Gangaridai on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
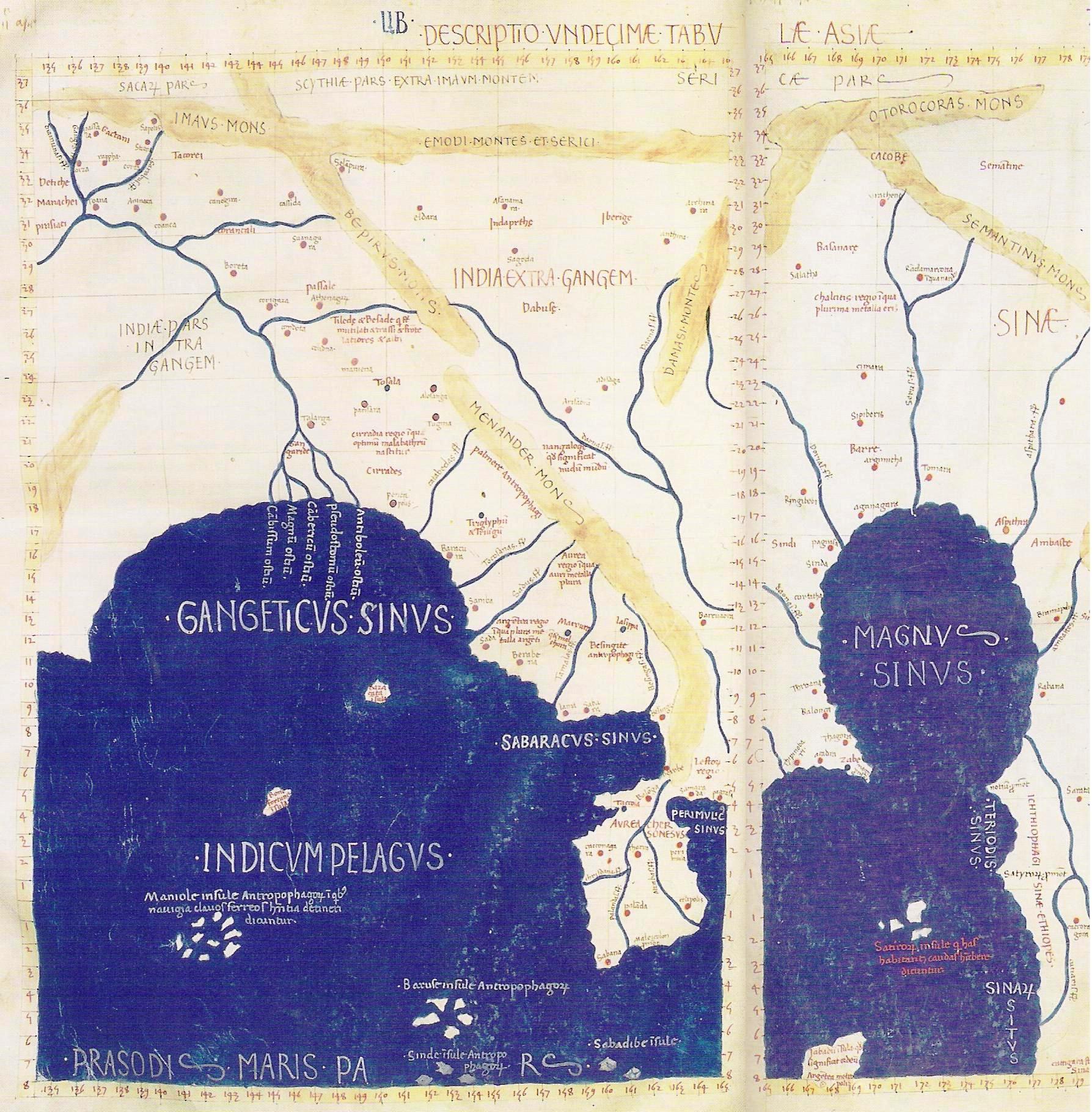 Gangaridai (, ) is a term used by the ancient Greco-Roman writers (1st century BCE–2nd century AD) to describe
Gangaridai (, ) is a term used by the ancient Greco-Roman writers (1st century BCE–2nd century AD) to describe
 The earliest surviving description of Gangaridai appears in ''
The earliest surviving description of Gangaridai appears in ''


 The ancient Greek writers provide vague information about the centre of the Gangaridai power. As a result, the later historians have put forward various theories about its location.
The ancient Greek writers provide vague information about the centre of the Gangaridai power. As a result, the later historians have put forward various theories about its location.
 Gangaridai (, ) is a term used by the ancient Greco-Roman writers (1st century BCE–2nd century AD) to describe
Gangaridai (, ) is a term used by the ancient Greco-Roman writers (1st century BCE–2nd century AD) to describe people
The term "the people" refers to the public or Common people, common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. I ...
or a geographical region of the ancient Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
. Some of these writers state that Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
withdrew from the Indian subcontinent because of the strong war elephant
A war elephant is an elephant that is Animal training, trained and guided by humans for combat purposes. Historically, the war elephant's main use was to charge (warfare), charge the enemy, break their ranks, and instill terror and fear. Elep ...
force of the Gangaridai.
A number of modern scholars locate Gangaridai in the Ganges Delta of the Bengal
Bengal ( ) is a Historical geography, historical geographical, ethnolinguistic and cultural term referring to a region in the Eastern South Asia, eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. The region of Benga ...
region, although alternative theories also exist. Gange or Ganges, the capital of the Gangaridai (according to Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzant ...
), has been identified with several sites in the region, including Chandraketugarh and Wari-Bateshwar.
Names
The Greek writers use the names "Gandaridae" (Diodorus), "Gandaritae", and "Gandridae" (Plutarch) to describe these people. The ancient Latin writers use the name "Gangaridae", a term that seems to have been coined by the 1st century BCE poetVirgil
Publius Vergilius Maro (; 15 October 70 BC21 September 19 BC), usually called Virgil or Vergil ( ) in English, was an ancient Rome, ancient Roman poet of the Augustan literature (ancient Rome), Augustan period. He composed three of the most fa ...
.
Some modern etymologies of the word Gangaridai split it as " Gaṅgā-rāṣṭra", "Gaṅgā- rāḍha" or "Gaṅgā- hṛdaya". For example, it has been suggested that Gangarid is a Greek formation of the Indian word "Ganga-hṛd", meaning 'the land with the Ganges at its heart'. The meaning fits well with the description of the region given by the author of Periplus. However, historian D. C. Sircar believes that the word is simply the plural form of "Gangarid" (derived from the base "Ganga"), and means "Ganga (Ganges) people".
Some earlier scholars considered "Gangaridae" as a corruption of or distinct from "Gandaridae", a region they located in north-western part of the Indian subcontinent. For example, W. W. Tarn (1948) equated the term with Gandhara
Gandhara () was an ancient Indo-Aryan people, Indo-Aryan civilization in present-day northwest Pakistan and northeast Afghanistan. The core of the region of Gandhara was the Peshawar valley, Peshawar (Pushkalawati) and Swat valleys extending ...
; and T.R. Robinson (1993) equated it to Gandaris or Gandarae, an area in present-day Punjab mentioned by ancient Greek writers. However, the ancient Greco-Roman works make it clear that Gandaridae was located in the Ganges plain: it was another name for Gangaridae, and was different from Gandhara and Gandaris.
Greek accounts
Several ancient Greek writers mention Gangaridai, but their accounts are largely based on hearsay.Diodorus
 The earliest surviving description of Gangaridai appears in ''
The earliest surviving description of Gangaridai appears in ''Bibliotheca historica
''Bibliotheca historica'' (, ) is a work of Universal history (genre), universal history by Diodorus Siculus. It consisted of forty books, which were divided into three sections. The first six books are geographical in theme, and describe the h ...
'' of writer Diodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus or Diodorus of Sicily (; 1st century BC) was an ancient Greece, ancient Greek historian from Sicily. He is known for writing the monumental Universal history (genre), universal history ''Bibliotheca historica'', in forty ...
(69 BCE-16AD). This account is based on a now-lost work, probably the writings of either Megasthenes or Hieronymus of Cardia.
In Book 2 of ''Bibliotheca historica'', Diodorus states that "Gandaridae" (i.e. Gangaridai) territory was located to the east of the Ganges river, which was 30 stades wide. He mentions that no foreign enemy had ever conquered Gandaridae, because it of its strong elephant
Elephants are the largest living land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant ('' Loxodonta africana''), the African forest elephant (''L. cyclotis''), and the Asian elephant ('' Elephas maximus ...
force. He further states that Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
advanced up to Ganges after subjugating other Indians, but decided to retreat when he heard that the Gandaridae had 4,000 elephants.
In Book 17 of ''Bibliotheca historica'', Diodorus once again describes the "Gandaridae", and states that Alexander had to retreat after his soldiers refused to take an expedition against the Gandaridae. The book (17.91.1) also mentions that a nephew of Porus fled to the land of the Gandaridae, although C. Bradford Welles translates the name of this land as " Gandara".
In Book 18 of ''Bibliotheca historica'', Diodorus describes India as a large kingdom comprising several nations, the largest of which was "Tyndaridae" (which seems to be a scribal error for "Gandaridae"). He further states that a river separated this nation from their neighbouring territory; this 30-stadia wide river was the greatest river in this region of India (Diodorus does not mention the name of the river in this book). He goes on to mention that Alexander did not campaign against this nation, because they had a large number of elephants. The Book 18 description is as follows:
Diodorus' account of India in the Book 2 is based on ''Indica'', a book written by the 4th century BCE writer Megasthenes, who actually visited India. Megasthenes' ''Indica'' is now lost, although it has been reconstructed from the writings of Diodorus and other later writers. J. W. McCrindle (1877) attributed Diodorus' Book 2 passage about the Gangaridai to Megasthenes in his reconstruction of ''Indica''. However, according to A. B. Bosworth (1996), Diodorus' source for the information about the Gangaridai was Hieronymus of Cardia (354–250 BCE), who was a contemporary of Alexander and the main source of information for Diodorus' Book 18. Bosworth points out that Diodorus describes Ganges as 30 stadia wide; but it is well-attested by other sources that Megasthenes described the median (or minimum) width of Ganges as 100 stadia. This suggests that Diodorus obtained the information about the Gandaridae from another source, and appended it to Megasthenes' description of India in Book 2.
Plutarch

Plutarch
Plutarch (; , ''Ploútarchos'', ; – 120s) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo (Delphi), Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his ''Parallel Lives'', ...
(46-120 CE) mentions the Gangaridai as "'Gandaritae" (in ''Parallel Lives
*
Culture of ancient Greece
Culture of ancient Rome
Ancient Greek biographical works
Ethics literature
History books about ancient Rome
Cultural depictions of Gaius Marius
Cultural depictions of Mark Antony
Cultural depictions of Cicero
...
- Life of Alexander'' 62.3) and as "Gandridae" (in '' Moralia'' 327b.).
Other writers

Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzant ...
(2nd century CE), in his ''Geography
Geography (from Ancient Greek ; combining 'Earth' and 'write', literally 'Earth writing') is the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding o ...
'', states that the Gangaridae occupied "all the region about the mouths of the Ganges". He names a city called Gange as their capital. This suggests that Gange was the name of a city, derived from the name of the river. Based on the city's name, the Greek writers used the word "Gangaridai" to describe the local people.
The ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea
The ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' (), also known by its Latin name as the , is a Greco-Roman world, Greco-Roman periplus written in Koine Greek that describes navigation and Roman commerce, trading opportunities from Roman Egyptian ports lik ...
'' does not mention the Gangaridai, but attests the existence of a city that the Greco-Romans described as "Ganges":
Dionysius Periegetes (2nd-3rd century CE) mentions "Gargaridae" located near the "gold-bearing Hypanis" ( Beas) river. "Gargaridae" is sometimes believed to be a variant of "Gangaridae", but another theory identifies it with Gandhari people. A. B. Bosworth dismisses Dionysius' account as "a farrago of nonsense", noting that he inaccurately describes the Hypanis river as flowing down into the Gangetic plain.
Gangaridai also finds a mention in Greek mythology. In Valerius' ''Argonautica''' (1st century CE), Datis, a chieftain, leader of the Gangaridae who was in the army of Perses III, fought against Aeetes during the Colchian civil war. Colchis
In classical antiquity and Greco-Roman geography, Colchis (; ) was an exonym for the Georgian polity of Egrisi ( ka, ეგრისი) located on the eastern coast of the Black Sea, centered in present-day western Georgia.
Its population, the ...
was situated in modern-day Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
, on the east of the Black Sea. Aeetes was the famous king of Colchia against whom Jason
Jason ( ; ) was an ancient Greek mythological hero and leader of the Argonauts, whose quest for the Golden Fleece is featured in Greek literature. He was the son of Aeson, the rightful king of Iolcos. He was married to the sorceress Med ...
and the Argonauts
The Argonauts ( ; ) were a band of heroes in Greek mythology, who in the years before the Trojan War (around 1300 BC) accompanied Jason to Colchis in his quest to find the Golden Fleece. Their name comes from their ship, ''Argo'', named after it ...
undertook their expedition in search of the " Golden Fleece". Perses III was the brother of Aeetes and king of the Taurian tribe.
Roman accounts
The Roman poetVirgil
Publius Vergilius Maro (; 15 October 70 BC21 September 19 BC), usually called Virgil or Vergil ( ) in English, was an ancient Rome, ancient Roman poet of the Augustan literature (ancient Rome), Augustan period. He composed three of the most fa ...
speaks of the valour of the Gangaridae in his ''Georgics
The ''Georgics'' ( ; ) is a poem by Latin poet Virgil, likely published in 29 BCE. As the name suggests (from the Greek language, Greek word , ''geōrgiká'', i.e. "agricultural hings) the subject of the poem is agriculture; but far from bei ...
'' (c. 29 BCE).
Quintus Curtius Rufus
Quintus Curtius Rufus (; ) was a Ancient Rome, Roman historian, probably of the 1st century, author of his only known and only surviving work, ''Historiae Alexandri Magni'', "Histories of Alexander the Great", or more fully ''Historiarum Alex ...
(possibly 1st century CE) noted the two nations Gangaridae and Prasii:
Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vesp ...
(23–79 CE) states:
Identification
 The ancient Greek writers provide vague information about the centre of the Gangaridai power. As a result, the later historians have put forward various theories about its location.
The ancient Greek writers provide vague information about the centre of the Gangaridai power. As a result, the later historians have put forward various theories about its location.
Gangetic plains
Pliny (1st century CE) in his '' NH'', terms the Gangaridai as the ''novisima gens'' (nearest people) of the Ganges river. It cannot be determined from his writings whether he means "nearest to the mouth" or "nearest to the headwaters". But the later writer Ptolemy (2nd century CE), in his ''Geography
Geography (from Ancient Greek ; combining 'Earth' and 'write', literally 'Earth writing') is the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding o ...
'', explicitly locates the Gangaridai near the mouths of the Ganges.
A. B. Bosworth notes that the ancient Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
writers almost always use the word "Gangaridae" to define the people, and associate them with the Prasii people. According to Megasthenes, who actually lived in India, the Prasii people lived near the Ganges. Besides, Pliny explicitly mentions that the Gangaridae lived beside the Ganges, naming their capital as Pertalis. All these evidences suggest that the Gangaridae lived in the Gangetic plains.
The term ''Prasii'' is a transcription of the Sanskrit word ''prāchya''s, literally ''"The Easterners"''.Rarh region
Diodorus (1st century BCE) states that the Ganges river formed the eastern boundary of the Gangaridai. Based on Diodorus's writings and the identification of Ganges with Bhāgirathi-Hooghly (a western distributary of Ganges), Gangaridai can be identified with the Rarh region inWest Bengal
West Bengal (; Bengali language, Bengali: , , abbr. WB) is a States and union territories of India, state in the East India, eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabi ...
.
Larger part of Bengal
The Rarh is located to the west of the Bhāgirathi-Hooghly (Ganges) river. However,Plutarch
Plutarch (; , ''Ploútarchos'', ; – 120s) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo (Delphi), Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his ''Parallel Lives'', ...
(1st century CE), Curtius (possibly 1st century CE) and Solinus (3rd century CE), suggest that Gangaridai was located on the eastern banks of the Gangaridai river. Historian R. C. Majumdar theorized that the earlier historians like Diodorus used the word Ganga for the Padma River
The Padma () is a major river in Bangladesh. It is the eastern and main distributary of the Ganges, flowing generally southeast for to its confluence with the Meghna River, near the Bay of Bengal. The city of Rajshahi is situated on the banks ...
(an eastern distributary of Ganges).
Pliny names five mouths of the Ganges river, and states that the Gangaridai occupied the entire region about these mouths. He names five mouths of Ganges as Kambyson, Mega, Kamberikon, Pseudostomon and Antebole. These exact present-day locations of these mouths cannot be determined with certainty because of the changing river courses. According to D. C. Sircar, the region encompassing these mouths appears to be the region lying between the Bhāgirathi-Hooghly River in the west and the Padma River in the east. This suggests that the Gangaridai territory included the coastal region of present-day West Bengal and Bangladesh, up to the Padma river in the east. Gaurishankar De and Subhradip De believe that the five mouths may refer to the Bidyadhari, Jamuna and other branches of Bhāgirathi-Hooghly at the entrance of Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean. Geographically it is positioned between the Indian subcontinent and the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese peninsula, located below the Bengal region.
Many South Asian and Southe ...
.
According to the archaeologist Dilip Kumar Chakrabarti
Dilip Kumar Chakrabarti (born 27 April 1941) is an Indian archaeologist, Professor Emeritus of South Asian Archaeology at Cambridge University, and a Senior Fellow at the McDonald Institute for Archaeological Research, Cambridge University. He ...
, the centre of the Gangaridai power was located in vicinity of Adi Ganga (a now dried-up flow of the Hooghly river). Chakrabarti considers Chandraketugarh as the strongest candidate for the centre, followed by Mandirtala. James Wise believed that Kotalipara in present-day Bangladesh was the capital of Gangaridai. Archaeologist Habibullah Pathan identified the Wari-Bateshwar ruins as the Gangaridai territory.
North-western India
William Woodthorpe Tarn (1948) identifies the "Gandaridae" mentioned by Diodorus with the people ofGandhara
Gandhara () was an ancient Indo-Aryan people, Indo-Aryan civilization in present-day northwest Pakistan and northeast Afghanistan. The core of the region of Gandhara was the Peshawar valley, Peshawar (Pushkalawati) and Swat valleys extending ...
. Historian T. R. Robinson (1993) locates the Gangaridai to the immediately east of the Beas River, in the Punjab region
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panjāb or Panj-Āb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
. According to him, the unnamed river described in Diodorus' Book 18 is Beas (Hyphasis); Diodorus misinterpreted his source, and incompetently combined it with other material from Megasthenes, erroneously naming the river as Ganges in Book 2. Robinson identified the Gandaridae with the ancient Yaudheyas.
A. B. Bosworth (1996) rejects this theory, pointing out that Diodorus describes the unnamed river in Book 18 as the greatest river in the region. But Beas is not the largest river in its region. Even if one excludes the territory captured by Alexander in "the region" (thus excluding the Indus River
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayas, Himalayan river of South Asia, South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northw ...
), the largest river in the region is Chenab (Acesines). Robison argues that Diodorus describes the unnamed river as "the greatest river in its own ''immediate'' area", but Bosworth believes that this interpretation is not supported by Diodorus's wording. Bosworth also notes that Yaudheyas were an autonomous confederation, and do not match the ancient descriptions that describe Gandaridae as part of a strong kingdom.
Other
According to Nitish K. Sengupta, it is possible that the term "Gangaridai" refers to the whole of northern India from the Beas River to the western part of Bengal. Pliny mentions the Gangaridae and the Calingae ( Kalinga) together. One interpretation based on this reading suggests that Gangaridae and the Calingae were part of the Kalinga tribe, which spread into the Ganges delta. N. K. Sahu of Utkal University identifies Gangaridae as the northern part of Kalinga.Political status
Diodorus mentions Gangaridai and Prasii as one nation, naming Xandramas as the king of this nation. Diodorus calls them "two nations under one king." Historian A. B. Bosworth believes that this is a reference to the Nanda dynasty, and the Nanda territory matches the ancient descriptions of kingdom in which the Gangaridae were located. According to Nitish K. Sengupta, it is possible that Gangaridai and Prasii are actually two different names of the same people, or closely allied people. However, this cannot be said with certainty. Historian Hem Chandra Raychaudhuri writes: "It may reasonably be inferred from the statements of the Greek and Latin writers that about the time of Alexander's invasion, the Gangaridai were a very powerful nation, and either formed a dual monarchy with the Pasioi rasii or were closely associated with them on equal terms in a common cause against the foreign invader.Chowdhury, ''The History of Bengal'' Volume I, p. 44.References
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{South 24 Parganas topics Ancient Bengal Historical Indian regions