GNA (nucleic Acid) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
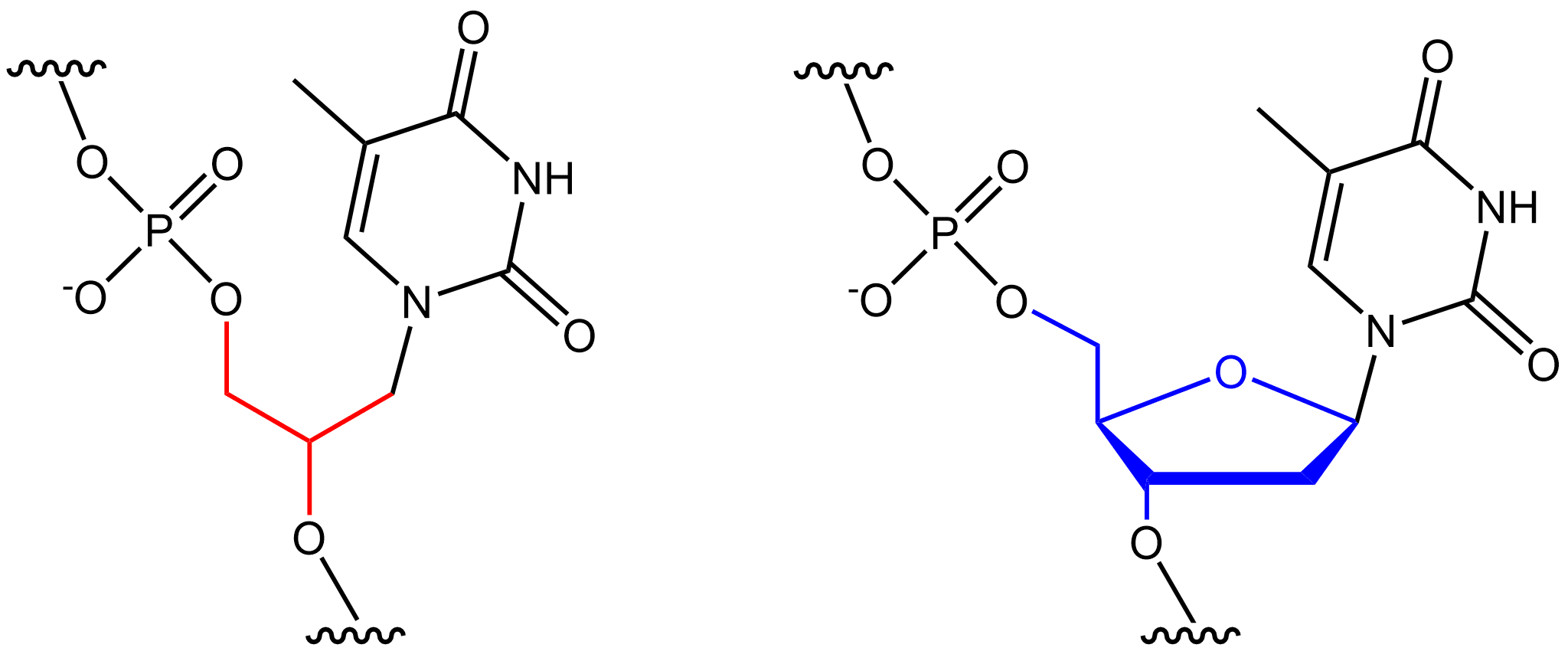 Glycol nucleic acid (GNA), sometimes also referred to as glycerol nucleic acid, is a nucleic acid similar to
Glycol nucleic acid (GNA), sometimes also referred to as glycerol nucleic acid, is a nucleic acid similar to
Simpler than DNA
- Chemical & Engineering News Nucleic acids {{genetics-stub
 Glycol nucleic acid (GNA), sometimes also referred to as glycerol nucleic acid, is a nucleic acid similar to
Glycol nucleic acid (GNA), sometimes also referred to as glycerol nucleic acid, is a nucleic acid similar to DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
or RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself (non-coding RNA) or by forming a template for the production of proteins (messenger RNA). RNA and deoxyrib ...
but differing in the composition of its sugar-phosphodiester backbone, using propylene glycol
Propylene glycol ( IUPAC name: propane-1,2-diol) is a viscous, colorless liquid. It is almost odorless and has a faintly sweet taste. Its chemical formula is CH3CH(OH)CH2OH.
As it contains two alcohol groups, it is classified as a diol. An al ...
in place of ribose or deoxyribose. GNA is chemically stable but not known to occur naturally. However, due to its simplicity, it might have played a role in the evolution of life.
The 2,3-dihydroxypropyl nucleoside analogues were first prepared by Ueda et al. (1971). Soon thereafter it was shown that phosphate-linked oligomer
In chemistry and biochemistry, an oligomer () is a molecule that consists of a few repeating units which could be derived, actually or conceptually, from smaller molecules, monomers.Quote: ''Oligomer molecule: A molecule of intermediate relativ ...
s of the analogues do in fact exhibit hypochromicity in the presence of RNA and DNA in solution (Seita et al. 1972). The preparation of the polymers was later described by Cook et al. (1995, 1999) and Acevedo and Andrews (1996). However the ability of GNA-GNA self-pairing was first reported by Zhang and Meggers in 2005. Crystal structures of a GNA duplexes were subsequently reported by Essen and Meggers.
DNA and RNA have a deoxyribose
Deoxyribose, or more precisely 2-deoxyribose, is a monosaccharide with idealized formula H−(C=O)−(CH2)−(CHOH)3−H. Its name indicates that it is a deoxy sugar, meaning that it is derived from the sugar ribose by loss of a hydroxy group. D ...
and ribose
Ribose is a simple sugar and carbohydrate with molecular formula C5H10O5 and the linear-form composition H−(C=O)−(CHOH)4−H. The naturally occurring form, , is a component of the ribonucleotides from which RNA is built, and so this comp ...
sugar backbone, respectively, whereas GNA's backbone is composed of repeating glycol units linked by phosphodiester bond
In chemistry, a phosphodiester bond occurs when exactly two of the hydroxyl groups () in phosphoric acid react with hydroxyl groups on other molecules to form two ester bonds. The "bond" involves this linkage . Discussion of phosphodiesters is d ...
s. The glycol unit has just three carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
atoms and still shows Watson–Crick base pairing
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA ...
. The Watson–Crick base pairing is much more stable in GNA than its natural counterparts DNA and RNA as it requires a high temperature to melt a duplex of GNA. It is possibly the simplest of the nucleic acids, making it a hypothetical precursor to RNA.
See also
*Abiogenesis
Abiogenesis is the natural process by which life arises from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The prevailing scientific hypothesis is that the transition from non-living to living entities on Earth was not a single even ...
* Locked nucleic acid
A locked nucleic acid (LNA), also known as bridged nucleic acid (BNA), and often referred to as inaccessible RNA, is a modified RNA nucleotide in which the ribose moiety is modified with an extra bridge connecting the 2' oxygen and 4' carbon. The ...
* Oligonucleotide synthesis
Oligonucleotide synthesis is the chemical synthesis of relatively short fragments of nucleic acids with defined chemical structure (sequence). The technique is extremely useful in current laboratory practice because it provides a rapid and inexpens ...
* Peptide nucleic acid
Peptide nucleic acid (PNA) is an artificially synthesized polymer similar to DNA or RNA.
Synthetic peptide nucleic acid oligomers have been used in recent years in molecular biology procedures, diagnostic assays, and antisense therapies. Due to ...
* Threose nucleic acid
Threose nucleic acid (TNA) is an artificial genetic polymer in which the natural five-carbon ribose sugar found in RNA has been replaced by an unnatural four-carbon threose sugar.Schöning, K. U. ''et al.'' Chemical etiology of nucleic acid structu ...
References
Further reading
* * * * * *External links
Simpler than DNA
- Chemical & Engineering News Nucleic acids {{genetics-stub