The unification of Germany (, ) was a process of building the first
nation-state
A nation state, or nation-state, is a political entity in which the state (a centralized political organization ruling over a population within a territory) and the nation (a community based on a common identity) are (broadly or ideally) con ...
for
Germans
Germans (, ) are the natives or inhabitants of Germany, or sometimes more broadly any people who are of German descent or native speakers of the German language. The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, constitution of Germany, imple ...
with
federal features based on the concept of
Lesser Germany
The term "Lesser Germany" ( German: , ) or "Lesser German solution" (German: {{Lang, de, Kleindeutsche Lösung) denoted essentially exclusion of the multinational Austria of the Habsburgs from the planned German unification as an option for sol ...
(one without
Habsburgs
The House of Habsburg (; ), also known as the House of Austria, was one of the most powerful dynasties in the history of Europe and Western civilization. They were best known for their inbreeding and for ruling vast realms throughout Europe d ...
' multi-ethnic Austria or its German-speaking part). It commenced on 18 August 1866 with the adoption of the
North German Confederation Treaty
The North German Confederation Treaty (in German ''Augustbündnis'', or Alliance of August) (also called the North German Federation Treaty and the Treaty of 18 August 1866) was the treaty between the Kingdom of Prussia and other northern and centr ...
establishing the
North German Confederation
The North German Confederation () was initially a German military alliance established in August 1866 under the leadership of the Kingdom of Prussia, which was transformed in the subsequent year into a confederated state (a ''de facto'' feder ...
, initially a
military alliance
A military alliance is a formal Alliance, agreement between nations that specifies mutual obligations regarding national security. In the event a nation is attacked, members of the alliance are often obligated to come to their defense regardless ...
''de facto'' dominated by the
Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (, ) was a German state that existed from 1701 to 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It played a signif ...
which was subsequently deepened through adoption of the
North German Constitution.
The process symbolically concluded when most of the south German states joined the North German Confederation with the ceremonial
proclamation of the German Empire
The proclamation of the German Empire, also known as the ''Deutsche Reichsgründung'', took place in January 1871 after the joint victory of the German states in the Franco-Prussian War. As a result of the November Treaties of 1870, the souther ...
(
German Reich
German ''Reich'' (, from ) was the constitutional name for the German nation state that existed from 1871 to 1945. The ''Reich'' became understood as deriving its authority and sovereignty entirely from a continuing unitary German ''Volk'' ("na ...
) having
25 member states and led by the Kingdom of Prussia of
Hohenzollerns on 18 January 1871; the event was typically celebrated as the date of the
German Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperia ...
's foundation, although the legally meaningful events relevant to the completion of unification occurred on 1 January 1871 (
accession of South German states and constitutional adoption of the name "German Empire"), 4 May 1871 (entry into force of the permanent
Constitution of the German Empire
The Constitution of the German Empire () was the basic law of the German Empire. It came into effect on 4 May 1871 and lasted formally until 14 August 1919. Some German historians refer to it as Bismarck's imperial constitution (German: , BRV). ...
) and 10 May 1871 (
Treaty of Frankfurt and recognition of the Empire by the
French Third Republic
The French Third Republic (, sometimes written as ) was the system of government adopted in France from 4 September 1870, when the Second French Empire collapsed during the Franco-Prussian War, until 10 July 1940, after the Fall of France durin ...
).
Despite the legal, administrative, and political disruption caused by the
dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire
The dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire occurred on 6 August 1806, when the last Holy Roman Emperor, Francis II, Holy Roman Emperor, Francis II of the House of Habsburg-Lorraine, abdicated his title and released all Imperial estate, Imperial s ...
in 1806, the German-speaking people of the old Empire had a common linguistic, cultural, and legal tradition.
European liberalism offered an intellectual basis for unification by challenging
dynastic and
absolutist models of social and political organization; its German manifestation emphasized the importance of tradition, education, and linguistic unity. Economically, the creation of the Prussian (customs union) in 1818, and its subsequent expansion to include other states of the Austrian (under
Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire, officially known as the Empire of Austria, was a Multinational state, multinational European Great Powers, great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the Habsburg monarchy, realms of the Habsburgs. Duri ...
)-led
German Confederation
The German Confederation ( ) was an association of 39 predominantly German-speaking sovereign states in Central Europe. It was created by the Congress of Vienna in 1815 as a replacement of the former Holy Roman Empire, which had been dissolved ...
, reduced competition between and within states. Emerging modes of transportation facilitated business and recreational travel, leading to contact and sometimes conflict between and among German-speakers from throughout
Central Europe
Central Europe is a geographical region of Europe between Eastern Europe, Eastern, Southern Europe, Southern, Western Europe, Western and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Central Europe is known for its cultural diversity; however, countries in ...
. The model of diplomatic
spheres of influence
In the field of international relations, a sphere of influence (SOI) is a spatial region or concept division over which a state or organization has a level of cultural, economic, military, or political exclusivity.
While there may be a formal a ...
resulting from the
Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon, Napol ...
in 1814–1815 after the Napoleonic Wars endorsed Austrian dominance in Central Europe through
Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (; ), also known as the House of Austria, was one of the most powerful dynasties in the history of Europe and Western civilization. They were best known for their inbreeding and for ruling vast realms throughout Europe d ...
leadership of the German Confederation, designed to replace the Holy Roman Empire. The negotiators at
Vienna
Vienna ( ; ; ) is the capital city, capital, List of largest cities in Austria, most populous city, and one of Federal states of Austria, nine federal states of Austria. It is Austria's primate city, with just over two million inhabitants. ...
underestimated Prussia's growing internal strength and declined to create a second coalition of the German states under Prussia's influence, and so failed to foresee that Prussia (Kingdom of Prussia) would rise to challenge Austria for leadership of the German peoples. This
German dualism presented
two solutions to the problem of unification: , the small Germany solution (Germany without Austria), or , the greater Germany solution (Germany with Austria or its German-speaking part), ultimately settled in favor of the former solution in the
Peace of Prague.
Historians debate whether
Otto von Bismarck
Otto, Prince of Bismarck, Count of Bismarck-Schönhausen, Duke of Lauenburg (; born ''Otto Eduard Leopold von Bismarck''; 1 April 1815 – 30 July 1898) was a German statesman and diplomat who oversaw the unification of Germany and served as ...
—
Minister President of Prussia
The Minister-President (), or Prime Minister, of Prussia was the head of government of the Prussian state. The office existed from 1848, when it was formed by Frederick William IV of Prussia, King Frederick William IV during the German revolutio ...
—had a master plan to expand the
North German Confederation
The North German Confederation () was initially a German military alliance established in August 1866 under the leadership of the Kingdom of Prussia, which was transformed in the subsequent year into a confederated state (a ''de facto'' feder ...
of 1866 to include the remaining independent German states into a single entity or simply that he planned to expand the
power of the Kingdom of Prussia. They conclude that factors other than the strength of Bismarck's led a collection of early modern
polities
A polity is a group of people with a collective identity, who are organized by some form of political institutionalized social relations, and have a capacity to mobilize resources.
A polity can be any group of people organized for governance ...
to reorganize their political, economic, military, and diplomatic relationships in the 19th century. Reaction to Danish and
French nationalism
French nationalism () usually manifests as civic nationalism, civic or cultural nationalism, promoting the cultural unity of France.
History
French nationalism emerged during the Hundred Years' War, which consisted of a series of intermitte ...
prompted expressions of German unity. Military successes—especially those of Prussia—in three regional wars generated enthusiasm and pride that politicians could harness to promote unification. This experience echoed the memory of mutual accomplishment in the Napoleonic Wars, particularly in the
War of Liberation of 1813–1814. By establishing a Germany without
multi-ethnic Austria (under
Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, also referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Dual Monarchy or the Habsburg Monarchy, was a multi-national constitutional monarchy in Central Europe#Before World War I, Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. A military ...
) or its
German-speaking part, the political and administrative unification of 1871 avoided, at least temporarily, the problem of dualism.
Despite undergoing in later years several further changes of its name and borders, overhauls of its constitutional system, periods of limited sovereignty and interrupted unity of its territory or government, and despite
dissolution of its dominant founding federated state, the polity resulting from the unification process continues today, surviving as the
Federal Republic of Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen constituent states have a total population of over 84 ...
.
Early history
Germans emerged in medieval times among the descendants of the Romanized
Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples were tribal groups who lived in Northern Europe in Classical antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. In modern scholarship, they typically include not only the Roman-era ''Germani'' who lived in both ''Germania'' and parts of ...
in the area of modern western Germany, between the
Rhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the List of rivers of Europe, major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Austria–Swit ...
and
Elbe
The Elbe ( ; ; or ''Elv''; Upper Sorbian, Upper and , ) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Republic), then Ge ...
rivers, particularly the
Franks
file:Frankish arms.JPG, Aristocratic Frankish burial items from the Merovingian dynasty
The Franks ( or ; ; ) were originally a group of Germanic peoples who lived near the Rhine river, Rhine-river military border of Germania Inferior, which wa ...
,
Frisians
The Frisians () are an ethnic group indigenous to the German Bight, coastal regions of the Netherlands, north-western Germany and southern Denmark. They inhabit an area known as Frisia and are concentrated in the Dutch provinces of Friesland an ...
,
Saxons
The Saxons, sometimes called the Old Saxons or Continental Saxons, were a Germanic people of early medieval "Old" Saxony () which became a Carolingian " stem duchy" in 804, in what is now northern Germany. Many of their neighbours were, like th ...
,
Thuringii,
Alemanni
The Alemanni or Alamanni were a confederation of Germanic peoples, Germanic tribes
*
*
*
on the Upper Rhine River during the first millennium. First mentioned by Cassius Dio in the context of the campaign of Roman emperor Caracalla of 213 CE ...
, and
Baiuvarii
The Baiuvarii or Bavarii, sometimes simply called Bavarians (; ) were a Germanic people who lived in and near present-day southern Bavaria, which is named after them.
They began to appear in records by the 6th century AD, and their culture, lang ...
.
The region was divided into long-lasting divisions, or "
Stem duchies", based upon these ethnic designations, under the dominance of the western Franks starting with
Clovis I
Clovis (; reconstructed Old Frankish, Frankish: ; – 27 November 511) was the first List of Frankish kings, king of the Franks to unite all of the Franks under one ruler, changing the form of leadership from a group of petty kings to rule by a ...
, who established control of the Romanized and Frankish population of Gaul in the 5th century, and began a new process of conquering the peoples east of the Rhine. In subsequent centuries the power of the Franks grew considerably. By the early 9th century AD, large parts of Europe had been united under the rule of the Frankish leader
Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( ; 2 April 748 – 28 January 814) was List of Frankish kings, King of the Franks from 768, List of kings of the Lombards, King of the Lombards from 774, and Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of what is now known as the Carolingian ...
, who expanded the
Frankish Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–887) was a Frankish-dominated empire in Western and Central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the Lomba ...
(Francia) in several directions including east of the Rhine, where he conquered
Saxons
The Saxons, sometimes called the Old Saxons or Continental Saxons, were a Germanic people of early medieval "Old" Saxony () which became a Carolingian " stem duchy" in 804, in what is now northern Germany. Many of their neighbours were, like th ...
and
Frisians
The Frisians () are an ethnic group indigenous to the German Bight, coastal regions of the Netherlands, north-western Germany and southern Denmark. They inhabit an area known as Frisia and are concentrated in the Dutch provinces of Friesland an ...
.
A confederated realm of German princedoms, along with some adjacent lands, had been in existence for over a thousand years; dating to the
Treaty of Verdun
The Treaty of Verdun (; ), agreed to on 10 August 843, ended the Carolingian civil war and divided the Carolingian Empire between Lothair I, Louis the German, Louis II and Charles the Bald, Charles II, the surviving sons of the emperor Louis the ...
i.e. the establishment of
East Francia
East Francia (Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the East Franks () was a successor state of Charlemagne's empire created in 843 and ruled by the Carolingian dynasty until 911. It was established through the Treaty of Verdun (843) which divided the for ...
from eastern Frankish Empire in east of the Rhine in 843, especially when the
Ottonian dynasty
The Ottonian dynasty () was a Saxons, Saxon dynasty of German monarchs (919–1024), named after three of its kings and Holy Roman emperors, especially Otto the Great. It is also known as the Saxon dynasty after the family's origin in the German ...
took power to rule East Francia in 919. The realm later in 962 made up the core of the
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
, which at times included
more than 1,000 entities and was called the "Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation" from 1512 with the
Diet of Cologne (new title was adopted partly because the Empire lost most of its territories in Italy and
Burgundy
Burgundy ( ; ; Burgundian: ''Bregogne'') is a historical territory and former administrative region and province of east-central France. The province was once home to the Dukes of Burgundy from the early 11th until the late 15th century. ...
to the south and west by the late 15th century, but also to emphasize the new importance of the German
Imperial Estate
An Imperial Estate (; , plural: ') was an entity or an individual of the Holy Roman Empire with representation and the right to vote in the Imperial Diet (Holy Roman Empire), Imperial Diet ('). Rulers of these Estates were able to exercise signi ...
s in ruling the Empire due to the
Imperial Reform
Imperial Reform (, ) is the name given to repeated attempts in the 15th and 16th centuries to adapt the structure and the constitutional order () of the Holy Roman Empire to the requirements of the early modern state and to give it a unified gove ...
). The states of the Holy Roman Empire ranged in size from the small and complex territories of the princely
Hohenlohe
The House of Hohenlohe () is a German princely dynasty. It formerly ruled an immediate territory within the Holy Roman Empire, which was divided between several branches. In 1806, the area of Hohenlohe was 1,760 km² and its estimated pop ...
family branches to sizable, well-defined territories such as the
Electorate of Bavaria
The Electorate of Bavaria () was a quasi-independent hereditary electorate of the Holy Roman Empire from 1623 to 1806, when it was succeeded by the Kingdom of Bavaria.
The Wittelsbach dynasty which ruled the Duchy of Bavaria was the younger ...
, the
Margraviate of Brandenburg
The Margraviate of Brandenburg () was a major principality of the Holy Roman Empire from 1157 to 1806 that, having electoral status although being quite poor, grew rapidly in importance after inheriting the Duchy of Prussia in 1618 and then came ...
or the
Kingdom of Bohemia
The Kingdom of Bohemia (), sometimes referenced in English literature as the Czech Kingdom, was a History of the Czech lands in the High Middle Ages, medieval and History of the Czech lands, early modern monarchy in Central Europe. It was the pr ...
. Their governance varied: they included
free imperial cities, also of different sizes, such as the powerful
Augsburg
Augsburg ( , ; ; ) is a city in the Bavaria, Bavarian part of Swabia, Germany, around west of the Bavarian capital Munich. It is a College town, university town and the regional seat of the Swabia (administrative region), Swabia with a well ...
and the minuscule
Weil der Stadt; ecclesiastical territories, also of varying sizes and influence, such as the wealthy
Abbey of Reichenau and the powerful
Archbishopric of Cologne; and dynastic states such as
Württemberg
Württemberg ( ; ) is a historical German territory roughly corresponding to the cultural and linguistic region of Swabia. The main town of the region is Stuttgart.
Together with Baden and Province of Hohenzollern, Hohenzollern, two other histo ...
. Among the German-speaking states, the Holy Roman Empire's administrative and legal mechanisms provided a venue to resolve disputes between peasants and landlords, between jurisdictions, and within jurisdictions. Through the organization of
imperial circles (''Reichskreise''), groups of states consolidated resources and promoted regional and organizational interests, including economic cooperation and military protection.
Early modern era and Eighteenth century
Since the 15th century, with few exceptions, the Empire's
Prince-elector
The prince-electors ( pl. , , ) were the members of the Electoral College of the Holy Roman Empire, which elected the Holy Roman Emperor. Usually, half of the electors were archbishops.
From the 13th century onwards, a small group of prince- ...
s had chosen successive heads of the
House of Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (; ), also known as the House of Austria, was one of the most powerful Dynasty, dynasties in the history of Europe and Western civilization. They were best known for their inbreeding and for ruling vast realms throughout ...
from the
Duchy of Austria
The Duchy of Austria (; ) was a medieval principality of the Holy Roman Empire, established in 1156 by the '' Privilegium Minus'', when the Margraviate of Austria ('' Ostarrîchi'') was detached from Bavaria and elevated to a duchy in its own ri ...
to hold the title of
Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans (disambiguation), Emperor of the Romans (; ) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period (; ), was the ruler and h ...
. Although they initially sought to restore central Imperial power, preserving a weak and fragmented Empire was convenient for France and Sweden, and therefore, their ensuing intervention led to the
Peace of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia (, ) is the collective name for two peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and brought peace to the Holy Roman Empire ...
which effectively precluded any serious attempts to reinforce the imperial central authority and petrified fragmentation and leading to the existence of more than 300 German-speaking political entities, most of them being parts of the
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
, as the
Napoleonic Wars
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Napoleonic Wars
, partof = the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars
, image = Napoleonic Wars (revision).jpg
, caption = Left to right, top to bottom:Battl ...
dawned. Still though, portions of the extensive
Habsburg Monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy, also known as Habsburg Empire, or Habsburg Realm (), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities (composite monarchy) that were ruled by the House of Habsburg. From the 18th century it is ...
(exclusively its large non-German-speaking territories:
Lands of the Crown of Saint Stephen
The Lands of the Crown of Saint Stephen (), informally Transleithania (meaning the lands or region "beyond" the Leitha River), were the Hungarian territories of Austria-Hungary, throughout the latter's entire existence (30 March 1867 – 16 ...
and the Austrian partition of Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth) or of the
Hohenzollern
The House of Hohenzollern (, ; , ; ) is a formerly royal (and from 1871 to 1918, imperial) German dynasty whose members were variously princes, electors, kings and emperors of Hohenzollern, Brandenburg, Prussia, the German Empire, and Romania. ...
Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (, ) was a German state that existed from 1701 to 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It played a signif ...
(both the German-speaking former
Duchy of Prussia
The Duchy of Prussia (, , ) or Ducal Prussia (; ) was a duchy in the region of Prussia established as a result of secularization of the Monastic Prussia, the territory that remained under the control of the State of the Teutonic Order until t ...
and the non-German-speaking entire territory of the Prussian partition of Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth) as well as the German-speaking Swiss cantons were outside of the Imperial borders. This became known as the practice of ("small-statery") As a further consequence, there was no typical German national identity as late as 1800, mainly due to the highly autonomous or semi-independent nature of the princely states; most inhabitants of the
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
, outside of those ruled by the emperor directly, identified themselves mainly with their prince rather than with the Empire or the nation as a whole. However, by the 19th century, transportation and communication improvements started to bring these regions closer together.
Dissolution of the Old Empire
Invasion of the Holy Roman Empire by the
First French Empire
The First French Empire or French Empire (; ), also known as Napoleonic France, was the empire ruled by Napoleon Bonaparte, who established French hegemony over much of continental Europe at the beginning of the 19th century. It lasted from ...
in the
War of the Second Coalition
The War of the Second Coalition () (1798/9 – 1801/2, depending on periodisation) was the second war targeting French Revolution, revolutionary French First Republic, France by many European monarchies, led by Kingdom of Great Britain, Britai ...
(1798–1802) resulted in a massive military defeat for the Empire's and allied forces at the hands of
Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career ...
. The treaties of
Lunéville (1801) and the
Mediatization of 1803 secularized the ecclesiastical principalities and abolished most free imperial cities and so these territories along with their inhabitants were absorbed by dynastic states. This transfer particularly expanded the territories of
Württemberg
Württemberg ( ; ) is a historical German territory roughly corresponding to the cultural and linguistic region of Swabia. The main town of the region is Stuttgart.
Together with Baden and Province of Hohenzollern, Hohenzollern, two other histo ...
and
Baden
Baden (; ) is a historical territory in southern Germany. In earlier times it was considered to be on both sides of the Upper Rhine, but since the Napoleonic Wars, it has been considered only East of the Rhine.
History
The margraves of Ba ...
. In 1806, after a successful invasion of Prussia and the defeat of Prussia at the joint battles of
Jena-Auerstedt 1806 during the
War of the Third Coalition
The War of the Third Coalition () was a European conflict lasting from 1805 to 1806 and was the first conflict of the Napoleonic Wars. During the war, First French Empire, France and French client republic, its client states under Napoleon I an ...
, Napoleon dictated the
Treaty of Pressburg which included the formal
dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire
The dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire occurred on 6 August 1806, when the last Holy Roman Emperor, Francis II, Holy Roman Emperor, Francis II of the House of Habsburg-Lorraine, abdicated his title and released all Imperial estate, Imperial s ...
and the abdication of
Emperor Francis II from the nominal reign over it. Napoleon established instead a German
client state
A client state in the context of international relations is a State (polity), state that is economically, politically, and militarily subordinated to a more powerful controlling state. Alternative terms for a ''client state'' are satellite state, ...
of France known as the
Confederation of the Rhine
The Confederated States of the Rhine, simply known as the Confederation of the Rhine or Rhine Confederation, was a confederation of German client states established at the behest of Napoleon some months after he defeated Austrian Empire, Austria ...
which, ''inter alia'', provided for the mediatization of over a hundred petty princes and counts and the absorption of their territories, as well as those of hundreds of
imperial knights
The Free Imperial Knights (, ) were free nobles of the Holy Roman Empire, whose direct overlord was the Emperor. They were the remnants of the medieval free nobility ('' edelfrei'') and the ministeriales. What distinguished them from other kn ...
, by the Confederation's member-states. Several states were promoted to kingdoms including the
Kingdom of Bavaria
The Kingdom of Bavaria ( ; ; spelled ''Baiern'' until 1825) was a German state that succeeded the former Electorate of Bavaria in 1806 and continued to exist until 1918. With the unification of Germany into the German Empire in 1871, the kingd ...
, the
Kingdom of Saxony
The Kingdom of Saxony () was a German monarchy in Central Europe between 1806 and 1918, the successor of the Electorate of Saxony. It joined the Confederation of the Rhine after the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, later joining the German ...
or the
Kingdom of Hanover
The Kingdom of Hanover () was established in October 1814 by the Congress of Vienna, with the restoration of George III to his Hanoverian territories after the Napoleonic Wars, Napoleonic era. It succeeded the former Electorate of Hanover, and j ...
. Following the formal secession from the Empire of the majority of its constituent states, the Emperor dissolved the Holy Roman Empire. In his abdication, Francis released all former estates from their duties and obligations to him, and took upon himself solely the title of Emperor of Austria, which had been established since 1804.
Rise of German nationalism under Napoleon
Under the
hegemony of the First French Empire (1804–1814), popular German nationalism thrived in the reorganized German states. Due in part to German-speaking peoples' shared experience, albeit under French rule, various justifications emerged to identify "Germany" as a potential future single state. For the German philosopher
Johann Gottlieb Fichte
Johann Gottlieb Fichte (; ; 19 May 1762 – 29 January 1814) was a German philosopher who became a founding figure of the philosophical movement known as German idealism, which developed from the theoretical and ethical writings of Immanuel Ka ...
,

A common language may have been seen to serve as the basis of a nation, but as contemporary historians of 19th-century Germany noted, it took more than linguistic similarity to unify these several hundred polities. The experience of German-speaking Central Europe during the years of French hegemony contributed to a sense of common cause to expel the French invaders and reassert control over their own lands.
Napoleon's campaigns in Poland (1806–07) resulting in his decision to re-establish a form of Polish statehood (the
Duchy of Warsaw
The Duchy of Warsaw (; ; ), also known as the Grand Duchy of Warsaw and Napoleonic Poland, was a First French Empire, French client state established by Napoleon Bonaparte in 1807, during the Napoleonic Wars. It initially comprised the ethnical ...
) at the cost of Prussian-conquered Polish territories, as well as his campaigns on
the Iberian Peninsula, in western Germany, and his disastrous
invasion of Russia in 1812, disillusioned many Germans, princes and peasants alike. Napoleon's
Continental System nearly ruined the Central European economy. The invasion of Russia included nearly 125,000 troops from German lands, and the destruction of that army encouraged many Germans, both high- and low-born, to envision a Central Europe free of Napoleon's influence. The creation of student militias such as the
Lützow Free Corps exemplified this tendency.
The debacle in Russia loosened the French grip on German princes. In 1813, Napoleon mounted a campaign in the German states to bring them back into the French orbit; the subsequent
War of Liberation culminated in the great
Battle of Leipzig
The Battle of Leipzig, also known as the Battle of the Nations, was fought from 16 to 19 October 1813 at Leipzig, Saxony. The Coalition armies of Austria, Prussia, Sweden, and Russia, led by Tsar Alexander I, Karl von Schwarzenberg, and G ...
, also known as the
Battle of Nations. In October 1813, more than 500,000 combatants engaged in ferocious fighting over three days, making it the largest European land battle of the 19th century. The engagement resulted in a decisive victory for the
Coalition
A coalition is formed when two or more people or groups temporarily work together to achieve a common goal. The term is most frequently used to denote a formation of power in political, military, or economic spaces.
Formation
According to ''A G ...
of Austria, Prussia, Russia, Saxony, and Sweden. As a result, the
Confederation of the Rhine
The Confederated States of the Rhine, simply known as the Confederation of the Rhine or Rhine Confederation, was a confederation of German client states established at the behest of Napoleon some months after he defeated Austrian Empire, Austria ...
collapsed and the
French period
In Northern European historiography, the term French period (, , ) refers to the period between 1794 and 1815 during which most of Northern Europe was controlled by Republican or Napoleonic France.Eduard Rothert''Rheinland-Westfalen im Wechsel d ...
came to an end. Success encouraged the Coalition forces to pursue Napoleon across the Rhine; his army and his government collapsed, and the victorious Coalition incarcerated Napoleon on
Elba
Elba (, ; ) is a Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean island in Tuscany, Italy, from the coastal town of Piombino on the Italian mainland, and the largest island of the Tuscan Archipelago. It is also part of the Arcipelago Toscano National Park, a ...
. During the brief Napoleonic restoration known as the
100 Days of 1815, forces of the
Seventh Coalition, including an Anglo-Allied army under the command of the
Duke of Wellington
Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, grand dukes, and above sovereign princes. As royalty or nobility, they ar ...
and a
Prussian army under the command of
Gebhard von Blücher, were victorious at
Waterloo (18 June 1815). The critical role played by Blücher's troops, especially after having to retreat from the field at
Ligny
Ligny (; ) is a village of Wallonia and a district of the municipality of Sombreffe, located in the province of Namur, Belgium.
Previously its own municipality, a 1977 fusion of the Belgian municipalities made it an '' ancienne commune'' of So ...
on the 17th, helped to turn the tide of combat against the French. The Prussian cavalry pursued the defeated French on the evening of the 18th of June, sealing the allied victory. From the German perspective, the actions of Blücher's troops at Waterloo, and the combined efforts at Leipzig, offered a rallying point of pride and enthusiasm. This interpretation became a key building block of the
''Borussian'' myth expounded by the pro-Prussian nationalist historians later in the 19th century.
Congress of Vienna and the rise of German dualism

After Napoleon's defeat, the
Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon, Napol ...
established a new European political-diplomatic system based on the
balance of power. This system reorganized Europe into
spheres of influence
In the field of international relations, a sphere of influence (SOI) is a spatial region or concept division over which a state or organization has a level of cultural, economic, military, or political exclusivity.
While there may be a formal a ...
, which, in some cases, suppressed the aspirations of the various nationalities, including the Germans and Italians.
Generally, an enlarged Prussia and the 38 other states consolidated from the mediatized territories of 1803 were confederated within the
Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire, officially known as the Empire of Austria, was a Multinational state, multinational European Great Powers, great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the Habsburg monarchy, realms of the Habsburgs. Duri ...
's sphere of influence. The Congress established a loose
German Confederation
The German Confederation ( ) was an association of 39 predominantly German-speaking sovereign states in Central Europe. It was created by the Congress of Vienna in 1815 as a replacement of the former Holy Roman Empire, which had been dissolved ...
(1815–1866), headed by Austria, with a "Federal
Diet" (called the ''Bundestag'' or ''
Bundesversammlung'', an assembly of appointed leaders) that met in the city of
Frankfurt am Main
Frankfurt am Main () is the most populous city in the States of Germany, German state of Hesse. Its 773,068 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the List of cities in Germany by population, fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located in the forela ...
. Its borders resembled those of its predecessor, the Holy Roman Empire (though there were some deviations e.g. Prussian territory in the Confederation was extended to include the formerly Polish territories of the
Lauenburg and Bütow Land and the former
Starostwo of Draheim, while the Austrian part was extended to include the formerly Polish territories of the
Duchy of Oświęcim
The Duchy of Oświęcim (), or the Duchy of Auschwitz (), was one of the Duchies of Silesia in the lands of Lesser Poland (Małopolska), formed in the aftermath of the fragmentation of Poland, centered around Oświęcim.
It was established a ...
and the
Duchy of Zator) for the years 1818–1850, meaning that large portions of both Prussia and Austria were left outside the new borders. In recognition of the imperial position traditionally held by the Habsburgs, the emperors of Austria became the titular presidents of this parliament. Despite the term ''Diet'' (Assembly or Parliament), this institution should in no way be construed as a broadly, or popularly, elected group of representatives. Many of the states did not have constitutions, and those that did, such as the
Duchy of Baden, based
suffrage
Suffrage, political franchise, or simply franchise is the right to vote in public, political elections and referendums (although the term is sometimes used for any right to vote). In some languages, and occasionally in English, the right to v ...
on strict property requirements which effectively limited suffrage to a small portion of the male population.
Problems of reorganization

Problematically, the built-in Austrian dominance failed to take into account Prussia's 18th-century emergence in Imperial politics. This impractical solution did not reflect the new status of Prussia in the overall set-up. Although the Prussian army had been dramatically defeated in the 1806
Battle of Jena-Auerstedt, it had made a spectacular comeback at Waterloo. Consequently, Prussian leaders expected to play a pivotal role in German politics. Ever since the
Prince-Elector
The prince-electors ( pl. , , ) were the members of the Electoral College of the Holy Roman Empire, which elected the Holy Roman Emperor. Usually, half of the electors were archbishops.
From the 13th century onwards, a small group of prince- ...
of
Brandenburg
Brandenburg, officially the State of Brandenburg, is a States of Germany, state in northeastern Germany. Brandenburg borders Poland and the states of Berlin, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony. It is the List of Ger ...
had made himself
King in Prussia
King ''in'' Prussia (German language, German: ''König in Preußen'') was a title used by the Prussian kings (also in personal union Elector of Brandenburg, Electors of Brandenburg) from 1701 to 1772. Subsequently, they used the title King ''of' ...
at the beginning of that century, their domains had steadily increased through inheritance and war. Prussia's consolidated strength had become particularly apparent during the
Partitions of Poland
The Partitions of Poland were three partition (politics), partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that took place between 1772 and 1795, toward the end of the 18th century. They ended the existence of the state, resulting in the eli ...
, the
War of the Austrian Succession
The War of the Austrian Succession was a European conflict fought between 1740 and 1748, primarily in Central Europe, the Austrian Netherlands, Italian Peninsula, Italy, the Atlantic Ocean and Mediterranean Sea. Related conflicts include King Ge ...
and the
Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War, 1756 to 1763, was a Great Power conflict fought primarily in Europe, with significant subsidiary campaigns in North America and South Asia. The protagonists were Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of Prus ...
under
Frederick the Great
Frederick II (; 24 January 171217 August 1786) was the monarch of Prussia from 1740 until his death in 1786. He was the last Hohenzollern monarch titled ''King in Prussia'', declaring himself ''King of Prussia'' after annexing Royal Prussia ...
. As
Maria Theresa
Maria Theresa (Maria Theresia Walburga Amalia Christina; 13 May 1717 – 29 November 1780) was the ruler of the Habsburg monarchy from 1740 until her death in 1780, and the only woman to hold the position suo jure, in her own right. She was the ...
and
Joseph
Joseph is a common male name, derived from the Hebrew (). "Joseph" is used, along with " Josef", mostly in English, French and partially German languages. This spelling is also found as a variant in the languages of the modern-day Nordic count ...
tried to restore Habsburg hegemony in the Holy Roman Empire, Frederick countered with the creation of the ''
Fürstenbund'' (Union of Princes) in 1785. Austrian-Prussian
dualism
Dualism most commonly refers to:
* Mind–body dualism, a philosophical view which holds that mental phenomena are, at least in certain respects, not physical phenomena, or that the mind and the body are distinct and separable from one another
* P ...
lay firmly rooted in old Imperial politics. Those balance of power manoeuvers were epitomized by the
War of the Bavarian Succession
The War of the Bavarian Succession (; 3 July 1778 – 13 May 1779) was a dispute between the Austrian Habsburg monarchy and an alliance of Electorate of Saxony, Saxony and Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia over succession to the Electorate of Bavaria ...
, or "
Potato War" among common folk. Even after the end of the Holy Roman Empire, this competition influenced the growth and development of nationalist movements in the 19th century.
Prelude
''Vormärz''
The period of Austrian and Prussian police-states and vast censorship between the Congress of Vienna and the
Revolutions of 1848 in Germany later became widely known as the ''
Vormärz
' (; English: ''pre-March'') was a period in the history of Germany preceding the 1848 March Revolution in the states of the German Confederation. The beginning of the period is less well-defined. Some place the starting point directly after ...
'' ("before March"), referring to March 1848. During this period, European liberalism gained momentum; the agenda included economic, social, and political issues. Most European liberals in the ''Vormärz'' sought unification under nationalist principles, promoted the transition to capitalism, and sought the expansion of male suffrage, among other issues. Their "radicalization" depended upon where they stood on the spectrum of
male suffrage: the wider the definition of suffrage, the more radical they had the potential to be.
The surge of German
nationalism
Nationalism is an idea or movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, it presupposes the existence and tends to promote the interests of a particular nation, Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: Theory, I ...
, stimulated by the experience of Germans in the Napoleonic period and initially allied with
liberalism
Liberalism is a Political philosophy, political and moral philosophy based on the Individual rights, rights of the individual, liberty, consent of the governed, political equality, the right to private property, and equality before the law. ...
, shifted political, social, and cultural relationships within the German states. In this context, one can detect nationalism's roots in the experience of Germans in the Napoleonic period. Furthermore, implicit and sometimes explicit promises made during the
German Campaign of 1813
The German campaign () was fought in 1813. Members of the Sixth Coalition, including the German states of Austria and Prussia, plus Russia and Sweden, fought a series of battles in Germany against the French Emperor Napoleon, his marshals, and th ...
engendered an expectation of
popular sovereignty
Popular sovereignty is the principle that the leaders of a state and its government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a State (polity), state.
In the case of its broad associativ ...
and widespread participation in the political process, promises that largely went unfulfilled once peace had been achieved.
Emergence of liberal nationalism and conservative response

Despite considerable conservative reaction, ideas of unity joined with notions of popular sovereignty in German-speaking lands. The ''
Burschenschaft'' student organizations and popular demonstrations, such as those held at
Wartburg Castle in October 1817, contributed to a growing sense of unity among German speakers of Central Europe.
At the
Wartburg Festival in 1817 the first real movements among students were formed – fraternities and student organizations emerged. The colors black, red and gold were symbolic of this. Agitation by student organizations led conservative leaders such as
Klemens Wenzel, Prince von Metternich, to fear the rise of nationalist sentiment.
The assassination of German dramatist
August von Kotzebue
August Friedrich Ferdinand von Kotzebue (, ; – ) was a German playwright, who had also worked as a Russian diplomat.
In 1817, one of Kotzebue's books was burned during the Wartburg festival. He was murdered in 1819 by Karl Ludwig Sand, a ...
in March 1819 by a radical student seeking unification was followed on 20 September 1819 by the proclamation of the
Carlsbad Decrees
The Carlsbad Decrees () were a set of reactionary restrictions introduced in the states of the German Confederation by resolution of the Bundesversammlung on 20 September 1819 after a conference held in the spa town of Carlsbad, Austrian Empire. ...
, which hindered intellectual leadership of the nationalist movement. Metternich was able to harness conservative outrage at the assassination to consolidate legislation that would further limit the press and constrain the rising liberal and nationalist movements. Accordingly, these decrees drove the ''Burschenschaften'' underground, restricted the publication of nationalist materials, expanded censorship of the press and private correspondence, and limited academic speech by prohibiting university professors from encouraging nationalist discussion. The decrees were the subject of
Johann Joseph von Görres's pamphlet ''Teutschland
rchaic: Deutschlandund die Revolution'' (''Germany and the Revolution'') (1820), in which he concluded that it was both impossible and undesirable to repress the free utterance of public opinion by reactionary measures.
The
Hambach Festival (''Hambacher Fest'') in May 1832 was attended by a crowd of more than 30,000. Promoted as a
county fair
An agricultural show is a public event exhibiting the equipment, animals, sports and recreation associated with agriculture and animal husbandry. The largest comprise a livestock show (a judged event or display in which breeding stock is exhib ...
, its participants celebrating fraternity, liberty, and national unity. Celebrants gathered in the town below and marched to the ruins of
Hambach Castle on the heights above the small town of Hambach, in the Palatinate province of Bavaria. Carrying flags, beating drums, and singing, the participants took the better part of the morning and mid-day to arrive at the castle grounds, where they listened to speeches by nationalist orators from across the political spectrum. The overall content of the speeches suggested a fundamental difference between the German nationalism of the 1830s and the French nationalism of the
July Revolution
The French Revolution of 1830, also known as the July Revolution (), Second French Revolution, or ("Three Glorious ays), was a second French Revolution after French Revolution, the first of 1789–99. It led to the overthrow of King Cha ...
: the focus of German nationalism lay in the education of the people; once the populace was educated as to what was needed, it would reach those goals. The Hambach rhetoric emphasized the overall peaceable nature of German nationalism: the point was not to build barricades, a very "French" form of nationalism, but to build emotional bridges between groups. As he had done in 1819, after the
Kotzebue assassination, Metternich used the popular demonstration at Hambach to push conservative social policy. The "Six Articles" of 28 June 1832 above all else reaffirmed the principle of monarchical authority. On 5 July, the Frankfurt Diet voted for an additional 10 articles, which reiterated existing rules on censorship, restricted political organizations, and limited other public activity. Furthermore, the member states agreed to send military assistance to any government threatened by unrest.
Prince Wrede led half of the Bavarian army to the Palatinate to "subdue" the province. Several hapless Hambach speakers were arrested, tried and imprisoned; one, Karl Heinrich Brüggemann (1810–1887), a law student and representative of the secretive ''Burschenschaft'', was sent to Prussia, where he was first condemned to death, but later pardoned.
Crucially, both the Wartburg rally in 1817 and the Hambach Festival in 1832 had lacked any clear-cut vision for unification. At Hambach, the positions of the many speakers illustrated their disparate agendas. Held together only by the idea of unification, their notions of how to achieve this did not include specific plans but instead rested on the nebulous idea that the ''Volk'' (the people), if properly educated, would bring about unification on their own. Grand speeches, flags, exuberant students, and picnic lunches did not translate into a new political, bureaucratic, or administrative apparatus. While many spoke about the need for a constitution, no such document emerged from the key nationalist rallies. In 1848, nationalists sought to remedy that problem.
Economy and the customs union

Several other factors complicated the rise of
nationalism
Nationalism is an idea or movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, it presupposes the existence and tends to promote the interests of a particular nation, Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: Theory, I ...
in the German states. The man-made factors included political rivalries between members of the German confederation, particularly between the Austrians and the Prussians, and socio-economic competition among the commercial and merchant interests, and the old land-owning and aristocratic interests. Natural factors included widespread drought in the early 1830s, and again in the 1840s, and a food crisis in the 1840s. Further complications emerged as a result of a shift in industrialization and manufacturing; as people sought jobs, they left their villages and small towns to work during the week in cities, returning for a day and a half on weekends.
The economic, social and cultural dislocation of ordinary people, the economic hardship of an economy in transition, and the pressures of meteorological disasters all contributed to growing problems in Central Europe. The failure of most of the governments to deal with the food crisis of the mid-1840s, caused by the
potato blight (related to the
Great Irish Famine
The Great Famine, also known as the Great Hunger ( ), the Famine and the Irish Potato Famine, was a period of mass starvation and disease in Ireland lasting from 1845 to 1852 that constituted a historical social crisis and had a major impact o ...
) and several seasons of bad weather, encouraged many to think that the rich and powerful had no interest in their problems. Those in authority were concerned about the growing unrest, political and social agitation among the working classes, and the disaffection of the
intelligentsia
The intelligentsia is a status class composed of the university-educated people of a society who engage in the complex mental labours by which they critique, shape, and lead in the politics, policies, and culture of their society; as such, the i ...
. No amount of censorship, fines, imprisonment, or banishment, it seemed, could stem the criticism. Furthermore, it was becoming increasingly clear that both Austria and Prussia wanted to be the leaders in any resulting unification; each would inhibit the drive of the other to take the lead in unification.
Formation of the ''
Zollverein
The (), or German Customs Union, was a coalition of States of the German Confederation, German states formed to manage tariffs and economic policies within their territories. Organized by the 1833 treaties, it formally started on 1 January 1 ...
'', an institution key to unifying the German states economically, helped to create a larger sense of economic unification. Initially conceived by the Prussian Finance Minister
Hans, Count von Bülow, as a Prussian
customs union
A customs union is generally defined as a type of trade bloc which is composed of a free trade area with a common external tariff.GATTArticle 24 s. 8 (a)
Customs unions are established through trade pacts where the participant countries set u ...
in 1818, the ''Zollverein'' linked the many Prussian and
Hohenzollern
The House of Hohenzollern (, ; , ; ) is a formerly royal (and from 1871 to 1918, imperial) German dynasty whose members were variously princes, electors, kings and emperors of Hohenzollern, Brandenburg, Prussia, the German Empire, and Romania. ...
territories. Over the ensuing thirty years (and more) other German states joined. The Union helped to reduce protectionist barriers between the German states, especially improving the transport of raw materials and finished goods, making it both easier to move goods across territorial borders and less costly to buy, transport, and sell raw materials. This was particularly important for the emerging industrial centers, most of which were located in the Prussian regions of the
Rhineland
The Rhineland ( ; ; ; ) is a loosely defined area of Western Germany along the Rhine, chiefly Middle Rhine, its middle section. It is the main industrial heartland of Germany because of its many factories, and it has historic ties to the Holy ...
, the
Saar
Saar or SAAR has several meanings:
People Given name
* Sarr Boubacar (born 1951), Senegalese professional football player
* Saar Ganor, Israeli archaeologist
* Saar Klein (born 1967), American film editor
Surname
* Ain Saar (born 1968), E ...
, and the
Ruhr
The Ruhr ( ; , also ''Ruhrpott'' ), also referred to as the Ruhr Area, sometimes Ruhr District, Ruhr Region, or Ruhr Valley, is a polycentric urban area in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With a population density of 1,160/km2 and a populati ...
valleys. States more distant from the coast joined the Customs Union earlier. Not being a member mattered more for the states of south Germany, since the external tariff of the Customs Union prevented customs-free access to the coast (which gave access to international markets). Thus, by 1836, all states to the south of Prussia had joined the Customs Union, except Austria.
In contrast, the coastal states already had barrier free access to international trade and did not want consumers and producers burdened with the import duties they would pay if they were within the Zollverein customs border. Hanover on the north coast formed its own customs union – the "Tax Union" or
Steuerverein – in 1834 with Brunswick and with Oldenburg in 1836. The external tariffs on finished goods and overseas raw materials were below the rates of the Zollverein. Brunswick joined the Zollverein Customs Union in 1842, while Hanover and Oldenburg finally joined in 1854 After the Austro-Prussian war of 1866, Schleswig, Holstein and Lauenburg were annexed by Prussia and thus annexed also to the Customs Union, while the two Mecklenburg states and the city states of Hamburg and Bremen joined later because they were reliant on international trade. The Mecklenburgs joined in 1867, while Bremen and
Hamburg joined in 1888.
Roads and railways
By the early 19th century, German roads had deteriorated to an appalling extent. Travelers, both foreign and local, complained bitterly about the state of the ''Heerstraßen'', the military roads previously maintained for easy troop movement. As German states ceased to be a military crossroads, however, the roads improved; the length of hard–surfaced roads in Prussia increased from in 1816 to in 1852, helped in part by the invention of
macadam
Macadam is a type of road construction pioneered by Scottish engineer John Loudon McAdam , in which crushed stone is placed in shallow, convex layers and compacted thoroughly. A binding layer of stone dust (crushed stone from the original mat ...
. By 1835,
Heinrich von Gagern wrote that roads were the "veins and arteries of the body politic..." and predicted that they would promote freedom, independence and prosperity.As people moved around, they came into contact with others, on trains, at hotels, in restaurants, and for some, at fashionable resorts such as the spa in
Baden-Baden
Baden-Baden () is a spa town in the states of Germany, state of Baden-Württemberg, south-western Germany, at the north-western border of the Black Forest mountain range on the small river Oos (river), Oos, ten kilometres (six miles) east of the ...
. Water transportation also improved. The blockades on the Rhine had been removed by Napoleon's orders, but by the 1820s, steam engines freed riverboats from the cumbersome system of men and animals that towed them upstream. By 1846, 180 steamers plied German rivers and
Lake Constance
Lake Constance (, ) refers to three bodies of water on the Rhine at the northern foot of the Alps: Upper Lake Constance (''Obersee''), Lower Lake Constance (''Untersee''), and a connecting stretch of the Rhine, called the Seerhein (). These ...
, and a network of canals extended from the
Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
, the
Weser
The Weser () is a river of Lower Saxony in north-west Germany. It begins at Hannoversch Münden through the confluence of the Werra and Fulda. It passes through the Hanseatic city of Bremen. Its mouth is further north against the ports o ...
, and the
Elbe
The Elbe ( ; ; or ''Elv''; Upper Sorbian, Upper and , ) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Republic), then Ge ...
rivers.
As important as these improvements were, they could paled in comparison to the impact of the railway. German economist
Friedrich List
Daniel Friedrich List (6 August 1789 – 30 November 1846) was a German entrepreneur, diplomat, economist and political theory, political theorist who developed the Economic nationalism, nationalist theory of political economy in both Europe and t ...
called the railways and the Customs Union "Siamese Twins", emphasizing their important mutually beneficial relationship. He was not alone: the poet
August Heinrich Hoffmann von Fallersleben
August Heinrich Hoffmann (, calling himself von Fallersleben, after his hometown; 2 April 179819 January 1874) was a German poet. He is best known for writing "", whose third stanza is now the national anthem of Germany, and a number of popular ...
wrote a poem in which he extolled the virtues of the ''Zollverein'', which he began with a list of commodities that had contributed more to German unity than politics or diplomacy. Historians of the
German Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperia ...
later regarded the railways as the first indicator of a unified state; the patriotic novelist,
Wilhelm Raabe, wrote: "The German empire was founded with the construction of the first railway..." Not everyone greeted the ''iron monster'' with enthusiasm. The Prussian king
Frederick William III saw no advantage in traveling from Berlin to
Potsdam
Potsdam () is the capital and largest city of the Germany, German States of Germany, state of Brandenburg. It is part of the Berlin/Brandenburg Metropolitan Region. Potsdam sits on the Havel, River Havel, a tributary of the Elbe, downstream of B ...
a few hours faster, and Metternich refused to ride it at all. Others wondered if the railways were an "evil" that threatened the landscape:
Nikolaus Lenau's 1838 poem ''An den Frühling'' (''To Spring'') bemoaned the way trains destroyed the pristine quietude of German forests.
The
Bavarian Ludwig Railway
The Bavarian Ludwig Railway (''Bayerische Ludwigseisenbahn'' or ''Ludwigsbahn'') was the first steam-hauled railway opened in Germany. The ''Königlich privilegierte Ludwigs-Eisenbahn-Gesellschaft'' ("Royal Privileged Ludwig Railway Company ...
, which was the first passenger or freight rail line in the German lands, connected
Nuremberg
Nuremberg (, ; ; in the local East Franconian dialect: ''Nämberch'' ) is the Franconia#Towns and cities, largest city in Franconia, the List of cities in Bavaria by population, second-largest city in the States of Germany, German state of Bav ...
and
Fürth
Fürth (; East Franconian German, East Franconian: ; ) is a List of cities and towns in Germany, city in northern Bavaria, Germany, in the administrative division (''Regierungsbezirk'') of Middle Franconia.
It is the Franconia#Towns and cities, s ...
in 1835. Although it was long and only operated in daylight, it proved both profitable and popular. Within three years, of track had been laid, by 1840, , and by 1860, . Lacking a geographically central organizing feature (such as a national capital), the rails were laid in webs, linking towns and markets within regions, regions within larger regions, and so on. As the rail network expanded, it became cheaper to transport goods: in 1840, 18 ''
Pfennig
The pfennig (; . 'pfennigs' or 'pfennige' ; currency symbol, symbol pf or ₰) or penny is a former Germany, German coin or note, which was an official currency from the 9th century until the introduction of the euro in 2002. While a valua ...
s'' per ton per kilometer and in 1870, five ''Pfennigs''. The effects of the railway were immediate. For example, raw materials could travel up and down the
Ruhr
The Ruhr ( ; , also ''Ruhrpott'' ), also referred to as the Ruhr Area, sometimes Ruhr District, Ruhr Region, or Ruhr Valley, is a polycentric urban area in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With a population density of 1,160/km2 and a populati ...
Valley without having to unload and reload. Railway lines stumulated economic activity by creating demand for commodities and by facilitating commerce. In 1850, inland shipping carried three times more freight than railroads; by 1870, the situation was reversed, and railroads carried four times more. Rail travel changed how cities looked and how people traveled. Its impact reached throughout the social order, affecting the highest born to the lowest. Although some of the outlying German provinces were not serviced by rail until the 1890s, the majority of the population, manufacturing centers, and production centers were linked to the rail network by 1865.
Geography, patriotism and language

As travel became easier, faster, and less expensive, Germans started to see unity in factors ''other'' than their language. The
Brothers Grimm
The Brothers Grimm ( or ), Jacob Grimm, Jacob (1785–1863) and Wilhelm Grimm, Wilhelm (1786–1859), were Germans, German academics who together collected and published folklore. The brothers are among the best-known storytellers of Oral tradit ...
, who compiled a massive dictionary known as ''The Grimm'', also assembled a compendium of folk tales and fables, which highlighted the story-telling parallels between different regions.
Karl Baedeker
Karl Ludwig Johannes Baedeker ( , ; born Bädeker; 3 November 1801 – 4 October 1859) was a German publisher whose company, Baedeker, set the standard for authoritative guidebooks for tourists.
Karl Baedeker was descended from a long line ...
wrote guidebooks to different cities and regions of Central Europe, indicating places to stay, sites to visit, and giving a short history of castles, battlefields, famous buildings, and famous people. His guides also included distances, roads to avoid, and hiking paths to follow.
The words of
August Heinrich Hoffmann von Fallersleben
August Heinrich Hoffmann (, calling himself von Fallersleben, after his hometown; 2 April 179819 January 1874) was a German poet. He is best known for writing "", whose third stanza is now the national anthem of Germany, and a number of popular ...
expressed not only the linguistic unity of the German people but also their geographic unity. In ''Deutschland, Deutschland über Alles'', officially called ''
Das Lied der Deutschen
The "", officially titled "", is a Germany, German poem written by August Heinrich Hoffmann von Fallersleben . A popular song which was made for the cause of creating a unified German state, it was adopted in its entirety in 1922 by the Weima ...
'' ("''The Song of the Germans''"), Fallersleben called upon sovereigns throughout the German states to recognize the unifying characteristics of the German people. Such other patriotic songs as "
Die Wacht am Rhein" ("The Watch on the Rhine") by
Max Schneckenburger began to focus attention on geographic space, not limiting "Germanness" to a common language. Schneckenburger wrote "The Watch on the Rhine" in a specific patriotic response to French assertions that the Rhine was France's "natural" eastern boundary. In the refrain, "Dear fatherland, dear fatherland, put your mind to rest / The watch stands true on the Rhine", and in other such patriotic poetry as Nicholaus Becker's "Das Rheinlied" ("The Rhine"), Germans were called upon to defend their territorial homeland. In 1807,
Alexander von Humboldt
Friedrich Wilhelm Heinrich Alexander von Humboldt (14 September 1769 – 6 May 1859) was a German polymath, geographer, natural history, naturalist, List of explorers, explorer, and proponent of Romanticism, Romantic philosophy and Romanticism ...
argued that national character reflected geographic influence, linking landscape to people. Concurrent with this idea, movements to preserve old fortresses and historic sites emerged, and these particularly focused on the Rhineland, the site of so many confrontations with France and Spain.
German revolutions and Polish uprising of 1848–1849
The widespread—mainly German—
revolutions of 1848–49 sought unification of Germany under a single constitution. The revolutionaries pressured various state governments, particularly those in the
Rhineland
The Rhineland ( ; ; ; ) is a loosely defined area of Western Germany along the Rhine, chiefly Middle Rhine, its middle section. It is the main industrial heartland of Germany because of its many factories, and it has historic ties to the Holy ...
, for a parliamentary assembly that would have the responsibility to draft a constitution. Ultimately, many of the left-wing revolutionaries hoped this constitution would establish
universal male suffrage
Universal manhood suffrage is a form of voting rights in which all adult male citizens within a political system are allowed to vote, regardless of income, property, religion, race, or any other qualification. It is sometimes summarized by the sl ...
, a permanent national parliament, and a unified Germany, possibly under the leadership of the Prussian king. This seemed to be the most logical course since Prussia was the strongest of the German states, as well as the largest in geographic size. Meanwhile, center-right revolutionaries sought some kind of expanded suffrage within their states and potentially, a form of loose unification. Finally, the Polish majority living in the share of Polish territory annexed by Prussia
pursued their own liberation agenda.
Frankfurt Parliament
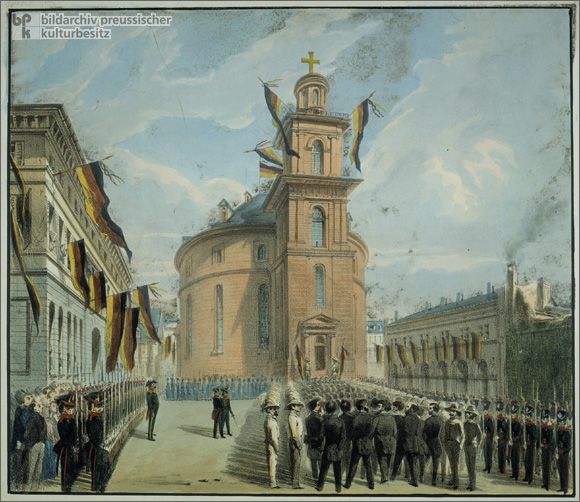

Their pressure resulted in a variety of elections, based on different voting qualifications, such as the
Prussian three-class franchise, which weighted votes based on the amount of taxes paid and therefore gave some electoral groups—chiefly the wealthier, landed ones—greater representative power.
On 27 March 1849, the
Frankfurt Parliament
The Frankfurt National Assembly () was the first freely elected parliament for all German Confederation, German states, including the German-populated areas of the Austrian Empire, elected on 1 May 1848 (see German federal election, 1848).
The ...
passed the ''
Paulskirchenverfassung'' (Constitution of St. Paul's Church) and offered the title of ''Kaiser'' (Emperor) to the Prussian king
Frederick William IV the next month. He refused for a variety of reasons. Publicly, he replied that he could not accept a crown without the consent of the actual states, by which he meant the princes. Privately, he feared opposition from the other German princes and military intervention from Austria or Russia. He also held a fundamental distaste for the idea of accepting a crown from a popularly elected parliament: he would not accept a crown of "clay". Despite franchise requirements that often perpetuated many of the problems of sovereignty and political participation liberals sought to overcome, the Frankfurt Parliament did manage to draft a constitution and reach an agreement on the ''kleindeutsch'' solution. While the liberals failed to achieve the unification they sought, they did manage to gain a partial victory by working with the German princes on many constitutional issues and collaborating with them on reforms.
The aborted 1848–1849 German Empire in retrospective analysis
Scholars of German history have engaged in decades of debate over how the successes and failures of the Frankfurt Parliament contribute to the historiographical explanations of German nation building. One school of thought, which emerged after
The Great War and gained momentum in the aftermath of
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, maintains that the failure of German liberals in the Frankfurt Parliament led to
bourgeoisie
The bourgeoisie ( , ) are a class of business owners, merchants and wealthy people, in general, which emerged in the Late Middle Ages, originally as a "middle class" between the peasantry and aristocracy. They are traditionally contrasted wi ...
compromise with conservatives (especially the conservative
Junker
Junker (, , , , , , ka, იუნკერი, ) is a noble honorific, derived from Middle High German , meaning 'young nobleman'Duden; Meaning of Junker, in German/ref> or otherwise 'young lord' (derivation of and ). The term is traditionally ...
landholders), which subsequently led to the so-called ''
Sonderweg'' (distinctive path) of 20th-century German history. Failure to achieve unification in 1848, this argument holds, resulted in the late formation of the nation-state in 1871, which in turn delayed the development of positive national values.
Hitler
Adolf Hitler (20 April 1889 – 30 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his suicide in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the lea ...
often called on the German public to sacrifice all for the cause of their great nation, but his regime did not create German nationalism: it merely capitalized on an intrinsic cultural value of German society that still remains prevalent even to this day. Furthermore, this argument maintains, the "failure" of 1848 reaffirmed latent aristocratic longings among the German middle class; consequently, this group never developed a self-conscious program of modernization.
More recent scholarship has rejected this idea, claiming that Germany did not have an actual "distinctive path" any more than any other nation, a historiographic idea known as
exceptionalism
Exceptionalism is the perception or belief that a species, country, society, institution, movement, individual, or time period is "wiktionary:exceptional, exceptional" (i.e., unusual or extraordinary). The term carries the implication, whether or ...
. Instead, modern historians claim 1848 saw specific achievements by the liberal politicians. Many of their ideas and programs were later incorporated into Bismarck's social programs (e.g., social insurance, education programs, and wider definitions of suffrage). In addition, the notion of a distinctive path relies upon the underlying assumption that some other nation's path (in this case, the United Kingdom's) is the accepted norm. This new argument further challenges the norms of the British-centric model of development: studies of national development in Britain and other "normal" states (e.g., France or the United States) have suggested that even in these cases, the modern nation-state did not develop evenly. Nor did it develop particularly early, being rather a largely mid-to-late-19th-century phenomenon. Since the end of the 1990s, this view has become widely accepted, although some historians still find the ''Sonderweg'' analysis helpful in understanding the period of
National Socialism
Nazism (), formally named National Socialism (NS; , ), is the far-right totalitarian socio-political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Germany. During Hitler's rise to power, it was frequ ...
.
Problem of spheres of influence: The Erfurt Union and the Punctation of Olmütz
After the Frankfurt Parliament disbanded, Frederick William IV, under the influence of General
Joseph Maria von Radowitz, supported the establishment of the
Erfurt Union
The Erfurt Union () was a short-lived union of German states under a federation, proposed by the Kingdom of Prussia at Erfurt, for which the Erfurt Union Parliament (''Erfurter Unionsparlament''), officially lasting from March 20 to April 29, 1 ...
—a federation of German states, excluding Austria—by the free agreement of the German princes. This limited union under Prussia would have almost eliminated Austrian influence on the other German states. Combined diplomatic pressure from Austria and Russia (a guarantor of the 1815 agreements that established European spheres of influence) forced Prussia to relinquish the idea of the Erfurt Union at a meeting in the small town of
Olmütz in Moravia. In November 1850, the Prussians—specifically Radowitz and Frederick William—agreed to the restoration of the German Confederation under Austrian leadership. This became known as the
Punctation of Olmütz, but among Prussians it was known as the "Humiliation of Olmütz."
Although seemingly minor events, the Erfurt Union proposal and the Punctation of Olmütz brought the problems of influence in the German states into sharp focus. The question became not a matter of ''if'' but rather ''when'' unification would occur, and ''when'' was contingent upon strength. One of the former Frankfurt Parliament members,
Johann Gustav Droysen, summed up the problem:
Unification under these conditions raised a basic diplomatic problem. The possibility of German (or
Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, a Romance ethnic group related to or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance languag ...
) unification would overturn the overlapping
spheres of influence
In the field of international relations, a sphere of influence (SOI) is a spatial region or concept division over which a state or organization has a level of cultural, economic, military, or political exclusivity.
While there may be a formal a ...
system created in 1815 at the Congress of Vienna. The principal architects of this convention,
Metternich
Klemens Wenzel Nepomuk Lothar, Prince of Metternich-Winneburg zu Beilstein ( ; 15 May 1773 – 11 June 1859), known as Klemens von Metternich () or Prince Metternich, was a Germans, German statesman and diplomat in the service of the Austrian ...
,
Castlereagh, and
Tsar Alexander (with his foreign secretary Count
Karl Nesselrode
Karl Robert Reichsgraf von Nesselrode-Ehreshoven, also known as Charles de Nesselrode (; 14 December 1780 – 23 March 1862), was a Foreign policy of the Russian Empire, Russian diplomat of German nobility, German noble descent. For 40 years ( ...
), had conceived of and organized a Europe balanced and guaranteed by four "
great powers
A great power is a sovereign state that is recognized as having the ability and expertise to exert its influence on a global scale. Great powers characteristically possess military and economic strength, as well as diplomatic and soft power ...
": Great Britain, France, Russia, and Austria, with each power having a geographic sphere of influence. France's sphere included the Iberian Peninsula and a share of influence in the Italian states. Russia's included the eastern regions of Central Europe and a balancing influence in the Balkans. Austria's sphere expanded throughout much of the Central European territories formerly held by the
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
. Britain's sphere was the rest of the world, especially the seas.
This sphere of influence system depended upon the fragmentation of the German and Italian states, not their consolidation. Consequently, a German nation united under one banner presented significant questions. There was no readily applicable definition for who the German people would be or how far the borders of a German nation would stretch. There was also uncertainty as to who would best lead and defend "Germany", however it was defined. Different groups offered different solutions to this problem. In the ''
Kleindeutschland'' ("Lesser Germany") solution, the German states would be united under the leadership of the
Prussian Hohenzollerns; in the ''
Grossdeutschland'' ("Greater Germany") solution, the German states would be united under the leadership of the
Austrian Habsburgs. This controversy, the latest phase of the
German dualism debate that had dominated the politics of the German states and Austro-Prussian diplomacy since the 1701 creation of the
Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (, ) was a German state that existed from 1701 to 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It played a signif ...
, would come to a head during the following twenty years.
External expectations of a unified Germany
Other nationalists had high hopes for the German unification movement, and the frustration with lasting German unification after 1850 seemed to set the national movement back. Revolutionaries associated national unification with progress. As
Giuseppe Garibaldi
Giuseppe Maria Garibaldi ( , ;In his native Ligurian language, he is known as (). In his particular Niçard dialect of Ligurian, he was known as () or (). 4 July 1807 – 2 June 1882) was an Italian general, revolutionary and republican. H ...
wrote to German revolutionary
Karl Blind on 10 April 1865, "The progress of humanity seems to have come to a halt, and you with your superior intelligence will know why. The reason is that the world lacks a nation
hat
A hat is a Headgear, head covering which is worn for various reasons, including protection against weather conditions, ceremonial reasons such as university graduation, religious reasons, safety, or as a fashion accessory. Hats which incorpor ...
possesses true leadership. Such leadership, of course, is required not to dominate other peoples but to lead them along the path of duty, to lead them toward the brotherhood of nations where all the barriers erected by egoism will be destroyed." Garibaldi looked to Germany for the "kind of leadership
hat
A hat is a Headgear, head covering which is worn for various reasons, including protection against weather conditions, ceremonial reasons such as university graduation, religious reasons, safety, or as a fashion accessory. Hats which incorpor ...
in the true tradition of medieval chivalry, would devote itself to redressing wrongs, supporting the weak, sacrificing momentary gains and material advantage for the much finer and more satisfying achievement of relieving the suffering of our fellow men. We need a nation courageous enough to give us a lead in this direction. It would rally to its cause all those who are suffering wrong or who aspire to a better life and all those who are now enduring foreign oppression."
German unification had also been viewed as a prerequisite for the creation of a European federation, which
Giuseppe Mazzini
Giuseppe Mazzini (, ; ; 22 June 1805 – 10 March 1872) was an Italian politician, journalist, and activist for the unification of Italy (Risorgimento) and spearhead of the Italian revolutionary movement. His efforts helped bring about the ...
and other European patriots had been promoting for more than three decades:
Prussia's growing strength: ''Realpolitik''

King
Frederick William IV suffered a stroke in 1857 and could no longer rule. This led to his brother
William
William is a masculine given name of Germanic languages, Germanic origin. It became popular in England after the Norman Conquest, Norman conquest in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle ...
becoming
prince regent
A prince regent or princess regent is a prince or princess who, due to their position in the line of succession, rules a monarchy as regent in the stead of a monarch, e.g., as a result of the sovereign's incapacity (minority or illness) or ab ...
of the Kingdom of Prussia in 1858. Meanwhile,
Helmuth von Moltke had become chief of the
Prussian General Staff in 1857, and
Albrecht von Roon
Albrecht Theodor Emil Graf von Roon (; 30 April 1803 – 23 February 1879) was a Prussian soldier and statesman. As Minister of War from 1859 to 1873, Roon, along with Otto von Bismarck and Helmuth von Moltke, was a dominating figure in Pruss ...
would become
Prussian Minister of War
The Prussian Ministry of War was the highest state authority of the Prussian Army, Royal Prussian Army and was responsible for the central administration of the army of the Kingdom of Prussia and, later, the Imperial German Army. The ministry e ...
in 1859. This shuffling of authority within the Prussian military establishment would have important consequences. Von Roon and William (who took an active interest in military structures) began reorganizing the Prussian army, while Moltke redesigned the strategic defense of Prussia by streamlining operational command. Prussian army reforms (especially how to pay for them) caused a
constitutional crisis
In political science, a constitutional crisis is a problem or conflict in the function of a government that the constitution, political constitution or other fundamental governing law is perceived to be unable to resolve. There are several variat ...
beginning in 1860 because both parliament and William—via his minister of war—wanted control over the military budget. William, crowned King Wilhelm I in 1861, appointed
Otto von Bismarck
Otto, Prince of Bismarck, Count of Bismarck-Schönhausen, Duke of Lauenburg (; born ''Otto Eduard Leopold von Bismarck''; 1 April 1815 – 30 July 1898) was a German statesman and diplomat who oversaw the unification of Germany and served as ...
to the position of
Minister-President of Prussia in 1862. Bismarck resolved the crisis in favor of the war minister.
The
Crimean War
The Crimean War was fought between the Russian Empire and an alliance of the Ottoman Empire, the Second French Empire, the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, and the Kingdom of Sardinia (1720–1861), Kingdom of Sardinia-Piedmont fro ...
of 1854–55 and the
Italian War of 1859 disrupted relations among Great Britain, France, Austria, and Russia. In the aftermath of this disarray, the convergence of von Moltke's operational redesign, von Roon and Wilhelm's army restructure, and Bismarck's diplomacy influenced the realignment of the European balance of power. Their combined agendas established Prussia as the leading German power through a combination of foreign diplomatic triumphs—backed up by the possible use of Prussian military might—and an internal conservatism tempered by pragmatism, which came to be known as ''
Realpolitik
''Realpolitik'' ( ; ) is the approach of conducting diplomatic or political policies based primarily on considerations of given circumstances and factors, rather than strictly following ideological, moral, or ethical premises. In this respect, ...
''.
Bismarck expressed the essence of ''Realpolitik'' in his subsequently famous
"Blood and Iron" speech to the Budget Committee of the Prussian Chamber of Deputies on 30 September 1862, shortly after he became Minister President: "The great questions of the time will not be resolved by speeches and majority decisions—that was the great mistake of 1848 and 1849—but by iron and blood." Bismarck's words, "iron and blood" (or "blood and iron", as often attributed), have often been misappropriated as evidence of a German lust for blood and power. First, the phrase from his speech "the great questions of time will not be resolved by speeches and majority decisions" is often interpreted as a repudiation of the political process—a repudiation Bismarck did not himself advocate. Second, his emphasis on blood and iron did not imply simply the unrivaled military might of the Prussian army but rather two important aspects: the ability of the assorted German states to produce iron and other related war materials and the willingness to use those war materials if necessary.
By 1862, when Bismarck made his speech, the idea of a German nation-state in the peaceful spirit of
Pan-Germanism
Pan-Germanism ( or '), also occasionally known as Pan-Germanicism, is a pan-nationalist political idea. Pan-Germanism seeks to unify all ethnic Germans, German-speaking people, and possibly also non-German Germanic peoples – into a sin ...
had shifted from the liberal and democratic character of 1848 to accommodate Bismarck's more conservative ''Realpolitik''. Bismarck sought to link a unified state to the Hohenzollern dynasty, which for some historians remains one of Bismarck's primary contributions to the creation of the
German Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperia ...
in 1871. While the conditions of the treaties binding the various German states to one another prohibited Bismarck from taking unilateral action, the politician and diplomat in him realized the impracticality of this. To get the German states to unify, Bismarck needed a single, outside enemy that would declare war on one of the German states first, thus providing a ''
casus belli
A (; ) is an act or an event that either provokes or is used to justify a war. A ''casus belli'' involves direct offenses or threats against the nation declaring the war, whereas a ' involves offenses or threats against its ally—usually one bou ...
'' to rally all Germans behind. This opportunity arose with the outbreak of the
Franco-Prussian War
The Franco-Prussian War or Franco-German War, often referred to in France as the War of 1870, was a conflict between the Second French Empire and the North German Confederation led by the Kingdom of Prussia. Lasting from 19 July 1870 to 28 Janua ...
in 1870. Historians have long debated Bismarck's role in the events leading up to the war. The traditional view, promulgated in large part by late 19th- and early 20th-century pro-Prussian historians, maintains that Bismarck's intent was always German unification. Post-1945 historians, however, see more short-term opportunism and cynicism in Bismarck's manipulation of the circumstances to create a war, rather than a grand scheme to unify a nation-state. Regardless of motivation, by manipulating events of 1866 and 1870, Bismarck demonstrated the political and diplomatic skill that had caused Wilhelm to turn to him in 1862.
Three episodes proved fundamental to the unification of Germany. First, the death
without male heirs of
Frederick VII of Denmark
Frederick VII (Frederik Carl Christian; 6 October 1808 – 15 November 1863) was King of Denmark from 1848 to 1863. He was the last Danish monarch of the older Royal branch of the House of Oldenburg and the last monarch, king of Denmark to r ...
led to the
Second War of Schleswig
The Second Schleswig War (; or German Danish War), also sometimes known as the Dano-Prussian War or Prusso-Danish War, was the second military conflict over the Schleswig–Holstein question of the nineteenth century. The war began on 1 Februar ...
in 1864. Second, the
unification of Italy
The unification of Italy ( ), also known as the Risorgimento (; ), was the 19th century Political movement, political and social movement that in 1861 ended in the Proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, annexation of List of historic states of ...
provided Prussia an ally against Austria in the
Austro-Prussian War
The Austro-Prussian War (German: ''Preußisch-Österreichischer Krieg''), also known by many other names,Seven Weeks' War, German Civil War, Second War of Unification, Brothers War or Fraternal War, known in Germany as ("German War"), ''Deutsc ...
of 1866. Finally, France—fearing Hohenzollern encirclement—declared war on Prussia in 1870, resulting in the
Franco-Prussian War
The Franco-Prussian War or Franco-German War, often referred to in France as the War of 1870, was a conflict between the Second French Empire and the North German Confederation led by the Kingdom of Prussia. Lasting from 19 July 1870 to 28 Janua ...
. Through a combination of Bismarck's diplomacy and political leadership,
von Roon's military reorganization, and
von Moltke's military strategy, Prussia demonstrated that none of the European signatories of the
1815 peace treaty could guarantee Austria's sphere of influence in Central Europe, thus achieving Prussian hegemony in Germany and ending the dualism debate.
The Schleswig-Holstein Question
The first episode in the saga of German unification under Bismarck came with the Schleswig-Holstein Question. On 15 November 1863,
Christian IX became king of Denmark and duke of
Schleswig
The Duchy of Schleswig (; ; ; ; ; ) was a duchy in Southern Jutland () covering the area between about 60 km (35 miles) north and 70 km (45 mi) south of the current border between Germany and Denmark. The territory has been di ...
,
Holstein
Holstein (; ; ; ; ) is the region between the rivers Elbe and Eider (river), Eider. It is the southern half of Schleswig-Holstein, the northernmost States of Germany, state of Germany.
Holstein once existed as the German County of Holstein (; 8 ...
, and
Lauenburg
Lauenburg (), or Lauenburg an der Elbe (; ), is a town in the state of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is situated on the northern bank of the river Elbe, east of Hamburg. It is overall the southernmost town of Schleswig-Holstein and belongs to ...
, which the Danish king held in
personal union
A personal union is a combination of two or more monarchical states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, involves the constituent states being to some extent in ...
. On 18 November 1863, he signed the
Danish November Constitution which replaced The Law of Sjælland and The Law of Jutland, which meant the new constitution applied to the Duchy of Schleswig. The
German Confederation
The German Confederation ( ) was an association of 39 predominantly German-speaking sovereign states in Central Europe. It was created by the Congress of Vienna in 1815 as a replacement of the former Holy Roman Empire, which had been dissolved ...
saw this act as a violation of the
London Protocol of 1852, which emphasized the status of the Kingdom of Denmark as distinct from the three independent duchies. The German Confederation could use the ethnicities of the area as a rallying cry: Holstein and Lauenburg were largely of German origin and spoke German in everyday life, while Schleswig had a significant Danish population and history. Diplomatic attempts to have the November Constitution repealed collapsed, and fighting began when Prussian and Austrian troops crossed the
Eider river on 1 February 1864.
Initially, the Danes attempted to defend their country using an ancient earthen wall known as the ''
Danevirke
The Danevirke or Danework (modern Danish language, Danish spelling: ''Dannevirke''; in Old Norse language, Old Norse: ''Danavirki'', in German language, German: ''Danewerk'', literally meaning ''Earthworks (archaeology), earthwork of the Danes'') ...
'', but this proved futile. The Danes were no match for the combined Prussian and Austrian forces and their modern armaments. The
needle gun, one of the first
bolt action rifles to be used in conflict, aided the Prussians in both this war and the
Austro-Prussian War
The Austro-Prussian War (German: ''Preußisch-Österreichischer Krieg''), also known by many other names,Seven Weeks' War, German Civil War, Second War of Unification, Brothers War or Fraternal War, known in Germany as ("German War"), ''Deutsc ...
two years later. The rifle enabled a Prussian soldier to fire five shots while lying prone, while its muzzle-loading counterpart could only fire one shot and had to be reloaded while standing. The
Second Schleswig War
The Second Schleswig War (; or German Danish War), also sometimes known as the Dano-Prussian War or Prusso-Danish War, was the second military conflict over the Schleswig–Holstein question of the nineteenth century. The war began on 1 Februar ...
resulted in victory for the combined armies of Prussia and Austria, and the two countries won control of Schleswig and Holstein in the concluding
peace of Vienna, signed on 30 October 1864.
War between Austria and Prussia, 1866

The second episode in Bismarck's unification efforts occurred in 1866. In concert with
the newly formed Italy, Bismarck created a diplomatic environment in which Austria declared war on Prussia. The dramatic prelude to the war occurred largely in Frankfurt, where the two powers claimed to speak for all the German states in the parliament. In April 1866, the Prussian representative in
Florence
Florence ( ; ) is the capital city of the Italy, Italian region of Tuscany. It is also the most populated city in Tuscany, with 362,353 inhabitants, and 989,460 in Metropolitan City of Florence, its metropolitan province as of 2025.
Florence ...
signed a secret agreement with the Italian government, committing each state to assist the other in a war against Austria. The next day, the Prussian delegate to the Frankfurt assembly presented a plan calling for a national constitution, a directly elected national Diet, and universal suffrage. German liberals were justifiably skeptical of this plan, having witnessed Bismarck's difficult and ambiguous relationship with the Prussian ''Landtag'' (State Parliament), a relationship characterized by Bismarck's cajoling and riding roughshod over the representatives. These skeptics saw the proposal as a ploy to enhance Prussian power rather than a progressive agenda of reform.
Choosing sides
The debate over the proposed national constitution became moot when news of Italian troop movements in
Tyrol
Tyrol ( ; historically the Tyrole; ; ) is a historical region in the Alps of Northern Italy and western Austria. The area was historically the core of the County of Tyrol, part of the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian Empire and Austria-Hungary, f ...
and near the Venetian border reached Vienna in April 1866. The Austrian government ordered partial
mobilization
Mobilization (alternatively spelled as mobilisation) is the act of assembling and readying military troops and supplies for war. The word ''mobilization'' was first used in a military context in the 1850s to describe the preparation of the ...
in the southern regions; the Italians responded by ordering full mobilization. Despite calls for rational thought and action, Italy, Prussia, and Austria continued to rush toward armed conflict. On 1 May, Wilhelm gave
von Moltke command over the Prussian armed forces, and the next day he began full-scale mobilization.
In the Diet, the group of middle-sized states, known as ''Mittelstaaten'' (
Bavaria
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a States of Germany, state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the list of German states by area, largest German state by land area, comprising approximately 1/5 of the total l ...
,
Württemberg
Württemberg ( ; ) is a historical German territory roughly corresponding to the cultural and linguistic region of Swabia. The main town of the region is Stuttgart.
Together with Baden and Province of Hohenzollern, Hohenzollern, two other histo ...
, the grand duchies of
Baden
Baden (; ) is a historical territory in southern Germany. In earlier times it was considered to be on both sides of the Upper Rhine, but since the Napoleonic Wars, it has been considered only East of the Rhine.
History
The margraves of Ba ...
and
Hesse
Hesse or Hessen ( ), officially the State of Hesse (), is a States of Germany, state in Germany. Its capital city is Wiesbaden, and the largest urban area is Frankfurt, which is also the country's principal financial centre. Two other major hist ...
, and the duchies of
Saxony–Weimar,
Saxony–Meiningen,
Saxony–Coburg, and
Nassau), supported complete demobilization within the Confederation. These individual governments rejected the potent combination of enticing promises and subtle (or outright) threats Bismarck used to try to gain their support against the Habsburgs. The Prussian
war cabinet understood that its only supporters among the German states against the Habsburgs were two small principalities bordering on
Brandenburg
Brandenburg, officially the State of Brandenburg, is a States of Germany, state in northeastern Germany. Brandenburg borders Poland and the states of Berlin, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony. It is the List of Ger ...
that had little military strength or political clout: the Grand Duchies of
Mecklenburg-Schwerin
The Duchy of Mecklenburg-Schwerin () was a duchy in northern Germany created in 1701, when Frederick William, Duke of Mecklenburg-Schwerin, Frederick William and Adolphus Frederick II, Duke of Mecklenburg-Strelitz, Adolphus Frederick II divided ...
and
Mecklenburg-Strelitz
The Duchy of Mecklenburg-Strelitz was a duchy in Northern Germany consisting of the eastern fifth of the historic Mecklenburg region, roughly corresponding with the present-day Mecklenburg-Strelitz district (the former Lordship of Stargard) ...
. They also understood that Prussia's only ally abroad was Italy.
Opposition to Prussia's strong-armed tactics surfaced in other social and political groups. Throughout the German states, city councils, liberal parliamentary members who favored a unified state, and chambers of commerce—which would see great benefits from unification—opposed any war between Prussia and Austria. They believed any such conflict would only serve the interests of royal dynasties. Their own interests, which they understood as "civil" or "bourgeois", seemed irrelevant. Public opinion also opposed Prussian domination. Catholic populations along the
Rhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the List of rivers of Europe, major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Austria–Swit ...
—especially in such cosmopolitan regions as
Cologne
Cologne ( ; ; ) is the largest city of the States of Germany, German state of North Rhine-Westphalia and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with nearly 1.1 million inhabitants in the city pr ...
and in the heavily populated
Ruhr
The Ruhr ( ; , also ''Ruhrpott'' ), also referred to as the Ruhr Area, sometimes Ruhr District, Ruhr Region, or Ruhr Valley, is a polycentric urban area in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With a population density of 1,160/km2 and a populati ...
Valley—continued to support Austria. By late spring, most important states opposed Berlin's effort to reorganize the German states by force. The Prussian cabinet saw German unity as an issue of power and a question of who had the strength and will to wield that power. Meanwhile, the liberals in the Frankfurt assembly saw German unity as a process of negotiation that would lead to the distribution of power among the many parties.
Austria isolated

Although several German states initially sided with Austria, they stayed on the defensive and failed to take effective initiatives against Prussian troops. The Austrian army therefore faced the
technologically superior Prussian army with support only from
Saxony
Saxony, officially the Free State of Saxony, is a landlocked state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, and Bavaria, as well as the countries of Poland and the Czech Republic. Its capital is Dresden, and ...
. France promised aid, but it came late and was insufficient. Complicating the situation for Austria, the Italian mobilization on Austria's southern border required a diversion of forces away from battle with Prussia to fight the
Third Italian War of Independence
The Third Italian War of Independence () was a war between the Kingdom of Italy and the Austrian Empire fought between June and August 1866. The conflict paralleled the Austro-Prussian War and resulted in Austria giving the region of Venetia (p ...
on a second front in
Venetia and on the Adriatic sea.

A quick peace was essential to keep Russia from entering the conflict on Austria's side. In the day-long
Battle of Königgrätz, near the village of
Sadová,
Friedrich Carl and his troops arrived late, and in the wrong place. Once he arrived, however, he ordered his troops immediately into the fray. The battle was a decisive victory for Prussia and forced the Habsburgs to end the war with the unfavorable
Peace of Prague, laying the groundwork for the ''Kleindeutschland'' (little Germany) solution, or "Germany without Austria."
Founding a unified state
Peace of Prague and the North German Confederation
The
Peace of Prague sealed the dissolution of the
German Confederation
The German Confederation ( ) was an association of 39 predominantly German-speaking sovereign states in Central Europe. It was created by the Congress of Vienna in 1815 as a replacement of the former Holy Roman Empire, which had been dissolved ...
. Its former leading state, the Austrian Empire, was along with the majority of its allies excluded from the ensuing
North German Confederation Treaty
The North German Confederation Treaty (in German ''Augustbündnis'', or Alliance of August) (also called the North German Federation Treaty and the Treaty of 18 August 1866) was the treaty between the Kingdom of Prussia and other northern and centr ...
sponsored by Prussia which directly annexed
Hanover
Hanover ( ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the States of Germany, German state of Lower Saxony. Its population of 535,932 (2021) makes it the List of cities in Germany by population, 13th-largest city in Germany as well as the fourth-l ...
,
Hesse-Kassel
The Landgraviate of Hesse-Kassel (), spelled Hesse-Cassel during its entire existence, also known as the Hessian Palatinate (), was a state of the Holy Roman Empire. The state was created in 1567 when the Landgraviate of Hesse was divided upon t ...
,
Nassau, and the
city of Frankfurt, while
Hesse Darmstadt lost some territory but kept its statehood. At the same time, the original East Prussian cradle of the Prussian statehood as well as the Prussian-held Polish- or Kashubian-speaking territories of
Province of Posen
The Province of Posen (; ) was a Provinces of Prussia, province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1848 to 1920, occupying most of the historical Greater Poland. The province was established following the Greater Poland Uprising (1848), Poznań Uprisi ...
and
West Prussia
The Province of West Prussia (; ; ) was a province of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and from 1878 to 1919. West Prussia was established as a province of the Kingdom of Prussia in 1773, formed from Royal Prussia of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonweal ...
were formally annexed into the
North German Confederation
The North German Confederation () was initially a German military alliance established in August 1866 under the leadership of the Kingdom of Prussia, which was transformed in the subsequent year into a confederated state (a ''de facto'' feder ...
, thus Germany. Following adoption of the
North German Constitution, the new state obtained its own constitution, flag, and governmental and administrative structures.
Through military victory, Prussia under Bismarck's influence had overcome Austria's active resistance to the idea of a unified Germany. The states south of the
Main River (Baden, Württemberg, and Bavaria) signed separate treaties requiring them to pay indemnities and to form alliances bringing them into Prussia's sphere of influence. Austria's influence over the German states may have been broken, but the war also splintered the spirit of pan-German unity, as many German states resented Prussian power politics.
Unified Italy and Austro-Hungarian Compromise
The
Peace of Prague offered lenient terms to Austria but its relationship with the new nation-state of Italy underwent major restructuring. Although the Austrians were far more successful in the military field against Italian troops, the monarchy lost the important province of
Venetia. The Habsburgs ceded Venetia to France, which then formally transferred control to Italy.
The end of Austrian dominance of the German states shifted Austria's attention to the Balkans. The reality of defeat for Austria also caused a reevaluation of internal divisions, local autonomy, and liberalism. In 1867, the Austrian emperor
Franz Joseph
Franz Joseph I or Francis Joseph I ( ; ; 18 August 1830 – 21 November 1916) was Emperor of Austria, King of Hungary, and the ruler of the Grand title of the emperor of Austria, other states of the Habsburg monarchy from 1848 until his death ...
accepted a settlement (the
Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867
The Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867 (, ) established the dual monarchy of Austria-Hungary, which was a military and diplomatic alliance of two sovereign states. The Compromise only partially re-established the former pre-1848 sovereign ...
) in which he gave his Hungarian holdings equal status with his Austrian domains, creating the Dual Monarchy of
Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, also referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Dual Monarchy or the Habsburg Monarchy, was a multi-national constitutional monarchy in Central Europe#Before World War I, Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. A military ...
.
War with France
The French public resented the Prussian victory and demanded ''Revanche pour Sadová'' ("Revenge for Sadova"), illustrating anti-Prussian sentiment in France—a problem that would accelerate in the months leading up to the
Franco-Prussian War
The Franco-Prussian War or Franco-German War, often referred to in France as the War of 1870, was a conflict between the Second French Empire and the North German Confederation led by the Kingdom of Prussia. Lasting from 19 July 1870 to 28 Janua ...
. The Austro-Prussian War also damaged relations with the French government. At a meeting in
Biarritz
Biarritz ( , , , ; also spelled ; ) is a city on the Bay of Biscay, on the Atlantic coast in the Pyrénées-Atlantiques department in the French Basque Country in southwestern France. It is located from the border with Spain. It is a luxu ...
in September 1865 with
Napoleon III
Napoleon III (Charles-Louis Napoléon Bonaparte; 20 April 18089 January 1873) was President of France from 1848 to 1852 and then Emperor of the French from 1852 until his deposition in 1870. He was the first president, second emperor, and last ...
, Bismarck had let it be understood (or Napoleon had thought he understood) that France might annex parts of Belgium and
Luxembourg
Luxembourg, officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, is a landlocked country in Western Europe. It is bordered by Belgium to the west and north, Germany to the east, and France on the south. Its capital and most populous city, Luxembour ...
in exchange for its neutrality in the war. These annexations did not happen, resulting in animosity from Napoleon towards Bismarck.
Background
By 1870 three of the important lessons of the Austro-Prussian war had become apparent. The first lesson was that, through force of arms, a powerful state could challenge the old alliances and spheres of influence established in 1815. Second, through diplomatic maneuvering, a skilful leader could create an environment in which a rival state would declare war first, thus forcing states allied with the "victim" of external aggression to come to the leader's aid. Finally, as Prussian military capacity far exceeded that of Austria, Prussia was clearly the only state within the Confederation (or among the German states generally) capable of protecting all of them from potential interference or aggression. In 1866, most mid-sized German states had opposed Prussia, but by 1870 these states had been coerced and coaxed into mutually protective alliances with Prussia. If a European state declared war on one of their members, then they all would come to the defense of the attacked state. With skilful manipulation of European politics, Bismarck created a situation in which France would play the role of aggressor in German affairs, while Prussia would play that of the protector of German rights and liberties.
At the Congress of Vienna in 1815, Metternich and his conservative allies had reestablished the Spanish monarchy under
King Ferdinand VII
Ferdinand VII (; 14 October 1784 – 29 September 1833) was King of Spain during the early 19th century. He reigned briefly in 1808 and then again from 1813 to his death in 1833. Before 1813 he was known as ''el Deseado'' (the Desired), and af ...
. Over the following forty years, the great powers supported the Spanish monarchy, but events in 1868 would further test the old system, finally providing the external trigger needed by Bismarck.
Spanish prelude
A revolution in Spain overthrew
Queen Isabella II, and the throne remained empty while Isabella lived in sumptuous exile in Paris. The Spanish, looking for a suitable Catholic successor, had offered the post to three European princes, each of whom was rejected by
Napoleon III
Napoleon III (Charles-Louis Napoléon Bonaparte; 20 April 18089 January 1873) was President of France from 1848 to 1852 and then Emperor of the French from 1852 until his deposition in 1870. He was the first president, second emperor, and last ...
, who served as regional power-broker. Finally, in 1870 the Regency offered the crown to
Leopold of
Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen
Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen () was a principality in southwestern Germany. Its rulers belonged to the junior House of Hohenzollern#Swabian branch, Swabian branch of the House of Hohenzollern. The Swabian Hohenzollerns were elevated to princes in 162 ...
, a prince of the Catholic cadet Hohenzollern line. The ensuing furor has been dubbed by historians as the Hohenzollern candidature. Over the next few weeks, the Spanish offer turned into the talk of Europe. Bismarck encouraged Leopold to accept the offer. A successful installment of a Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen king in Spain would mean that two countries on either side of France would both have German kings of Hohenzollern descent. This may have been a pleasing prospect for Bismarck, but it was unacceptable to either Napoleon III or to
Agenor, duc de Gramont, his minister of foreign affairs. Gramont wrote a sharply formulated ultimatum to Wilhelm, as head of the Hohenzollern family, stating that if any Hohenzollern prince should accept the crown of Spain, the French government would respond—although he left ambiguous the nature of such response. The prince withdrew as a candidate, thus defusing the crisis, but the French ambassador to Berlin would not let the issue lie. He approached the Prussian king directly while Wilhelm was vacationing in
Ems Spa, demanding that the King release a statement saying he would never support the installation of a Hohenzollern on the throne of Spain. Wilhelm refused to give such an encompassing statement, and he sent Bismarck a dispatch by telegram describing the French demands. Bismarck used the king's telegram, called the
Ems Dispatch, as a template for a short statement to the press. With its wording shortened and sharpened by Bismarck—and further alterations made in the course of its translation by the French agency
Havas
Havas NV () is a French multinational corporation, multinational advertising agency, advertising and public relations company, with its registered office and head office in Puteaux, France.
Havas operates in more than 100 countries. The group ...
—the Ems Dispatch raised an angry furor in France. The French public, still aggravated over the defeat at Sadová, demanded war.
Open hostilities and the disastrous end of the Second French Empire

Napoleon III had tried to secure territorial concessions from both sides before and after the Austro-Prussian War, but despite his role as mediator during the peace negotiations, he ended up with nothing. He then hoped that Austria would join in a war of revenge and that its former allies—particularly the southern German states of Baden, Württemberg, and Bavaria—would join in the cause. This hope would prove futile since the 1866 treaty came into effect and united all German states militarily—if not happily—to fight against France. Instead of a war of revenge against Prussia, supported by various German allies, France engaged in a war against all of the German states without any allies of its own.
The reorganization of the military by
von Roon and the operational strategy of
Moltke combined against France to great effect. The speed of Prussian mobilization astonished the French, and the Prussian ability to concentrate power at specific points—reminiscent of Napoleon I's strategies seventy years earlier—overwhelmed French mobilization. Utilizing their efficiently laid rail grid, Prussian troops were delivered to battle areas rested and prepared to fight, whereas French troops had to march for considerable distances to reach combat zones. After a number of battles, notably
Spicheren,
Wörth,
Mars la Tour, and
Gravelotte, the Prussians defeated the main French armies and advanced on the primary city of
Metz
Metz ( , , , then ) is a city in northeast France located at the confluence of the Moselle (river), Moselle and the Seille (Moselle), Seille rivers. Metz is the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Moselle (department), Moselle Departments ...
and the French capital of Paris. They captured Napoleon III and took an entire army as prisoners at
Sedan on 1 September 1870.
Proclamation of the German Empire
The humiliating capture of the French emperor and the loss of the French army itself, which marched into captivity at a makeshift camp in the Saarland ("Camp Misery"), threw the French government into turmoil; Napoleon's energetic opponents overthrew his government and proclaimed the
Third Republic. "In the days after Sedan, Prussian envoys met with the French and demanded a large cash indemnity as well as the cession of Alsace and Lorraine. All parties in France rejected the terms, insisting that any armistice be forged "on the basis of territorial integrity." France, in other words, would pay reparations for starting the war, but would, in Jules Favre's famous phrase, "cede neither a clod of our earth nor a stone of our fortresses". The German High Command expected an overture of peace from the French, but the new republic refused to surrender. The Prussian army
invested Paris and
held it under siege until mid-January, with the city being "ineffectually bombarded". Nevertheless, in January, the Germans fired some 12,000 shells, 300–400 grenades daily into the city. On January 18, 1871, the German princes and senior military commanders
proclaimed Wilhelm "German Emperor" in the Hall of Mirrors at the Palace of Versailles. Under the subsequent
Treaty of Frankfurt, France relinquished most of its traditionally German regions (
Alsace
Alsace (, ; ) is a cultural region and a territorial collectivity in the Grand Est administrative region of northeastern France, on the west bank of the upper Rhine, next to Germany and Switzerland. In January 2021, it had a population of 1,9 ...
and the German-speaking part of Lorraine (province), Lorraine); paid an indemnity, calculated (on the basis of population) as the precise equivalent of the indemnity that Napoleon Bonaparte imposed on Prussia in 1807; and accepted German administration of Paris and most of northern France, with "German troops to be withdrawn stage by stage with each installment of the indemnity payment".
War as ″the capstone of the unification process″
Victory in the Franco-Prussian War proved the capstone of the unification process. In the first half of the 1860s, Austria and Prussia both contended to speak for the German states; both maintained they could support German interests abroad and protect German interests at home. In responding to the Schleswig-Holstein Question, they both proved equally diligent in doing so. After the victory over Austria in 1866, Prussia began internally asserting its authority to speak for the German states and defend German interests, while Austria began directing more and more of its attention to possessions in the Balkans. The victory over France in 1871 expanded Prussian hegemony in the German states (aside from Austria) to the international level. With the proclamation of Wilhelm as ''Kaiser'', Prussia assumed the leadership of the new empire. The southern states became officially incorporated into a unified Germany at the Treaty of Versailles of 1871 (signed 26 February 1871; later ratified in the
Treaty of Frankfurt of 10 May 1871), which formally ended the war. Although Bismarck had led the transformation of Germany from a loose confederation into a federal nation state, he had not done it alone. Unification was achieved by building on a tradition of legal collaboration under the Holy Roman Empire and economic collaboration through the ''Zollverein.'' The difficulties of the ''Vormärz'', the impact of the 1848 liberals, the importance of von Roon's military reorganization, and von Moltke's strategic brilliance all played a part in political unification. "Einheit – unity – was achieved at the expense of Freiheit – freedom. The German Empire became," in Karl Marx's words, "a military despotism cloaked in parliamentary forms with a feudal ingredient, influenced by the bourgeoisie, festooned with bureaucrats and guarded by police." Indeed, many historians would see Germany's "escape into war" in 1914 as a flight from all of the internal-political contradictions forged by Bismarck at Versailles in the fall of 1870.
Internal political and administrative unification
The new
German Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperia ...
included 26 political entities: twenty-five constituent states (or ''Bundesstaaten'') and one Imperial Territory (or ''Reichsland''). It realized the ''Kleindeutsche Lösung'' ("Lesser German Solution", with the exclusion of Austria) as opposed to a ''German question, Großdeutsche Lösung'' or "Greater German Solution", which would have included Austria. Unifying various states into one nation required more than some military victories, however much these might have boosted morale. It also required a rethinking of political, social, and cultural behaviors and the construction of new metaphors about "us" and "them". Who were the new members of this new nation? What did they stand for? How were they to be organized?
Constituent states of the Empire
Though often characterized as a federation of monarchs, the German Empire, strictly speaking, federated a group of 26 constituent entities with different forms of government, ranging from the main four constitutional monarchies to the three republican Hanseatic League, Hanseatic cities.
Political structure of the Empire
The 1866
North German Constitution became (with some semantic adjustments) the 1871
Constitution of the German Empire
The Constitution of the German Empire () was the basic law of the German Empire. It came into effect on 4 May 1871 and lasted formally until 14 August 1919. Some German historians refer to it as Bismarck's imperial constitution (German: , BRV). ...
. With this constitution, the new Germany acquired some democratic features: notably the Reichstag (German Empire), Imperial Diet, which—in contrast to the parliament of Prussia—gave citizens representation on the basis of elections by direct and equal Universal suffrage, suffrage of all males who had reached the age of 25. Furthermore, elections were generally free of chicanery, engendering pride in the national parliament. However, legislation required the consent of the ''Bundesrat'', the federal council of deputies from the states, in and over which Prussia had a powerful influence; Prussia could appoint 17 of 58 delegates with only 14 votes needed for a veto. Prussia thus exercised influence in both bodies, with executive power vested in the Prussian King as ''Kaiser'', who appointed the federal chancellor. The chancellor was accountable solely to, and served entirely at the discretion of, the Emperor. Officially, the chancellor functioned as a one-man cabinet and was responsible for the conduct of all state affairs; in practice, the State Secretary, State Secretaries (bureaucratic top officials in charge of such fields as finance, war, foreign affairs, etc.) acted as unofficial portfolio ministers. With the exception of the years 1872–1873 and 1892–1894, the imperial chancellor was always simultaneously the prime minister of the imperial dynasty's hegemonic home-kingdom, Prussia. The Imperial Diet had the power to pass, amend, or reject bills, but it could not initiate legislation. (The power of initiating legislation rested with the chancellor.) The other states retained their own governments, but the military forces of the smaller states came under Prussian control. The militaries of the larger states (such as the Kingdoms of Kingdom of Bavaria, Bavaria and Kingdom of Saxony, Saxony) retained some autonomy, but they underwent major reforms to coordinate with Prussian military principles and came under federal government control in wartime.
Historical arguments and the Empire's social anatomy

The ''Sonderweg'' hypothesis attributed Germany's difficult 20th century to the weak political, legal, and economic basis of the new empire. The Prussian landed elites, the ''Prussian Junkers, Junkers'', retained a substantial share of political power in the unified state. The ''Sonderweg'' hypothesis attributed their power to the absence of a revolutionary breakthrough by the middle classes, or by peasants in combination with the urban workers, in 1848 and again in 1871. Recent research into the role of the Grand Bourgeoisie—which included bankers, merchants, industrialists, and entrepreneurs—in the construction of the new state has largely refuted the claim of political and economic dominance of the ''Junkers'' as a social group. This newer scholarship has demonstrated the importance of the merchant classes of the Hanseatic League, Hanseatic cities and the industrial leadership (the latter particularly important in the Rhineland) in the ongoing development of the Second Empire.
Additional studies of different groups in Wilhelmine Germany have all contributed to a new view of the period. Although the ''Junkers'' did, indeed, continue to control the officer corps, they did not dominate social, political, and economic matters as much as the ''Sonderweg'' theorists had hypothesized. Eastern ''Junker'' power had a counterweight in the western provinces in the form of the Grand Bourgeoisie and in the growing professional class of bureaucrats, teachers, professors, doctors, lawyers, scientists, etc.
Beyond the political mechanism: forming a nation

If the Wartburg and Hambach rallies had lacked a constitution and administrative apparatus, that problem was addressed between 1867 and 1871. Yet, as Germans discovered, grand speeches, flags, and enthusiastic crowds, a constitution, a political reorganization, and the provision of an imperial superstructure; and the revised Customs Union of 1867–68, still did not make a nation.
A key element of the
nation-state
A nation state, or nation-state, is a political entity in which the state (a centralized political organization ruling over a population within a territory) and the nation (a community based on a common identity) are (broadly or ideally) con ...
is the creation of a national culture, frequently—although not necessarily—through deliberate national policy. In the new German nation, a ''Kulturkampf'' (1872–78) that followed political, economic, and administrative unification attempted to address, with a remarkable lack of success, some of the contradictions in German society. In particular, it involved a struggle over language, education, and religion. A policy of Germanization of non-German people of the empire's population, including the Polish people, Polish and Danish people, Danish minorities, started with language, in particular, the German language, compulsory schooling (Germanization), and the attempted creation of standardized curricula for those schools to promote and celebrate the idea of a shared past. Finally, it extended to the religion of the new Empire's population.
''Kulturkampf''
For some Germans, the definition of ''nation'' did not include pluralism, and Roman Catholicism, Catholics in particular came under scrutiny; some Germans, and especially Bismarck, feared that the Catholics' connection to the papacy might make them less loyal to the nation. As Chancellor of Germany#Chancellor of the German Empire (1871–1918), chancellor, Bismarck tried without much success to limit the influence of the Roman Catholic Church and of its party-political arm, the Catholic Centre Party, in schools and education- and language-related policies. The Catholic Centre Party remained particularly well entrenched in the Catholic strongholds of Bavaria and southern Baden, and in urban areas that held high populations of displaced rural workers seeking jobs in the heavy industry, and sought to protect the rights not only of Catholics, but other minorities, including the Poles, and the French minorities in the Alsatian lands. The May Laws of 1873 brought the appointment of priests, and their education, under the control of the state, resulting in the closure of many seminaries, and a shortage of priests. The Kulturkampf#Congregations Law 1875, Congregations Law of 1875 abolished religious orders, ended state subsidies to the Catholic Church, and removed religious protections from the Prussian constitution.
Integrating the Jewish community

The History of the Jews in Germany, Germanized Jews remained another vulnerable population in the new German nation-state. Since 1780, after emancipation by the Holy Roman Emperor Joseph II, Holy Roman Emperor, Joseph II, Jews in the former Habsburg territories had enjoyed considerable economic and legal privileges that their counterparts in other German-speaking territories did not: they could own land, for example, and they did not have to live in a Jewish quarter (also called the ''Ghetto, Judengasse'', or "Jews' alley"). They could also attend universities and enter the professions. During the Revolutionary and Napoleonic eras, many of the previously strong barriers between Jews and Christians broke down. Napoleon had ordered the Jewish emancipation, emancipation of Jews throughout territories under French hegemony. Like their French counterparts, wealthy German Jews sponsored Salon (gathering), salons; in particular, several Jewish ''salonnières'' held important gatherings in Frankfurt and Berlin during which German intellectuals developed their own form of republican intellectualism. Throughout the subsequent decades, beginning almost immediately after the defeat of the French, reaction against the mixing of Jews and Christians limited the intellectual impact of these salons. Beyond the salons, Jews continued a process of Germanization in which they intentionally adopted German modes of dress and speech, working to insert themselves into the emerging 19th-century German public sphere. The religious reform movement among German Jews reflected this effort.
By the years of unification, German Jews played an important role in the intellectual underpinnings of the German professional, intellectual, and social life. The expulsion of Jews from Russia in the 1880s and 1890s complicated integration into the German public sphere. Russian Jews arrived in north German cities in the thousands; considerably less educated and less affluent, their often dismal poverty dismayed many of the Germanized Jews. Many of the problems related to poverty (such as illness, overcrowded housing, unemployment, school absenteeism, refusal to learn German, etc.) emphasized their distinctiveness for not only the Christian Germans, but for the local Jewish populations as well.
Writing the story of the nation
Another important element in nation-building, the story of the heroic past, fell to such nationalist German historians as the liberal constitutionalist Friedrich Christoph Dahlmann, Friedrich Dahlmann (1785–1860), his conservative student Heinrich von Treitschke (1834–1896), and others less conservative, such as Theodor Mommsen (1817–1903) and Heinrich von Sybel (1817–1895), to name two. Dahlmann himself died before unification, but he laid the groundwork for the nationalist histories to come through his histories of the English and French revolutions, by casting these revolutions as fundamental to the construction of a nation, and Dahlmann himself viewed Prussia as the logical agent of unification.
Heinrich von Treitschke's ''History of Germany in the Nineteenth Century'', published in 1879, has perhaps a misleading title: it privileges the history of Prussia over the history of other German states, and it tells the story of the German-speaking peoples through the guise of Prussia's destiny to unite all German states under its leadership. The creation of this
''Borussian'' myth (''Borussia'' is the Latin name for Prussia) established Prussia as Germany's savior; it was the destiny of all Germans to be united, this myth maintains, and it was Prussia's destiny to accomplish this.
According to this story, Prussia played the dominant role in bringing the German states together as a nation-state; only Prussia could protect German liberties from being crushed by French or Russian influence. The story continues by drawing on Prussia's role in saving Germans from the resurgence of Napoleon's power in 1815, at Waterloo, creating some semblance of economic unity, and uniting Germans under one proud flag after 1871.
Mommsen's contributions to the ''Monumenta Germaniae Historica'' laid the groundwork for additional scholarship on the study of the German nation, expanding the notion of "Germany" to mean other areas beyond Prussia. A liberal professor, historian, and theologian, and generally a titan among late 19th-century scholars, Mommsen served as a delegate to the Prussian House of Representatives from 1863 to 1866 and 1873 to 1879; he also served as a delegate to the ''Reichstag'' from 1881 to 1884, for the liberal German Progress Party (''Deutsche Fortschrittspartei'') and later for the National Liberal Party (Germany), National Liberal Party. He opposed the Antisemitism, antisemitic programs of Bismarck's ''Kulturkampf'' and the vitriolic text that Treitschke often employed in the publication of his ''Studien über die Judenfrage'' (''Studies of the Jewish Question''), which encouraged assimilation and Germanization of Jews.
See also
*Italian unification
*Unification of Moldavia and Wallachia, Formation of Romania
*Reichsbürgerbewegung
*
Pan-Germanism
Pan-Germanism ( or '), also occasionally known as Pan-Germanicism, is a pan-nationalist political idea. Pan-Germanism seeks to unify all ethnic Germans, German-speaking people, and possibly also non-German Germanic peoples – into a sin ...
*Qin's wars of unification, Qin's wars of Chinese unification
Notes
References
Sources
*
**
*
*
*
*
**
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
**
*
*
** )
*
Further reading
*
*
*
**
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
**
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
Documents of German Unification
{{Authority control
Pan-Germanism, *
Modern history of Germany
National unifications, Germany
North German Confederation
1871 in Germany
Conflicts in 1866
Conflicts in 1871
19th century in politics
 A common language may have been seen to serve as the basis of a nation, but as contemporary historians of 19th-century Germany noted, it took more than linguistic similarity to unify these several hundred polities. The experience of German-speaking Central Europe during the years of French hegemony contributed to a sense of common cause to expel the French invaders and reassert control over their own lands. Napoleon's campaigns in Poland (1806–07) resulting in his decision to re-establish a form of Polish statehood (the
A common language may have been seen to serve as the basis of a nation, but as contemporary historians of 19th-century Germany noted, it took more than linguistic similarity to unify these several hundred polities. The experience of German-speaking Central Europe during the years of French hegemony contributed to a sense of common cause to expel the French invaders and reassert control over their own lands. Napoleon's campaigns in Poland (1806–07) resulting in his decision to re-establish a form of Polish statehood (the  Despite considerable conservative reaction, ideas of unity joined with notions of popular sovereignty in German-speaking lands. The '' Burschenschaft'' student organizations and popular demonstrations, such as those held at Wartburg Castle in October 1817, contributed to a growing sense of unity among German speakers of Central Europe.
At the Wartburg Festival in 1817 the first real movements among students were formed – fraternities and student organizations emerged. The colors black, red and gold were symbolic of this. Agitation by student organizations led conservative leaders such as Klemens Wenzel, Prince von Metternich, to fear the rise of nationalist sentiment.
The assassination of German dramatist
Despite considerable conservative reaction, ideas of unity joined with notions of popular sovereignty in German-speaking lands. The '' Burschenschaft'' student organizations and popular demonstrations, such as those held at Wartburg Castle in October 1817, contributed to a growing sense of unity among German speakers of Central Europe.
At the Wartburg Festival in 1817 the first real movements among students were formed – fraternities and student organizations emerged. The colors black, red and gold were symbolic of this. Agitation by student organizations led conservative leaders such as Klemens Wenzel, Prince von Metternich, to fear the rise of nationalist sentiment.
The assassination of German dramatist  Several other factors complicated the rise of
Several other factors complicated the rise of  Their pressure resulted in a variety of elections, based on different voting qualifications, such as the Prussian three-class franchise, which weighted votes based on the amount of taxes paid and therefore gave some electoral groups—chiefly the wealthier, landed ones—greater representative power.
On 27 March 1849, the
Their pressure resulted in a variety of elections, based on different voting qualifications, such as the Prussian three-class franchise, which weighted votes based on the amount of taxes paid and therefore gave some electoral groups—chiefly the wealthier, landed ones—greater representative power.
On 27 March 1849, the  King Frederick William IV suffered a stroke in 1857 and could no longer rule. This led to his brother
King Frederick William IV suffered a stroke in 1857 and could no longer rule. This led to his brother  Although several German states initially sided with Austria, they stayed on the defensive and failed to take effective initiatives against Prussian troops. The Austrian army therefore faced the technologically superior Prussian army with support only from
Although several German states initially sided with Austria, they stayed on the defensive and failed to take effective initiatives against Prussian troops. The Austrian army therefore faced the technologically superior Prussian army with support only from  Napoleon III had tried to secure territorial concessions from both sides before and after the Austro-Prussian War, but despite his role as mediator during the peace negotiations, he ended up with nothing. He then hoped that Austria would join in a war of revenge and that its former allies—particularly the southern German states of Baden, Württemberg, and Bavaria—would join in the cause. This hope would prove futile since the 1866 treaty came into effect and united all German states militarily—if not happily—to fight against France. Instead of a war of revenge against Prussia, supported by various German allies, France engaged in a war against all of the German states without any allies of its own.
The reorganization of the military by von Roon and the operational strategy of Moltke combined against France to great effect. The speed of Prussian mobilization astonished the French, and the Prussian ability to concentrate power at specific points—reminiscent of Napoleon I's strategies seventy years earlier—overwhelmed French mobilization. Utilizing their efficiently laid rail grid, Prussian troops were delivered to battle areas rested and prepared to fight, whereas French troops had to march for considerable distances to reach combat zones. After a number of battles, notably Spicheren, Wörth, Mars la Tour, and Gravelotte, the Prussians defeated the main French armies and advanced on the primary city of
Napoleon III had tried to secure territorial concessions from both sides before and after the Austro-Prussian War, but despite his role as mediator during the peace negotiations, he ended up with nothing. He then hoped that Austria would join in a war of revenge and that its former allies—particularly the southern German states of Baden, Württemberg, and Bavaria—would join in the cause. This hope would prove futile since the 1866 treaty came into effect and united all German states militarily—if not happily—to fight against France. Instead of a war of revenge against Prussia, supported by various German allies, France engaged in a war against all of the German states without any allies of its own.
The reorganization of the military by von Roon and the operational strategy of Moltke combined against France to great effect. The speed of Prussian mobilization astonished the French, and the Prussian ability to concentrate power at specific points—reminiscent of Napoleon I's strategies seventy years earlier—overwhelmed French mobilization. Utilizing their efficiently laid rail grid, Prussian troops were delivered to battle areas rested and prepared to fight, whereas French troops had to march for considerable distances to reach combat zones. After a number of battles, notably Spicheren, Wörth, Mars la Tour, and Gravelotte, the Prussians defeated the main French armies and advanced on the primary city of  If the Wartburg and Hambach rallies had lacked a constitution and administrative apparatus, that problem was addressed between 1867 and 1871. Yet, as Germans discovered, grand speeches, flags, and enthusiastic crowds, a constitution, a political reorganization, and the provision of an imperial superstructure; and the revised Customs Union of 1867–68, still did not make a nation.
A key element of the
If the Wartburg and Hambach rallies had lacked a constitution and administrative apparatus, that problem was addressed between 1867 and 1871. Yet, as Germans discovered, grand speeches, flags, and enthusiastic crowds, a constitution, a political reorganization, and the provision of an imperial superstructure; and the revised Customs Union of 1867–68, still did not make a nation.
A key element of the  The History of the Jews in Germany, Germanized Jews remained another vulnerable population in the new German nation-state. Since 1780, after emancipation by the Holy Roman Emperor Joseph II, Holy Roman Emperor, Joseph II, Jews in the former Habsburg territories had enjoyed considerable economic and legal privileges that their counterparts in other German-speaking territories did not: they could own land, for example, and they did not have to live in a Jewish quarter (also called the ''Ghetto, Judengasse'', or "Jews' alley"). They could also attend universities and enter the professions. During the Revolutionary and Napoleonic eras, many of the previously strong barriers between Jews and Christians broke down. Napoleon had ordered the Jewish emancipation, emancipation of Jews throughout territories under French hegemony. Like their French counterparts, wealthy German Jews sponsored Salon (gathering), salons; in particular, several Jewish ''salonnières'' held important gatherings in Frankfurt and Berlin during which German intellectuals developed their own form of republican intellectualism. Throughout the subsequent decades, beginning almost immediately after the defeat of the French, reaction against the mixing of Jews and Christians limited the intellectual impact of these salons. Beyond the salons, Jews continued a process of Germanization in which they intentionally adopted German modes of dress and speech, working to insert themselves into the emerging 19th-century German public sphere. The religious reform movement among German Jews reflected this effort.
By the years of unification, German Jews played an important role in the intellectual underpinnings of the German professional, intellectual, and social life. The expulsion of Jews from Russia in the 1880s and 1890s complicated integration into the German public sphere. Russian Jews arrived in north German cities in the thousands; considerably less educated and less affluent, their often dismal poverty dismayed many of the Germanized Jews. Many of the problems related to poverty (such as illness, overcrowded housing, unemployment, school absenteeism, refusal to learn German, etc.) emphasized their distinctiveness for not only the Christian Germans, but for the local Jewish populations as well.
The History of the Jews in Germany, Germanized Jews remained another vulnerable population in the new German nation-state. Since 1780, after emancipation by the Holy Roman Emperor Joseph II, Holy Roman Emperor, Joseph II, Jews in the former Habsburg territories had enjoyed considerable economic and legal privileges that their counterparts in other German-speaking territories did not: they could own land, for example, and they did not have to live in a Jewish quarter (also called the ''Ghetto, Judengasse'', or "Jews' alley"). They could also attend universities and enter the professions. During the Revolutionary and Napoleonic eras, many of the previously strong barriers between Jews and Christians broke down. Napoleon had ordered the Jewish emancipation, emancipation of Jews throughout territories under French hegemony. Like their French counterparts, wealthy German Jews sponsored Salon (gathering), salons; in particular, several Jewish ''salonnières'' held important gatherings in Frankfurt and Berlin during which German intellectuals developed their own form of republican intellectualism. Throughout the subsequent decades, beginning almost immediately after the defeat of the French, reaction against the mixing of Jews and Christians limited the intellectual impact of these salons. Beyond the salons, Jews continued a process of Germanization in which they intentionally adopted German modes of dress and speech, working to insert themselves into the emerging 19th-century German public sphere. The religious reform movement among German Jews reflected this effort.
By the years of unification, German Jews played an important role in the intellectual underpinnings of the German professional, intellectual, and social life. The expulsion of Jews from Russia in the 1880s and 1890s complicated integration into the German public sphere. Russian Jews arrived in north German cities in the thousands; considerably less educated and less affluent, their often dismal poverty dismayed many of the Germanized Jews. Many of the problems related to poverty (such as illness, overcrowded housing, unemployment, school absenteeism, refusal to learn German, etc.) emphasized their distinctiveness for not only the Christian Germans, but for the local Jewish populations as well.