Glaciers Of Sweden on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A
World Glacier Inventory
* World Glacier Monitoring Service
Global Land Ice Measurements from Space (GLIMS) Glacier DatabaseRandolph Glacier Inventory (RGI)
 Africa, specifically
Africa, specifically
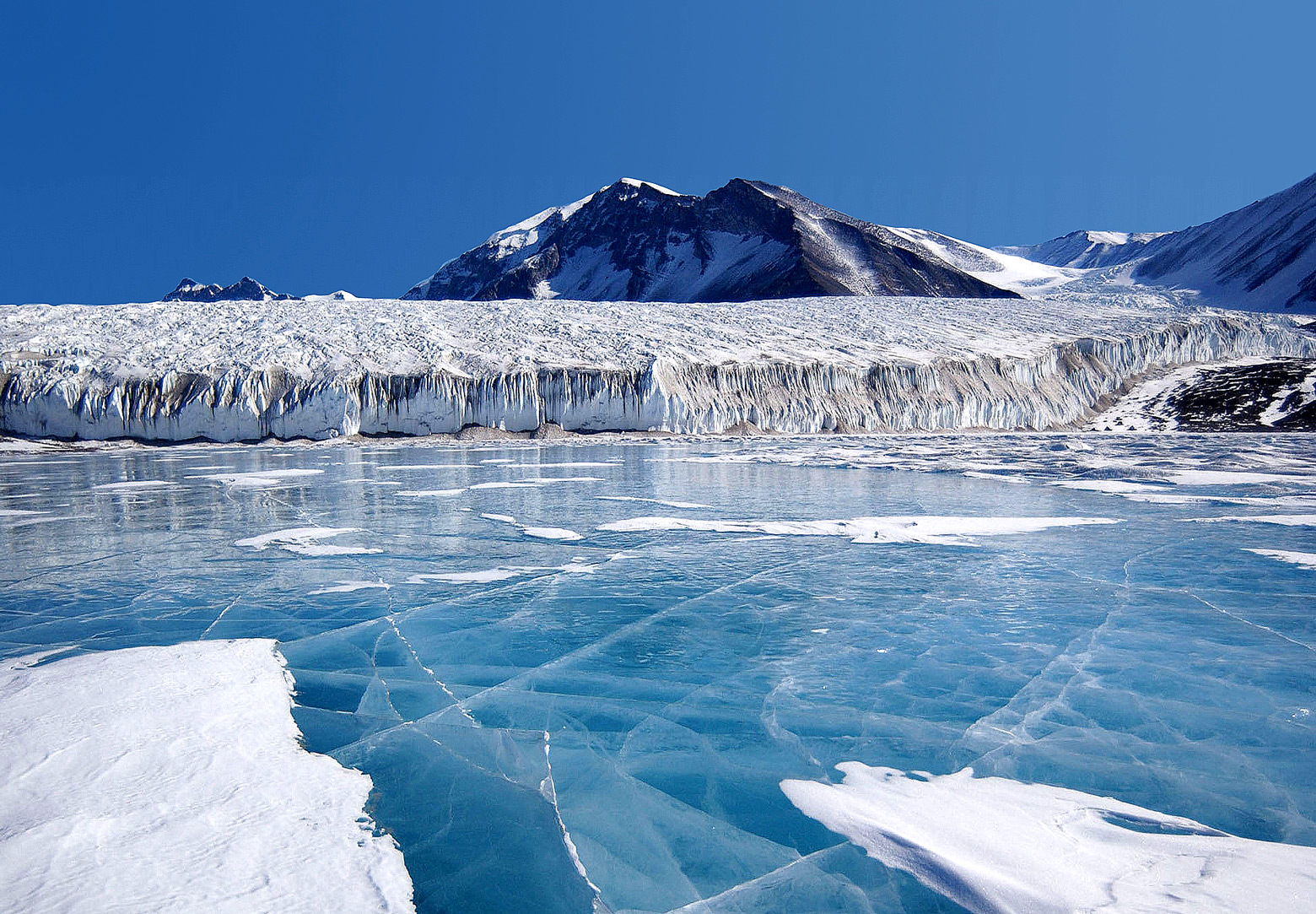 There are many glaciers in the Antarctic. This set of lists does not include
There are many glaciers in the Antarctic. This set of lists does not include
 No glaciers remain on the
No glaciers remain on the
 Glaciers in South America develop exclusively on the
Glaciers in South America develop exclusively on the
 * Christensen Glacier –
* Christensen Glacier –
glacier
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of rock, that is constantly moving downhill under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires ...
( ) or () is a persistent body of dense ice
Ice is water that is frozen into a solid state, typically forming at or below temperatures of 0 ° C, 32 ° F, or 273.15 K. It occurs naturally on Earth, on other planets, in Oort cloud objects, and as interstellar ice. As a naturally oc ...
that is constantly moving under its own weight; it forms where the accumulation of snow
Snow consists of individual ice crystals that grow while suspended in the atmosphere—usually within clouds—and then fall, accumulating on the ground where they undergo further changes.
It consists of frozen crystalline water througho ...
exceeds its ablation
Ablation ( – removal) is the removal or destruction of something from an object by vaporization, chipping, erosion, erosive processes, or by other means. Examples of ablative materials are described below, including spacecraft material for as ...
(melting and sublimation) over many years, often centuries
A century is a period of 100 years or 10 decades. Centuries are numbered ordinally in English and many other languages. The word ''century'' comes from the Latin ''centum'', meaning ''one hundred''. ''Century'' is sometimes abbreviated as c.
A ...
. Glaciers slowly deform and flow due to stresses induced by their weight, creating crevasse
A crevasse is a deep crack that forms in a glacier or ice sheet. Crevasses form as a result of the movement and resulting stress associated with the shear stress generated when two semi-rigid pieces above a plastic substrate have different rate ...
s, serac
A serac () (from Swiss French ''sérac'') is a block or column of glacial ice, often formed by intersecting crevasses on a glacier. Commonly house-sized or larger, they are dangerous to mountaineers, since they may topple with little warning. ...
s, and other distinguishing features. Because glacial mass is affected by long-term climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in a region, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteoro ...
changes, e.g., precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls from clouds due to gravitational pull. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, rain and snow mixed ("sleet" in Commonwe ...
, mean temperature, and cloud cover
Cloud cover (also known as cloudiness, cloudage, or cloud amount) refers to the fraction of the sky obscured by clouds on average when observed from a particular location. Okta is the usual unit for measurement of the cloud cover. The cloud c ...
, glacial mass changes are considered among the most sensitive indicators of climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
. There are about 198,000 to 200,000 glaciers in the world.
Catalogs of glaciers include:World Glacier Inventory
* World Glacier Monitoring Service
Global Land Ice Measurements from Space (GLIMS) Glacier Database
Glaciers by continent
Africa
East Africa
East Africa, also known as Eastern Africa or the East of Africa, is a region at the eastern edge of the Africa, African continent, distinguished by its unique geographical, historical, and cultural landscape. Defined in varying scopes, the regi ...
, has contained glacial
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of rock, that is constantly moving downhill under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires ...
regions, possibly as far back as the last glacier maximum 10 to 15 thousand years ago. Seasonal snow does exist on the highest peaks of East Africa as well as in the Drakensberg Range of South Africa, the Stormberg Mountains, and the Atlas Mountains
The Atlas Mountains are a mountain range in the Maghreb in North Africa. They separate the Sahara Desert from the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean; the name "Atlantic" is derived from the mountain range, which stretches around through M ...
in Morocco. Currently, the only remaining glaciers on the continent exist on Mount Kilimanjaro
Mount Kilimanjaro () is a dormant volcano in Tanzania. It is the highest mountain in Africa and the highest free-standing mountain above sea level in the world, at above sea level and above its plateau base. It is also the highest volcano i ...
, Mount Kenya
Mount Kenya (Meru people, Meru: ''Kĩrĩmaara,'' Kikuyu people, Kikuyu: ''Kĩrĩnyaga'', Kamba language, Kamba: ''Ki nyaa'', Embu language, Embu: ''Kĩ nyaga'') is an extinct volcano in Kenya and the Highest mountain peaks of Africa, second-highe ...
, and the Rwenzori
The Rwenzori (also known as the Ruwenzori, Rwenzururu or Rwenjura) are a range of mountains in eastern equatorial Africa, located on the border between Uganda and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The highest peak of the Ruwenzori reaches , ...
.
Antarctica
 There are many glaciers in the Antarctic. This set of lists does not include
There are many glaciers in the Antarctic. This set of lists does not include ice sheet
In glaciology, an ice sheet, also known as a continental glacier, is a mass of glacier, glacial ice that covers surrounding terrain and is greater than . The only current ice sheets are the Antarctic ice sheet and the Greenland ice sheet. Ice s ...
s, ice cap
In glaciology, an ice cap is a mass of ice that covers less than of land area (usually covering a highland area). Larger ice masses covering more than are termed ice sheets.
Description
By definition, ice caps are not constrained by topogra ...
s or ice field
An ice field (also spelled icefield) is a mass of interconnected valley glaciers (also called mountain glaciers or alpine glaciers) on a mountain mass with protruding rock ridges or summits. They are often found in the colder climates and high ...
s, such as the Antarctic ice sheet
The Antarctic ice sheet is a continental glacier covering 98% of the Antarctic continent, with an area of and an average thickness of over . It is the largest of Earth's two current ice sheets, containing of ice, which is equivalent to 61% of ...
, but includes glacial
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of rock, that is constantly moving downhill under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires ...
features that are defined by their flow, rather than general bodies of ice. The lists include outlet glaciers, valley glaciers, cirque glaciers, tidewater glaciers and ice stream
An ice stream is a region of fast-moving ice within an ice sheet. It is a type of glacier, a body of ice that moves under its own weight. They can move upwards of a year, and can be up to in width, and hundreds of kilometers in length. They t ...
s. Ice streams are a type of glacier and many of them have "glacier" in their name, e.g. Pine Island Glacier
Pine Island Glacier (PIG) is a large ice stream, and the fastest melting glacier in Antarctica. responsible for about 13% of Antarctica's ice loss. The glacier flows west-northwest along the south side of the Hudson Mountains into Pine Island B ...
. Ice shelves
An ice shelf is a large platform of glacial ice floating on the ocean, fed by one or multiple tributary glaciers. Ice shelves form along coastlines where the ice thickness is insufficient to Displacement (fluid), displace the more dense surround ...
are listed separately in the List of Antarctic ice shelves. For the purposes of these lists, the Antarctic
The Antarctic (, ; commonly ) is the polar regions of Earth, polar region of Earth that surrounds the South Pole, lying within the Antarctic Circle. It is antipodes, diametrically opposite of the Arctic region around the North Pole.
The Antar ...
is defined as any latitude
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at t ...
further south than 60° (the continental limit according to the Antarctic Treaty System
The Antarctic Treaty and related agreements, collectively known as the Antarctic Treaty System (ATS), regulate international relations with respect to Antarctica, Earth's only continent without a native human population. It was the first arms ...
).
There are also glaciers in the subantarctic. This includes one snow field
A snow field, snowfield or neve is an accumulation of permanent snow and ice, typically found above the snow line, normally in mountainous and glacial terrain.
Glaciers
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of r ...
( Murray Snowfield). Snow fields are not glaciers in the strict sense of the word, but they are commonly found at the accumulation zone
On a glacier, the accumulation zone is the area above the firn line, where snowfall accumulates and exceeds the losses from ablation, ( melting, evaporation, and sublimation). The annual equilibrium line separates the accumulation and ablation ...
or head of a glacier. For the purposes of this list, Antarctica is defined as any latitude further south than 60° (the continental limit according to the Antarctic Treaty).
Asia
* List of glaciers in Bhutan * List of glaciers in India * List of glaciers in Nepal *List of glaciers in Pakistan
With more than 7,253 known glaciers, Pakistan contains more glacial ice than any other country on Earth outside the polar regions. However, a recent study by Pakistan's Ministry of Climate Change and Italian research organization EvK2CNR, indicat ...
Europe
The majority of Europe's glaciers are found in theAlps
The Alps () are some of the highest and most extensive mountain ranges in Europe, stretching approximately across eight Alpine countries (from west to east): Monaco, France, Switzerland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Germany, Austria and Slovenia.
...
, Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region spanning Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is situated between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, comprising parts of Southern Russia, Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan. The Caucasus Mountains, i ...
and the Scandinavian Mountains
The Scandinavian Mountains or the Scandes is a mountain range that runs through the Scandinavian Peninsula. The western sides of the mountains drop precipitously into the North Sea and Norwegian Sea, forming the fjords of Norway, whereas to th ...
(mostly Norway) as well as in Iceland. Iceland has the largest glacier in Europe, Vatnajökull
Vatnajökull ( Icelandic pronunciation: , literally "Glacier of Lakes"; sometimes translated as Vatna Glacier in English) is the largest and most voluminous ice cap in Iceland, and the second largest in area in Europe after the Severny Island i ...
Glacier, that covers between 8,100 and 8,300 km2 in area and 3,100 km3 in volume. Norway alone has more than 2500 glaciers (including very small ones) covering an estimated 1% of mainland Norway's surface area. Several of mainland Europe's biggest glaciers are found here including; Jostedalsbreen
Jostedal Glacier or is the largest glacier in continental Europe. It is in Vestland county in Western Norway. Jostedalsbreen lies in the municipalities of Luster, Sogndal, Sunnfjord, and Stryn. The highest peak in the area is Lodalskåpa a ...
(the largest in mainland Europe at 487 km2), Vestre Svartisen (221 km2), Søndre Folgefonna (168 km2) and Østre Svartisen (148 km2). The two Svartisen glaciers used to be one connected entity during the Little Ice Age but has since separated.
*List of glaciers in Iceland
The glaciers and ice caps of Iceland covered 11% of the land area of the country, up to about 2008. this was down to 10%. They have a considerable impact on its landscape and meteorology. Glaciers are also contributing to the Icelandic economy, w ...
*List of glaciers in Norway
These are the largest glaciers on mainland Norway.The largest glaciers ...
**List of glaciers in Svalbard
This is a list of glaciers in Svalbard. It includes glaciers and ice caps in Svalbard, Norway. List of glaciers and ice caps
Ice caps
*Austfonna
*Biscayarfonna
*Glitnefonna
*Lomonosovfonna
*Løvenskioldfonna
*Valhallfonna
*Vegafonna
*Vestfonna
...
*List of glaciers in Russia
This is a list of glaciers in Russia. It includes glaciers, ice caps and ice domes located in the Russian Federation.
List of glaciers and ice caps
Ice caps
* Academy of Sciences Glacier () – Severnaya Zemlya. Largest single ice formatio ...
*List of glaciers in Switzerland
This is a non-exhaustive list of the major glaciers in Switzerland. It contains their surface area, their lengths since the start of measurement and the most current year, their height and their outflow. Most of them are retreating and many wil ...
*Southernmost glacial mass in Europe The southernmost persistent glacial masses in Europe are mainly small glaciers, glacierets, and perennial firn fields and patches, located in the highest mountains of the three big southern European peninsulas - the Balkans, Balkan, the Italian Peni ...
North America
There are a number of glaciers existing in North America, currently or in recent centuries. In the United States, theseglacier
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of rock, that is constantly moving downhill under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires ...
s are located in nine states, all in the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in great-circle distance, straight-line distance from the northernmost part of Western Can ...
or further west. The southernmost named glacier among them is the Lilliput Glacier
Lilliput Glacier is the smallest named glacier in the Sierra Nevada of California. The glacier has an area of , which is approximately 12.2 acres. In terms of area this is about the size of 48 typical suburb (1/4 acre or approx. 100' × 100') lo ...
in Tulare County
Tulare County ( ) is a county located in the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 census, the population was 473,117. The county seat is Visalia. The county is named for Tulare Lake, once the largest freshwater lake west of the Great Lake ...
, east of the Central Valley of California.
Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
has about two dozen glaciers, all of which are located on Pico de Orizaba
Citlaltépetl (from Nahuan languages, Náhuatl = star, and = mountain), otherwise known as Pico de Orizaba, is an active volcano, the highest mountain in Mexico and Table of the highest major summits of North America, third highest in North Ame ...
(Citlaltépetl), Popocatépetl
Popocatépetl ( , , ; ) is an active stratovolcano located in the states of Puebla, Morelos, and Mexico in central Mexico. It lies in the eastern half of the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt. At it is the second highest peak in Mexico, after Ci ...
and Iztaccíhuatl
Iztaccíhuatl or Ixtaccíhuatl (both forms also spelled without the accent) ( or, as spelled with the x, ) is a dormant volcanic mountain in Mexico located on the border between the State of Mexico and Puebla within Izta-Popo Zoquiapan National ...
, the three tallest mountains in the country.
*List of glaciers in Canada
A comprehensive list of glaciers in Canada began with glacial surveys by the Water Survey of Canada (WSC) from 1945 to 1980, including an inventory begun for the International Geophysical Year (1957–58) and contributions to the World Glacier I ...
*List of glaciers in Greenland
This is a list of glaciers in Greenland. Details on the size and flow of some of the major Greenlandic glaciers are listed by Eric Rignot and Pannir Kanagaratnam (2006)
Ice sheets and caps
*Greenland Ice Sheet
*Ad Astra Ice Cap (Greenland), ...
*List of glaciers in Mexico
Mexico has about two dozen glaciers, all of which are located on Pico de Orizaba (Citlaltépetl), Popocatépetl and Iztaccíhuatl, the three tallest mountains in the country.
Puebla / Mexico State
;; Popocatépetl
* Glaciar del Ventorrillo
* Gla ...
*List of glaciers in the United States
Glaciers are located in ten states, with the vast majority in Alaska. The southernmost named glacier is the Lilliput Glacier in Tulare County, California, Tulare County, east of the Central Valley (California), Central Valley of California.
Apa ...
Oceania
 No glaciers remain on the
No glaciers remain on the Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
mainland or Tasmania
Tasmania (; palawa kani: ''Lutruwita'') is an island States and territories of Australia, state of Australia. It is located to the south of the Mainland Australia, Australian mainland, and is separated from it by the Bass Strait. The sta ...
. A few, like the Heard Island glaciers are located in the territory of Heard Island and McDonald Islands
The Territory of Heard Island and McDonald Islands (HIMI) is an Australian States and territories of Australia, external territory comprising a volcanic group of mostly barren Antarctic islands, about two-thirds of the way from Madagascar to An ...
in the southern Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or approximately 20% of the water area of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia (continent), ...
.
New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; , fossilized , also known as Papua or historically ) is the List of islands by area, world's second-largest island, with an area of . Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is ...
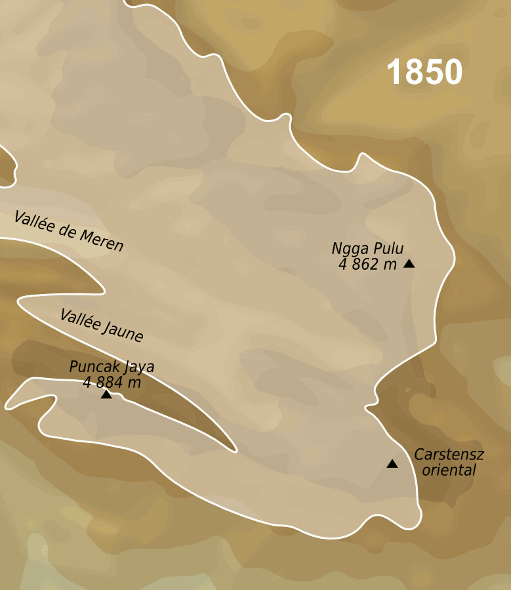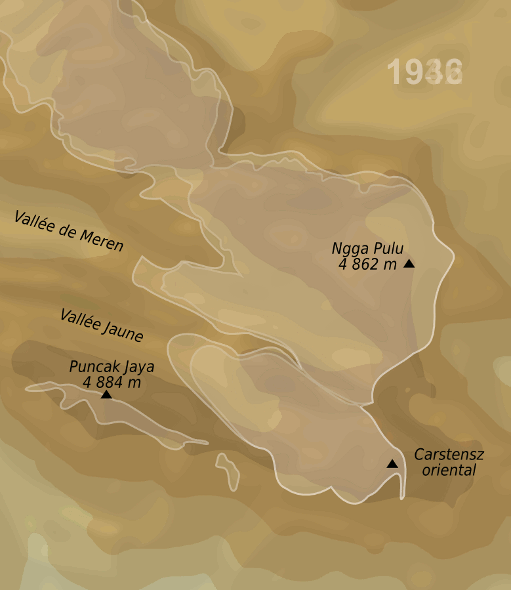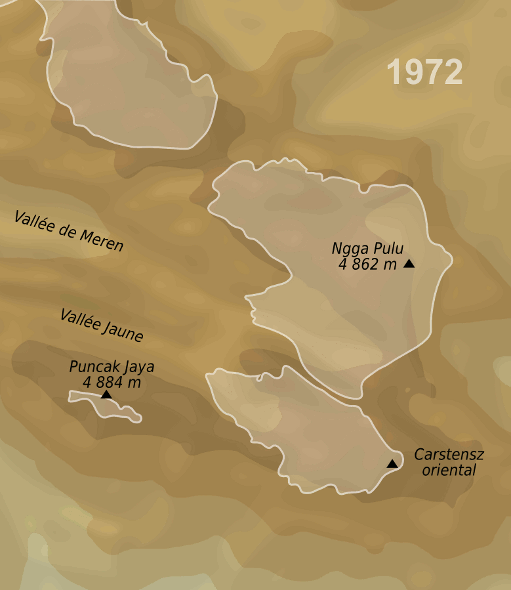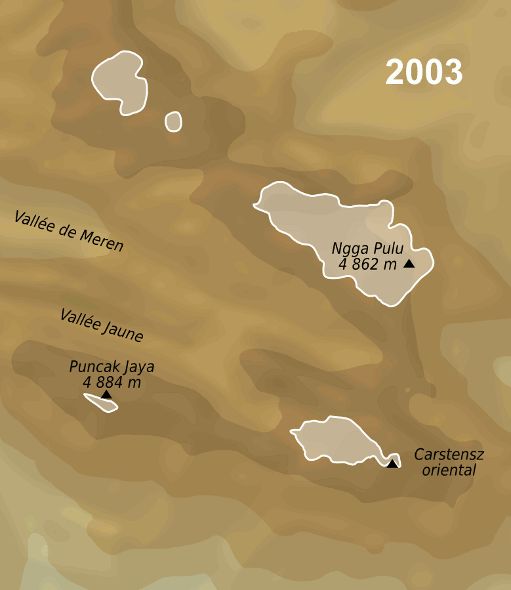
has the Puncak Jaya
Puncak Jaya (; literally "Victorious Peak", Amungme: ''Nemangkawi Ninggok'') or Carstensz Pyramid (, , ) on the island of New Guinea, with an elevation of , is the highest mountain peak of an island on Earth, and the highest peak in Indones ...
glacier.
New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
contains many glacier
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of rock, that is constantly moving downhill under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires ...
s, mostly located near the Main Divide of the Southern Alps
The Southern Alps (; officially Southern Alps / Kā Tiritiri o te Moana) are a mountain range extending along much of the length of New Zealand, New Zealand's South Island, reaching its greatest elevations near the range's western side. The n ...
in the South Island
The South Island ( , 'the waters of Pounamu, Greenstone') is the largest of the three major islands of New Zealand by surface area, the others being the smaller but more populous North Island and Stewart Island. It is bordered to the north by ...
. They are classed as mid-latitude mountain glaciers. There are eighteen small glaciers in the North Island
The North Island ( , 'the fish of Māui', historically New Ulster) is one of the two main islands of New Zealand, islands of New Zealand, separated from the larger but less populous South Island by Cook Strait. With an area of , it is the List ...
on Mount Ruapehu
Mount Ruapehu (; English ) is an active stratovolcano at the southern end of the Taupō Volcanic Zone and North Island North Island Volcanic Plateau, volcanic plateau in New Zealand. It is northeast of Ohakune and southwest of the southern s ...
.
An inventory of South Island glaciers compiled in the 1980s indicated there were about 3,155 glaciers with an area of at least one hectare (2.5 acres). Approximately one sixth of these glaciers covered more than 10 hectares. These include:
*Fox Glacier
Fox Glacier (; officially Fox Glacier / Te Moeka o Tuawe) is a temperate maritime glacier located in Westland Tai Poutini National Park on the West Coast of New Zealand's South Island. Like nearby Franz Josef Glacier, Fox Glacier is one of th ...
* Franz Josef Glacier
* Hooker Glacier
*Mueller Glacier
The Mueller Glacier is a long glacier flowing through Aoraki / Mount Cook National Park in the South Island of New Zealand. It lies to the west of Mount Cook Village within the Southern Alps, flowing roughly north-west from its névé near M ...
*Murchison Glacier
The Murchison Glacier is an long glacier flowing through Aoraki / Mount Cook National Park in the South Island of New Zealand. Lying to the east of the Malte Brun range and west of the Liebig Range, high in the Southern Alps, it flows from the ...
*Tasman Glacier
Tasman Glacier (officially Haupapa / Tasman Glacier) is the largest glacier in New Zealand, and one of several large glaciers which flow south and east towards the Mackenzie Basin from the Southern Alps in New Zealand's South Island.
Geography ...
*Volta Glacier
The Volta Glacier is located in Mount Aspiring National Park in the Southern Alps of the South Island of New Zealand.
It is split into upper and lower glaciers which are connected by an icefall. The Upper Volta Glacier is between in altitude an ...
South America
 Glaciers in South America develop exclusively on the
Glaciers in South America develop exclusively on the Andes
The Andes ( ), Andes Mountains or Andean Mountain Range (; ) are the List of longest mountain chains on Earth, longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range ...
and are subject of the Andes various climatic regimes namely the Tropical Andes
The Tropical Andes is northern of the three climate-delineated parts of the Andes, the others being the Dry Andes and the Wet Andes. The Tropical Andes' area spans .
Geography and ecology
file:Andes_clima.png, 200px, Map of the climatic regio ...
, Dry Andes
200px, Map of the climatic regions of the Andes. The Dry Andes are shown in yellow. The Wet_Andes.html" ;"title="Tropical Andes are shown in green and the Wet Andes">Tropical Andes are shown in green and the Wet Andes in dark blue.
The Dry Andes ...
and the Wet Andes
200px, Map of the climatic regions of the Andes. The Wet Andes are shown in dark blue. The Tropical_Andes.html" ;"title="Dry Andes are shown in yellow and the Tropical Andes">Dry Andes are shown in yellow and the Tropical Andes in green.
The Wet ...
. Apart from this there is a wide range of latitudes on which glaciers develop from 5000 m in the Altiplano
The Altiplano (Spanish language, Spanish for "high plain"), Collao (Quechuan languages, Quechua and Aymara language, Aymara: Qullaw, meaning "place of the Qulla people, Qulla") or Andean Plateau, in west-central South America, is the most extens ...
mountains
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher ...
and volcanoes
A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often fo ...
to reaching sealevel as tidewater glaciers from San Rafael Lagoon
San Rafael Lake is an arc-shaped coastal lake located in the Aysén del General Carlos Ibáñez del Campo Region of Chile, within the national park that bears its name. To the north the lagoon is connected to the Moraleda Channel, to the south l ...
(45° S) and southwards. South America hosts two large ice field
An ice field (also spelled icefield) is a mass of interconnected valley glaciers (also called mountain glaciers or alpine glaciers) on a mountain mass with protruding rock ridges or summits. They are often found in the colder climates and high ...
s, the Northern
Northern may refer to the following:
Geography
* North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating ...
and Southern Patagonian Ice Field
The Southern Patagonian Ice Field (), located at the Southern Patagonic Andes between Chile and Argentina, is the world's second largest contiguous extrapolar ice field. It is the bigger of two remnant parts of the Patagonian Ice Sheet, which c ...
s, of which the latter is the second largest contiguous body of glaciers in extrapolar regions.
The glaciers of Venezuela are located in the mountains of the Sierra Nevada de Mérida
The Sierra Nevada de Mérida is the highest mountain range in the largest massif in Venezuela, the Cordillera de Mérida, which in turn is part of the northern extent of the Cordillera de los Andes (Andes Mountains). The Sierra Nevada de Mérida i ...
. In 1910, maps made by the explorer Alfredo Jahn showed the Sierra Nevada glaciers covering about . An ice trade
The ice trade, also known as the frozen water trade, was a 19th-century and early 20th-century industry, centering on the east coast of the United States and Norway, involving the large-scale harvesting, transport and sale of natural ice, and ...
at that time saw ice men or hieleros transporting glacier ice by mule or on foot to Mérida for sale, a six hour journey.
Venezuela's glacier coverage shrank to about in 1952, and in 1985.
The last remaining glacier, located on Pico Humboldt
Pico Humboldt is Venezuela's second highest peak, at 4,925 metres above sea level. It is located in the Sierra Nevada de Merida, in the Venezuelan Andes of ( Mérida State). The peak, its sister peak Pico Bonpland, and the surrounding páramos ...
, was estimated to cover in 2011.
Remote islands
Bouvet Island
Bouvet Island ( ; ) is an uninhabited subantarctic volcanic island and dependency of Norway. It is a protected nature reserve, and situated in the South Atlantic Ocean at the southern end of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, it is the world's most extre ...
, Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
*Cook Glacier
The Cook Ice Cap or Cook Glacier ( or ''Glacier Cook'') is a large ice cap in the Kerguelen Islands in the French Southern Territories zone of the far Southern Indian Ocean.
Geography
The Cook Ice Cap reaches a maximum elevation of in its centr ...
– Kerguelen Islands
The Kerguelen Islands ( or ; in French commonly ' but officially ', ), also known as the Desolation Islands (' in French), are a group of islands in the subantarctic, sub-Antarctic region. They are among the Extremes on Earth#Remoteness, most i ...
, Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or approximately 20% of the water area of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia (continent), ...
*Fortuna Glacier
Fortuna Glacier is a tidewater glacier at the mouth of Cumberland Bay on the island of South Georgia. It flows in a northeast direction to its terminus just west of Cape Best, with an eastern distributary almost reaching the west side of Fortu ...
– South Georgia Island
South Georgia is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic Ocean that is part of the British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands. It lies around east of the Falkland Islands. ...
, Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
*Jacka Glacier
Following is a list of glaciers of Heard Island and McDonald Islands in Antarctica. This list may not reflect recently named glaciers in Heard Island and McDonald Islands.
Context
Heard Island is a volcanic island in the Southern Ocean that is ...
– Anzac Peak
Anzac Peak is a volcano on the Laurens Peninsula of Heard Island in the Southern Ocean. It lies to the northwest of Mawson Peak. Despite its low elevation of just over 700 metres high, the peak and several neighbouring peaks have permanent snow ...
, Heard Island
The Territory of Heard Island and McDonald Islands (HIMI) is an Australian external territory comprising a volcanic group of mostly barren Antarctic islands, about two-thirds of the way from Madagascar to Antarctica. The group's overall land ...
, Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or approximately 20% of the water area of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia (continent), ...
*Mawson Peak
Mawson Peak is an active volcanic summit of the Big Ben massif on Heard Island, an external Australian territory in the Indian Ocean.
With an elevation of , it is the third highest peak in any state, territory or claimed territory of Aus ...
– Heard Island
The Territory of Heard Island and McDonald Islands (HIMI) is an Australian external territory comprising a volcanic group of mostly barren Antarctic islands, about two-thirds of the way from Madagascar to Antarctica. The group's overall land ...
, Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or approximately 20% of the water area of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia (continent), ...
* Posadowsky Glacier – Bouvet Island
Bouvet Island ( ; ) is an uninhabited subantarctic volcanic island and dependency of Norway. It is a protected nature reserve, and situated in the South Atlantic Ocean at the southern end of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, it is the world's most extre ...
, Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
List of longest glaciers on Earth in non-polar regions
The following is the list of longest glaciers in the non-polar regions, generally regarded as between 60 degrees north and 60 degrees south latitude, though some definitions expand it slightly. # Vanch-Yakh Glacier,Tajikistan
Tajikistan, officially the Republic of Tajikistan, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Dushanbe is the capital city, capital and most populous city. Tajikistan borders Afghanistan to the Afghanistan–Tajikistan border, south, Uzbekistan to ...
– Exact lengths are relatively easy to determine with modern maps and imagery so as to include recent glacial retreat
The retreat of glaciers since 1850 is a well-documented effect of climate change. The retreat of mountain glaciers provides evidence for the rise in global temperatures since the late 19th century. Examples include mountain glaciers in western ...
. Measurements are from recent imagery, supplemented with Russian 1:200,000 scale topographic mapping as well as the 1990 "Orographic Sketch Map: Karakoram: Sheet 2", Swiss Foundation for Alpine Research, Zurich.
# Siachen Glacier
The Siachen Glacier is a glacier located in the eastern Karakoram range of the Himalayas, just northeast of the point NJ9842 where the Line of Control between India and Pakistan ends in northeastern Kashmir. At long, it is the longest glaci ...
, Ladakh
Ladakh () is a region administered by India as a union territory and constitutes an eastern portion of the larger Kashmir region that has been the subject of a Kashmir#Kashmir dispute, dispute between India and Pakistan since 1947 and India an ...
controlled by India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
, near India–Pakistan border
The India–Pakistan border is the international boundary that separates the nations of the Republic of India and the Islamic Republic of Pakistan. At its northern end is the Line of Control, which separates Indian-administered Jammu & Kashmi ...
– when measuring from Indira Col
__NOTOC__
Indira Col West () is a mountain pass at altitude on the Indira Ridge of Siachen Muztagh in Karakoram Range. It is on the border between Indian-controlled Siachen Glacier and the Chinese-controlled Trans-Karakoram Tract (both in the d ...
or 76 km (47 mi) using the longest route as is done when determining river lengths
# Biafo Glacier
The Biafo Glacier () is a glacier located within the Karakoram mountain range in the Hispar Valley, Nagar District of Gilgit-Baltistan, Pakistan. It extends over a considerable distance, measuring in length, and ranks as one of the largest gla ...
, Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
–
# Brüg Glacier, Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in western South America. It is the southernmost country in the world and the closest to Antarctica, stretching along a narrow strip of land between the Andes, Andes Mountains and the Paci ...
–
# Baltoro Glacier
The Baltoro Glacier (; ) is a glacier located in the Shigar District of the Gilgit-Baltistan region in Pakistan. It stretches for in length. It is one of the longest glaciers outside the polar regions. It is home to some of the world’s high ...
, Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
–
# South Inylchek Glacier, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
and Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan, officially the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia lying in the Tian Shan and Pamir Mountains, Pamir mountain ranges. Bishkek is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Kyrgyzstan, largest city. Kyrgyz ...
–
# Batura Glacier
Batura Glacier (), long, is one of the largest and longest glaciers outside of the polar regions.Tajikistan's Fedchenko Glacier is long, Siachen Glacier is long, Biafo Glacier long, and Baltoro Glacier long. The Bruggen or Pio XI Glacier ...
, Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
–
See also
*Cryoseism
A cryoseism, ice quake or frost quake, is a seismic event caused by a sudden cracking action in frozen soil or rock saturated with water or ice, or by stresses generated at frozen lakes. As water drains into the ground, it may eventually freeze ...
* Glacier growing
Glacier growing, artificial glaciation or glacier grafting, is a practice carried out in the Hindu Kush and Himalaya regions aimed at creating small new glaciers to increase water supply for crops and in some cases to sustain micro hydro power. I ...
* Glaciers on Mars
Glaciers, loosely defined as patches of currently or recently flowing ice, are thought to be present across large but restricted areas of the modern Martian surface, and are inferred to have been more widely distributed at times in the past."The S ...
* Ice dam
* Retreat of glaciers since 1850
The retreat of glaciers since 1850 is a well-documented effects of climate change, effect of climate change. The retreat of Mountain glacier, mountain glaciers provides evidence for the Instrumental temperature record, rise in global temperatures ...
* Ice field
An ice field (also spelled icefield) is a mass of interconnected valley glaciers (also called mountain glaciers or alpine glaciers) on a mountain mass with protruding rock ridges or summits. They are often found in the colder climates and high ...
* Snow field
A snow field, snowfield or neve is an accumulation of permanent snow and ice, typically found above the snow line, normally in mountainous and glacial terrain.
Glaciers
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of r ...
* Rock glacier
Rock glaciers are distinctive geomorphological landforms that consist either of angular rock debris frozen in interstitial ice, former "true" glaciers overlain by a layer of talus, or something in between. Rock glaciers are normally found at hi ...
* Sag (geology)
In geology a sag, or Trough (geology), trough, is a depressed, persistent, low area; the opposite of an arch, or ridge, a raised, persistent, high area. The terms sag and arch were used historically to describe very large features, for example, cha ...
References
{{Glaciers *Glaciers
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of rock, that is constantly moving downhill under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires ...