personal union in Scandinavia, agreed at Kalmar in Sweden as designed by Queen Margaret I of Denmark, Margaret of Denmark. From 1397 to 1523, it joined under a single monarch the three kingdoms of Denmark, Sweden (then in ...
of Scandinavia
Scandinavia is a subregion#Europe, subregion of northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. It can sometimes also ...
by selling the island of Gotland to Queen Margaret of Denmark, Norway and Sweden.
The authority of the landsting was successively eroded after the island was occupied by the Teutonic Order, then sold to Eric of Pomerania
Erik of Pomerania ( 1381/1382 – 24 September 1459) ruled over the Kalmar Union from 1396 until 1439. He was initially co-ruler with his great-aunt Margaret I of Denmark, Margaret I until her death in 1412. Erik is known as Erik III as King of ...
and after 1449 ruled by Danish governors. In late medieval times, the ting consisted of twelve representatives for the farmers, free-holders or tenants.
Early modern period
 Since the Treaty of Brömsebro in 1645, the island has remained under Swedish rule.
On 19 September 1806,
Since the Treaty of Brömsebro in 1645, the island has remained under Swedish rule.
On 19 September 1806, Gustav IV Adolf
Gustav IV Adolf or Gustav IV Adolph (1 November 1778 – 7 February 1837) was King of Sweden from 1792 until he was deposed in a coup in 1809. He was also the last Swedish monarch to be the ruler of Finland.
The occupation of Finland in 180 ...
offered the sovereignty of Gotland to the Order of St. John of Jerusalem
The Order of Knights of the Hospital of Saint John of Jerusalem, commonly known as the Knights Hospitaller (), is a Catholic military order. It was founded in the crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem in the 12th century and had headquarters there un ...
, who had been expelled from Malta
Malta, officially the Republic of Malta, is an island country in Southern Europe located in the Mediterranean Sea, between Sicily and North Africa. It consists of an archipelago south of Italy, east of Tunisia, and north of Libya. The two ...
in 1798, but the Order rejected the offer since it would have meant renouncing their claim to Malta. The Order never regained its territory, and eventually it reestablished itself in Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
as the Sovereign Military Order of Malta
The Sovereign Military Order of Malta (SMOM), officially the Sovereign Military Hospitaller Order of Saint John of Jerusalem, of Rhodes and of Malta, and commonly known as the Order of Malta or the Knights of Malta, is a Catholic lay religious ...
.
 On 22 April 1808, during the
On 22 April 1808, during the Finnish War
The Finnish War (; ; ) was fought between the Gustavian era, Kingdom of Sweden and the Russian Empire from 21 February 1808 to 17 September 1809 as part of the Napoleonic Wars. As a result of the war, the eastern third of Sweden was established a ...
between Sweden and Russia, a Russian army landed on the southeastern shores of Gotland near Grötlingbo
Grötlingbo is a populated area, a socken (not to be confused with parish), on the Swedish island of Gotland. It comprises the same area as the administrative Grötlingbo District, established on 1January 2016.
The Kattlund farm in Grötlingbo ...
. Under command of Nikolai Andreevich Bodisko 1,800 Russians took the city of Visby
Visby () is an urban areas in Sweden, urban area in Sweden and the seat of Gotland Municipality in Gotland County on the island of Gotland with 24,330 inhabitants . Visby is also the episcopal see for the Diocese of Visby. The Hanseatic League, ...
without any combat or engagement, and occupied the island. A Swedish naval force rescue expedition was sent from Karlskrona
Karlskrona (, , ) is a locality and the seat of Karlskrona Municipality, Blekinge County, Sweden with a population of 66,675 in 2018. It is also the capital of Blekinge County. Karlskrona is known as Sweden's only baroque city and is host to ...
under the command of admiral Rudolf Cederström
Olof Rudolf Cederström (8 February 1764 – 1 June 1833) was a Sweden, Swedish naval commander. Cederström enlisted in the Sweden, Swedish admiralty in 1779 and as captain, he conducted a raid against Paldiski, Rogervik. He distinguished himself ...
with 2,000 men; the island was liberated and the Russians capitulated. Russian forces left the island on 18 May 1808.
Administration
The traditionalprovinces of Sweden
The 25 provinces of Sweden () are historical, geographical and cultural regions. They have no administrative function, but retain their own cultural identities, dialects and folklore.
Several were administrative subdivisions until 1634, when t ...
serve no administrative or political purposes today, but are historical and cultural entities. In the case of Gotland, however, due to its insular position, the administrative county
A county () is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesL. Brookes (ed.) '' Chambers Dictionary''. Edinburgh: Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, 2005. in some nations. The term is derived from the Old French denoti ...
(''län''), Gotland County
Gotland County () is a county or of Sweden. Gotland is located in the Baltic Sea to the east of Öland, and is the largest of Sweden's islands. Counties are usually sub-divided into municipalities, but Gotland County consists of only one count ...
, and the municipality
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having municipal corporation, corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality' ...
(''kommun''), Region Gotland
Region Gotland, legally Gotlands kommun ('), is a municipality with regional responsibilities that covers the entire island of Gotland in Sweden. The city of Visby is the municipality's seat. Gotland Municipality is the 39th most populous municip ...
, both cover the same territory as the province. Furthermore, the diocese of Visby
The Diocese of Visby () is a division of the Church of Sweden consisting of the island of Gotland. Its seat is Visby Cathedral located in the largest town on Gotland, Visby.
The Bishop of Visby is also responsible for the episcopal oversight of ...
is also congruent with the province. Gotland is traditionally divided into 92 socken
Socken ( or ) is the name used for a part of a counties of Sweden, county in Sweden. In Denmark, similar areas are known as , in Norway or and in Finland or . A is a rural area formed around a church, typically in the Middle Ages. A socken ...
s. On 1January 2016, they were all reconstituted into Districts
A district is a type of administrative division that in some countries is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivisions ...
, administrative areas with the same borders as the former sockens.
Heraldry
coat of arms
A coat of arms is a heraldry, heraldic communication design, visual design on an escutcheon (heraldry), escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the last two being outer garments), originating in Europe. The coat of arms on an escutcheon f ...
is represented with a ducal coronet. Blazon: "Azure a ram statant Argent armed Or holding on a cross-staff of the same a banner Gules bordered and with five tails of the third." The county was granted the same coat of arms in 1936. The municipality, created in 1971, uses the same picture, but with other tinctures
A tincture is typically an extract of plant or animal material dissolution (chemistry), dissolved in ethanol (ethyl alcohol). Solvent concentrations of 25–60% are common, but may run as high as 90%.Groot Handboek Geneeskrachtige Planten by Ge ...
.
Geography

 Gotland is Sweden's largest island, and it is the largest island fully encompassed by the Baltic Sea (with Denmark's
Gotland is Sweden's largest island, and it is the largest island fully encompassed by the Baltic Sea (with Denmark's Zealand
Zealand ( ) is the largest and most populous islands of Denmark, island in Denmark proper (thus excluding Greenland and Disko Island, which are larger in size) at 7,031 km2 (2715 sq. mi.). Zealand had a population of 2,319,705 on 1 Januar ...
at the Baltic's edge). With its total area of the island of Gotland and the other areas of the province of Gotland make up 0.8% of Sweden's total land area. The province includes the small islands of Fårö and Gotska Sandön to the north, as well as the Karlsö Islands, (Lilla and Stora) to the west, which are even smaller. The island of Gotland has an area of , whereas the province has of land excluding the lakes and rivers The population is 61,001 as of December 2021. As of 2016, approximately 23,600 people (about 40% of residents) lived in Visby, which is the seat of the municipality and the capital of the county.
Gotland is located about east of the Swedish mainland and about from the Baltic states
The Baltic states or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term encompassing Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, and the OECD. The three sovereign states on the eastern co ...
, Latvia
Latvia, officially the Republic of Latvia, is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is one of the three Baltic states, along with Estonia to the north and Lithuania to the south. It borders Russia to the east and Belarus to t ...
being the nearest. Gotland is the name of the main island, but the adjacent islands are generally considered part of Gotland and the Gotlandic culture:
* Furillen
Furillen (older spelling Furilden) is an island in Rute on the northeast coast of Gotland, Sweden. For most of the 20th century, there was a limestone industry on the island until it was closed to the public by the Swedish military in the 1970s� ...
* Fårö
Fårö () or in Gutnish is a Baltic Sea island just north of the island of Gotland, itself off mainland Sweden's southeastern coast. It is the second-largest island in the county and it is a popular summer resort. It has its own language, Fårö ...
* Gotska Sandön
Gotska Sandön (literally translated as "The Gotlandic Sand Island") is an uninhabited Swedish island north of Gotland in the Baltic Sea. It has been a national park since 1909.
Geography
Sandön is situated north of Fårö in the Baltic Se ...
, a National park of Sweden
* The Karlsö Islands (Stora Karlsö
Stora Karlsö is a small Swedish island in the Baltic Sea, situated about west of the island of Gotland and part of Eksta socken.
Environment
Stora Karlsö has an area of about . It is mainly a limestone plateau, up to in height, bordered by ...
and Lilla Karlsö
Lilla Karlsö is a small Swedish island in the Baltic Sea, situated about off the west coast of Gotland and from Stora Karlsö; it is part of Eksta socken. During summer there are tour boats from Djupvik south of Klintehamn.
Environment
The ...
)
* Laus holmar
* Ytterholmen
* Östergarnsholm
There are several shallow lakes located near the shores of the island. The biggest is Lake Bästeträsk, located near Fleringe
Fleringe is a populated area, a socken (not to be confused with parish), on the Swedish island of Gotland. It comprises the same area as the administrative Fleringe District, established on 1January 2016.
Community
The name is known since 1304 ...
in the northern part of Gotland. The Hoburg Shoal
Hoburg Shoal, also known as Hoburgs bank, is a shoal located in the Baltic Sea, in the southern zone of the Gotland shelf, south of Hoburgen.
The shoal is a bird reserve encompassing about .
Geography
It is a long shoal, comprising a northern a ...
bird reserve
A bird reserve (also called ornithological reserve) is a wildlife refuge designed to protect bird species. Like other wildlife refuges, the main goal of a reserve is to prevent species from becoming endangered or extinct. Typically, bird species in ...
is situated on the southern tip of the island. The highest point of the island is Lojsta Hed which stands above sea level. The average height of the island is 29 meters.
Settlements besides Visby include:
* Burgsvik
Burgsvik is a locality situated in Öja in the Swedish island of Gotland with 350 inhabitants in 2014. Burgsvik lies in the southern part of the island of Gotland
Gotland (; ; ''Gutland'' in Gutnish), also historically spelled Gottland or Go ...
* Fårösund
Fårösund is a locality situated on the Swedish island of Gotland with 800 inhabitants in 2014. The village can be reached by car from Visby. The island of Fårö can be reached by ferry from Fårösund.
Fårösund is the northernmost town in t ...
* Hemse
Hemse is a locality situated on the Swedish island of Gotland with 1,700 inhabitants in 2014. It is the second largest locality (after Visby) on the island. Hemse is the main center of population in the southern part of the island, and it is know ...
* Klintehamn
Klintehamn () is a locality in Klinte on the Swedish island of Gotland with 1,350 inhabitants in 2010.
Transportation
Klintehamn is a shipping port on the west coast of Gotland where timber and agricultural products are shipped to mainland Swe ...
* Roma
Roma or ROMA may refer to:
People, characters, figures, names
* Roma or Romani people, an ethnic group living mostly in Europe and the Americas.
* Roma called Roy, ancient Egyptian High Priest of Amun
* Roma (footballer, born 1979), born ''Paul ...
* Slite
Slite is a locality situated in Gotland Municipality, Gotland County, on the island of Gotland, Sweden with 1,500 inhabitants in 2014.
Geography
Slite is situated on the northern east coast of Gotland. The town is divided by the Sjuströmmar in ...
* Tofta
* Vibble
Vibble is a locality in Västerhejde on the Swedish island of Gotland. Sweden with 1,300 inhabitants in 2010. Situated south of Visby, it is sometimes regarded as a suburb to the town of Visby. The main business in Vibble is tourism. The relocated ...
Of these, Hemse is the largest settlement in southern Gotland and along with Roma the two largest inland villages. Burgsvik is the southernmost locality and Fårösund the northernmost. The island of Fårö is permanently settled, but with only a few hundred year-round residents and lacks a permanent fixed link to the main island. Residents are depending on an around the clock, free of charge, car ferry for transportation over a strait roughly wide, taking about eight minutes. Fårö may get connected to the main island with a bridge
A bridge is a structure built to Span (engineering), span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or railway) without blocking the path underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, whi ...
in the future, but the project has had plenty of delays related to funding. At the closest point, the two islands are separated by less than , although that is at a distance from road connections.
Slite is the largest settlement on Gotland's sparsely populated east coast. The eastern coast of Gotland, including the adjacent marine waters and islets, has been designated an 150,000 ha Important Bird Area
An Important Bird and Biodiversity Area (IBA) is an area identified using an internationally agreed set of criteria as being globally important for the conservation of bird populations.
IBA was developed and sites are identified by BirdLife Int ...
(IBA) by BirdLife International
BirdLife International is a global partnership of non-governmental organizations that strives to conserve birds and their habitats. BirdLife International's priorities include preventing extinction of bird species, identifying and safeguarding i ...
because it supports a suite of waterfowl
Anseriformes is an order of birds also known as waterfowl that comprises about 180 living species of birds in three families: Anhimidae (three species of screamers), Anseranatidae (the magpie goose), and Anatidae, the largest family, which i ...
, wader
245px, A flock of Red_knot.html" ;"title="Dunlins and Red knot">Dunlins and Red knots
Waders or shorebirds are birds of the order Charadriiformes commonly found wikt:wade#Etymology 1, wading along shorelines and mudflats in order to foraging, ...
s and tern
Terns are seabirds in the family Laridae, subfamily Sterninae, that have a worldwide distribution and are normally found near the sea, rivers, or wetlands. Terns are treated in eleven genera in a subgroup of the family Laridae, which also ...
s.
Climate
Gotland has a semi-continental variety of amarine climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate or maritime climate, is the temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification represented as ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring co ...
(Cfb CFB may refer to:
*College football, in the United States
*Canadian Forces base, military installation of the Canadian forces
* Caminho de Ferro de Benguela, railway in Angola
*Carrollton-Farmers Branch Independent School District
*Cipher feedback, ...
). This results in larger seasonal differences than typical of marine climates in spite of it being surrounded by the Baltic Sea for large distances in all directions. This is due to strong continental winds travelling over the sea from surrounding great landmasses.
Seasonal temperature variation is smaller in more isolated places on the island such as Hoburgen or Östergarnsholm, having warmer autumn and winter, but are cooler during spring and summer days.
Seasonal lag being exceptionally strong in the weather station Östergarnsholm. As an example, December is warmer than March with temperature lows being similar to April. August is typically the warmest month, an unusual occurrence in Swedish sites. In capital Visby, July and August temperatures tend to be quite even.
Since winters usually remain just above freezing and brackish water
Brackish water, sometimes termed brack water, is water occurring in a natural environment that has more salinity than freshwater, but not as much as seawater. It may result from mixing seawater (salt water) and fresh water together, as in estuary ...
remaining liquid longer than freshwater, the sea remains ice-free all year round, except during rare extreme cold wave
A cold wave (known in some regions as a cold snap, cold spell or Arctic Snap) is a weather phenomenon that is distinguished by a cooling of the air. Specifically, as used by the U.S. National Weather Service, a cold wave is a rapid fall in temp ...
s. The last time the whole passage from the mainland to Gotland froze was in 1987 when icebreaker
An icebreaker is a special-purpose ship or boat designed to move and navigate through ice-covered waters, and provide safe waterways for other boats and ships. Although the term usually refers to ice-breaking ships, it may also refer to smaller ...
s were used to maintain passenger and goods traffic to the island.
Geology
Gotland is made up of a sequence ofsedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock (geology), rock formed by the cementation (geology), cementation of sediments—i.e. particles made of minerals (geological detritus) or organic matter (biological detritus)—that have been accumulated or de ...
s of a Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 23.5 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the third and shortest period of t ...
age, dipping to the south-east.
The main Silurian succession of limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science) ...
s and shale
Shale is a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock formed from mud that is a mix of flakes of Clay mineral, clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g., Kaolinite, kaolin, aluminium, Al2Silicon, Si2Oxygen, O5(hydroxide, OH)4) and tiny f ...
s comprises thirteen units spanning of stratigraphic thickness, being thickest in the south, and overlies a thick Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and System (geology), system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era (geology), Era, and the second of twelve periods of the Phanerozoic Eon (geology), Eon. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years f ...
sequence.
It was deposited in a shallow, hot, and salty sea on the edge of an equatorial continent. The water depth never exceeded , and became shallower over time as bioherm
A reef knoll is a landform that comprises an immense pile of calcareous material that had previously accumulated on an ancient sea floor. Reef knolls are geological remnants of reefs and other organic concentrations of calcareous organisms. Reef kn ...
detritus and terrestrial sediments filled the basin. Reef growth started in the Llandovery Epoch, when the sea was , and reefs continued to dominate the sedimentary record. Some sandstones are present in the youngest rocks towards the south of the island, which represent sand bars deposited very close to the shoreline.
The lime rocks have been weathered into characteristic karst
Karst () is a topography formed from the dissolution of soluble carbonate rocks such as limestone and Dolomite (rock), dolomite. It is characterized by features like poljes above and drainage systems with sinkholes and caves underground. Ther ...
ic rock formations
A rock formation is an isolated, scenic, or spectacular surface rock (geology), rock outcrop. Rock formations are usually the result of weathering and erosion sculpting the existing rock. The term ''rock Geological formation, formation ...
known as rauk
A rauk is a column-like landform in Sweden, often equivalent to a stack (geology), stack. Rauks often occur in groups called ''raukfält'' 'rauk fields'. The limestone rauks of Gotland in the Baltic Sea are among the best known examples.
Sweden ...
s. Fossils, mainly of crinoid
Crinoids are marine invertebrates that make up the class Crinoidea. Crinoids that remain attached to the sea floor by a stalk in their adult form are commonly called sea lilies, while the unstalked forms, called feather stars or comatulids, are ...
s, rugose
Rugose means "wrinkled". It may refer to:
* Rugosa, an extinct order of coral, whose rugose shape earned it the name
* Rugose, adjectival form of rugae
Species with "rugose" in their names
* ''Idiosoma nigrum'', more commonly, a black rugose tra ...
coral
Corals are colonial marine invertebrates within the subphylum Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact Colony (biology), colonies of many identical individual polyp (zoology), polyps. Coral species include the important Coral ...
s and brachiopod
Brachiopods (), phylum (biology), phylum Brachiopoda, are a phylum of animals that have hard "valves" (shells) on the upper and lower surfaces, unlike the left and right arrangement in bivalve molluscs. Brachiopod valves are hinged at the rear e ...
s, are abundant throughout the island; palæo- sea-stacks are preserved in places.
Economy
The island's main sources of income are agriculture along with food processing, tourism, IT solutions, design and some heavy industry such as concrete production from locally minedlimestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science) ...
. Most of Gotland's economy is based on small scale production.
In 2012, there were over 7,500 registered companies on Gotland. 1,500 of these had more than one employee. Gotland has the world's northernmost established vineyard and winery, located in Hablingbo
Hablingbo () is a populated area, a ''socken'' (not to be confused with parish), on the Swedish island of Gotland. It comprises the same area as the administrative Hablingbo District, established on 1January 2016.
In 1961, the Havor Hoard was f ...
.
Military
Gotland occupies a strategic location in the Baltic sea from a defence viewpoint. In March 2015, the Swedish government decided to begin reestablishing a permanent military presence on Gotland, starting with an initial 150 troop garrison, consisting primarily of elements from theSwedish Army
The Swedish Army () is the army, land force of the Swedish Armed Forces of the Kingdom of Sweden. Beginning with its service in 1521, the Swedish Army has been active for more than 500 years.
History
Svea Life Guards dates back to the year 1 ...
. It has been reported that the bulk of this initial garrison will make up a new motorised rifle battalion,Gotland får permanent militär styrkahelagotland.se alternatively referred to in other reports as a "modular-structured rapid response Army battalion". A later report claimed that plans were at an advanced stage for a support helicopter squadron and an Air Force "fast response Gripen jet squadron" to also be based on the island to support the new garrison and further reinforce the defences. Prior to the disbandment of the original garrison, there had been a continuous Swedish military presence on Gotland in one form or another, for nearly 200 years. After the standing down of the original garrison, a battalion of the
Swedish Home Guard
The Home Guard – National Security Forces () is a military reserve force of the Swedish Armed Forces. It was formally established on May 29, 1940, during World War II upon popular demand. While originally composed of former militia groups, tod ...
is based on Gotland for emergencies as part of the Eastern Military Region (''MR E''). The unit, ''32:a Gotlandsbataljonen'' (the 32nd Gotland battalion), acts as a reserve component of the Swedish Amphibious Corps
The Amphibious Corps (, Amf) is the Marines, marine infantry arm of the Swedish Navy, with an emphasis on coastal defence. It has its roots in the Swedish Coastal Artillery, coastal artillery (, KA) but after the end of the Cold War it was seen as ...
. Among the residual war reserve stock
A war reserve stock (WRS)/pre-positioned stocks (PPS), is a collection of warfighting materiel held in reserve in pre-positioned storage to be used if needed in wartime. They may be located strategically depending on where it is believed they will ...
s reported to be still in storage on Gotland in March 2015, were 14 tanks (Stridsvagn 122
Stridsvagn 122 (strv 122, ) is a Swedish main battle tank that, like the German Leopard 2A5, is based on the German Leopard 2 Improved variant using such newer technology as command, control, and fire-control systems, reinforced armour, and ...
s) at the ''Tofta skjutfält'' (the Tofta firing range), but without any crews or dedicated maintenance personnel assigned to them.
 Gotland currently has no local air defence capability. Despite its importance as a naval base in the past, , there are no naval units based on Gotland. The Tofta firing range itself (also known as the Tofta Tank firing range), is a military training ground which is located south of Visby. Another less common name for the range is the Toftasjön firing range. Tracing its origins back to 1898, the range extended over . It was a major training and storage facility for the Gotland garrison during its existence, and was still occasionally used for training by various elements of the
Gotland currently has no local air defence capability. Despite its importance as a naval base in the past, , there are no naval units based on Gotland. The Tofta firing range itself (also known as the Tofta Tank firing range), is a military training ground which is located south of Visby. Another less common name for the range is the Toftasjön firing range. Tracing its origins back to 1898, the range extended over . It was a major training and storage facility for the Gotland garrison during its existence, and was still occasionally used for training by various elements of the Armed Forces
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. Militaries are typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with their members identifiable by a ...
since the garrison was shut down in 2005. However, from the second half of 2014 onwards, there has been a marked increase in the use of the range, especially by armored units (mostly company sized), as tensions in Northeastern Europe have escalated. At least one of the buildings on the range, the former tank repair shop, is currently owned by a private company (Peab
Peab AB (originally Paulsson Entreprenad AktieBolag ) is a construction and civil engineering company headquartered in Förslöv, Scania, listed on NASDAQ OMX Stockholm. It is the third largest construction company in Sweden and the Nordic regi ...
), with the military renting back the top floor for its own use.
When not used by the military, a number of cultural and sports events have been held at the range, one of the most notable being the , the world's largest enduro
Enduro is a form of motorcycle sport run on extended cross-country, off-road courses. Enduro consists of many different obstacles and challenges. The main type of enduro event, and the format to which the World Enduro Championship is run, is ...
race, from 1984 to 2023.
During the late 2010s and early 2020s, Gotland has seen an increased focus on its strategic importance and an increase in military spending. The Gotland Regiment
The Gotland Regiment (, P 18) is a Swedish Army armoured warfare, armoured regiment which has been active in various forms between 1963–1994 and 2000–2005, when it was disbanded. The regiment was re-established on 1 January 2018. The regiment ...
was re-established in 2018, the first time since World War II that a new regiment has been established in Sweden. Following the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, , starting the largest and deadliest war in Europe since World War II, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, conflict between the two countries which began in 2014. The fighting has caused hundreds of thou ...
and Sweden's accession to NATO, military readiness on Gotland increased, with the Swedish government spending 150 million euros to expand military infrastructure on the island.
Tourism
The first modern day tourists came to Gotland during the 19th century and were known as "bathers". Gotland became very popular with socialites at the time throughPrincess Eugenie
Princess Eugenie, Mrs Jack Brooksbank ( ; Eugenie Victoria Helena; born 23 March 1990) is a member of the British royal family. She is the younger daughter of Prince Andrew, Duke of York, and Sarah, Duchess of York. She is a niece of King Cha ...
who lived in Västerhejde
Västerhejde is a locality on the Swedish island of Gotland.
Västerhejde is also the name of the larger populated area, socken (not to be confused with parish). It comprises the same area as the administrative Västerhejde District, established ...
, in the west part of the island from the 1860s.
When a new law ensuring two weeks vacation for all employees in Sweden was passed in 1938, camping became a popular pastime among the Swedes, and in 1955, Gotland was visited by 80,000 people. In the 1970s mostly young people were attracted to Gotland. Since 2010 the island has become a more versatile vacation spot visited by people from all over the world, in all manner of ways.
In 2001, it was the fifth largest tourist destination in Sweden based on the total number of guest nights. Gotland is usually the part of Sweden which receives the most hours of sunlight during a year with Visby statistically the location with the most sunshine in Sweden. In 2007 approximately 750,000 people visited Gotland.
In 1996, for the first time, ferries between Gotland and mainland Sweden carried more than 1 million passengers in a year. In 2007, the number of passengers exceeded 1.5 million. In 2012, the ferries had 1,590,271 passengers and the airlines 327,255 passengers. Even during the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
tourism did not change much as Swedes chose to visit the island instead of travelling abroad.
Cruise ships and new pier
The main port of call on Gotland is Visby. The city is visited by a number of cruise ships every year. About 40 cruise lines frequent the Baltic sea with Visby as one of their destinations. In 2005, 147 ships docked at Visby, in 2010 the number was 69. In 2014, 62 ships are scheduled to visit Visby. The decrease in visiting ships is due to the fact that the modern cruise ships are too large to enter Visby harbor. Ships must anchor a fair distance from shore whereupon passengers are shuttled to shore in small boats, which is not possible during bad weather. In 2007, the first proposition for building a new pier at Visby harbor, large enough to serve the modern cruise ships, was made. In 2011, the matter of the new pier was discussed in theRiksdag
The Riksdag ( , ; also or , ) is the parliament and the parliamentary sovereignty, supreme decision-making body of the Kingdom of Sweden. Since 1971, the Riksdag has been a unicameral parliament with 349 members (), elected proportional rep ...
and in 2012 research and planning for the pier began. In January 2014, a letter of intent for building a new cruise pier in Visby harbor was signed by Region Gotland
Region Gotland, legally Gotlands kommun ('), is a municipality with regional responsibilities that covers the entire island of Gotland in Sweden. The city of Visby is the municipality's seat. Gotland Municipality is the 39th most populous municip ...
and Copenhagen Malmö Port (CMP). The pier was finished in 2018. The estimated cost is 250 million crowns (about US$38.52 million).
Culture
A number of stones withgrooves
Groove or Grooves may refer to:
Music
* Groove (music)
* Groove (drumming)
* The Groove (band), an Australian rock/pop band of the 1960s
* The Groove (Sirius XM), a US radio station
* Groove 101.7FM, a former Perth, Australia, radio station
* ...
exist on Gotland. Archaeologists interpret these grooves as traces of an unknown industrial process in the High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the periodization, period of European history between and ; it was preceded by the Early Middle Ages and followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended according to historiographical convention ...
. There are approximately 3,700 grinding grooves, of which about 750 occur in the solid limestone outcrop and the rest in other rock formations. The latter often consist of hard rocks such as granite or gneiss, but also soft rocks such as sandstone occur. Grinding grooves are also found in Skåne, in southern Sweden and in Finland. Astronomer Göran Henriksson dates a number of these grinding grooves to the Stone Age, from to , based on astronomical alignments, although his methodology has been heavily criticized.

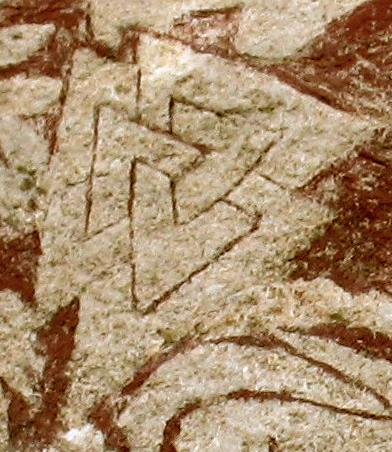 The Medieval town of Visby has been entered as a site of the
The Medieval town of Visby has been entered as a site of the UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
World heritage
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
programme. An impressive feature of Visby is the fortress wall that surrounds the old city, dating from the 13th century.
Many of the residents still speak Gutnish
Gutnish ( ), or rarely Gutnic ( or ), is a North Germanic language spoken sporadically on the islands of Gotland and Fårö. The different dialects of Gutnish, while stemming from the Old Gutnish () variety of Old Norse, are sometimes considere ...
(Gutamål), the autochthonous language
An indigenous language, or autochthonous language, is a language that is native to a region and spoken by its indigenous peoples. Indigenous languages are not necessarily national languages but they can be; for example, Aymara is both an indigeno ...
on the islands. But most of them now speak Gotlandic
Gotlandic () is the form of Swedish spoken on the islands of Gotland and Fårö in the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Pola ...
(), a Gutnish-influenced Swedish dialect. In the 13th century, a work containing the laws of the island, called "the Gotlandic law" (Gutalagen), was published in Old Gutnish
Old Gutnish was a stage in the development of the North Germanic language Gutnish, spoken on the Baltic Sea, Baltic island of Gotland and Fårö. The extant body of Old Gutnish is small, and Gutalagen and the Guta saga constitute its majority. ...
, as well as the Gutasaga
Gutasaga (''Gutasagan'') is a saga regarding the history of Gotland before its Christianization. It was recorded in the 13th century and survives in only a single manuscript, the Codex Holm. B 64, dating to , kept at the National Library of Sweden ...
.
Gotland is noted for its 94 Medieval churches
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
, most of which are restored and in active use. These churches exhibit two major styles of architecture: Romanesque and Gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, a Germanic people
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Gothic alphabet, an alphabet used to write the Gothic language
** Gothic ( ...
. The older churches were constructed in the Romanesque style from 1150 to 1250. The newer churches were constructed in the Gothic architectural style that prevailed from about 1250–1400. The oldest painting inside one of the churches on Gotland stretches as far back in time as the 12th century.
Traditional games of skill like Kubb
Kubb (pronounced in Swedish and Gutnish) is a lawn game where the objective is to knock over wooden blocks () by throwing wooden batons () at them. Kubb can be described as a combination of bowling and horseshoes. Play takes place on a sma ...
, Pärk
Pärk or Paerk is a game somewhat similar to a game of baseball but where the aim is to gain ground like in American football, that has been played for centuries on the island of Gotland in Baltic Sea. The game is played with two teams of 7 people ...
, and Varpa
Varpa is an outdoor game of physical skill that allegedly dates back to the Viking Age and survived in Gotland. It is similar to boules and horseshoes but is played with a flat and heavy object called a "varpa" instead of balls. Varpas used to ...
are played on Gotland. They are part of what has become called "Gutniska Lekar", and are performed preferably on the Midsummer's Eve celebration on the island, but also throughout the summer months. The games have widespread renown; some of them are played by people as far away as in the United States.
The knotwork design subsequently named the "Valknut
The valknut is a symbol consisting of three interlocked triangles forming subliminal triskelion at its center. It appears on a variety of objects from the archaeological record of the ancient Germanic peoples. The term ''valknut'' is a moder ...
" has the most attested historic instances on picture stone
A picture stone, image stone or figure stone is an ornate slab of stone, usually limestone, which was raised in Germanic Iron Age or Viking Age Scandinavia, and in the greatest number on Gotland.The article ''Bildstenar'' in ''Nationalencyklopedi ...
s in Gotland, which include being on both the Stora Hammars I and the Tängelgårda stones.
Gotland also has a rich heritage of folklore, including myths about the bysen, '' Di sma undar jordi'', Hoburgsgubben and the Martebo lights.
Gotland gives its name to the traditional farmhouse ale Gotlandsdricka
Gotlandsdricka (in modern Gutnish ''drikke'' or ''drikko'', and ''drikku'') is a traditional homebrewing, homebrewed alcoholic beverage made on the island of Gotland, Sweden. It is a kind of ale, closely related to the Finnish ''sahti'', and Norwe ...
, a turbid beer with much in common with Finnish sahti
Sahti is a Finnish type of farmhouse ale made from malted and unmalted grains including barley and rye. Traditionally the beer is flavored with juniper in addition to, or instead of, hops;
, and related beers from the Baltic states
The Baltic states or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term encompassing Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, and the OECD. The three sovereign states on the eastern co ...
.
Notable people
There are a number of notable people born or living on Gotland, or in other major ways associated with the island.Sport
Events
* Gotland competes in the biennialIsland Games
The Island Games (currently known as the NatWest International Island Games for sponsorship reasons) are biennial international multi-sports events organised by the International Island Games Association (IIGA). Competitor teams each represent ...
, which it hosted in 1999
1999 was designated as the International Year of Older Persons.
Events January
* January 1 – The euro currency is established and the European Central Bank assumes its full powers.
* January 3 – The Mars Polar Lander is launc ...
and 2017
2017 was designated as the International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development by the United Nations General Assembly.
Events January
* January 1 – Istanbul nightclub shooting: A gunman dressed as Santa Claus opens fire at the ...
.
* Round Gotland Race
The Round Gotland Race (), for sponsorship reasons referred to as ÅF Offshore Race in commercial situations, is an offshore sailing race in the Baltic Sea, arranged by the Royal Swedish Yacht Club at the turn of the month June/July each year with ...
-sailing event ("ÅF Offshore Race") starting at Stockholm, around the island of Gotland and back.
* (GGN) is an annual enduro
Enduro is a form of motorcycle sport run on extended cross-country, off-road courses. Enduro consists of many different obstacles and challenges. The main type of enduro event, and the format to which the World Enduro Championship is run, is ...
race on Gotland. GGN is a part of the Swedish ''enduroklassikern'' (enduro classics, Ränneslättsloppet, Stångebroslaget and Gotland Grand National). GNN is the world's largest enduro race.
* Stånga Games
The Stånga Games (in Swedish Stångaspelen), also referred to as the "Gotland Olympic Games", is an annual sports competition in Stånga on the Swedish island of Gotland. The first Stånga Games were held on 27 July 1924. The games are held duri ...
are annual games for Gotlandic sports. The games are held during five days each summer in Stånga
Stånga is a urban areas in Sweden, locality on the Swedish island of Gotland, with 491 inhabitants in 2014.
Stånga is also the name of the larger populated area, socken (not to be confused with Parishes of the Church of Sweden, parish). It compr ...
. The games are unofficially called "the Gotland Olympic Games". Some of the sports at the Stånga Games are pärk
Pärk or Paerk is a game somewhat similar to a game of baseball but where the aim is to gain ground like in American football, that has been played for centuries on the island of Gotland in Baltic Sea. The game is played with two teams of 7 people ...
, varpa
Varpa is an outdoor game of physical skill that allegedly dates back to the Viking Age and survived in Gotland. It is similar to boules and horseshoes but is played with a flat and heavy object called a "varpa" instead of balls. Varpas used to ...
and caber toss
The caber toss () is a traditional Scottish athletic event in which competitors toss a large tapered pole called a "caber" (), normally practised at the Scottish Highland Games.
The term "caber" derives from the Gaelic word ''cabar'', whi ...
.
