|
French Conquest Of Algeria
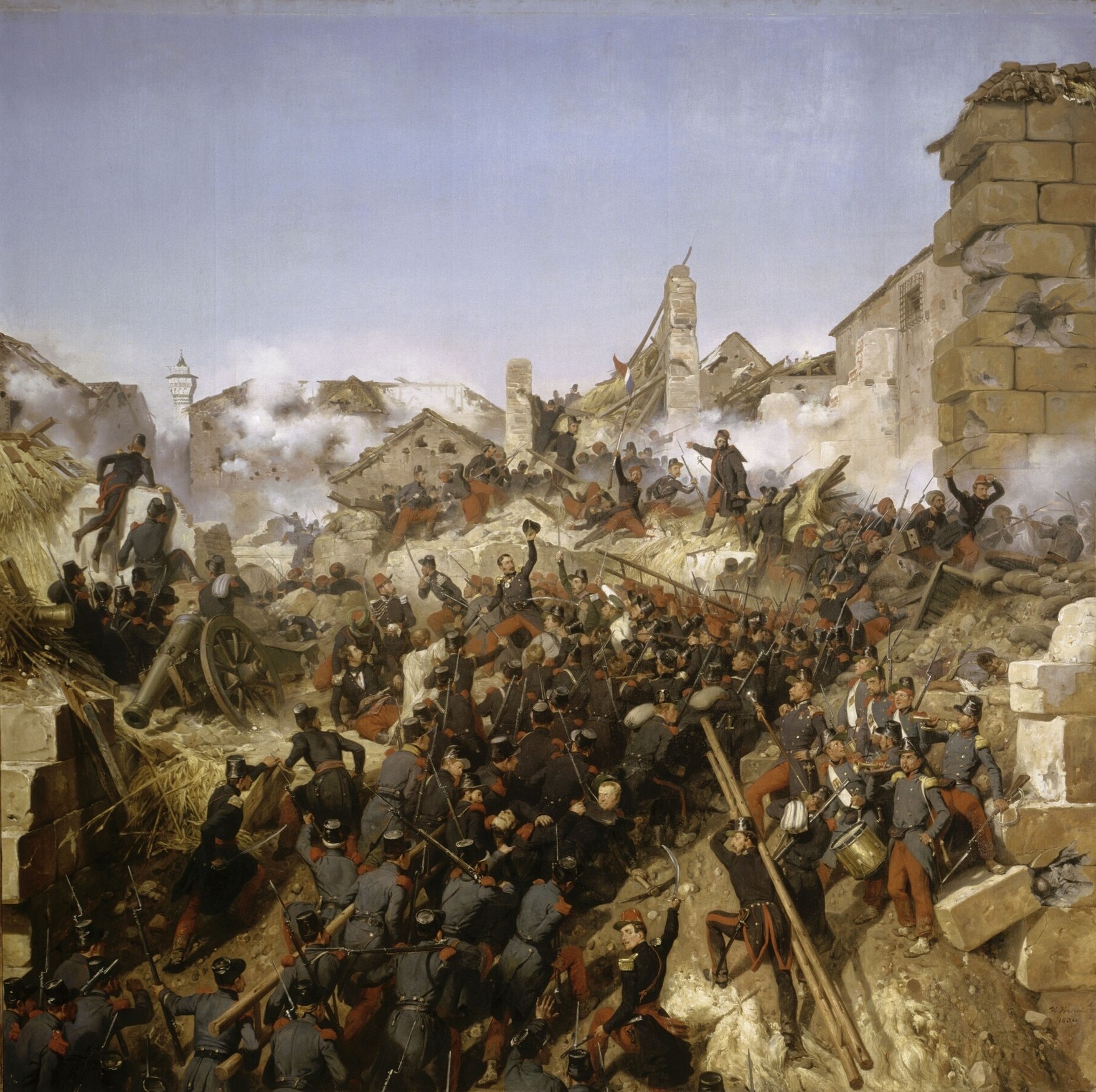
The French conquest of Algeria (; ) took place between 1830 and 1903. In 1827, an argument between Hussein Dey, the ruler of the Regency of Algiers, and the French consul (representative), consul escalated into a blockade, following which the July Monarchy of France invaded and quickly seized Algiers in 1830, and seized other coastal communities. Amid internal political strife in France, decisions were repeatedly taken to retain control of the territory, and additional military forces were brought in over the following years to quell resistance in the interior of the country. Initially, the Algerian resistance was mainly divided between forces under Ahmed Bey ben Mohamed Chérif at Constantine, Algeria, Constantine, seeking to reinstate the Regency of Algiers, primarily in the east, and nationalist forces in the west and center. Treaties with the nationalists under Emir Abdelkader enabled the French to first focus on the elimination of the remnants of the Deylik, achieved with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Colonial Empire
The French colonial empire () comprised the overseas Colony, colonies, protectorates, and League of Nations mandate, mandate territories that came under French rule from the 16th century onward. A distinction is generally made between the "First French colonial empire", that existed until 1814, by which time most of it had been lost or sold, and the "Second French colonial empire", which began with the French conquest of Algeria, conquest of Algiers in 1830. On the eve of World War I, France's colonial empire was List of largest empires, the second-largest in the world after the British Empire. France began to establish colonies in the French colonization of the Americas, Americas, the Caribbean, and French India, India in the 16th century but lost most of its possessions after its defeat in the Seven Years' War. The North American possessions were lost to Britain and Spain, but Louisiana (New France), Spain later returned Louisiana to France in 1800. The territory was then Loui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles X Of France
Charles X (Charles Philippe; 9 October 1757 – 6 November 1836) was King of France from 16 September 1824 until 2 August 1830. An uncle of the uncrowned Louis XVII and younger brother of reigning kings Louis XVI and Louis XVIII, he supported the latter in exile. After the Bourbon Restoration in France, Bourbon Restoration in 1814, Charles (as heir-presumptive) became the leader of the ultra-royalists, a radical monarchist faction within the French court that affirmed absolute monarchy by Divine Right of Kings, divine right and opposed the constitutional monarchy concessions towards Classical liberalism, liberals and the guarantees of civil liberties granted by the Charter of 1814. Charles gained influence within the French court after the assassination of his son Charles Ferdinand, Duke of Berry, in 1820 and succeeded his brother Louis XVIII in 1824. Charles's reign of almost six years proved to be deeply unpopular amongst the liberals in France from the moment of Coronation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Berthezène
Pierre, baron Berthezène (; 24 March 1775, Vendargues – 9 October 1847, Vendargues) was a French general. Life Early military career Pierre's parents, Jacques Berthezène and Marguerite Causse, were from a modest background. They chose a career in the church for him and the village priest taught him in preparation for the seminary at Montpellier. Berthezène was still studying when the French Revolution broke out. On 15 September 1793 he joined the 5th volunteer battalion of Hérault, amalgamated into the 7th provisional battle demi-brigade, which later became the 10th line infantry regiment in year 4. He rose to corporal, sergeant and sergeant-major on 17, 19 and 22 September. In this regiment he met other non-commissioned officers such as Lannes and Victor. Revolutionary wars He joined the armée des Pyrénées orientales, but a few days after the affair at Peyrestortes, the brigade went to reinforce the corps besieging Toulon. At the capture of the British redoubt whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Juchault De Lamoricière
Louis may refer to: People * Louis (given name), origin and several individuals with this name * Louis (surname) * Louis (singer), Serbian singer Other uses * Louis (coin), a French coin * HMS ''Louis'', two ships of the Royal Navy See also * Derived terms * King Louis (other) * Saint Louis (other) * Louis Cruise Lines * Louis dressing, for salad * Louis Quinze, design style Associated terms * Lewis (other) * Louie (other) * Luis (other) * Louise (other) * Louisville (other) Associated names * * Chlodwig, the origin of the name Ludwig, which is translated to English as "Louis" * Ladislav and László - names sometimes erroneously associated with "Louis" * Ludovic, Ludwig, Ludwick, Ludwik Ludwik () is a Polish given name. Notable people with the name include: * Ludwik Czyżewski, Polish WWII general * Ludwik Fleck (1896–1961), Polish medical doctor and biologist * Ludwik Gintel (1899–1973), Polish- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aimable Pélissier
Aimable-Jean-Jacques Pélissier, 1st Duc de Malakoff (6 November 179422 May 1864), was a Marshal of France. He served in Algeria where he became widely known for his cruel conduct and extermination of entire tribes. He also served elsewhere, and as a general commanded the French forces in the Crimean War. Biography Pélissier was born at Maromme ('' Seine Inférieure''), of a family of prosperous artisans, his father being employed in a powder-magazine. After attending the military college of La Flèche and the special school of St Cyr, he entered the army in 1815 as second-lieutenant in an artillery regiment. Brilliant examination results in 1819 secured his appointment to the staff. He served as '' aide-de-camp'' in the Spanish campaign of 1823, and in the Morea expedition 1828–1829. In 1830, he took part in the expedition to Algeria, and on his return was promoted to the rank of '' chef d'escadron''. Endnote: See Marbaud, ''Le Maréchal Pélissier'' (1863), Castille, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles-Marie Denys De Damrémont
Charles-Marie Denys, comte de Damrémont (8 February 1783 – 12 October 1837) was a French general and military governor of French Algeria. He was killed in combat during the siege of Constantine. Early life Charles-Marie Denys was born in Chaumont, Haute-Marne on 8 February 1783. His father was Antoine Denys de Damrémont (1730-1807) who belonged to a family of merchants from Bologna and who got rich in forges in the 17th century. Military training He entered the military school at Fontainebleau in 1803. After graduating from the school on 1804 he became a lieutenant in the 12th regiment of chasseurs à cheval. Campaigns of Napoleon He took part in the Wars of the War of the Third Coalition, Third and War of the Fourth Coalition, Fourth Coalitions. In 1807 he became aide-de-camp to Jean-Marie Defrance, General Defrance and afterwards to Auguste de Marmont, Marshal Marmont. In 1811 and 1812 Damrémont served in the Peninsular War but in 1813 he transferred to the Grande Armé ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sylvain Charles Valée
Sylvain-Charles, comte Valée (17 December 1773 – 16 August 1846), born in Brienne-le-Château, was a Marshal of France. Service in the revolutionary and Napoleonic wars Upon the outbreak of the French Revolution, Valée enlisted in the French revolutionary army and was sent to serve in the ''Army of the Nord''. Promoted to captain in 1795 he fought in the Rhine campaign of 1799-1800 including fighting at Hohenlinden. By1804 he was lieutenant colonel. When the war of the third coalition broke out in 1805 he was the inspector general of the train of the artillery reserve of the Grande Armée in this role he fought at Ulm, Austerlitz and Jena, distinguishing himself at Jena. In November 1806 Valée was made chief of staff of artillery of the Grande Armée.Valée was made colonel in a few months later along with command of the 1st Artillery Regiment which he led in the 1808 campaigning season. In 1809, Valée was sent to Spain seeing service at the siege of Zaragoza befo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Auguste Victor De Ghaisne De Bourmont
Louis may refer to: People * Louis (given name), origin and several individuals with this name * Louis (surname) * Louis (singer), Serbian singer Other uses * Louis (coin), a French coin * HMS ''Louis'', two ships of the Royal Navy See also * Derived terms * King Louis (other) * Saint Louis (other) * Louis Cruise Lines * Louis dressing, for salad * Louis Quinze, design style Associated terms * Lewis (other) * Louie (other) * Luis (other) * Louise (other) * Louisville (other) Associated names * * Chlodwig, the origin of the name Ludwig, which is translated to English as "Louis" * Ladislav and László - names sometimes erroneously associated with "Louis" * Ludovic, Ludwig, Ludwick, Ludwik Ludwik () is a Polish given name. Notable people with the name include: * Ludwik Czyżewski, Polish WWII general * Ludwik Fleck (1896–1961), Polish medical doctor and biologist * Ludwik Gintel (1899–1973), Polish-Israel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Émile Loubet
Émile François Loubet (; 30 December 183820 December 1929) was the 45th Prime Minister of France from February to December 1892 and later President of France from 1899 to 1906. Trained in law, he became Mayor (France), mayor of Montélimar, where he was noted as a forceful orator. He was elected to the Chamber of Deputies in 1876 and the Senate in 1885. He was appointed as a Republican minister under Carnot and Ribot. He was briefly Prime Minister of France in 1892. As President, he saw the successful Exposition Universelle (1900), Paris Exhibition of 1900, and the forging of the Entente Cordiale with the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, resolving their sharp differences over the Boer War and the Dreyfus Affair. Early life Loubet was born on 30 December 1838, the son of a peasant proprietor and Mayor (France), mayor of Marsanne, Drôme, Marsanne (Drôme). Admitted to the Parisian bar in 1862, he took his doctorate in law the next year. He was still a student when h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jules Grévy
François Judith Paul Grévy (15 August 1807 – 9 September 1891), known as Jules Grévy (), was a French people, French lawyer and politician who served as President of France from 1879 to 1887. He was a leader of the Opportunist Republicans, Moderate Republicans, and given that his predecessors were Monarchism in France, monarchists who tried without success to restore the French monarchy, Grévy is considered the first real Republicanism, republican president of France. During Grévy's presidency from 1879 to 1887, according to David Bell, there was a disunity among his cabinets. Only one survived more than a year. Grévy paid attention chiefly to defense, internal order, and foreign relations. Critics argue that Grévy's confusing approach to appointments set a bad precedent for handling crises. Grévy's son-in-law was implicated in a corruption scandal in 1887, and Grévy had to resign after exhausting the pool of willing politicians to form a fresh government. Born in a sm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |