Gel cell on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A valve regulated lead‐acid (VRLA) battery, commonly known as a sealed lead-acid (SLA) battery, is a type of lead-acid battery characterized by a limited amount of electrolyte ("starved" electrolyte) absorbed in a plate separator or formed into a gel, proportioning of the negative and positive plates so that oxygen recombination is facilitated within the cell, and the presence of a relief valve that retains the battery contents independent of the position of the cells.
There are two primary types of VRLA batteries: absorbent glass mat (AGM) and gel cell (gel battery). Gel cells add silica dust to the electrolyte, forming a thick putty-like gel; AGM (absorbent glass mat) batteries feature fiberglass mesh between the battery plates, which serves to contain the electrolyte and separate the plates. Both types of VRLA batteries offer advantages and disadvantages compared to flooded vented lead-acid (VLA) batteries or each other.
Due to their construction, the gel cell and AGM types of VRLA can be mounted in any orientation and do not require constant maintenance. The term "maintenance-free" is a misnomer, as VRLA batteries still require cleaning and regular functional testing. They are widely used in large portable electrical devices, off-grid power systems (including uninterruptible power systems), low-cost
A valve regulated lead‐acid (VRLA) battery, commonly known as a sealed lead-acid (SLA) battery, is a type of lead-acid battery characterized by a limited amount of electrolyte ("starved" electrolyte) absorbed in a plate separator or formed into a gel, proportioning of the negative and positive plates so that oxygen recombination is facilitated within the cell, and the presence of a relief valve that retains the battery contents independent of the position of the cells.
There are two primary types of VRLA batteries: absorbent glass mat (AGM) and gel cell (gel battery). Gel cells add silica dust to the electrolyte, forming a thick putty-like gel; AGM (absorbent glass mat) batteries feature fiberglass mesh between the battery plates, which serves to contain the electrolyte and separate the plates. Both types of VRLA batteries offer advantages and disadvantages compared to flooded vented lead-acid (VLA) batteries or each other.
Due to their construction, the gel cell and AGM types of VRLA can be mounted in any orientation and do not require constant maintenance. The term "maintenance-free" is a misnomer, as VRLA batteries still require cleaning and regular functional testing. They are widely used in large portable electrical devices, off-grid power systems (including uninterruptible power systems), low-cost
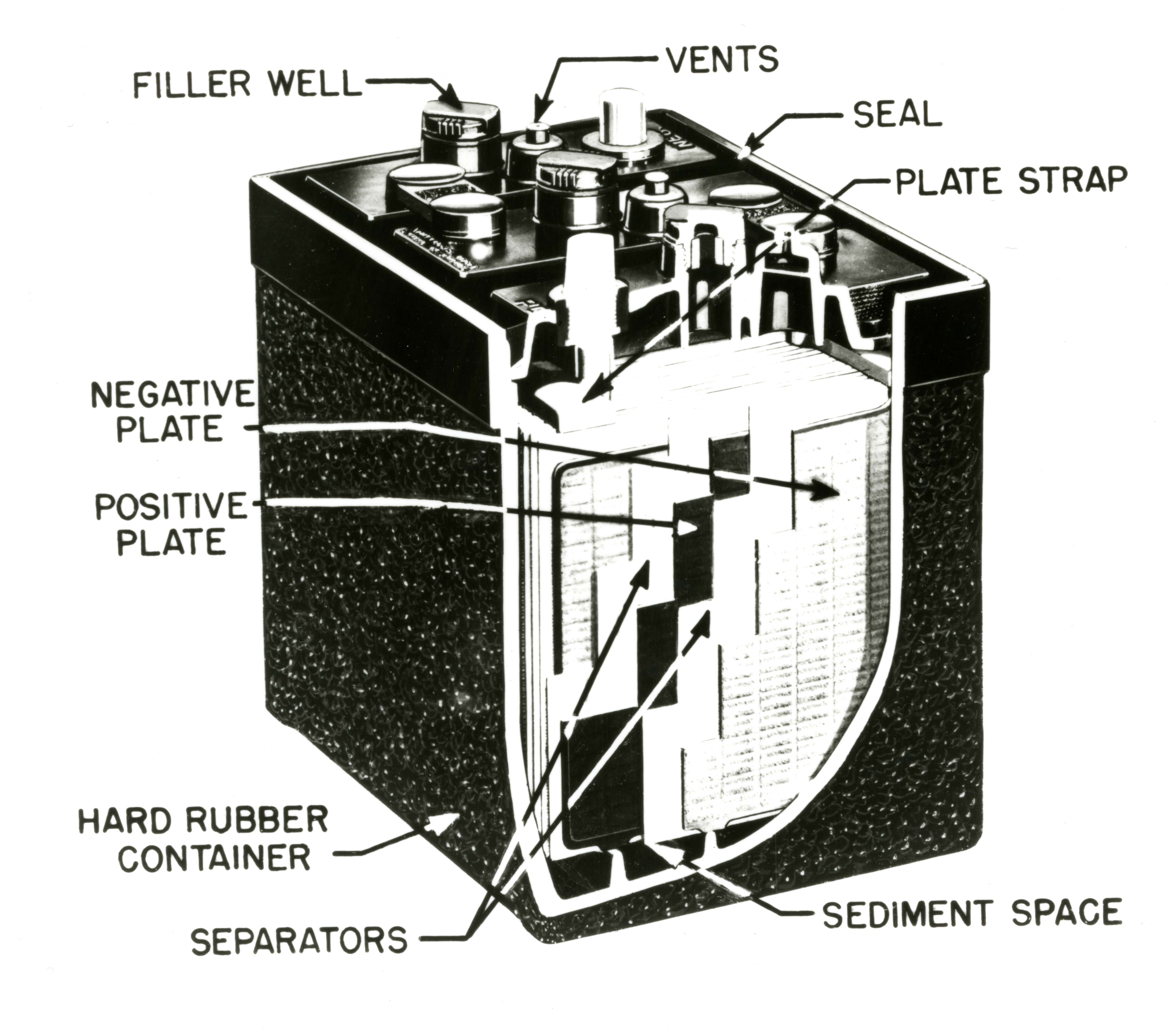 Lead-acid cells consist of two plates of lead, which serve as
Lead-acid cells consist of two plates of lead, which serve as
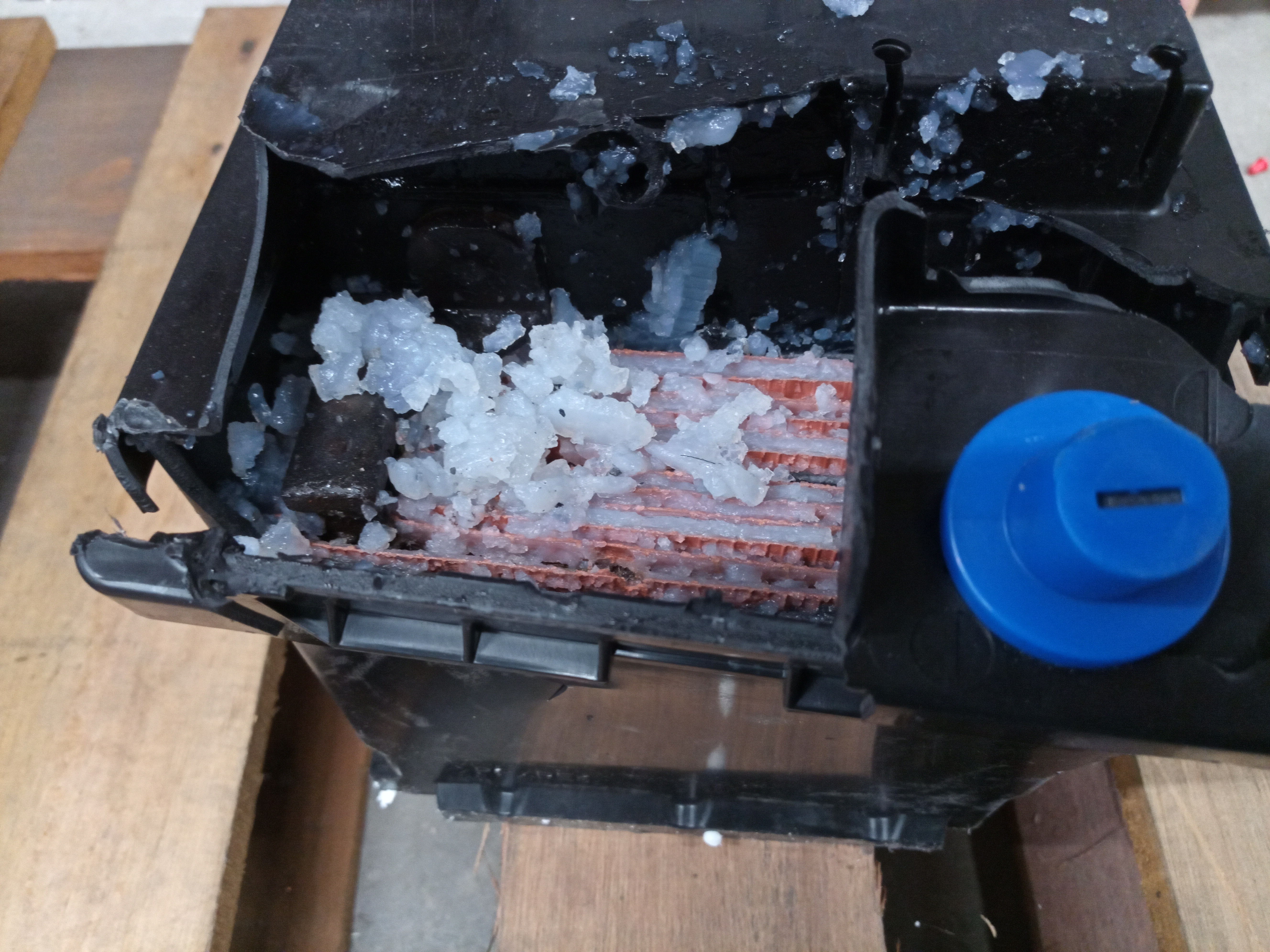 Originally a kind of gel battery was produced in the early 1930s for portable valve (tube) radio LT supply (2, 4, or 6 V) by adding silica to the sulfuric acid. By this time, the glass case was being replaced by celluloid, and later, in the 1930s, other plastics. Earlier "wet" cells in glass jars used special valves to allow tilt from vertical to one horizontal direction, in 1927 to 1931 or 1932. The gel cells were less likely to
Originally a kind of gel battery was produced in the early 1930s for portable valve (tube) radio LT supply (2, 4, or 6 V) by adding silica to the sulfuric acid. By this time, the glass case was being replaced by celluloid, and later, in the 1930s, other plastics. Earlier "wet" cells in glass jars used special valves to allow tilt from vertical to one horizontal direction, in 1927 to 1931 or 1932. The gel cells were less likely to
GR-4228
''Valve-Regulated Lead-Acid (VRLA) Battery String Certification Levels Based on Requirements for Safety and Performance,'' are recommended for deployment in the Outside Plant (OSP) at locations such as Controlled Environmental Vaults (CEVs), Electronic Equipment Enclosures (EEEs), and huts, and in uncontrolled structures such as cabinets. Relative to VRLA in telecommunications, the use of VRLA Ohmic Measurement Type Equipment (OMTE) and OMTE-like measurement equipment is a fairly new process to evaluate telecommunications battery plants. The proper use of ohmic test equipment allows battery testing without the need to remove batteries from service to perform costly and time-consuming discharge tests.
p202
* Vinal, G.W. (1955 Jan 01) Storage batteries. A general treatise on the physics and chemistry of secondary batteries and their engineering applications. Energy Citations Database (ECD)
Document #7308501
* John McGavack
The Absorption of Sulfur Dioxide by the Gel of Silicic Acid
Eschenbach Print. Company, 1920.
Why do I need a special battery for the automatic start-stop system?
published by Varta
Pros and cons of AGM batteries
published by Lifeline {{Galvanic cells Lead Rechargeable batteries Sulfuric acid
 A valve regulated lead‐acid (VRLA) battery, commonly known as a sealed lead-acid (SLA) battery, is a type of lead-acid battery characterized by a limited amount of electrolyte ("starved" electrolyte) absorbed in a plate separator or formed into a gel, proportioning of the negative and positive plates so that oxygen recombination is facilitated within the cell, and the presence of a relief valve that retains the battery contents independent of the position of the cells.
There are two primary types of VRLA batteries: absorbent glass mat (AGM) and gel cell (gel battery). Gel cells add silica dust to the electrolyte, forming a thick putty-like gel; AGM (absorbent glass mat) batteries feature fiberglass mesh between the battery plates, which serves to contain the electrolyte and separate the plates. Both types of VRLA batteries offer advantages and disadvantages compared to flooded vented lead-acid (VLA) batteries or each other.
Due to their construction, the gel cell and AGM types of VRLA can be mounted in any orientation and do not require constant maintenance. The term "maintenance-free" is a misnomer, as VRLA batteries still require cleaning and regular functional testing. They are widely used in large portable electrical devices, off-grid power systems (including uninterruptible power systems), low-cost
A valve regulated lead‐acid (VRLA) battery, commonly known as a sealed lead-acid (SLA) battery, is a type of lead-acid battery characterized by a limited amount of electrolyte ("starved" electrolyte) absorbed in a plate separator or formed into a gel, proportioning of the negative and positive plates so that oxygen recombination is facilitated within the cell, and the presence of a relief valve that retains the battery contents independent of the position of the cells.
There are two primary types of VRLA batteries: absorbent glass mat (AGM) and gel cell (gel battery). Gel cells add silica dust to the electrolyte, forming a thick putty-like gel; AGM (absorbent glass mat) batteries feature fiberglass mesh between the battery plates, which serves to contain the electrolyte and separate the plates. Both types of VRLA batteries offer advantages and disadvantages compared to flooded vented lead-acid (VLA) batteries or each other.
Due to their construction, the gel cell and AGM types of VRLA can be mounted in any orientation and do not require constant maintenance. The term "maintenance-free" is a misnomer, as VRLA batteries still require cleaning and regular functional testing. They are widely used in large portable electrical devices, off-grid power systems (including uninterruptible power systems), low-cost electric vehicle
An electric vehicle (EV) is a motor vehicle whose propulsion is powered fully or mostly by electricity. EVs encompass a wide range of transportation modes, including road vehicle, road and rail vehicles, electric boats and Submersible, submer ...
s, and similar roles, where large amounts of storage are needed at a lower cost than other low-maintenance technologies like lithium ion.
History
The first lead-acid gel battery was invented by Elektrotechnische Fabrik Sonneberg in 1934. The modern gel, or VRLA, battery was invented by Otto Jache of Sonnenschein in 1957. The first AGM cell was the Cyclon, patented by Gates Rubber Corporation in 1972 and now produced by EnerSys. The Cyclon was a spiral-wound cell with thin lead foil electrodes. A number of manufacturers adopted the technology to implement it in cells with conventional flat plates. In the mid-1980s, two UK companies, Chloride Group and Tungstone Products, simultaneously introduced "ten-year life" AGM batteries in capacities up to 400 Ah, stimulated by a British Telecom specification for backup batteries to support new digital exchanges. In the same period, Gates acquired another UK company, Varley, specializing in aircraft and military batteries. Varley adapted the Cyclon lead foil technology to produce flat-plate batteries with exceptional high rate output. These gained approval for a variety of aircraft, including the BAE 125 and 146 business jets, theHarrier jump jet
The Harrier, informally referred to as the Harrier jump jet, is a family of jet-powered attack aircraft capable of vertical/short takeoff and landing operations (V/STOL). Named after the bird of prey, it was originally developed by British ...
and its derivative the AV-8B, and some F16 variants, as the first alternatives to then standard nickel–cadmium (Ni-Cd) batteries.
Basic principle
 Lead-acid cells consist of two plates of lead, which serve as
Lead-acid cells consist of two plates of lead, which serve as electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or a gas). In electrochemical cells, electrodes are essential parts that can consist of a varie ...
s, suspended in an electrolyte
An electrolyte is a substance that conducts electricity through the movement of ions, but not through the movement of electrons. This includes most soluble Salt (chemistry), salts, acids, and Base (chemistry), bases, dissolved in a polar solven ...
consisting of diluted sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen, ...
. VRLA cells have the same chemistry except that the electrolyte is immobilized. In AGMs, this is accomplished with a fiberglass mat; in gel batteries or "gel cells", the electrolyte is in the form of a paste-like gel created by adding silica and other gelling agents to the electrolyte.
When a cell discharges, the lead and diluted acid undergo a chemical reaction that produces lead sulfate and water. When a cell is subsequently charged, the lead sulfate and water are turned back into lead and acid. In all lead-acid battery designs, charging current must be adjusted to match the ability of the battery to absorb the energy. If the charging current is too great, electrolysis
In chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a technique that uses Direct current, direct electric current (DC) to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction. Electrolysis is commercially important as a stage in the separation of c ...
will occur, decomposing water into hydrogen and oxygen, in addition to the intended conversion of lead sulfate and water into lead dioxide, lead, and sulfuric acid (the reverse of the discharge process). If these gases are allowed to escape, as in a conventional flooded cell, the battery will need to have water (or electrolyte) added from time to time. In contrast, VRLA batteries retain generated gases within the battery as long as the pressure remains within safe levels. Under normal operating conditions, the gases can then recombine within the battery itself, sometimes with the help of a catalyst, and no additional electrolyte is needed. However, if the pressure exceeds safety limits, safety valves open to allow the excess gases to escape, and in doing so regulate the pressure back to safe levels (hence "valve regulated" in "VRLA"). Ronald Dell, David Anthony James Rand, Robert Bailey, Jr., ''Understanding Batteries'', Royal Society of Chemistry, 2001, p. 101, pp.120-122
Construction
Each cell in a VRLA battery has a pressure relief valve that will activate when the battery starts building pressure of hydrogen gas, generally a result of being recharged. The cell covers typically have gas diffusers built into them, which allow safe dispersal of any excess hydrogen that may be formed during overcharge. They are not permanently sealed but are designated to be maintenance-free. They can be oriented in any manner, unlike normal lead-acid batteries, which must be kept upright to avoid acid spills and to keep the plates' orientation vertical. Cells may be operated with the plates horizontal (''pancake'' style), which may improve cycle life.Absorbent glass mat (AGM)
AGM batteries differ from flooded lead-acid batteries in that the electrolyte is held in the glass mats, as opposed to freely flooding the plates. Very thin glass fibers are woven into a mat to increase the surface area enough to hold a sufficient amount of electrolyte on the cells for their lifetime. The fibers that compose the fine glass mat do not absorb and are not affected by the acidic electrolyte. These mats are wrung out 2–5% after being soaked in acids just prior to finish manufacturing. The plates in an AGM battery may be of any shape. Some are flat, whereas others are bent or rolled. Both deep-cycle and starting type of AGM batteries are built into a rectangular case according toBattery Council International
Battery Council International (BCI) is a trade association
A trade association, also known as an industry trade group, business association, sector association or industry body, is an organization founded and funded by businesses that operate i ...
(BCI) battery code specifications.
AGM batteries are more resistant to self-discharging than conventional batteries within a wide range of temperatures.
As with lead-acid batteries, in order to maximize the life of an AGM battery, it is important to follow the manufacturer's charging specifications. The use of a voltage-regulated charger is recommended. There is a direct correlation between the depth of discharge (DOD) and the cycle life of the battery, with differences between 500 and 1300 cycles, depending on DOD.
Gel battery
 Originally a kind of gel battery was produced in the early 1930s for portable valve (tube) radio LT supply (2, 4, or 6 V) by adding silica to the sulfuric acid. By this time, the glass case was being replaced by celluloid, and later, in the 1930s, other plastics. Earlier "wet" cells in glass jars used special valves to allow tilt from vertical to one horizontal direction, in 1927 to 1931 or 1932. The gel cells were less likely to
Originally a kind of gel battery was produced in the early 1930s for portable valve (tube) radio LT supply (2, 4, or 6 V) by adding silica to the sulfuric acid. By this time, the glass case was being replaced by celluloid, and later, in the 1930s, other plastics. Earlier "wet" cells in glass jars used special valves to allow tilt from vertical to one horizontal direction, in 1927 to 1931 or 1932. The gel cells were less likely to leak
A leak is a way (usually an opening) for fluid to escape a container or fluid-containing system, such as a Water tank, tank or a Ship, ship's Hull (watercraft), hull, through which the contents of the container can escape or outside matter can e ...
when the portable set was handled roughly.
A modern gel battery is a VRLA battery with a gelated electrolyte
An electrolyte is a substance that conducts electricity through the movement of ions, but not through the movement of electrons. This includes most soluble Salt (chemistry), salts, acids, and Base (chemistry), bases, dissolved in a polar solven ...
; the sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen, ...
is mixed with fumed silica
Fumed silica (CAS_Registry_Number, CAS number 7631-86-9, also 112945-52-5), also known as pyrogenic silica because it is produced in a flame, consists of microscopic droplets of amorphous silica fused into branched, chainlike, three-dimensional ...
, which makes the resulting mass gel-like and immobile. Unlike a flooded wet cell lead-acid battery, these batteries do not need to be kept upright. Gel batteries reduce the electrolyte evaporation, spillage (and subsequent corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engine ...
problems) common to the wet cell battery, and boast greater resistance to shock and vibration
Vibration () is a mechanical phenomenon whereby oscillations occur about an equilibrium point. Vibration may be deterministic if the oscillations can be characterised precisely (e.g. the periodic motion of a pendulum), or random if the os ...
. Chemically, they are almost the same as wet (non-sealed) batteries except that the antimony
Antimony is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Sb () and atomic number 51. A lustrous grey metal or metalloid, it is found in nature mainly as the sulfide mineral stibnite (). Antimony compounds have been known since ancient t ...
in the lead plates is replaced by calcium
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to it ...
, and gas recombination can take place.
Comparison: AGM vs. Gel
While both Absorbent Glass Mat (AGM) and Gel batteries are categorized as Valve-Regulated Lead-Acid (VRLA) batteries and are commonly used in vehicles and backup power systems, they differ in several key performance aspects. The comparison below highlights major differences based on characteristics such as charge speed, vibration resistance, and deep cycle capability.Applications
Many modern motorcycles andall-terrain vehicle
An all-terrain vehicle (ATV), also known as a light utility vehicle (LUV), a quad bike or quad (if it has four wheels), as defined by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), is a vehicle that travels on low-pressure tires, has a seat ...
s (ATVs) on the market use AGM batteries to reduce the likelihood of acid spilling during cornering, vibration, or after accidents, and for packaging reasons. The lighter, smaller battery can be installed at an odd angle if needed for the design of the motorcycle. Due to the higher manufacturing costs compared with flooded lead-acid batteries, AGM batteries are currently used on luxury vehicles. As vehicles become heavier and equipped with more electronic devices such as navigation and stability control
Electronic stability control (ESC), also referred to as electronic stability program (ESP) or dynamic stability control (DSC), is a computerized technology that improves a vehicle's stability by detecting and reducing loss of traction ( skiddi ...
, AGM batteries are being employed to lower vehicle weight and provide better electrical reliability compared with flooded lead-acid batteries.
5 series
The BMW 5 Series is an executive car manufactured and marketed by BMW since 1972. It is the successor to the BMW New Class#New Class Sedans, BMW New Class sedans and is currently in its eighth generation. The car is sold as either a sedan (car), s ...
BMW
Bayerische Motoren Werke AG, trading as BMW Group (commonly abbreviated to BMW (), sometimes anglicised as Bavarian Motor Works), is a German multinational manufacturer of vehicles and motorcycles headquartered in Munich, Bavaria, Germany. Th ...
s from March 2007 incorporate AGM batteries in conjunction with devices for recovering brake energy using regenerative braking
Regenerative braking is an energy recovery mechanism that slows down a moving vehicle or object by converting its kinetic energy or potential energy into a form that can be either used immediately or stored until needed.
Typically, regenerativ ...
and computer control to ensure that the alternator charges the battery when the car is decelerating. Vehicles used in auto racing
Auto racing (also known as car racing, motor racing, or automobile racing) is a motorsport involving the racing of automobiles for competition. In North America, the term is commonly used to describe all forms of automobile sport including non ...
may use AGM batteries due to their vibration resistance. AGM batteries are also commonly used in classic vehicles, since they are much less likely to leak electrolyte, which could damage hard-to-replace body panels.
Deep-cycle AGMs are also commonly used in off-grid solar power
Solar power, also known as solar electricity, is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV) or indirectly using concentrated solar power. Solar panels use the photovoltaic effect to c ...
and wind power
Wind power is the use of wind energy to generate useful work. Historically, wind power was used by sails, windmills and windpumps, but today it is mostly used to generate electricity. This article deals only with wind power for electricity ge ...
installations as an energy storage
Energy storage is the capture of energy produced at one time for use at a later time to reduce imbalances between energy demand and energy production. A device that stores energy is generally called an Accumulator (energy), accumulator or Batte ...
bank and in large-scale amateur robotics, such as the FIRST and IGVC competitions.
AGM batteries are routinely chosen for remote sensors such as ice monitoring stations in the Arctic
The Arctic (; . ) is the polar regions of Earth, polar region of Earth that surrounds the North Pole, lying within the Arctic Circle. The Arctic region, from the IERS Reference Meridian travelling east, consists of parts of northern Norway ( ...
. AGM batteries, due to their lack of free electrolyte, will not crack and leak in these cold environments.
VRLA batteries are used extensively in power wheelchairs and mobility scooters, as the extremely low gas and acid output makes them much safer for indoor use. VRLA batteries are also used in uninterruptible power supplies
An uninterruptible power supply (UPS) or uninterruptible power source is a type of continual power system that provides automated backup electric power to a load when the input power source or mains power fails. A UPS differs from a tradition ...
(UPSs) as a backup when the electrical power goes off.
VRLA batteries are also the standard power source in sailplanes, due to their ability to withstand a variety of flight attitudes and a relatively large ambient temperature range with no adverse effects. However, charging regimes must be adapted with varying temperatures.
VRLA batteries are used in the US Nuclear Submarine fleet, due to their power density, elimination of gassing, reduced maintenance, and enhanced safety.
AGM and gel-cell batteries are also used for recreational marine purposes, with AGM being more commonly available. AGM deep-cycle marine batteries are offered by a number of suppliers. They typically are favored for their low-maintenance and spillproof qualities, although they are generally considered a less cost-effective solution relative to traditional flooded cells.
In telecommunications applications, VRLA batteries that comply with criteria in Telcordia Technologies requirements documenGR-4228
''Valve-Regulated Lead-Acid (VRLA) Battery String Certification Levels Based on Requirements for Safety and Performance,'' are recommended for deployment in the Outside Plant (OSP) at locations such as Controlled Environmental Vaults (CEVs), Electronic Equipment Enclosures (EEEs), and huts, and in uncontrolled structures such as cabinets. Relative to VRLA in telecommunications, the use of VRLA Ohmic Measurement Type Equipment (OMTE) and OMTE-like measurement equipment is a fairly new process to evaluate telecommunications battery plants. The proper use of ohmic test equipment allows battery testing without the need to remove batteries from service to perform costly and time-consuming discharge tests.
Comparison with flooded lead-acid cells
VRLA gel and AGM batteries offer several advantages compared with VRLA flooded lead-acid and conventional lead-acid batteries. The battery can be mounted in any position, since the valves only operate on over-pressure faults. Since the battery system is designed to be recombinant and eliminate the emission of gases on overcharge, room ventilation requirements are reduced, and no acid fumes are emitted during normal operation. Flooded-cell gas emissions are of little consequence in all but the smallest confined areas and pose very little threat to a domestic user, so a wet-cell battery designed for longevity gives lower costs per kWh. In a gel battery, the volume of free electrolyte that could be released on damage to the case or venting is very small. There is no need (or ability) to check the level of electrolyte or to top up water lost due to electrolysis, thus reducing inspection and maintenance requirements. Wet-cell batteries can be maintained by a self-watering system or by topping up every three months. The requirement to add distilled water is normally caused by overcharging. A well-regulated system should not require top-up more often than every three months.All lead-acid batteries — charging requirements
An underlying disadvantage with all lead-acid (LA) batteries is the requirement for a relatively long recharge cycle time arising from an inherent three-stage charging process: bulk charge, absorption charge, and (maintenance) float charge stages. All lead-acid batteries, irrespective of type, are quick to bulk charge to about 70% of capacity, during which the battery will accept a large current input, determined at a voltage setpoint, within a few hours (with a charge source capable of supplying the designC-rate
A battery charger, recharger, or simply charger, is a device that stores energy in an electric battery by running current through it. The charging protocol—how much voltage and current, for how long and what to do when charging is complete� ...
bulk stage current for a given Ah battery).
However, they then require a longer time spent in the current-tapering-off intermediate absorption charge stage after the initial bulk charge, when the LA battery charge acceptance rate gradually reduces and the battery will not accept a higher C-rate. When the absorption stage voltage setpoint is reached (and charge current has tapered off), the charger switches to a float voltage setpoint at a very low C-rate to maintain the battery's fully charged state indefinitely (the float stage offsets the battery's normal self-discharge over time).
If the charger fails to supply a sufficient absorption stage charge duration and C-rate (it 'plateaus' or times out, a common fault of cheap solar chargers) and a suitable float charge profile, the battery's capacity and longevity will be dramatically reduced.
To ensure maximum life, a lead-acid battery should be fully recharged as soon after a discharge cycle as possible to prevent sulfation
Sulfation (sometimes spelled sulphation in British English) is the chemical reaction that entails the addition of SO3 group. In principle, many sulfations would involve reactions of sulfur trioxide (SO3). In practice, most sulfations are effected ...
, and kept at a full charge level by a float source when stored or idle (or stored dry new from the factory, an uncommon practice today).
When working a discharge cycle, a lead-acid battery should be kept at a depth-of-discharge (DOD) of less than 50%, ideally no more than 20–40% DOD; a true LA deep-cycle battery
A deep-cycle battery is a battery designed to be regularly deeply discharged using most of its capacity. The term is traditionally mainly used for Lead–acid battery, lead–acid batteries in the same form factor as automotive batteries; and con ...
can be taken to a lower DOD (even an occasional 80%), but these greater DOD cycles always impose a longevity price.
Lead-acid battery lifetime cycles will vary with the care given, and with the best care, they may achieve 500 to 1000 cycles. With less careful use, a lifetime as few as 100 cycles might be expected (all dependent upon the use environment too).
Charging sealed batteries
Because of calcium added to its plates to reduce water loss, a sealed AGM or gel battery recharges more quickly than a flooded lead-acid battery of either VRLA or conventional design.(stating sealed battery plates are hardened with calcium to reduce water loss which "raises the batteries' internal resistance and prevents rapid charging.") Compared to flooded batteries, VRLA batteries are more vulnerable tothermal runaway
Thermal runaway describes a process that is accelerated by increased temperature, in turn releasing Thermal energy, energy that further increases temperature. Thermal runaway occurs in situations where an increase in temperature changes the cond ...
during abusive charging. The electrolyte cannot be tested by hydrometer to diagnose improper charging that can reduce battery life.
Comparison summary
AGM automobile batteries are typically about twice the price of flooded-cell batteries in a given BCI size group; gel batteries as much as five times the price. AGM and gel VRLA batteries: * Have a shorter recharge time than flooded lead-acid batteries; * Cannot tolerate overcharging (overcharging leads to premature failure); * Have a shorter useful life compared to properly maintained wet-cell batteries; * Discharge significantly less hydrogen gas; * Are by nature safer for the environment and safer to use; * Can be used or positioned in any orientation.See also
*List of battery types
This list is a summary of notable electric battery types composed of one or more electrochemical cells. Three lists are provided in the table. The primary (non-rechargeable) and secondary (rechargeable) cell lists are lists of battery chemistry. ...
*
*
References
Further reading
Books and papers
* Valve-Regulated Lead–Acid Batteries. Edited by Patrick T. Moseley, Jurgen Garche, C.D. Parker, D.A.J. Randp202
* Vinal, G.W. (1955 Jan 01) Storage batteries. A general treatise on the physics and chemistry of secondary batteries and their engineering applications. Energy Citations Database (ECD)
Document #7308501
* John McGavack
The Absorption of Sulfur Dioxide by the Gel of Silicic Acid
Eschenbach Print. Company, 1920.
Patents
* – Treatment Of Porous Pots For Electric Batteries. Erhard Ludwig Mayer and Henry Liepmann * – Solid Acid Storage Battery Electrolyte. Alexander Koenig et al. * – Composite battery plate grid * – Lead acid battery plate with starch coated glass fibers * – Method of making a lead storage battery and lead storage battery made according to this method. Otto Jache's and Heinz SchroederExternal links
Why do I need a special battery for the automatic start-stop system?
published by Varta
Pros and cons of AGM batteries
published by Lifeline {{Galvanic cells Lead Rechargeable batteries Sulfuric acid