|
Schwabach
Schwabach () is a German city of about 40,000 inhabitants near Nuremberg in the centre of the region of Franconia in the north of Bavaria. Together with the neighboring cities of Nuremberg, Fürth and Erlangen, Schwabach forms one of the three metropolitan areas in Bavaria. The city is an autonomous administrative district (''kreisfreie Stadt''). Schwabach is also the name of the river which runs through the city prior to joining the Rednitz. Schwabach is famous for its crafts made of gold, particularly gold foil. In 2004, Schwabach celebrated this tradition with an anniversary festival, marking "500 years gold foil in Schwabach". Around 1500, a local typesetter developed the "Schwabacher" font. This font was used for printing the first Bible in German, which had been worked out by Martin Luther. Etymology The name derives from the old Franconian name ''Suapaha'' (later ''Suabaha'', then ''Villa Suabach'') which translates as "Schwaben-Bach" in modern German, which means " S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schwabacher
The German language, German word Schwabacher (pronounced ) refers to a specific style of blackletter typefaces which evolved from Gothic Blackletter#Textualis, Textualis (''Textura'') under the influence of Humanist minuscule, Humanist type design in Kingdom of Italy (Holy Roman Empire), Italy during the 15th century. Schwabacher typesetting was the most common typeface in Germany, until it was replaced by Fraktur from the mid 16th century onwards. In the course of the 18th and 19th centuries (but in Germany not until 1941), Fraktur gave way in turn to Antiqua (typeface class), Antiqua. Etymology The term may derive from the Franconian town of Schwabach, where, in 1529, the Articles of Schwabach, a Lutheranism, Lutheran creed, were adopted; the Articles became the basis of the 1530 Confessio Augustana, and possibly also promoted the use of Schwabacher types. Characteristics Similar to Rotunda (script), Rotunda, the rounded Schwabacher types were nearer to handwriting than the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erlangen
Erlangen (; , ) is a Middle Franconian city in Bavaria, Germany. It is the seat of the administrative district Erlangen-Höchstadt (former administrative district Erlangen), and with 119,810 inhabitants (as of 30 September 2024), it is the smallest of the eight major cities () in Bavaria. The number of inhabitants exceeded the threshold of 100,000 in 1974, making Erlangen a major city according to the statistical definition officially used in Germany. Together with Nuremberg, Fürth, and Schwabach, Erlangen forms one of the three metropolises in Bavaria. With the surrounding area, these cities form the Nuremberg Metropolitan Region, European Metropolitan Region of Nuremberg, one of 11 metropolitan areas in Germany. The cities of Nuremberg, Fürth, and Erlangen also form a triangle on a map, which represents the heartland of the Nuremberg conurbation. An element of the city that goes back a long way in history, but is still noticeable, is the settlement of Huguenots after the Revo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Language
German (, ) is a West Germanic language in the Indo-European language family, mainly spoken in Western Europe, Western and Central Europe. It is the majority and Official language, official (or co-official) language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, and Liechtenstein. It is also an official language of Luxembourg, German-speaking Community of Belgium, Belgium and the Italian autonomous province of South Tyrol, as well as a recognized national language in Namibia. There are also notable German-speaking communities in other parts of Europe, including: Poland (Upper Silesia), the Czech Republic (North Bohemia), Denmark (South Jutland County, North Schleswig), Slovakia (Krahule), Germans of Romania, Romania, Hungary (Sopron), and France (European Collectivity of Alsace, Alsace). Overseas, sizeable communities of German-speakers are found in the Americas. German is one of the global language system, major languages of the world, with nearly 80 million native speakers and over 130 mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollo-Optik
Apollo-Optik is a German optics company owned by EssilorLuxottica focusing on retail eyewear. It shares its logo with British eyewear retailer VisionExpress, which is also a brand of EssilorLuxottica. Overview It was founded 1972 in Schwabach Schwabach () is a German city of about 40,000 inhabitants near Nuremberg in the centre of the region of Franconia in the north of Bavaria. Together with the neighboring cities of Nuremberg, Fürth and Erlangen, Schwabach forms one of the three me ... and is operating in 40 countries. It is the biggest optics company in Europe. References External links Official Website {{Eyewear retailers Eyewear retailers in Germany Companies based in Bavaria Eyewear companies of Germany Retail companies established in 1972 1972 establishments in West Germany Schwabach EssilorLuxottica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matthias Volz
Matthias Max Volz (4 May 1910 in Schwabach – 26 August 2004 in Spalt) was a German gymnast who competed in the 1936 Summer Olympics The 1936 Summer Olympics (), officially the Games of the XI Olympiad () and officially branded as Berlin 1936, were an international multi-sport event held from 1 to 16 August 1936 in Berlin, then capital of Nazi Germany. Berlin won the bid to .... References External links * 1910 births 2004 deaths German male artistic gymnasts Olympic gymnasts for Germany Gymnasts at the 1936 Summer Olympics Olympic gold medalists for Germany Olympic bronze medalists for Germany Olympic medalists in gymnastics Medalists at the 1936 Summer Olympics People from Schwabach Sportspeople from Middle Franconia 20th-century German sportsmen 21st-century German people {{Germany-artistic-gymnastics-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fürth
Fürth (; East Franconian German, East Franconian: ; ) is a List of cities and towns in Germany, city in northern Bavaria, Germany, in the administrative division (''Regierungsbezirk'') of Middle Franconia. It is the Franconia#Towns and cities, second-largest city in Franconia and now contiguous with the larger city of Nuremberg, the centres of the two cities being only apart. The city forms a continuous conurbation with the neighbouring cities of Nuremberg, Erlangen and Schwabach, which is the heart of an urban area region with around 1.4 million inhabitants, while the larger Nuremberg Metropolitan Region has a population of approximately 3.6 million. Fürth celebrated its thousand-year anniversary in 2007, its first mention being on 1 November 1007. Geography The historic centre of the town is to the east and south of the rivers Rednitz and Pegnitz River, Pegnitz, which join to form the Regnitz to the northwest of the Old Town. To the west of the town, on the far side ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
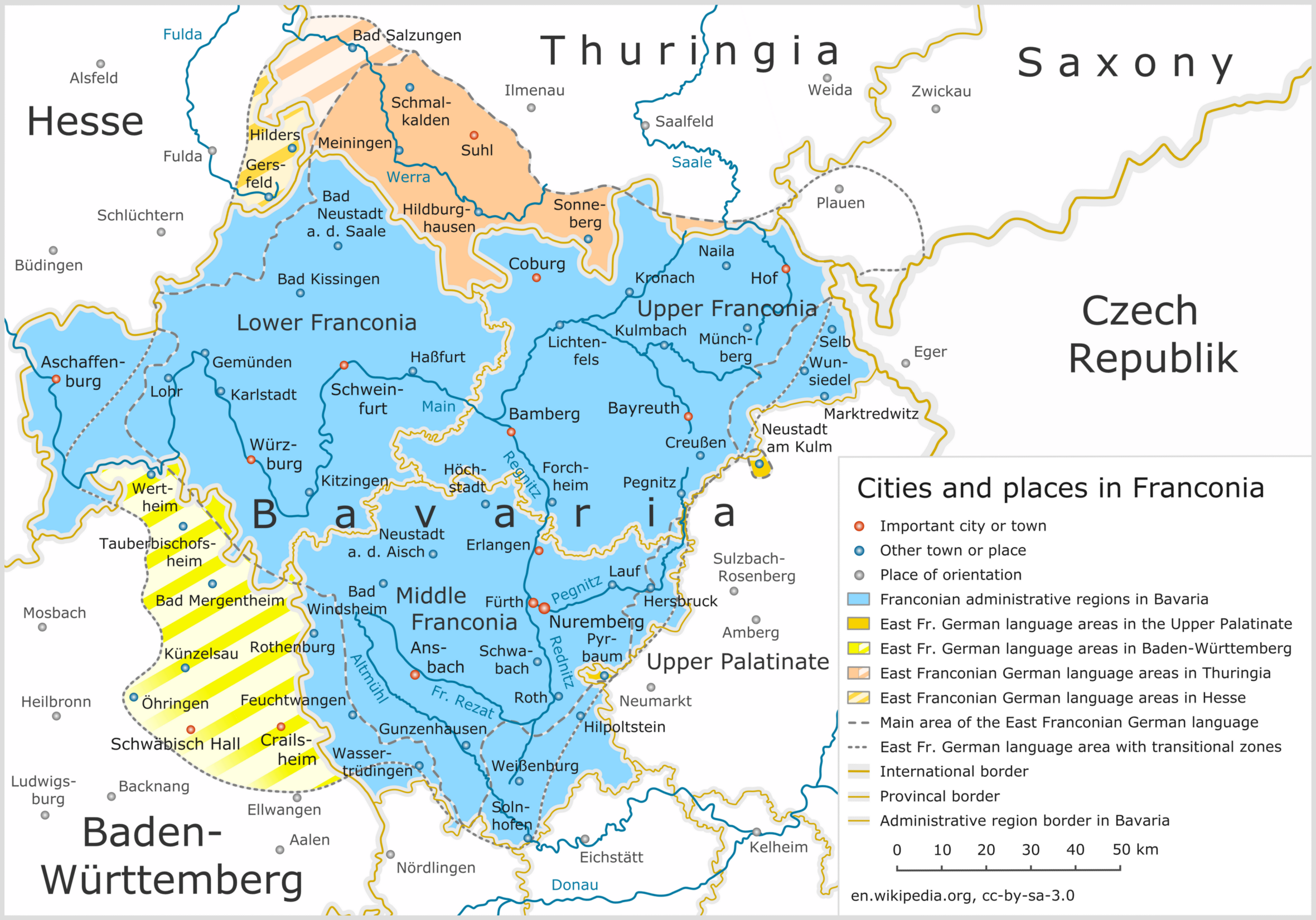
Franconia
Franconia ( ; ; ) is a geographical region of Germany, characterised by its culture and East Franconian dialect (). Franconia is made up of the three (governmental districts) of Lower Franconia, Lower, Middle Franconia, Middle and Upper Franconia in Bavaria, the adjacent, East Franconian, Franconian-speaking South Thuringia, south of the Thuringian Forest—which constitutes the language boundary between Franconian and Thuringian—and the eastern parts of Heilbronn-Franconia in Baden-Württemberg. Those parts of the Vogtland lying in Saxony (largest city: Plauen) are sometimes regarded as Franconian as well, because the Vogtlandian dialects are mostly East Franconian. The inhabitants of Saxon Vogtland, however, mostly do not consider themselves Franconian. On the other hand, the inhabitants of the Hessian dialect, Hessian-speaking parts of Lower Franconia west of the Spessart (largest city: Aschaffenburg) do consider themselves Franconian, although not speaking the dialect. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Schuberth
Hans Schuberth (April 5, 1897 in Schwabach – September 2, 1976 in Munich) was a German politician who from 1949 to 1953 was the first Federal Minister of Post and Telecommunications in Konrad Adenauer's first cabinet. Biography After graduation in 1914 Schuberth participated as a soldier in the First World War. After being seriously wounded, as a result of which he had to have a leg amputated, he was from 1915 to 1916 working as an intern at a machines factory in Germany in Dortmund. After he graduated in 1916 to study mechanical engineering at the Technical University Munich, which he finished in 1920 as a graduate engineer (mechanical engineering). During his studies he became a member of the Catholic Student Association KDSt.V. Rheno - Franconia in Munich CV. He then worked as an engineer at the German Werke AG in Dachau and Munich. From 1925 to 1926 he completed an additional study of electrical engineering, which he also graduated with a diploma. He then entered 1926 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolf Von Henselt
Georg Martin Adolf von Henselt (9 May 181410 October 1889) was a German composer and virtuoso pianist. Life Henselt was born at Schwabach, in Bavaria. At the age of three he began to learn the violin, and at five the piano under Josepha von Fladt (1778–1843), who had trained in composition with Franz Danzi, Abbé (George Joseph) Vogler, Joseph Graetz and studied piano with Franz Lauska (who later coached Meyerbeer, Felix and Fanny Mendelssohn). His concert debut was at the Odeon in Munich, where he played the opening Allegro to one of Mozart's C major concertos, a free fantasy with variations on a theme from Weber's ''Der Freischütz'', and a rondo by Kalkbrenner. It was through Fladt's influence with King Ludwig I of Bavaria that Henselt was provided the financial means to undertake further study with Johann Nepomuk Hummel in Weimar in 1832 for some months. Later that year, he went to Vienna, where, besides studying composition under Simon Sechter (the later teacher of An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Gottfried Zinn
Johann Gottfried Zinn (; December 4, 1727 – April 6, 1759) was a German Anatomy, anatomist and botanist and was a member of the Prussian Academy of Sciences, Berlin Academy. Biography Johann Gottfried Zinn was born in Schwabach. Considering his short life span, Zinn made a great contribution to the study of anatomy. In his book ''Descriptio anatomica oculi humani'', he provided the first detailed and comprehensive anatomy of the human eye. In 1753 Johann Gottfried Zinn became director of the Botanic garden of the University of Göttingen, and in 1755, professor in the medical faculty. In 1757 Zinn described the orchid genus ''Epipactis'' that belongs to the family (biology), family Orchidaceae. He died in Göttingen. Eponyms Botanist Carl Linnaeus designated a genus of flowers in the family Asteraceae native from Mexico as ''Zinnia'' in his honour. He coined the anatomic terms: * ''Zonula ciliaris Zinnii'', now called ''Zonule of Zinn'' * ''Anulus tendineus communis'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bavaria
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a States of Germany, state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the list of German states by area, largest German state by land area, comprising approximately 1/5 of the total land area of Germany, and with over 13.08 million inhabitants, it is the list of German states by population, second most populous German state, behind only North Rhine-Westphalia; however, due to its large land area, its population density is list of German states by population density, below the German average. Major cities include Munich (its capital and List of cities in Bavaria by population, largest city, which is also the list of cities in Germany by population, third largest city in Germany), Nuremberg, and Augsburg. The history of Bavaria includes its earliest settlement by Iron Age Celts, Celtic tribes, followed by the conquests of the Roman Empire in the 1st century BC, when the territory was incorporated into the provinces of Ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rednitz
The Rednitz () is a long river in Franconia, Germany, tributary of the Regnitz (more precisely: its southern, left headstream). Slightly richer in water than the other source river Pegnitz and also richer in tributaries, it is hydrographically regarded as the upper reaches of the Regnitz, although the longest flow path in its system is approx. 3 km shorter than that in the Pegnitz system. The Rednitz is formed by the confluence of the rivers Franconian Rezat and Swabian Rezat, in Georgensgmünd ( district of Roth). The Rednitz flows north through Roth bei Nürnberg, Schwabach and the southwestern quarters of Nuremberg. The Rednitz joins the Pegnitz to form the Regnitz in Fürth. The river first appeared in written sources in the 8th century with the Latin name Radantia. In the 11th century, the name of the river was given as Ratenza. Sources Franz X. Bogner: ''Rednitz und Regnitz. Eine Luftbildreise von Weißenburg bis Bamberg''. Luftbildband. Verlag Fränkischer Tag, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |