Franconia Branch on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Franconia (german: Franken, ; Franconian dialect: ''Franggn'' ; bar, Frankn) is a region of Germany, characterised by its culture and Franconian dialect (German: ''Fränkisch'').
The three
online version
(PDF). The restructuring of the south German states by

 The German name for Franconia, ''Franken'', comes from the
The German name for Franconia, ''Franken'', comes from the
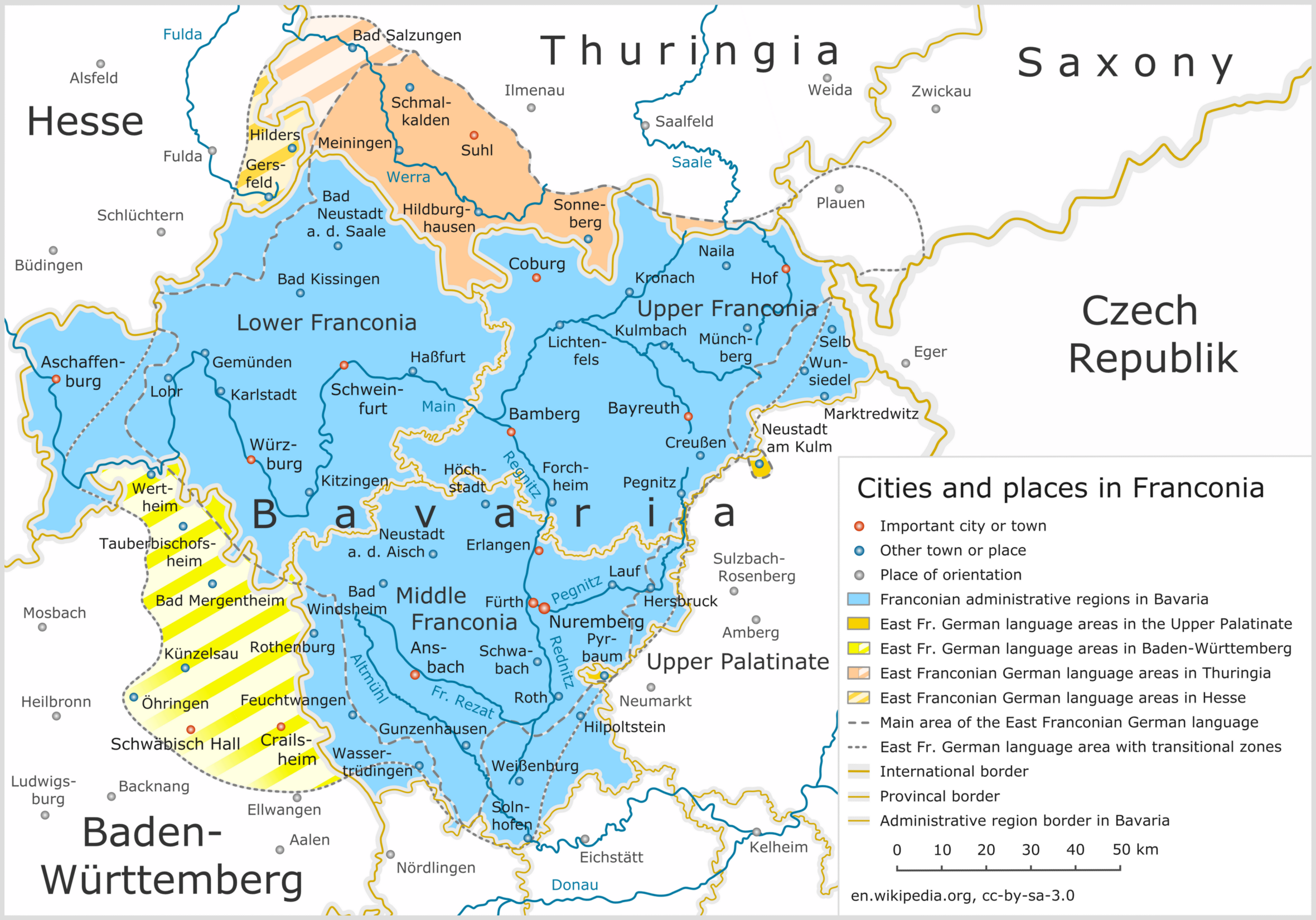 The Franconian lands lie principally in Bavaria, north and south of the sinuous River Main which, together with the left (southern) Regnitz tributary, including its Rednitz and Pegnitz headstreams, drains most of Franconia. Other large rivers include the upper Werra in Thuringia and the Tauber, as well as the upper Jagst and
The Franconian lands lie principally in Bavaria, north and south of the sinuous River Main which, together with the left (southern) Regnitz tributary, including its Rednitz and Pegnitz headstreams, drains most of Franconia. Other large rivers include the upper Werra in Thuringia and the Tauber, as well as the upper Jagst and
administrative regions
Administrative division, administrative unit,Article 3(1). country subdivision, administrative region, subnational entity, constituent state, as well as many similar terms, are generic names for geographical areas into which a particular, ind ...
of Lower, Middle and Upper Franconia (largest cities, respectively: Würzburg, Nuremberg and Bamberg
Bamberg (, , ; East Franconian: ''Bambärch'') is a town in Upper Franconia, Germany, on the river Regnitz close to its confluence with the river Main. The town dates back to the 9th century, when its name was derived from the nearby ' castle. C ...
) in the State of Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total lan ...
are part of the cultural region of Franconia, as are the adjacent Franconian-speaking South Thuringia South Thuringia (german: Südthüringen) refers to all the Franconia regions in the German Free State of Thuringia south of the Rennsteig and the Salzbogen, but including the entire former county of Kreis_Bad_Salzungen, Bad Salzungen. The region is, ...
, south of the Rennsteig
The () is a ridge walk as well as an historical boundary path in the Thuringian Forest, Thuringian Highland and Franconian Forest in Central Germany. The long-distance trail runs for about from and the valley in the northwest to and the r ...
ridge (largest city: Suhl), Heilbronn-Franconia (largest city: Schwäbisch Hall
Schwäbisch Hall (; "Swabian Hall"; from 1802 until 1934 and colloquially: ''Hall'' ) is a city in the German state of Baden-Württemberg located in the valley of the Kocher river, the longest tributary (together with its headwater Lein) of the ...
) in the state of Baden-Württemberg, and small parts of the state of Hesse.
Those parts of the Vogtland lying in the state of Saxony (largest city: Plauen
Plauen (; Czech language, Czech: ''Plavno'') is, with around 65,000 inhabitants, the fifth-largest city of Saxony, Germany after Leipzig, Dresden, Chemnitz and Zwickau, the second-largest city of the Vogtland after Gera, as well as the larges ...
) are sometimes regarded as Franconian as well, because the Vogtlandian
Vogtlandian (german: Vogtländisch, links=no ; Vogtländisch: ''Vuuchtländisch'', Klingenthal pronunciation: ) is an East Franconian dialect, spoken in Vogtland.
Distribution and history
Vogtlandian is mainly spoken in rural areas. Speakers are ...
dialects are mostly East Franconian. The inhabitants of Saxon Vogtland, however, mostly do not consider themselves as Franconian. On the other hand, the inhabitants of the Hessian
A Hessian is an inhabitant of the German state of Hesse.
Hessian may also refer to:
Named from the toponym
*Hessian (soldier), eighteenth-century German regiments in service with the British Empire
**Hessian (boot), a style of boot
**Hessian f ...
-speaking parts of Lower Franconia west of the Spessart mountains (largest city: Aschaffenburg) do consider themselves as Franconian. Heilbronn-Franconia's largest city of Heilbronn
Heilbronn () is a List of cities and towns in Germany, city in northern Baden-Württemberg, Germany, surrounded by Heilbronn (district), Heilbronn District. With over 126,000 residents, it is the sixth-largest city in the state.
From the late Mid ...
and its surrounding areas being South Franconian
South Franconian (german: Südfränkisch) or South Rhine Franconian (german: Südrheinfränkisch) is an Upper German dialect which is spoken in the northernmost part of Baden-Württemberg in Germany, around Karlsruhe, Mosbach and Heilbronn. Lik ...
-speaking, those are only sometimes regarded as Franconian.
Franconia's largest city and unofficial capital is Nuremberg, which is contiguous with Erlangen and Fürth, with which it forms a large conurbation, with around 1.3 million inhabitants.
The German word ''Franken''—Franconians—also refers to the ethnic group
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
, which is mainly to be found in this region. They are to be distinguished from the Germanic tribe of the Franks, and historically formed their easternmost settlement area. The origins of Franconia lie in the settlement of the Franks from the 6th century in the area probably populated until then mainly by the Elbe Germanic people in the Main river area, known from the 9th century as East Francia
East Francia (Medieval Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the East Franks () was a successor state of Charlemagne's Carolingian Empire, empire ruled by the Carolingian dynasty until 911. It was created through the Treaty of Verdun (843) which divided t ...
(''Francia Orientalis''). In the Middle Ages the region formed much of the eastern part of the Duchy of Franconia and, from 1500, the Franconian Circle.Rudolf Endres: "''Der Fränkische Reichskreis''. In: ''Hefte zur Bayerischen Geschichte und Kultur 29'', published by the Haus der Bayerischen Geschichte, Regensburg, 2003, p. 6, seonline version
(PDF). The restructuring of the south German states by
Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
, after the demise of the Holy Roman Empire, saw most of Franconia awarded to Bavaria.
Etymology
 The German name for Franconia, ''Franken'', comes from the
The German name for Franconia, ''Franken'', comes from the dative
In grammar, the dative case (abbreviated , or sometimes when it is a core argument) is a grammatical case used in some languages to indicate the recipient or beneficiary of an action, as in "Maria Jacobo potum dedit", Latin for "Maria gave Jacob a ...
plural form of ''Franke,'' a member of the Germanic tribe known as the Franks.
The name of the Franks
The name of the Franks (Latin ''Franci''), alongside the derived names of ''Francia'' and ''Franconia'' (and the adjectives ''Frankish'' and ''Franconian''), are derived from the name given to a Germanic tribal confederation which emerged in the ...
in turn derives from a word meaning "daring, bold", cognate with old Norwegian ''frakkr'', "quick, bold". Franks from the Middle and Lower Rhine gradually gained control of (and so gave their name to) what is now Franconia during the 6th to 8th centuries.
English distinguishes between ''Franks'' (the early medieval Germanic people) and ''Franconians'' in reference to the high medieval stem duchy
A stem duchy (german: Stammesherzogtum, from '' Stamm'', meaning "tribe", in reference to the Franks, Saxons, Bavarians and Swabians) was a constituent duchy of the German Empire at the time of the extinction of the Carolingian dynasty (death o ...
, following Middle Latin
Medieval Latin was the form of Literary Latin used in Roman Catholic Church, Roman Catholic Western Europe during the Middle Ages. In this region it served as the primary written language, though local languages were also written to varying deg ...
use of ''Francia'' for France vs. ''Franconia'' for the German duchy. In German the name ''Franken'' is equally used for both, while the French are called ''Franzosen'', after Old French ''françois
François () is a French masculine given name and surname, equivalent to the English name Francis.
People with the given name
* Francis I of France, King of France (), known as "the Father and Restorer of Letters"
* Francis II of France, Kin ...
'', from Latin ''franciscus'', from Late Latin ''Francus'', from ''Frank'', the Germanic tribe.
Geography
Overview
 The Franconian lands lie principally in Bavaria, north and south of the sinuous River Main which, together with the left (southern) Regnitz tributary, including its Rednitz and Pegnitz headstreams, drains most of Franconia. Other large rivers include the upper Werra in Thuringia and the Tauber, as well as the upper Jagst and
The Franconian lands lie principally in Bavaria, north and south of the sinuous River Main which, together with the left (southern) Regnitz tributary, including its Rednitz and Pegnitz headstreams, drains most of Franconia. Other large rivers include the upper Werra in Thuringia and the Tauber, as well as the upper Jagst and Kocher
The Kocher () is a -longincluding its source river Schwarzer Kocher right tributary of the Neckar in the north-eastern part of Baden-Württemberg, Germany. The name "Kocher" originates from its Celtic name "cochan" and probably means winding, mea ...
streams in the west, both right tributaries of the Neckar
The Neckar () is a river in Germany, mainly flowing through the southwestern state of Baden-Württemberg, with a short section through Hesse. The Neckar is a major right tributary of the Rhine. Rising in the Schwarzwald-Baar-Kreis near Schwenn ...
. In southern Middle Franconia, the Altmühl
The Altmühl (, la, Alchmona, Alcmana, Almonus)
s.v. is a river in flows towards the Danube; the Rhine–Main–Danube Canal crosses the European Watershed. The man-made
File:Rothenburg BW 4.JPG,
 Franconia may be distinguished from the regions that surround it by its peculiar historical factors and its cultural and especially linguistic characteristics, but it is not a political entity with a fixed or tightly defined area. As a result, it is debated whether some areas belong to Franconia or not. Pointers to a more precise definition of Franconia's boundaries include: the territories covered by the former Duchy of Franconia and former Franconian Circle,Rudolf Endres: ''Der Fränkische Reichskreis.'' In: ''Hefte zur Bayerischen Geschichte und Kultur 29,'' published by the House of Bavarian History, Regensburg, 2003, p. 37, se
Franconia may be distinguished from the regions that surround it by its peculiar historical factors and its cultural and especially linguistic characteristics, but it is not a political entity with a fixed or tightly defined area. As a result, it is debated whether some areas belong to Franconia or not. Pointers to a more precise definition of Franconia's boundaries include: the territories covered by the former Duchy of Franconia and former Franconian Circle,Rudolf Endres: ''Der Fränkische Reichskreis.'' In: ''Hefte zur Bayerischen Geschichte und Kultur 29,'' published by the House of Bavarian History, Regensburg, 2003, p. 37, se
online version
(pdf) the range of the East Franconian dialect group, the common culture and history of the region and the use of the Franconian Rake on coats of arms, flags and seals. However, a sense of popular consciousness of being Franconian is only detectable from the 19th century onwards, which is why the circumstances of the emergence of a Frankish identity are disputed. Franconia has many cultural peculiarities which have been adopted from other regions and further developed. The following regions are counted as part of Franconia today: the Bavarian provinces of Lower Franconia, Upper Franconia and Middle Franconia, the municipality of
Bayerischer Rundfunk, Bayern 2 and the Hessian-speaking region around Aschaffenburg, which was never part of the Franconian Imperial Circle. The affiliation of the city of
see online pdf
is also controversial. Moreover, the sense of belonging to Franconia in the Frankish-speaking areas of Upper Palatinate, South Thuringia and Hesse is sometimes less marked.

 The region of Franconia is divided among the states of Hesse, Thuringia, Bavaria and Baden-Württemberg. The largest part of Franconia, both by population and area, belongs to the Free State of Bavaria and is divided into the three administrative regions (''Regierungsbezirke'') of Middle Franconia (capital: Ansbach), Upper Franconia (capital:
The region of Franconia is divided among the states of Hesse, Thuringia, Bavaria and Baden-Württemberg. The largest part of Franconia, both by population and area, belongs to the Free State of Bavaria and is divided into the three administrative regions (''Regierungsbezirke'') of Middle Franconia (capital: Ansbach), Upper Franconia (capital:
 The two most important rivers of the region are the Main and its primary tributary, the Regnitz. The tributaries of these two rivers in Franconia are the Tauber, Pegnitz, Rednitz and
The two most important rivers of the region are the Main and its primary tributary, the Regnitz. The tributaries of these two rivers in Franconia are the Tauber, Pegnitz, Rednitz and
s.v. is a river in flows towards the Danube; the Rhine–Main–Danube Canal crosses the European Watershed. The man-made
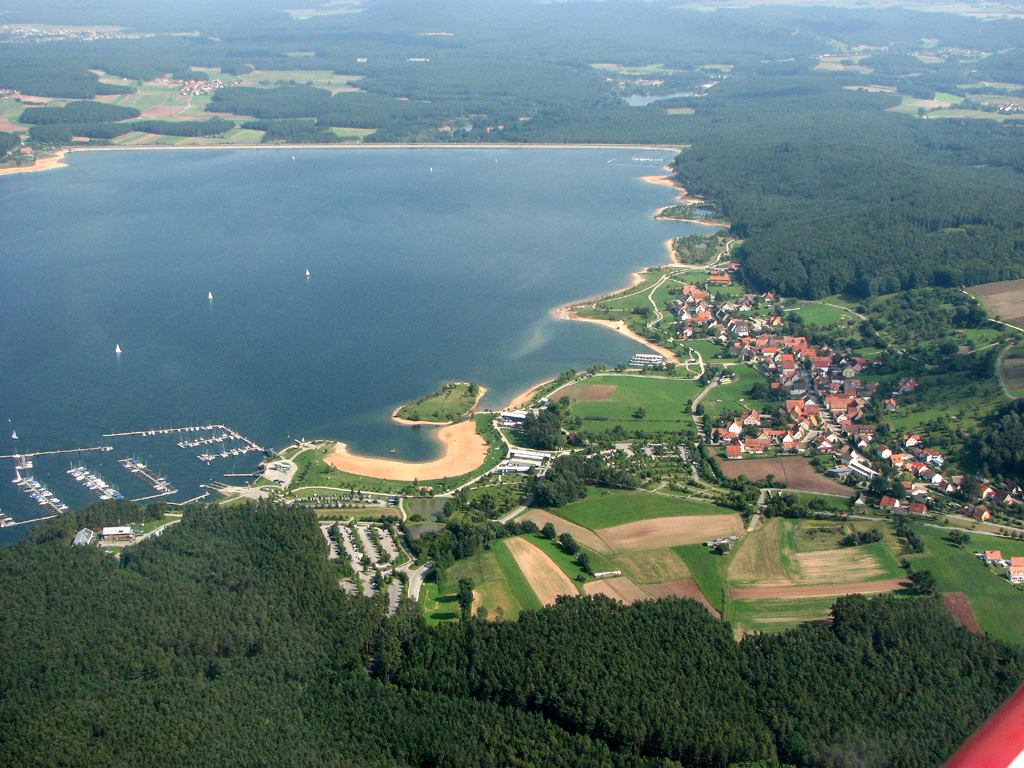
Franconian Lake District
The Franconian Lake District lies south-west of Nuremberg in northern Bavaria, Germany. It was created as a result of one of Germany's largest water-management projects and was completed by the flooding of the Großer Brombachsee (" Great Bromba ...
has become a popular destination for day-trippers and tourists.
The landscape is characterized by numerous '' Mittelgebirge'' ranges of the German Central Uplands. The Western natural border of Franconia is formed by the Spessart and Rhön Mountains
The Rhön Mountains () are a group of low mountains (or ''Mittelgebirge'') in central Germany, located around the border area where the states of Hesse, Bavaria and Thuringia come together. These mountains, which are at the extreme southeast end o ...
, separating it from the former Rhenish Franconian lands around Aschaffenburg (officially part of Lower Franconia), whose inhabitants speak Hessian dialects. To the north rise the Rennsteig
The () is a ridge walk as well as an historical boundary path in the Thuringian Forest, Thuringian Highland and Franconian Forest in Central Germany. The long-distance trail runs for about from and the valley in the northwest to and the r ...
ridge of the Thuringian Forest, the Thuringian Highland
The Thuringian Highland, Thuringian Highlands or Thuringian-Vogtlandian Slate MountainsKohl, Horst; Marcinek, Joachim and Nitz, Bernhard (1986). ''Geography of the German Democratic Republic'', VEB Hermann Haack, Gotha, p. 7 ff. . (german: Thüring ...
and the Franconian Forest
View to Döbraberg
The Franconian Forest''Franconian Forest''
at www.britannica.com. Acce ...
, the border with the at www.britannica.com. Acce ...
Upper Saxon
Upper Saxon (german: Obersächsisch, ; ) is an East Central German language spoken in much of the modern German state of Saxony and in adjacent parts of southeastern Saxony-Anhalt and eastern Thuringia. As of the early 21st century, it's mostl ...
lands of Thuringia. The Franconian lands include the present-day South Thuringian districts of Schmalkalden-Meiningen, Hildburghausen and Sonneberg, the historical '' Gau'' of Grabfeld
The Grabfeld is a region in Germany, on the border between Bavaria and Thuringia. It is situated southeast of the Rhön Mountains. Its highest elevation is 679 metres high in the little Gleichberge mountain range. The Grabfeld gave its name to t ...
, held by the House of Henneberg from the 11th century and later part of the Wettin duchy of Saxe-Meiningen.
In the east, the Fichtel Mountains
The Fichtel MountainsRandlesome, C. et al. (2011). ''Business Cultures in Europe'', 2nd ed., Routledge, Abingdon and New York, p. 52. . (german: Fichtelgebirge, cs, Smrčiny), form a small horseshoe-shaped mountain range in northeastern Bavaria ...
lead to Vogtland, Bohemian Egerland (''Chebsko'') in the Czech Republic, and the Bavarian Upper Palatinate. The hills of the Franconian Jura in the south mark the border with the Upper Bavarian region (''Altbayern
Altbayern ( Bavarian: ''Oidbayern'', also written Altbaiern, English: "Old Bavaria") is the territory and people of the three oldest parts of the Free State of Bavaria, which were earlier known as Kurbayern (English: "Electoral Bavaria") after the ...
''), historical Swabia
Swabia ; german: Schwaben , colloquially ''Schwabenland'' or ''Ländle''; archaic English also Suabia or Svebia is a cultural, historic and linguistic region in southwestern Germany.
The name is ultimately derived from the medieval Duchy of ...
, and the Danube basin. The northern parts of the Upper Bavarian Eichstätt District, territory of the historical Bishopric of Eichstätt
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associate ...
, are also counted as part of Franconia.
In the west, Franconia proper comprises the Tauber Franconia
The region of Tauber Franconia (german: Tauberfranken) is a part of the region of Franconia, most of which lies in the German state of Baden-Württemberg. Tauber Franconia is almost coextensive with the county of Main-Tauber-Kreis, which is bisecte ...
region along the Tauber river, which is largely part of the Main-Tauber-Kreis in Baden-Württemberg. The state's larger Heilbronn-Franken region also includes the adjacent Hohenlohe and Schwäbisch Hall districts. In the city of Heilbronn
Heilbronn () is a List of cities and towns in Germany, city in northern Baden-Württemberg, Germany, surrounded by Heilbronn (district), Heilbronn District. With over 126,000 residents, it is the sixth-largest city in the state.
From the late Mid ...
, beyond the Haller Ebene
The Haller Ebene is a plain in the German state of Baden-Württemberg which forms part of the Hohenlohe Plain and stretches from Bad Mergentheim via Rothenburg, Uffenheim, Crailsheim, Öhringen as far as Schwäbisch Hall
Schwäbisch Hall (; " ...
plateau, South Franconian
South Franconian (german: Südfränkisch) or South Rhine Franconian (german: Südrheinfränkisch) is an Upper German dialect which is spoken in the northernmost part of Baden-Württemberg in Germany, around Karlsruhe, Mosbach and Heilbronn. Lik ...
dialects are spoken. Furthermore, in those easternmost parts of the Neckar-Odenwald-Kreis which had formerly belonged to the Bishopric of Würzburg, the inhabitants have preserved their Franconian identity. Franconian areas in East Hesse along Spessart and Rhön comprise Gersfeld
Gersfeld is a town in the district of Fulda, in Hesse, Germany. It is situated on the Fulda River, in the Rhön Mountains, southeast of Fulda. It belonged to the abbey-principality of Fulda before secularisation in 1803. It then belonged to the ...
and Ehrenberg.
The two largest cities of Franconia are Nuremberg and Fürth. Though located on the southeastern periphery of the area, the Nuremberg metropolitan area is often identified as the economic and cultural centre of Franconia. Further cities in Bavarian Franconia include Fürth, Erlangen, Bayreuth
Bayreuth (, ; bar, Bareid) is a town in northern Bavaria, Germany, on the Red Main river in a valley between the Franconian Jura and the Fichtelgebirge Mountains. The town's roots date back to 1194. In the 21st century, it is the capital of U ...
, Bamberg
Bamberg (, , ; East Franconian: ''Bambärch'') is a town in Upper Franconia, Germany, on the river Regnitz close to its confluence with the river Main. The town dates back to the 9th century, when its name was derived from the nearby ' castle. C ...
, Aschaffenburg, Schweinfurt, Hof, Coburg, Ansbach and Schwabach. The major (East) Franconian towns in Baden-Württemberg are Schwäbisch Hall
Schwäbisch Hall (; "Swabian Hall"; from 1802 until 1934 and colloquially: ''Hall'' ) is a city in the German state of Baden-Württemberg located in the valley of the Kocher river, the longest tributary (together with its headwater Lein) of the ...
on the Kocher — the imperial city
In the Holy Roman Empire, the collective term free and imperial cities (german: Freie und Reichsstädte), briefly worded free imperial city (', la, urbs imperialis libera), was used from the fifteenth century to denote a self-ruling city that ...
declared itself "Swabian" in 1442 — and Crailsheim on the Jagst river. The main towns in Thuringia are Suhl and Meiningen
Meiningen () is a town in the southern part of the state of Thuringia, Germany. It is located in the region of Franconia and has a population of around 25,000 (2021).
.
Rothenburg Rothenburg is a German language placename and refers to:
Places
*Rothenburg ob der Tauber, Bavaria, Germany
*Rothenburg, Oberlausitz, Saxony, Germany
*Rothenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Saxony-Anhalt, Germany
*Rothenburg, Switzerland, Canton of Lucerne, S ...
is one of the best known towns in Franconia
File:Walberla 2008.jpg, Walberla in Franconia
File:Möhrendorf Vierzigmannrad Flügel.jpg, Water wheel at the Regnitz
File:Nuremberg panorama morning 3.jpg, Nuremberg is the largest city of Franconia
File:Aerial image of the Coburg Fortress.jpg, Aerial view of the Veste Coburg
Extent
 Franconia may be distinguished from the regions that surround it by its peculiar historical factors and its cultural and especially linguistic characteristics, but it is not a political entity with a fixed or tightly defined area. As a result, it is debated whether some areas belong to Franconia or not. Pointers to a more precise definition of Franconia's boundaries include: the territories covered by the former Duchy of Franconia and former Franconian Circle,Rudolf Endres: ''Der Fränkische Reichskreis.'' In: ''Hefte zur Bayerischen Geschichte und Kultur 29,'' published by the House of Bavarian History, Regensburg, 2003, p. 37, se
Franconia may be distinguished from the regions that surround it by its peculiar historical factors and its cultural and especially linguistic characteristics, but it is not a political entity with a fixed or tightly defined area. As a result, it is debated whether some areas belong to Franconia or not. Pointers to a more precise definition of Franconia's boundaries include: the territories covered by the former Duchy of Franconia and former Franconian Circle,Rudolf Endres: ''Der Fränkische Reichskreis.'' In: ''Hefte zur Bayerischen Geschichte und Kultur 29,'' published by the House of Bavarian History, Regensburg, 2003, p. 37, seonline version
(pdf) the range of the East Franconian dialect group, the common culture and history of the region and the use of the Franconian Rake on coats of arms, flags and seals. However, a sense of popular consciousness of being Franconian is only detectable from the 19th century onwards, which is why the circumstances of the emergence of a Frankish identity are disputed. Franconia has many cultural peculiarities which have been adopted from other regions and further developed. The following regions are counted as part of Franconia today: the Bavarian provinces of Lower Franconia, Upper Franconia and Middle Franconia, the municipality of
Pyrbaum
Pyrbaum is a municipality in the district of Neumarkt in Bavaria in Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and ...
in the county of Neumarkt in der Oberpfalz, the northwestern part of the Upper Bavarian county of Eichstätt (covering the same area as the old county of Alt-Eichstätt), the East Franconian counties of South Thuringia South Thuringia (german: Südthüringen) refers to all the Franconia regions in the German Free State of Thuringia south of the Rennsteig and the Salzbogen, but including the entire former county of Kreis_Bad_Salzungen, Bad Salzungen. The region is, ...
, parts of Fulda
Fulda () (historically in English called Fuld) is a town in Hesse, Germany; it is located on the river Fulda and is the administrative seat of the Fulda district (''Kreis''). In 1990, the town hosted the 30th Hessentag state festival.
History ...
and the Odenwaldkreis in Hesse, the Baden-Württemberg regions of Tauber Franconia
The region of Tauber Franconia (german: Tauberfranken) is a part of the region of Franconia, most of which lies in the German state of Baden-Württemberg. Tauber Franconia is almost coextensive with the county of Main-Tauber-Kreis, which is bisecte ...
and Hohenlohe as well as the region around the Badenian Buchen.
In individual cases the membership of some areas is disputed. These include the Bavarian language area of Alt- Eichstätt''Was ist fränkisch? Wie eine Region definiert wird''Bayerischer Rundfunk, Bayern 2 and the Hessian-speaking region around Aschaffenburg, which was never part of the Franconian Imperial Circle. The affiliation of the city of
Heilbronn
Heilbronn () is a List of cities and towns in Germany, city in northern Baden-Württemberg, Germany, surrounded by Heilbronn (district), Heilbronn District. With over 126,000 residents, it is the sixth-largest city in the state.
From the late Mid ...
, whose inhabitants do not call themselves Franks,Ulrich Maier (Justinus-Kerner-Gymnasium Weinsberg): ''Schwäbisch oder fränkisch? Mundart im Raum Heilbronn Bausteine zu einer Unterrichtseinheit.'see online pdf
is also controversial. Moreover, the sense of belonging to Franconia in the Frankish-speaking areas of Upper Palatinate, South Thuringia and Hesse is sometimes less marked.
Administrative divisions
Bayreuth
Bayreuth (, ; bar, Bareid) is a town in northern Bavaria, Germany, on the Red Main river in a valley between the Franconian Jura and the Fichtelgebirge Mountains. The town's roots date back to 1194. In the 21st century, it is the capital of U ...
) and Lower Franconia (capital: Würzburg). The name of these regions, as in the case of Upper
Upper may refer to:
* Shoe upper or ''vamp'', the part of a shoe on the top of the foot
* Stimulant, drugs which induce temporary improvements in either mental or physical function or both
* ''Upper'', the original film title for the 2013 found fo ...
and Lower Bavaria, refers to their situation with respect to the river Main. Thus Upper Franconia lies on the upper reaches of the river, Lower Franconia on its lower reaches and Middle Franconia lies in between, although the Main itself does not flow through Middle Franconia. Where the boundaries of these three provinces meet (the ' tripoint') is the ''Dreifrankenstein
The Dreifrankenstein (German for ''Three Franconias Stone'') is a boundary stone that marks the tripoint where the three Franconian provinces of Upper, Middle and Lower Franconia meet in southern Germany. As part of the regional reforms in 1972 ...
'' ("Three Franconias Rock").
Small parts of Franconia also belong to the Bavarian regions of Upper Palatinate and Upper Bavaria.
The Franconian territories of Baden-Württemberg are the regions of Tauber Franconia
The region of Tauber Franconia (german: Tauberfranken) is a part of the region of Franconia, most of which lies in the German state of Baden-Württemberg. Tauber Franconia is almost coextensive with the county of Main-Tauber-Kreis, which is bisecte ...
and Hohenlohe (which belong to the Heilbronn-Franconia Region
Heilbronn-Franken is a region in northeastern Baden-Württemberg, Germany, in the Stuttgart (region), Stuttgart subdivision (Regierungsbezirk). It consists of the former Free imperial city of Heilbronn, Heilbronn (district), Heilbronn district an ...
with its office in Heilbronn and form part of the Stuttgart Region
Stuttgart Region (Baden-Württemberg, Germany) is an urban agglomeration at the heart of the Stuttgart Metropolitan Region. It consists of the city of Stuttgart and the surrounding districts of Ludwigsburg, Esslingen, Böblingen, Rems-Murr and ...
) and the area around the Badenian Buchen in the Rhein-Neckar Region.
The Franconian parts of Thuringia (Henneberg Franconia
Henneberg Franconia (german: Henneberg-Franken) is an historically correct term for the Franconian part of the Free State of Thuringia in Germany that is generally referred to as South Thuringia (''Südthüringen''). The region is almost exactly ...
) lie within the Southwest Thuringia Planning Region.
The Franconian regions in Hesse form the smaller parts of the districts of Fulda
Fulda () (historically in English called Fuld) is a town in Hesse, Germany; it is located on the river Fulda and is the administrative seat of the Fulda district (''Kreis''). In 1990, the town hosted the 30th Hessentag state festival.
History ...
( Kassel region) and the Odenwaldkreis ( Darmstadt region), or lie on the borders with Bavaria or Thuringia.
Rivers and lakes
 The two most important rivers of the region are the Main and its primary tributary, the Regnitz. The tributaries of these two rivers in Franconia are the Tauber, Pegnitz, Rednitz and
The two most important rivers of the region are the Main and its primary tributary, the Regnitz. The tributaries of these two rivers in Franconia are the Tauber, Pegnitz, Rednitz and Franconian Saale
The Franconian Saale (german: Fränkische Saale) is a 140 km long river in Bavaria, Germany. It is a right-bank tributary of the Main, in Lower Franconia. It should not be confused with the larger Saxon Saale (german: Sächsische Saale), whi ...
. Other major rivers in the region are the Jagst and Kocher
The Kocher () is a -longincluding its source river Schwarzer Kocher right tributary of the Neckar in the north-eastern part of Baden-Württemberg, Germany. The name "Kocher" originates from its Celtic name "cochan" and probably means winding, mea ...
in Hohenlohe-Franconia, which empty into the Neckar
The Neckar () is a river in Germany, mainly flowing through the southwestern state of Baden-Württemberg, with a short section through Hesse. The Neckar is a major right tributary of the Rhine. Rising in the Schwarzwald-Baar-Kreis near Schwenn ...
north of Heilbronn in Baden-Württemberg, the Altmühl
The Altmühl (, la, Alchmona, Alcmana, Almonus)
s.v. is a river in and the
 Franconia's flora is dominated by deciduous and coniferous forests. Natural forests in Franconia occur mainly in the ranges of the Spessart, Franconian Forest, Odenwald and Steigerwald. The Nuremberg ''Reichswald'' is another great forest, located within the metropolitan region of Nuremberg. Other large areas of forest in the region are the Mönchswald, the Reichsforst in the Fichtel Mountains and the
Franconia's flora is dominated by deciduous and coniferous forests. Natural forests in Franconia occur mainly in the ranges of the Spessart, Franconian Forest, Odenwald and Steigerwald. The Nuremberg ''Reichswald'' is another great forest, located within the metropolitan region of Nuremberg. Other large areas of forest in the region are the Mönchswald, the Reichsforst in the Fichtel Mountains and the
s.v. is a river in and the
Wörnitz
Wörnitz is a municipality in the district of Ansbach, in Bavaria, Germany. It is situated on the river Wörnitz, west of Ansbach
Ansbach (; ; East Franconian: ''Anschba'') is a city in the German state of Bavaria. It is the capital of ...
in Middle Franconia, both tributaries of the Danube, and the upper and middle reaches of the Werra, the right-hand headstream of the Weser. In the northeast of Upper Franconia rise two left-hand tributaries of the Elbe: the Saxon Saale
The Saale (), also known as the Saxon Saale (german: Sächsische Saale) and Thuringian Saale (german: Thüringische Saale), is a river in Germany and a left-bank tributary of the Elbe. It is not to be confused with the smaller Franconian Saale, ...
and the Eger.
The Main-Danube Canal connects the Main and Danube across Franconia, running from Bamberg via Nuremberg to Kelheim. It thus complements the Rhine, Main and Danube, helping to ensure a continuous navigable waterway between the North Sea and the Black Sea. In Franconia, there are only a few, often very small, natural lakes. This is due to fact that most natural lakes in Germany are glacial or volcanic in origin, and Franconia escaped both influences in recent earth history. Among the largest waterbodies are reservoirs, which are mostly used as water reserves for the relatively dry landscapes of Franconia. These includes the waters of the Franconian Lake District
The Franconian Lake District lies south-west of Nuremberg in northern Bavaria, Germany. It was created as a result of one of Germany's largest water-management projects and was completed by the flooding of the Großer Brombachsee (" Great Bromba ...
, which was established in the 1970s and is also a tourist attraction. The heart of these lakes is the Großer Brombachsee
Großer Brombachsee is a reservoir in the Franconian Lake District
The Franconian Lake District lies south-west of Nuremberg in northern Bavaria, Germany. It was created as a result of one of Germany's largest water-management projects and was ...
, which has an area of 8.7 km2 and is thus the largest waterbody in Franconia by surface area.
Hills, mountains and plains
SeveralCentral Upland
The Central UplandsDickinson (1964), p.18 ff. (german: die MittelgebirgeN.B. In German die ''Mittelgebirge'' (plural) refers to the Central Uplands; das ''Mittelgebirge'' refers to a low mountain range or upland region (''Mittel'' = "medium" and ...
ranges dominate the Franconian countryside. In the southeast, Franconia is shielded from the rest of Bavaria by the Franconian Jura. In the east, the Fichtel Mountains
The Fichtel MountainsRandlesome, C. et al. (2011). ''Business Cultures in Europe'', 2nd ed., Routledge, Abingdon and New York, p. 52. . (german: Fichtelgebirge, cs, Smrčiny), form a small horseshoe-shaped mountain range in northeastern Bavaria ...
form the border; in the north are Franconian Forest
View to Döbraberg
The Franconian Forest''Franconian Forest''
at www.britannica.com. Acce ...
, the Thuringian Forest, the at www.britannica.com. Acce ...
Rhön Mountains
The Rhön Mountains () are a group of low mountains (or ''Mittelgebirge'') in central Germany, located around the border area where the states of Hesse, Bavaria and Thuringia come together. These mountains, which are at the extreme southeast end o ...
and the Spessart form a kind of natural barrier. To the west are the Franconian Heights
The Franconian HeightsBavarian State Chancellery, ''Information about Bavaria'', 1981, p. 11. (german: Frankenhöhe) are a hill ridge, up to , in Bavaria and Baden-Württemberg in South Germany.
Location and boundaries
The Franconian Heights l ...
and the Swabian-Franconian Forest
The Swabian-Franconian Forest (german: Schwäbisch-Fränkischen Waldberge, also ''Schwäbisch-Fränkischer Wald'') is a mainly forested, deeply incised upland region, 1,187 km² in area and up to , in the northeast of Baden-Württemberg. It fo ...
. In the Franconian part of South Hesse is the Odenwald
The Odenwald () is a low mountain range in the German states of Hesse, Bavaria and Baden-Württemberg.
Location
The Odenwald is located between the Upper Rhine Plain with the Bergstraße and the ''Hessisches Ried'' (the northeastern section ...
. Parts of the southern Thuringian Forest border on Franconia. The most important hill ranges in the interior of the region are the Steigerwald and the Franconian Jura with their sub-ranges of Hahnenkamm
Hahnenkamm (means "comb") may refer to
*Hahnenkamm (Verwaltungsgemeinschaft), a federation of municipalities in Bavaria, Germany
* Hahnenkamm, Greenland, a mountain in the Stauning Alps, Greenland
*Hahnenkamm, Kitzbühel
The Hahnenkamm is a mo ...
and Franconian Switzerland
Franconian Switzerland (german: Fränkische Schweiz) is an upland in Upper Franconia, Bavaria, Germany and a popular tourist retreat. Located between the River Pegnitz in the east and the south, the River Regnitz in the west and the River Main i ...
. The highest mountain in Franconia is the Schneeberg in the Fichtel Mountains which is . Other well-known mountains include the Ochsenkopf (1,024mSource: the BfN
The German Federal Agency for Nature Conservation (german: Bundesamt für Naturschutz, ''BfN'') is the German government's scientific authority with responsibility for national and international nature conservation. BfN is one of the government' ...
map), the Kreuzberg (927.8m) and the Hesselberg
Hesselberg (; 689 m above sea level) is the highest point in Middle Franconia and the Franconian Jura and is situated 60 km south west of Nuremberg, Germany. The mountain stands isolated and far from the center of the Franconian Jura, i ...
(689.4m). The outliers of the region include the Hesselberg and the Gleichberge. The lowest point in Franconia is the water level of the river Main in Kahl which lies at a height of 100 metres above sea level.
In addition to the hill and mountain ranges, there are also several very level areas, including the Middle Franconian Basin
Middle or The Middle may refer to:
* Centre (geometry), the point equally distant from the outer limits.
Places
* Middle (sheading), a subdivision of the Isle of Man
* Middle Bay (disambiguation)
* Middle Brook (disambiguation)
* Middle Creek (di ...
and the Hohenlohe Plain
The House of Hohenlohe () is a German princely dynasty. It ruled an immediate territory within the Holy Roman Empire which was divided between several branches. The Hohenlohes became imperial counts in 1450. The county was divided numerous time ...
. In the south of Franconia are smaller parts of the flat Nördlinger Ries, one of the best preserved impact craters on earth.
Forests, reserves, flora and fauna
 Franconia's flora is dominated by deciduous and coniferous forests. Natural forests in Franconia occur mainly in the ranges of the Spessart, Franconian Forest, Odenwald and Steigerwald. The Nuremberg ''Reichswald'' is another great forest, located within the metropolitan region of Nuremberg. Other large areas of forest in the region are the Mönchswald, the Reichsforst in the Fichtel Mountains and the
Franconia's flora is dominated by deciduous and coniferous forests. Natural forests in Franconia occur mainly in the ranges of the Spessart, Franconian Forest, Odenwald and Steigerwald. The Nuremberg ''Reichswald'' is another great forest, located within the metropolitan region of Nuremberg. Other large areas of forest in the region are the Mönchswald, the Reichsforst in the Fichtel Mountains and the Selb Forest
Selb is a town in the district of Wunsiedel, in Upper Franconia, Bavaria, Germany. It is situated in the Fichtelgebirge, on the border with the Czech Republic, 20 km northwest of Cheb and 23 km southeast of Hof.
Selb is well known fo ...
. In the river valleys along the Main and Tauber, the countryside was developed for viticulture. In Spessart there are great oak forests. Also widespread are calcareous grasslands, extensively used pastures on very oligotrophic
An oligotroph is an organism that can live in an environment that offers very low levels of nutrients. They may be contrasted with copiotrophs, which prefer nutritionally rich environments. Oligotrophs are characterized by slow growth, low rates of ...
, poor sites. In particular, the southern Franconian Jura, with the Altmühl Valley
The Altmühl (, la, Alchmona, Alcmana, Almonus)
s.v. is a river in , is characterized by poor grassland of this type. Many of these places have been designated as a
: ''Mittelfranken'', stellvertretend für alle Europäischen Vogelschutzgebieten in Franken There are also numerous Special Areas of Conservation and protected landscapes. In Franconia there are very many tufas, raised stream beds near river sources within the
, retrieved 2 Jun 2014. and

 Only in the extreme northeast of Franconia and in the Spessart are there
Only in the extreme northeast of Franconia and in the Spessart are there
online
), p. 4 Rocks which were unchanged or only lightly metamorphosed, because they had been deformed at shallow crustal depths, include the Lower Carboniferous shale and greywacke of Franconian Forest. The Fichtel mountains, the Münchberg Plateau and the Spessart, by contrast, have more metamorphic rocks ( phyllite, schist,
online
), p. 24 While the Fichtel and Franconian Forest can be assigned to the Saxo-Thuringian Zone of Central European Variscan orogeny, the Spessart belongs to the Central German Crystalline Zone. The Münchberg mass is variously attributed to the Saxo-Thuringian or Moldanubian Zones. A substantially larger part of the shallow subsurface in Franconia comprises Mesozoic, unmetamorphosed, unfolded rocks of the
online
), p. 26 The regional geological element of the South German Scarplands is the Franconian Platform (''Süddeutsche Großscholle''). At the so-called Franconian Line, a significant fault line, the Saxo-Thuringian-Moldanubian basement was uplifted in places up to 2000 m above the Franconian Platform. The western two-thirds of Franconia is dominated by the Triassic with its sandstones,
online
), p. 40 ff. Following a drop in the sea level towards the end of the Upper Jurassic, larger areas also became part of the mainland at the beginning of the subsequent Cretaceous period. During the Upper Cretaceous, the sea advanced again up to the area of the Franconian Jura. At the end of the Cretaceous, the sea then retreated again from the region. In addition, large parts of South and Central Germany experienced a general uplift -or in areas where the basement had broken through a substantial uplift - the course of formation of the Alps during the Tertiary. Since then, Franconia has been mainly influenced by erosion and weathering (especially in the Jura in the form of
 The oldest macrofossils in Franconia, which are also the oldest in Bavaria, are archaeocyatha, sponge-like, goblet-shaped marine organisms, which were discovered in 2013 in a limestone block of Late Lower Cambrian age, about 520 million years old. The block comes from the vicinity
The oldest macrofossils in Franconia, which are also the oldest in Bavaria, are archaeocyatha, sponge-like, goblet-shaped marine organisms, which were discovered in 2013 in a limestone block of Late Lower Cambrian age, about 520 million years old. The block comes from the vicinity
online
There the deposits are somewhat younger (Upper Bunter Sandstone), and the corresponding stratigraphic interval is called the Franconian Chirotherium Beds (''Fränkische Chirotherienschichten''). Among the less significant body fossil records of vertebrates are the procolophonid ''Anomoiodon liliensterni'' from
 Fossil finds show that the region was already settled by Caveman, primitive man, ''Homo erectus'', in the middle Last Glacial Period, Ice Age about 600,000 years ago. Probably the oldest human remains in the Bavarian part of Franconia were found in the cave ruins of Hunas at Pommelsbrunn in the county of Nuremberg Land. In the late Bronze Age, the region was probably only sparsely inhabited, as few noble metals occur here and the soils are only moderately fertile. In the subsequent Iron Age (from about 800 B.C.) the Celts become the first nation to be discernible in the region. In northern Franconia they built a chain of hill forts as a line of defence against the Germani advancing from the north. On the Staffelberg they built a powerful settlement, to which Ptolemy gave the name ''Menosgada, oppidum Menosgada'', and on the Gleichberge is the largest surviving ''oppidum'' in Central Germany (geography), Central Germany, the Oppidum Steinsburg, Steinsburg. With the increased expansion of Roman Empire, Rome in the first century B.C. and the simultaneous advance of the Elbe Germans, Elbe Germanic tribes from the north, the Celtic culture began to fall into decline. The southern parts of present-day Franconia soon fell under Roman control; however, most of the region remained in Free Germania. Initially Rome tried extend its direct influence far to the northeast; in the longer term, however, the Germanic-Roman frontier formed further southwest.
Fossil finds show that the region was already settled by Caveman, primitive man, ''Homo erectus'', in the middle Last Glacial Period, Ice Age about 600,000 years ago. Probably the oldest human remains in the Bavarian part of Franconia were found in the cave ruins of Hunas at Pommelsbrunn in the county of Nuremberg Land. In the late Bronze Age, the region was probably only sparsely inhabited, as few noble metals occur here and the soils are only moderately fertile. In the subsequent Iron Age (from about 800 B.C.) the Celts become the first nation to be discernible in the region. In northern Franconia they built a chain of hill forts as a line of defence against the Germani advancing from the north. On the Staffelberg they built a powerful settlement, to which Ptolemy gave the name ''Menosgada, oppidum Menosgada'', and on the Gleichberge is the largest surviving ''oppidum'' in Central Germany (geography), Central Germany, the Oppidum Steinsburg, Steinsburg. With the increased expansion of Roman Empire, Rome in the first century B.C. and the simultaneous advance of the Elbe Germans, Elbe Germanic tribes from the north, the Celtic culture began to fall into decline. The southern parts of present-day Franconia soon fell under Roman control; however, most of the region remained in Free Germania. Initially Rome tried extend its direct influence far to the northeast; in the longer term, however, the Germanic-Roman frontier formed further southwest.
 Under the emperors, Domitian (81-96), Trajan (98-117) and Hadrian (emperor), Hadrian (117-138), the Rhaetian Limes was built as a border facing the Germanic tribes to the north. This defensive line ran through the south of Franconia and described an arc across the region whose northernmost point lay at present-day Gunzenhausen. To protect it, the Romans built several forts like Biriciana at Weißenburg in Bayern, Weißenburg, but by the mid-third century, the border could no longer be maintained and by 250 A.D. the Alemanni occupied the areas up to the Danube. Fortified settlements such as the Gelbe Bürg at Dittenheim controlled the new areas.Wilfried Menghin: ''Grundlegung: Das frühe Mittelalter''. In: Handbuch der Bayerischen Geschichte, begr. von Max Spindler, 3rd vol., 1st sub-vol.: Geschichte Frankens bis zum Ausgang des 18. Jahrhunderts, re-published by Andreas Kraus, 3rd, revised edition, Munich, 1997, pp. 47–69, here: p. 60 More such Gau forts have been detected north of the former Limes as well. To which tribe their occupants belonged is unknown in most cases. However, it is likely that it was mainly Alemanni and Juthungi in especially in the south.Wilfried Menghin: ''Grundlegung: Das frühe Mittelalter''. In: Handbuch der Bayerischen Geschichte, begr. von Max Spindler, 3. Bd., 1. Teilbd: Geschichte Frankens bis zum Ausgang des 18. Jahrhunderts, re-published by Andreas Kraus, 3rd, revised edition, Munich, 1997, pp. 47–69, here: S. 55.
By contrast, it was the Burgundians who settled on the Lower and Middle Main. Many of these hill forts appear to have been destroyed, however, no later than 500 A.D. The reasons are not entirely clear, but it could have been as a result of invasions by the Huns which thus triggered the Migration Period, Great Migration. In many cases, however, it was probably conquest by the Franks that spelt the end of these hilltop settlements.
Under the emperors, Domitian (81-96), Trajan (98-117) and Hadrian (emperor), Hadrian (117-138), the Rhaetian Limes was built as a border facing the Germanic tribes to the north. This defensive line ran through the south of Franconia and described an arc across the region whose northernmost point lay at present-day Gunzenhausen. To protect it, the Romans built several forts like Biriciana at Weißenburg in Bayern, Weißenburg, but by the mid-third century, the border could no longer be maintained and by 250 A.D. the Alemanni occupied the areas up to the Danube. Fortified settlements such as the Gelbe Bürg at Dittenheim controlled the new areas.Wilfried Menghin: ''Grundlegung: Das frühe Mittelalter''. In: Handbuch der Bayerischen Geschichte, begr. von Max Spindler, 3rd vol., 1st sub-vol.: Geschichte Frankens bis zum Ausgang des 18. Jahrhunderts, re-published by Andreas Kraus, 3rd, revised edition, Munich, 1997, pp. 47–69, here: p. 60 More such Gau forts have been detected north of the former Limes as well. To which tribe their occupants belonged is unknown in most cases. However, it is likely that it was mainly Alemanni and Juthungi in especially in the south.Wilfried Menghin: ''Grundlegung: Das frühe Mittelalter''. In: Handbuch der Bayerischen Geschichte, begr. von Max Spindler, 3. Bd., 1. Teilbd: Geschichte Frankens bis zum Ausgang des 18. Jahrhunderts, re-published by Andreas Kraus, 3rd, revised edition, Munich, 1997, pp. 47–69, here: S. 55.
By contrast, it was the Burgundians who settled on the Lower and Middle Main. Many of these hill forts appear to have been destroyed, however, no later than 500 A.D. The reasons are not entirely clear, but it could have been as a result of invasions by the Huns which thus triggered the Migration Period, Great Migration. In many cases, however, it was probably conquest by the Franks that spelt the end of these hilltop settlements.

 With their victories over the heartlands of the Alamanni and Thuringians in the 6th century, the present region of Franconia also fell to the Franks.Karten zur Geschichte Bayerns: Jutta Schumann / Dieter J. Weiß, in: ''Edel und Frei. Franken im Mittelalter'', ed. by Wolfgang Jahn / Jutta Schumann / Evamaria Brockhoff, Augsburg, 2004 (Veröffentlichungen zur Bayerischen Geschichte und Kultur 47/04), pp. 174–176, Cat. No. 51. Sieh
With their victories over the heartlands of the Alamanni and Thuringians in the 6th century, the present region of Franconia also fell to the Franks.Karten zur Geschichte Bayerns: Jutta Schumann / Dieter J. Weiß, in: ''Edel und Frei. Franken im Mittelalter'', ed. by Wolfgang Jahn / Jutta Schumann / Evamaria Brockhoff, Augsburg, 2004 (Veröffentlichungen zur Bayerischen Geschichte und Kultur 47/04), pp. 174–176, Cat. No. 51. Sieh
Haus der Bayerischen Geschichte
/ref> After the division of the Frankish Empire, East Francia (''Francia orientialis'') was formed from the territories of the dioceses of Mainz, Worms, Germany, Worms, Würzburg and Speyer. Later, the diocese of Bamberg was added. In the 7th century, the Slavs started to populate the northeastern parts of the region from the east, because the area of today's Upper Franconia was very sparsely populated (Bavaria Slavica).Franz-Joseph Schmale, Wilhelm Störmer: ''Die politische Entwicklung bis zur Eingliederung ins Merowingische Frankenreich''. In: Handbuch der Bayerischen Geschichte, begr. von Max Spindler, 3rd vol., 1st sub-vol.: Geschichte Frankens bis zum Ausgang des 18. Jahrhunderts, re-published by Andreas Kraus, 3rd, revised edition, Munich, 1997, pp. 89–114, here: p. 80. However, in the 10th and 11th centuries, they largely gave up their own language and cultural tradition. The majority of the population of Franconia was pagan well into the Early Middle Ages, The first people to spread the Christian faith strongly were wandering Ireland (island), Irish Anglo-Saxon monks in the early 7th century. Saint Kilian, who together with his companions, Saint Colman (martyr), Saint Colman and Saint Totnan are considered to be the apostles to the Franks, suffering martyrdom in Würzburg in the late 7th century, probably did not encounter any pagans in the ducal court. It was probably Saint Boniface who carried the Christian mission deep into the heart of the ordinary population of Franconia. In the mid-9th century the Duchy of Franconia, tribal Duchy of Franconia emerged, one of the five tribal or stem duchies of
Haus der Bayerischen Geschichte
Unlike the other stem duchies, Franconia became the homeland and power base of East Frankish and German kings after the Ottonians died out in 1024.Josef Kirmeier: ''Bayern und das Deutsche Reich (10.-12. Jahrhundert)'', In: ''Politische Geschichte Bayerns'', published by the Haus der Bayerischen Geschichte as Issue 9 of the ''Hefte zur Bayerischen Geschichte und Kultur'', pp. 7–9, here: p. 7 As a result, in the High Middle Ages, the region did not become a strong regional force such as those which formed in Saxony, Bavaria and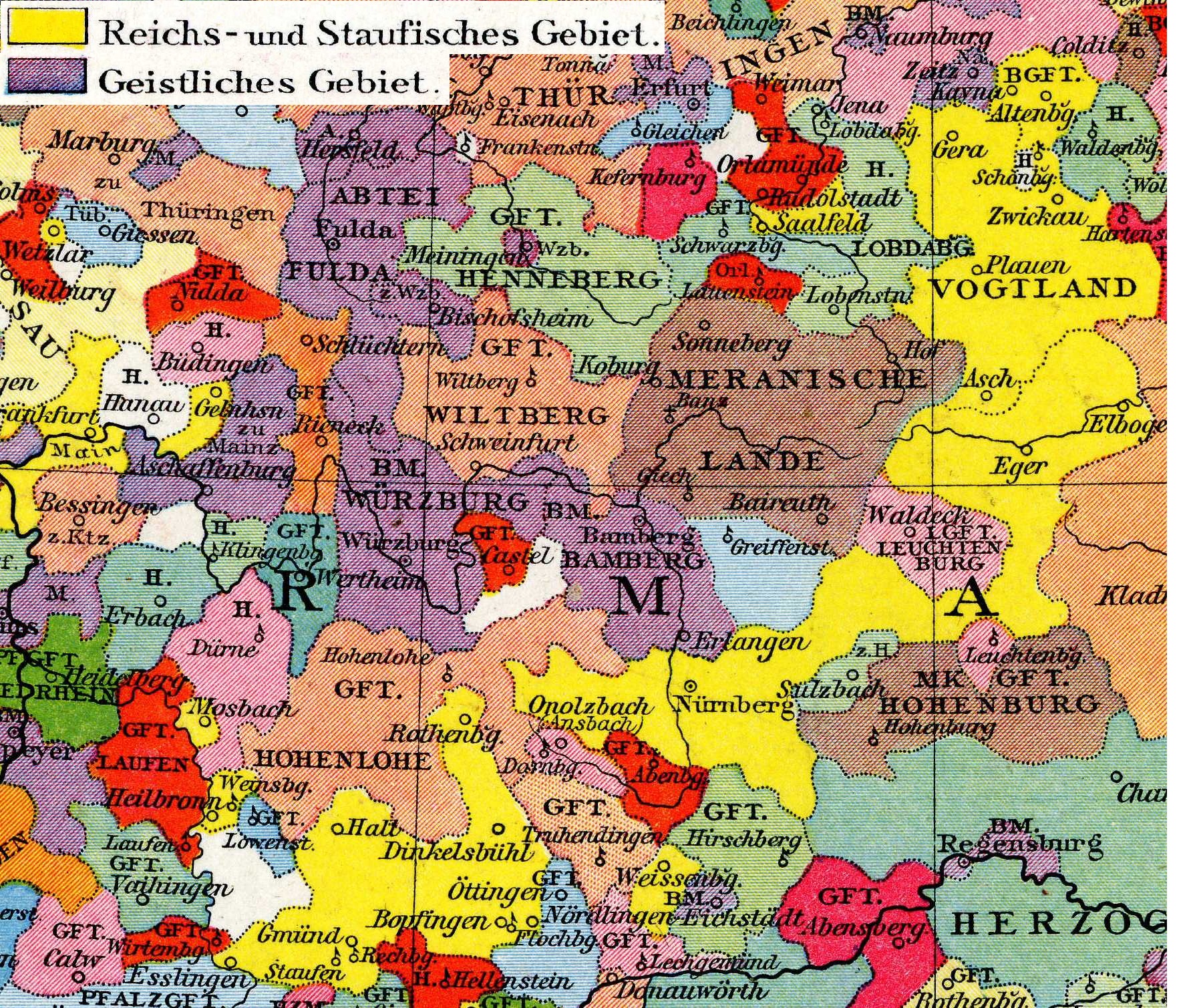 From the 12th century Nuremberg Castle was the seat of the Burgraviate of Nuremberg. The burgraviate was ruled from about 1190 by the Zollerns, the Franconian line of the later House of Hohenzollern, which provided the German emperors of the 19th and 20th century. Under the Hohenstaufen kings, Conrad III (HRR), Conrad III and Frederick I (HRR), Frederick Barbarossa, Franconia became the centre of power in the Empire. During the time when there was no emperor, the Interregnum (Holy Roman Empire), Interregnum (1254–1273), some territorial princes became ever more powerful. After the Interregnum, however, the rulers succeeded in re-establishing a stronger royal lordship in Franconia. Franconia soon played an important role again for the monarchy at the time of Rudolf I (HRR), Rudolf of Habsburg; the itineraries of his successors showing their preference for the Rhine-Main region. In 1376 the Swabian League of Cities was founded and was joined later by several Franconian imperial cities. During the 13th century the Teutonic Order was formed, taking over its first possession in Franconia in 1209, the Bailiwick of Franconia. The foundation of many schools and hospitals and the construction of numerous churches and castles in this area goes back to the work of this Roman Catholic military order. The residence place of the bailiwick was at Ellingen until 1789 when it was transferred to today's Bad Mergentheim.Rudolf Endres: ''Staat und Gesellschaft. Zweiter Teil: 1500-1800''. In: Handbuch der Bayerischen Geschichte, begr. von Max Spindler, 3rd vol., 1st sub-vol.: Geschichte Frankens bis zum Ausgang des 18. Jahrhunderts, re-published by Andreas Kraus, 3rd, revised edition, Munich, 1997, pp. 702–781, here: pp. 752ff Other orders such as the Knights Templar could not gain a foothold in Franconia; the Order of St. John worked in the Bishopric of Würzburg and had short term commands.Wilhelm Störmer: ''Die innere Entwicklung: Staat, Gesellschaft, Kirche, Wirtschaft''. In: Handbuch der Bayerischen Geschichte, begr. von Max Spindler, 3rd vol., 1st sub-vol.: Geschichte Frankens bis zum Ausgang des 18. Jahrhunderts, re-published by Andreas Kraus, 3rd revised edition, Munich, 1997, pp. 210–315, here: p. 314.
From the 12th century Nuremberg Castle was the seat of the Burgraviate of Nuremberg. The burgraviate was ruled from about 1190 by the Zollerns, the Franconian line of the later House of Hohenzollern, which provided the German emperors of the 19th and 20th century. Under the Hohenstaufen kings, Conrad III (HRR), Conrad III and Frederick I (HRR), Frederick Barbarossa, Franconia became the centre of power in the Empire. During the time when there was no emperor, the Interregnum (Holy Roman Empire), Interregnum (1254–1273), some territorial princes became ever more powerful. After the Interregnum, however, the rulers succeeded in re-establishing a stronger royal lordship in Franconia. Franconia soon played an important role again for the monarchy at the time of Rudolf I (HRR), Rudolf of Habsburg; the itineraries of his successors showing their preference for the Rhine-Main region. In 1376 the Swabian League of Cities was founded and was joined later by several Franconian imperial cities. During the 13th century the Teutonic Order was formed, taking over its first possession in Franconia in 1209, the Bailiwick of Franconia. The foundation of many schools and hospitals and the construction of numerous churches and castles in this area goes back to the work of this Roman Catholic military order. The residence place of the bailiwick was at Ellingen until 1789 when it was transferred to today's Bad Mergentheim.Rudolf Endres: ''Staat und Gesellschaft. Zweiter Teil: 1500-1800''. In: Handbuch der Bayerischen Geschichte, begr. von Max Spindler, 3rd vol., 1st sub-vol.: Geschichte Frankens bis zum Ausgang des 18. Jahrhunderts, re-published by Andreas Kraus, 3rd, revised edition, Munich, 1997, pp. 702–781, here: pp. 752ff Other orders such as the Knights Templar could not gain a foothold in Franconia; the Order of St. John worked in the Bishopric of Würzburg and had short term commands.Wilhelm Störmer: ''Die innere Entwicklung: Staat, Gesellschaft, Kirche, Wirtschaft''. In: Handbuch der Bayerischen Geschichte, begr. von Max Spindler, 3rd vol., 1st sub-vol.: Geschichte Frankens bis zum Ausgang des 18. Jahrhunderts, re-published by Andreas Kraus, 3rd revised edition, Munich, 1997, pp. 210–315, here: p. 314.
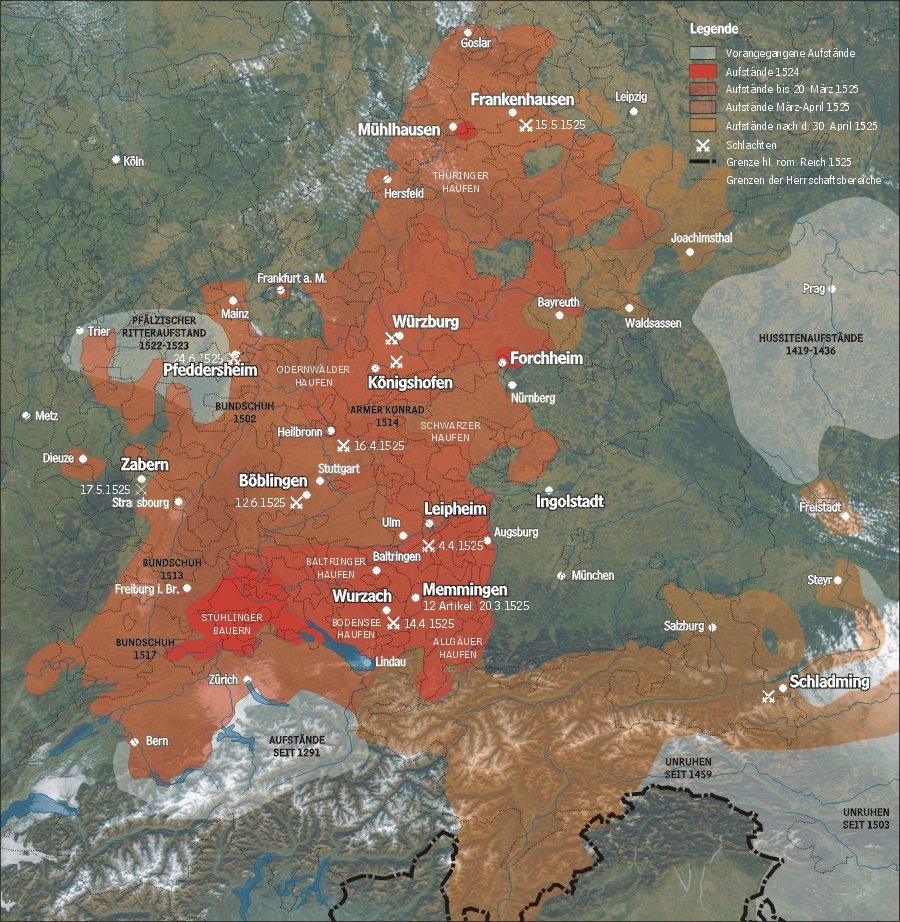 In 1525, the burden of heavy taxation and socage combined with new, liberal ideas that chimed with the Reformation movement, unleashed the German Peasants' War. The Würzburg area was particularly hard hit with numerous castles and monasteries being burned down.''Stadthistorische Streiflichter (24)''
In 1525, the burden of heavy taxation and socage combined with new, liberal ideas that chimed with the Reformation movement, unleashed the German Peasants' War. The Würzburg area was particularly hard hit with numerous castles and monasteries being burned down.''Stadthistorische Streiflichter (24)''
www.wuerzburg.de, accessed 7 June 2014. In the end, however, the uprisings were suppressed and for centuries the lowest strata of society were excluded from all political activity. From 1552, Margrave Albert Alcibiades attempted to break the supremacy of the mighty imperial city of Nuremberg and to secularise the ecclesial estates in the Second Margrave War,Rudolf Endres: ''Von der Bildung des Fränkischen Reichskreises und dem Beginn der Reformation bis zum Augsburger Religionsfrieden von 1555''. In: Handbuch der Bayerischen Geschichte, ed. Max Spindler, 3 vols., 1 sub-vol: History of Franconia to the end of the 18th century, revised by Andreas Kraus, 3rd revised edition, Munich, 1997, pp. 451-472, here: p. 469 to create a duchy over which he would rule. Large areas of Franconia were eventually devastated in the fighting until King Ferdinand I (HRR), Ferdinand I together with several dukes and princes decided to overthrow Albert. In 1608, the reformed princes merged into a so-called Protestant Union, Union within the Empire. In Franconia, the margraves of Ansbach and Bayreuth as well as the imperial cities were part of this alliance. The Catholic side responded in 1609 with a counter-alliance, the Catholic League (1609), League. The conflicts between the two camps ultimately resulted in the Thirty Years' War, which was the greatest strain on the cohesion of the Franconian Circle Initially, Franconia was not a theatre of war, although marauding armies repeatedly crossed its territory. However, in 1631, Swedish troops under Gustavus II Adolphus (Sweden), Gustavus Adolphus advanced into Franconia and established a large encampment in summer 1632 around Nuremberg.Rudolf Endres: ''Vom Augsburger Religionsfrieden bis zum Dreißigjährigen Krieg''. In: Handbuch der Bayerischen Geschichte, ed. Max Spindler, 3rd vol., 1st sub-vol: Geschichte Frankens bis zum Ausgang des 18. Jahrhunderts, revised by Andreas Kraus, 3rd revised edn., Munich, 1997, pp. 473–495, here: p. 490. However, the Swedes lost the Battle of the Alte Veste against Wallenstein's troops and eventually withdrew. Franconia was one of the poorest regions in the Empire and lost its imperial political significance.Michael Henker: ''Bayern im Zeitalter von Reformation und Gegenreformation (16./17. Jahrhundert)'', In: ''Politische Geschichte Bayerns'', published by the House of Bavarian History as Issue 9 of the ''Hefte zur Bayerischen Geschichte und Kultur'', pp. 14–17, here: p. 17 During the course of the war, about half the local population lost their lives. To compensate for these losses about 150,000 displaced Protestants settled in Protestant areas, including Austrian exiles.
In 1608, the reformed princes merged into a so-called Protestant Union, Union within the Empire. In Franconia, the margraves of Ansbach and Bayreuth as well as the imperial cities were part of this alliance. The Catholic side responded in 1609 with a counter-alliance, the Catholic League (1609), League. The conflicts between the two camps ultimately resulted in the Thirty Years' War, which was the greatest strain on the cohesion of the Franconian Circle Initially, Franconia was not a theatre of war, although marauding armies repeatedly crossed its territory. However, in 1631, Swedish troops under Gustavus II Adolphus (Sweden), Gustavus Adolphus advanced into Franconia and established a large encampment in summer 1632 around Nuremberg.Rudolf Endres: ''Vom Augsburger Religionsfrieden bis zum Dreißigjährigen Krieg''. In: Handbuch der Bayerischen Geschichte, ed. Max Spindler, 3rd vol., 1st sub-vol: Geschichte Frankens bis zum Ausgang des 18. Jahrhunderts, revised by Andreas Kraus, 3rd revised edn., Munich, 1997, pp. 473–495, here: p. 490. However, the Swedes lost the Battle of the Alte Veste against Wallenstein's troops and eventually withdrew. Franconia was one of the poorest regions in the Empire and lost its imperial political significance.Michael Henker: ''Bayern im Zeitalter von Reformation und Gegenreformation (16./17. Jahrhundert)'', In: ''Politische Geschichte Bayerns'', published by the House of Bavarian History as Issue 9 of the ''Hefte zur Bayerischen Geschichte und Kultur'', pp. 14–17, here: p. 17 During the course of the war, about half the local population lost their lives. To compensate for these losses about 150,000 displaced Protestants settled in Protestant areas, including Austrian exiles.
 Franconia never developed into a unified territorial state, because the patchwork quilt of small states (''Kleinstaaterei'') survived the Middle Ages and lasted until the 18th century.Karlheinz Scherr: ''Bayern im Zeitalter des Fürstlichen Absolutismus (17./18. Jahrhundert)'', In: ''Politische Geschichte Bayerns'', published by the House of Bavarian History as Issue 9 of the ''Hefte zur Bayerischen Geschichte und Kultur'', pp. 18–21, here: p. 20 As a result, the Franconian Circle had the important task of preserving peace, preventing abuses and to repairing war damage and had a regulatory role in the region until the end of the Holy Roman Empire. Until the War of the Spanish Succession, the Circle had become an almost independent organization and joined the Grand Alliance (League of Augsburg), Grand Alliance against Louis XIV as an almost sovereign state. The Circle also developed early forms of a welfare state. It also played a major role in the control of disease during the 16th and 17th centuries. After Charles Alexander (Brandenburg-Ansbach-Bayreuth), Charles Alexander abdicated in 1792, the former margraviates of Ansbach and Bayreuth were annexed by Prussia. Karl August Freiherr von Hardenberg was appointed as governor of these areas by Prussia.
Franconia never developed into a unified territorial state, because the patchwork quilt of small states (''Kleinstaaterei'') survived the Middle Ages and lasted until the 18th century.Karlheinz Scherr: ''Bayern im Zeitalter des Fürstlichen Absolutismus (17./18. Jahrhundert)'', In: ''Politische Geschichte Bayerns'', published by the House of Bavarian History as Issue 9 of the ''Hefte zur Bayerischen Geschichte und Kultur'', pp. 18–21, here: p. 20 As a result, the Franconian Circle had the important task of preserving peace, preventing abuses and to repairing war damage and had a regulatory role in the region until the end of the Holy Roman Empire. Until the War of the Spanish Succession, the Circle had become an almost independent organization and joined the Grand Alliance (League of Augsburg), Grand Alliance against Louis XIV as an almost sovereign state. The Circle also developed early forms of a welfare state. It also played a major role in the control of disease during the 16th and 17th centuries. After Charles Alexander (Brandenburg-Ansbach-Bayreuth), Charles Alexander abdicated in 1792, the former margraviates of Ansbach and Bayreuth were annexed by Prussia. Karl August Freiherr von Hardenberg was appointed as governor of these areas by Prussia.
House of Bavarian History , retrieved 7 June 2014. As a reward Bavaria was promised other estates, including the city of Nuremberg. In the so-called ''Rittersturm'' of 1803, Bavaria, Württemberg and Baden seized the territories of the Imperial Knights and Franconian nobility, whose estates were often no bigger than a few parishes, even though the ''Reichsdeputationshauptschluss'' had not authorised this. In 1806 and 1810, Prussia had to release the territories of Ansbach and Bayreuth, which it had annexed in 1792, to Bavaria, whereby Prussia lost its supremacy in the region.''Preußen in Franken 1792 - 1806''
, material from the State Exhibition in 1999 by the House of Bavarian History In 1814, as a result of the Congress of Vienna, the territories of the Principality of Aschaffenburg and Grand Duchy of Würzburg went to the Kingdom of Bavaria. In order to merge the patchwork quilt of small states in Franconia and Swabia into a greater Bavaria, Maximilian Montgelas, Maximilian Joseph Montgelas reformed the political structure. Out of this in January 1838 emerged the Franconian provinces with their present names of Middle, Upper and Lower Franconia. Considerable resentment arose in parts of the Franconian territories over their new membership of Bavaria.Hans Maier: ''Die Franken in Bayern'', p. 6
see pdf
, retrieved 12 July 2014. There were liberal demands for republican structures which erupted in the German Revolution (1848/1849), revolts of 1848 and 1849 and the Gaibach Festival in 1832. On the one hand the reconciliation policy of the Wittelsbachs and Montgelas' aforementioned policy of unification, and, on the other hand, the inclusion of Bavaria in the German Empire in 1871, which weakened her power Bavaria slightly, the conflict between Franconia and Bavaria eased considerably. From 1836 to 1846, the Kingdom of Bavaria built the Ludwig Canal from Bamberg to Kelheim, which was only abandoned in 1950. However, the canal lost much of its importance shortly after the arrival of the railways. Between 1843 and 1854, the Ludwig South-North Railway was established within Franconia, which ran from Lindau (Lake Constance), Lindau on Lake Constance via Nuremberg,
''Politische Geschichte Bayerns''
published by the House of Bavarian History as No. 9 of the booklets on Bavarian History and Culture, 1989, pp. 26-28, here: p. 26 In 1919 the Free State of Coburg voted in a referendum against joining Thuringia and was instead united with Bavaria on 1 July 1920. During the Nazi Germany, Nazi era Nuremberg played a prominent role in the self-expression of the Nazism, National Socialists as the permanent seat of the Nazi Party. Gunzenhausen made its mark as one of the first towns in the Reich itself to exercise discrimination against the Jewish population. The first Hitler Monument in Germany was established there in April 1933. On 25 March 1934 the first anti-Jewish pogrom in Bavaria took place in Gunzenhausen. The attack brought the town negative press coverage worldwide.Werner Falk: ''Ein früher Hass auf Juden'' in Nürnberger Nachrichten, 25 March 2009. On 15 September, a Reichstag (Nazi Germany), Reichstag was specially convened in Nuremberg for the purpose of passing the Nuremberg Laws, under which the antisemitism, antisemitic ideology of the Nazis became a legal basis for such actions. Like all parts of the German Reich, Franconia was badly affected by Allies of World War II, Allied airstrike, air raids. Nuremberg, as a major industrial centre and transportation hub, was hit particularly hard. Between 1940 and 1945 the city was the target of dozens of air raids. Many other places were also affected by air raids. For example, the air raid on Heilbronn, air raid on 4 December 1944 on Heilbronn and the bombing of Würzburg on 16 March 1945, bombing of Würzburg on 16 March 1945, in which both old towns were almost completely destroyed, was a disaster for both cities. By contrast, the old town of Bamberg was almost completely spared. In order to protect cultural artefacts, the Historischer Kunstbunker, historic art bunker was built below Nuremberg Castle. In the closing stages of the Second World War, at the end of March and April 1945, Franconian towns and cities were captured by formations of the United States Army, US Army who advanced from the west after the failure of the Battle of the Bulge and Operation Nordwind. The Battle of Nuremberg (1945), Battle of Nuremberg lasted five days and resulted in at least 901 deaths. The Battle of Crailsheim lasted 16 days, the Battle of Würzburg (1945), Battle of Würzburg seven and the Battle of Merkendorf three days. Following the unconditional surrender of the Wehrmacht, unconditional surrender on 8 May 1945, Bavarian Franconia became part of the American zone of occupation; whilst South Thuringia, with the exception of smaller enclaves like Ostheim, became part of the Soviet occupation zone of Germany, Soviet zone and the Franconian parts of today's Baden-Württemberg also went to the American zone The most important part of the Allied prosecution programme against leaders of the Nazi regime were the Nuremberg Trials against leaders of the German Empire during the Nazi era, held from 20 November 1945 to 14 April 1949. The Nuremberg Trials are considered a breakthrough for the principle that, for a core set of crimes, there is no diplomatic immunity, immunity from prosecution. For the first time, the representatives of a sovereignty, sovereign state were held accountable for their actions. In autumn 1946, the Free State of Bavaria was reconstituted with the enactment of the Constitution of Bavaria, Bavarian Constitution. The state of Württemberg-Baden was founded on 19 September 1945. On 25 April 1952 this state merged with Baden (South Baden), Baden and Württemberg-Hohenzollern (both from the former French occupation zone) to create the present state of Baden-Württemberg. On 1 December 1945 the state of Hesse was founded. Beginning in 1945, Flight and expulsion of Germans (1944–50), refugees and displaced persons from Eastern Europe were settled particularly in rural areas. After 1945, Bavaria and Baden-Württemberg managed the transition from economies that were predominantly agriculture to become leading industrial states in the so-called ''Wirtschaftswunder''. In Lower and Upper Franconia, there was still the problem, however, of the zone along the Inner German Border which was a long way from the markets for its agricultural produce, and was affected by migration and relatively high unemployment, which is why these areas received special support from federal and state governments. By contrast, the state of Thuringia was restored by the Soviet Military Administration in Germany, Soviets in 1945. On 7 October 1949 the German Democratic Republic, commonly known as East Germany, was founded. In 1952 in the course of the Administrative divisions of East Germany, 1952 administrative reform in East Germany, the state of Thuringia was relieved of its function. The Soviet occupying forces exacted a high level of reparations (especially the Allied plans for German industry after World War II, dismantling of industrial facilities) which made the initial economic conditions in East Germany very difficult. Along with the failed economic policies of the GDR, this led to a general frustration that fuelled the uprising of 17 June. There were protests in the Franconian territories too, for example in Schmalkalden. The village of Mödlareuth became famous because, for 41 years, it was divided by the Inner German Border and was nicknamed 'Little Berlin. After ''Die Wende'', the fall of the Berlin Wall on 9 November 1989 and German reunification, reunification on 3 October 1990, made possible mainly by mass demonstrations in East Germany and local exodus of East Germans, the state of Thuringia was reformed with effect from 14 October 1990.Steffen Raßloff: ''Geschichte Thüringens.'' Munich, 2010, p. 106 In the years from 1971 to 1980 an administrative reform was carried out in Bavaria with the aim of creating more efficient municipalities (''Gemeinde (Germany), Gemeinden'') and counties (''Landkreise''). Against sometimes great protests by the population, the number of municipalities was reduced by a third and the number of counties by about a half. Among the changes was the transfer of the Middle Franconian county of Landkreis Eichstätt, Eichstätt to Upper Bavaria. On 18 May 2006, the Bavarian Landtag approved the introduction of Franconia Day (''Tag der Franken'') in the Franconian territories of the free state.Document 15/5583 of the Bavarian Landtag
In the years from 1971 to 1980 an administrative reform was carried out in Bavaria with the aim of creating more efficient municipalities (''Gemeinde (Germany), Gemeinden'') and counties (''Landkreise''). Against sometimes great protests by the population, the number of municipalities was reduced by a third and the number of counties by about a half. Among the changes was the transfer of the Middle Franconian county of Landkreis Eichstätt, Eichstätt to Upper Bavaria. On 18 May 2006, the Bavarian Landtag approved the introduction of Franconia Day (''Tag der Franken'') in the Franconian territories of the free state.Document 15/5583 of the Bavarian Landtag
(pdf; 86 kB) Since ''Die Wende'', new markets have opened up for the Franconian region of Bavaria in the new (formerly East German) federal states and the Czech Republic, enabling the economy to recover. Today, Franconia is in the centre of the EU (at Oberwestern near Westerngrund; ).
(xls file; 4.0 MB) (population figures from the 2011 census) The largest places in the Thuringian part are Suhl (35,665), Sonneberg (23,796) and
House of Bavarian History
In the late medieval period it was dominated by mainly smaller towns with a few hundred to a thousand inhabitants, whose size barely distinguished them from the villages. Many towns grew up along large rivers or were founded by the prince-bishops and nobility. Even the Hohenstaufens operated in many towns, most of which later became Imperial Cities with a strong orientation towards Nuremberg. The smallest town in Franconia is Thuringia's Ummerstadt with 487 inhabitants.
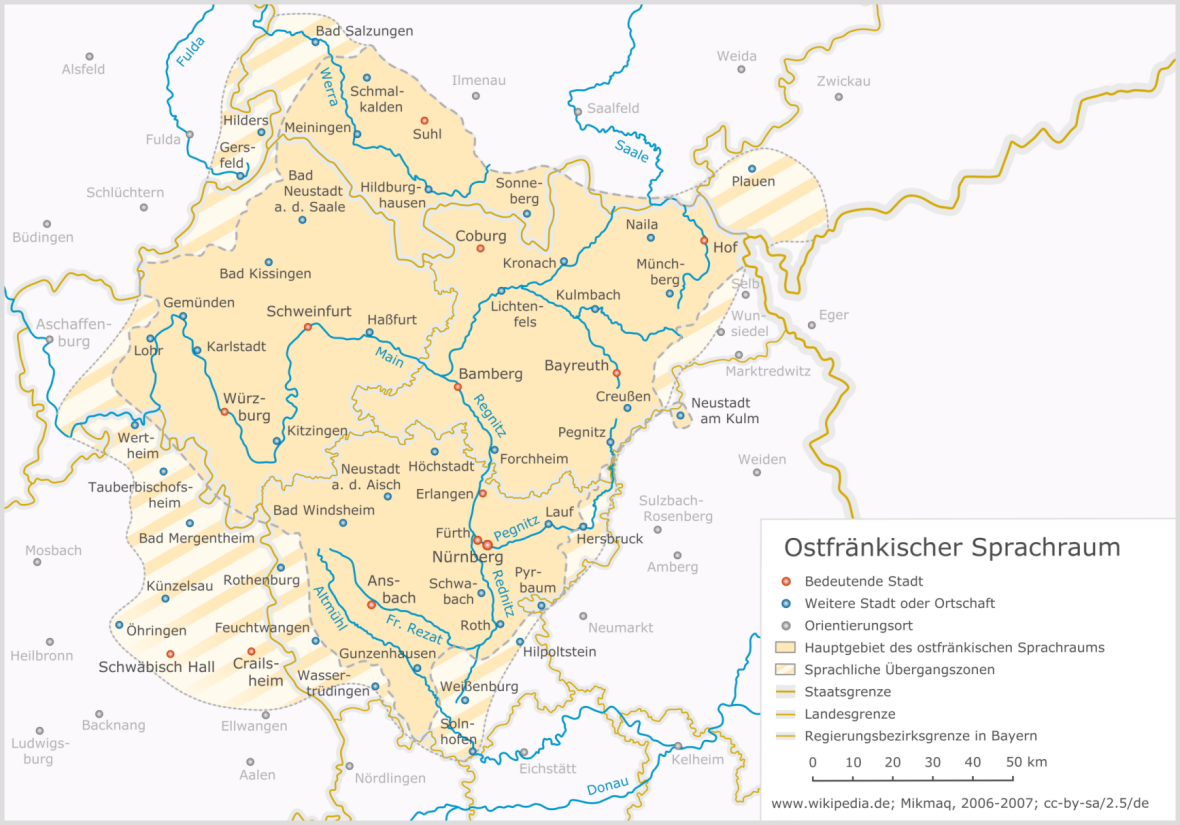 German is the official language and also the ''lingua franca''. Numerous other languages are spoken that come from other language regions or the native countries of immigrants.
East Franconian German, the dialect spoken in Franconia, is entirely different from the Austro-Bavarian dialect continuum which is mainly to be found in the Upper Palatinate, Upper and Lower Bavaria, the greater part of Austria and some parts of Northern Italy. This is one of the reasons why hardly any Franconian would call himself a Bavarian. Even though there is no Franconian state, red and white are regarded as the state colours (''Landesfarben'') of Franconia (compared to blue and white for Bavaria).
German is the official language and also the ''lingua franca''. Numerous other languages are spoken that come from other language regions or the native countries of immigrants.
East Franconian German, the dialect spoken in Franconia, is entirely different from the Austro-Bavarian dialect continuum which is mainly to be found in the Upper Palatinate, Upper and Lower Bavaria, the greater part of Austria and some parts of Northern Italy. This is one of the reasons why hardly any Franconian would call himself a Bavarian. Even though there is no Franconian state, red and white are regarded as the state colours (''Landesfarben'') of Franconia (compared to blue and white for Bavaria).
House of Bavarian History
Large areas of Middle and Upper Franconia are mainly Protestant. The religious denomination, denominational orientation today still reflects the territorial structure of Franconia at the time of the Franconian Circle. For example, regions, that used to be under the care of the bishoprics of Bamberg, Würzburg and Eichstätt, are mainly Catholic today. On the other hand, all former territories of the imperial cities and the margraviates of Ansbach and Bayreuth have remained mainly Lutheran. The region around the city of Erlangen, which belonged to the Margraviate of Bayreuth, was a refuge for the Huguenots who fled there after the St Bartholomew's Day massacre in France. Following the success of the Reformation in Nuremberg under Andreas Osiander, it had been an exclusively Protestant imperial city and belonged to the Protestant league of imperial states, the Corpus Evangelicorum, within the ''Reichstag (Holy Roman Empire), Reichstag''. Subsequent historical events such as the Flight and expulsion of Germans (1944–50), stream of refugees after the Second World War and the increasing mobility of the population has since blurred denominational geographical boundaries, however. The influx of immigrants from Eastern Europe has also seen the establishment of an Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox community in Franconia. The Romanian Orthodox Metropolis of Germany, Central and Northern Europe has its headquarters in Nuremberg.
Image:Schaeufele 01.jpg, ''Schäufele, Schäuferla''
Image:Nuernberg Drei im Weckla 001.JPG, Three Nuremberger Bratwurst, Bratwürste in a roll (''Drei im Weckla'')
Image:GravityTap.jpg, Schlenkerla Smoked beer, Rauchbier straight from the cask
File:Bocksbeutels.jpg, Franconia (wine region), Franconian wine is traditionally filled up in Bocksbeutels
Image:Kroder Karpfen.JPG, Fried Carp with beer and salad

 The tourism industry stresses the romantic character of Franconia. Arguments for this include the picturesque countryside and the many historic buildings that present the long history and culture of the region.''Franken. Allianz Reiseführer'', 2011, pp. 12ff In addition, the relatively few industrial towns outside of the main industrial cities is highlighted. Franconian wine, the rich tradition of beer brewing and local culinary specialties, such as ''Lebküchnerei'' or gingerbread baking, are also seen as a draw that is worth marketing, and which make Franconia a popular tourist destination in Germany. The Romantic Road, the best known German theme route, links several of the tourist points in western Franconia. The Castle Road runs through the whole Franconian region with its numerous castles and other medieval structures.
Cycling along the large rivers is very popular, for example along the Main Cycleway, which was the first German long distance cycleway to be awarded five stars by the Allgemeiner Deutscher Fahrrad-Club (ADFC). The Tauber Valley Cycleway, a 101 kilometre-long cycle trail in
The tourism industry stresses the romantic character of Franconia. Arguments for this include the picturesque countryside and the many historic buildings that present the long history and culture of the region.''Franken. Allianz Reiseführer'', 2011, pp. 12ff In addition, the relatively few industrial towns outside of the main industrial cities is highlighted. Franconian wine, the rich tradition of beer brewing and local culinary specialties, such as ''Lebküchnerei'' or gingerbread baking, are also seen as a draw that is worth marketing, and which make Franconia a popular tourist destination in Germany. The Romantic Road, the best known German theme route, links several of the tourist points in western Franconia. The Castle Road runs through the whole Franconian region with its numerous castles and other medieval structures.
Cycling along the large rivers is very popular, for example along the Main Cycleway, which was the first German long distance cycleway to be awarded five stars by the Allgemeiner Deutscher Fahrrad-Club (ADFC). The Tauber Valley Cycleway, a 101 kilometre-long cycle trail in
''Fünf Sterne für den "Klassiker"''
In: Tauber-Zeitung. Online at www.swp.de. 31 October 2009; retrieved 6 April 2010.
review
. * Petersohn, Jürgen. ''Franken im Mittelalter. Identität und Profil im Spiegel von Bewußtsein und Vorstellung.'' (Vorträge und Forschungen, Sonderband 51), Ostfildern, 2008 (c.f
. * Timothy Reuter, Reuter, Timothy. ''Germany in the Early Middle Ages 800–1056''. New York: Longman, 1991. . * Scherzer, Conrad. ''Franken, Land, Volk, Geschichte und Wirtschaft.'' Verlag Nürnberger Presse Drexel, Merkel & Co., Nuremberg, 1955, . * Schiener, Anna. ''Kleine Geschichte Frankens.'' Verlag Friedrich Pustet, Regensburg, 2008, . * Stützel, Ada. ''100 berühmte Franken.'' Sutton Verlag, Erfurt, 2007, . * Wüst, Wolfgang (ed.): ''Frankens Städte und Territorien als Kulturdrehscheibe. Kommunikation in der Mitte Deutschlands.'' Interdisciplinary conference 29 to 30 September 2006 in Weißenburg i. Bayern (Mittelfränkische Studien 19) Ansbach, 2008, .
Bezirk of Lower Franconia
Government of Lower Franconia
Bezirk of Middle Franconia
Government of Middle Franconia
Bezirk of Upper Franconia
Government of Upper Franconia
English pages available
The Baden-Württemberg region of Heilbronn-Franken
{{Authority control Franconia, Dukes of Franconia Frankish people Regions of Bavaria History of the Palatinate (region)
s.v. is a river in , is characterized by poor grassland of this type. Many of these places have been designated as a
protected area
Protected areas or conservation areas are locations which receive protection because of their recognized natural, ecological or cultural values. There are several kinds of protected areas, which vary by level of protection depending on the ena ...
s.
Franconia has several regions with sandy habitats that are unique for south Germany and are protected as the so-called Sand Belt of Franconia or '' Sandachse Franken''. When the Altmühlsee reservoir was built, a bird island was created and designated as a nature reserve where a variety of birds nest. Another important reserve is the Black Moor Black Moor may refer to:
* Black Moor (musical group), a heavy metal band
* Black Moor (Rhön), a wetland habitat in Germany
* Black Telescope goldfish, known as black moor, a variant of telescope eye goldfish
* " Harap Alb", a 1877 Romanian-lang ...
in the Rhön, which is one of the most important bog areas in Central Europe. A well known reserve is the Luisenburg Rock Labyrinth
The Luisenburg Rock Labyrinth (german: Luisenburg-Felsenlabyrinth) is a felsenmeer made of granite blocks several metres across and is part of the ''Großes Labyrinth'' Nature Reserve near Wunsiedel in Germany. For a long time its formation was be ...
at Wunsiedel, a felsenmeer of granite blocks up to several metres across. The establishment of the first Franconian national park
A national park is a nature park, natural park in use for conservation (ethic), conservation purposes, created and protected by national governments. Often it is a reserve of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that a sovereign state dec ...
in the Steigerwald caused controversy and its designation was rejected in July 2011 by the Bavarian government
The politics of Bavaria takes place within a framework of a federal parliamentary representative democratic republic, where the Federal Government of Germany exercises sovereign rights with certain powers reserved to the states of Germany inclu ...
. The reason was the negative attitude of local population. Conservationists are now demanding protection for parts of the Steigerwald by nominating it for a World Heritage Site. Press report on the rejected Steigerwald National Park at BR-online, Studio-Franken There are several nature park
A nature park, or sometimes natural park, is a designation for a protected natural area by means of long-term land planning, sustainable resource management and limitation of agricultural and real estate developments. These valuable landscape ...
s in Franconia, including the Altmühl Valley Nature Park
The Altmühl Valley Nature Park (german: Naturpark Altmühltal) is a nature park, 2,962 km² in area, in the south German state of Bavaria. The area of the park is almost coextensive with that of the natural region major unit of the Southern ...
, which, since 1969, has been one of the largest in Germany.
Other nature park
A nature park, or sometimes natural park, is a designation for a protected natural area by means of long-term land planning, sustainable resource management and limitation of agricultural and real estate developments. These valuable landscape ...
s are the Swabian-Franconian Forest Nature Park
The Swabian-Franconian Forest (german: Schwäbisch-Fränkischen Waldberge, also ''Schwäbisch-Fränkischer Wald'') is a mainly forested, deeply incised upland region, 1,187 km² in area and up to , in the northeast of Baden-Württemberg. It fo ...
in Baden-Württemberg, and the nature parks of Bavarian Rhön, Fichtel Mountains
The Fichtel MountainsRandlesome, C. et al. (2011). ''Business Cultures in Europe'', 2nd ed., Routledge, Abingdon and New York, p. 52. . (german: Fichtelgebirge, cs, Smrčiny), form a small horseshoe-shaped mountain range in northeastern Bavaria ...
, Franconian Heights
The Franconian HeightsBavarian State Chancellery, ''Information about Bavaria'', 1981, p. 11. (german: Frankenhöhe) are a hill ridge, up to , in Bavaria and Baden-Württemberg in South Germany.
Location and boundaries
The Franconian Heights l ...
, Franconian Forest
View to Döbraberg
The Franconian Forest''Franconian Forest''
at www.britannica.com. Acce ...
, Franconian Switzerland-Franconian Jura, Haßberge, Spessart and Steigerwald in Bavaria, as well as the at www.britannica.com. Acce ...
Bergstraße-Odenwald Nature Park
The Bergstraße-Odenwald Nature Park (german: Geo-Naturpark Bergstraße-Odenwald) is a nature park in southern Germany with an area of 3,500 km² that lies between the rivers Rhine, Main (river) and Neckar. In the south it overlaps in places ...
which straddles Bavaria, Baden-Württemberg and Hesse. Nature parks cover almost half the area of Franconia.
In 1991 UNESCO recognised the Rhön as a biosphere reserve. Among the most picturesque geotopes in Bavaria, are the Franconian sites of '' Fossa Carolina'', the Twelve Apostle Rocks (''Zwölf-Apostel-Felsen''), the Ehrenbürg
The Ehrenbürg is a double-peaked butte on the edge of the Franconian Jura in Bavaria, Germany. It is in the district of Forchheim in Upper Franconia, in the municipalities of Kirchehrenbach, Leutenbach and Wiesenthau. The north peak is the ...
, the cave ruins of Riesenburg
Prabuty (german: Riesenburg) is a town in Kwidzyn County within the Pomeranian Voivodeship of northern Poland. Before World War I, the town belonged to the German province of West Prussia. It was ceded to Poland in 1945. Between 1975 and 1998, P ...
and the lake of Frickenhäuser See. The European Bird Reserve
A Special Protection Area (SPA) is a designation under the European Union Directive on the Conservation of Wild Birds. Under the Directive, Member States of the European Union (EU) have a duty to safeguard the habitats of migratory birds and cert ...
s in Franconia are found mainly in uplands like the Steigerwald, in large forests like Nuremberg's Imperial Forest or along rivers like the Altmühl.Karte der Vogelschutzgebiete: ''Mittelfranken'', stellvertretend für alle Europäischen Vogelschutzgebieten in Franken There are also numerous Special Areas of Conservation and protected landscapes. In Franconia there are very many tufas, raised stream beds near river sources within the
karst
Karst is a topography formed from the dissolution of soluble rocks such as limestone, dolomite, and gypsum. It is characterized by underground drainage systems with sinkholes and caves. It has also been documented for more weathering-resistant ro ...
landscape that are known as 'stone runnels' ('' Steinerne Rinnen''). There are protected examples at Heidenheim and Wolfsbronn.
Like large parts of Germany, Franconia only has a few large species of wild animal. Forest dwellers include various species of marten
A marten is a weasel-like mammal in the genus ''Martes'' within the subfamily Guloninae, in the family Mustelidae. They have bushy tails and large paws with partially retractile claws. The fur varies from yellowish to dark brown, depending on t ...
, fallow deer, red deer, roe deer, wild boar and fox
Foxes are small to medium-sized, omnivorous mammals belonging to several genera of the family Canidae. They have a flattened skull, upright, triangular ears, a pointed, slightly upturned snout, and a long bushy tail (or ''brush'').
Twelve sp ...
. In natural areas such as the Fichtel mountains there are populations of lynx
A lynx is a type of wild cat.
Lynx may also refer to:
Astronomy
* Lynx (constellation)
* Lynx (Chinese astronomy)
* Lynx X-ray Observatory, a NASA-funded mission concept for a next-generation X-ray space observatory
Places Canada
* Lynx, Ontar ...
and capercaillie
''Tetrao'' is a genus of birds in the grouse subfamily known as capercaillies. They are some of the largest living grouse.
Taxonomy
The genus ''Tetrao'' was introduced in 1758 by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in the tenth edition of his ...
,''Fichtelgebirge Nature Park'', retrieved 2 Jun 2014. and
beaver
Beavers are large, semiaquatic rodents in the genus ''Castor'' native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere. There are two extant species: the North American beaver (''Castor canadensis'') and the Eurasian beaver (''C. fiber''). Beavers ar ...
and otter
Otters are carnivorous mammals in the subfamily Lutrinae. The 13 extant otter species are all semiaquatic, aquatic, or marine, with diets based on fish and invertebrates. Lutrinae is a branch of the Mustelidae family, which also includes wea ...
have grown in numbers. There are occasional sightings of animals that had long been extinct in Central Europe, for example, the wolf.
Geology
General


 Only in the extreme northeast of Franconia and in the Spessart are there
Only in the extreme northeast of Franconia and in the Spessart are there Variscan
The Variscan or Hercynian orogeny was a geologic mountain-building event caused by Late Paleozoic continental collision between Euramerica (Laurussia) and Gondwana to form the supercontinent of Pangaea.
Nomenclature
The name ''Variscan'', comes f ...
outcrops of the crystalline basement
A basement or cellar is one or more floors of a building that are completely or partly below the ground floor. It generally is used as a utility space for a building, where such items as the furnace, water heater, breaker panel or fuse box, ...
, which were uplifted from below the surface when the Alps exerted a northwards-oriented pressure. These are rocks of pre- Permian vintage, which were folded during various stages of Variscan orogeny in the Late Palaeozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon.
The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838
by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ' ...
- before about 380 to 300 million years ago - and, in places, were metamorphosed under high pressure and temperature or were crystallized by ascending magma in the Earth's crust
Earth's crust is Earth's thin outer shell of rock, referring to less than 1% of Earth's radius and volume. It is the top component of the lithosphere, a division of Earth's layers that includes the crust and the upper part of the mantle. The ...
.Stefan Glaser, Gerhard Doppler and Klaus fword (eds.): ''GeoBavaria. 600 Millionen Jahre Bayern. Internationale Edition.'' Bayerisches Geologisches Landesamt, Munich, 2004online
), p. 4 Rocks which were unchanged or only lightly metamorphosed, because they had been deformed at shallow crustal depths, include the Lower Carboniferous shale and greywacke of Franconian Forest. The Fichtel mountains, the Münchberg Plateau and the Spessart, by contrast, have more metamorphic rocks ( phyllite, schist,
amphibolite
Amphibolite () is a metamorphic rock that contains amphibole, especially hornblende and actinolite, as well as plagioclase feldspar, but with little or no quartz. It is typically dark-colored and dense, with a weakly foliated or schistose (flaky ...
, gneiss). The Fichtel mountains are also characterized by large granite bodies, called post-kinematic plutons which, in the late phase of Variscan orogeny, intruded into the metamorphic rocks. In most cases these are S-type granites whose melting was caused by heated-up sedimentary rocks sunk deep into the Earth's crust.Stefan Glaser, Gerhard Doppler and Klaus fword. (eds.): ''GeoBavaria. 600 Millionen Jahre Bayern. Internationale Edition.'' Bayerisches Geologisches Landesamt, Munich, 2004online
), p. 24 While the Fichtel and Franconian Forest can be assigned to the Saxo-Thuringian Zone of Central European Variscan orogeny, the Spessart belongs to the Central German Crystalline Zone. The Münchberg mass is variously attributed to the Saxo-Thuringian or Moldanubian Zones. A substantially larger part of the shallow subsurface in Franconia comprises Mesozoic, unmetamorphosed, unfolded rocks of the
South German Scarplands
The South German Scarplands is a geological and geomorphological natural region or landscape in Switzerland and the south German states of Bavaria and Baden-Württemberg. The landscape is characterised by escarpments.
It is variously referred to ...
.Stefan Glaser, Gerhard Doppler and Klaus Schwerd (eds.): ''GeoBavaria. 600 million years Bavaria. International Edition. GeoBavaria. 600 Millionen Jahre Bayern. Internationale Edition.'' Bayerisches Geologisches Landesamt, Munich, 2004online
), p. 26 The regional geological element of the South German Scarplands is the Franconian Platform (''Süddeutsche Großscholle''). At the so-called Franconian Line, a significant fault line, the Saxo-Thuringian-Moldanubian basement was uplifted in places up to 2000 m above the Franconian Platform. The western two-thirds of Franconia is dominated by the Triassic with its sandstones,
siltstone
Siltstone, also known as aleurolite, is a clastic sedimentary rock that is composed mostly of silt. It is a form of mudrock with a low clay mineral content, which can be distinguished from shale by its lack of fissility.Blatt ''et al.'' 1980, p ...
s and claystone
Mudrocks are a class of fine-grained siliciclastic sedimentary rocks. The varying types of mudrocks include siltstone, claystone, mudstone, slate, and shale. Most of the particles of which the stone is composed are less than and are too sm ...
s (so-called siliciclastic
Siliciclastic (or ''siliclastic'') rocks are clastic noncarbonate sedimentary rocks that are composed primarily of silicate minerals, such as quartz or clay minerals. Siliciclasic rock types include mudrock, sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic ...
s) of the bunter sandstone
The Buntsandstein (German for ''coloured'' or ''colourful sandstone'') or Bunter sandstone is a lithostratigraphic and allostratigraphic unit (a sequence of rock strata) in the subsurface of large parts of west and central Europe. The Buntsands ...
; the limestones and marl
Marl is an earthy material rich in carbonate minerals, clays, and silt. When hardened into rock, this becomes marlstone. It is formed in marine or freshwater environments, often through the activities of algae.
Marl makes up the lower part o ...
s of the Muschelkalk and the mixed, but predominantly siliciclastic, sedimentary rocks of the Keuper
The Keuper is a lithostratigraphic unit (a sequence of rock strata) in the subsurface of large parts of west and central Europe. The Keuper consists of dolomite, shales or claystones and evaporites that were deposited during the Middle and Late ...
. In the Rhön, the Triassic rocks are overlain and intruded by volcanic rock ( basalts, basanites, phonolite
Phonolite is an uncommon extrusive rock, of intermediate chemical composition between felsic and mafic, with texture ranging from aphanitic (fine-grained) to porphyritic (mixed fine- and coarse-grained). Phonolite is a variation of the igneous ...
s and trachytes) of the Tertiary. The eastern third of Franconia is dominated by the Jurassic rocks of the Franconian Jura, with the dark shales of the Black Jura
The Black Jurassic or Black Jura (german: Schwarzer Jura) in earth history refers to the lowest of the three lithostratigraphic units of the South German Jurassic, the latter being understood not as a geographical, but a geological term in the sen ...
, the shales and ferruginous sandstones of the Brown Jura
The Brown Jurassic or Brown Jura (german: Brauner Jura or ''Braunjura'') in earth history refers to the middle of the three lithostratigraphic units of the South German Jurassic, the latter being understood not as a geographical, but a geological ...
and, the weathering-resistant limestones and dolomitic rocks of the White Jura
The White Jurassic or White Jura (german: Weißer Jura or ''Weißjura'') in earth history refers to the upper of the three lithostratigraphic units of the South German Jurassic, the latter being understood not as a geographical, but a geological t ...
, which stand out from the landscape and form the actual ridge of the Franconian Jura itself. In the Jura, mostly siliciclastic sedimentary rocks formed in the Cretaceous have survived.
The Mesozoic sediments have been deposited in largescale basin areas. During the Triassic, the Franconian part of these depressions was often part of the mainland, in the Jurassic it was covered for most of the time by a marginal sea of the western Tethys Ocean. At the time when the limestones and dolomites of the White Jura were being deposited, this sea was divided into sponge reefs and intervening lagoons. The reef bodies and the fine-grained lagoon limestones and marls are the material from which the majority of the Franconian Jura is composed today.Stefan Glaser, Gerhard Doppler and Klaus Schwerde. (eds.): Stefan Glaser, Gerhard Doppler und Klaus Schwerd (Red.): ''GeoBavaria. 600 Millionen Jahre Bayern. Internationale Edition.'' Bayerisches Geologisches Landesamt, Munich, 2004online
), p. 40 ff. Following a drop in the sea level towards the end of the Upper Jurassic, larger areas also became part of the mainland at the beginning of the subsequent Cretaceous period. During the Upper Cretaceous, the sea advanced again up to the area of the Franconian Jura. At the end of the Cretaceous, the sea then retreated again from the region. In addition, large parts of South and Central Germany experienced a general uplift -or in areas where the basement had broken through a substantial uplift - the course of formation of the Alps during the Tertiary. Since then, Franconia has been mainly influenced by erosion and weathering (especially in the Jura in the form of
karst
Karst is a topography formed from the dissolution of soluble rocks such as limestone, dolomite, and gypsum. It is characterized by underground drainage systems with sinkholes and caves. It has also been documented for more weathering-resistant ro ...
), which has ultimately led to formation of today's landscapes.
Fossils
 The oldest macrofossils in Franconia, which are also the oldest in Bavaria, are archaeocyatha, sponge-like, goblet-shaped marine organisms, which were discovered in 2013 in a limestone block of Late Lower Cambrian age, about 520 million years old. The block comes from the vicinity
The oldest macrofossils in Franconia, which are also the oldest in Bavaria, are archaeocyatha, sponge-like, goblet-shaped marine organisms, which were discovered in 2013 in a limestone block of Late Lower Cambrian age, about 520 million years old. The block comes from the vicinity Schwarzenbach am Wald
Schwarzenbach am Wald is a town in the district of Hof, in Bavaria, Germany. It is situated 21 km west of Hof, and 23 km northeast of Kulmbach
Kulmbach () is the capital of the district of Kulmbach in Bavaria in Germany. The town i ...
from the so-called Heinersreuth Block Conglomerate (''Heinersreuther Blockkonglomerat''), a Lower Carboniferous wildflysch
Flysch () is a sequence of sedimentary rock layers that progress from deep-water and turbidity flow deposits to shallow-water shales and sandstones. It is deposited when a deep basin forms rapidly on the continental side of a mountain building e ...
. However, the aforementioned archaeocyathids are not three-dimensional fossils, but two-dimensional thin sections. These thin sections had already been prepared and investigated in the 1970s but the archaeocyathids among them were apparently overlooked at that time.
Better known and more highly respected fossil finds in Franconia come from the unfolded sedimentary rocks of the Triassic and Jurassic. The bunter sandstone
The Buntsandstein (German for ''coloured'' or ''colourful sandstone'') or Bunter sandstone is a lithostratigraphic and allostratigraphic unit (a sequence of rock strata) in the subsurface of large parts of west and central Europe. The Buntsands ...
, however, only has a relatively small number of preserved whole fossils. Much more commonly, it contains trace fossils, especially the tetrapod footprints of ''Chirotherium
''Chirotherium'', also known as ''Cheirotherium'' (‘hand-beast’), is a Triassic trace fossil consisting of five-fingered (pentadactyle) footprints and whole tracks. These look, by coincidence, remarkably like the hands of apes and bears, with ...
''. The type locality for these animal track
__notoc__
An animal track is an imprint left behind in soil, snow, or mud, or on some other ground surface, by an animal walking across it. Animal tracks are used by hunters in tracking their prey and by naturalists to identify animals living ...
s is Hildburghausen in the Thuringian part of Franconia, where it occurs in the so-called Thuringian Chirotherium Sandstone (''Thüringer Chirotheriensandstein'', main Middle Bunter Sandstone). ''Chirotherium'' is also found in the Bavarian and Württemberg parts of Franconia. Sites include Aura
Aura most commonly refers to:
* Aura (paranormal), a field of luminous multicolored radiation around a person or object
* Aura (symptom), a symptom experienced before a migraine or seizure
Aura may also refer to:
Places Extraterrestrial
* 1488 ...
near Bad Kissingen, Karbach, Gambach and Külsheim.Frank-Otto Haderer, Georges Demathieu, Ronald Böttcher: ''Wirbeltier-Fährten aus dem Rötquarzit (Oberer Buntsandstein, Mittlere Trias) von Hardheim bei Wertheim/Main (Süddeutschland).'' Stuttgarter Beiträge zur Naturkunde, Serie B. No. 230, 1995online
There the deposits are somewhat younger (Upper Bunter Sandstone), and the corresponding stratigraphic interval is called the Franconian Chirotherium Beds (''Fränkische Chirotherienschichten''). Among the less significant body fossil records of vertebrates are the procolophonid ''Anomoiodon liliensterni'' from
Reurieth
Reurieth is a municipality in the district of Hildburghausen, in Thuringia, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russi ...
in the Thuringian part of Franconia and ''Koiloskiosaurus coburgiensis'' from Mittelberg near Coburg, both from the Thuringian Chirotherium Sandstone, and the Temnospondyle '' Mastodonsaurus ingens'' (possibly identical with the mastodonsaurus, ''Heptasaurus cappelensis
''Heptasaurus'' is an extinct genus of Triassic capitosaurian temnospondyl amphibian within the family Mastodonsauridae
Mastodonsauridae is a family of capitosauroid temnospondyls. Fossils belonging to this family have been found in North ...
'') from the Röt Formation, Upper Bunter at Gambach.
As early as the first decade of the 19th century George, Count of Münster began systematic fossil gathering and digs and in the Upper Muschelkalk at Bayreuth
Bayreuth (, ; bar, Bareid) is a town in northern Bavaria, Germany, on the Red Main river in a valley between the Franconian Jura and the Fichtelgebirge Mountains. The town's roots date back to 1194. In the 21st century, it is the capital of U ...
. For example, the Oschenberg hill near Laineck became the type locality of two relatively well-known marine reptiles of the Triassic period, later found in other parts of Central Europe: the "flat tooth lizard", ''Placodus'' and the "false lizard", ''Nothosaurus''.
In Franconia's middle Keuper
The Keuper is a lithostratigraphic unit (a sequence of rock strata) in the subsurface of large parts of west and central Europe. The Keuper consists of dolomite, shales or claystones and evaporites that were deposited during the Middle and Late ...
(the Feuerletten) is one of the best known and most common species of dinosaurs of Central Europe: ''Plateosaurus engelhardti'', an early representative of the sauropodomorpha. Its type locality is located at Heroldsberg south of Nuremberg. When the remains of ''Plateosaurus'' were first discovered there in 1834, it was the first discovery of a dinosaur on German soil, and this occurred even before the name "dinosauria" was coined. Another important ''Plateosaurus'' find in Franconia was made at Ellingen.
Far more famous than ''Plateosaurus'', ''Placodus'' and ''Nothosaurus'' is the ''Archaeopteryx'', probably the first bird geologically. It was discovered in the southern Franconian Jura, ''inter alia'' at the famous fossil site of Solnhofen in the Solnhofen Platform Limestone (''Solnhofener Plattenkalk'', (Solnhofen-Formation, early Tithonian, Upper Jurassic). In addition to ''Archaeopteryx'', in the very fine-grained, laminated lagoon limestones are the pterosaur ''Pterodactylus'' and various bony fishes as well as numerous extremely detailed examples of invertebrates e.g. feather stars and dragonflies. Eichstätt is the other "big" and similarly famous fossil locality in the Solnhofen Formation, situated on the southern edge of the Jura in Upper Bavaria. Here, as well as ''Archaeopteryx'', the theropod dinosaurs, ''Compsognathus'' and ''Juravenator'', were found.
An inglorious episode in the history of paleontology took place in Franconia: fake fossils, known as Beringer's Lying Stones, were acquired in the 1720s by Würzburg doctor and naturalist, Johann Beringer, for a lot of money and then described in a monograph, along with genuine fossils from the Würzburg area. However, it is not entirely clear whether the Beringer forgeries were actually planted or whether he himself was responsible for the fraud.
Climate
Franconia has a humid continental climate, humid cool temperate transitional climate, which is neither very continental nor very maritime. The average monthly temperatures vary depending on the area between about -1 to -2 °C in January and 17 to 19 °C in August, but may reach a peak of about 35 °C for a few days in the summer, especially in the large cities. The climate of Franconia is sunny and relatively warm. For part of the summer, for example, Lower Franconia is one of the sunniest areas in Germany. Daily temperatures in the Bavarian part of Franconia are an average of 0.1 °C higher than the average for Bavaria as a whole. Relatively less rain falls in Franconia, and likewise in the rest of North Bavaria rain than is usual for its geographic location; even summer storms are often less powerful than in other areas of South Germany. In southern Bavaria about 2,000 mm of precipitation falls annually and almost three times as much as in parts of Franconia (about 500–900 mm) in the rain shadow of the Spessart, Rhön and Odenwald.Quality of life
Franconia, as part of Germany, has a high quality of life. In the ''Worldwide Quality of Living Survey'' by Mercer (consulting firm), Mercer in 2010, the city of Nuremberg was one of the top 25 cities in the world in terms of quality of life and came sixth in Germany. In environmental ranking Nuremberg came thirteenth in the world and was the best German city In a survey by the German magazine, ''Focus (German magazine), Focus'', on quality of life in 2014, the districts of Eichstätt and Fürth were among the top positions in the table. In the ''Glücksatlas'' by Deutsche Post AG, Deutsche Post Franconia achieved some of the highest scores, but the region slipped in 2013 to 13th place out of 19.History
Name
Franconia is named after the Franks, a Germanic peoples, Germanic tribe who conquered most of Western Europe by the middle of the 8th century. Despite its name, Franconia is not the homeland of the Franks, but rather owes its name to being partially settled by Franks from the Rhineland during the 7th century following the defeat of the Alamanni and Thuringians who had dominated the region earlier. At the beginning of the 10th century a ''Duchy of Franconia'' (german: Herzogtum Franken, links=no) was established withinEast Francia
East Francia (Medieval Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the East Franks () was a successor state of Charlemagne's Carolingian Empire, empire ruled by the Carolingian dynasty until 911. It was created through the Treaty of Verdun (843) which divided t ...
, which comprised modern Hesse, Palatinate (region), Palatinate, parts of Baden-Württemberg and most of today's Franconia. After the dissolution of the so-called Stem duchy of Franconia, the Holy Roman Empire, Holy Roman Emperors created the Franconian Circle (German ''Fränkischer Reichskreis'') in 1500 to embrace the principalities that grew out of the eastern half of the former duchy. The territory of the Franconian Circle roughly corresponds with modern Franconia. The title of a ''Duke of Duchy of Franconia, Franconia'' was claimed by the Bishopric of Würzburg, Würzburg bishops until 1803 and by the kings of Kingdom of Bavaria, Bavaria until 1918. Examples of Franconian cities founded by Frankish noblemen are Würzburg, first mentioned in the 7th century, Ansbach, first mentioned in 748, and Weißenburg in Bayern, Weissenburg, founded in the 7th century.
Early history and Antiquity
 Fossil finds show that the region was already settled by Caveman, primitive man, ''Homo erectus'', in the middle Last Glacial Period, Ice Age about 600,000 years ago. Probably the oldest human remains in the Bavarian part of Franconia were found in the cave ruins of Hunas at Pommelsbrunn in the county of Nuremberg Land. In the late Bronze Age, the region was probably only sparsely inhabited, as few noble metals occur here and the soils are only moderately fertile. In the subsequent Iron Age (from about 800 B.C.) the Celts become the first nation to be discernible in the region. In northern Franconia they built a chain of hill forts as a line of defence against the Germani advancing from the north. On the Staffelberg they built a powerful settlement, to which Ptolemy gave the name ''Menosgada, oppidum Menosgada'', and on the Gleichberge is the largest surviving ''oppidum'' in Central Germany (geography), Central Germany, the Oppidum Steinsburg, Steinsburg. With the increased expansion of Roman Empire, Rome in the first century B.C. and the simultaneous advance of the Elbe Germans, Elbe Germanic tribes from the north, the Celtic culture began to fall into decline. The southern parts of present-day Franconia soon fell under Roman control; however, most of the region remained in Free Germania. Initially Rome tried extend its direct influence far to the northeast; in the longer term, however, the Germanic-Roman frontier formed further southwest.
Fossil finds show that the region was already settled by Caveman, primitive man, ''Homo erectus'', in the middle Last Glacial Period, Ice Age about 600,000 years ago. Probably the oldest human remains in the Bavarian part of Franconia were found in the cave ruins of Hunas at Pommelsbrunn in the county of Nuremberg Land. In the late Bronze Age, the region was probably only sparsely inhabited, as few noble metals occur here and the soils are only moderately fertile. In the subsequent Iron Age (from about 800 B.C.) the Celts become the first nation to be discernible in the region. In northern Franconia they built a chain of hill forts as a line of defence against the Germani advancing from the north. On the Staffelberg they built a powerful settlement, to which Ptolemy gave the name ''Menosgada, oppidum Menosgada'', and on the Gleichberge is the largest surviving ''oppidum'' in Central Germany (geography), Central Germany, the Oppidum Steinsburg, Steinsburg. With the increased expansion of Roman Empire, Rome in the first century B.C. and the simultaneous advance of the Elbe Germans, Elbe Germanic tribes from the north, the Celtic culture began to fall into decline. The southern parts of present-day Franconia soon fell under Roman control; however, most of the region remained in Free Germania. Initially Rome tried extend its direct influence far to the northeast; in the longer term, however, the Germanic-Roman frontier formed further southwest.
 Under the emperors, Domitian (81-96), Trajan (98-117) and Hadrian (emperor), Hadrian (117-138), the Rhaetian Limes was built as a border facing the Germanic tribes to the north. This defensive line ran through the south of Franconia and described an arc across the region whose northernmost point lay at present-day Gunzenhausen. To protect it, the Romans built several forts like Biriciana at Weißenburg in Bayern, Weißenburg, but by the mid-third century, the border could no longer be maintained and by 250 A.D. the Alemanni occupied the areas up to the Danube. Fortified settlements such as the Gelbe Bürg at Dittenheim controlled the new areas.Wilfried Menghin: ''Grundlegung: Das frühe Mittelalter''. In: Handbuch der Bayerischen Geschichte, begr. von Max Spindler, 3rd vol., 1st sub-vol.: Geschichte Frankens bis zum Ausgang des 18. Jahrhunderts, re-published by Andreas Kraus, 3rd, revised edition, Munich, 1997, pp. 47–69, here: p. 60 More such Gau forts have been detected north of the former Limes as well. To which tribe their occupants belonged is unknown in most cases. However, it is likely that it was mainly Alemanni and Juthungi in especially in the south.Wilfried Menghin: ''Grundlegung: Das frühe Mittelalter''. In: Handbuch der Bayerischen Geschichte, begr. von Max Spindler, 3. Bd., 1. Teilbd: Geschichte Frankens bis zum Ausgang des 18. Jahrhunderts, re-published by Andreas Kraus, 3rd, revised edition, Munich, 1997, pp. 47–69, here: S. 55.
By contrast, it was the Burgundians who settled on the Lower and Middle Main. Many of these hill forts appear to have been destroyed, however, no later than 500 A.D. The reasons are not entirely clear, but it could have been as a result of invasions by the Huns which thus triggered the Migration Period, Great Migration. In many cases, however, it was probably conquest by the Franks that spelt the end of these hilltop settlements.
Under the emperors, Domitian (81-96), Trajan (98-117) and Hadrian (emperor), Hadrian (117-138), the Rhaetian Limes was built as a border facing the Germanic tribes to the north. This defensive line ran through the south of Franconia and described an arc across the region whose northernmost point lay at present-day Gunzenhausen. To protect it, the Romans built several forts like Biriciana at Weißenburg in Bayern, Weißenburg, but by the mid-third century, the border could no longer be maintained and by 250 A.D. the Alemanni occupied the areas up to the Danube. Fortified settlements such as the Gelbe Bürg at Dittenheim controlled the new areas.Wilfried Menghin: ''Grundlegung: Das frühe Mittelalter''. In: Handbuch der Bayerischen Geschichte, begr. von Max Spindler, 3rd vol., 1st sub-vol.: Geschichte Frankens bis zum Ausgang des 18. Jahrhunderts, re-published by Andreas Kraus, 3rd, revised edition, Munich, 1997, pp. 47–69, here: p. 60 More such Gau forts have been detected north of the former Limes as well. To which tribe their occupants belonged is unknown in most cases. However, it is likely that it was mainly Alemanni and Juthungi in especially in the south.Wilfried Menghin: ''Grundlegung: Das frühe Mittelalter''. In: Handbuch der Bayerischen Geschichte, begr. von Max Spindler, 3. Bd., 1. Teilbd: Geschichte Frankens bis zum Ausgang des 18. Jahrhunderts, re-published by Andreas Kraus, 3rd, revised edition, Munich, 1997, pp. 47–69, here: S. 55.
By contrast, it was the Burgundians who settled on the Lower and Middle Main. Many of these hill forts appear to have been destroyed, however, no later than 500 A.D. The reasons are not entirely clear, but it could have been as a result of invasions by the Huns which thus triggered the Migration Period, Great Migration. In many cases, however, it was probably conquest by the Franks that spelt the end of these hilltop settlements.
Middle Ages
 With their victories over the heartlands of the Alamanni and Thuringians in the 6th century, the present region of Franconia also fell to the Franks.Karten zur Geschichte Bayerns: Jutta Schumann / Dieter J. Weiß, in: ''Edel und Frei. Franken im Mittelalter'', ed. by Wolfgang Jahn / Jutta Schumann / Evamaria Brockhoff, Augsburg, 2004 (Veröffentlichungen zur Bayerischen Geschichte und Kultur 47/04), pp. 174–176, Cat. No. 51. Sieh
With their victories over the heartlands of the Alamanni and Thuringians in the 6th century, the present region of Franconia also fell to the Franks.Karten zur Geschichte Bayerns: Jutta Schumann / Dieter J. Weiß, in: ''Edel und Frei. Franken im Mittelalter'', ed. by Wolfgang Jahn / Jutta Schumann / Evamaria Brockhoff, Augsburg, 2004 (Veröffentlichungen zur Bayerischen Geschichte und Kultur 47/04), pp. 174–176, Cat. No. 51. SiehHaus der Bayerischen Geschichte
/ref> After the division of the Frankish Empire, East Francia (''Francia orientialis'') was formed from the territories of the dioceses of Mainz, Worms, Germany, Worms, Würzburg and Speyer. Later, the diocese of Bamberg was added. In the 7th century, the Slavs started to populate the northeastern parts of the region from the east, because the area of today's Upper Franconia was very sparsely populated (Bavaria Slavica).Franz-Joseph Schmale, Wilhelm Störmer: ''Die politische Entwicklung bis zur Eingliederung ins Merowingische Frankenreich''. In: Handbuch der Bayerischen Geschichte, begr. von Max Spindler, 3rd vol., 1st sub-vol.: Geschichte Frankens bis zum Ausgang des 18. Jahrhunderts, re-published by Andreas Kraus, 3rd, revised edition, Munich, 1997, pp. 89–114, here: p. 80. However, in the 10th and 11th centuries, they largely gave up their own language and cultural tradition. The majority of the population of Franconia was pagan well into the Early Middle Ages, The first people to spread the Christian faith strongly were wandering Ireland (island), Irish Anglo-Saxon monks in the early 7th century. Saint Kilian, who together with his companions, Saint Colman (martyr), Saint Colman and Saint Totnan are considered to be the apostles to the Franks, suffering martyrdom in Würzburg in the late 7th century, probably did not encounter any pagans in the ducal court. It was probably Saint Boniface who carried the Christian mission deep into the heart of the ordinary population of Franconia. In the mid-9th century the Duchy of Franconia, tribal Duchy of Franconia emerged, one of the five tribal or stem duchies of
East Francia
East Francia (Medieval Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the East Franks () was a successor state of Charlemagne's Carolingian Empire, empire ruled by the Carolingian dynasty until 911. It was created through the Treaty of Verdun (843) which divided t ...
. The territory of the stem duchy was far bigger than modern Franconia and covered the whole of present-day Hesse, northern Baden-Württemberg, southern Thuringia, large parts of Rhineland-Palatinate and parts of the Franconian provinces in Bavaria. It extended as far west as Speyer, Mainz, and Worms, Germany, Worms (west of the Rhine) and even included Frankfurt ("ford of the Franks"). In the early 10th century, the Babenbergs and Conradines fought for power in Franconia. Ultimately this discord led to the Babenberg Feud which was fuelled and controlled by the crown. The outcome of this feud meant the loss of power for the Babenbergs, but indirectly resulted in the Conradines winning the crown of East Francia. Sometime around 906, Conrad I of Germany, Conrad succeeded in establishing his ducal hegemony over Franconia, but when the direct Carolingian male line failed in 911, Conrad was acclaimed List of German Kings and Emperors, King of the Germans, largely because of his weak position in his own duchy. Franconia, like Alamannia was fairly fragmented and the duke's position was often disputed between the chief families. Conrad had granted Franconia to his brother Eberhard of Franconia, Eberhard on his succession, but when Eberhard rebelled against Otto I, Holy Roman Emperor, Otto I in 938, he was deposed from his duchy, which disintegrated in 939 on Eberhard's death into West or Rhenish Franconia (), and East Franconia (')East Franconia should not be confused with the eastern division of the Frankish Empire, East Francia
East Francia (Medieval Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the East Franks () was a successor state of Charlemagne's Carolingian Empire, empire ruled by the Carolingian dynasty until 911. It was created through the Treaty of Verdun (843) which divided t ...
, which was also known as in Latin. This refers to the much larger area which later became the German Kingdom and of which the whole of the Duchy of Franconia was a part. and was directly subordinated to the Reich. Only after that was the former considered to be under the sphere of the bishops of Würzburg as the true Franconia, its territory gradually shrinking to its present area.
Meanwhile, the inhabitants of parts of present-day Upper and Middle Franconia, who were not under the control of Würzburg, probably also considered themselves to be Franks at that time, and certainly their dialect distinguished them from the inhabitants of Bavaria and Swabia
Swabia ; german: Schwaben , colloquially ''Schwabenland'' or ''Ländle''; archaic English also Suabia or Svebia is a cultural, historic and linguistic region in southwestern Germany.
The name is ultimately derived from the medieval Duchy of ...
.Karten zur Geschichte Bayerns: Jutta Schumann / Dieter J. Weiß, in: Edel und Frei. Franken im Mittelalter, ed. by Wolfgang Jahn / Jutta Schumann / Evamaria Brockhoff, Augsburg, 2004 (Veröffentlichungen zur Bayerischen Geschichte und Kultur 47/04), pp. 174–176, Cat. No. 51. SeHaus der Bayerischen Geschichte
Unlike the other stem duchies, Franconia became the homeland and power base of East Frankish and German kings after the Ottonians died out in 1024.Josef Kirmeier: ''Bayern und das Deutsche Reich (10.-12. Jahrhundert)'', In: ''Politische Geschichte Bayerns'', published by the Haus der Bayerischen Geschichte as Issue 9 of the ''Hefte zur Bayerischen Geschichte und Kultur'', pp. 7–9, here: p. 7 As a result, in the High Middle Ages, the region did not become a strong regional force such as those which formed in Saxony, Bavaria and
Swabia
Swabia ; german: Schwaben , colloquially ''Schwabenland'' or ''Ländle''; archaic English also Suabia or Svebia is a cultural, historic and linguistic region in southwestern Germany.
The name is ultimately derived from the medieval Duchy of ...
. In 1007, the later canonized Henry II founded the Arcbishopric of Bamberg, Bishopric of Bamberg and endowed it with rich estates. Bamberg became a favoured ''Kaiserpfalz, Pfalz'' and an important centre of the Empire. Because parts of the Bishopric of Würzburg also fell to Bamberg, Würzburg was enfeoffed several royal estates by King Henry II by way of compensation.
 From the 12th century Nuremberg Castle was the seat of the Burgraviate of Nuremberg. The burgraviate was ruled from about 1190 by the Zollerns, the Franconian line of the later House of Hohenzollern, which provided the German emperors of the 19th and 20th century. Under the Hohenstaufen kings, Conrad III (HRR), Conrad III and Frederick I (HRR), Frederick Barbarossa, Franconia became the centre of power in the Empire. During the time when there was no emperor, the Interregnum (Holy Roman Empire), Interregnum (1254–1273), some territorial princes became ever more powerful. After the Interregnum, however, the rulers succeeded in re-establishing a stronger royal lordship in Franconia. Franconia soon played an important role again for the monarchy at the time of Rudolf I (HRR), Rudolf of Habsburg; the itineraries of his successors showing their preference for the Rhine-Main region. In 1376 the Swabian League of Cities was founded and was joined later by several Franconian imperial cities. During the 13th century the Teutonic Order was formed, taking over its first possession in Franconia in 1209, the Bailiwick of Franconia. The foundation of many schools and hospitals and the construction of numerous churches and castles in this area goes back to the work of this Roman Catholic military order. The residence place of the bailiwick was at Ellingen until 1789 when it was transferred to today's Bad Mergentheim.Rudolf Endres: ''Staat und Gesellschaft. Zweiter Teil: 1500-1800''. In: Handbuch der Bayerischen Geschichte, begr. von Max Spindler, 3rd vol., 1st sub-vol.: Geschichte Frankens bis zum Ausgang des 18. Jahrhunderts, re-published by Andreas Kraus, 3rd, revised edition, Munich, 1997, pp. 702–781, here: pp. 752ff Other orders such as the Knights Templar could not gain a foothold in Franconia; the Order of St. John worked in the Bishopric of Würzburg and had short term commands.Wilhelm Störmer: ''Die innere Entwicklung: Staat, Gesellschaft, Kirche, Wirtschaft''. In: Handbuch der Bayerischen Geschichte, begr. von Max Spindler, 3rd vol., 1st sub-vol.: Geschichte Frankens bis zum Ausgang des 18. Jahrhunderts, re-published by Andreas Kraus, 3rd revised edition, Munich, 1997, pp. 210–315, here: p. 314.
From the 12th century Nuremberg Castle was the seat of the Burgraviate of Nuremberg. The burgraviate was ruled from about 1190 by the Zollerns, the Franconian line of the later House of Hohenzollern, which provided the German emperors of the 19th and 20th century. Under the Hohenstaufen kings, Conrad III (HRR), Conrad III and Frederick I (HRR), Frederick Barbarossa, Franconia became the centre of power in the Empire. During the time when there was no emperor, the Interregnum (Holy Roman Empire), Interregnum (1254–1273), some territorial princes became ever more powerful. After the Interregnum, however, the rulers succeeded in re-establishing a stronger royal lordship in Franconia. Franconia soon played an important role again for the monarchy at the time of Rudolf I (HRR), Rudolf of Habsburg; the itineraries of his successors showing their preference for the Rhine-Main region. In 1376 the Swabian League of Cities was founded and was joined later by several Franconian imperial cities. During the 13th century the Teutonic Order was formed, taking over its first possession in Franconia in 1209, the Bailiwick of Franconia. The foundation of many schools and hospitals and the construction of numerous churches and castles in this area goes back to the work of this Roman Catholic military order. The residence place of the bailiwick was at Ellingen until 1789 when it was transferred to today's Bad Mergentheim.Rudolf Endres: ''Staat und Gesellschaft. Zweiter Teil: 1500-1800''. In: Handbuch der Bayerischen Geschichte, begr. von Max Spindler, 3rd vol., 1st sub-vol.: Geschichte Frankens bis zum Ausgang des 18. Jahrhunderts, re-published by Andreas Kraus, 3rd, revised edition, Munich, 1997, pp. 702–781, here: pp. 752ff Other orders such as the Knights Templar could not gain a foothold in Franconia; the Order of St. John worked in the Bishopric of Würzburg and had short term commands.Wilhelm Störmer: ''Die innere Entwicklung: Staat, Gesellschaft, Kirche, Wirtschaft''. In: Handbuch der Bayerischen Geschichte, begr. von Max Spindler, 3rd vol., 1st sub-vol.: Geschichte Frankens bis zum Ausgang des 18. Jahrhunderts, re-published by Andreas Kraus, 3rd revised edition, Munich, 1997, pp. 210–315, here: p. 314.
Successor states of East Francia
As of the 13th century, the following states, among others, had formed in the territory of the former Duchy:Modern Period
Early Modern Period
On 2 July 1500 during the reign of Emperor Maximilian I (HRR), Maximilian I, as part of the Imperial Reform (Holy Roman Empire), Imperial Reform Movement, the Empire was divided into Imperial Circles. This led in 1512 to the formation of the Franconian Circle. Seen from a modern perspective, the Franconian Circle may be viewed as an important basis for the sense of a common Franconian identity that exists today. The Franconian Circle also shaped the geographical limits of the present-day Franconia. In the late Middle Ages and Early Modern Period, the Imperial Circle was severely affected by ''Kleinstaaterei'', the patchwork of tiny states in this region of Germany. As during the late Middle Ages, the bishops of Würzburg used the nominal title of Duke of Franconia during the time of the Imperial Circle. In 1559, the Franconian Circle was given jurisdiction over coinage (''Münzaufsicht'') and, in 1572, was the only Circle to issue its own police ordinance. Members of the Franconian Circle included the imperial cities, the prince-bishoprics, the Bailiwick of Franconia of the Teutonic Order and several counties. The Imperial Knights with their tiny territories, of which there was a particularly large number in Franconia, were outside the Circle assembly and, until 1806, formed the Franconian Knights Circle (''Fränkischer Ritterkreis'') consisting of six Knights' Cantons. Because the extent of Franconia, already referred to above, is disputed, there were many areas that might be counted as part of Franconia today, that lay outside the Franconian Circle. For example, the area of Aschaffenburg belonged to Electoral Mainz and was a part of the Electoral Rhenish Circle, the area of Coburg belonged to the Upper Saxon Circle and the Heilbronn area to the Swabian Circle. In the 16th century, the College of Franconian Counts was founded to represent the interests of the counts in Franconia. Franconia played an important role in the spread of the Reformation initiated by Martin Luther,Rudolf Endres: ''Von der Bildung des Fränkischen Reichskreises und dem Beginn der Reformation bis zum Augsburger Religionsfrieden von 1555''. In: Handbuch der Bayerischen Geschichte, edited by Max Spindler, 3rd vol., 1st sub-vol.: Geschichte Frankens bis zum Ausgang des 18. Jahrhunderts, re-published by Andreas Kraus, 3rd revised edition, Munich, 1997, pp. 451–472, here: pp. 455ff. Nuremberg being one of the places where the Luther Bible was printed. The majority of other Franconian imperial cities and imperial knights embraced the new confession.Rudolf Endres: ''Von der Bildung des Fränkischen Reichskreises und dem Beginn der Reformation bis zum Augsburger Religionsfrieden von 1555''. In: Handbuch der Bayerischen Geschichte, edited by Max Spindler, 3rd vol., 1st sub-vol.: Geschichte Frankens bis zum Ausgang des 18. Jahrhunderts, re-published by Andreas Kraus, 3rd revised edition, Munich, 1997, pp. 451–472, here: p. 467. In the course of the counter-reformation several regions of Franconia returned to Catholicism, however, and there was also an increase in witch trials. In addition to Lutheranism, the Radical Reformation, radical reformatory baptist movement spread early on across the Franconian area. Important Baptist centres were Königsberg in Bayern, Königsberg and Nuremberg. In 1525, the burden of heavy taxation and socage combined with new, liberal ideas that chimed with the Reformation movement, unleashed the German Peasants' War. The Würzburg area was particularly hard hit with numerous castles and monasteries being burned down.''Stadthistorische Streiflichter (24)''
In 1525, the burden of heavy taxation and socage combined with new, liberal ideas that chimed with the Reformation movement, unleashed the German Peasants' War. The Würzburg area was particularly hard hit with numerous castles and monasteries being burned down.''Stadthistorische Streiflichter (24)''www.wuerzburg.de, accessed 7 June 2014. In the end, however, the uprisings were suppressed and for centuries the lowest strata of society were excluded from all political activity. From 1552, Margrave Albert Alcibiades attempted to break the supremacy of the mighty imperial city of Nuremberg and to secularise the ecclesial estates in the Second Margrave War,Rudolf Endres: ''Von der Bildung des Fränkischen Reichskreises und dem Beginn der Reformation bis zum Augsburger Religionsfrieden von 1555''. In: Handbuch der Bayerischen Geschichte, ed. Max Spindler, 3 vols., 1 sub-vol: History of Franconia to the end of the 18th century, revised by Andreas Kraus, 3rd revised edition, Munich, 1997, pp. 451-472, here: p. 469 to create a duchy over which he would rule. Large areas of Franconia were eventually devastated in the fighting until King Ferdinand I (HRR), Ferdinand I together with several dukes and princes decided to overthrow Albert.
 In 1608, the reformed princes merged into a so-called Protestant Union, Union within the Empire. In Franconia, the margraves of Ansbach and Bayreuth as well as the imperial cities were part of this alliance. The Catholic side responded in 1609 with a counter-alliance, the Catholic League (1609), League. The conflicts between the two camps ultimately resulted in the Thirty Years' War, which was the greatest strain on the cohesion of the Franconian Circle Initially, Franconia was not a theatre of war, although marauding armies repeatedly crossed its territory. However, in 1631, Swedish troops under Gustavus II Adolphus (Sweden), Gustavus Adolphus advanced into Franconia and established a large encampment in summer 1632 around Nuremberg.Rudolf Endres: ''Vom Augsburger Religionsfrieden bis zum Dreißigjährigen Krieg''. In: Handbuch der Bayerischen Geschichte, ed. Max Spindler, 3rd vol., 1st sub-vol: Geschichte Frankens bis zum Ausgang des 18. Jahrhunderts, revised by Andreas Kraus, 3rd revised edn., Munich, 1997, pp. 473–495, here: p. 490. However, the Swedes lost the Battle of the Alte Veste against Wallenstein's troops and eventually withdrew. Franconia was one of the poorest regions in the Empire and lost its imperial political significance.Michael Henker: ''Bayern im Zeitalter von Reformation und Gegenreformation (16./17. Jahrhundert)'', In: ''Politische Geschichte Bayerns'', published by the House of Bavarian History as Issue 9 of the ''Hefte zur Bayerischen Geschichte und Kultur'', pp. 14–17, here: p. 17 During the course of the war, about half the local population lost their lives. To compensate for these losses about 150,000 displaced Protestants settled in Protestant areas, including Austrian exiles.
In 1608, the reformed princes merged into a so-called Protestant Union, Union within the Empire. In Franconia, the margraves of Ansbach and Bayreuth as well as the imperial cities were part of this alliance. The Catholic side responded in 1609 with a counter-alliance, the Catholic League (1609), League. The conflicts between the two camps ultimately resulted in the Thirty Years' War, which was the greatest strain on the cohesion of the Franconian Circle Initially, Franconia was not a theatre of war, although marauding armies repeatedly crossed its territory. However, in 1631, Swedish troops under Gustavus II Adolphus (Sweden), Gustavus Adolphus advanced into Franconia and established a large encampment in summer 1632 around Nuremberg.Rudolf Endres: ''Vom Augsburger Religionsfrieden bis zum Dreißigjährigen Krieg''. In: Handbuch der Bayerischen Geschichte, ed. Max Spindler, 3rd vol., 1st sub-vol: Geschichte Frankens bis zum Ausgang des 18. Jahrhunderts, revised by Andreas Kraus, 3rd revised edn., Munich, 1997, pp. 473–495, here: p. 490. However, the Swedes lost the Battle of the Alte Veste against Wallenstein's troops and eventually withdrew. Franconia was one of the poorest regions in the Empire and lost its imperial political significance.Michael Henker: ''Bayern im Zeitalter von Reformation und Gegenreformation (16./17. Jahrhundert)'', In: ''Politische Geschichte Bayerns'', published by the House of Bavarian History as Issue 9 of the ''Hefte zur Bayerischen Geschichte und Kultur'', pp. 14–17, here: p. 17 During the course of the war, about half the local population lost their lives. To compensate for these losses about 150,000 displaced Protestants settled in Protestant areas, including Austrian exiles.
 Franconia never developed into a unified territorial state, because the patchwork quilt of small states (''Kleinstaaterei'') survived the Middle Ages and lasted until the 18th century.Karlheinz Scherr: ''Bayern im Zeitalter des Fürstlichen Absolutismus (17./18. Jahrhundert)'', In: ''Politische Geschichte Bayerns'', published by the House of Bavarian History as Issue 9 of the ''Hefte zur Bayerischen Geschichte und Kultur'', pp. 18–21, here: p. 20 As a result, the Franconian Circle had the important task of preserving peace, preventing abuses and to repairing war damage and had a regulatory role in the region until the end of the Holy Roman Empire. Until the War of the Spanish Succession, the Circle had become an almost independent organization and joined the Grand Alliance (League of Augsburg), Grand Alliance against Louis XIV as an almost sovereign state. The Circle also developed early forms of a welfare state. It also played a major role in the control of disease during the 16th and 17th centuries. After Charles Alexander (Brandenburg-Ansbach-Bayreuth), Charles Alexander abdicated in 1792, the former margraviates of Ansbach and Bayreuth were annexed by Prussia. Karl August Freiherr von Hardenberg was appointed as governor of these areas by Prussia.
Franconia never developed into a unified territorial state, because the patchwork quilt of small states (''Kleinstaaterei'') survived the Middle Ages and lasted until the 18th century.Karlheinz Scherr: ''Bayern im Zeitalter des Fürstlichen Absolutismus (17./18. Jahrhundert)'', In: ''Politische Geschichte Bayerns'', published by the House of Bavarian History as Issue 9 of the ''Hefte zur Bayerischen Geschichte und Kultur'', pp. 18–21, here: p. 20 As a result, the Franconian Circle had the important task of preserving peace, preventing abuses and to repairing war damage and had a regulatory role in the region until the end of the Holy Roman Empire. Until the War of the Spanish Succession, the Circle had become an almost independent organization and joined the Grand Alliance (League of Augsburg), Grand Alliance against Louis XIV as an almost sovereign state. The Circle also developed early forms of a welfare state. It also played a major role in the control of disease during the 16th and 17th centuries. After Charles Alexander (Brandenburg-Ansbach-Bayreuth), Charles Alexander abdicated in 1792, the former margraviates of Ansbach and Bayreuth were annexed by Prussia. Karl August Freiherr von Hardenberg was appointed as governor of these areas by Prussia.
Later Modern Period
Most of modern-day Franconia became part of Bavaria in 1803 thanks to Bavaria's alliance withNapoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
. Culturally it is in many ways different from Bavaria proper ("Altbayern", Old Bavaria), however. The ancient name was resurrected in 1837 by Ludwig I of Bavaria. During the Nazi period, Bavaria was broken up into several different Gau (country subdivision), Gaue, including Gau Franconia, Franconia and Gau Mainfranken, Main-Franconia.
= 19th century
= In 1803, what was to become the Kingdom of Bavaria was given large parts of Franconia through the enactment of the ''Reichsdeputationshauptschluss'' under pressure fromNapoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
for secularization and German mediatisation, mediatisation. In 1806, the Act of Confederation led to stronger ties between Bavaria, Württemberg, Baden and other areas with France, whereupon the Holy Roman Empire including the Franconian Circle fell apart.''Rheinbundakte, deutsche Fassung (1806)''House of Bavarian History , retrieved 7 June 2014. As a reward Bavaria was promised other estates, including the city of Nuremberg. In the so-called ''Rittersturm'' of 1803, Bavaria, Württemberg and Baden seized the territories of the Imperial Knights and Franconian nobility, whose estates were often no bigger than a few parishes, even though the ''Reichsdeputationshauptschluss'' had not authorised this. In 1806 and 1810, Prussia had to release the territories of Ansbach and Bayreuth, which it had annexed in 1792, to Bavaria, whereby Prussia lost its supremacy in the region.''Preußen in Franken 1792 - 1806''
, material from the State Exhibition in 1999 by the House of Bavarian History In 1814, as a result of the Congress of Vienna, the territories of the Principality of Aschaffenburg and Grand Duchy of Würzburg went to the Kingdom of Bavaria. In order to merge the patchwork quilt of small states in Franconia and Swabia into a greater Bavaria, Maximilian Montgelas, Maximilian Joseph Montgelas reformed the political structure. Out of this in January 1838 emerged the Franconian provinces with their present names of Middle, Upper and Lower Franconia. Considerable resentment arose in parts of the Franconian territories over their new membership of Bavaria.Hans Maier: ''Die Franken in Bayern'', p. 6
see pdf
, retrieved 12 July 2014. There were liberal demands for republican structures which erupted in the German Revolution (1848/1849), revolts of 1848 and 1849 and the Gaibach Festival in 1832. On the one hand the reconciliation policy of the Wittelsbachs and Montgelas' aforementioned policy of unification, and, on the other hand, the inclusion of Bavaria in the German Empire in 1871, which weakened her power Bavaria slightly, the conflict between Franconia and Bavaria eased considerably. From 1836 to 1846, the Kingdom of Bavaria built the Ludwig Canal from Bamberg to Kelheim, which was only abandoned in 1950. However, the canal lost much of its importance shortly after the arrival of the railways. Between 1843 and 1854, the Ludwig South-North Railway was established within Franconia, which ran from Lindau (Lake Constance), Lindau on Lake Constance via Nuremberg,
Bamberg
Bamberg (, , ; East Franconian: ''Bambärch'') is a town in Upper Franconia, Germany, on the river Regnitz close to its confluence with the river Main. The town dates back to the 9th century, when its name was derived from the nearby ' castle. C ...
and Kulmbach to Hof (Saale), Hof. The first locomotive to run on German soil steamed 1835 from Nuremberg to Fürth on 7 December 1835.
= 20th century
= After the World War I, First World War the monarchy in Bavaria was abolished, but the state could not agree on a compromise between a Soviet system and Parliamentary system, parliamentarianism. This caused fighting between the opposing camps and the then prime minister was shot. As a result, the government fled to Bamberg in 1919, where the Bamberg Constitution was adopted while, in Munich, the Bavarian Soviet Republic reigned briefly.Wolf Weigand: ''Bayern zur Zeit der Weimarer Republik und des Nationalsozialismus (1918 - 1945).'' In''Politische Geschichte Bayerns''
published by the House of Bavarian History as No. 9 of the booklets on Bavarian History and Culture, 1989, pp. 26-28, here: p. 26 In 1919 the Free State of Coburg voted in a referendum against joining Thuringia and was instead united with Bavaria on 1 July 1920. During the Nazi Germany, Nazi era Nuremberg played a prominent role in the self-expression of the Nazism, National Socialists as the permanent seat of the Nazi Party. Gunzenhausen made its mark as one of the first towns in the Reich itself to exercise discrimination against the Jewish population. The first Hitler Monument in Germany was established there in April 1933. On 25 March 1934 the first anti-Jewish pogrom in Bavaria took place in Gunzenhausen. The attack brought the town negative press coverage worldwide.Werner Falk: ''Ein früher Hass auf Juden'' in Nürnberger Nachrichten, 25 March 2009. On 15 September, a Reichstag (Nazi Germany), Reichstag was specially convened in Nuremberg for the purpose of passing the Nuremberg Laws, under which the antisemitism, antisemitic ideology of the Nazis became a legal basis for such actions. Like all parts of the German Reich, Franconia was badly affected by Allies of World War II, Allied airstrike, air raids. Nuremberg, as a major industrial centre and transportation hub, was hit particularly hard. Between 1940 and 1945 the city was the target of dozens of air raids. Many other places were also affected by air raids. For example, the air raid on Heilbronn, air raid on 4 December 1944 on Heilbronn and the bombing of Würzburg on 16 March 1945, bombing of Würzburg on 16 March 1945, in which both old towns were almost completely destroyed, was a disaster for both cities. By contrast, the old town of Bamberg was almost completely spared. In order to protect cultural artefacts, the Historischer Kunstbunker, historic art bunker was built below Nuremberg Castle. In the closing stages of the Second World War, at the end of March and April 1945, Franconian towns and cities were captured by formations of the United States Army, US Army who advanced from the west after the failure of the Battle of the Bulge and Operation Nordwind. The Battle of Nuremberg (1945), Battle of Nuremberg lasted five days and resulted in at least 901 deaths. The Battle of Crailsheim lasted 16 days, the Battle of Würzburg (1945), Battle of Würzburg seven and the Battle of Merkendorf three days. Following the unconditional surrender of the Wehrmacht, unconditional surrender on 8 May 1945, Bavarian Franconia became part of the American zone of occupation; whilst South Thuringia, with the exception of smaller enclaves like Ostheim, became part of the Soviet occupation zone of Germany, Soviet zone and the Franconian parts of today's Baden-Württemberg also went to the American zone The most important part of the Allied prosecution programme against leaders of the Nazi regime were the Nuremberg Trials against leaders of the German Empire during the Nazi era, held from 20 November 1945 to 14 April 1949. The Nuremberg Trials are considered a breakthrough for the principle that, for a core set of crimes, there is no diplomatic immunity, immunity from prosecution. For the first time, the representatives of a sovereignty, sovereign state were held accountable for their actions. In autumn 1946, the Free State of Bavaria was reconstituted with the enactment of the Constitution of Bavaria, Bavarian Constitution. The state of Württemberg-Baden was founded on 19 September 1945. On 25 April 1952 this state merged with Baden (South Baden), Baden and Württemberg-Hohenzollern (both from the former French occupation zone) to create the present state of Baden-Württemberg. On 1 December 1945 the state of Hesse was founded. Beginning in 1945, Flight and expulsion of Germans (1944–50), refugees and displaced persons from Eastern Europe were settled particularly in rural areas. After 1945, Bavaria and Baden-Württemberg managed the transition from economies that were predominantly agriculture to become leading industrial states in the so-called ''Wirtschaftswunder''. In Lower and Upper Franconia, there was still the problem, however, of the zone along the Inner German Border which was a long way from the markets for its agricultural produce, and was affected by migration and relatively high unemployment, which is why these areas received special support from federal and state governments. By contrast, the state of Thuringia was restored by the Soviet Military Administration in Germany, Soviets in 1945. On 7 October 1949 the German Democratic Republic, commonly known as East Germany, was founded. In 1952 in the course of the Administrative divisions of East Germany, 1952 administrative reform in East Germany, the state of Thuringia was relieved of its function. The Soviet occupying forces exacted a high level of reparations (especially the Allied plans for German industry after World War II, dismantling of industrial facilities) which made the initial economic conditions in East Germany very difficult. Along with the failed economic policies of the GDR, this led to a general frustration that fuelled the uprising of 17 June. There were protests in the Franconian territories too, for example in Schmalkalden. The village of Mödlareuth became famous because, for 41 years, it was divided by the Inner German Border and was nicknamed 'Little Berlin. After ''Die Wende'', the fall of the Berlin Wall on 9 November 1989 and German reunification, reunification on 3 October 1990, made possible mainly by mass demonstrations in East Germany and local exodus of East Germans, the state of Thuringia was reformed with effect from 14 October 1990.Steffen Raßloff: ''Geschichte Thüringens.'' Munich, 2010, p. 106
 In the years from 1971 to 1980 an administrative reform was carried out in Bavaria with the aim of creating more efficient municipalities (''Gemeinde (Germany), Gemeinden'') and counties (''Landkreise''). Against sometimes great protests by the population, the number of municipalities was reduced by a third and the number of counties by about a half. Among the changes was the transfer of the Middle Franconian county of Landkreis Eichstätt, Eichstätt to Upper Bavaria. On 18 May 2006, the Bavarian Landtag approved the introduction of Franconia Day (''Tag der Franken'') in the Franconian territories of the free state.Document 15/5583 of the Bavarian Landtag
In the years from 1971 to 1980 an administrative reform was carried out in Bavaria with the aim of creating more efficient municipalities (''Gemeinde (Germany), Gemeinden'') and counties (''Landkreise''). Against sometimes great protests by the population, the number of municipalities was reduced by a third and the number of counties by about a half. Among the changes was the transfer of the Middle Franconian county of Landkreis Eichstätt, Eichstätt to Upper Bavaria. On 18 May 2006, the Bavarian Landtag approved the introduction of Franconia Day (''Tag der Franken'') in the Franconian territories of the free state.Document 15/5583 of the Bavarian Landtag(pdf; 86 kB) Since ''Die Wende'', new markets have opened up for the Franconian region of Bavaria in the new (formerly East German) federal states and the Czech Republic, enabling the economy to recover. Today, Franconia is in the centre of the EU (at Oberwestern near Westerngrund; ).
Contemporary Franconia
While Old Bavaria is overwhelmingly Roman Catholic, Franconia is a mixed area. Lower Franconia and the western half of Upper Franconia (Bamberg
Bamberg (, , ; East Franconian: ''Bambärch'') is a town in Upper Franconia, Germany, on the river Regnitz close to its confluence with the river Main. The town dates back to the 9th century, when its name was derived from the nearby ' castle. C ...
, Lichtenfels, Bavaria, Lichtenfels, Kronach) is predominantly Catholic, while most of Middle and the eastern half of Upper Franconia (Bayreuth
Bayreuth (, ; bar, Bareid) is a town in northern Bavaria, Germany, on the Red Main river in a valley between the Franconian Jura and the Fichtelgebirge Mountains. The town's roots date back to 1194. In the 21st century, it is the capital of U ...
, Hof, Kulmbach) are predominantly Protestantism, Protestant (Evangelical Church in Germany).
The city of Fürth in Middle Franconia historically (before the Nazi era) had a large Jewish population; Henry Kissinger was born there.
Population
A large part of the population of Franconia, which has a population of five million, consider themselves Franconians (''Franken'', in German homonymous with the name of the historical Franks), a sub-ethnic group of the German people alongside Alemanni, Swabians, Bavarians, Thuringians and Saxons. Such an ethnic identity is generally not shared by other parts of the Franconian languages, Franconian-speaking area (members of which may identify as Rhine Franconians (''Rheinfranken'') or Moselle Franconians (''Moselfranken''). The Free State of Bavaria counts Franconians as one of the "four tribes of Bavaria" (''vier Stämme Bayerns''), alongside Bavarians, Swabians and Sudeten Germans.Towns and cities
With the exception ofHeilbronn
Heilbronn () is a List of cities and towns in Germany, city in northern Baden-Württemberg, Germany, surrounded by Heilbronn (district), Heilbronn District. With over 126,000 residents, it is the sixth-largest city in the state.
From the late Mid ...
, all cities in Franconia and all towns with a population of over 50,000 are within the Free State of Bavaria. The five cities of Franconia are Nuremberg, Würzburg, Fürth, Heilbronn and Erlangen. In Middle Franconia, in the metropolitan region of Nuremberg there is a densely populated urban area consisting of Nuremberg, Fürth, Erlangen and Schwabach. Nuremberg is the fourteenth largest city in Germany and the second largest in Bavaria.
The largest settlements in Baden-Württemberg's Franconian region are Heilbronn (pop: 117,531), Schwäbisch Hall
Schwäbisch Hall (; "Swabian Hall"; from 1802 until 1934 and colloquially: ''Hall'' ) is a city in the German state of Baden-Württemberg located in the valley of the Kocher river, the longest tributary (together with its headwater Lein) of the ...
(37,096) and Crailsheim (32,417).Statistisches Bundesamt – Gemeinden in Deutschland mit Bevölkerung am 31. Dezember 2012(xls file; 4.0 MB) (population figures from the 2011 census) The largest places in the Thuringian part are Suhl (35,665), Sonneberg (23,796) and
Meiningen
Meiningen () is a town in the southern part of the state of Thuringia, Germany. It is located in the region of Franconia and has a population of around 25,000 (2021).
(20,966).
The largest place in the Hessian part of Franconia is Gersfeld (Rhön), Gersfeld with just 5,512 inhabitants. The largest cities within Bavaria are Nuremberg (495,121), Würzburg (124,577), Fürth (118,358) and Erlangen (105,412).
In the Middle Ages Franconia, with its numerous towns, was separate and not part of other territories such as the Duchy of Bavaria.Karten zur Geschichte Bayerns: Helmut Flachenecker, in: Edel und Frei. Franken im Mittelalter, ed. by Wolfgang Jahn / Jutta Schumann / Evamaria Brockhoff, Augsburg, 2004 (Veröffentlichungen zur Bayerischen Geschichte und Kultur 47/04), pp. 308–313, Cat. No. 134. SeHouse of Bavarian History
In the late medieval period it was dominated by mainly smaller towns with a few hundred to a thousand inhabitants, whose size barely distinguished them from the villages. Many towns grew up along large rivers or were founded by the prince-bishops and nobility. Even the Hohenstaufens operated in many towns, most of which later became Imperial Cities with a strong orientation towards Nuremberg. The smallest town in Franconia is Thuringia's Ummerstadt with 487 inhabitants.
Language
 German is the official language and also the ''lingua franca''. Numerous other languages are spoken that come from other language regions or the native countries of immigrants.
East Franconian German, the dialect spoken in Franconia, is entirely different from the Austro-Bavarian dialect continuum which is mainly to be found in the Upper Palatinate, Upper and Lower Bavaria, the greater part of Austria and some parts of Northern Italy. This is one of the reasons why hardly any Franconian would call himself a Bavarian. Even though there is no Franconian state, red and white are regarded as the state colours (''Landesfarben'') of Franconia (compared to blue and white for Bavaria).
German is the official language and also the ''lingua franca''. Numerous other languages are spoken that come from other language regions or the native countries of immigrants.
East Franconian German, the dialect spoken in Franconia, is entirely different from the Austro-Bavarian dialect continuum which is mainly to be found in the Upper Palatinate, Upper and Lower Bavaria, the greater part of Austria and some parts of Northern Italy. This is one of the reasons why hardly any Franconian would call himself a Bavarian. Even though there is no Franconian state, red and white are regarded as the state colours (''Landesfarben'') of Franconia (compared to blue and white for Bavaria).
Religions
Christianity
The proportion of Roman Catholic Church, Roman Catholics and Evangelical Church in Germany, Protestants among the population of Franconia is roughly the same, but varies from region to region.Karten zur Geschichte Bayerns: ''Überwiegend protestantische und überwiegend katholische Gebiete in Franken.'' In: Kirmeier, Josef et al. (ed.): ''200 Jahre Franken in Bayern.'' Aufsatzband zur Landesausstellung 2006, Augsburg, 2006 (Veröffentlichungen zur Bayerischen Geschichte und Kultur 51), seHouse of Bavarian History
Large areas of Middle and Upper Franconia are mainly Protestant. The religious denomination, denominational orientation today still reflects the territorial structure of Franconia at the time of the Franconian Circle. For example, regions, that used to be under the care of the bishoprics of Bamberg, Würzburg and Eichstätt, are mainly Catholic today. On the other hand, all former territories of the imperial cities and the margraviates of Ansbach and Bayreuth have remained mainly Lutheran. The region around the city of Erlangen, which belonged to the Margraviate of Bayreuth, was a refuge for the Huguenots who fled there after the St Bartholomew's Day massacre in France. Following the success of the Reformation in Nuremberg under Andreas Osiander, it had been an exclusively Protestant imperial city and belonged to the Protestant league of imperial states, the Corpus Evangelicorum, within the ''Reichstag (Holy Roman Empire), Reichstag''. Subsequent historical events such as the Flight and expulsion of Germans (1944–50), stream of refugees after the Second World War and the increasing mobility of the population has since blurred denominational geographical boundaries, however. The influx of immigrants from Eastern Europe has also seen the establishment of an Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox community in Franconia. The Romanian Orthodox Metropolis of Germany, Central and Northern Europe has its headquarters in Nuremberg.
Judaism
Before the Nazi era Franconia was a region with significant Jewish communities, most of whom were Ashkenazi Jews.Steven M. Lowenstein: ''Alltag und Tradition: Eine fränkisch-jüdische Geographie.'' In: ''Die Juden in Franken.'' (= ''Studien zur Jüdischen Geschichte und Kultur in Bayern'', Volume 5) Munich, 2012 pp. 5-24, here: pg. 5. The first Jewish communities appeared in Franconia in the 12th and 13th centuries and thus later than, for example, in Regensburg. In the Middle Ages, Franconia was a stronghold of Torah studies. But Franconia also began to exclude the Jewish populations particularly early on. For example, there were two Jewish massacres - the Rintfleisch massacres of 1298 and the Armleder Uprising of 1336-1338 - and in the 15th and 16th centuries many cities exiled their Jewish populations, which is why many Jews settled in rural communities. Franconia also rose to early prominence in the discrimination of Jews during the Nazi era.Steven M. Lowenstein: ''Alltag und Tradition: Eine fränkisch-jüdische Geographie.'' In: ''Die Juden in Franken.'' (= ''Studien zur Jüdischen Geschichte und Kultur in Bayern'', Volume 5) Munich, 2012 pp. 5-24, here: pp. 5-6. One of the first casualties of the organized Nazi persecution of Jews took place on 21 March in Künzelsau and on 25/26 March 1933 in Creglingen, where police and Sturmabteilung, SA troops under the leadership of ''Standartenführer'' Fritz Klein led so-called "weapons search operations". In 1818, about 65% of Bavarian Jews lived in the Bavarian part of Franconia,Steven M. Lowenstein: ''Alltag und Tradition: Eine fränkisch-jüdische Geographie.'' In: ''Die Juden in Franken.'' (= ''Studien zur Jüdischen Geschichte und Kultur in Bayern'', Volume 5) Munich, 2012 pp. 5-24, here: pg. 14 today there are Jewish communities only in Bamberg, Bayreuth, Erlangen, Fürth, Hof, Nuremberg and Würzburg and in Heilbronn in Baden-Württemberg.Islam
Adherents of Islam continue to grow, especially in the larger cities, due to the influx of ''gastarbeiters'' and other immigrants from Muslim countries. As a result, many "backyard mosques" (''Hinterhofmoscheen'') have sprung up, which are gradually being replaced by purpose-built mosques.Culture
Franconia has almost 300 small breweries. The northwestern parts, the areas around the river Main called Franconia (wine region), Franconian wine region also produce a lot of wine. Franconian cuisine, Food typical for the region includes Bratwurst (especially the famous small Nuremberger Bratwurst), Schäufele, ''Schäuferla'' (roast pork shoulder), Sauerbraten, dumplings, potato salad (typically made with broth), fried Common carp, carp, Obatzda, Grupfder (seasoned cheese spread), ''Presssack'' (a type of Head cheese: pressed or jellied pork trimmings, like tongue, cheeks, etc.). Lebkuchen are a traditional type of gingerbread, and Knieküchle, Küchla is a sort of sweet fried pastry.Tourism
 The tourism industry stresses the romantic character of Franconia. Arguments for this include the picturesque countryside and the many historic buildings that present the long history and culture of the region.''Franken. Allianz Reiseführer'', 2011, pp. 12ff In addition, the relatively few industrial towns outside of the main industrial cities is highlighted. Franconian wine, the rich tradition of beer brewing and local culinary specialties, such as ''Lebküchnerei'' or gingerbread baking, are also seen as a draw that is worth marketing, and which make Franconia a popular tourist destination in Germany. The Romantic Road, the best known German theme route, links several of the tourist points in western Franconia. The Castle Road runs through the whole Franconian region with its numerous castles and other medieval structures.
Cycling along the large rivers is very popular, for example along the Main Cycleway, which was the first German long distance cycleway to be awarded five stars by the Allgemeiner Deutscher Fahrrad-Club (ADFC). The Tauber Valley Cycleway, a 101 kilometre-long cycle trail in
The tourism industry stresses the romantic character of Franconia. Arguments for this include the picturesque countryside and the many historic buildings that present the long history and culture of the region.''Franken. Allianz Reiseführer'', 2011, pp. 12ff In addition, the relatively few industrial towns outside of the main industrial cities is highlighted. Franconian wine, the rich tradition of beer brewing and local culinary specialties, such as ''Lebküchnerei'' or gingerbread baking, are also seen as a draw that is worth marketing, and which make Franconia a popular tourist destination in Germany. The Romantic Road, the best known German theme route, links several of the tourist points in western Franconia. The Castle Road runs through the whole Franconian region with its numerous castles and other medieval structures.
Cycling along the large rivers is very popular, for example along the Main Cycleway, which was the first German long distance cycleway to be awarded five stars by the Allgemeiner Deutscher Fahrrad-Club (ADFC). The Tauber Valley Cycleway, a 101 kilometre-long cycle trail in Tauber Franconia
The region of Tauber Franconia (german: Tauberfranken) is a part of the region of Franconia, most of which lies in the German state of Baden-Württemberg. Tauber Franconia is almost coextensive with the county of Main-Tauber-Kreis, which is bisecte ...
, was the second German long distance cycleway to receive five stars.Touristikgemeinschaft Liebliches Taubertal''Fünf Sterne für den "Klassiker"''
In: Tauber-Zeitung. Online at www.swp.de. 31 October 2009; retrieved 6 April 2010.
See also
* * East Franconian German * Franconia (wine region) * Franconian Flag * Franconian Rake * FränkelNotes
References
Footnotes
Bibliography
* Andert, Reinhold. ''Der fränkische Reiter.'' Dingsda-Verlag Querfurt, Leipzig, 2006, . * Beckstein, Günther (text) and Erich Weiß (photographs). ''Franken, Mein Franken - Impressionen aus meiner Heimat.'' Bamberg, 2009, . * Bernet, Claus. ''Himmlisches Franken.'' Norderstedt, 2012, . * Blessing, Werner K. and Dieter Weiß (eds.): ''Franken. Vorstellung und Wirklichkeit in der Geschichte.'' (= ''Franconia.'' Appendices to the Yearbook for Franconian State Research, Vol. 1), Neustadt (Aisch), 2003. * Bogner, Franz X. ''Franken aus der Luft.'' Stürtz-Verlag Würzburg, 2008, . * Bogner, Franz X. ''Oberfranken aus der Luft.'' Ellwanger-Verlag, 128 pages. Bayreuth, 2011, . * Bötzinger, Martin. ''Leben und Leiden während des Dreißigjährigen Krieges in Thüringen und Franken.'' Langensalza, ²1997, . * Norman Cantor, Cantor, Norman. ''The Civilization of the Middle Ages''. 1993. . * Elkar, Rainer S. ''Geschichtslandschaft Franken - wohlbestelltes Feld mit Lücken''. In: Jahrbuch für Regionalgeschichte 23 (2005), pp. 145–158. * Fischer,Berndt. ''Naturerlebnis Franken. Streifzüge durch eine Seelenlandschaft.'' Buch & Kunstverlag Oberpfalz, Amberg, 2001, . * Nestmeyer, Ralf: ''Franken. Ein Reisehandbuch.'' Michael-Müller-Verlag, Erlangen, 2013, . * Peters, Michael. ''Geschichte Frankens. Vom Ausgang der Antike bis zum Ende des Alten Reiches.'' Katz Verlag, 2007, (c.freview
. * Petersohn, Jürgen. ''Franken im Mittelalter. Identität und Profil im Spiegel von Bewußtsein und Vorstellung.'' (Vorträge und Forschungen, Sonderband 51), Ostfildern, 2008 (c.f
. * Timothy Reuter, Reuter, Timothy. ''Germany in the Early Middle Ages 800–1056''. New York: Longman, 1991. . * Scherzer, Conrad. ''Franken, Land, Volk, Geschichte und Wirtschaft.'' Verlag Nürnberger Presse Drexel, Merkel & Co., Nuremberg, 1955, . * Schiener, Anna. ''Kleine Geschichte Frankens.'' Verlag Friedrich Pustet, Regensburg, 2008, . * Stützel, Ada. ''100 berühmte Franken.'' Sutton Verlag, Erfurt, 2007, . * Wüst, Wolfgang (ed.): ''Frankens Städte und Territorien als Kulturdrehscheibe. Kommunikation in der Mitte Deutschlands.'' Interdisciplinary conference 29 to 30 September 2006 in Weißenburg i. Bayern (Mittelfränkische Studien 19) Ansbach, 2008, .
External links
Bezirk of Lower Franconia
Government of Lower Franconia
Bezirk of Middle Franconia
Government of Middle Franconia
Bezirk of Upper Franconia
Government of Upper Franconia
English pages available
The Baden-Württemberg region of Heilbronn-Franken
{{Authority control Franconia, Dukes of Franconia Frankish people Regions of Bavaria History of the Palatinate (region)