|
Float Voltage
Float voltage is the voltage at which a battery is maintained after being fully charged to maintain that capacity by compensating for self-discharge of the battery. The voltage could be held constant for the entire duration of the cell's operation (such as in an automotive battery) or could be held for a particular phase of charging by the charger. The appropriate float voltage varies significantly with the chemistry and construction of the battery, and ambient temperature. With the appropriate voltage for the battery type and with proper temperature compensation, a float charger may be kept connected indefinitely without damaging the battery. However, it should be understood that the concept of a float voltage does not apply equally to all battery chemistries. For instance, lithium ion cells have to be float charged with extra care because if they are float charged at just a little over optimum voltage, which is generally the full output voltage of the lithium cell, the chemical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Voltage
Voltage, also known as (electrical) potential difference, electric pressure, or electric tension, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a Electrostatics, static electric field, it corresponds to the Work (electrical), work needed per unit of Electric charge, charge to move a positive Test particle#Electrostatics, test charge from the first point to the second point. In the SI unit, International System of Units (SI), the SI derived unit, derived unit for voltage is the ''volt'' (''V''). The voltage between points can be caused by the build-up of electric charge (e.g., a capacitor), and from an electromotive force (e.g., electromagnetic induction in a Electric generator, generator). On a macroscopic scale, a potential difference can be caused by electrochemical processes (e.g., cells and batteries), the pressure-induced piezoelectric effect, and the thermoelectric effect. Since it is the difference in electric potential, it is a physical Scalar (physics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Self-discharge
Self-discharge is a phenomenon in batteries. Self-discharge decreases the shelf life Shelf life is the length of time that a commodity may be stored without becoming unfit for use, consumption, or sale. In other words, it might refer to whether a commodity should no longer be on a pantry shelf (unfit for use), or no longer on a s ... of batteries and causes them to have less than a full charge when actually put to use. How fast self-discharge in a battery occurs is dependent on the type of battery, state of charge, charging current, ambient temperature and other factors. Primary batteries are not designed for recharging between manufacturing and use, and thus to be practical they must have much lower self-discharge rates than older types of secondary cells. Later, secondary cells with similar very low self-discharge rates were developed, like low-self-discharge nickel–metal hydride cells. Self-discharge is a chemical reaction, just as closed-circuit discharge is, and tends ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Automotive Battery
An automotive battery, or car battery, is a usually 12 Volt lead-acid rechargeable battery that is used to start a motor vehicle, and to power lights, screen wiper etc. while the engine is off. Its main purpose is to provide an electric current to the electric-powered starting motor, which in turn starts the chemically-powered internal combustion engine that actually propels the vehicle. Once the engine is running, power for the car's electrical systems is still supplied by the battery, with the alternator charging the battery as demands increase or decrease. Battery in modern cars Gasoline and diesel engine Typically, starting uses less than three percent of the battery capacity. For this reason, automotive batteries are designed to deliver maximum current for a short period of time. They are sometimes referred to as "SLI batteries" for this reason, for starting, lighting and ignition. SLI batteries are not designed for deep discharging, and a full discharge can reduce the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Lithium Ion
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery that uses the reversible intercalation of Li+ ions into electronically conducting solids to store energy. Li-ion batteries are characterized by higher specific energy, energy density, and energy efficiency and a longer cycle life and calendar life than other types of rechargeable batteries. Also noteworthy is a dramatic improvement in lithium-ion battery properties after their market introduction in 1991; over the following 30 years, their volumetric energy density increased threefold while their cost dropped tenfold. In late 2024 global demand passed per year, while production capacity was more than twice that. The invention and commercialization of Li-ion batteries has had a large impact on technology, as recognized by the 2019 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Li-ion batteries have enabled portable consumer electronics, laptop computers, cellular phones, and electric cars. Li-ion batteries also see significant use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Battery Management System
A battery management system (BMS) is any electronic system that manages a rechargeable battery (cell or battery pack) by facilitating the safe usage and a long life of the battery in practical scenarios while monitoring and estimating its various states (such as state of health and state of charge), calculating secondary data, reporting that data, controlling its environment, authenticating or balancing it. Protection circuit module (PCM) is a simpler alternative to BMS. A battery pack built together with a BMS with an external communication data bus is a smart battery pack. A smart battery pack must be charged by a smart battery charger. Functions Monitor A BMS may monitor the state of the battery as represented by various items, such as: * Voltage: total voltage, voltages of individual cells, or voltage of * Temperature: average temperature, coolant intake temperature, coolant output temperature, or temperatures of individual cells * Coolant flow: for liquid cooled b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
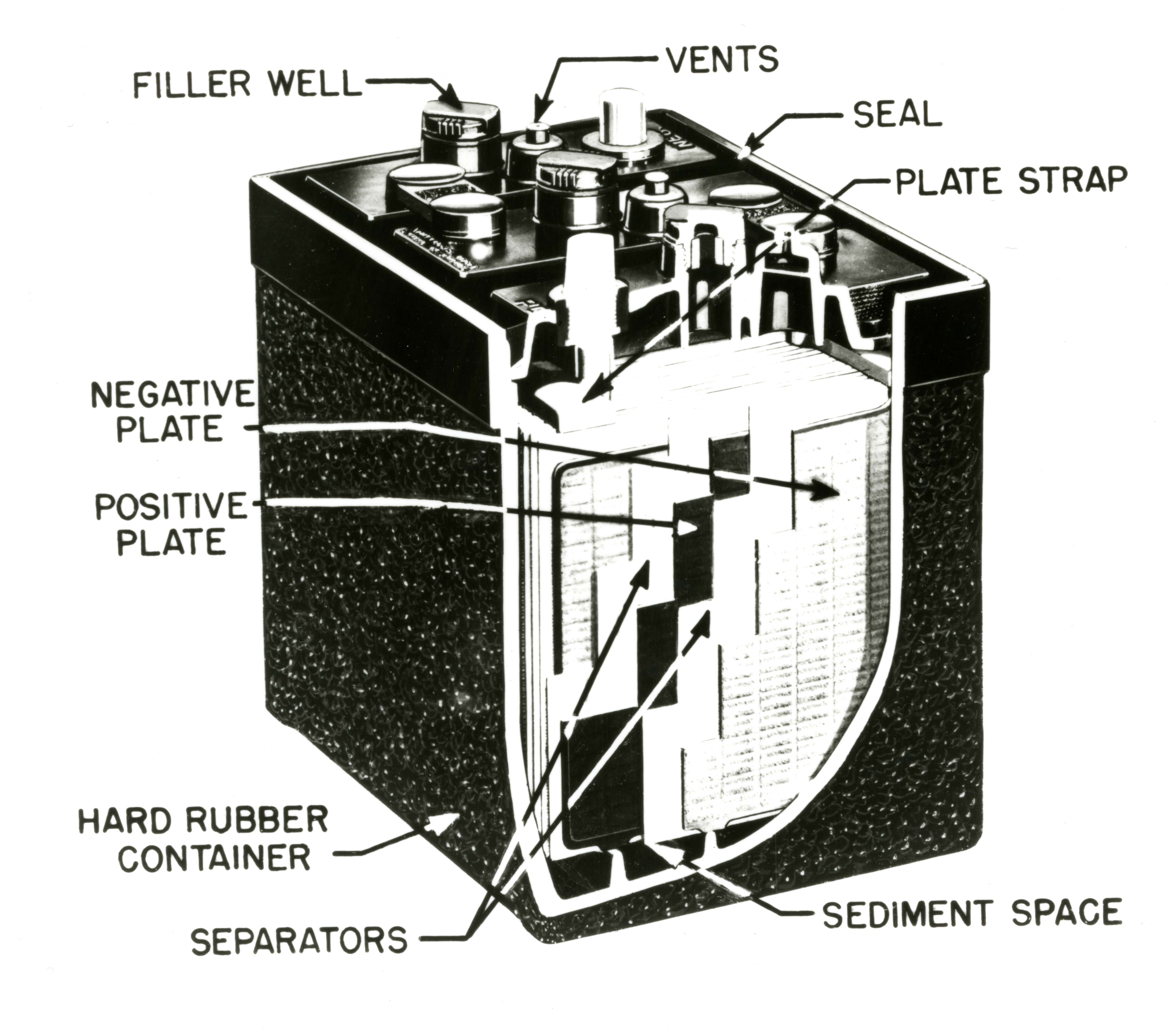
Lead–acid Battery
The lead–acid battery is a type of rechargeable battery first invented in 1859 by French physicist Gaston Planté. It was the first type of rechargeable battery to be invented. Compared to modern rechargeable batteries, lead–acid batteries have relatively low energy density. Despite this, they are able to supply high surge currents. These features, along with their low cost, make them attractive for use in motor vehicles in order to provide the high current required by starter motors. Lead–acid batteries suffer from relatively short cycle lifespan (usually less than 500 deep cycles) and overall lifespan (due to the ''double sulfation'' in the discharged state), as well as long charging times. As they are not as expensive when compared to newer technologies, lead–acid batteries are widely used even when surge current is not important and other designs could provide higher energy densities. In 1999, lead–acid battery sales accounted for 40–50% of the value from batteries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Gel Battery
A valve regulated lead‐acid (VRLA) battery, commonly known as a sealed lead-acid (SLA) battery, is a type of lead-acid battery characterized by a limited amount of electrolyte ("starved" electrolyte) absorbed in a plate separator or formed into a gel, proportioning of the negative and positive plates so that oxygen recombination is facilitated within the cell, and the presence of a relief valve that retains the battery contents independent of the position of the cells. There are two primary types of VRLA batteries: absorbent glass mat (AGM) and gel cell (gel battery). Gel cells add silica dust to the electrolyte, forming a thick putty-like gel; AGM (absorbent glass mat) batteries feature fiberglass mesh between the battery plates, which serves to contain the electrolyte and separate the plates. Both types of VRLA batteries offer advantages and disadvantages compared to flooded vented lead-acid (VLA) batteries or each other. Due to their construction, the gel cell and AGM typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Flooded Lead–acid Cell
A flood is an overflow of water ( or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are of significant concern in agriculture, civil engineering and public health. Human changes to the environment often increase the intensity and frequency of flooding. Examples for human changes are land use changes such as deforestation and removal of wetlands, changes in waterway course or flood controls such as with levees. Global environmental issues also influence causes of floods, namely climate change which causes an intensification of the water cycle and sea level rise. For example, climate change makes extreme weather events more frequent and stronger. This leads to more intense floods and increased flood risk. Natural types of floods include river flooding, groundwater flooding coastal flooding and urban flooding sometimes known as flash flooding. Tidal flooding may inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
VRLA Battery
A valve regulated lead‐acid (VRLA) battery, commonly known as a sealed lead-acid (SLA) battery, is a type of lead-acid battery characterized by a limited amount of electrolyte ("starved" electrolyte) absorbed in a plate separator or formed into a gel, proportioning of the negative and positive plates so that oxygen recombination is facilitated within the cell, and the presence of a relief valve that retains the battery contents independent of the position of the cells. There are two primary types of VRLA batteries: absorbent glass mat (AGM) and gel cell (gel battery). Gel cells add silica dust to the electrolyte, forming a thick putty-like gel; AGM (absorbent glass mat) batteries feature fiberglass mesh between the battery plates, which serves to contain the electrolyte and separate the plates. Both types of VRLA batteries offer advantages and disadvantages compared to flooded vented lead-acid (VLA) batteries or each other. Due to their construction, the gel cell and AGM typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |