Geography Of Lithuania on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Lithuania is situated on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania's boundaries have changed several times since 1918, but they have been stable since 1945. Currently, Lithuania covers an area of about . It is larger than
Lithuania is situated on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania's boundaries have changed several times since 1918, but they have been stable since 1945. Currently, Lithuania covers an area of about . It is larger than
 Lithuania lies at the edge of the
Lithuania lies at the edge of the

 Lithuania has an abundance of
Lithuania has an abundance of
Kursiu Nerija National Park
{{DEFAULTSORT:Geography Of Lithuania
Lithuania
Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, P ...
is one of the countries in the Baltic region
The Baltic Sea Region, alternatively the Baltic Rim countries (or simply the Baltic Rim), and the Baltic Sea countries/states, refers to the general area surrounding the Baltic Sea, including parts of Northern, Central and Eastern Europe. Un ...
of Europe. The most populous of the Baltic states
The Baltic states or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term encompassing Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, and the OECD. The three sovereign states on the eastern co ...
, Lithuania
Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, P ...
has of coastline consisting of the continental coast and the "Curonian Spit" coast. Lithuania's major warm-water port of Klaipėda
Klaipėda ( ; ) is a city in Lithuania on the Baltic Sea coast. It is the List of cities in Lithuania, third-largest city in Lithuania, the List of cities in the Baltic states by population, fifth-largest city in the Baltic States, and the capi ...
lies at the narrow mouth of Curonian Lagoon
The Curonian Lagoon (or Bay, Gulf; Prussian: ''Kursjanmari'', , ) is a freshwater lagoon separated from the Baltic Sea by the Curonian Spit. Its surface area is . The Neman River () supplies about 90% of its inflows; its watershed consists of ...
, a shallow lagoon
A lagoon is a shallow body of water separated from a larger body of water by a narrow landform, such as reefs, barrier islands, barrier peninsulas, or isthmuses. Lagoons are commonly divided into ''coastal lagoons'' (or ''barrier lagoons'') an ...
extending south to Kaliningrad
Kaliningrad,. known as Königsberg; ; . until 1946, is the largest city and administrative centre of Kaliningrad Oblast, an Enclave and exclave, exclave of Russia between Lithuania and Poland ( west of the bulk of Russia), located on the Prego ...
and separated from the Baltic sea by Curonian Spit, where Kuršių Nerija National Park was established for its remarkable sand dunes.
The Neman River
Neman, Nemunas or Niemen is a river in Europe that rises in central Belarus and flows through Lithuania then forms Lithuania–Russia border, the northern border of Kaliningrad Oblast, Russia's western exclave, which specifically follows its s ...
and some of its tributaries
A tributary, or an ''affluent'', is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream ('' main stem'' or ''"parent"''), river, or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries, and the main stem river into which the ...
are used for internal shipping (in 2000, 89 inland ships carried 900,000 tons of cargo, which is less than 1% of the total goods traffic).
Situated between 56.27 and 53.53 latitudes and 20.56 and 26.50 longitudes, Lithuania is glacial
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of rock, that is constantly moving downhill under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires ...
ly flat, except for morainic hills in the western uplands and eastern highlands no higher than 300 metres. The terrain is marked by numerous small lakes and swamp
A swamp is a forested wetland.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p. Swamps are considered to be transition zones because both land and water play a role in ...
s, and a mixed forest zone covers over 33% of the country. The growing season lasts 169 days in the east and 202 days in the west, with most farmland consisting of sandy- or clay-loam soils. Limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science) ...
, clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolinite, ). Most pure clay minerals are white or light-coloured, but natural clays show a variety of colours from impuriti ...
, sand
Sand is a granular material composed of finely divided mineral particles. Sand has various compositions but is usually defined by its grain size. Sand grains are smaller than gravel and coarser than silt. Sand can also refer to a textural ...
, and gravel
Gravel () is a loose aggregation of rock fragments. Gravel occurs naturally on Earth as a result of sedimentation, sedimentary and erosion, erosive geological processes; it is also produced in large quantities commercially as crushed stone.
Gr ...
are Lithuania's primary natural resources, but the coastal shelf offers perhaps of oil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) and lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturate ...
deposits, and the southeast could provide high yields of iron ore
Iron ores are rocks and minerals from which metallic iron can be economically extracted. The ores are usually rich in iron oxides and vary in color from dark grey, bright yellow, or deep purple to rusty red. The iron is usually found in the f ...
and granite
Granite ( ) is a coarse-grained (phanerite, phaneritic) intrusive rock, intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly coo ...
.
Geographical position

 Lithuania is situated on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania's boundaries have changed several times since 1918, but they have been stable since 1945. Currently, Lithuania covers an area of about . It is larger than
Lithuania is situated on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania's boundaries have changed several times since 1918, but they have been stable since 1945. Currently, Lithuania covers an area of about . It is larger than Belgium
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. Situated in a coastal lowland region known as the Low Countries, it is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeas ...
, Denmark
Denmark is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe. It is the metropole and most populous constituent of the Kingdom of Denmark,, . also known as the Danish Realm, a constitutionally unitary state that includes the Autonomous a ...
, Latvia
Latvia, officially the Republic of Latvia, is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is one of the three Baltic states, along with Estonia to the north and Lithuania to the south. It borders Russia to the east and Belarus to t ...
, Estonia
Estonia, officially the Republic of Estonia, is a country in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Ru ...
, the Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
, Slovakia
Slovakia, officially the Slovak Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the west, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's m ...
, Slovenia
Slovenia, officially the Republic of Slovenia, is a country in Central Europe. It borders Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the south and southeast, and a short (46.6 km) coastline within the Adriati ...
or Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
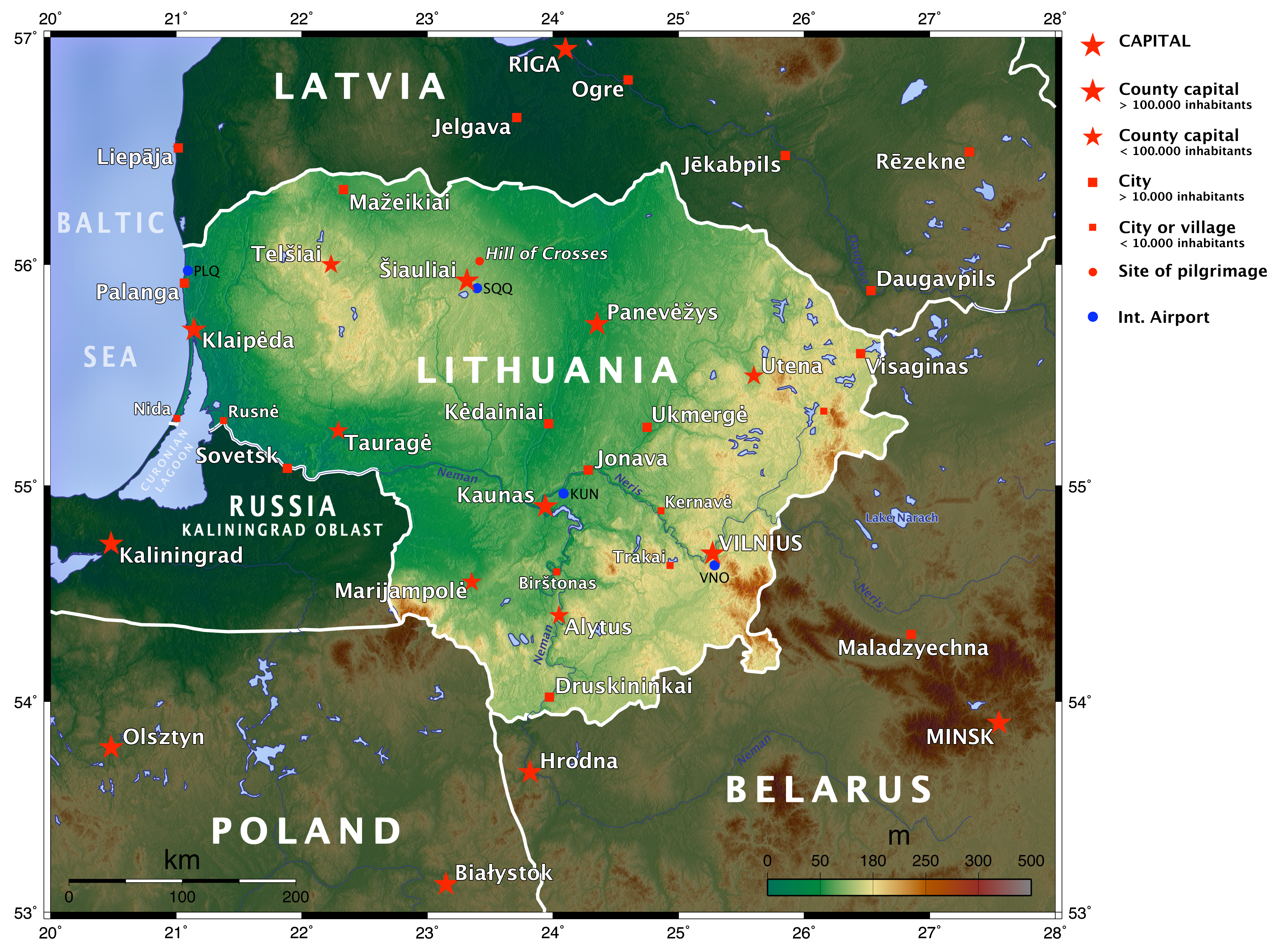
. Lithuania borders Latvia on the north, Belarus on the east and south, and Poland and the Kaliningrad region of Russia on the southwest. The Eastern border together with Latvia in the South of its East comes along with the Krokuva-Vilnius
Vilnius ( , ) is the capital of and List of cities in Lithuania#Cities, largest city in Lithuania and the List of cities in the Baltic states by population, most-populous city in the Baltic states. The city's estimated January 2025 population w ...
-Veliky Novgorod
Veliky Novgorod ( ; , ; ), also known simply as Novgorod (), is the largest city and administrative centre of Novgorod Oblast, Russia. It is one of the oldest cities in Russia, being first mentioned in the 9th century. The city lies along the ...
route with it chiefly within the territory. It is a country of gently rolling hills, many forests, rivers and streams, and lakes. Its principal natural resource is agricultural land.
Lithuania's northern neighbor is Latvia. The two countries share a border that extends 453 kilometres. Lithuania's eastern border with Belarus
Belarus, officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Belarus spans an a ...
is longer, stretching 502 kilometers. The border with Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
on the south is relatively short, only 91 kilometers, but it is very busy because of international traffic. Lithuania also has a 227-kilometer border with Russia. Russian territory adjacent to Lithuania is Kaliningrad Oblast
Kaliningrad Oblast () is the westernmost federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of the Russian Federation. It is a Enclave and exclave, semi-exclave on the Baltic Sea within the Baltic region of Prussia (region), Prussia, surrounded by Pola ...
, which is the northern part of the former German East Prussia
East Prussia was a Provinces of Prussia, province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1772 to 1829 and again from 1878 (with the Kingdom itself being part of the German Empire from 1871); following World War I it formed part of the Weimar Republic's ...
, including the city of Kaliningrad
Kaliningrad,. known as Königsberg; ; . until 1946, is the largest city and administrative centre of Kaliningrad Oblast, an Enclave and exclave, exclave of Russia between Lithuania and Poland ( west of the bulk of Russia), located on the Prego ...
. Finally, Lithuania has 108 kilometers of Baltic seashore with an ice-free harbor at Klaipėda. The Baltic coast offers sandy beaches and pine forests and attracts thousands of vacationers.
According to some geographers, the geographical midpoint of Europe
The location of the geographical centre of Europe depends on the definition of the borders of Europe, mainly whether remote islands are included to define the extreme points of Europe, and on the method of calculating the final result. Thus, sev ...
is just north of Lithuania's capital, Vilnius
Vilnius ( , ) is the capital of and List of cities in Lithuania#Cities, largest city in Lithuania and the List of cities in the Baltic states by population, most-populous city in the Baltic states. The city's estimated January 2025 population w ...
.
Major coordinates
In terms of latitude or climate fifteen degrees (corresponding to the longitude or anhour
An hour (symbol: h; also abbreviated hr) is a unit of time historically reckoned as of a day and defined contemporarily as exactly 3,600 seconds ( SI). There are 60 minutes in an hour, and 24 hours in a day.
The hour was initially establis ...
fifteen degrees, except the polar climate sums being 7°30´ in latitude) Lithuania situates within the 52°30´-N - 67°30´-N latitude, that is northwards from Southend
Southend-on-Sea (), commonly referred to as Southend (), is a coastal city and unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area with Borough status in the United Kingdom, borough status in south-eastern Essex, England. It lies on the nor ...
latitude, together with the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Denmark, Norway, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium, and France. A sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian Se ...
major body, the Far North of Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
, Siberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states ...
. It situates in the southern quarter of the climate fifteen degrees, stretching northwards from the southern mark of the climate fifteen degrees further than in nearly one tenth or the sum of <1°30´, that is kind of an edge zone of the climate fifteen degrees, being generally boggy in the western Belarus
Belarus, officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Belarus spans an a ...
, and on the 54°-N latitude the one tenth zone is marked by the greatest bog in Lithuania the Čepkeliai Marsh.
With the Eastern Hemisphere
The Eastern Hemisphere is the half of the planet Earth which is east of the prime meridian (which crosses Greenwich, London, United Kingdom) and west of the antimeridian (which crosses the Pacific Ocean and relatively little land from pole to p ...
core longitude on the 67°30´-E, the hour or its longitude fifteen degrees that set on Lithuania are 15°-E - 30°-E (Greenwich
Greenwich ( , , ) is an List of areas of London, area in south-east London, England, within the Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county of Greater London, east-south-east of Charing Cross.
Greenwich is notable for its maritime hi ...
, London) longitude, the core of which coming on the 22°30´-E longitude also marks the western one fourth, or the sum of 45° in the West of the Eastern Hemisphere if marking it with the Cape Verde
Cape Verde or Cabo Verde, officially the Republic of Cabo Verde, is an island country and archipelagic state of West Africa in the central Atlantic Ocean, consisting of ten volcanic islands with a combined land area of about . These islands ...
archipelago and the Transantarctic Mountains
The Transantarctic Mountains (abbreviated TAM) comprise a mountain range of uplifted rock (primarily sedimentary) in Antarctica which extends, with some interruptions, across the continent from Cape Adare in northern Victoria Land to Coats L ...
. The 22°30´-E longitude comes in the West of Lithuania, with the river Jūra (pronounced as in ''Euro'' except the ending vowel) meaning ''sea'' locally flowing on the mark. Tilsit
Sovetsk (; ) is a town in Kaliningrad Oblast, Russia, located on the south bank of the Neman River which forms the border with Lithuania.
History Early history
Tilsit, which received civic rights from Albert, Duke of Prussia in 1552,''Sło ...
(Kaliningrad Oblast
Kaliningrad Oblast () is the westernmost federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of the Russian Federation. It is a Enclave and exclave, semi-exclave on the Baltic Sea within the Baltic region of Prussia (region), Prussia, surrounded by Pola ...
), Telšiai
Telšiai (; Samogitian language, Samogitian: ''Telšē'') is a city in Lithuania with about 21,499 inhabitants. It is the capital of Telšiai County and Samogitia region, and it is located on the shores of Lake Mastis.
Telšiai is one of the ol ...
as the Greek ''thalassa'' situate in the western one fourth of the Eastern Hemisphere, although Talsi
Talsi (; , ) (population 11,371) is a town in the Courland region of Latvia. It is the administrative centre of Talsi Municipality. It is nicknamed the "green pearl of Courland".
Etymology
It is believed that the name is derived from an old Livo ...
(Latvia
Latvia, officially the Republic of Latvia, is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is one of the three Baltic states, along with Estonia to the north and Lithuania to the south. It borders Russia to the east and Belarus to t ...
) situate eastwards from the mark. The rivers Šešupė
The Šešupė (); ; ; ) is a 298 km long riverŠešupė
''VLE'' that flows through Poland (27 km), Lithuania (158 ...
, Šešuvis, ''VLE'' that flows through Poland (27 km), Lithuania (158 ...
Šušvė
Šušvė () is a river in central Lithuania, a right (the longest) tributary of the Nevėžis river. It begins in Kelmė district municipality, 6 km (4 mi) southeast from Tytuvėnai. The 134.6 km (83.6 mi) long river passes through Tytuv ...
plus Šyša situate in the sum of approximately 2°30´ longitude or one sixth of an hour fifteen degrees (''šeši'' - ''six'' in Lithuanian), in the both sides of the 22°30´-E mark.
Topography and drainage
 Lithuania lies at the edge of the
Lithuania lies at the edge of the North European Plain
The North European Plain ( – North German Plain; ; – Central European Plain; and ; French: ''Plaine d'Europe du Nord'') is a geomorphological region in Europe that covers all or parts of Belgium, the Netherlands (i.e. the Low Countries), ...
. Its landscape was shaped by the glaciers of the last Ice Age, which retreated about 25,000–22,000 years BP (Before Present
Before Present (BP) or "years before present (YBP)" is a time scale used mainly in archaeology, geology, and other scientific disciplines to specify when events occurred relative to the origin of practical radiocarbon dating in the 1950s. Because ...
). Lithuania's terrain is an alternation of moderate lowlands and highlands. The highest elevation is 297.84 meters above sea level, found in the eastern part of the republic and separated from the uplands of the western region of Samogitia
Samogitia, often known by its Lithuanian language, Lithuanian name ''Žemaitija'' (Samogitian language, Samogitian: ''Žemaitėjė''; see Samogitia#Etymology and alternative names, below for alternative and historical names) is one of the five ...
by the fertile plains of the southwestern and central regions. The landscape is punctuated by 2,833 lakes larger than and 1,600 smaller ponds. The majority of the lakes are found in the eastern part of the country. Lithuania also has 758 rivers longer than . The largest river is the Nemunas (total length ), which originates in Belarus. The other larger waterways are the Neris
The river Neris () or Vilija (, ) rises in northern Belarus. It flows westward, passing through Vilnius (Lithuania's capital) and in the south-centre of that country it flows into the Nemunas (Neman) from the right bank, at Kaunas, as its ma ...
(), Venta (), and Šešupė
The Šešupė (); ; ; ) is a 298 km long riverŠešupė
''VLE'' that flows through Poland (27 km), Lithuania (158 ...
() rivers. However, only of Lithuania's rivers are navigable.
Once a heavily forested land, Lithuania's territory today consists of only 32.8 percent woodlands—primarily ''VLE'' that flows through Poland (27 km), Lithuania (158 ...
pine
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae.
''World Flora Online'' accepts 134 species-rank taxa (119 species and 15 nothospecies) of pines as cu ...
, spruce
A spruce is a tree of the genus ''Picea'' ( ), a genus of about 40 species of coniferous evergreen trees in the family Pinaceae, found in the northern temperate and boreal ecosystem, boreal (taiga) regions of the Northern hemisphere. ''Picea'' ...
, and birch
A birch is a thin-leaved deciduous hardwood tree of the genus ''Betula'' (), in the family Betulaceae, which also includes alders, hazels, and hornbeams. It is closely related to the beech- oak family Fagaceae. The genus ''Betula'' contains 3 ...
forests. Ash and oak are very scarce. The forests are rich in mushrooms and berries, as well as a variety of plants.
Climate
Lithuania has ahumid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers, and cold ...
(''Dfb'' in the Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (te ...
). Average temperatures on the coast are in January and in July. In Vilnius the average temperatures are in January and in July. Simply speaking, is frequent on summer days and at night. Temperatures occasionally reach in summer. Winters when easterly flows from Siberia predominate, like 1941–42, 1955–56 and 1984–85, are very cold, whereas winters dominated by westerly maritime airflows like 1924–25, 1960–61 and 1988–89 are mild with temperatures above freezing a normal occurrence. occurs almost every winter. Winter extremes are at the coast and in the east of Lithuania. The average annual precipitation is on the coast, in Samogitia highlands, and in the eastern part of the country. Snow occurs every year, it can be snowing from October to April. In some years sleet can fall in September or May. The growing season lasts 202 days in the western part of the country and 169 days in the eastern part. Severe storms are rare in the eastern part of Lithuania and common nearer the coast.
The longest measured temperature records from the Baltic area cover about 250 years. The data show that there were warm periods during the latter half of the eighteenth century and that the nineteenth century was a relatively cool period. An early twentieth century warming culminated in the 1930s, followed by a smaller cooling that lasted until the 1960s. A warming trend has persisted since then.
Lithuania experienced a drought
A drought is a period of drier-than-normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, ...
in 2002, causing forest and peat
Peat is an accumulation of partially Decomposition, decayed vegetation or organic matter. It is unique to natural areas called peatlands, bogs, mires, Moorland, moors, or muskegs. ''Sphagnum'' moss, also called peat moss, is one of the most ...
bog fires. The country suffered along with the rest of Northwestern Europe during a heatwave in the summer of 2006.
Examples
General averages
Cities
Environment
Concerned with environmental deterioration, Lithuanian governments have created severalnational parks
A national park is a nature park designated for conservation (ethic), conservation purposes because of unparalleled national natural, historic, or cultural significance. It is an area of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that is protecte ...
and reservations. The country's flora and fauna have suffered, however, from an almost fanatical drainage of land for agricultural use. Environmental problems of a different nature were created by the development of environmentally unsafe industries. Air pollution
Air pollution is the presence of substances in the Atmosphere of Earth, air that are harmful to humans, other living beings or the environment. Pollutants can be Gas, gases like Ground-level ozone, ozone or nitrogen oxides or small particles li ...
problems exist mainly in the cities, such as Vilnius
Vilnius ( , ) is the capital of and List of cities in Lithuania#Cities, largest city in Lithuania and the List of cities in the Baltic states by population, most-populous city in the Baltic states. The city's estimated January 2025 population w ...
, Kaunas
Kaunas (; ) is the second-largest city in Lithuania after Vilnius, the fourth largest List of cities in the Baltic states by population, city in the Baltic States and an important centre of Lithuanian economic, academic, and cultural life. Kaun ...
, Jonava
Jonava () is the ninth largest city in Lithuania with a population of .
It is located in Kaunas County in central Lithuania, north east of Kaunas, the second-largest city in Lithuania. It is served by Kaunas International Airport. ''Achema'', t ...
, Mažeikiai
Mažeikiai (; Samogitian: ''Mažeikē''; ; ) is a city in northwestern Lithuania, on the Venta River. It has a population of around 32,000, making it the eighth largest city in Lithuania and eighteenth largest city in the Baltic States. Th ...
, Elektrėnai
Elektrėnai () is a city of about 11,000 inhabitants in Vilnius County, Lithuania; since 2000 it has been the capital of the Elektrėnai Municipality. It is situated between the two largest cities in Lithuania – Vilnius and Kaunas.
History
His ...
, and Naujoji Akmenė—the sites of fertilizer and other chemical plants, an oil refinery, power station, and a cement factory.
Water quality has also been an issue. The city of Kaunas, with a population of about 400,000, had no water purification plant until 1999; sewage was sent directly into the Neman River
Neman, Nemunas or Niemen is a river in Europe that rises in central Belarus and flows through Lithuania then forms Lithuania–Russia border, the northern border of Kaliningrad Oblast, Russia's western exclave, which specifically follows its s ...
. Tertiary wastewater treatment is scheduled to come on-line in 2007. River and lake pollution are other legacies of Soviet carelessness with the environment. The Courland Lagoon, for example, separated from the Baltic Sea by a strip of high dunes and pine forests, is about 85 percent contaminated. Beaches in the Baltic resorts, such as the well-known vacation area of Palanga
Palanga (; ; ) is a resort town, resort city in western Lithuania, on the shore of the Baltic Sea.
Palanga is the busiest and the largest summer resort in Lithuania and has sand, sandy beaches (18 km, 11 miles long and up to 300 metres, 10 ...
, are frequently closed for swimming because of contamination. Forests affected by acid rain
Acid rain is rain or any other form of Precipitation (meteorology), precipitation that is unusually acidic, meaning that it has elevated levels of hydrogen ions (low pH). Most water, including drinking water, has a neutral pH that exists b ...
are found in the vicinity of Jonava, Mažeikiai, and Elektrėnai, which are the chemical, oil, and power-generation centers. Lithuania was among the first former Soviet republics to introduce environmental regulations. However, because of Moscow's emphasis on increasing production and because of numerous local violations, technological backwardness, and political apathy, serious environmental problems now exist.
Natural hazards:
hurricane-force storms, blizzards, droughts, floods
Environment—current issues:
contamination of soil and groundwater with petroleum products and chemicals at former Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
military bases
Environment—international agreements:
* ''party to:''
Air Pollution
Air pollution is the presence of substances in the Atmosphere of Earth, air that are harmful to humans, other living beings or the environment. Pollutants can be Gas, gases like Ground-level ozone, ozone or nitrogen oxides or small particles li ...
, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulphur 85, Air Pollution-Sulphur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Biodiversity
Biodiversity is the variability of life, life on Earth. It can be measured on various levels. There is for example genetic variability, species diversity, ecosystem diversity and Phylogenetics, phylogenetic diversity. Diversity is not distribut ...
, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol
The was an international treaty which extended the 1992 United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) that commits state parties to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, based on the scientific consensus that global warming is oc ...
, Desertification
Desertification is a type of gradual land degradation of Soil fertility, fertile land into arid desert due to a combination of natural processes and human activities.
The immediate cause of desertification is the loss of most vegetation. This i ...
, Endangered Species
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching, inv ...
, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea
Law of the sea (or ocean law) is a body of international law governing the rights and duties of State (polity), states in Ocean, maritime environments. It concerns matters such as navigational rights, sea mineral claims, and coastal waters juris ...
, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution
A ship is a large watercraft, vessel that travels the world's oceans and other Waterway, navigable waterways, carrying cargo or passengers, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research and fishing. Ships are generally disti ...
, Wetlands
A wetland is a distinct semi-aquatic ecosystem whose groundcovers are flooded or saturated in water, either permanently, for years or decades, or only seasonally. Flooding results in oxygen-poor ( anoxic) processes taking place, especially ...
* ''signed, but not ratified:''
Natural resources

limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science) ...
, clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolinite, ). Most pure clay minerals are white or light-coloured, but natural clays show a variety of colours from impuriti ...
, quartz sand, gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate Hydrate, dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, drywall and blackboard or sidewalk ...
sand, and dolomite, which are suitable for making high-quality cement
A cement is a binder, a chemical substance used for construction that sets, hardens, and adheres to other materials to bind them together. Cement is seldom used on its own, but rather to bind sand and gravel ( aggregate) together. Cement mi ...
, glass
Glass is an amorphous (non-crystalline solid, non-crystalline) solid. Because it is often transparency and translucency, transparent and chemically inert, glass has found widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in window pane ...
, and ceramics
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant, and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porce ...
. There also is an ample supply of mineral water
Mineral water is water from a mineral spring that contains various minerals, such as salts and sulfur compounds. It is usually still, but may be sparkling ( carbonated/ effervescent).
Traditionally, mineral waters were used or consumed at t ...
, but energy sources and industrial materials are all in short supply. Oil was discovered in Lithuania in the 1950s, but only a few wells operate, and all that do are located in the western part of the country. It is estimated that the Baltic Sea shelf and the western region of Lithuania hold commercially viable amounts of oil, but if exploited this oil would satisfy only about 20 percent of Lithuania's annual need for petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil or simply oil, is a naturally occurring, yellowish-black liquid chemical mixture found in geological formations, consisting mainly of hydrocarbons. The term ''petroleum'' refers both to naturally occurring un ...
products for the next twenty years. Lithuania has a large amount of thermal energy
The term "thermal energy" is often used ambiguously in physics and engineering. It can denote several different physical concepts, including:
* Internal energy: The energy contained within a body of matter or radiation, excluding the potential en ...
along the Baltic Sea coast which could be used to heat hundreds of thousands of homes, as is done in Iceland
Iceland is a Nordic countries, Nordic island country between the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between North America and Europe. It is culturally and politically linked with Europe and is the regi ...
. In addition, iron ore
Iron ores are rocks and minerals from which metallic iron can be economically extracted. The ores are usually rich in iron oxides and vary in color from dark grey, bright yellow, or deep purple to rusty red. The iron is usually found in the f ...
deposits have been found in the southern region of Lithuania. But commercial exploitation of these deposits probably would require strip mining, which is environmentally unsound. Moreover, exploitation of these resources will depend on Lithuania's ability to attract capital and technology from abroad.
Lithuania and Denmark
Denmark is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe. It is the metropole and most populous constituent of the Kingdom of Denmark,, . also known as the Danish Realm, a constitutionally unitary state that includes the Autonomous a ...
are the only countries in Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
, which are fully equipped with fresh groundwater. The Lithuanians consume about 0.5 million cubic metres of water per day, which is only 12–14 percent of all explored fresh groundwater resources. Water quality in the country is very high and is determined by the fact that drinking water comes from deep layers that are protected from pollution on the surface of the earth. Drilling depth usually reaches 30–50 metres, but in Klaipėda Region
The Klaipėda Region () or Memel Territory ( or ''Memelgebiet'') was defined by the 1919 Treaty of Versailles in 1920 and refers to the northernmost part of the German province of East Prussia, when, as Memelland, it was put under the administr ...
it even reaches 250 metres. Consequently, Lithuania is one of very few European countries where groundwater is used for centralized water supply. With a large underground fresh water reserves, Lithuania exports mineral-rich water to other countries. Approved mineral water quantity is about 2.7 million cubic metres per year, while production is only 4–5 percent of all mineral water resources.
Lithuania's capital Vilnius
Vilnius ( , ) is the capital of and List of cities in Lithuania#Cities, largest city in Lithuania and the List of cities in the Baltic states by population, most-populous city in the Baltic states. The city's estimated January 2025 population w ...
is the only Baltic
Baltic may refer to:
Peoples and languages
*Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian
*Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originatin ...
capital city that uses centralized water supplying from deep water springs, which are protected from pollution and has no nitrates
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula . Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are soluble in water. An example of an insol ...
or nitrites
The nitrite polyatomic ion, ion has the chemical formula . Nitrite (mostly sodium nitrite) is widely used throughout chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The nitrite anion is a pervasive intermediate in the nitrogen cycle in nature. The name ...
that are harmful to the human body. Water is cleaned without chemicals in Lithuania. About 20% of the consumed water in the state is a non-filtered very high quality water.
''Natural resources:''
peat, arable land, amber.
Land use:
* ''arable land:'' 33.48%
* ''permanent crops:'' 0.47%
* ''other:'' 66.05% (2011)
Irrigated land:
13.4 km2 (2011)
Total renewable water resources:
24.9 km3 (2011)
Area and boundaries
Area: * ''Total:'' 65,300 km2 * ''Land:'' 62,680 km2 * ''Water:'' 2,620 km2 Comparative area *Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
comparative: slightly smaller (5.5%) than Tasmania
Tasmania (; palawa kani: ''Lutruwita'') is an island States and territories of Australia, state of Australia. It is located to the south of the Mainland Australia, Australian mainland, and is separated from it by the Bass Strait. The sta ...
*Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
comparative: about 9% smaller than New Brunswick
New Brunswick is a Provinces and Territories of Canada, province of Canada, bordering Quebec to the north, Nova Scotia to the east, the Gulf of Saint Lawrence to the northeast, the Bay of Fundy to the southeast, and the U.S. state of Maine to ...
*United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
comparative: about 17% smaller than Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjac ...
*United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
comparative: slightly larger (4%) than West Virginia
West Virginia is a mountainous U.S. state, state in the Southern United States, Southern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States.The United States Census Bureau, Census Bureau and the Association of American ...
Land boundaries:
* ''Total:'' 1,574 km
* ''Border countries:'' Belarus 680 km, Latvia 576 km, Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
91 km, Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
(Kaliningrad) 227 km
Coastline: . The coastline consists of 20 kilometres from Klaipėda, 50 kilometres at Cape Nehrung, and 21 kilometres in the region of Palanga and the mouth of the Šventoji river. Lithuania Minor
Lithuania Minor (; ; ) or Prussian Lithuania (; ; ) is one of five ethnographic regions of Lithuania. It is a historical region of Prussia, where Prussian Lithuanians (or Lietuvininkai) lived, now located in Lithuania and the Kaliningrad Obla ...
occupies two-thirds of the Lithuanian coast-line.
Maritime claims:
* ''Territorial sea:''
* ''Exclusive Economic Zone
An exclusive economic zone (EEZ), as prescribed by the 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, is an area of the sea in which a sovereign state has exclusive rights regarding the exploration and use of marine natural resource, reso ...
:'' with
Latitude and longitude
*''Northern point:'' near former Lemkinė village on the shores of Nemunėlis in the Biržai district municipality *''Southern point:'' in theVarėna district municipality
Varėna () is a city in Dzūkija, southern Lithuania. It is the capital of the Varėna district municipality, district of Varėna. Currently, there are 7,794 residents. The Varėna district is the largest and most forested Municipalities of Lithu ...
, in uninhabitable forest area, cadastrally belonging to village Musteika. The southernmost habitable place is in the village Ašašninkai, so called fraction Plaskiniškės.
*''Eastern point:'' near Vosiūnai village in the Ignalina district municipality
Ignalina District Municipality is one of 60 municipalities in Lithuania.
Structure
District structure:
* 2 cities – Dūkštas and Ignalina;
* 3 towns – Mielagėnai, Rimšė and Tverečius;
* 726 villages.
* Ignalina District Municipality ...
*''Western point:'' Nida
Elevation extremes:
* ''Lowest point:'' Baltic Sea 0 m
* ''Highest point:'' Aukštojas Hill
See also
* List of protected areas of Lithuania *Lithuania
Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, P ...
* ''''
References
External links
Kursiu Nerija National Park
{{DEFAULTSORT:Geography Of Lithuania