The French colonial empire () comprised the overseas
colonies
A colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule, which rules the territory and its indigenous peoples separated from the foreign rulers, the colonizer, and their '' metropole'' (or "mother country"). This separated rule was often or ...
,
protectorate
A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a State (polity), state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over ...
s, and
mandate territories that came under French rule from the 16th century onward. A distinction is generally made between the "First French colonial empire", that existed until 1814, by which time most of it had been lost or sold, and the "Second French colonial empire", which began with the
conquest of Algiers in 1830. On the eve of
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, France's colonial empire was
the second-largest in the world after the
British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It bega ...
.
France began to establish colonies in the
Americas
The Americas, sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America and South America.''Webster's New World College Dictionary'', 2010 by Wiley Publishing, Inc., Cleveland, Ohio. When viewed as a sing ...
, the
Caribbean
The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America ...
, and
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
in the 16th century but lost most of its possessions after its defeat in the
Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War, 1756 to 1763, was a Great Power conflict fought primarily in Europe, with significant subsidiary campaigns in North America and South Asia. The protagonists were Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of Prus ...
. The North American possessions were lost to Britain and Spain, but
Spain later returned Louisiana to France in 1800. The territory was then
sold to the United States in 1803. France rebuilt a new empire mostly after 1850, concentrating chiefly
in Africa as well as
Indochina
Mainland Southeast Asia (historically known as Indochina and the Indochinese Peninsula) is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to th ...
and the South
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
. As it developed, the new French empire took on roles of trade with the
metropole
A metropole () is the homeland, central territory or the state exercising power over a colonial empire.
From the 19th century, the English term ''metropole'' was mainly used in the scope of the British, Spanish, French, Dutch, Portugu ...
, supplying raw materials and purchasing manufactured items. Especially after the disastrous
Franco-Prussian War
The Franco-Prussian War or Franco-German War, often referred to in France as the War of 1870, was a conflict between the Second French Empire and the North German Confederation led by the Kingdom of Prussia. Lasting from 19 July 1870 to 28 Janua ...
, which saw Germany become the leading economic and military power of the continent of Europe. Acquiring colonies and rebuilding an empire was seen as a way to restore French prestige in the world. It was also to provide manpower during the world wars.
A major stated justification of
colonialism
Colonialism is the control of another territory, natural resources and people by a foreign group. Colonizers control the political and tribal power of the colonised territory. While frequently an Imperialism, imperialist project, colonialism c ...
was the or "
civilizing mission
The civilizing mission (; ; ) is a political rationale for military intervention and for colonization purporting to facilitate the cultural assimilation of indigenous peoples, especially in the period from the 15th to the 20th centuries. As ...
". In 1884, the leading proponent of colonialism,
Jules Ferry
Jules François Camille Ferry (; 5 April 183217 March 1893) was a French statesman and republican philosopher. He was one of the leaders of the Opportunist Republicans, Moderate Republicans and served as Prime Minister of France from 1880 to 18 ...
, declared: "The higher races have a right over the lower races, they have a
duty to civilize the inferior races." Full citizenship rights – – were offered, although in reality "assimilation was always receding
ndthe colonial populations treated like subjects not citizens." France sent small numbers of settlers to its empire, with the notable exception of Algeria, where the
French settlers took power while being a minority.
In
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
,
Charles de Gaulle
Charles André Joseph Marie de Gaulle (22 November 18909 November 1970) was a French general and statesman who led the Free France, Free French Forces against Nazi Germany in World War II and chaired the Provisional Government of the French Re ...
and the
Free French
Free France () was a resistance government
claiming to be the legitimate government of France following the dissolution of the Third French Republic, Third Republic during World War II. Led by General , Free France was established as a gover ...
took control of the overseas colonies one-by-one and used them as a base from which they prepared to
liberate France. Historian Tony Chafer argues that: "In an effort to restore its world-power status after the humiliation of defeat and occupation, France was eager to maintain its overseas empire at the end of the Second World War." However, after 1945,
anti-colonial movements began to challenge European authority. Revolts in
Indochina
Mainland Southeast Asia (historically known as Indochina and the Indochinese Peninsula) is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to th ...
and
Algeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Alger ...
proved costly and France lost both colonies. After these conflicts, a relatively peaceful
decolonization
Decolonization is the undoing of colonialism, the latter being the process whereby Imperialism, imperial nations establish and dominate foreign territories, often overseas. The meanings and applications of the term are disputed. Some scholar ...
took place elsewhere after 1960. The
French Constitution of 27 October 1946
The Constitution of the French Republic of 27 October 1946 was the constitution of the French Fourth Republic.
Adopted by the on 29 September 1946, and promulgated by Georges Bidault, president of the Provisional Government of the French ...
(Fourth French Republic) established the
French Union
The French Union () was a political entity created by the French Fourth Republic to replace the old French colonial empire system, colloquially known as the " French Empire" (). It was ''de jure'' the end of the "indigenous" () status of Frenc ...
, which endured until 1958. Newer remnants of the colonial empire were integrated into France as
overseas departments and territories within the French Republic. These now total altogether 119,394 km
2 (46,098 sq. miles), with 2.8 million people in 2021. Links between France and its former colonies persist through
La francophonie
LA most frequently refers to Los Angeles, the second most populous city in the United States of America.
La, LA, or L.A. may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Music
* La (musical note), or A, the sixth note
*"L.A.", a song by Elliott Smi ...
, the
CFA franc
CFA franc (, ) is the name of two currencies used by 210 million people (as of 2023) in fourteen African countries: the West African CFA franc (where "CFA" stands for , i.e. "African Financial Community" in English), used in eight West African c ...
, and joint military operations such as
Operation Serval
Operation Serval () was a French military operation in Mali. The aim of the operation was to oust Islamic militants from the north of Mali, who had begun a push into the center of Mali.
Operation Serval followed the United Nations Security ...
.
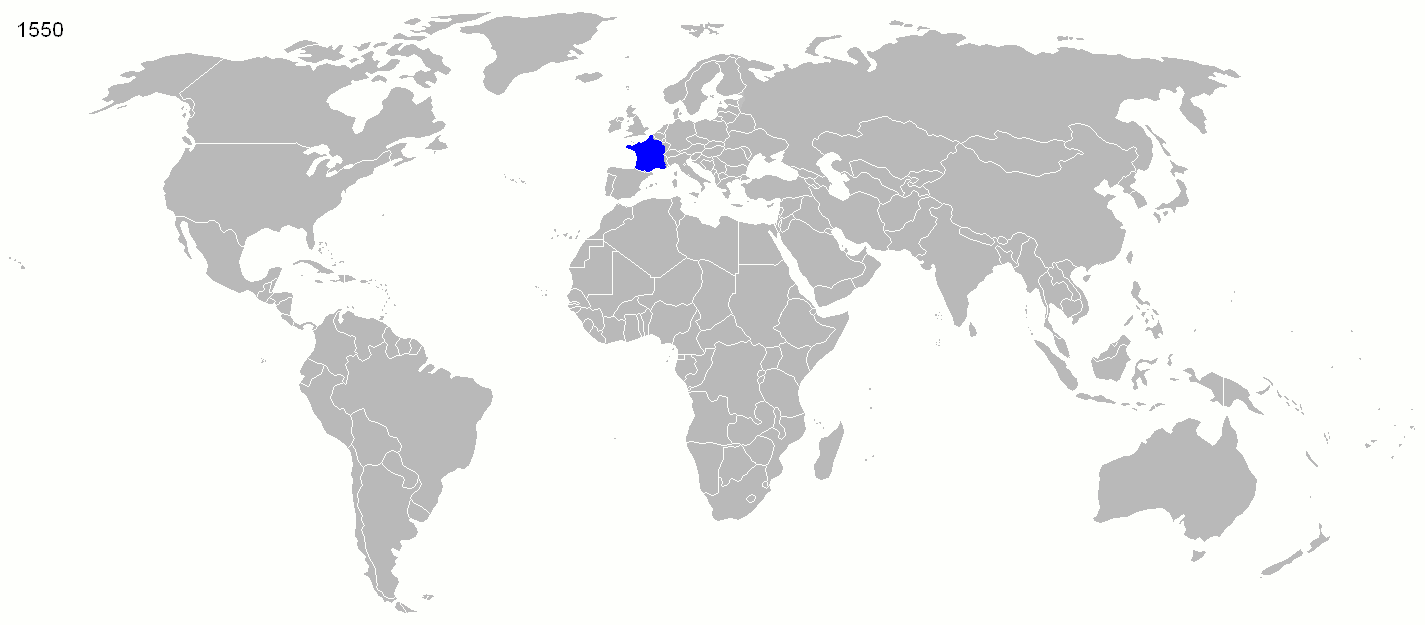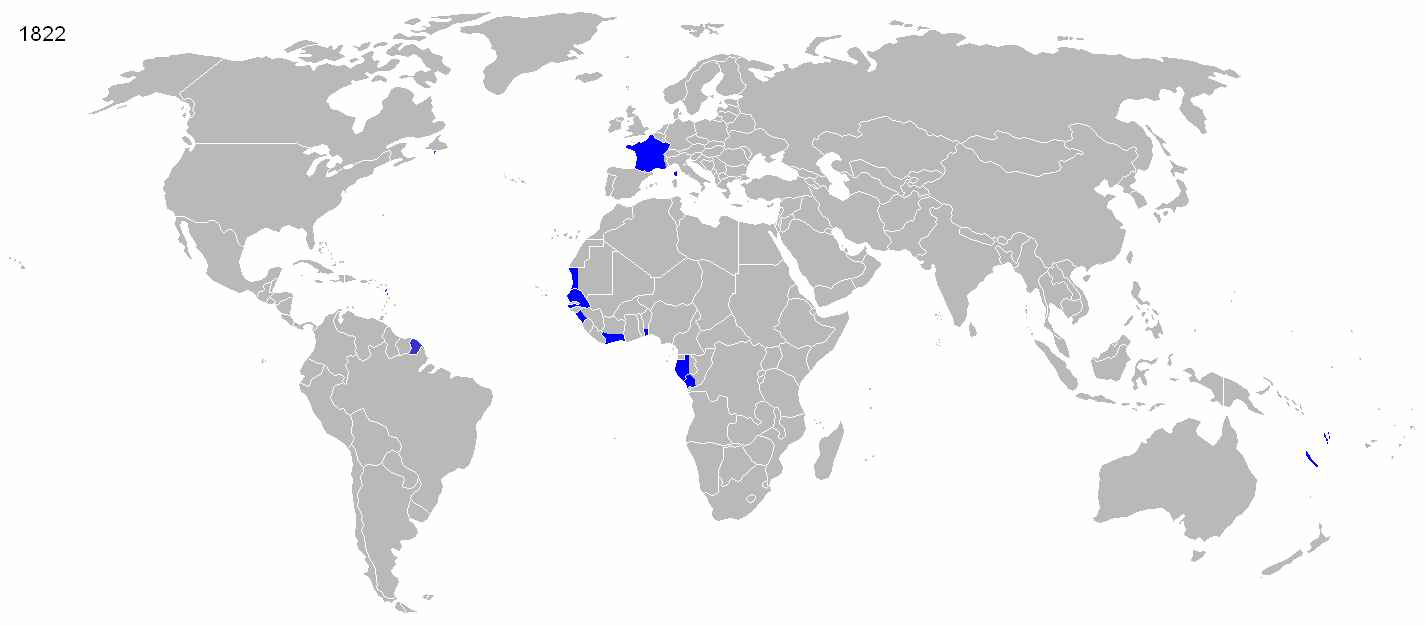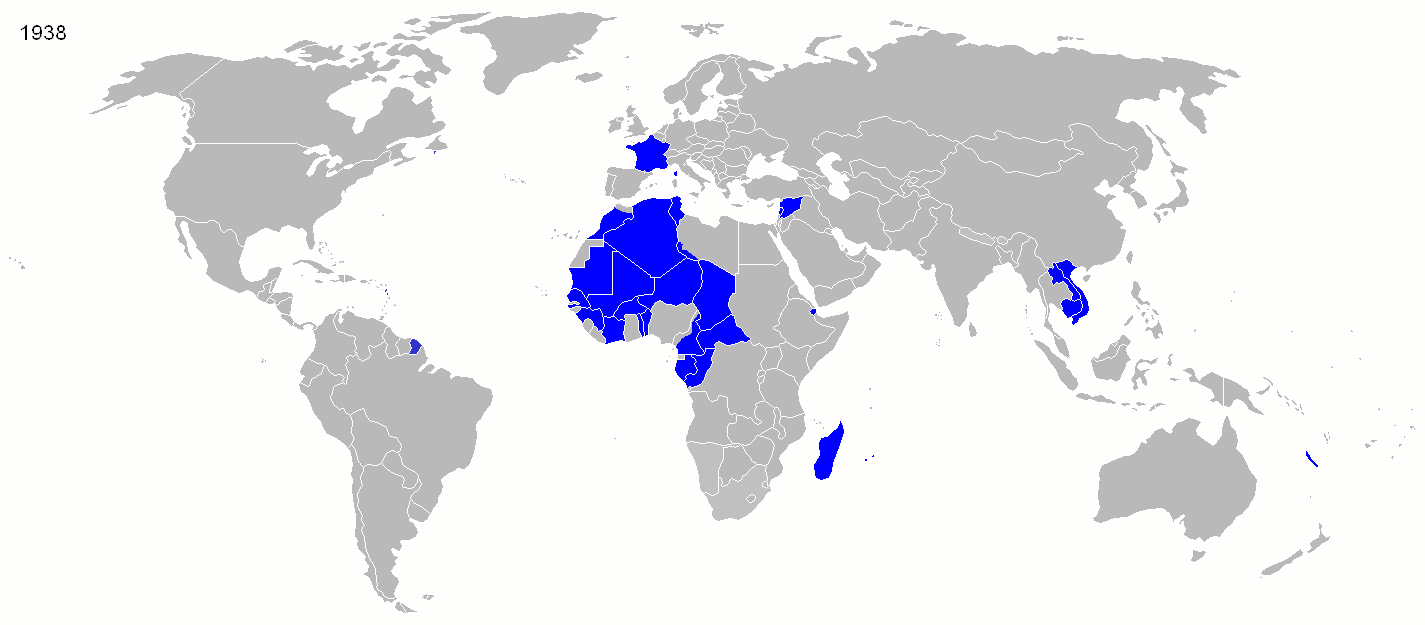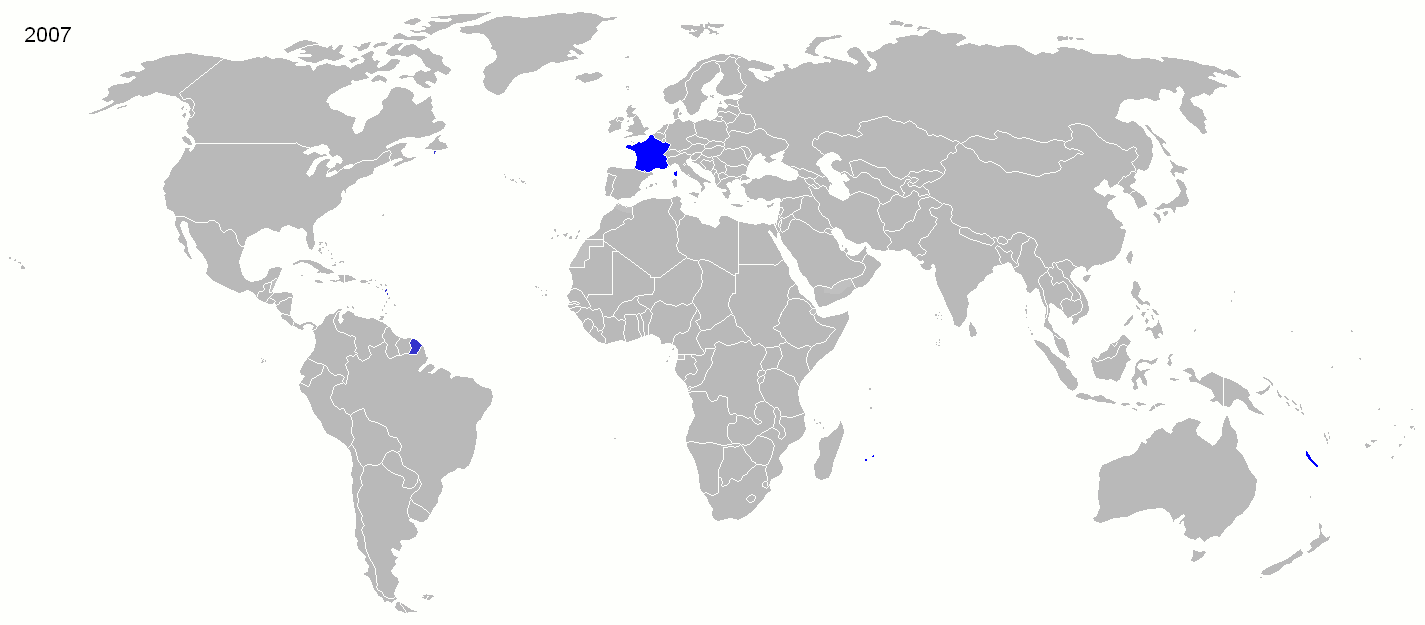
First French colonial empire (16th century to 1814)
The Americas
During the 16th century, the
French colonization of the Americas
France began colonizing America in the 16th century and continued into the following centuries as it established a colonial empire in the Western Hemisphere. France established colonies in much of eastern North America, on several Caribbean is ...
began. Excursions of
Giovanni da Verrazzano
Giovanni da Verrazzano ( , ; often misspelled Verrazano in English; 1491–1528) was an Italian ( Florentine) explorer of North America, who led most of his later expeditions, including the one to America, in the service of King Francis I of ...
and
Jacques Cartier
Jacques Cartier (; 31 December 14911 September 1557) was a French maritime explorer from Brittany. Jacques Cartier was the first Europeans, European to describe and map the Gulf of Saint Lawrence and the shores of the Saint Lawrence River, wh ...
in the early 16th century, as well as the frequent voyages of French boats and fishermen to the
Grand Banks
The Grand Banks of Newfoundland are a series of underwater plateaus south-east of the island of Newfoundland on the North American continental shelf. The Grand Banks are one of the world's richest fishing grounds, supporting Atlantic cod, swordfi ...
off
Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region of Labrador, having a total size of . As of 2025 the population ...
throughout that century, were the precursors to the story of France's colonial expansion. But Spain's defense of its American monopoly, and the further distractions caused in France itself in the later 16th century by the
French Wars of Religion
The French Wars of Religion were a series of civil wars between French Catholic Church, Catholics and Protestantism, Protestants (called Huguenots) from 1562 to 1598. Between two and four million people died from violence, famine or disease di ...
, prevented any constant efforts by France to settle colonies. Early French attempts to found colonies in Brazil, in 1555 at
Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro, or simply Rio, is the capital of the Rio de Janeiro (state), state of Rio de Janeiro. It is the List of cities in Brazil by population, second-most-populous city in Brazil (after São Paulo) and the Largest cities in the America ...
("
France Antarctique
France Antarctique (formerly also spelled ''France antartique'') was a French colony in Rio de Janeiro, in modern-day Brazil, which existed between 1555 and 1567, and had control over the coast from Rio de Janeiro to Cabo Frio. The colony quickl ...
") and in Florida (including
Fort Caroline
Fort Caroline was an attempted French colonial settlement in Florida, located on the banks of the St. Johns River in present-day Duval County. It was established under the leadership of René Goulaine de Laudonnière on 22 June 1564, follow ...
in 1562), and in 1612 at
São Luís ("
France Équinoxiale"), were not successful, due to a lack of official interest and to Portuguese and Spanish vigilance.
The story of France's colonial empire truly began on 27 July 1605, with the foundation of
Port Royal
Port Royal () was a town located at the end of the Palisadoes, at the mouth of Kingston Harbour, in southeastern Jamaica. Founded in 1494 by the Spanish, it was once the largest and most prosperous city in the Caribbean, functioning as the cen ...
in the colony of
Acadia
Acadia (; ) was a colony of New France in northeastern North America which included parts of what are now the The Maritimes, Maritime provinces, the Gaspé Peninsula and Maine to the Kennebec River. The population of Acadia included the various ...
in North America, in what is now
Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, located on its east coast. It is one of the three Maritime Canada, Maritime provinces and Population of Canada by province and territory, most populous province in Atlan ...
, Canada. A few years later, in 1608,
Samuel de Champlain
Samuel de Champlain (; 13 August 1574#Fichier]For a detailed analysis of his baptismal record, see #Ritch, RitchThe baptism act does not contain information about the age of Samuel, neither his birth date nor his place of birth. – 25 December ...
founded
Quebec City, Quebec, which was to become the capital of the enormous, but sparsely settled, fur-trading colony of
New France
New France (, ) was the territory colonized by Kingdom of France, France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Kingdom of Great Br ...
(also called Canada).
New France had a rather small population, which resulted from more emphasis being placed on the fur trade rather than agricultural settlements. Due to this emphasis, the French relied heavily on creating friendly contacts with the local First Nations community. Without the appetite of New England for land, and by relying solely on Aboriginals to supply them with fur at the trading posts, the French composed a complex series of military, commercial, and diplomatic connections. These became the most enduring alliances between the French and the First Nation community. The French were, however, under pressure from religious orders to convert them to
Catholicism
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
.
Through alliances with various Native American tribes, the French were able to exert a loose control over much of the North American continent. Areas of French settlement were generally limited to the
St. Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (, ) is a large international river in the middle latitudes of North America connecting the Great Lakes to the North Atlantic Ocean. Its waters flow in a northeasterly direction from Lake Ontario to the Gulf of St. Lawren ...
Valley. Prior to the establishment of the 1663
Sovereign Council, the territories of New France were developed as
mercantile colonies. It is only after the arrival of intendant
Jean Talon in 1665 that France gave its American colonies the proper means to develop population colonies comparable to that of the British. Acadia itself was lost to the British in the
Treaty of Utrecht
The Peace of Utrecht was a series of peace treaty, peace treaties signed by the belligerents in the War of the Spanish Succession, in the Dutch city of Utrecht between April 1713 and February 1715. The war involved three contenders for the vac ...
in 1713. Back in France, there was relatively little interest in colonialism, which concentrated rather on dominance within Europe, and for most of its history, New France was far behind the
British North America
British North America comprised the colonial territories of the British Empire in North America from 1783 onwards. English colonisation of North America began in the 16th century in Newfoundland, then further south at Roanoke and Jamestown, ...
n colonies in both population and economic development.
In 1699, French territorial claims in North America expanded still further, with the foundation of
Louisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25 ...
in the basin of the
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the main stem, primary river of the largest drainage basin in the United States. It is the second-longest river in the United States, behind only the Missouri River, Missouri. From its traditional source of Lake Ita ...
. The extensive trading network throughout the region connected to Canada through the
Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes spanning the Canada–United States border. The five lakes are Lake Superior, Superior, Lake Michigan, Michigan, Lake Huron, H ...
, was maintained through a vast system of fortifications, many of them centred in the
Illinois Country
The Illinois Country ( ; ; ), also referred to as Upper Louisiana ( ; ), was a vast region of New France claimed in the 1600s that later fell under Spanish and British control before becoming what is now part of the Midwestern United States. Whi ...
and in present-day Arkansas.
As the French empire in North America grew, the French also began to build a smaller but more profitable empire in the
West Indies
The West Indies is an island subregion of the Americas, surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, which comprises 13 independent island country, island countries and 19 dependent territory, dependencies in thr ...
. Settlement along the South American coast in what is today
French Guiana
French Guiana, or Guyane in French, is an Overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France located on the northern coast of South America in the Guianas and the West Indies. Bordered by Suriname to the west ...
began in 1624, and a colony was founded on
Saint Kitts
Saint Kitts, officially Saint Christopher, is an island in the West Indies. The west side of the island borders the Caribbean Sea, and the eastern coast faces the Atlantic Ocean. Saint Kitts and the neighbouring island of Nevis constitute one ...
in 1625 (the island had to be shared with the English until the
Treaty of Utrecht
The Peace of Utrecht was a series of peace treaty, peace treaties signed by the belligerents in the War of the Spanish Succession, in the Dutch city of Utrecht between April 1713 and February 1715. The war involved three contenders for the vac ...
in 1713, when it was ceded outright). The current isle of the
Commonwealth of Dominica in the eastern Caribbean also fell under increasing French settlement from the early 1630s. The ''
Compagnie des Îles de l'Amérique The Company of the American Islands () was a French chartered company that in 1635 took over the administration of the French portion of ''Saint-Christophe island'' (Saint Kitts) from the Compagnie de Saint-Christophe which was the only French settl ...
'' founded colonies in
Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe is an Overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France in the Caribbean. It consists of six inhabited islands—Basse-Terre Island, Basse-Terre, Grande-Terre, Guadeloupe, Grande-Terre, Marie-Galant ...
and
Martinique
Martinique ( ; or ; Kalinago language, Kalinago: or ) is an island in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the eastern Caribbean Sea. It was previously known as Iguanacaera which translates to iguana island in Carib language, Kariʼn ...
in 1635, and a colony was later founded on
Saint Lucia
Saint Lucia is an island country of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean. Part of the Windward Islands of the Lesser Antilles, it is located north/northeast of the island of Saint Vincent (Saint Vincent and the Grenadines), Saint Vincent ...
by (1650). The food-producing plantations of these colonies were built and sustained through slavery, with the supply of slaves dependent on the
African slave trade
Slavery has historically been widespread in Africa. Systems of servitude and slavery were once commonplace in parts of Africa, as they were in much of the rest of the ancient and medieval world. When the trans-Saharan slave trade, Red Sea s ...
. Local resistance by the
indigenous peoples
There is no generally accepted definition of Indigenous peoples, although in the 21st century the focus has been on self-identification, cultural difference from other groups in a state, a special relationship with their traditional territ ...
resulted in the
Carib Expulsion of 1660. France's most important Caribbean colonial possession was established in 1664, when the colony of
Saint-Domingue
Saint-Domingue () was a French colonization of the Americas, French colony in the western portion of the Caribbean island of Hispaniola, in the area of modern-day Haiti, from 1659 to 1803. The name derives from the Spanish main city on the isl ...
(today's
Haiti
Haiti, officially the Republic of Haiti, is a country on the island of Hispaniola in the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and south of the Bahamas. It occupies the western three-eighths of the island, which it shares with the Dominican ...
) was founded on the western half of the Spanish island of
Hispaniola
Hispaniola (, also ) is an island between Geography of Cuba, Cuba and Geography of Puerto Rico, Puerto Rico in the Greater Antilles of the Caribbean. Hispaniola is the most populous island in the West Indies, and the second-largest by List of C ...
. In the 18th century, Saint-Domingue grew to be the richest sugar colony in the Caribbean. The eastern half of Hispaniola (today's
Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles of the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean. It shares a Maritime boundary, maritime border with Puerto Rico to the east and ...
) also came under French rule for a short period, after being given to France by Spain in 1795.
Asia
With the end of the
French Wars of Religion
The French Wars of Religion were a series of civil wars between French Catholic Church, Catholics and Protestantism, Protestants (called Huguenots) from 1562 to 1598. Between two and four million people died from violence, famine or disease di ...
, in 1598, King
Henry IV encouraged various enterprises to establish trade with the Africa and Asia due to their relations at the time. In December 1600, a company was formed through the association of
Saint-Malo
Saint-Malo (, , ; Gallo language, Gallo: ; ) is a historic French port in Ille-et-Vilaine, Brittany (administrative region), Brittany.
The Fortification, walled city on the English Channel coast had a long history of piracy, earning much wealth ...
,
Laval, and
Vitré to trade with the
Moluccas
The Maluku Islands ( ; , ) or the Moluccas ( ; ) are an archipelago in the eastern part of Indonesia. Tectonically they are located on the Halmahera Plate within the Molucca Sea Collision Zone. Geographically they are located in West Melanesi ...
and Japan.
[''Asia in the Making of Europe, Volume III: A Century of Advance. Book 1'', Donald F. Lach pp. 93–9]
/ref> Two ships, the ''Croissant'' and the ''Corbin'', were sent around the Cape of Good Hope
The Cape of Good Hope ( ) is a rocky headland on the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast of the Cape Peninsula in South Africa.
A List of common misconceptions#Geography, common misconception is that the Cape of Good Hope is the southern tip of Afri ...
in May 1601. One was wrecked in the Maldives
The Maldives, officially the Republic of Maldives, and historically known as the Maldive Islands, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in South Asia located in the Indian Ocean. The Maldives is southwest of Sri Lanka and India, abou ...
, leading to the adventure of François Pyrard de Laval, who managed to return to France in 1611.Ceylon
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
and traded with Aceh
Aceh ( , ; , Jawi script, Jawoë: ; Van Ophuijsen Spelling System, Old Spelling: ''Atjeh'') is the westernmost Provinces of Indonesia, province of Indonesia. It is located on the northern end of Sumatra island, with Banda Aceh being its capit ...
in Sumatra
Sumatra () is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the list of islands by area, sixth-largest island in the world at 482,286.55 km2 (182,812 mi. ...
, but was captured by the Dutch on the return leg at Cape Finisterre
Cape Finisterre (, also ; ; ) is a rock-bound peninsula on the west coast of Galicia, Spain.
In Roman times it was believed to be an end of the known world. The name Finisterre, like that of Finistère in France, derives from the Latin , mean ...
.Dieppe
Dieppe (; ; or Old Norse ) is a coastal commune in the Seine-Maritime department, Normandy, northern France.
Dieppe is a seaport on the English Channel at the mouth of the river Arques. A regular ferry service runs to Newhaven in England ...
merchants to form the first French East Indies Company, giving them exclusive rights to Asian trade for 15 years. No ships were sent, however, until 1616.Akbar
Akbar (Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar, – ), popularly known as Akbar the Great, was the third Mughal emperor, who reigned from 1556 to 1605. Akbar succeeded his father, Humayun, under a regent, Bairam Khan, who helped the young emperor expa ...
.Chandernagore
Chandannagar (), also known by its former names Chandannagore and Chandernagor (), is a city in the Hooghly district in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is headquarter of the Chandannagore subdivision and is a part of the area covered by ...
(1673) and Pondichéry in the south east (1674), and later at Yanam (1723), Mahe (1725), and Karikal
Karaikal (, , Help:IPA/French, /kaʁikal/) is a port city of the Indian States and territories of India, Union Territory of Puducherry (union territory), Puducherry. It is the administrative headquarters of the Karaikal district, Karaikal Di ...
(1739) (see French India
French India, formally the (), was a French colony comprising five geographically separated enclaves on the Indian subcontinent that had initially been factories of the French East India Company. They were ''de facto'' incorporated into the ...
).
In 1664, the French East India Company was established to compete for trade in the east.
Africa
Although initial French colonization primarily occurred in the Americas
The Americas, sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America and South America.''Webster's New World College Dictionary'', 2010 by Wiley Publishing, Inc., Cleveland, Ohio. When viewed as a sing ...
and in Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which ...
, the French did establish a few colonies and trading posts on the African continent. Initial French colonization in Africa began in modern-day Senegal
Senegal, officially the Republic of Senegal, is the westernmost country in West Africa, situated on the Atlantic Ocean coastline. It borders Mauritania to Mauritania–Senegal border, the north, Mali to Mali–Senegal border, the east, Guinea t ...
, Madagascar
Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, is an island country that includes the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Lying off the southeastern coast of Africa, it is the world's List of islands by area, f ...
, and along the Mascarene Islands
The Mascarene Islands (, ) or Mascarenes or Mascarenhas Archipelago is a group of islands in the Indian Ocean east of Madagascar consisting of islands belonging to the Republic of Mauritius as well as the French department of Réunion. Their na ...
. Initial French colonial projects, partially administered by the French East India Company, prioritized plantation economies and slave labor. These economies were based on monoculture agriculture and forced African labor. Poor living conditions, famines, and disease made enslaved labor conditions particularly lethal across French colonies. French presence in Senegal
Senegal, officially the Republic of Senegal, is the westernmost country in West Africa, situated on the Atlantic Ocean coastline. It borders Mauritania to Mauritania–Senegal border, the north, Mali to Mali–Senegal border, the east, Guinea t ...
began in 1626, although formal colonies and trading posts were not established until 1659 with the founding of Saint-Louis, and 1677 with the founding of Gorée
(; "Gorée Island"; ) is one of the 19 (i.e. districts) of the city of Dakar, Senegal. It is an island located at sea from the main harbour of Dakar (), famous as a destination for people interested in the Atlantic slave trade.
Its populatio ...
. Additionally, the first settlement of Madagascar
Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, is an island country that includes the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Lying off the southeastern coast of Africa, it is the world's List of islands by area, f ...
began in 1642 with the establishment of Fort Dauphin.
Initial French colonial expansion in Senegal
Senegal, officially the Republic of Senegal, is the westernmost country in West Africa, situated on the Atlantic Ocean coastline. It borders Mauritania to Mauritania–Senegal border, the north, Mali to Mali–Senegal border, the east, Guinea t ...
and Madagascar
Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, is an island country that includes the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Lying off the southeastern coast of Africa, it is the world's List of islands by area, f ...
was primarily motivated by desires to secure access to natural resources including gum arabic, groundnuts (or peanuts) and other raw materials.Senegal
Senegal, officially the Republic of Senegal, is the westernmost country in West Africa, situated on the Atlantic Ocean coastline. It borders Mauritania to Mauritania–Senegal border, the north, Mali to Mali–Senegal border, the east, Guinea t ...
.Mascarene Islands
The Mascarene Islands (, ) or Mascarenes or Mascarenhas Archipelago is a group of islands in the Indian Ocean east of Madagascar consisting of islands belonging to the Republic of Mauritius as well as the French department of Réunion. Their na ...
which include Reunion Island
Reunion may refer to:
* Class reunion
* Family reunion
Reunion, Réunion, Re-union, Reunions or The Reunion may also refer to:
Places
* Réunion, a French overseas department and island in the Indian Ocean
* Reunion, Commerce City, Colorado, U ...
, Mauritius
Mauritius, officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island country in the Indian Ocean, about off the southeastern coast of East Africa, east of Madagascar. It includes the main island (also called Mauritius), as well as Rodrigues, Ag ...
, and Rodrigues
Rodrigues ( ; Mauritian Creole, Creole: ) is a Autonomous administrative division, autonomous Outer islands of Mauritius, outer island of the Republic of Mauritius in the Indian Ocean, about east of Mauritius. It is part of the Mascarene Isl ...
. Reunion Island was first settled in 1642 and was administered by the French East India Company starting in 1665.Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
, France took control of Mauritius, which it renamed the Island of France in 1721.Rodrigues
Rodrigues ( ; Mauritian Creole, Creole: ) is a Autonomous administrative division, autonomous Outer islands of Mauritius, outer island of the Republic of Mauritius in the Indian Ocean, about east of Mauritius. It is part of the Mascarene Isl ...
in 1735 and Seychelles
Seychelles (, ; ), officially the Republic of Seychelles (; Seychellois Creole: ), is an island country and archipelagic state consisting of 155 islands (as per the Constitution) in the Indian Ocean. Its capital and largest city, Victoria, ...
in 1756.
Collapse of First French colonial empire
Colonial conflict with Britain
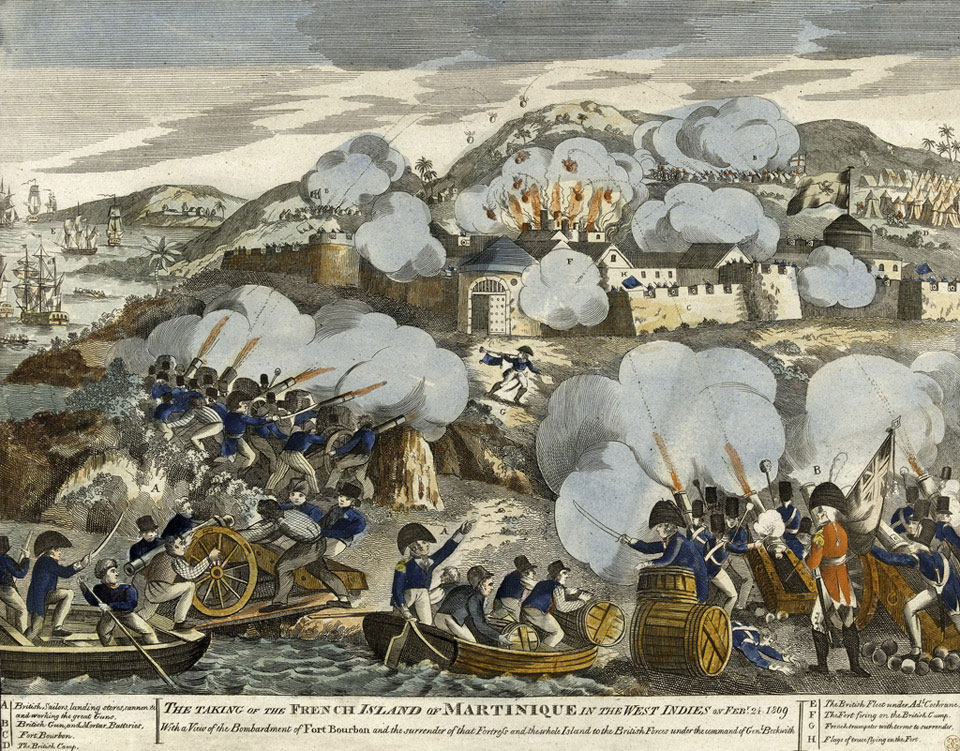
 In the middle of the 18th century, a series of colonial conflicts began between France and
In the middle of the 18th century, a series of colonial conflicts began between France and Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* Great Britain, a large island comprising the countries of England, Scotland and Wales
* The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, a sovereign state in Europe comprising Great Britain and the north-eas ...
, which ultimately resulted in the destruction of most of the first French colonial empire and the near-complete expulsion of France from the Americas. These wars were the War of the Austrian Succession
The War of the Austrian Succession was a European conflict fought between 1740 and 1748, primarily in Central Europe, the Austrian Netherlands, Italian Peninsula, Italy, the Atlantic Ocean and Mediterranean Sea. Related conflicts include King Ge ...
(1740–1748), the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War, 1756 to 1763, was a Great Power conflict fought primarily in Europe, with significant subsidiary campaigns in North America and South Asia. The protagonists were Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of Prus ...
(1756–1763), the American Revolution
The American Revolution (1765–1783) was a colonial rebellion and war of independence in which the Thirteen Colonies broke from British America, British rule to form the United States of America. The revolution culminated in the American ...
(1775–1783), the French Revolutionary Wars
The French Revolutionary Wars () were a series of sweeping military conflicts resulting from the French Revolution that lasted from 1792 until 1802. They pitted French First Republic, France against Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain, Habsb ...
(1793–1802) and the Napoleonic Wars
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Napoleonic Wars
, partof = the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars
, image = Napoleonic Wars (revision).jpg
, caption = Left to right, top to bottom:Battl ...
(1803–1815). It may even be seen further back in time to the first of the French and Indian Wars
The French and Indian Wars were a series of conflicts that occurred in North America between 1688 and 1763, some of which indirectly were related to the European dynastic wars. The title ''French and Indian War'' in the singular is used in the U ...
. This cyclic conflict is sometimes known as the Second Hundred Years' War
The Second Hundred Years' War is a periodization or historical era term used by some historians to describe the series of military conflicts around the globe between Great Britain and France that occurred from about 1689 (or some say 1714) to 1 ...
.
Although the War of the Austrian Succession was indecisive – despite French successes in India under the French Governor-General Joseph François Dupleix
Joseph Marquis Dupleix (; Unknown – 10 November 1763) was Governor-General of French India and rival of Robert Clive.
Biography
Dupleix was born in Landrecies, on January 23, 1697. His father, François Dupleix, a wealthy '' fermier gén� ...
and Europe under Marshal Saxe – the Seven Years' War, after early French successes in Menorca
Menorca or Minorca (from , later ''Minorica'') is one of the Balearic Islands located in the Mediterranean Sea belonging to Spain. Its name derives from its size, contrasting it with nearby Mallorca. Its capital is Maó, situated on the isl ...
and North America, saw a French defeat, with the numerically superior British (over one million to about 50 thousand French settlers) conquering not only New France
New France (, ) was the territory colonized by Kingdom of France, France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Kingdom of Great Br ...
(excluding the small islands of Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Pierre and Miquelon ( ), officially the Territorial Collectivity of Saint Pierre and Miquelon (), is a self-governing territorial overseas collectivity of France in the northwestern Atlantic Ocean, located near the Canada, Canadian prov ...
), but also most of France's West Indian (Caribbean) colonies, and all of the French Indian outposts.
While the peace treaty saw France's Indian outposts, and the Caribbean islands of Martinique and Guadeloupe restored to France, the competition for influence in India had been won by the British, and North America was entirely lost – most of New France
New France (, ) was the territory colonized by Kingdom of France, France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Kingdom of Great Br ...
was taken by Britain (also referred to as British North America
British North America comprised the colonial territories of the British Empire in North America from 1783 onwards. English colonisation of North America began in the 16th century in Newfoundland, then further south at Roanoke and Jamestown, ...
), except Louisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25 ...
, which France ceded to Spain as payment for Spain's late entrance into the war (and as compensation for Britain's annexation of Spanish Florida). Also ceded to the British were Grenada
Grenada is an island country of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean Sea. The southernmost of the Windward Islands, Grenada is directly south of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines and about north of Trinidad and Tobago, Trinidad and the So ...
and Saint Lucia
Saint Lucia is an island country of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean. Part of the Windward Islands of the Lesser Antilles, it is located north/northeast of the island of Saint Vincent (Saint Vincent and the Grenadines), Saint Vincent ...
in the West Indies. Although the loss of Canada would cause much regret in future generations, it excited little unhappiness at the time; colonialism was widely regarded as both unimportant to France, and immoral.
Some recovery of the French colonial empire was made during the French intervention in the American Revolution, with Saint Lucia being returned to France by the Treaty of Paris in 1783, but not nearly as much as had been hoped for at the time of French intervention.
Haitian Revolution
True disaster came to what remained of France's colonial empire in 1791 when Saint Domingue (the Western third of the Caribbean island of Hispaniola
Hispaniola (, also ) is an island between Geography of Cuba, Cuba and Geography of Puerto Rico, Puerto Rico in the Greater Antilles of the Caribbean. Hispaniola is the most populous island in the West Indies, and the second-largest by List of C ...
), France's richest and most important colony, was riven by a massive slave revolt, caused partly by the divisions among the island's elite, which had resulted from the French Revolution of 1789.
The slaves, led eventually by Toussaint L'Ouverture
François-Dominique Toussaint Louverture (, ) also known as Toussaint L'Ouverture or Toussaint Bréda (20 May 1743 – 7 April 1803), was a Haitian general and the most prominent leader of the Haitian Revolution. During his life, Louvertu ...
and then, following his capture by the French in 1801, by Jean-Jacques Dessalines
Jean-Jacques Dessalines (Haitian Creole: ''Jan-Jak Desalin''; ; 20 September 1758 – 17 October 1806) was the first Haitian Emperor, leader of the Haitian Revolution, and the first ruler of an independent First Empire of Haiti, Haiti under th ...
, held their own against French and British opponents. The French launched a failed expedition in 1802, and were up against a crippling Royal Naval blockade the following year. As a result, the Empire of Haiti ultimately achieved independence in 1804 (becoming the first black republic in the world, followed by Liberia in 1847). The black and mulatto population of the island (including the Spanish east) had declined from 700,000 in 1789 to 351,819 in 1804. About 80,000 Haitians died in the 1802–03 campaign alone. Of the 55,131 French soldiers dispatched to Haiti in 1802–03, 45,000, including 18 generals, died, along with 10,000 sailors, the great majority from disease. Captain irst name unknownSorrell of the British navy observed, "France lost there one of the finest armies she ever sent forth, composed of picked veterans, the conquerors of Italy and of German legions. She is now entirely deprived of her influence and her power in the West Indies."
Meanwhile, France's newly resumed war with Britain resulted in the British capture of practically all remaining French colonies. These were restored at the Treaty of Amiens
The Treaty of Amiens (, ) temporarily ended hostilities between France, the Spanish Empire, and the United Kingdom at the end of the War of the Second Coalition. It marked the end of the French Revolutionary Wars; after a short peace it set t ...
in 1802, but when war resumed in 1803, the British soon recaptured them. France's 1800 recovery of Louisiana from Spain in the secret Third Treaty of San Ildefonso
The Third Treaty of San Ildefonso was a secret agreement signed on 1 October 1800 between Spain and the French Republic by which Spain agreed in principle to exchange its North American colony of Louisiana for territories in Tuscany. The terms we ...
came to nothing, as the success of the Haitian Revolution
The Haitian Revolution ( or ; ) was a successful insurrection by slave revolt, self-liberated slaves against French colonial rule in Saint-Domingue, now the sovereign state of Haiti. The revolution was the only known Slave rebellion, slave up ...
convinced Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career ...
that holding Louisiana would not be worth the cost, leading to its sale to the United States in 1803.
Failed invasion of Egypt
The French attempt to establish a colony in Egypt in 1798–1801 was not successful. Battle casualties for the campaign were at least 15,000 killed or wounded and 8,500 prisoners for France; 50,000 killed or wounded and 15,000 prisoners for Turkey, Egypt, other Ottoman lands, and Britain.
Second French colonial empire (post-1830)
 At the close of the
At the close of the Napoleonic Wars
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Napoleonic Wars
, partof = the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars
, image = Napoleonic Wars (revision).jpg
, caption = Left to right, top to bottom:Battl ...
, most of France's colonies were restored to it by Britain, notably Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe is an Overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France in the Caribbean. It consists of six inhabited islands—Basse-Terre Island, Basse-Terre, Grande-Terre, Guadeloupe, Grande-Terre, Marie-Galant ...
and Martinique
Martinique ( ; or ; Kalinago language, Kalinago: or ) is an island in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the eastern Caribbean Sea. It was previously known as Iguanacaera which translates to iguana island in Carib language, Kariʼn ...
in the West Indies
The West Indies is an island subregion of the Americas, surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, which comprises 13 independent island country, island countries and 19 dependent territory, dependencies in thr ...
, French Guiana
French Guiana, or Guyane in French, is an Overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France located on the northern coast of South America in the Guianas and the West Indies. Bordered by Suriname to the west ...
on the coast of South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
, various trading posts in Senegal
Senegal, officially the Republic of Senegal, is the westernmost country in West Africa, situated on the Atlantic Ocean coastline. It borders Mauritania to Mauritania–Senegal border, the north, Mali to Mali–Senegal border, the east, Guinea t ...
, the ''Île Bourbon'' (Réunion
Réunion (; ; ; known as before 1848) is an island in the Indian Ocean that is an overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France. Part of the Mascarene Islands, it is located approximately east of the isl ...
) in the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or approximately 20% of the water area of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia (continent), ...
, and France's tiny Indian possessions; however, Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* Great Britain, a large island comprising the countries of England, Scotland and Wales
* The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, a sovereign state in Europe comprising Great Britain and the north-eas ...
finally annexed Saint Lucia
Saint Lucia is an island country of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean. Part of the Windward Islands of the Lesser Antilles, it is located north/northeast of the island of Saint Vincent (Saint Vincent and the Grenadines), Saint Vincent ...
, Tobago
Tobago, officially the Ward of Tobago, is an List of islands of Trinidad and Tobago, island and Regions and municipalities of Trinidad and Tobago, ward within the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago. It is located northeast of the larger islan ...
, the Seychelles
Seychelles (, ; ), officially the Republic of Seychelles (; Seychellois Creole: ), is an island country and archipelagic state consisting of 155 islands (as per the Constitution) in the Indian Ocean. Its capital and largest city, Victoria, ...
, and the ''Isle de France'' (now Mauritius
Mauritius, officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island country in the Indian Ocean, about off the southeastern coast of East Africa, east of Madagascar. It includes the main island (also called Mauritius), as well as Rodrigues, Ag ...
).
In 1825 Charles X Charles X may refer to:
* Charles X of France (1757–1836)
* Charles X Gustav (1622–1660), King of Sweden
* Charles, Cardinal de Bourbon (1523–1590), recognized as Charles X of France but renounced the royal title
See also
*
* King Charle ...
sent an expedition to Haïti, resulting in the Haiti indemnity controversy
The Haitian independence debt involves an 1825 agreement between Haiti and France that included France demanding an indemnity of 150 million francs in five annual payments of 30 million to be paid by Haiti in claims over property including Haitia ...
.
The beginnings of the second French colonial empire were laid in 1830 with the French invasion of Algeria, which was fully conquered by 1903. Historian Ben Kiernan
Benedict F. "Ben" Kiernan (born 29 January 1953) is an Australian-born American historian who is the Whitney Griswold Professor Emeritus of History, Professor of International and Area Studies and Director of the Genocide Studies Program at Yale ...
estimates that 825,000 Algerians died during the conquest by 1875.
Africa
Morocco
 The French Colonial Empire established a protectorate in Morocco between the years of 1912 to 1956. France's general approach to governing the protectorate of Morocco was a policy of in-direct rule where they co-opted existing governance systems to control the protectorate.
The French Colonial Empire established a protectorate in Morocco between the years of 1912 to 1956. France's general approach to governing the protectorate of Morocco was a policy of in-direct rule where they co-opted existing governance systems to control the protectorate.Battle of Annual
The Battle of Annual was fought on 22 July 1921 at Annual, Morocco, Annual, in northeastern Morocco, between the Spanish Army and Rifians, Rifian Berbers during the Rif War. The Spanish suffered a major military defeat, which is almost always ref ...
. El-Krim founded an independent Rif Republic that operated until 1926 but had no international recognition. Paris and Madrid agreed to collaborate to destroy it. They sent in 200,000 soldiers, forcing el-Krim to surrender in 1926; he was exiled in the Pacific until 1947. Morocco became quiet, and in 1936 became the base from which Francisco Franco
Francisco Franco Bahamonde (born Francisco Paulino Hermenegildo Teódulo Franco Bahamonde; 4 December 1892 – 20 November 1975) was a Spanish general and dictator who led the Nationalist faction (Spanish Civil War), Nationalist forces i ...
launched his revolt against Madrid.
Tunisia
The French protectorate of Tunisia lasted from 1881 to 1956. The protectorate was initially established after the successful invasion of Tunisia in 1881. The groundwork for occupation was laid on April 24, 1881, when the French deployed 35,000 troops from Algeria to invade several Tunisian cities.
French West Africa
French West Africa was a confederation of eight other French colonial territories including French Mauritania, French Senegal
The history of Senegal is commonly divided into a number of periods, encompassing the prehistoric era, the precolonial period, colonialism, and the contemporary era.
Paleolithic
The earliest evidence of human life is found in the valley of the ...
, French Guinea, French Ivory Coast, French Niger, French Upper Volta, French Dahomey, French Togoland, and French Sudan
French Sudan (; ') was a French colonial territory in the Federation of French West Africa from around 1880 until 1959, when it joined the Mali Federation, and then in 1960, when it became the independent state of Mali. The colony was formall ...
.
At the beginning of Napoleon III's reign, the presence of France in Senegal
Senegal, officially the Republic of Senegal, is the westernmost country in West Africa, situated on the Atlantic Ocean coastline. It borders Mauritania to Mauritania–Senegal border, the north, Mali to Mali–Senegal border, the east, Guinea t ...
was limited to a trading post on the island of Gorée
(; "Gorée Island"; ) is one of the 19 (i.e. districts) of the city of Dakar, Senegal. It is an island located at sea from the main harbour of Dakar (), famous as a destination for people interested in the Atlantic slave trade.
Its populatio ...
, a narrow strip on the coast, the town of Saint-Louis, and a handful of trading posts in the interior. The economy had largely been based on the slave trade Slave trade may refer to:
* History of slavery - overview of slavery
It may also refer to slave trades in specific countries, areas:
* Al-Andalus slave trade
* Atlantic slave trade
** Brazilian slave trade
** Bristol slave trade
** Danish sl ...
, carried out by the rulers of the small kingdoms of the interior, as well as elite families, until France abolished slavery in its colonies in 1848. In 1854, Napoleon III named an enterprising French officer, Louis Faidherbe, to govern and expand the colony, and to give it the beginning of a modern economy. Faidherbe built a series of forts along the Senegal River, formed alliances with leaders in the interior, and sent expeditions against those who resisted French rule. He built a new port at Dakar
Dakar ( ; ; ) is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Senegal, largest city of Senegal. The Departments of Senegal, department of Dakar has a population of 1,278,469, and the population of the Dakar metropolitan area was at 4.0 mill ...
, established and protected telegraph lines and roads, followed these with a rail line between Dakar and Saint-Louis and another into the interior. He built schools, bridges, and systems to supply fresh water to the towns. He also introduced the large-scale cultivation of Bambara groundnuts and peanuts as a commercial crop. Reaching into the Niger
Niger, officially the Republic of the Niger, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is a unitary state Geography of Niger#Political geography, bordered by Libya to the Libya–Niger border, north-east, Chad to the Chad–Niger border, east ...
valley, Senegal became the primary French base in West Africa
West Africa, also known as Western Africa, is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations geoscheme for Africa#Western Africa, United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Gha ...
and a model colony. Dakar became one of the most important cities of the French Empire and of Africa.
French Equatorial Africa
French Equatorial Africa was a confederation of French colonial possessions in the Sahel and Congo River regions of Africa. Colonies included in French Equatorial Africa include French Gabon, French Congo
The French Congo (), also known as Middle Congo (), was a French colony which at one time comprised the present-day area of the Republic of the Congo and parts of Gabon, and the Central African Republic. In 1910, it was made part of the larger ...
, Ubangui-Shari, and French Chad
Chad was a part of the French colonial empire from 1900 to 1960. Colonialism, Colonial rule under the French began in 1900 when the Military Territory of Chad was established. From 1905, Chad was linked to the federation of French colonial poss ...
.
Cameroon
Cameroon was initially colonized by the German Empire in 1884. The indigenous people of Cameroon refused to work on German related projects, which turned into force labor. However, after World War One, the colony was partitioned by France and Britain. The French colony lasted from 1916 to until self-rule was achieved in 1960.
Madagascar
 French colonialism in Madagascar began in 1896 when France established a protectorate by force and ended in the 1960s with the beginning of self-rule. Under French control, the colony of Madagascar included the dependencies of
French colonialism in Madagascar began in 1896 when France established a protectorate by force and ended in the 1960s with the beginning of self-rule. Under French control, the colony of Madagascar included the dependencies of Comoros
The Comoros, officially the Union of the Comoros, is an archipelagic country made up of three islands in Southeastern Africa, located at the northern end of the Mozambique Channel in the Indian Ocean. Its capital and largest city is Moroni, ...
, Mayotte
Mayotte ( ; , ; , ; , ), officially the Department of Mayotte (), is an Overseas France, overseas Overseas departments and regions of France, department and region and single territorial collectivity of France. It is one of the Overseas departm ...
, Réunion
Réunion (; ; ; known as before 1848) is an island in the Indian Ocean that is an overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France. Part of the Mascarene Islands, it is located approximately east of the isl ...
, Kerguelen, Île Saint-Paul
is an island forming part of the French Southern and Antarctic Lands (, TAAF) in the Indian Ocean, with an area of . The island is located about south of the larger Île Amsterdam , northeast of the Kerguelen Islands, and southeast of Réuni ...
, Amsterdam Island, Crozet Islands
The Crozet Islands (; or, officially, ''Archipel Crozet'') are a sub-Antarctic archipelago of small islands in the southern Indian Ocean. They form one of the five administrative districts of the French Southern and Antarctic Lands.
History ...
, Bassas da India, Europa Island, Juan de Nova Island, Glorioso Islands, and Tromelin.
Algeria
The French conquest of Algeria began in 1830 with the invasion of Algiers, and was mostly completed by 1852. Not until 1903 was the conquest fully complete. French colonization of Algeria was undertaken through military conquest and the overthrow of existing structures of government. French colonial rule lasted until Algerian independence in 1962. French colonization of Algeria was defined by its lethality for indigenous Algerians, the dissolution of the Algerian government, and the creation of oppressive and segregationist structures which discriminated against the indigenous population.
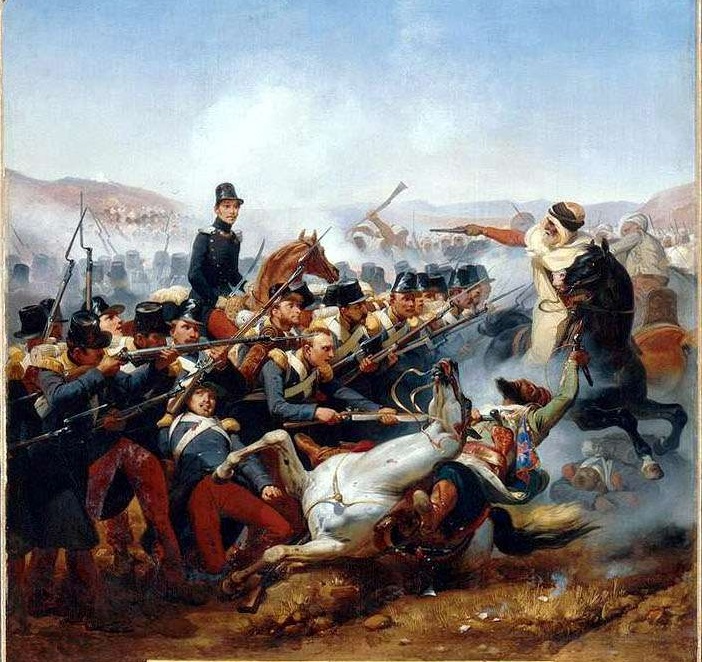 The French military invasion of Algeria began in 1830 with a naval blockade around Algeria followed by the landing of 37,000 French soldiers in Algeria. The French captured the strategic port of Algiers in 1830 deposing
The French military invasion of Algeria began in 1830 with a naval blockade around Algeria followed by the landing of 37,000 French soldiers in Algeria. The French captured the strategic port of Algiers in 1830 deposing Hussein Dey
Hussein Dey (real name Hüseyin bin Hüseyin; 1765–1838; ) was the last Dey of the Deylik of Algiers.
Early life
He was born either in İzmir or Urla in the Ottoman Empire. He went to Istanbul and joined the Canoneers (Topçular in Turkis ...
, the ruler of the Deylik of Algiers. They also seized other coastal communities. Around 100,000 French soldiers were deployed in the conquest of Algeria. Algerian armed resistance against the French invasionSharia
Sharia, Sharī'ah, Shari'a, or Shariah () is a body of religious law that forms a part of the Islamic tradition based on Islamic holy books, scriptures of Islam, particularly the Quran, Qur'an and hadith. In Islamic terminology ''sharīʿah'' ...
courts. This was interpreted by some Muslims as requiring them to give up parts of their religion to obtain citizenship and was resented.
 More importantly, Napoleon III changed the system of land tenure. While ostensibly well-intentioned, in effect this move destroyed the traditional system of land management and deprived many Algerians of land. While Napoleon did renounce state claims to tribal lands, he also began a process of dismantling tribal land ownership in favour of individual land ownership. This process was corrupted by French officials sympathetic to the French in Algeria who took much of the land they surveyed into public domain. In addition, many tribal leaders, chosen for loyalty to the French rather than influence in their tribe, immediately sold communal land for cash.
His attempted reforms were interrupted in 1864 by an Arab insurrection, which required more than a year and an army of 85,000 soldiers to suppress. Nonetheless, he did not give up his idea of making Algeria a model where French colonists and Arabs could live and work together as equals. He traveled to Algiers for a second time on 3 May 1865, and this time he remained for a month, meeting with tribal leaders and local officials. He offered a wide amnesty to participants of the insurrection, and promised to name Arabs to high positions in his government. He also promised a large public works program of new ports, railroads, and roads. However, once again his plans met a major natural obstacle in 1866 and 1868, Algeria was struck by an epidemic of cholera, clouds of locusts, drought and famine, and his reforms were hindered by the French colonists, who voted massively against him in the plebiscites of his late reign. Up to 500,000 people died from the famine and epidemics.
More importantly, Napoleon III changed the system of land tenure. While ostensibly well-intentioned, in effect this move destroyed the traditional system of land management and deprived many Algerians of land. While Napoleon did renounce state claims to tribal lands, he also began a process of dismantling tribal land ownership in favour of individual land ownership. This process was corrupted by French officials sympathetic to the French in Algeria who took much of the land they surveyed into public domain. In addition, many tribal leaders, chosen for loyalty to the French rather than influence in their tribe, immediately sold communal land for cash.
His attempted reforms were interrupted in 1864 by an Arab insurrection, which required more than a year and an army of 85,000 soldiers to suppress. Nonetheless, he did not give up his idea of making Algeria a model where French colonists and Arabs could live and work together as equals. He traveled to Algiers for a second time on 3 May 1865, and this time he remained for a month, meeting with tribal leaders and local officials. He offered a wide amnesty to participants of the insurrection, and promised to name Arabs to high positions in his government. He also promised a large public works program of new ports, railroads, and roads. However, once again his plans met a major natural obstacle in 1866 and 1868, Algeria was struck by an epidemic of cholera, clouds of locusts, drought and famine, and his reforms were hindered by the French colonists, who voted massively against him in the plebiscites of his late reign. Up to 500,000 people died from the famine and epidemics.Mokrani Revolt
The Mokrani Revolt (; ) was the most important local uprising against France in Algeria since the French conquest of Algeria, conquest in 1830.
The revolt broke out on March 16, 1871, with the uprising of more than 250 tribes, around a third of ...
in the Kabylia erupted, which spread through much of Algeria. By April 1871, 250 tribes were rebelling. The uprising was defeated in 1872. There were roughly 130,000 colonists in Algeria in 1871 and by 1900, there were one million. In 1902, a French military expedition entered Hoggar Mountains and defeated the kingdom of Kel Ahaggar
Kel Ahaggar was a Tuareg confederation inhabiting the Hoggar Mountains in Algeria. The confederation is believed to have been founded by the Tuareg matriarch Tin Hinan, whose monumental tomb is located at Abalessa. The official establishment ...
. The conquest of Algeria was completed in 1920 when the Kel Ajjer Kel Ajjer (also Kel Azjar, Kel Azjer) is a Tuareg people, Tuareg confederation inhabiting in southwestern Libya and southeastern Algeria. Their main stronghold was Ghat, Libya, Ghat, followed by Ubari, both in the Fezzan, Fezzan region of southweste ...
gave up their resistance to the French colonial power.
Summary of additional colonization in Africa
France also extended its influence in North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of t ...
after 1870, establishing a protectorate in Tunisia
Tunisia, officially the Republic of Tunisia, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered by Algeria to the west and southwest, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Tunisia also shares m ...
in 1881 with the Bardo Treaty. Gradually, French control crystallised over much of North, West
West is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some Romance langu ...
, and Central Africa
Central Africa (French language, French: ''Afrique centrale''; Spanish language, Spanish: ''África central''; Portuguese language, Portuguese: ''África Central'') is a subregion of the African continent comprising various countries accordin ...
by around the start of the 20th century (including the modern states of Mauritania
Mauritania, officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania, is a sovereign country in Maghreb, Northwest Africa. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Western Sahara to Mauritania–Western Sahara border, the north and northwest, ...
, Senegal
Senegal, officially the Republic of Senegal, is the westernmost country in West Africa, situated on the Atlantic Ocean coastline. It borders Mauritania to Mauritania–Senegal border, the north, Mali to Mali–Senegal border, the east, Guinea t ...
, Guinea
Guinea, officially the Republic of Guinea, is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Guinea-Bissau to the northwest, Senegal to the north, Mali to the northeast, Côte d'Ivoire to the southeast, and Sier ...
, Mali
Mali, officially the Republic of Mali, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is the List of African countries by area, eighth-largest country in Africa, with an area of over . The country is bordered to the north by Algeria, to the east b ...
, Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire and officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital city of Yamoussoukro is located in the centre of the country, while its largest List of ci ...
, Benin
Benin, officially the Republic of Benin, is a country in West Africa. It was formerly known as Dahomey. It is bordered by Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east, Burkina Faso to the north-west, and Niger to the north-east. The majority of its po ...
, Niger
Niger, officially the Republic of the Niger, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is a unitary state Geography of Niger#Political geography, bordered by Libya to the Libya–Niger border, north-east, Chad to the Chad–Niger border, east ...
, Chad
Chad, officially the Republic of Chad, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of North Africa, North and Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to Chad–Libya border, the north, Sudan to Chad–Sudan border, the east, the Central Afric ...
, Central African Republic
The Central African Republic (CAR) is a landlocked country in Central Africa. It is bordered by Chad to Central African Republic–Chad border, the north, Sudan to Central African Republic–Sudan border, the northeast, South Sudan to Central ...
, Republic of the Congo
The Republic of the Congo, also known as Congo-Brazzaville, the Congo Republic or simply the Congo (the last ambiguously also referring to the neighbouring Democratic Republic of the Congo), is a country located on the western coast of Central ...
, Gabon
Gabon ( ; ), officially the Gabonese Republic (), is a country on the Atlantic coast of Central Africa, on the equator, bordered by Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the north, the Republic of the Congo to the east and south, and ...
, Cameroon
Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon, is a country in Central Africa. It shares boundaries with Nigeria to the west and north, Chad to the northeast, the Central African Republic to the east, and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the R ...
, the east Africa
East Africa, also known as Eastern Africa or the East of Africa, is a region at the eastern edge of the Africa, African continent, distinguished by its unique geographical, historical, and cultural landscape. Defined in varying scopes, the regi ...
n coastal enclave of Djibouti
Djibouti, officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden to the east. The country has an area ...
( Obock Territory), and the island of Madagascar
Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, is an island country that includes the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Lying off the southeastern coast of Africa, it is the world's List of islands by area, f ...
.
Pierre Savorgnan de Brazza
Pierre Paul François Camille Savorgnan de Brazza (born Pietro Paolo Savorgnan di Brazzà; 26 January 1852 – 14 September 1905) was an Italian-French explorer. With his family's financial help, he explored the Ogooué region of Central Africa, ...
helped to formalise French control in Gabon and on the northern banks of the Congo River
The Congo River, formerly also known as the Zaire River, is the second-longest river in Africa, shorter only than the Nile, as well as the third-largest river in the world list of rivers by discharge, by discharge volume, following the Amazon Ri ...
from the early 1880s. The explorer Colonel Parfait-Louis Monteil traveled from Senegal to Lake Chad
Lake Chad (, Kanuri language, Kanuri: ''Sádǝ'', ) is an endorheic freshwater lake located at the junction of four countries: Nigeria, Niger, Chad, and Cameroon, in western and central Africa respectively, with a catchment area in excess of . ...
in 1890–1892, signing treaties of friendship and protection with the rulers of several of the countries he passed through, and gaining much knowledge of the geography and politics of the region.Voulet–Chanoine Mission
The Voulet–Chanoine Mission, also called Central African-Chad Mission (), was a French military expedition sent out from Senegal in 1898 to conquer the Chad Basin and unify all French territories in West Africa. This expedition operated jointly ...
, a military expedition, set out from Senegal in 1898 to conquer the Chad Basin
The Chad Basin is the largest endorheic basin in Africa, centered approximately on Lake Chad. It has no outlet to the sea and contains large areas of semi-arid desert and savanna. The drainage basin is approximately coterminous with the sedimenta ...
and to unify all French territories in West Africa. This expedition operated jointly with two other expeditions, the Foureau–Lamy and Gentil Missions, which advanced from Algeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Alger ...
and Middle Congo respectively. With the death (April 1900) of the Muslim warlord Rabih az-Zubayr
Rabih az-Zubayr ibn Fadl Allah (; c. 1842 – April 22, 1900), also known as Rabih Fadlallah and usually known as Rabah in French, was a Sudanese warlord and slave trader who established a powerful empire east of Lake Chad, in today's Chad.
B ...
, the greatest ruler in the region, and the creation of the Military Territory of Chad (September 1900), the Voulet–Chanoine Mission had accomplished all its goals. The ruthlessness of the mission provoked a scandal in Paris.
 As a part of the
As a part of the Scramble for Africa
The Scramble for Africa was the invasion, conquest, and colonialism, colonisation of most of Africa by seven Western European powers driven by the Second Industrial Revolution during the late 19th century and early 20th century in the era of ...
, France aimed to establish a continuous west–east axis across the continent, in contrast with the proposed British north–south axis. Tensions between Britain and France heightened in Africa. At several points war seemed possible, but no outbreak occurred. The most serious episode was the Fashoda Incident
The Fashoda Incident, also known as the Fashoda Crisis ( French: ''Crise de Fachoda''), was the climax of imperialist territorial disputes between Britain and France in East Africa, occurring between 10 July to 3 November 1898. A French expedit ...
of 1898. French troops tried to claim an area in the Southern Sudan, and a British force purporting to act in the interests of the Khedive of Egypt
The Khedivate of Egypt ( or , ; ') was an autonomous tributary state of the Ottoman Empire, established and ruled by the Muhammad Ali Dynasty following the defeat and expulsion of Napoleon Bonaparte's forces which brought an end to the short-li ...
arrived to confront them. Under heavy pressure, the French withdrew, implicitly acknowledging Anglo-Egyptian control over the area. An agreement between the two states recognised the ''status quo''. The British were to maintain control over Egypt, while France remained the dominant power in Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
. Still, it is commonly believed that France suffered a humiliating defeat overall.
During the Agadir Crisis
The Agadir Crisis, Agadir Incident, or Second Moroccan Crisis, was a brief crisis sparked by the deployment of a substantial force of French troops in the interior of Morocco in July 1911 and the deployment of the German gunboat to Agadir, ...
in 1911, Britain supported France against Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
, and Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
became a French protectorate.
The French made their last major colonial gains after World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, when they gained mandates over the former territories of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
that make up what is now Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
and Lebanon
Lebanon, officially the Republic of Lebanon, is a country in the Levant region of West Asia. Situated at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian Peninsula, it is bordered by Syria to the north and east, Israel to the south ...
, as well as most of the former German colonies of Togo
Togo, officially the Togolese Republic, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Ghana to Ghana–Togo border, the west, Benin to Benin–Togo border, the east and Burkina Faso to Burkina Faso–Togo border, the north. It is one of the le ...
and Cameroon
Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon, is a country in Central Africa. It shares boundaries with Nigeria to the west and north, Chad to the northeast, the Central African Republic to the east, and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the R ...
.
Pacific Islands
 In 1838, the French naval commander Abel Aubert du Petit-Thouars responded to complaints of the mistreatment of French Catholic missionary in the
In 1838, the French naval commander Abel Aubert du Petit-Thouars responded to complaints of the mistreatment of French Catholic missionary in the Kingdom of Tahiti
The Kingdom of Tahiti or the Tahitian Kingdom was a Polynesian monarchy founded by paramount chief Pōmare I, who, with the aid of British missionaries and traders, and European weaponry, unified the islands of Tahiti, Moʻorea, Teti‘aroa, ...
ruled by Queen Pōmare IV. Dupetit Thouars forced the native government to pay an indemnity and sign a treaty of friendship with France respecting the rights of French subjects in the islands including any future Catholic missionaries. Four years later, claiming the Tahitians had violated the treaty, a French protectorate was forcibly installed and the queen made to sign a request for French protection.Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in January 1901. Her reign of 63 year ...
. The Franco-Tahitian War broke out between the Tahitian people and the French from 1844 to 1847 as France attempted to consolidate their rule and extend their rule into the Leeward Islands
The Leeward Islands () are a group of islands situated where the northeastern Caribbean Sea meets the western Atlantic Ocean. Starting with the Virgin Islands east of Puerto Rico, they extend southeast to Guadeloupe and its dependencies. In Engl ...
where Queen Pōmare sought refuge with her relatives. The British remained officially neutral during the war but diplomatic tensions existed between the French and British. The French succeeded in subduing the guerilla forces on Tahiti but failed to hold the other islands. In February 1847, Queen Pōmare IV returned from her self-imposed exile and acquiesced to rule under the protectorate. Although victorious, the French were not able to annex the islands due to diplomatic pressure from Great Britain, so Tahiti and its dependency Moorea continued to be ruled under the protectorate. A clause to the war settlement, known as the Jarnac Convention or the Anglo-French Convention of 1847, was signed by France and Great Britain, in which the two powers agreed to respect the independence of Queen Pōmare's allies in Leeward Islands. The French continued the guise of protection until the 1880s when they formally annexed Tahiti with the abdication of King Pōmare V on 29 June 1880. The Leeward Islands were annexed through the Leewards War which ended in 1897. These conflicts and the annexation of other Pacific islands formed French Oceania.New Caledonia
New Caledonia ( ; ) is a group of islands in the southwest Pacific Ocean, southwest of Vanuatu and east of Australia. Located from Metropolitan France, it forms a Overseas France#Sui generis collectivity, ''sui generis'' collectivity of t ...
and Port-de-France (Nouméa) was founded 25 June 1854. A few dozen free settlers settled on the west coast in the following years, but New Caledonia became a penal colony
A penal colony or exile colony is a settlement used to exile prisoners and separate them from the general population by placing them in a remote location, often an island or distant colonial territory. Although the term can be used to refer ...
and, from the 1860s until the end of the transportations in 1897, about 22,000 criminals and political prisoners were sent to New Caledonia.German Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperia ...
planned to take over their island kingdoms. After years of diplomatic negotiation, Britain and France agreed to abrogate the convention in 1887 and the French formally annexed all the Leeward Islands without official treaties of cession from the islands' sovereign governments. From 1888 to 1897, the natives of the kingdom of Raiatea and Tahaa led by a minor chief, Teraupo'o
Teraupo'o ( – 23 December 1918) was a Tahitian (Maohi) resistance leader of the islands of Raiatea and Tahaa who fought off French rule from 1887 to 1897 during the decade-long Leeward Islands War.
Born during the decades following the Fr ...
, fought off French rule and the annexation of the Leeward Islands. Anti-French factions in the kingdom of Huahine
Huahine is an island located among the Society Islands, in French Polynesia, an overseas territory of France in the Pacific Ocean, South Pacific Ocean. It is part of the Leeward Islands (Society Islands), Leeward Islands group ''(Îles sous le V ...
also attempted to fight off the French under Queen Teuhe while the kingdom of Bora Bora
Bora Bora (French language, French: ''Bora-Bora''; Tahitian language, Tahitian: ''Pora Pora'') is an island group in the Leeward Islands (Society Islands), Leeward Islands in the Pacific Ocean, South Pacific. The Leeward Islands comprise the we ...
remained neutral but hostile to the French. The conflict ended in 1897 with the capture and exile of rebel leaders to New Caledonia and more than one hundred rebels to the Marquesas. These conflicts and the annexation of other Pacific islands formed French Polynesia.New Caledonia
New Caledonia ( ; ) is a group of islands in the southwest Pacific Ocean, southwest of Vanuatu and east of Australia. Located from Metropolitan France, it forms a Overseas France#Sui generis collectivity, ''sui generis'' collectivity of t ...
, the various island groups which make up French Polynesia
French Polynesia ( ; ; ) is an overseas collectivity of France and its sole #Governance, overseas country. It comprises 121 geographically dispersed islands and atolls stretching over more than in the Pacific Ocean, South Pacific Ocean. The t ...
(including the Society Islands
The Society Islands ( , officially ; ) are an archipelago in the South Pacific Ocean that includes the major islands of Tahiti, Mo'orea, Moorea, Raiatea, Bora Bora and Huahine. Politically, they are part of French Polynesia, an overseas country ...
, the Marquesas
The Marquesas Islands ( ; or ' or ' ; Marquesan: ' ( North Marquesan) and ' ( South Marquesan), both meaning "the land of men") are a group of volcanic islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France in the southern Pacific ...
, the Gambier Islands
The Gambier Islands ( or ) are an archipelago in French Polynesia, located at the southeast terminus of the Tuamotu archipelago. They cover an area of , and are made up of the Mangareva Islands, a group of high islands remnants of a caldera alo ...
, the Austral Islands
The Austral Islands ( officially ''Archipel des Australes;'' ) are the southernmost group of islands in French Polynesia, an overseas country of France, overseas country of the France, French Republic in the Oceania, South Pacific. Geographicall ...
and the Tuamotus
The Tuamotu Archipelago or the Tuamotu Islands (, officially ) are a French Polynesian chain of just under 80 islands and atolls in the southern Pacific Ocean. They constitute the largest chain of atolls in the world, extending (from northwest to ...
), and established joint control of the New Hebrides
New Hebrides, officially the New Hebrides Condominium () and named after the Hebrides in Scotland, was the colonial name for the island group in the South Pacific Ocean that is now Vanuatu. Native people had inhabited the islands for three th ...
with Britain.
Napoleon III: 1852–1870
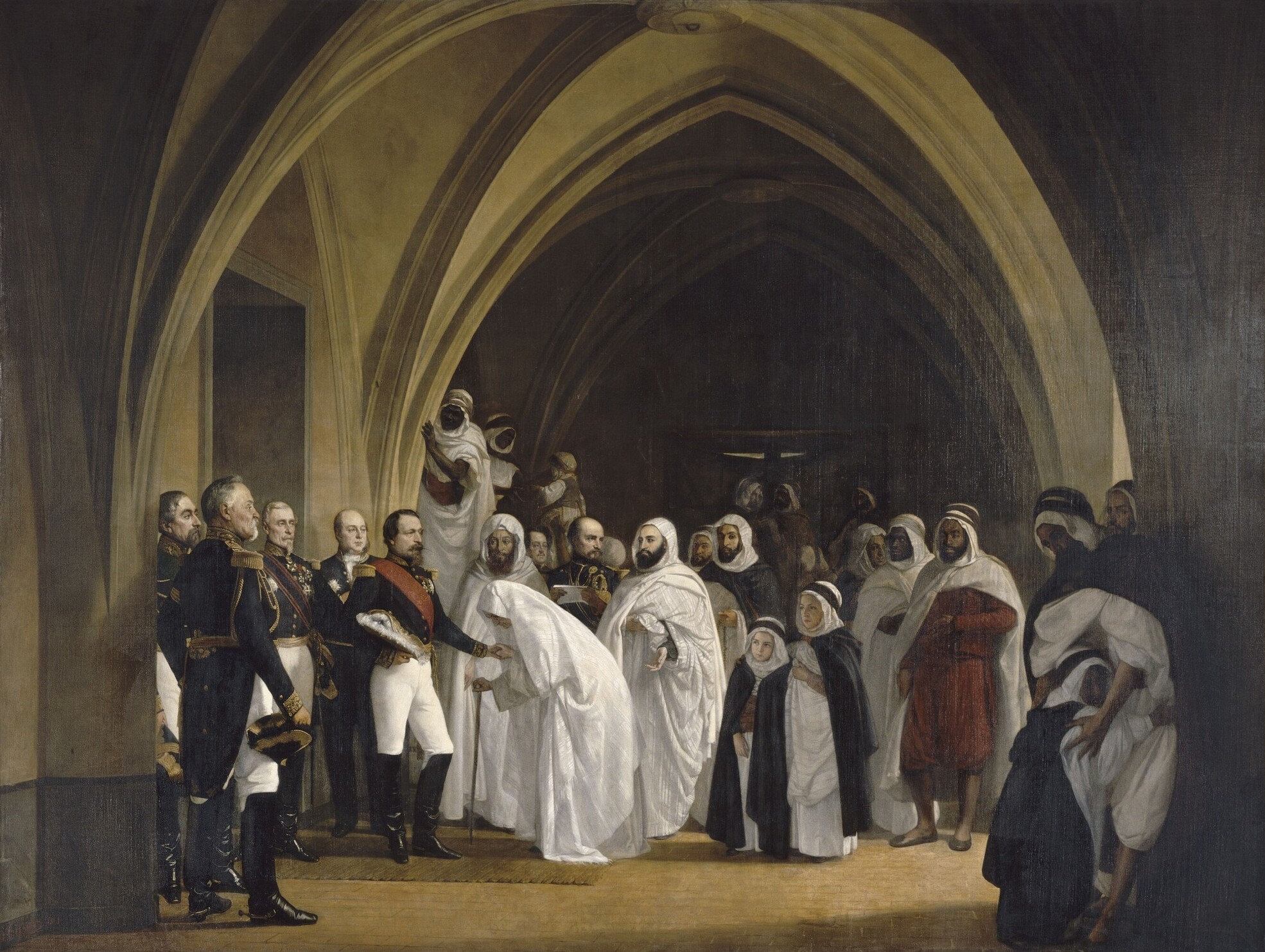

Napoleon III
Napoleon III (Charles-Louis Napoléon Bonaparte; 20 April 18089 January 1873) was President of France from 1848 to 1852 and then Emperor of the French from 1852 until his deposition in 1870. He was the first president, second emperor, and last ...
doubled the area of the French overseas Empire; he established French rule in New Caledonia
New Caledonia ( ; ) is a group of islands in the southwest Pacific Ocean, southwest of Vanuatu and east of Australia. Located from Metropolitan France, it forms a Overseas France#Sui generis collectivity, ''sui generis'' collectivity of t ...
, and Cochinchina
Cochinchina or Cochin-China (, ; ; ; ; ) is a historical exonym and endonym, exonym for part of Vietnam, depending on the contexts, usually for Southern Vietnam. Sometimes it referred to the whole of Vietnam, but it was commonly used to refer t ...
, established a protectorate in Cambodia
Cambodia, officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. It is bordered by Thailand to the northwest, Laos to the north, and Vietnam to the east, and has a coastline ...
(1863); and colonized parts of Africa.
To carry out his new overseas projects, Napoleon III created a new Ministry of the Navy and the Colonies and appointed an energetic minister, Prosper, Marquis of Chasseloup-Laubat, to head it. A key part of the enterprise was the modernization of the French Navy; he began the construction of 15 powerful new battle cruisers powered by steam and driven by propellers; and a fleet of steam-powered troop transports. The French Navy
The French Navy (, , ), informally (, ), is the Navy, maritime arm of the French Armed Forces and one of the four military service branches of History of France, France. It is among the largest and most powerful List of navies, naval forces i ...
became the second most powerful in the world, after Britain's. He also created a new force of colonial troops, including elite units of naval infantry, Zouaves, the Chasseurs d'Afrique, and Algerian sharpshooters, and he expanded the Foreign Legion, which had been founded in 1831 and won fame in the Crimea, Italy and Mexico. By the end of Napoleon III's reign, the French overseas territories had tripled in the area; in 1870 they covered a , with more than 5 million inhabitants.
Asia
Napoleon III also acted to increase the French presence in Indochina. An important factor in his decision was the belief that France risked becoming a second-rate power by not expanding its influence in East Asia. Deeper down was the sense that France owed the world a civilizing mission.
French missionaries had been active in Vietnam since the 17th century, when the Jesuit priest Alexandre de Rhodes opened a mission there. In 1858 the Vietnamese emperor of the Nguyen dynasty
Nguyễn (阮) (sometimes abbreviated as Ng̃) is the most common surname of the Vietnamese people.
Outside of Vietnam, the surname is commonly rendered without diacritics as ''Nguyen''.
By some estimates 30 to 39 percent of Vietnamese peopl ...
felt threatened by the French influence and tried to expel the missionaries. Napoleon III sent a naval force of fourteen gunships, carrying three thousand French and three thousand Filipino troops provided by Spain, under Charles Rigault de Genouilly, to compel the government to accept the missionaries and to stop the persecution of Catholics. In September 1858 the expeditionary force captured and occupied the port of Da Nang
Da Nang or DanangSee also Danang Dragons (, ) is the fifth-largest city in Vietnam by municipal population. It lies on the coast of the Western Pacific Ocean of Vietnam at the mouth of the Hàn River, and is one of Vietnam's most important p ...
, and then in February 1859 moved south and captured Saigon
Ho Chi Minh City (HCMC) ('','' TP.HCM; ), commonly known as Saigon (; ), is the most populous city in Vietnam with a population of around 14 million in 2025.
The city's geography is defined by rivers and canals, of which the largest is Saigo ...
. The Vietnamese ruler was compelled to cede three provinces to France, and to offer protection to the Catholics. The French troops departed for a time to take part in the expedition to China, but in 1862, when the agreements were not fully followed by the Vietnamese emperor, they returned. The Emperor was forced to open treaty ports in Annam and Tonkin
Tonkin, also spelled Tongkin, Tonquin or Tongking, is an exonym referring to the northern region of Vietnam. During the 17th and 18th centuries, this term referred to the domain '' Đàng Ngoài'' under Trịnh lords' control, including both the ...
, and all of Cochinchina
Cochinchina or Cochin-China (, ; ; ; ; ) is a historical exonym and endonym, exonym for part of Vietnam, depending on the contexts, usually for Southern Vietnam. Sometimes it referred to the whole of Vietnam, but it was commonly used to refer t ...
became a French territory in 1864.
In 1863, the ruler of Cambodia
Cambodia, officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. It is bordered by Thailand to the northwest, Laos to the north, and Vietnam to the east, and has a coastline ...
, King Norodom, who had been placed in power by the government of Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
, rebelled against his sponsors and sought the protection of France. The Thai king granted authority over Cambodia to France, in exchange for two provinces of Laos
Laos, officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic (LPDR), is the only landlocked country in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by Myanmar and China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the southeast, and Thailand to the west and ...
, which were ceded by Cambodia to Thailand. In 1867, Cambodia formally became a protectorate of France.
File:Prise de Saigon 18 Fevrier 1859 Antoine Morel-Fatio.jpg, Capture of Saigon by Charles Rigault de Genouilly on 18 February 1859, painted by Antoine Morel-Fatio
File:Jean-Leon Gerome 001.JPG, Napoleon III receiving the Siamese embassy at the palace of Fontainebleau in 1864
File:Presidential Palace of Vietnam.jpg, The Presidential Palace of Vietnam
Presidential may refer to:
* Presidential (song), "Presidential" (song), a 2005 song by YoungBloodZ
* Presidential Airways (charter), an American charter airline based in Florida
* Presidential Airways (scheduled), an American passenger airline ac ...
, in Hanoi, was built between 1900 and 1906 to house the French Governor-General of Indochina.
It was only after its defeat in the Franco-Prussian War
The Franco-Prussian War or Franco-German War, often referred to in France as the War of 1870, was a conflict between the Second French Empire and the North German Confederation led by the Kingdom of Prussia. Lasting from 19 July 1870 to 28 Janua ...
of 1870–1871 and the founding of the Third Republic (1871–1940) that most of France's later colonial possessions were acquired. From their base in Cochinchina, the French took over Tonkin
Tonkin, also spelled Tongkin, Tonquin or Tongking, is an exonym referring to the northern region of Vietnam. During the 17th and 18th centuries, this term referred to the domain '' Đàng Ngoài'' under Trịnh lords' control, including both the ...
(in modern northern Vietnam
Northern Vietnam or '' Tonkin'' () is one of three geographical regions in Vietnam. It consists of three geographic sub-regions: the Northwest (Vùng Tây Bắc), the Northeast (Vùng Đông Bắc), and the Red River Delta (Đồng Bằng Sôn ...
) and Annam (in modern central Vietnam
Central Vietnam ( or ), also known as Middle Vietnam or The Middle, formerly known as by the State of Vietnam, by the Republic of Vietnam, or '' Annam'' under French colonial rule, is one of the three geographical regions within Vietnam.
Th ...
) and made them become French protectorates with the Treaty of Hue between France and Vietnam's Nguyen dynasty in 1883. These, together with Cambodia and Cochinchina, formed French Indochina
French Indochina (previously spelled as French Indo-China), officially known as the Indochinese Union and after 1941 as the Indochinese Federation, was a group of French dependent territories in Southeast Asia from 1887 to 1954. It was initial ...
in 1887 (to which Laos
Laos, officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic (LPDR), is the only landlocked country in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by Myanmar and China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the southeast, and Thailand to the west and ...
was added in 1893 and Guangzhouwan
The Leased Territory of Guangzhouwan, officially the and historically known in English as Kwangchowan or Kwangchow Wan, was a coastal territory of Zhanjiang, China leased to France and administered by French Indochina. The capital of the t ...
in 1900).
In 1849, the French Concession in Shanghai was established, and in 1860, the French Concession in Tientsin (now called Tianjin
Tianjin is a direct-administered municipality in North China, northern China on the shore of the Bohai Sea. It is one of the National Central City, nine national central cities, with a total population of 13,866,009 inhabitants at the time of the ...
) was set up. Both concessions lasted until 1946. The French also had smaller concessions in Guangzhou
Guangzhou, Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Canton or Kwangchow, is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Guangdong Provinces of China, province in South China, southern China. Located on the Pearl River about nor ...
and Hankou
Hankou, alternately romanized as Hankow (), was one of the three towns (the other two were Wuchang and Hanyang) merged to become modern-day Wuhan city, the capital of the Hubei province, China. It stands north of the Han and Yangtze Rivers w ...
(now part of Wuhan
Wuhan; is the capital of Hubei, China. With a population of over eleven million, it is the most populous city in Hubei and the List of cities in China by population, eighth-most-populous city in China. It is also one of the nine National cent ...
).
The Third Anglo-Burmese War
The Third Anglo-Burmese War (), also known as the Third Burma War, took place during 7–29 November 1885, with sporadic resistance continuing into 1887. It was the final of three wars fought in the 19th century between the Burmese and the Br ...
, in which Britain conquered and annexed the hitherto independent Upper Burma
Upper Myanmar ( or , also called Upper Burma) is one of two geographic regions in Myanmar, the other being Lower Myanmar. Located in the country's centre and north stretches, Upper Myanmar encompasses six inland states and regions, including ...
, was in part motivated by British apprehension at France advancing and gaining possession of territories near to Burma.
Middle East
In the spring of 1860, a war broke out in Lebanon
Lebanon, officially the Republic of Lebanon, is a country in the Levant region of West Asia. Situated at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian Peninsula, it is bordered by Syria to the north and east, Israel to the south ...
, then part of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
, between the Druze
The Druze ( ; , ' or ', , '), who Endonym and exonym, call themselves al-Muwaḥḥidūn (), are an Arabs, Arab Eastern esotericism, esoteric Religious denomination, religious group from West Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic ...
population and the Maronite Christians
Maronites (; ) are a Syriac Christian ethnoreligious group native to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant (particularly Lebanon) whose members belong to the Maronite Church. The largest concentration has traditionally resided near Mount ...
. The Ottoman authorities in Lebanon could not stop the violence, and it spread into neighboring Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
, with the massacre of many Christians. In Damascus
Damascus ( , ; ) is the capital and List of largest cities in the Levant region by population, largest city of Syria. It is the oldest capital in the world and, according to some, the fourth Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. Kno ...
, the Emir Abd-el-Kadr protected the Christians there against the Muslim rioters. Napoleon III felt obliged to intervene on behalf of the Christians, despite the opposition of London, which feared it would lead to a wider French presence in the Middle East. After long and difficult negotiations to obtain the approval of the British government, Napoleon III sent a French contingent of seven thousand men for a period of six months. The troops arrived in Beirut in August 1860, and took positions in the mountains between the Christian and Muslim communities. Napoleon III organized an international conference in Paris, where the country was placed under the rule of a Christian governor named by the Ottoman Sultan, which restored a fragile peace. The French troops departed in June 1861, after just under one year. The French intervention alarmed the British, but was highly popular with the powerful Catholic political faction in France, which had been alarmed by Louis Napoleon's dispute with the Pope over his territories in Italy.
 Despite the signing of the 1860 Cobden–Chevalier Treaty, a historic free trade agreement between Britain and France, and the joint operations conducted by France and Britain in the Crimea, China and Mexico, diplomatic relations between Britain and France never became close during the colonial era.
Despite the signing of the 1860 Cobden–Chevalier Treaty, a historic free trade agreement between Britain and France, and the joint operations conducted by France and Britain in the Crimea, China and Mexico, diplomatic relations between Britain and France never became close during the colonial era. Lord Palmerston
Henry John Temple, 3rd Viscount Palmerston (20 October 1784 – 18 October 1865), known as Lord Palmerston, was a British statesman and politician who served as prime minister of the United Kingdom from 1855 to 1858 and from 1859 to 1865. A m ...
, the British foreign minister from 1846 to 1851 and prime minister
A prime minister or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. A prime minister is not the head of state, but r ...
from 1855 to 1865, sought to maintain the balance of power in Europe; this rarely involved an alignment with France. In 1859 there were even briefly fears that France might try to invade Britain. Palmerston was suspicious of France's interventions in Lebanon, Southeast Asia and Mexico. Palmerston was also concerned that France might intervene in the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
(1861–65) on the side of the South. The British also felt threatened by the construction of the Suez Canal
The Suez Canal (; , ') is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, Indo-Mediterranean, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia (and by extension, the Sinai Peninsula from the rest ...
(1859–1869) by Ferdinand de Lesseps
Ferdinand Marie, Comte de Lesseps (; 19 November 1805 – 7 December 1894) was a French Orientalist diplomat and owner of Main Idea of the Suez Canal, which in 1869 joined the Mediterranean and Red Seas, substantially reducing sailing distan ...
in Egypt. They tried to oppose its completion by diplomatic pressures and by promoting revolts among workers.
The Suez Canal was successfully built by a French-backed company, which was to remain under French control even after the British government acquired almost half of the shares. Both nations saw it as vital to maintaining their influence and respective empire in East Africa and Asia. In 1882, ongoing civil disturbances in Egypt prompted Britain to intervene, extending a hand to France. France's leading expansionist Jules Ferry
Jules François Camille Ferry (; 5 April 183217 March 1893) was a French statesman and republican philosopher. He was one of the leaders of the Opportunist Republicans, Moderate Republicans and served as Prime Minister of France from 1880 to 18 ...
was out of office, and Paris allowed London to take effective control of Egypt.
Evolution in the use of the term Empire between the years of 1870–1939
After the downfall of Napoleon III, few writers used the word 'empire', which had become associated with despotism, decadence, and weakness, preferring the word 'colonies'. However, by the 1880s and 1890s, as Republicans consolidated their control over the political system, increasing numbers of politicians, intellectuals and writers began using the phrase "colonial empire", linking it to republicanism and the French nation.
Most Frenchmen ignored foreign affairs and colonial issues. In 1914 the chief pressure group was the ''Parti colonial'', a coalition of 50 organizations with a combined total of only 5,000 members.

Causes and justifications for colonialism
Civilizing Mission
 A hallmark of the French colonial project in the late 19th century and early 20th century was the
A hallmark of the French colonial project in the late 19th century and early 20th century was the civilising mission
The civilizing mission (; ; ) is a political rationale for military intervention and for colonization purporting to facilitate the cultural assimilation of indigenous peoples, especially in the period from the 15th to the 20th centuries. As ...
(''mission civilisatrice''), the principle that it was Europe's duty to bring civilisation to benighted peoples. As such, colonial officials undertook a policy of Franco-Europeanisation in French colonies, most notably French West Africa
French West Africa (, ) was a federation of eight French colonial empires#Second French colonial empire, French colonial territories in West Africa: Colonial Mauritania, Mauritania, French Senegal, Senegal, French Sudan (now Mali), French Guin ...
and Madagascar
Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, is an island country that includes the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Lying off the southeastern coast of Africa, it is the world's List of islands by area, f ...
. During the 19th century, French citizenship along with the right to elect a deputy to the French Chamber of Deputies was granted to the four old colonies of Guadeloupe, Martinique, Guyanne and Réunion as well as to the residents of French India
French India, formally the (), was a French colony comprising five geographically separated enclaves on the Indian subcontinent that had initially been factories of the French East India Company. They were ''de facto'' incorporated into the ...
and the " Four Communes" in Senegal. In most cases, the elected deputies were white Frenchmen, although there were some blacks, such as the Senegalese Blaise Diagne, who was elected in 1914.[Segalla, Spencer. 2009, ''The Moroccan Soul: French Education, Colonial Ethnology, and Muslim Resistance, 1912–1956''. Nebraska University Press]
Racism and notions of white supremacy
White supremacy is the belief that white people are superior to those of other races. The belief favors the maintenance and defense of any power and privilege held by white people. White supremacy has roots in the now-discredited doctrine ...
were integral to justifying the concept of the civilizing mission. French colonialists viewed non-European societies as uncivilized, and their colonial subjects as needing European re-education.slavery
Slavery is the ownership of a person as property, especially in regards to their labour. Slavery typically involves compulsory work, with the slave's location of work and residence dictated by the party that holds them in bondage. Enslavemen ...
in most of French West Africa. From 1906 to 1911, over a million slaves in French West Africa fled from their masters to earlier homes. In Madagascar
Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, is an island country that includes the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Lying off the southeastern coast of Africa, it is the world's List of islands by area, f ...
over 500,000 slaves were freed following French abolition in 1896.
Education
French colonial officials, influenced by the revolutionary ideal of equality, standardized schools, curricula, and teaching methods as much as possible. They did not establish colonial school systems with the idea of furthering the ambitions of the local people, but rather simply exported the systems and methods in vogue in the mother nation. Having a moderately trained lower bureaucracy was of great use to colonial officials. The emerging French-educated indigenous elite saw little value in educating rural peoples. After 1946 the policy was to bring the best students to Paris for advanced training. The result was to immerse the next generation of leaders in the growing anti-colonial diaspora centered in Paris. Impressionistic colonials could mingle with studious scholars or radical revolutionaries or so everything in between. Ho Chi Minh
(born ; 19 May 1890 – 2 September 1969), colloquially known as Uncle Ho () among other aliases and sobriquets, was a Vietnamese revolutionary and politician who served as the founder and first President of Vietnam, president of the ...
and other young radicals in Paris formed the French Communist party in 1920.
Tunisia was exceptional. The colony was administered by Paul Cambon, who built an educational system for colonists and indigenous people alike that was closely modeled on mainland France. He emphasized female and vocational education. By independence, the quality of Tunisian education nearly equalled that in France.
African nationalists rejected such a public education system, which they perceived as an attempt to retard African development and maintain colonial superiority. One of the first demands of the emerging nationalist movement after World War II was the introduction of full metropolitan-style education in French West Africa with its promise of equality with Europeans.
In Algeria, the debate was polarized. The French set up schools based on the scientific method and French culture. The Pied-Noir
The (; ; : ) are an ethno-cultural group of people of French and other European descent who were born in Algeria during the period of French colonial rule from 1830 to 1962. Many of them departed for mainland France during and after the ...
(Catholic migrants from Europe) welcomed this. Those goals were rejected by the Moslem Arabs, who prized mental agility and their distinctive religious tradition. The Arabs refused to become patriotic and cultured Frenchmen and a unified educational system was impossible until the Pied-Noir and their Arab allies went into exile after 1962.
Critics of French colonialism
 Critics of French colonialism gained an international audience in the 1920s, and often used documentary reportage and access to agencies such as the
Critics of French colonialism gained an international audience in the 1920s, and often used documentary reportage and access to agencies such as the League of Nations
The League of Nations (LN or LoN; , SdN) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference (1919–1920), Paris Peace ...
and the International Labour Organization
The International Labour Organization (ILO) is a United Nations agency whose mandate is to advance social and economic justice by setting international labour standards. Founded in October 1919 under the League of Nations, it is one of the firs ...
to make their protests heard. The main criticism was the high level of violence and suffering among the natives. Major critics included Albert Londres
Albert Londres (1 November 1884 – 16 May 1932) was a French journalist and writer. One of the inventors of investigative journalism, Londres not only reported news but created it, and reported it from a personal perspective. He criticized abu ...
, Félicien Challaye, and Paul Monet, whose books and articles were widely read.
Decolonization
The French colonial empire began to fall during the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, when various parts were occupied by foreign powers (Japan in Indochina, Britain in Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
, Lebanon, and Madagascar
Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, is an island country that includes the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Lying off the southeastern coast of Africa, it is the world's List of islands by area, f ...
, the United States and Britain in Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
and Algeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Alger ...
, and Germany and Italy in Tunisia
Tunisia, officially the Republic of Tunisia, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered by Algeria to the west and southwest, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Tunisia also shares m ...
). However, control was gradually reestablished by Charles de Gaulle
Charles André Joseph Marie de Gaulle (22 November 18909 November 1970) was a French general and statesman who led the Free France, Free French Forces against Nazi Germany in World War II and chaired the Provisional Government of the French Re ...
. The French Union
The French Union () was a political entity created by the French Fourth Republic to replace the old French colonial empire system, colloquially known as the " French Empire" (). It was ''de jure'' the end of the "indigenous" () status of Frenc ...
, included in the Constitution of 1946, nominally replaced the former colonial empire, but officials in Paris remained in full control. The colonies were given local assemblies with only limited local power and budgets. There emerged a group of elites, known as "evolués", who were natives of the overseas territories but lived in metropolitan France.
World War II
 During World War II, allied
During World War II, allied Free France
Free France () was a resistance government
claiming to be the legitimate government of France following the dissolution of the Third French Republic, Third Republic during World War II. Led by General , Free France was established as a gover ...
, often with British support, and Axis-aligned Vichy France
Vichy France (; 10 July 1940 – 9 August 1944), officially the French State ('), was a French rump state headed by Marshal Philippe Pétain during World War II, established as a result of the French capitulation after the Battle of France, ...
struggled for control of the colonies, sometimes with outright military combat. By 1943, all of the colonies, except for Indochina under Japanese control, had joined the Free French cause.
The overseas empire helped liberate France as 300,000 North African Arabs fought in the ranks of the Free French. However Charles de Gaulle
Charles André Joseph Marie de Gaulle (22 November 18909 November 1970) was a French general and statesman who led the Free France, Free French Forces against Nazi Germany in World War II and chaired the Provisional Government of the French Re ...
had no intention of liberating the colonies. He assembled the conference of colonial governors (excluding the nationalist leaders) in Brazzaville in January 1944 to announce plans for postwar Union that would replace the Empire. The Brazzaville manifesto proclaimed:
: the goals of the work of civilization undertaken by France in the colonies exclude all idea of autonomy, all possibility of development outside the French block of the Empire; the possible constitutional self-government in the colonies is to be dismissed.
The manifesto angered nationalists across the Empire, and set the stage for long-term wars in Indochina and Algeria that France would lose in humiliating fashion.
Conflict
France was immediately confronted with the beginnings of the decolonisation
Decolonization is the undoing of colonialism, the latter being the process whereby Imperialism, imperial nations establish and dominate foreign territories, often overseas. The meanings and applications of the term are disputed. Some scholar ...
movement. In Algeria demonstrations in May 1945 were repressed with an estimated 6,000 to 45,000 Algerians killed. Unrest in Haiphong, Indochina, in November 1946 was met by a warship bombarding the city. Paul Ramadier
Paul Ramadier (17 March 1888 – 14 October 1961) was a French statesman who served as Prime Minister of France in 1947.
Biography
The son of a psychiatrist, Ramadier graduated in law from the University of Toulouse and started his profess ...
's (SFIO
The C programming language provides many standard library functions for file input and output. These functions make up the bulk of the C standard library header . The functionality descends from a "portable I/O package" written by Mike Lesk at ...
) cabinet repressed the Malagasy Uprising in Madagascar in 1947. The French blamed education. French officials estimated the number of Malagasy killed from a low of 11,000 to a French Army estimate of 89,000.
Also in Indochina, Ho Chi Minh
(born ; 19 May 1890 – 2 September 1969), colloquially known as Uncle Ho () among other aliases and sobriquets, was a Vietnamese revolutionary and politician who served as the founder and first President of Vietnam, president of the ...
's Viet Minh
The Việt Minh (, ) is the common and abbreviated name of the League for Independence of Vietnam ( or , ; ), which was a Communist Party of Vietnam, communist-led national independence coalition formed at Pác Bó by Hồ Chí Minh on 19 May 1 ...
, which was backed by the Soviet Union and China, declared Vietnam
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and depende ...
's independence, which started the First Indochina War
The First Indochina War (generally known as the Indochina War in France, and as the Anti-French Resistance War in Vietnam, and alternatively internationally as the French-Indochina War) was fought between French Fourth Republic, France and Việ ...
. The war dragged on until 1954, when the Viet Minh decisively defeated the French at the Battle of Điện Biên Phủ
The Battle of Điện Biên Phủ was a climactic confrontation of the First Indochina War that took place between 13 March and 7 May 1954. It was fought between the forces of the French Union and Viet Minh.
The French began an operation to in ...
in northern Vietnam, which was the last major battle between the French and the Vietnamese in the First Indochina War.
 Following the Vietnamese victory at Điện Biên Phủ and the signing of the 1954 Geneva Accords, France agreed to withdraw its forces from all its colonies in
Following the Vietnamese victory at Điện Biên Phủ and the signing of the 1954 Geneva Accords, France agreed to withdraw its forces from all its colonies in French Indochina
French Indochina (previously spelled as French Indo-China), officially known as the Indochinese Union and after 1941 as the Indochinese Federation, was a group of French dependent territories in Southeast Asia from 1887 to 1954. It was initial ...
, while stipulating that Vietnam would be temporarily divided at the 17th parallel, with control of the north given to the Soviet-backed Viet Minh as the Democratic Republic of Vietnam
North Vietnam, officially the Democratic Republic of Vietnam (DRV; ; VNDCCH), was a country in Southeast Asia from 1945 to 1976, with sovereignty fully recognized in 1954. A member of the communist Eastern Bloc, it opposed the French-suppor ...
under Ho Chi Minh
(born ; 19 May 1890 – 2 September 1969), colloquially known as Uncle Ho () among other aliases and sobriquets, was a Vietnamese revolutionary and politician who served as the founder and first President of Vietnam, president of the ...
, and the south becoming the State of Vietnam
The State of Vietnam (; chữ Hán: 國家越南; ) was a state in Southeast Asia that existed from 1949 until 1955, first as an associated state of the French Union and later as an independent state (from 20 July 1954 to 26 October 1955). The s ...
under former Nguyen-dynasty Emperor Bảo Đại
Bảo Đại (, vi-hantu, , , 22 October 191331 July 1997), born Nguyễn Phúc (Phước) Vĩnh Thụy (), was the 13th and final emperor of the Nguyễn dynasty, the last ruling dynasty of Vietnam. From 1926 to 1945, he was ''de jure'' em ...
, who abdicated following the 1945 August Revolution under pressure from Ho. However, in 1955, the State of Vietnam's Prime Minister, Ngô Đình Diệm
Ngô Đình Diệm ( , or ; ; 3 January 1901 – 2 November 1963) was a South Vietnamese politician who was the final prime minister of the State of Vietnam (1954–1955) and later the first president of South Vietnam ( Republic of ...
, toppled Bảo Đại
Bảo Đại (, vi-hantu, , , 22 October 191331 July 1997), born Nguyễn Phúc (Phước) Vĩnh Thụy (), was the 13th and final emperor of the Nguyễn dynasty, the last ruling dynasty of Vietnam. From 1926 to 1945, he was ''de jure'' em ...
in a fraud-ridden referendum
A referendum, plebiscite, or ballot measure is a Direct democracy, direct vote by the Constituency, electorate (rather than their Representative democracy, representatives) on a proposal, law, or political issue. A referendum may be either bin ...
and proclaimed himself president of the new Republic of Vietnam
South Vietnam, officially the Republic of Vietnam (RVN; , VNCH), was a country in Southeast Asia that existed from 1955 to 1975. It first garnered international recognition in 1949 as the State of Vietnam within the French Union, with it ...
. The refusal of Ngô Đình Diệm
Ngô Đình Diệm ( , or ; ; 3 January 1901 – 2 November 1963) was a South Vietnamese politician who was the final prime minister of the State of Vietnam (1954–1955) and later the first president of South Vietnam ( Republic of ...
, the US-supported president of the first Republic of Vietnam VN to allow elections in 1956 – as had been stipulated by the Geneva Conference – in fear of Ho Chi Minh's victory and subsequently a total communist takeover, eventually led to the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (1 November 1955 – 30 April 1975) was an armed conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia fought between North Vietnam (Democratic Republic of Vietnam) and South Vietnam (Republic of Vietnam) and their allies. North Vietnam w ...
.
In France's African colonies, the Union of the Peoples of Cameroon's insurrection, which started in 1955 and headed by Ruben Um Nyobé, was violently repressed over a two-year period, with perhaps as many as 100 people killed. However, France formally relinquished its protectorate over Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
and granted it independence in 1956.
French involvement in Algeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Alger ...
stretched back a century. The movements of Ferhat Abbas
Ferhat Abbas (; ALA-LC: ; 24 August 1899 – 24 December 1985) was an Algerian politician who acted in a provisional capacity as the then yet-to-become independent country's Prime Minister from 1958 to 1961, as well as the first President of the ...
and Messali Hadj
Ahmed Ben Messali Hadj (; May 16, 1898 – June 3, 1974; commonly known as Messali Hadj, ) was an Algerian nationalist politician dedicated to the independence of his homeland from French colonial rule. He is often called the "father" of Algeria ...
had marked the period between the two world wars, but both sides radicalised after the Second World War. In 1945, the Sétif massacre was carried out by the French army. The Algerian War
The Algerian War (also known as the Algerian Revolution or the Algerian War of Independence) ''; '' (and sometimes in Algeria as the ''War of 1 November'') was an armed conflict between France and the Algerian National Liberation Front (Algeri ...
started in 1954. Atrocities characterized both sides, and the number killed became highly controversial estimates that were made for propaganda purposes. Algeria was a three-way conflict due to the large number of "pieds-noirs
The (; ; : ) are an ethno-cultural group of people of French and other European descent who were born in Algeria during the period of French colonial rule from 1830 to 1962. Many of them departed for mainland France during and after the ...
" (Europeans who had settled there in the 125 years of French rule). The political crisis in France caused the collapse of the Fourth Republic, as Charles de Gaulle
Charles André Joseph Marie de Gaulle (22 November 18909 November 1970) was a French general and statesman who led the Free France, Free French Forces against Nazi Germany in World War II and chaired the Provisional Government of the French Re ...
returned to power in 1958 and finally pulled the French soldiers and settlers out of Algeria by 1962.
The French Union
The French Union () was a political entity created by the French Fourth Republic to replace the old French colonial empire system, colloquially known as the " French Empire" (). It was ''de jure'' the end of the "indigenous" () status of Frenc ...
was replaced in the Constitution of 1958 by the French Community
The French Community () was the constitutional organization set up in October 1958 between France and its remaining African colonies, then in the process of decolonization. It replaced the French Union, which had reorganized the colonial em ...
. Only Guinea
Guinea, officially the Republic of Guinea, is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Guinea-Bissau to the northwest, Senegal to the north, Mali to the northeast, Côte d'Ivoire to the southeast, and Sier ...
refused by referendum to take part in the new organisation. However, the French Community ceased to operate before the end of the Algerian War. Almost all of the other former African colonies achieved independence in 1960. The French government refused to allow the populations of the former colonies the right they had in the new French Constitution of 1958, as French citizens with equal rights, to choose for their territories to become full ''départements'' of France. The French government had ensured that a constitutional law (60-525) was passed which removed the need for a referendum in a territory to confirm a change in status towards independence or départementalisation, so the voters who had rejected independence in 1958 were not consulted about it in 1960. There are still a few former colonies that chose to remain part of France, under the status of overseas ''départements'' or territories.
Critics of neocolonialism
Neocolonialism is the control by a state (usually, a former colonial power) over another nominally independent state (usually, a former colony) through indirect means. The term ''neocolonialism'' was first used after World War II to refer to ...
claimed that the had replaced formal direct rule. They argued that while de Gaulle was granting independence on one hand, he was maintaining French dominance through the operations of Jacques Foccart, his counsellor for African matters. Foccart supported in particular Biafra in the Nigerian Civil War
The Nigerian Civil War (6 July 1967 – 15 January 1970), also known as the Biafran War, Nigeria-Biafra War, or Biafra War, was fought between Nigeria and the Republic of Biafra, a Secession, secessionist state which had declared its independen ...
during the late 1960s.
Robert Aldrich argues that with Algerian independence in 1962, it appeared that the Empire practically had come to an end, as the remaining colonies were quite small and lacked active nationalist movements. However, there was trouble in French Somaliland (Djibouti
Djibouti, officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden to the east. The country has an area ...
), which became independent in 1977. There also were complications and delays in the New Hebrides Vanuatu
Vanuatu ( or ; ), officially the Republic of Vanuatu (; ), is an island country in Melanesia located in the South Pacific Ocean. The archipelago, which is of volcanic origin, is east of northern Australia, northeast of New Caledonia, east o ...
, which was the last to gain independence in 1980. New Caledonia
New Caledonia ( ; ) is a group of islands in the southwest Pacific Ocean, southwest of Vanuatu and east of Australia. Located from Metropolitan France, it forms a Overseas France#Sui generis collectivity, ''sui generis'' collectivity of t ...
remains a special case under French suzerainty. The Indian Ocean island of Mayotte
Mayotte ( ; , ; , ; , ), officially the Department of Mayotte (), is an Overseas France, overseas Overseas departments and regions of France, department and region and single territorial collectivity of France. It is one of the Overseas departm ...
voted in referendum in 1974 to retain its link with France and not become independent like the other three islands of the Comoro archipelago.
Demographics
French census statistics from 1936 show an imperial population, outside of Metropolitan France
Metropolitan France ( or ), also known as European France (), is the area of France which is geographically in Europe and chiefly comprises #Hexagon, the mainland, popularly known as "the Hexagon" ( or ), and Corsica. This collective name for the ...
itself, of 69.1 million people.French Indochina
French Indochina (previously spelled as French Indo-China), officially known as the Indochinese Union and after 1941 as the Indochinese Federation, was a group of French dependent territories in Southeast Asia from 1887 to 1954. It was initial ...
(grouping five separate colonies and protectorates), with 23.0 million, the general governorate of French West Africa
French West Africa (, ) was a federation of eight French colonial empires#Second French colonial empire, French colonial territories in West Africa: Colonial Mauritania, Mauritania, French Senegal, Senegal, French Sudan (now Mali), French Guin ...
(grouping eight separate colonies), with 14.9 million, the general governorate of Algeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Alger ...
(grouping three departments
Department may refer to:
* Departmentalization, division of a larger organization into parts with specific responsibility
Government and military
* Department (administrative division), a geographical and administrative division within a country, ...
and four Saharan territories), with 7.2 million, the protectorate of Morocco, with 6.3 million, the general governorate of French Equatorial Africa
French Equatorial Africa (, or AEF) was a federation of French colonial territories in Equatorial Africa which consisted of Gabon, French Congo, Ubangi-Shari, and Chad. It existed from 1910 to 1958 and its administration was based in Brazzav ...
(grouping four separate colonies), with 3.9 million, and Madagascar and Dependencies (incl. the Comoro Islands
The Comoro Islands are a group of volcanic islands in the Mozambique Channel, an arm of the Indian Ocean lying between Madagascar and the African mainland. Three of the islands form the Union of the Comoros, a sovereign nation, while Mayotte bel ...
), with 3.8 million.Réunion
Réunion (; ; ; known as before 1848) is an island in the Indian Ocean that is an overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France. Part of the Mascarene Islands, it is located approximately east of the isl ...
, Martinique
Martinique ( ; or ; Kalinago language, Kalinago: or ) is an island in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the eastern Caribbean Sea. It was previously known as Iguanacaera which translates to iguana island in Carib language, Kariʼn ...
, Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe is an Overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France in the Caribbean. It consists of six inhabited islands—Basse-Terre Island, Basse-Terre, Grande-Terre, Guadeloupe, Grande-Terre, Marie-Galant ...
, and French Guiana
French Guiana, or Guyane in French, is an Overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France located on the northern coast of South America in the Guianas and the West Indies. Bordered by Suriname to the west ...
), as well as in the Four Communes of Senegal ( Saint-Louis, Dakar
Dakar ( ; ; ) is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Senegal, largest city of Senegal. The Departments of Senegal, department of Dakar has a population of 1,278,469, and the population of the Dakar metropolitan area was at 4.0 mill ...
, Gorée
(; "Gorée Island"; ) is one of the 19 (i.e. districts) of the city of Dakar, Senegal. It is an island located at sea from the main harbour of Dakar (), famous as a destination for people interested in the Atlantic slave trade.
Its populatio ...
, and Rufisque
Rufisque (; Wolof: Tëngeéj) is a city in the Dakar region of western Senegal, at the base of the Cap-Vert Peninsula east of Dakar, the capital. It has a population of 295,459 (2023 census). ) and in the colonies of the South Pacific.
French settlers
 Unlike elsewhere in Europe, France experienced relatively low levels of emigration to the Americas, except for the
Unlike elsewhere in Europe, France experienced relatively low levels of emigration to the Americas, except for the Huguenots
The Huguenots ( , ; ) are a Religious denomination, religious group of French people, French Protestants who held to the Reformed (Calvinist) tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, ...
in British or Dutch colonies. France generally had close to the slowest natural population growth in Europe, and emigration pressures were therefore quite small. A small but significant emigration, numbering only in the tens of thousands, of mainly Roman Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institut ...
French populations led to the settlement of the provinces of Acadia
Acadia (; ) was a colony of New France in northeastern North America which included parts of what are now the The Maritimes, Maritime provinces, the Gaspé Peninsula and Maine to the Kennebec River. The population of Acadia included the various ...
, Canada, and Louisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25 ...
, both (at the time) French possessions, and colonies in the West Indies
The West Indies is an island subregion of the Americas, surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, which comprises 13 independent island country, island countries and 19 dependent territory, dependencies in thr ...
, Mascarene
The Mascarene Islands (, ) or Mascarenes or Mascarenhas Archipelago is a group of islands in the Indian Ocean east of Madagascar consisting of islands belonging to the Republic of Mauritius as well as the French department of Réunion. Their na ...
islands and Africa. In New France, Huguenots were banned from settling in the territory, and Quebec was one of the most staunchly Catholic areas in the world until the Quiet Revolution
The Quiet Revolution () was a period of socio-political and socio-cultural transformation in French Canada, particularly in Quebec, following the 1960 Quebec general election. This period was marked by the secularization of the government, the ...
. The current French Canadian
French Canadians, referred to as Canadiens mainly before the nineteenth century, are an ethnic group descended from French people, French colonists first arriving in Canada (New France), France's colony of Canada in 1608. The vast majority of ...
population, which numbers in the millions, is descended almost entirely from New France's small settler population.
On 31 December 1687 a community of French Huguenots
The Huguenots ( , ; ) are a Religious denomination, religious group of French people, French Protestants who held to the Reformed (Calvinist) tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, ...
settled in South Africa. Most of these originally settled in the Cape Colony
The Cape Colony (), also known as the Cape of Good Hope, was a British Empire, British colony in present-day South Africa named after the Cape of Good Hope. It existed from 1795 to 1802, and again from 1806 to 1910, when it united with three ...
, but have since been quickly absorbed into the Afrikaner
Afrikaners () are a Southern African ethnic group descended from predominantly Dutch settlers who first arrived at the Cape of Good Hope in 1652.Entry: Cape Colony. ''Encyclopædia Britannica Volume 4 Part 2: Brain to Casting''. Encyclopæd ...
population. After Champlain's founding of Quebec City in 1608, it became the capital of New France
New France (, ) was the territory colonized by Kingdom of France, France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Kingdom of Great Br ...
. Encouraging settlement was difficult, and while some immigration did occur, by 1763 New France only had a population of some 65,000.
In 1787, there were 30,000 white colonists on France's colony of Saint-Domingue
Saint-Domingue () was a French colonization of the Americas, French colony in the western portion of the Caribbean island of Hispaniola, in the area of modern-day Haiti, from 1659 to 1803. The name derives from the Spanish main city on the isl ...
. In 1804 Dessalines, the first ruler of an independent Haiti (St. Domingue), ordered the massacre of whites remaining on the island. Out of the 40,000 inhabitants on Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe is an Overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France in the Caribbean. It consists of six inhabited islands—Basse-Terre Island, Basse-Terre, Grande-Terre, Guadeloupe, Grande-Terre, Marie-Galant ...
, at the end of the 17th century, there were more than 26,000 blacks and 9,000 whites. Bill Marshall wrote, "The first French effort to colonize Guiana, in 1763, failed utterly when tropical diseases and climate killed all but 2,000 of the initial 12,000 settlers."
French law made it easy for thousands of ''colons'', ethnic or national French from former colonies of North and West Africa, India and Indochina
Mainland Southeast Asia (historically known as Indochina and the Indochinese Peninsula) is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to th ...
, to live in mainland France. It is estimated that 20,000 ''colons'' were living in Saigon
Ho Chi Minh City (HCMC) ('','' TP.HCM; ), commonly known as Saigon (; ), is the most populous city in Vietnam with a population of around 14 million in 2025.
The city's geography is defined by rivers and canals, of which the largest is Saigo ...
in 1945. 1.6 million European '' pieds noirs'' migrated from Algeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Alger ...
, Tunisia and Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
. In just a few months in 1962, 900,000 French Algerians left Algeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Alger ...
in the largest relocation of population in Europe since World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
.Cambodia
Cambodia, officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. It is bordered by Thailand to the northwest, Laos to the north, and Vietnam to the east, and has a coastline ...
during the Khmer Rouge
The Khmer Rouge is the name that was popularly given to members of the Communist Party of Kampuchea (CPK), and by extension to Democratic Kampuchea, which ruled Cambodia between 1975 and 1979. The name was coined in the 1960s by Norodom Sihano ...
regime as the Pol Pot
Pol Pot (born Saloth Sâr; 19 May 1925 – 15 April 1998) was a Cambodian politician, revolutionary, and dictator who ruled the communist state of Democratic Kampuchea from 1976 until Cambodian–Vietnamese War, his overthrow in 1979. During ...
government confiscated their farms and land properties. In November 2004, several thousand of the estimated 14,000 French nationals in Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire and officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital city of Yamoussoukro is located in the centre of the country, while its largest List of ci ...
left the country after days of anti-white violence.France, U.N. Start Ivory Coast Evacuation
Fox News Channel
Apart from
French-Canadians
French Canadians, referred to as Canadiens mainly before the nineteenth century, are an ethnic group descended from French colonists first arriving in France's colony of Canada in 1608. The vast majority of French Canadians live in the provi ...
(
Québécois and
Acadians
The Acadians (; , ) are an ethnic group descended from the French colonial empire, French who settled in the New France colony of Acadia during the 17th and 18th centuries. Today, most descendants of Acadians live in either the Northern Americ ...
), francophone Louisianians (
Cajuns
The Cajuns (; Louisiana French language, French: ''les Cadjins'' or ''les Cadiens'' ), also known as Louisiana ''Acadians'' (French: ''les Acadiens''), are a Louisiana French people, Louisiana French ethnic group, ethnicity mainly found in t ...
and
Louisiana Creoles), and
Métis
The Métis ( , , , ) are a mixed-race Indigenous people whose historical homelands include Canada's three Prairie Provinces extending into parts of Ontario, British Columbia, the Northwest Territories and the northwest United States. They ha ...
, other populations of French ancestry outside metropolitan France include the ''
Caldoches'' of
New Caledonia
New Caledonia ( ; ) is a group of islands in the southwest Pacific Ocean, southwest of Vanuatu and east of Australia. Located from Metropolitan France, it forms a Overseas France#Sui generis collectivity, ''sui generis'' collectivity of t ...
, the so-called ''
Zoreilles'', ''Petits-blancs'' with the
Franco-Mauritian of various
Indian Ocean islands and the
Beke people of the French West Indies.
Territories
Africa
*
French Algeria
French Algeria ( until 1839, then afterwards; unofficially ; ), also known as Colonial Algeria, was the period of History of Algeria, Algerian history when the country was a colony and later an integral part of France. French rule lasted until ...
(1830–1961)
*
French Military Territory in Libya (1943–1951)
*
French Protectorate in Morocco
The French protectorate in Morocco, also known as French Morocco, was the period of French colonial rule in Morocco that lasted from 1912 to 1956. The protectorate was officially established 30 March 1912, when List of rulers of Morocco, Sultan ...
(1912–1956)
*
French Protectorate of Tunisia
The French protectorate of Tunisia (; '), officially the Regency of Tunis () and commonly referred to as simply French Tunisia, was established in 1881, during the French colonial empire era, and lasted until Tunisian independence in 1956.
T ...
(1881–1956)
*
French West Africa
French West Africa (, ) was a federation of eight French colonial empires#Second French colonial empire, French colonial territories in West Africa: Colonial Mauritania, Mauritania, French Senegal, Senegal, French Sudan (now Mali), French Guin ...
(1895–1958)
**
French Mauritania (1958–1960)
**
French Senegal
The history of Senegal is commonly divided into a number of periods, encompassing the prehistoric era, the precolonial period, colonialism, and the contemporary era.
Paleolithic
The earliest evidence of human life is found in the valley of the ...
(1958–1960)
**
French Guinea (1958–1960)
**
French Ivory Coast (1958–1960)
**
French Niger (1958–1960)
**
French Upper Volta (1958–1960)
**
French Dahomey (1958–1960)
**
French Togoland (1958–1960)
**
French Sudan
French Sudan (; ') was a French colonial territory in the Federation of French West Africa from around 1880 until 1959, when it joined the Mali Federation, and then in 1960, when it became the independent state of Mali. The colony was formall ...
(1959–1960)
*
French Equatorial Africa
French Equatorial Africa (, or AEF) was a federation of French colonial territories in Equatorial Africa which consisted of Gabon, French Congo, Ubangi-Shari, and Chad. It existed from 1910 to 1958 and its administration was based in Brazzav ...
(1910–1958)
**
French Gabon (1958–1960)
**
French Congo
The French Congo (), also known as Middle Congo (), was a French colony which at one time comprised the present-day area of the Republic of the Congo and parts of Gabon, and the Central African Republic. In 1910, it was made part of the larger ...
(1958–1960)
**
Ubangui-Shari (1958–1960)
**
French Chad
Chad was a part of the French colonial empire from 1900 to 1960. Colonialism, Colonial rule under the French began in 1900 when the Military Territory of Chad was established. From 1905, Chad was linked to the federation of French colonial poss ...
(1958–1960)
*
French Cameroon
French Cameroon, also known as the French Cameroons (), was a French mandate territory in Central Africa. It now forms part of the independent country of Cameroon.
Eastern part of the former German colony of Cameroon (). Its status, from ...
(1920–1960)
*
French Madagascar
The Colony of Madagascar and Dependencies () was a French colony off the coast of Southeast Africa between 1897 and 1958 in what is now Madagascar. The colony was formerly a protectorate of France known as Malagasy Protectorate. The protecto ...
(1897–1958)
**
Seychelles
Seychelles (, ; ), officially the Republic of Seychelles (; Seychellois Creole: ), is an island country and archipelagic state consisting of 155 islands (as per the Constitution) in the Indian Ocean. Its capital and largest city, Victoria, ...
(1756–1794)
**
Île de France (Mauritius) (1715–1810)
**
Comoros
The Comoros, officially the Union of the Comoros, is an archipelagic country made up of three islands in Southeastern Africa, located at the northern end of the Mozambique Channel in the Indian Ocean. Its capital and largest city is Moroni, ...
(1841–1975)
**
Mayotte
Mayotte ( ; , ; , ; , ), officially the Department of Mayotte (), is an Overseas France, overseas Overseas departments and regions of France, department and region and single territorial collectivity of France. It is one of the Overseas departm ...
(1843–)
**
Réunion
Réunion (; ; ; known as before 1848) is an island in the Indian Ocean that is an overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France. Part of the Mascarene Islands, it is located approximately east of the isl ...
(1665–)
**
Kerguelen (1924–)
**
Île Saint-Paul
is an island forming part of the French Southern and Antarctic Lands (, TAAF) in the Indian Ocean, with an area of . The island is located about south of the larger Île Amsterdam , northeast of the Kerguelen Islands, and southeast of Réuni ...
(1924–)
**
Amsterdam Island (1924–)
**
Crozet Islands
The Crozet Islands (; or, officially, ''Archipel Crozet'') are a sub-Antarctic archipelago of small islands in the southern Indian Ocean. They form one of the five administrative districts of the French Southern and Antarctic Lands.
History ...
(1772–)
**
Bassas da India (1897–)
**
Europa Island (1897 )
**
Juan de Nova Island (1897–)
**
Glorioso Islands (1892–)
**
Tromelin (1722–)
*
French Somalia (1896–1967)
*
French domains of St Helena (1854–)
Asia
*
French mandate of Syria
The Mandate for Syria and the Lebanon (; , also referred to as the Levant States; 1923−1946) was a League of Nations mandate founded in the aftermath of the First World War and the partitioning of the Ottoman Empire, concerning the territories ...
(1923–1946)
*
Greater Lebanon
The State of Greater Lebanon (; ), informally known as French Lebanon, was a state declared on 1 September 1920, which became the Lebanese Republic (; ) in May 1926, and is the predecessor of modern Lebanon.
The state was declared on 1 Septembe ...
(1923–1943)
*
French India
French India, formally the (), was a French colony comprising five geographically separated enclaves on the Indian subcontinent that had initially been factories of the French East India Company. They were ''de facto'' incorporated into the ...
(1673–1950)
*
French Indochina
French Indochina (previously spelled as French Indo-China), officially known as the Indochinese Union and after 1941 as the Indochinese Federation, was a group of French dependent territories in Southeast Asia from 1887 to 1954. It was initial ...
(1887–1954)
**
French Cochinchina
French Cochinchina (sometimes spelled ''Cochin-China''; ; , chữ Hán: ) was a colony of French Indochina from 1862 to 1949, encompassing what is now Southern Vietnam. The French operated a plantation economy whose primary strategic product wa ...
(1862–1946)
**
Tonkin
Tonkin, also spelled Tongkin, Tonquin or Tongking, is an exonym referring to the northern region of Vietnam. During the 17th and 18th centuries, this term referred to the domain '' Đàng Ngoài'' under Trịnh lords' control, including both the ...
(1883–1887)
**
Annam (1883–1950)
**
French protectorate of Cambodia
The French protectorate of Cambodia (; ) refers to the Kingdom of Cambodia when it was a French protectorate within French Indochina, a collection of Southeast Asian protectorates within the French colonial empire. The protectorate was establi ...
(1863–1956)
**
French protectorate of Laos
The French protectorate of Laos () was a French protectorate in Southeast Asia of what is today Laos between 1893 and 1953—with a brief interregnum as a Japanese puppet state in 1945—which constituted part of French Indochina. It was estab ...
(1893–1953)
*
Leased territory of Guangzhouwan (1898–1945)
*
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
concessions
**
French concession in Tianjin (1896–1943)
**
Shanghai French Concession
The Shanghai French Concession was a concessions in China, foreign concession in Shanghai, Republic of China (1912–1949), China from 1849 until 1943. For much of the 20th century, the area covered by the former French Concession remained the ...
(1896–1943)
**
Shamian Island
Shamian (also romanized as Shameen or Shamin, both from its Cantonese pronunciation) is a sandbank island in the Liwan, Guangzhou, Liwan District of Guangzhou, Guangdong, China. The island's name literally means "sandy surface" in Chinese ...
,
Guangzhou
Guangzhou, Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Canton or Kwangchow, is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Guangdong Provinces of China, province in South China, southern China. Located on the Pearl River about nor ...
(1896–1943)
The Caribbean
*
Commonwealth of Dominica (1690–1763)
*
Grenada
Grenada is an island country of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean Sea. The southernmost of the Windward Islands, Grenada is directly south of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines and about north of Trinidad and Tobago, Trinidad and the So ...
(1649–1763)
*
Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe is an Overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France in the Caribbean. It consists of six inhabited islands—Basse-Terre Island, Basse-Terre, Grande-Terre, Guadeloupe, Grande-Terre, Marie-Galant ...
(1635–)
*
Haiti
Haiti, officially the Republic of Haiti, is a country on the island of Hispaniola in the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and south of the Bahamas. It occupies the western three-eighths of the island, which it shares with the Dominican ...
(1697–1804)
*
Martinique
Martinique ( ; or ; Kalinago language, Kalinago: or ) is an island in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the eastern Caribbean Sea. It was previously known as Iguanacaera which translates to iguana island in Carib language, Kariʼn ...
(1635–)
*
Saint Barthélemy
Saint Barthélemy, officially the Collectivité territoriale de Saint-Barthélemy, also known as St. Barts (English) or St. Barth (French), is an overseas collectivity of France in the Caribbean. The island lies about southeast of the island ...
(1878–)
*
Saint Lucia
Saint Lucia is an island country of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean. Part of the Windward Islands of the Lesser Antilles, it is located north/northeast of the island of Saint Vincent (Saint Vincent and the Grenadines), Saint Vincent ...
(1674–1814)
*
Saint Martin (1648–)
*
Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles of the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean. It shares a Maritime boundary, maritime border with Puerto Rico to the east and ...
(1795–1815)
*
Virgin Islands
The Virgin Islands () are an archipelago between the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean and northeastern Caribbean Sea, geographically forming part of the Leeward Islands of the Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean, Caribbean islands or West Indie ...
**
Saint Croix
Saint Croix ( ; ; ; ; Danish language, Danish and ; ) is an island in the Caribbean Sea, and a county and constituent Districts and sub-districts of the United States Virgin Islands, district of the United States Virgin Islands (USVI), an Unin ...
(1664–1733)
**
Vieques
Vieques (; ), officially Isla de Vieques, is an island, town and municipality of Puerto Rico, and together with Culebra, it is geographically part of the Spanish Virgin Islands. Vieques lies about east of the mainland of Puerto Rico, measuri ...
(1698–1811)
South America
*
France Antarctique
France Antarctique (formerly also spelled ''France antartique'') was a French colony in Rio de Janeiro, in modern-day Brazil, which existed between 1555 and 1567, and had control over the coast from Rio de Janeiro to Cabo Frio. The colony quickl ...
(1555–1567)
*
French Guiana
French Guiana, or Guyane in French, is an Overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France located on the northern coast of South America in the Guianas and the West Indies. Bordered by Suriname to the west ...
(1503–)
*
Equinoctial France
Equinoctial France ( French: ''France équinoxiale'') was the contemporary name given to the colonization efforts of France in the 17th century in South America, around the line of the equator, before "tropical" had fully gained its modern meani ...
(1612–1615)
North America
*
New France
New France (, ) was the territory colonized by Kingdom of France, France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Kingdom of Great Br ...
(1534–1763)
**
Acadia
Acadia (; ) was a colony of New France in northeastern North America which included parts of what are now the The Maritimes, Maritime provinces, the Gaspé Peninsula and Maine to the Kennebec River. The population of Acadia included the various ...
(1604–1713)
**
Illinois Country
The Illinois Country ( ; ; ), also referred to as Upper Louisiana ( ; ), was a vast region of New France claimed in the 1600s that later fell under Spanish and British control before becoming what is now part of the Midwestern United States. Whi ...
(1675–1769), (1801–1803)
**
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
(1535–1763)
**
Louisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25 ...
(1682–1762), (1801–1803)
**
Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region of Labrador, having a total size of . As of 2025 the population ...
(1658–1713)
***
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Pierre and Miquelon ( ), officially the Territorial Collectivity of Saint Pierre and Miquelon (), is a self-governing territorial overseas collectivity of France in the northwestern Atlantic Ocean, located near the Canada, Canadian prov ...
(1536–)
Oceania
*
New Caledonia
New Caledonia ( ; ) is a group of islands in the southwest Pacific Ocean, southwest of Vanuatu and east of Australia. Located from Metropolitan France, it forms a Overseas France#Sui generis collectivity, ''sui generis'' collectivity of t ...
(1853–)
*
French Polynesia
French Polynesia ( ; ; ) is an overseas collectivity of France and its sole #Governance, overseas country. It comprises 121 geographically dispersed islands and atolls stretching over more than in the Pacific Ocean, South Pacific Ocean. The t ...
(1842–)
*
Wallis and Futuna
Wallis and Futuna, officially the Territory of the Wallis and Futuna Islands (), is a French island territorial collectivity, collectivity in the Oceania, South Pacific, situated between Tuvalu to the northwest, Fiji to the southwest, Tonga t ...
(1887–)
*
Clipperton Island
Clipperton Island ( ; ), also known as Clipperton Atoll and previously as Clipperton's Rock, is an uninhabited French coral atoll in the eastern Pacific Ocean. The only French territory in the North Pacific, Clipperton is from Paris, France ...
(1858–)
*
New Hebrides
New Hebrides, officially the New Hebrides Condominium () and named after the Hebrides in Scotland, was the colonial name for the island group in the South Pacific Ocean that is now Vanuatu. Native people had inhabited the islands for three th ...
(1887–1980)
See also
*
Army of the Levant
The Army of the Levant () identifies the armed forces of France and then Vichy France which occupied, and were in part recruited from, the Mandate for Syria and the Lebanon, French Mandated territories in the Levant during the interwar period and ...
*
CFA franc
CFA franc (, ) is the name of two currencies used by 210 million people (as of 2023) in fourteen African countries: the West African CFA franc (where "CFA" stands for , i.e. "African Financial Community" in English), used in eight West African c ...
*
Colonialism
Colonialism is the control of another territory, natural resources and people by a foreign group. Colonizers control the political and tribal power of the colonised territory. While frequently an Imperialism, imperialist project, colonialism c ...
*
Decolonization
Decolonization is the undoing of colonialism, the latter being the process whereby Imperialism, imperial nations establish and dominate foreign territories, often overseas. The meanings and applications of the term are disputed. Some scholar ...
*
Evolution of the French Empire
*
Francization
Francization (in American English, Canadian English, and Oxford English) or Francisation (in other British English), also known as Frenchification, is the expansion of French language use—either through willful adoption or coercion—by more an ...
*
French Army
The French Army, officially known as the Land Army (, , ), is the principal Army, land warfare force of France, and the largest component of the French Armed Forces; it is responsible to the Government of France, alongside the French Navy, Fren ...
units with a tradition of service overseas
** 1900–1958:
Troupes de marine
** 1900–1958:
Troupes coloniales
The ''Troupes coloniales'' (, "Colonial Troops") or ''Armée coloniale'' (,"Colonial Army"), commonly called ''La Coloniale'', were the colonial troops of the French colonial empire from 1900 until 1961. From 1822 to 1900, these troops wer ...
**
Tirailleurs
A tirailleur (), in the Napoleonic era, was a type of light infantry trained to skirmish ahead of the main columns. Later, the term "''tirailleur''" was used by the French Army as a designation for indigenous infantry recruited in the French c ...
**
Spahis
**
Zouaves
*
French colonial flags
Some colony, colonies, protectorates and mandates of the French Colonial Empire used distinctive colonial flags. These most commonly had a Flag of France, French Tricolour in the Flag terminology#Description of standard flag parts and terms, ca ...
*
French colonisation of the Americas
*
French law on colonialism
French may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France
** French people, a nation and ethnic group
** French cuisine, cooking traditions and practices
Arts and media
* The French (band), a ...
(for teachers, 2005)
*
History of France
The first written records for the history of France appeared in the Iron Age France, Iron Age.
What is now France made up the bulk of the region known to the Romans as Gaul. Greek writers noted the presence of three main ethno-linguistic grou ...
**
Second French Empire
The Second French Empire, officially the French Empire, was the government of France from 1852 to 1870. It was established on 2 December 1852 by Louis-Napoléon Bonaparte, president of France under the French Second Republic, who proclaimed hi ...
**
French Third Republic
The French Third Republic (, sometimes written as ) was the system of government adopted in France from 4 September 1870, when the Second French Empire collapsed during the Franco-Prussian War, until 10 July 1940, after the Fall of France durin ...
**
Kingdom of France
The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the Middle Ages, medieval and Early modern France, early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe from th ...
*
International relations (1814–1919)
This article covers worldwide diplomacy and, more generally, the international relations of the great powers from 1814 to 1919. This era covers the period from the end of the Napoleonic Wars and the Congress of Vienna (1814–1815), to the end o ...
*
List of French possessions and colonies
From the 16th to the 17th centuries, the First French colonial empire existed mainly in the Americas and Asia. During the 19th and 20th centuries, the second French colonial empire existed mainly in Africa and Asia. France had about 80 colonie ...
*
New France
New France (, ) was the territory colonized by Kingdom of France, France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Kingdom of Great Br ...
*
*
Overseas France
Overseas France (, also ) consists of 13 France, French territories outside Europe, mostly the remnants of the French colonial empire that remained a part of the French state under various statuses after decolonisation. Most are part of the E ...
*
Postage stamps of the French colonies
*
Scramble for Africa
The Scramble for Africa was the invasion, conquest, and colonialism, colonisation of most of Africa by seven Western European powers driven by the Second Industrial Revolution during the late 19th century and early 20th century in the era of ...
*
Timeline of imperialism
References
Further reading
* Langley, Michael. "Bizerta to the Bight: The French in Africa". ''History Today.'' (Oct 1972), pp 733–739. covers 1798 to 1900.
* Horne, Alistair. (1977). ''
A Savage War of Peace: Algeria, 1954-1962''. Viking Press.
* Hutton, Patrick H. ed. ''Historical Dictionary of the Third French Republic, 1870–1940'' (2 vol 1986).
* McDougall, James. (2017). ''
A History of Algeria''. Cambridge University Press.
* McDougall, James. (2006). ''
History and the culture of nationalism in Algeria''. Cambridge University Press.
* Northcutt, Wayne, ed. ''Historical Dictionary of the French Fourth and Fifth Republics, 1946–1991'' (1992).
Policies and colonies
* Aldrich, Robert. ''Greater France: A History of French Overseas Expansion'' (1996)
* Aldrich, Robert. ''The French Presence in the South Pacific, 1842–1940'' (1989).
* Anderson, Fred. ''Crucible of War: The Seven Years' War and the Fate of Empire in British North America, 1754–1766'' (2001), covers New France in Canada
* Baumgart, Winfried. ''Imperialism: The Idea and Reality of British and French Colonial Expansion, 1880–1914'' (1982)
* Betts, Raymond. ''Tricouleur: The French Overseas Empire'' (1978), 174pp
* Betts, Raymond. ''Assimilation and Association in French Colonial Theory, 1890–1914'' (2005
excerpt and text search* .
*
* Clayton, Anthony. ''The Wars of French Decolonization'' (1995)
* Cogneau, Denis, et al. "Taxation in Africa from Colonial Times to Present Evidence from former French colonies 1900-2018." (2021)
online* Conklin, Alice L. ''A Mission to Civilize: The Republican Idea of Empire in France and West Africa, 1895–1930'' (1997)
* Curtis, Sarah A. ''Civilizing habits: Women missionaries and the revival of French empire'' (Oxford UP, 2010); role of nuns
* Evans, Martin. "From colonialism to post-colonialism: the French empire since Napoleon". in Martin S. Alexander, ed., ''French History since Napoleon'' (1999) pp: 391–415.
* Gamble, Harry. ''Contesting French West Africa: Battles over Schools and the Colonial Order, 1900–1950'' (U of Nebraska Press, 2017). 378 pp
online review* Jennings, Eric T. ''Imperial Heights: Dalat and the Making and Undoing of French Indochina'' (2010).
*
* Lawrence, Adria. ''Imperial rule and the politics of nationalism: anti-colonial protest in the French empire'' (Cambridge UP, 2013).
* .
* Klein, Martin A. ''Slavery and colonial rule in French West Africa'' (Cambridge University Press, 1998)
* Manning, Patrick. ''Francophone Sub-Saharan Africa 1880-1995'' (Cambridge UP, 1998).
* Neres, Philip. ''French-speaking West Africa: From Colonial Status to Independence'' (1962)
* Priestley, Herbert Ingram. ''France overseas: a study of modern imperialism'' (1938) 464pp.
* Quinn, Frederick. ''The French Overseas Empire'' (2000)
* .
* Poddar, Prem, and Lars Jensen, eds., ''A historical companion to postcolonial literatures: Continental Europe and Its Empires'' (Edinburgh UP, 2008)
excerptals
entire text online* .
* Priestley, Herbert Ingram. (1938) ''France overseas;: A study of modern imperialism'' 463pp; encyclopedic coverage as of late 1930s
* Roberts, Stephen H. ''History of French Colonial Policy (1870-1925)'' (2 vol 1929
vol 1 onlineals
vol 2 online Comprehensive scholarly history
* Schnerb, Robert. "Napoleon III and the Second French Empire." ''Journal of Modern History'' 8#3 (1936), pp. 338–55
online* .
* Strother, Christian. "Waging War on Mosquitoes: Scientific Research and the Formation of Mosquito Brigades in French West Africa, 1899–1920". ''Journal of the history of medicine and allied sciences'' (2016): jrw005.
* Thomas, Martin. ''The French Empire Between the Wars: Imperialism, Politics and Society'' (2007) covers 1919–1939
* Thompson, Virginia, and Richard Adloff. ''French West Africa'' (Stanford UP, 1958).
* Wellington, Donald C. ''French East India companies: A historical account and record of trade'' (Hamilton Books, 2006)
* Wesseling, H.L. and
Arnold J. Pomerans. ''Divide and rule: The partition of Africa, 1880–1914'' (Praeger, 1996.)
* Wesseling, H.L. ''The European Colonial Empires: 1815–1919'' (Routledge, 2015).
* White, Owen, and James Patrick Daughton, eds. ''In God's Empire: French Missionaries in the Modern World'' (Oxford University Press, 2012)
online*Winnacker, R. A. (1938). "Elections in Algeria and the French Colonies under the Third Republic." ''The American Political Science Review'', 32(2), 261–277. https://doi.org/10.2307/1948669
Decolonization
* Betts, Raymond F. ''Decolonization'' (2nd ed. 2004)
* Betts, Raymond F. ''France and Decolonisation, 1900–1960'' (1991)
* Chafer, Tony. ''The end of empire in French West Africa: France's successful decolonization'' (Bloomsbury Publishing, 2002).
*
Chamberlain, Muriel E. ed. ''Longman Companion to European Decolonisation in the Twentieth Century'' (Routledge, 2014)
* Clayton, Anthony. ''The wars of French decolonization'' (Routledge, 2014).
* Cooper, Frederick. "French Africa, 1947–48: Reform, Violence, and Uncertainty in a Colonial Situation". ''Critical Inquiry'' (2014) 40#4 pp: 466–478
in JSTOR* Ikeda, Ryo. ''The Imperialism of French Decolonisation: French Policy and the Anglo-American Response in Tunisia and Morocco'' (Palgrave Macmillan, 2015)
* Jansen, Jan C. & Jürgen Osterhammel. ''Decolonization: A Short History'' (princeton UP, 2017)
* Jones, Max, et al. "Decolonising imperial heroes: Britain and France". ''Journal of Imperial and Commonwealth History'' 42#5 (2014): 787–825.
* Lawrence, Adria K. ''Imperial Rule and the Politics of Nationalism: Anti-Colonial Protest in the French Empire'' (Cambridge UP, 2013
online reviews*
McDougall, James. "The Impossible Republic: The Reconquest of Algeria and the Decolonization of France, 1945–1962", ''The Journal of Modern History'' 89#4 (December 2017) pp 772–81
excerpt* Rothermund, Dietmar. ''Memories of Post-Imperial Nations: The Aftermath of Decolonization, 1945–2013'' (2015
excerpt Compares the impact on Great Britain, the Netherlands, Belgium, France, Portugal, Italy and Japan
* Rothermund, Dietmar. ''The Routledge companion to decolonization'' (Routledge, 2006), comprehensive global coverage; 365pp
* Shepard, Todd. ''The Invention of Decolonization: The Algerian War and the Remaking of France'' (2006)
* Simpson, Alfred William Brian. ''Human Rights and the End of Empire: Britain and the Genesis of the European Convention'' (Oxford University Press, 2004).
* Smith, Tony. "A comparative study of French and British decolonization". ''Comparative Studies in Society and History'' (1978) 20#1 pp: 70–102
online
* Smith, Tony. "The French Colonial Consensus and People's War, 1946–58." ''Journal of Contemporary History'' (1974): 217–247
in JSTOR* Thomas, Martin, Bob Moore, and Lawrence J. Butler. ''Crises of Empire: Decolonization and Europe's imperial states'' (Bloomsbury Publishing, 2015)
* Von Albertini, Rudolf. ''Decolonization: the Administration and Future of the Colonies, 1919–1960'' (Doubleday, 1971), scholarly analysis of French policies, pp 265–469..
Images and impact on France
* Andrew, Christopher M., and Alexander Sydney Kanya-Forstner. "France, Africa, and the First World War". ''Journal of African History'' 19.1 (1978): 11–23.
*
online* Andrew, C. M., and A. S. Kanya-Forstner. "The French 'Colonial Party': Its Composition, Aims and Influence, 1885–1914". ''Historical Journal'' 14#1 (1971): 99–128
online
* August, Thomas G. ''The Selling of the Empire: British and French Imperialist Propaganda, 1890–1940'' (1985)
* Chafer, Tony, and Amanda Sackur. ''Promoting the Colonial Idea: Propaganda and Visions of Empire in France'' (2002)
* .
* Conkin, Alice L. ''A Mission to Civilize: The Republican Idea of Empire in France and West Africa, 1895–1930'' (1997) * Dobie, Madeleine. ''Trading Places: Colonization & Slavery in 18th-Century French Culture'' (2010)
* .
* Rosenblum, Mort. ''Mission to Civilize: The French Way'' (1986
* Rothermund, Dietmar. ''Memories of Post-Imperial Nations: The Aftermath of Decolonization, 1945–2013'' (2015
excerpt Compares the impact on Great Britain, the Netherlands, Belgium, France, Portugal, Italy and Japan.
* Singer, Barnett, and John Langdon. ''Cultured Force: Makers and Defenders of the French Colonial Empire'' (2008)
* Thomas, Martin, ed. ''The French Colonial Mind, Volume 1: Mental Maps of Empire and Colonial Encounters'' (France Overseas: Studies in Empire and D) (2012); ''The French Colonial Mind, Volume 2: Violence, Military Encounters, and Colonialism'' (2012).
Historiography and memoir
* Bennington, Alice. "Writing Empire? The Reception of Post-Colonial Studies in France". ''Historical Journal'' (2016) 59#4: 1157–1186
abstract* Dubois, Laurent. "The French Atlantic", in ''Atlantic History: A Critical Appraisal,'' ed. by Jack P. Greene and Philip D. Morgan, (Oxford UP, 2009) pp. 137–61.
* Dwyer, Philip. "Remembering and Forgetting in Contemporary France: Napoleon, Slavery, and the French History Wars", ''French Politics, Culture & Society'' (2008) 26#3 pp 110–122.
* .
* Greer, Allan. "National, Transnational, and Hypernational Historiographies: New France Meets Early American History", ''Canadian Historical Review,'' (2010) 91#4 pp 695–724
* Hodson, Christopher, and Brett Rushforth, "Absolutely Atlantic: Colonialism and the Early Modern French State in Recent Historiography", ''History Compass,'' (January 2010) 8#1 pp 101–117
* Pernsteiner, Alexis (translator). (2017). ''The Colonial Legacy in France: Fracture, Rupture, and Apartheid'' (N. Bancel, P. Blanchard, & D. Thomas, Eds.). Indiana University Press. https://doi.org/10.2307/j.ctt20060bg.
* Lawrence, Adria K. ''Imperial Rule and the Politics of Nationalism: Anti-Colonial Protest in the French Empire'' (Cambridge UP, 2013
online reviews
External links
French Colonial Historical Society
French Colonial Historical Society''French Colonial History''��an annual volume of refereed, scholarly articles
{{DEFAULTSORT:French Colonial Empire
1534 establishments in the French colonial empire
1977 disestablishments in the French colonial empire
Former empires
Historical transcontinental empires
History of European colonialism
Overseas empires

 In the middle of the 18th century, a series of colonial conflicts began between France and
In the middle of the 18th century, a series of colonial conflicts began between France and  At the close of the
At the close of the  The French Colonial Empire established a protectorate in Morocco between the years of 1912 to 1956. France's general approach to governing the protectorate of Morocco was a policy of in-direct rule where they co-opted existing governance systems to control the protectorate. Specifically, the Moroccan elite and Sultan were both left in control while being strongly influenced by the French government.
French colonialism in Morocco was discriminatory against native Moroccans and highly detrimental to the Moroccan economy. Moroccans were treated as second class citizens and discriminated against in all aspects of colonial life. Infrastructure was discriminatory in colonial Morocco. The French colonial government built 36.5 kilometers of sewers in the new neighborhoods created to accommodate new French settlers while only 4.3 kilometers of sewers were built in indigenous Moroccan communities. Additionally, land in Morocco was far more expensive for Moroccans than for French settlers. For example, while the average Moroccan had a plot of land 50 times smaller than their French settler counterparts, Moroccans were forced to pay 24% more per hectare. Moroccans were additionally prohibited from buying land from French settlers.
Colonial Morocco's economy was designed to benefit French businesses at the detriment of Moroccan laborers. Morocco was forced to import all of its goods from France despite higher costs. Additionally, improvements to agriculture and irrigation systems in Morocco exclusively benefited colonial agriculturalists while leaving Moroccan farms at a technological disadvantage.
Between the years of 1914 to 1921 the Zaian Confederation of Berber Tribes, primarily from the Atlas Mountain region of Morocco, staged an armed resistance against French colonial control. The outbreak of World War One prevented the French from committing fully to the conflict, and thus the French forces suffered high losses. For example, at the Battle of El Herri in 1914, 600 French soldiers were killed. The fighting was primarily characterized by Guerrilla warfare. The Zaian forces additionally received military and economic support from the Central Powers.
The Berber independence leader Abd el-Krim (1882–1963) organized armed resistance against the Spanish and French for control of Morocco. The Spanish had faced unrest off and on from the 1890s, but in 1921 Spanish forces were massacred at the
The French Colonial Empire established a protectorate in Morocco between the years of 1912 to 1956. France's general approach to governing the protectorate of Morocco was a policy of in-direct rule where they co-opted existing governance systems to control the protectorate. Specifically, the Moroccan elite and Sultan were both left in control while being strongly influenced by the French government.
French colonialism in Morocco was discriminatory against native Moroccans and highly detrimental to the Moroccan economy. Moroccans were treated as second class citizens and discriminated against in all aspects of colonial life. Infrastructure was discriminatory in colonial Morocco. The French colonial government built 36.5 kilometers of sewers in the new neighborhoods created to accommodate new French settlers while only 4.3 kilometers of sewers were built in indigenous Moroccan communities. Additionally, land in Morocco was far more expensive for Moroccans than for French settlers. For example, while the average Moroccan had a plot of land 50 times smaller than their French settler counterparts, Moroccans were forced to pay 24% more per hectare. Moroccans were additionally prohibited from buying land from French settlers.
Colonial Morocco's economy was designed to benefit French businesses at the detriment of Moroccan laborers. Morocco was forced to import all of its goods from France despite higher costs. Additionally, improvements to agriculture and irrigation systems in Morocco exclusively benefited colonial agriculturalists while leaving Moroccan farms at a technological disadvantage.
Between the years of 1914 to 1921 the Zaian Confederation of Berber Tribes, primarily from the Atlas Mountain region of Morocco, staged an armed resistance against French colonial control. The outbreak of World War One prevented the French from committing fully to the conflict, and thus the French forces suffered high losses. For example, at the Battle of El Herri in 1914, 600 French soldiers were killed. The fighting was primarily characterized by Guerrilla warfare. The Zaian forces additionally received military and economic support from the Central Powers.
The Berber independence leader Abd el-Krim (1882–1963) organized armed resistance against the Spanish and French for control of Morocco. The Spanish had faced unrest off and on from the 1890s, but in 1921 Spanish forces were massacred at the 
 French colonialism in Madagascar began in 1896 when France established a protectorate by force and ended in the 1960s with the beginning of self-rule. Under French control, the colony of Madagascar included the dependencies of
French colonialism in Madagascar began in 1896 when France established a protectorate by force and ended in the 1960s with the beginning of self-rule. Under French control, the colony of Madagascar included the dependencies of  The French military invasion of Algeria began in 1830 with a naval blockade around Algeria followed by the landing of 37,000 French soldiers in Algeria. The French captured the strategic port of Algiers in 1830 deposing
The French military invasion of Algeria began in 1830 with a naval blockade around Algeria followed by the landing of 37,000 French soldiers in Algeria. The French captured the strategic port of Algiers in 1830 deposing  More importantly, Napoleon III changed the system of land tenure. While ostensibly well-intentioned, in effect this move destroyed the traditional system of land management and deprived many Algerians of land. While Napoleon did renounce state claims to tribal lands, he also began a process of dismantling tribal land ownership in favour of individual land ownership. This process was corrupted by French officials sympathetic to the French in Algeria who took much of the land they surveyed into public domain. In addition, many tribal leaders, chosen for loyalty to the French rather than influence in their tribe, immediately sold communal land for cash.
His attempted reforms were interrupted in 1864 by an Arab insurrection, which required more than a year and an army of 85,000 soldiers to suppress. Nonetheless, he did not give up his idea of making Algeria a model where French colonists and Arabs could live and work together as equals. He traveled to Algiers for a second time on 3 May 1865, and this time he remained for a month, meeting with tribal leaders and local officials. He offered a wide amnesty to participants of the insurrection, and promised to name Arabs to high positions in his government. He also promised a large public works program of new ports, railroads, and roads. However, once again his plans met a major natural obstacle in 1866 and 1868, Algeria was struck by an epidemic of cholera, clouds of locusts, drought and famine, and his reforms were hindered by the French colonists, who voted massively against him in the plebiscites of his late reign. Up to 500,000 people died from the famine and epidemics.
In 1871, in response to prolonged famine and the French authorities' discriminatory treatment of Algerians, the
More importantly, Napoleon III changed the system of land tenure. While ostensibly well-intentioned, in effect this move destroyed the traditional system of land management and deprived many Algerians of land. While Napoleon did renounce state claims to tribal lands, he also began a process of dismantling tribal land ownership in favour of individual land ownership. This process was corrupted by French officials sympathetic to the French in Algeria who took much of the land they surveyed into public domain. In addition, many tribal leaders, chosen for loyalty to the French rather than influence in their tribe, immediately sold communal land for cash.
His attempted reforms were interrupted in 1864 by an Arab insurrection, which required more than a year and an army of 85,000 soldiers to suppress. Nonetheless, he did not give up his idea of making Algeria a model where French colonists and Arabs could live and work together as equals. He traveled to Algiers for a second time on 3 May 1865, and this time he remained for a month, meeting with tribal leaders and local officials. He offered a wide amnesty to participants of the insurrection, and promised to name Arabs to high positions in his government. He also promised a large public works program of new ports, railroads, and roads. However, once again his plans met a major natural obstacle in 1866 and 1868, Algeria was struck by an epidemic of cholera, clouds of locusts, drought and famine, and his reforms were hindered by the French colonists, who voted massively against him in the plebiscites of his late reign. Up to 500,000 people died from the famine and epidemics.
In 1871, in response to prolonged famine and the French authorities' discriminatory treatment of Algerians, the  In 1838, the French naval commander Abel Aubert du Petit-Thouars responded to complaints of the mistreatment of French Catholic missionary in the
In 1838, the French naval commander Abel Aubert du Petit-Thouars responded to complaints of the mistreatment of French Catholic missionary in the 
 Despite the signing of the 1860 Cobden–Chevalier Treaty, a historic free trade agreement between Britain and France, and the joint operations conducted by France and Britain in the Crimea, China and Mexico, diplomatic relations between Britain and France never became close during the colonial era.
Despite the signing of the 1860 Cobden–Chevalier Treaty, a historic free trade agreement between Britain and France, and the joint operations conducted by France and Britain in the Crimea, China and Mexico, diplomatic relations between Britain and France never became close during the colonial era. 
 A hallmark of the French colonial project in the late 19th century and early 20th century was the
A hallmark of the French colonial project in the late 19th century and early 20th century was the  Critics of French colonialism gained an international audience in the 1920s, and often used documentary reportage and access to agencies such as the
Critics of French colonialism gained an international audience in the 1920s, and often used documentary reportage and access to agencies such as the  During World War II, allied
During World War II, allied  Following the Vietnamese victory at Điện Biên Phủ and the signing of the 1954 Geneva Accords, France agreed to withdraw its forces from all its colonies in
Following the Vietnamese victory at Điện Biên Phủ and the signing of the 1954 Geneva Accords, France agreed to withdraw its forces from all its colonies in