Geldings on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A gelding ( /ˈɡɛldɪŋ/) is a castrated male
 Geldings are preferred over stallions for working purposes because they are calmer, easier to handle, and more tractable. Geldings are therefore a favorite for many
Geldings are preferred over stallions for working purposes because they are calmer, easier to handle, and more tractable. Geldings are therefore a favorite for many
Castration: Creation of a Gelding from a Colt or Stallion
. ''American Association of Equine Practitioners:Newsroom.'' Accessed July 17, 2007. While this means the horse loses any breeding value, a successful track career can often be a boost to the value of the stallion that sired the gelding. Sometimes a stallion used for breeding is castrated later in life, possibly due to sterility, because the offspring of the stallion are not up to expectations, or simply because the horse is not used much for breeding. Castration may allow a stallion to live peacefully with other horses, allowing a more social and comfortable existence. Under British
and definitely before he reaches sexual maturity. While it was once recommended to wait until a young horse was well over a year old, even two, this was a holdover from the days when castration was performed without
Costs and complications of equine castration: a UK practice-based study comparing 'standing nonsutured' and 'recumbent sutured' techniques
''Equine Veterinary Journal'' 37.5:468–472. and the horse then has the benefit of being able to be turned out safely with other horses and allowed to live a less restricted and isolated life than was allowed for a stallion.
 There are two major techniques commonly used in castrating a horse, one requiring only local anaesthesia and the other requiring
There are two major techniques commonly used in castrating a horse, one requiring only local anaesthesia and the other requiring
Equine perioperative fatalities associated with general anaesthesia at a private practice—a retrospective case series
. ''Veterinary Anaesthesia and Analgesia'' 34.1:23–30. For standing castration, the colt or
 Putting a horse under
Putting a horse under
Equine castration: Review of anatomy, approaches, techniques and complications in normal, cryptorchid and monorchid horses
. . ''Australian Veterinary Journal'' 77.7:428–434, p. 430. Accessed July 17, 2007. For simple castration of normal animals, the advantages to recumbent castration are that the horse is prone, better
Update on sheath cleaning, with how-to video link
{{Authority control Types of horse Horse health Veterinary castration Male horses
horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 mi ...
or other equine
Equinae is a subfamily of the family Equidae, known from the Hemingfordian stage of the Early Miocene (16 million years ago) onwards. They originated in North America, before dispersing to every continent except Australia and Antarctica. They are ...
, such as a pony
A pony is a type of small horse, usually measured under a specified height at maturity. Ponies often have thicker coats, manes and tails, compared to larger horses, and proportionally shorter legs, wider barrels, heavier , thicker necks and s ...
, donkey
The donkey or ass is a domesticated equine. It derives from the African wild ass, ''Equus africanus'', and may be classified either as a subspecies thereof, ''Equus africanus asinus'', or as a separate species, ''Equus asinus''. It was domes ...
or a mule
The mule is a domestic equine hybrid between a donkey, and a horse. It is the offspring of a male donkey (a jack) and a female horse (a mare). The horse and the donkey are different species, with different numbers of chromosomes; of the two ...
. The term is also used with certain other animals and livestock
Livestock are the Domestication, domesticated animals that are raised in an Agriculture, agricultural setting to provide labour and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, Egg as food, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The t ...
, such as domesticated camels. By comparison, the equivalent term for castrated male cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, bovid ungulates widely kept as livestock. They are prominent modern members of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus '' Bos''. Mature female cattle are calle ...
would be ''steer'' (or ''bullock''), and ''wether'' for sheep
Sheep (: sheep) or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are a domesticated, ruminant mammal typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus '' Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to d ...
and goats
The goat or domestic goat (''Capra hircus'') is a species of goat-antelope that is mostly kept as livestock. It was domesticated from the wild goat (''C. aegagrus'') of Southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of the famil ...
.
Castration allows a male animal to be more calm, better-behaved, less sexually aggressive, and more responsive to training efforts. This makes the animal generally more suitable as an everyday working animal
A working animal is an animal, usually domesticated, that is kept by humans and trained to perform tasks. Some are used for their physical strength (e.g. oxen and draft horses) or for transportation (e.g. riding horses and camels), while oth ...
, or as a pet
A pet, or companion animal, is an animal kept primarily for a person's company or entertainment rather than as a working animal, livestock, or a laboratory animal. Popular pets are often considered to have attractive/ cute appearances, inte ...
in the case of companion animals. The gerund
In linguistics, a gerund ( abbreviated ger) is any of various nonfinite verb forms in various languages; most often, but not exclusively, it is one that functions as a noun. The name is derived from Late Latin ''gerundium,'' meaning "which is ...
and participle
In linguistics, a participle (; abbr. ) is a nonfinite verb form that has some of the characteristics and functions of both verbs and adjectives. More narrowly, ''participle'' has been defined as "a word derived from a verb and used as an adject ...
"gelding" and the infinitive "to geld" refer to the castration procedure itself.
Etymology
The verb "to geld" comes from theOld Norse
Old Norse, also referred to as Old Nordic or Old Scandinavian, was a stage of development of North Germanic languages, North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants ...
, from the adjective . The noun "gelding" is from the Old Norse .
History
TheScythians
The Scythians ( or ) or Scyths (, but note Scytho- () in composition) and sometimes also referred to as the Pontic Scythians, were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian peoples, Iranian Eurasian noma ...
are thought to have been among the first to geld their horses, as they valued war horses that were quiet and less defensive, as well as easier to keep in groups and less likely to be territorial, without the temptation of reproductive/mating urges. Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
is said to have mentioned gelding as early as 350 BC.
Reasons for gelding
A male horse is often gelded to make him better-behaved and easier to control. Gelding can also remove lower-quality animals from thegene pool
The gene pool is the set of all genes, or genetic information, in any population, usually of a particular species.
Description
A large gene pool indicates extensive genetic diversity, which is associated with robust populations that can survi ...
.
To allow only the finest animals to breed on, while preserving adequate genetic diversity
Genetic diversity is the total number of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a species. It ranges widely, from the number of species to differences within species, and can be correlated to the span of survival for a species. It is d ...
, only a small percentage of all male horses should remain stallions. Mainstream sources place the percentage of stallions that should be kept as breeding stock at about 10%, while an extreme view states that only 0.5% of all males should be bred. In wild herds, the 10% ratio is largely maintained naturally, as a single dominant stallion usually protects and breeds with a herd which is seldom larger than 10 or 12 mares, though he may permit a less dominant junior stallion to live at the fringes of the herd. There are more males than just herd stallions, so unattached male horses group together for protection in small all-male " bachelor herds", where, in the absence of mares, they tend to behave much like geldings.
equestrians
Equestrianism (from Latin , , , 'horseman', 'horse'), commonly known as horse riding ( Commonwealth English) or horseback riding (American English), includes the disciplines of riding, driving, and vaulting. This broad description includes the ...
. In some horse show
A horse show is a judged exhibition of horses and pony, ponies. Many different horse breeds and equestrianism, equestrian disciplines hold competitions worldwide, from local to the international levels. Most horse shows run from one to three days ...
s, due to the dangers inherent in handling stallions, which require experienced handlers, youth exhibitors are not permitted to show stallions in classes limited to just those riders.
Geldings are often preferred over mares, because some mares become temperamental when in heat
In thermodynamics, heat is energy in transfer between a thermodynamic system and its surroundings by such mechanisms as thermal conduction, electromagnetic radiation, and friction, which are microscopic in nature, involving sub-atomic, ato ...
and the use of mares may be limited during the later months of pregnancy and while caring for a young foal
A foal is an equine up to one year old; this term is used mainly for horses, but can be used for donkeys. More specific terms are colt (horse), colt for a male foal and filly for a female foal, and are used until the horse is three or four. Whe ...
.
In horse racing
Horse racing is an equestrian performance activity, typically involving two or more horses ridden by jockeys (or sometimes driven without riders) over a set distance for competition. It is one of the most ancient of all sports, as its bas ...
, castrating a stallion may be considered worthwhile if the animal is easily distracted by other horses, difficult to handle, or otherwise not running to his full potential due to behavioral issues.Bramlage, Larry R. DVM, MS (May 29, 2003)Castration: Creation of a Gelding from a Colt or Stallion
. ''American Association of Equine Practitioners:Newsroom.'' Accessed July 17, 2007. While this means the horse loses any breeding value, a successful track career can often be a boost to the value of the stallion that sired the gelding. Sometimes a stallion used for breeding is castrated later in life, possibly due to sterility, because the offspring of the stallion are not up to expectations, or simply because the horse is not used much for breeding. Castration may allow a stallion to live peacefully with other horses, allowing a more social and comfortable existence. Under British
National Hunt racing
National Hunt Racing, also known as Jump Racing, is a form of horse racing particular to many European countries, including, but not limited to: France, horse racing in Great Britain, Great Britain and horse racing in Ireland, Ireland. Jump Racin ...
(i.e. Steeplechase) rules, to minimize health and safety risks, nearly all participating horses are gelded. On the other hand, in other parts of Europe, geldings are excluded from many of the most prestigious flat races including the Classics and the Prix de l'Arc de Triomphe
The Prix de l'Arc de Triomphe () is a Group 1 flat horse race in France open to thoroughbreds aged three years or older. It is run at Longchamp Racecourse in Paris over a distance ...
(with an exception being the French classic Prix Royal-Oak, open to geldings since 1986). In North American Thoroughbred racing, geldings, if otherwise qualified by age, winnings, or experience, are allowed in races open to intact males. The same applies in Australia.
Concerns about gelding
Some cultures historically did not and still seldom geld male horses, most notably theArab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
s, who usually used mares for everyday work and for war. In these cultures, most stallions are still not used for breeding, only those of the best quality. When used as ordinary riding animals, they are kept only with or near other male horses in a "bachelor" setting, which tends to produce calmer, less stallion-like behavior
Behavior (American English) or behaviour (British English) is the range of actions of Individual, individuals, organisms, systems or Artificial intelligence, artificial entities in some environment. These systems can include other systems or or ...
. Sometimes religious reasons for these practices exist; for example, castration of both animals and humans was categorically forbidden in the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
. '' Jewish law ''Halakha'' ( ; , ), also transliterated as ''halacha'', ''halakhah'', and ''halocho'' ( ), is the collective body of Jewish religious laws that are derived from the Written and Oral Torah. ''Halakha'' is based on biblical commandments ('' mit ...
.
Although castrations generally have few complications, there are risks. Castration can have complications, such as swelling, . '' Jewish law ''Halakha'' ( ; , ), also transliterated as ''halacha'', ''halakhah'', and ''halocho'' ( ), is the collective body of Jewish religious laws that are derived from the Written and Oral Torah. ''Halakha'' is based on biblical commandments ('' mit ...
hemorrhage
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, ...
or post-operative bleeding, infection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmis ...
s, and eventration. It can take up to six weeks for residual testosterone to clear from the new gelding's system and he may continue to exhibit stallion-like behaviors in that period. For reasons not always clear, about 30% of all geldings may still display a stallion-like manner, some because of a cryptorchid testicle retained in the horse, some due to previously learned behavior, but some for no clear reason. Training to eliminate these behaviors is generally effective. If a standing castration is performed, it is possible for the horse to injure the veterinarian during the procedure. If complications arise, the horse must be immediately anesthetized. Castration does not automatically change bad habits and poor manners. This must be accomplished by proper training.
Time of gelding
A horse may be gelded at any age; however, if an owner intends to geld a particular foal, it is now considered best to geld the horse prior to becoming a yearling,Archived copyand definitely before he reaches sexual maturity. While it was once recommended to wait until a young horse was well over a year old, even two, this was a holdover from the days when castration was performed without
anesthesia
Anesthesia (American English) or anaesthesia (British English) is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prev ...
and was thus far more stressful on the animal. Modern veterinary techniques can now accomplish castration with relatively little stress and minimal discomfort, so long as appropriate analgesics
An analgesic drug, also called simply an analgesic, antalgic, pain reliever, or painkiller, is any member of the group of drugs used for pain management. Analgesics are conceptually distinct from anesthetics, which temporarily reduce, and in s ...
are employed. A few horse owners delay gelding a horse on the grounds that the testosterone
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and androgen in Male, males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testicles and prostate, as well as promoting se ...
gained from being allowed to reach sexual maturity will make him larger. However, recent studies have shown that this is not so: any apparent muscle mass gained solely from the presence of hormones will be lost over time after the horse is gelded, and in the meantime, the energy spent developing muscle mass may actually take away from the energy a young horse might otherwise put into skeletal growth; the net effect is that castration has no effect on rate of growth (although it may increase the amount of fat the horse carries).
Many older stallions, no longer used at stud due to age or sterility, can benefit from being gelded. Modern veterinary techniques make gelding an even somewhat elderly stallion a fairly low-risk procedure,Mason, BJ, Newton, JR & Payne, RJ, et al. (2005)Costs and complications of equine castration: a UK practice-based study comparing 'standing nonsutured' and 'recumbent sutured' techniques
''Equine Veterinary Journal'' 37.5:468–472. and the horse then has the benefit of being able to be turned out safely with other horses and allowed to live a less restricted and isolated life than was allowed for a stallion.
Specialized maintenance of geldings
Owners of male horses, both geldings and stallions, need to occasionally check the horse's sheath, the pocket of skin that protects the penis of the horse when it is not in use forurination
Urination is the release of urine from the bladder through the urethra in Placentalia, placental mammals, or through the cloaca in other vertebrates. It is the urinary system's form of excretion. It is also known medically as micturition, v ...
(or, in the case of stallions, breeding). Geldings tend to accumulate smegma and other debris at a higher rate than stallions, probably because geldings rarely fully extrude the penis, and thus dirt and smegma build up in the folds of skin."Cut Through Smegma". ''Horse Journal'', August 2007, p. 19-20.
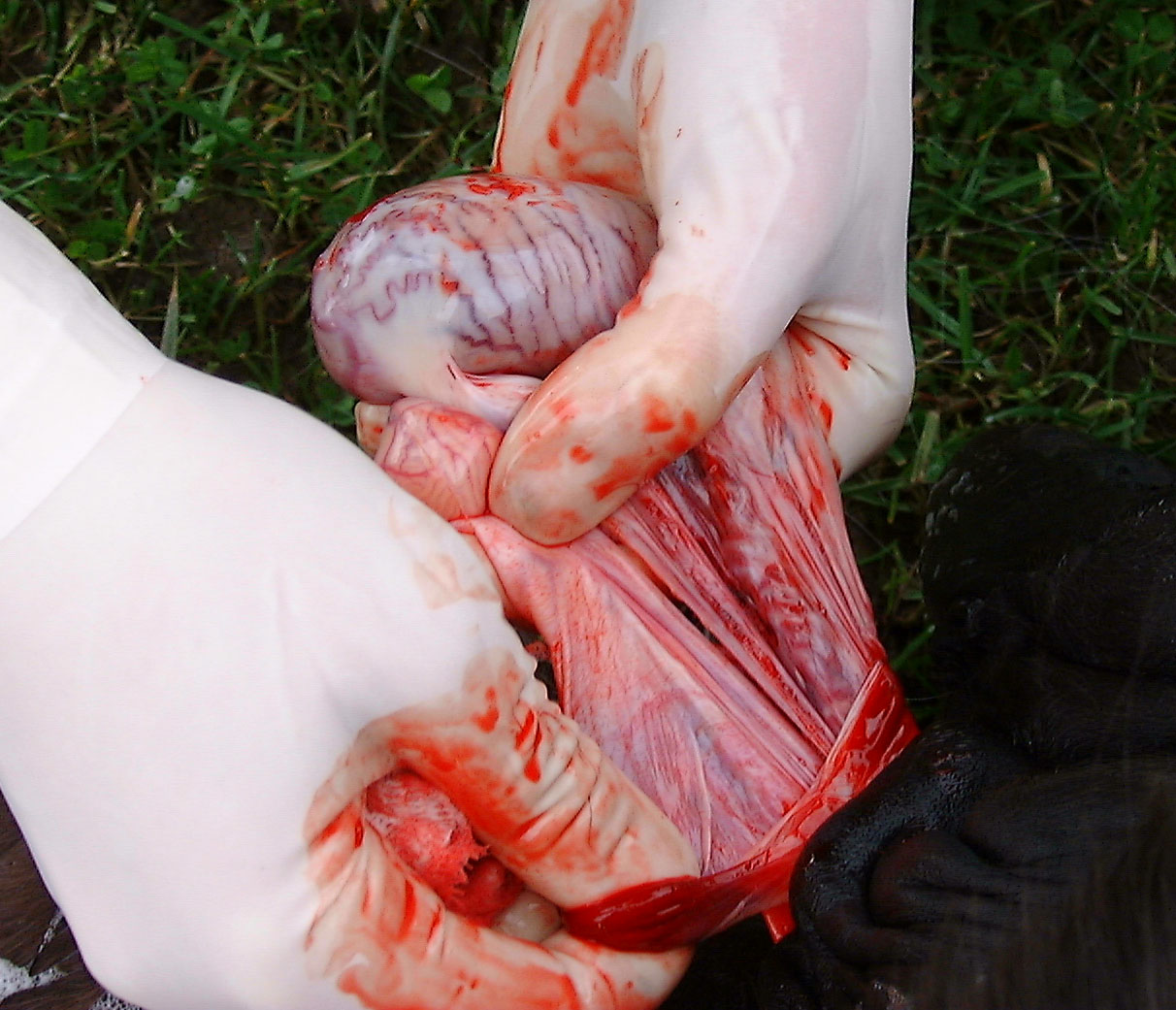
Castration techniques
 There are two major techniques commonly used in castrating a horse, one requiring only local anaesthesia and the other requiring
There are two major techniques commonly used in castrating a horse, one requiring only local anaesthesia and the other requiring general anaesthesia
General anaesthesia (UK) or general anesthesia (US) is medically induced loss of consciousness that renders a patient unarousable even by painful stimuli. It is achieved through medications, which can be injected or inhaled, often with an analges ...
. Each technique has advantages and disadvantages.
Standing castration
Standing castration is a technique where a horse is sedated and local anaesthesia is administered, without throwing the horse to the ground or putting him completely "under". It has the benefit thatgeneral anaesthesia
General anaesthesia (UK) or general anesthesia (US) is medically induced loss of consciousness that renders a patient unarousable even by painful stimuli. It is achieved through medications, which can be injected or inhaled, often with an analges ...
(GA) is not required. This method is advocated for simple procedures because the estimated mortality for GA in horses at a modern clinic is low, approximately one or two in 1000. Mortality in the field (where most horse castrations are performed) is probably higher, due to poorer facilities.Bidwell, Lori A., DVM; Bramlage, Larry R., DVM MS; and Rood, William A., DVM (2007).Equine perioperative fatalities associated with general anaesthesia at a private practice—a retrospective case series
. ''Veterinary Anaesthesia and Analgesia'' 34.1:23–30. For standing castration, the colt or
stallion
A stallion is an adult male horse that has not been gelded ( castrated). Stallions follow the conformation and phenotype of their breed, but within that standard, the presence of hormones such as testosterone may give stallions a thicker, "cre ...
is sedated, typically with detomidine with or without butorphanol, and often physically restrained. Local anaesthetic
A local anesthetic (LA) is a medication that causes absence of all sense, sensation (including pain) in a specific body part without loss of consciousness, providing local anesthesia, as opposed to a general anesthetic, which eliminates all sen ...
is injected into the parenchyma
upright=1.6, Lung parenchyma showing damage due to large subpleural bullae.
Parenchyma () is the bulk of functional substance in an animal organ such as the brain or lungs, or a structure such as a tumour. In zoology, it is the tissue that ...
of both testes
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of androgens, primarily testosterone.
The ...
. An incision is made through the scrotum
In most terrestrial mammals, the scrotum (: scrotums or scrota; possibly from Latin ''scortum'', meaning "hide" or "skin") or scrotal sac is a part of the external male genitalia located at the base of the penis. It consists of a sac of skin ...
and the testes are removed, then the spermatic cord
The spermatic cord is the cord-like structure in males formed by the vas deferens (''ductus deferens'') and surrounding tissue that runs from the deep inguinal ring down to each testicle. Its serosal covering, the tunica vaginalis, is an exten ...
is crushed, most commonly with either ligatures or emasculators, or both. The emasculators are applied for two to three minutes, then removed, and a careful check is made for signs of haemorrhage. Assuming that bleeding is at a minimum, the other side is castrated in the same manner. Most veterinarian
A veterinarian (vet) or veterinary surgeon is a medical professional who practices veterinary medicine. They manage a wide range of health conditions and injuries in non-human animals. Along with this, veterinarians also play a role in animal r ...
s remove the testis held most "tightly" (or close to the body) by the cremaster muscle first, so as to minimize the risk of the horse withdrawing it to the point where it is inaccessible. The horse, now a gelding, is allowed to recover.
Standing castration can be performed in more complicated cases. Some authorities have described a technique for the removal of abdominally retained testes from cryptorchid animals, but most surgeons still advocate a recumbent technique, as described below. The primary drawback to standing castration is the risk that, even with sedation and restraint, the horse may object to the procedure and kick or otherwise injure the individual performing the operation.
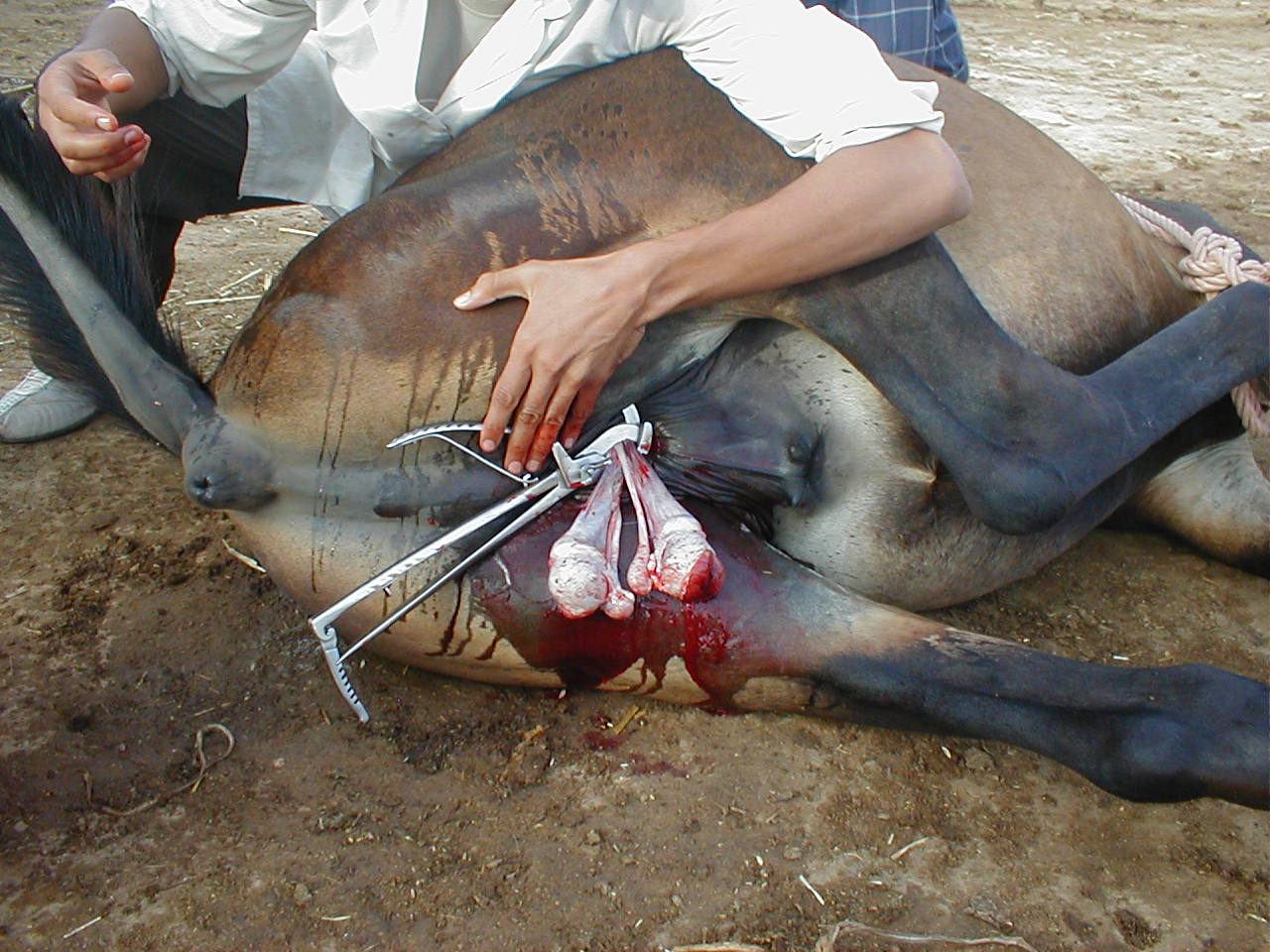
Recumbent castration
 Putting a horse under
Putting a horse under general anaesthesia
General anaesthesia (UK) or general anesthesia (US) is medically induced loss of consciousness that renders a patient unarousable even by painful stimuli. It is achieved through medications, which can be injected or inhaled, often with an analges ...
for castration is preferred by some veterinarians because "surgical exposure is improved and it carries less (overall) risk for surgeon and patient".Searle, D, Dart, AJ & Dart, CM, et al. (1999).Equine castration: Review of anatomy, approaches, techniques and complications in normal, cryptorchid and monorchid horses
. . ''Australian Veterinary Journal'' 77.7:428–434, p. 430. Accessed July 17, 2007. For simple castration of normal animals, the advantages to recumbent castration are that the horse is prone, better
asepsis
Asepsis is the state of being free from disease-causing micro-organisms (such as pathogenic bacteria, viruses, pathogenic fungi, and parasites). There are two categories of asepsis: medical and surgical. The modern day notion of asepsis is deri ...
(sterile environment) can be maintained, and better haemostasis (control of bleeding) is possible. In addition, there is significantly less risk of the surgeon or assistants being kicked. In a more complex situation such as castration of cryptorchid animals, the inguinal canal
The inguinal canal is a passage in the anterior abdominal wall on each side of the body (one on each side of the midline), which in males, convey the spermatic cords and in females, the round ligament of the uterus. The inguinal canals are lar ...
is more easily accessed. There are several different techniques (such as "open", "closed", and "semi-closed") that may be employed, but the basic surgery is similar. However, general anaesthesia is not without risks, including post-anaesthetic myopathy
In medicine, myopathy is a disease of the muscle in which the muscle fibers do not function properly. ''Myopathy'' means muscle disease ( Greek : myo- ''muscle'' + patheia '' -pathy'' : ''suffering''). This meaning implies that the primary defec ...
(muscle damage) and neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, refers to damage or disease affecting the nerves. Damage to nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland function, and/or organ function depending on which nerve fibers are affected. Neuropa ...
(nerve damage), respiratory dysfunction (V/Q mismatch), and cardiac depression. These complications occur with sufficient frequency that castration has a relatively high overall mortality rate. To minimize these concerns, the British Equine Veterinary Association guidelines recommend two veterinary surgeons should be present when an equine general anaesthesia is being performed.
Aftercare
With both castration techniques, the wound should be kept clean and allowed to drain freely to reduce the risk ofhematoma
A hematoma, also spelled haematoma, or blood suffusion is a localized bleeding outside of blood vessels, due to either disease or trauma including injury or surgery and may involve blood continuing to seep from broken capillaries. A hematoma is ...
formation, or development of an abscess
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body, usually caused by bacterial infection. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pre ...
. The use of tetanus antitoxin and analgesics
An analgesic drug, also called simply an analgesic, antalgic, pain reliever, or painkiller, is any member of the group of drugs used for pain management. Analgesics are conceptually distinct from anesthetics, which temporarily reduce, and in s ...
(painkillers) are necessary and antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
are also commonly administered. The horse is commonly walked in hand for some days to reduce the development of edema
Edema (American English), also spelled oedema (British English), and also known as fluid retention, swelling, dropsy and hydropsy, is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue (biology), tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. S ...
.
Possible complications
Minor complications following castration are relatively common, while serious complications are rare. According to one in-depth study, for standing castration the complication rate is 22%, while for recumbent castration it is 6% (although with a 1% mortality). The more common complications are: *Post-operative swelling (edema
Edema (American English), also spelled oedema (British English), and also known as fluid retention, swelling, dropsy and hydropsy, is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue (biology), tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. S ...
) – minor and very commonRailton, D. (1999). "Complications associated with castration in the horse". ''In Practice'' 1999 21: 298–307
*Scrotal/incisional infection – local seroma/abscess formation is relatively common, when the skin seals over before the deeper pocket has time to seal. This requires reopening the skin incision, to establish adequate drainage. To prevent the wounds from closing too quickly the horse needs to be exercised at least once daily after the procedure. It is common to treat the horse with a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a Indication (medicine), therapeutic drug class which Analgesic, reduces pain, Anti-inflammatory, decreases inflammation, Antipyretic, decreases fever, and Antithrombotic, prevents bl ...
to reduce the swelling and sometimes it is necessary to give antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
.
* Chronic infection leads to a schirrous cord – the formation of a granuloma
A granuloma is an aggregation of macrophages (along with other cells) that forms in response to chronic inflammation. This occurs when the immune system attempts to isolate foreign substances that it is otherwise unable to eliminate. Such sub ...
at the incision site, that may not be obvious for months or even years
* Evisceration, a condition where the abdominal organs "fall out" of the surgical incision, is uncommon, and while the survival rate is 85–100% if treated promptly, the mortality rate is high for those not dealt with immediately.
See also
* Spaying and neuteringReferences
External links
Update on sheath cleaning, with how-to video link
{{Authority control Types of horse Horse health Veterinary castration Male horses