Gerotor Pump on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A gerotor is a
A gerotor is a
Cascon Inc.
Nichols Portland LLC
Step by step drawing
* {{cite news , author=Jennifer Kho , title=Electricity from Waste Heat: Ener-G-Rotors' system harvests energy at lower temperatures , date=November 21, 2008 , work=
 A gerotor is a
A gerotor is a positive displacement pump
A pump is a device that moves fluids (liquids or gases), or sometimes slurries, by mechanical action, typically converted from electrical energy into hydraulic or pneumatic energy.
Mechanical pumps serve in a wide range of applications such ...
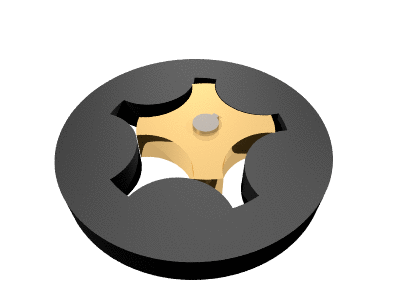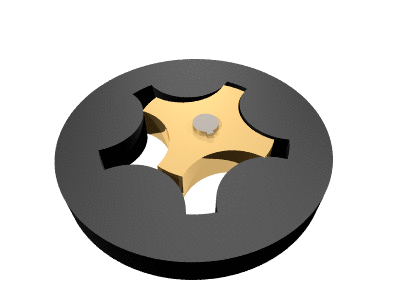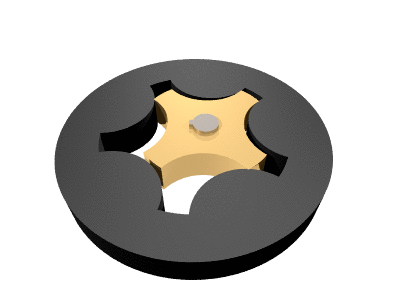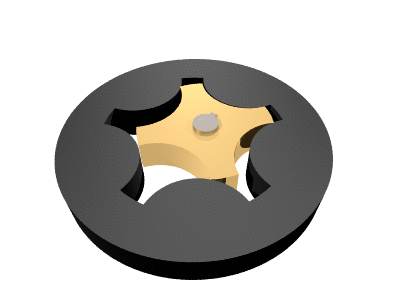
. The name ''gerotor'' is derived from "generated rotor
ROTOR was an elaborate air defence radar system built by the British Government in the early 1950s to counter possible attack by Soviet bombers. To get it operational as quickly as possible, it was initially made up primarily of WWII-era syst ...
." A gerotor unit consists of an inner and an outer rotor. The inner rotor has ''n'' teeth, while the outer rotor has ''n'' + 1 teeth, with ''n'' defined as a natural number
In mathematics, the natural numbers are the numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, and so on, possibly excluding 0. Some start counting with 0, defining the natural numbers as the non-negative integers , while others start with 1, defining them as the positive in ...
greater than or equal to 2. The axis of the inner rotor is offset from the axis of the outer rotor and both rotors rotate on their respective axes. The geometry of the two rotors partitions the volume between them into ''n'' different dynamically-changing volumes. During the assembly's rotation cycle, each of these volumes changes continuously, so any given volume first increases, and then decreases. An increase creates a vacuum
A vacuum (: vacuums or vacua) is space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective (neuter ) meaning "vacant" or "void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressur ...
. This vacuum creates suction
Suction is the day-to-day term for the movement of gases or liquids along a pressure gradient with the implication that the movement occurs because the lower pressure pulls the gas or liquid. However, the forces acting in this case do not orig ...
, and hence, this part of the cycle is where the inlet is located. As a volume decreases, compression
Compression may refer to:
Physical science
*Compression (physics), size reduction due to forces
*Compression member, a structural element such as a column
*Compressibility, susceptibility to compression
* Gas compression
*Compression ratio, of a ...
occurs. During this compression period, fluid
In physics, a fluid is a liquid, gas, or other material that may continuously motion, move and Deformation (physics), deform (''flow'') under an applied shear stress, or external force. They have zero shear modulus, or, in simpler terms, are M ...
s can be pumped or, if they are gaseous fluids, compressed.
Gerotor pumps are generally designed using a trochoid
In geometry, a trochoid () is a roulette curve formed by a circle rolling along a line. It is the curve traced out by a point fixed to a circle (where the point may be on, inside, or outside the circle) as it rolls along a straight line. If the ...
al inner rotor and an outer rotor formed by a circle with intersecting circular arcs.
A gerotor can also function as a pistonless rotary engine
A pistonless rotary engine is an internal combustion engine that does not use pistons in the way a reciprocating engine does. Designs vary widely but typically involve one or more wikt:rotor, rotors, sometimes called rotary pistons, as describe ...
. High-pressure gas enters the intake and pushes against the inner and outer rotors, causing both to rotate as the volume between the inner and outer rotor increases. During the compression period, the exhaust is pumped out.
History
At the most basic level, a gerotor is essentially one that is moved via fluid power. Originally, this fluid was water; today, the wider use is in hydraulic devices. Myron F. Hill, who might be called the father of the gerotor, in his booklet "Kinematics of Ge-rotors", lists efforts by Galloway in 1787, by Nash and Tilden in 1879, by Cooley in 1900, by Professor Lilly of Dublin University in 1915, and by Feuerheerd in 1918. These men were all working to perfect an internal gear mechanism by a one-tooth difference to provide displacement. Myron Hill made his first efforts in 1906, then in 1921, gave his entire time to developing the gerotor. He developed a great deal of geometric theory bearing upon these rotors, coined the word GE-ROTOR (meaning ''generated rotor''), and secured basic patents on GE-ROTOR. Gerotors are widely used today throughout industry, and are produced in a variety of shapes and sizes by a number of different methods.Uses
*Engine
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert one or more forms of energy into mechanical energy.
Available energy sources include potential energy (e.g. energy of the Earth's gravitational field as exploited in hydroelectric power ge ...
* Fuel pump
A Fuel pump is a component used in many liquid-fuelled engines (such as petrol/gasoline or diesel engines) to transfer the fuel from the fuel tank to the device where it is mixed with the intake air (such as the carburetor or fuel inject ...
* Gas compressor
A compressor is a mechanical device that increases the pressure of a gas by reducing its volume. An air compressor is a specific type of gas compressor.
Many compressors can be staged, that is, the gas is compressed several times in steps or ...
* Hydraulic motor
A hydraulic motor is a mechanical actuator that converts hydraulic pressure and flow into torque and angular displacement (rotation). The hydraulic motor is the rotary counterpart of the hydraulic cylinder as a linear actuator. Most broadly, ...
* Limited-slip differential
A limited-slip differential (LSD) is a type of differential gear train that allows its two output shafts to rotate at different speeds but limits the maximum difference between the two shafts. Limited-slip differentials are often known by the ...
* Oil pump (internal combustion engine)
The oil pump is an internal combustion engine part that circulates engine oil under pressure to the rotating bearings, the sliding pistons and the camshaft of the engine. This lubricates the bearings, allows the use of higher-capacity fluid bear ...
* Power steering
Power steering is a system for reducing a driver's effort to turn a steering wheel of a motor vehicle, by using a power source to assist steering.
Hydraulic or electric actuators add controlled energy to the steering mechanism, so the driver can ...
units
See also
*Conical screw compressor
The relatively recently developed conical screw compressor is a type of rotary-screw compressor using a different topology from the typical dual-screw type. In effect it can be thought of as a conical spiral extension of a gerotor
A gerotor ...
* Gear pump
A gear pump uses the meshing of gears to pump fluid by displacement. They are one of the most common types of pumps for hydraulic machinery, hydraulic fluid power applications. The gear pump was invented around 1600 by Johannes Kepler.
Gear ...
* Wankel engine
The Wankel engine (, ) is a type of internal combustion engine using an eccentric (mechanism), eccentric Pistonless rotary engine, rotary design to convert pressure into rotating motion. The concept was proven by German engineer Felix Wankel, f ...
References
*https://www.academia.edu/10200507/Gerotor_Modeling_with_NX3External links
Cascon Inc.
Nichols Portland LLC
Step by step drawing
* {{cite news , author=Jennifer Kho , title=Electricity from Waste Heat: Ener-G-Rotors' system harvests energy at lower temperatures , date=November 21, 2008 , work=
Technology Review
''MIT Technology Review'' is a bimonthly magazine wholly owned by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. It was founded in 1899 as ''The Technology Review'', and was re-launched without "''The''" in its name on April 23, 1998, under then pu ...
, publisher=Massachusetts Institute of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a Private university, private research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Established in 1861, MIT has played a significant role in the development of many areas of moder ...
(MIT) , url=https://www.technologyreview.com/2008/11/21/96006/electricity-from-waste-heat/ , accessdate=2021-01-30
Engine technology
Gas compressors
Pumps