Organizations
basketball
Basketball is a team sport in which two teams, most commonly of five players each, opposing one another on a rectangular Basketball court, court, compete with the primary objective of #Shooting, shooting a basketball (ball), basketball (appro ...
team Visby Ladies Basket Club (in Basketligan dam
Svenska Basketligan, or the Swedish Basketball League (SBL), is the premier league for professional basketball in Sweden. The league was originally established in 1992 as Basketligan and was known as that prior to the season of 2006–07, but whe ...
) and floorball
Floorball (also known by other names) is a sport played with five players and a goalkeeper in each team. It is played indoors with sticks and a hollow plastic ball with holes. Matches are played in three periods. The sport of bandy also playe ...
team Endre IF Endre may refer to:
People Hungary
Endre is a Hungarian masculine given name. It is a Hungarian form of ''Andrew'' and may refer to:
* Endre (vice-palatine), 13th-century nobleman
* Endre Ady, poet
* Endre Botka, footballer
* Endre Elekes, Oly ...
(in the Swedish Super League Swedish Super League or Svenska Superligan (SSL) may refer to
*Swedish Super League (men's floorball)
*Swedish Super League (women's floorball)
Swedish Super League (SSL, ; formerly named ''Elitserien'') is the highest league in the league syste ...
). Visby Ladies won the Swedish Championship in 2005.
Football in the province is administered by Gotlands Fotbollförbund
The Gotlands Fotbollförbund ''(Gotland Football Association)'' is one of the 24 district organisations of the Swedish Football Association. It administers lower tier football on the island of Gotland.
Background
Gotlands Fotbollförbund, com ...
. The leading football club is FC Gute
FC Gute, previously named ''Visby IF Gute'', is a Sweden, Swedish Association football, football club located in Visby on the island of Gotland. They currently play in the fourth-tier league Swedish football Division 2, Division 2 Norra Svealand.
...
, playing in the fourth-tier league Division 2 .
Visby/Roma HK
Visby/Roma HK is a Swedish ice hockey club located in Visby on Gotland. The club currently plays in group East of Hockeyettan
Hockeyettan is the third tier of ice hockey in Sweden. As of the 2015–16 season, the league consists of 39 teams ...
is a hockey
''Hockey'' is a family of List of stick sports, stick sports where two opposing teams use hockey sticks to propel a ball or disk into a goal. There are many types of hockey, and the individual sports vary in rules, numbers of players, apparel, ...
club located in Visby, currently playing in group East of Hockeyettan
Hockeyettan is the third tier of ice hockey in Sweden. As of the 2015–16 season, the league consists of 39 teams divided geographically into four groups. Hockeyettan operates a system of promotion and relegation with HockeyAllsvenskan and D ...
.
In popular culture
''The Long Ships
''The Long Ships'' or ''Red Orm'' (original Swedish: ''Röde Orm'' meaning ''Red Orm'', lit. ''Red Serpent'' or ''Red Snake'') is an adventure novel by the Swedish writer Frans G. Bengtsson.
The narrative is set in the late 10th century and ...
'', or ''Red Orm'' (original title: ''Röde Orm''), a best-selling Swedish novel written by Frans G. Bengtsson, contains a vivid description of Gotland in the Viking Age. A section of the book is devoted to a Viking ship setting out to Russia, stopping on its way at Gotland and engaging a pilot from the island who plays an important part in their voyage. Gotlanders of the Viking era are depicted as city people, more sophisticated and cosmopolitan than other Scandinavians of their time, and proud of their knowledge and skills.
Naomi Mitchison
Naomi Mary Margaret Mitchison, Baroness Mitchison (; 1 November 1897 – 11 January 1999) was a List of Scottish novelists, Scottish novelist and poet. Often called a doyenne of Scottish literature, she wrote more than 90 books of historical an ...
, in her autobiographic book "''You may well ask''", relates an experience during a walking tour in Sweden: "Over in Gotland I walked again, further than I would have if I had realized that the milestones were in old Swedish miles, so that my disappointing three-mile walk along the cold sea edge under the strange ancient fortifications was really fifteen English miles 4 km.Naomi Mitchison
Naomi Mary Margaret Mitchison, Baroness Mitchison (; 1 November 1897 – 11 January 1999) was a List of Scottish novelists, Scottish novelist and poet. Often called a doyenne of Scottish literature, she wrote more than 90 books of historical an ...
,
You may well ask", London, 1979, Part I, Chap 7.
The crime novels of Mari Jungstedt
Mari Jungstedt (born 31 October 1962, in Stockholm) is a Swedish journalist and crime fiction author.
Jungstedt worked as a reporter with Swedish national public radio and television, and was an occasional presenter on TV4's daily talk show ...
, featuring Detective Superintendent Anders Knutas, are set on Gotland.
In the '' Battlefield Vietnam'' video game modification
Modification may refer to:
* Modifications of school work for students with special educational needs
* Modifications (genetics), changes in appearance arising from changes in the environment
* Posttranslational modifications, changes to prote ...
''Invasion Gotland'', the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
invades Gotland in 1977.
For the 1989 Studio Ghibli film, ''Kiki's Delivery Service
is a 1989 Japanese Anime, animated fantasy film written, produced, and directed by Hayao Miyazaki, based on Eiko Kadono's 1985 novel ''Kiki's Delivery Service (novel), Kiki's Delivery Service''. Animated by Studio Ghibli, the film stars Minami ...
'', by Hayao Miyazaki, he and other illustrators spent time in Gotland in preparation for animation.
Astronomy
 A number of
A number of asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet—an object larger than a meteoroid that is neither a planet nor an identified comet—that orbits within the Solar System#Inner Solar System, inner Solar System or is co-orbital with Jupiter (Trojan asteroids). As ...
s in the main-belt
The asteroid belt is a torus-shaped region in the Solar System, centered on the Sun and roughly spanning the space between the orbits of the planets Jupiter and Mars. It contains a great many solid, irregularly shaped bodies called asteroids ...
are named after places on Gotland or Gotlanders, such as 10795 Babben
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sp ...
, 3250 Martebo
3 (three) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4, and is the smallest odd prime number and the only prime preceding a square number. It has religious and cultural significance in many societies ...
and 7545 Smaklösa
7545 Smaklösa, provisional designation , is a stony background asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 4 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 28 July 1978, by Swedish astronomer Claes-Ingvar Lagerkvist at Mou ...
. Most of them have been named by Swedish astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist in the field of astronomy who focuses on a specific question or field outside the scope of Earth. Astronomers observe astronomical objects, such as stars, planets, natural satellite, moons, comets and galaxy, galax ...
Claes-Ingvar Lagerkvist
Claes-Ingvar Lagerkvist (born 1944) is a Sweden, Swedish astronomer at the Uppsala Astronomical Observatory. He is known for his work on the shapes and spin properties of minor planets.
He has discovered three comets, P/1996 R2, C/1996 R3 and 308 ...
, a summer resident on Gotland. All the Gotlandic names are vividly described in NASA's JPL Small-Body Database
The JPL Small-Body Database (SBDB) is an astronomy database about small Solar System bodies. It is maintained by Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) and NASA and provides data for all known asteroids and several comets, including orbital parameters and ...
in connection to each asteroid.
See also
*Cold War II
The terms Second Cold War, Cold War II, or the New Cold War has been used to describe heightened geopolitical tensions in the 21st century, usually between, on one side, the United States and, on the other, either China or Russia—the latter o ...
* Geats
The Geats ( ; ; ; ), sometimes called ''Geats#Goths, Goths'', were a large North Germanic peoples, North Germanic tribe who inhabited ("land of the Geats") in modern southern Sweden from antiquity until the Late Middle Ages. They are one of ...
* Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples were tribal groups who lived in Northern Europe in Classical antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. In modern scholarship, they typically include not only the Roman-era ''Germani'' who lived in both ''Germania'' and parts of ...
* Gothic alphabet
The Gothic alphabet is an alphabet for writing the Gothic language. It was developed in the 4th century AD by Ulfilas (or Wulfila), a Gothic preacher of Cappadocian Greek descent, for the purpose of translating the Bible.
The alphabet e ...
* Gothic language
Gothic is an extinct language, extinct East Germanic languages, East Germanic language that was spoken by the Goths. It is known primarily from the ''Codex Argenteus'', a 6th-century copy of a 4th-century Bible translation, and is the only Ea ...
* Gotland Museum
The Gotland Museum () (previously known as ''Länsmuseet på Gotland'' or ''Gotlands Fornsal'') in Visby, Sweden, is the county museum of Gotland. It was founded by the Friends of Gotland's Antiquity society in 1875, at the initiative of Pehr Arvi ...
* Gotland National Conscription
The Gotland National Conscription () was a Swedish Army infantry unit that traced its origins back to the 19th century. It was split into two new regiments in 1887. The regiment's soldiers were recruited on the island of Gotland.
History
Gotland ...
* HVDC Gotland
The HVDC Gotland, on the Swedish east coast, was the first fully commercial static plant for high-voltage direct current transmission (HVDC) in the world.
Gotland 1
The first HVDC Gotland link (Gotland 1) went into service in 1954. It could t ...
* List of church ruins on Gotland
There are nineteen known ruined churches on the Swedish island of Gotland, twelve of which lie in Visby, the island's main town. Of these, ten lie within the medieval City wall of Visby, city walls. Three additional church ruins in Visby are know ...
* List of churches on Gotland
The Swedish island of Gotland has since the early Middle Ages had a large number of churches and chapels.
Medieval churches
There are 92 medieval churches on Gotland; the island has more well-preserved medieval churches than any other part of Sw ...
* Norsemen
The Norsemen (or Northmen) were a cultural group in the Early Middle Ages, originating among speakers of Old Norse in Scandinavia. During the late eighth century, Scandinavians embarked on a Viking expansion, large-scale expansion in all direc ...
* Old Norse
Old Norse, also referred to as Old Nordic or Old Scandinavian, was a stage of development of North Germanic languages, North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants ...
* Proto-Norse language
Proto-Norse (also called Ancient Nordic; Danish and ; ; ; ) was an Indo-European language spoken in Scandinavia that is thought to have evolved as a northern dialect of Proto-Germanic in the first centuries CE. It is the earliest stage of a c ...
* Scandza
Scandza was described as a "great island" by Gothic-Byzantine historian Jordanes in his work ''Getica''. The island was located in the Arctic regions of the sea that surrounded the world. The location is usually identified with Scandinavia.
Jor ...
* Sweden during World War II
Sweden maintained its policy of neutrality during World War II. When the war began on 1 September 1939, the fate of Sweden was unclear. But by a combination of its geopolitical location in the Scandinavian Peninsula, ''realpolitik'' maneuveri ...
* Sweden proper
Sweden proper (, literally ''Actual Sweden'') is a term used to distinguish those territories that were fully integrated into the Kingdom of Sweden, as opposed to the dominions and possessions of, or states in union with, Sweden. Only the est ...
References
Further reading
There are over 8,700 titles about Gotland in theNational Library of Sweden
The National Library of Sweden (, ''KB'', meaning "the Royal Library") is Sweden's national library. It collects and preserves all domestic printed and audio-visual materials in Swedish, as well as content with Swedish association published ab ...
online database LIBRIS
LIBRIS (Library Information System) is a Swedish national union catalogue maintained by the National Library of Sweden in Stockholm
Stockholm (; ) is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in Sweden by population, most populo ...
. About 560 of the books are in English. SeeLIBRIS
External links
* *''Gotland, facts and statistics 2013'', pdf, Gotland County.
Important years in Gotland' s history
''GotslandsResor'' tourist website
Official portal for Gotland County
Gotland administrative portal
Swedish Radio on Gotland, P4
Portal on Gotland with detailed facts about everything on the island
Commercial portal on Gotland
Official Gotland Tourist Association
Famous footprints – traveling on Gotland
Portal for eastern Gotland – Östergarnslandet
Portal for eastern Gotland – Ljugarn
Interactive map of Gotland
A short video (with music) with footage of the Gotland Grand National 2007
Gotland Grand National (GGN) webpage
(''Nordic Sport & Event'') {{Authority control Islands of Gotland County Important Bird Areas of Sweden Important Bird Areas of Baltic islands Swedish islands in the Baltic Ramsar sites in Sweden Provinces of Sweden