Francians on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Kingdom of the Franks (), also known as the Frankish Kingdom, or just Francia, was the largest post-Roman

 Clovis's sons made their capitals near the Frankish heartland in northeastern Gaul.
Clovis's sons made their capitals near the Frankish heartland in northeastern Gaul.
 In 561 Chlothar died and his realm was divided, in a replay of the events of fifty years prior, between his four sons, with the chief cities remaining the same. The eldest son,
In 561 Chlothar died and his realm was divided, in a replay of the events of fifty years prior, between his four sons, with the chief cities remaining the same. The eldest son, 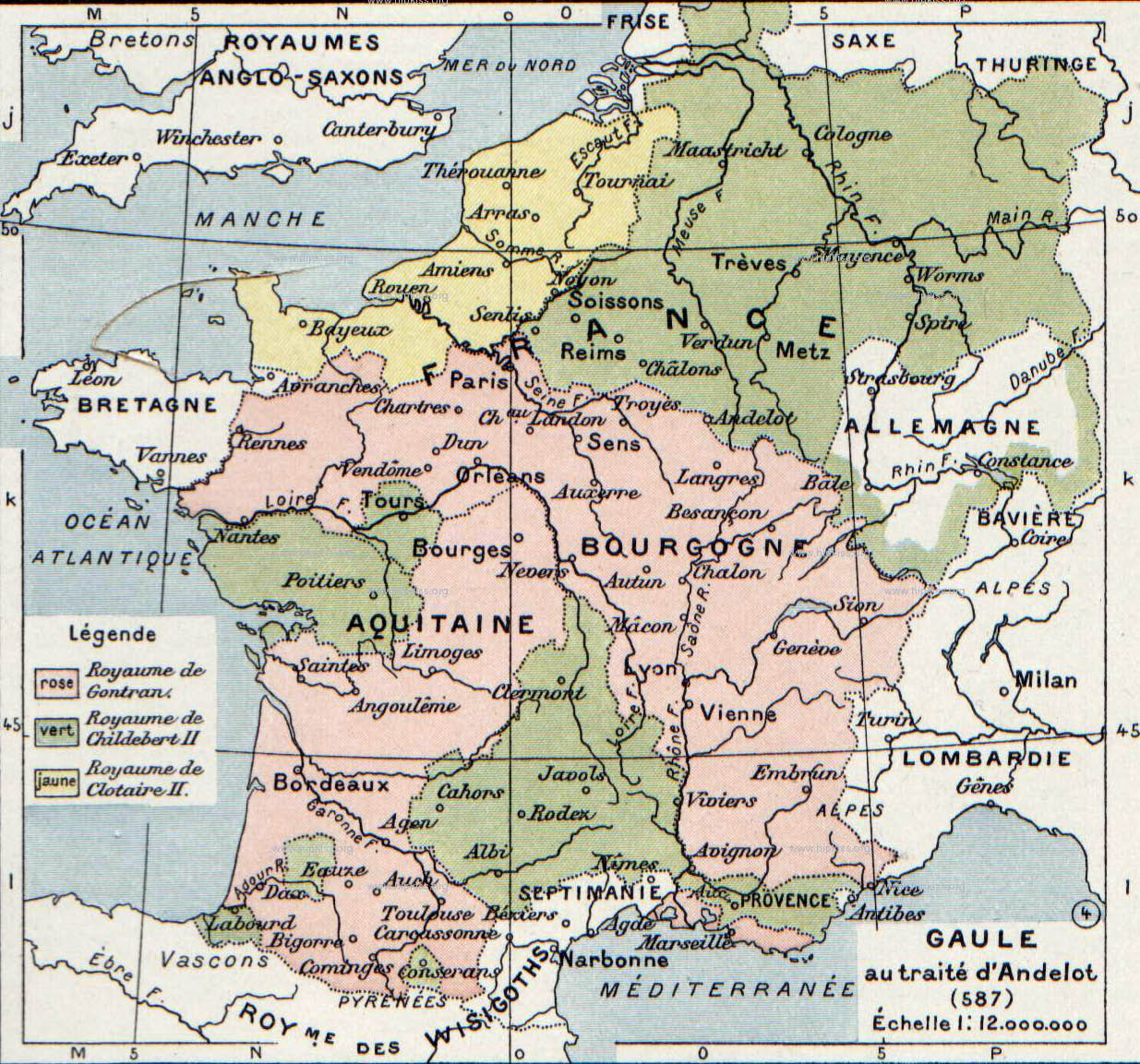
 During the joint reign of Chlothar and Dagobert, who have been called "the last ruling Merovingians", the Saxons, who had been loosely attached to Francia since the late 550s, rebelled under
During the joint reign of Chlothar and Dagobert, who have been called "the last ruling Merovingians", the Saxons, who had been loosely attached to Francia since the late 550s, rebelled under
 Dagobert, in his dealings with the Saxons, Alemans, and Thuringii, as well as the
Dagobert, in his dealings with the Saxons, Alemans, and Thuringii, as well as the
Roman History
'. trans. by Roger Pearse. London: Bohn, 1862. *Procopius. ''s:Author:Procopius, History of the Wars''. trans. by H. B. Dewing. *Fredegar.
The Fourth Book of the Chronicle of Fredegar with its Continuations
'. trans. by John Michael Wallace-Hadrill. Connecticut: Greenwood Press, 1960. *Fredegar.
Historia Epitomata
'. Woodruff, Jane Ellen. PhD Dissertation, University of Nebraska–Lincoln, 1987. *
''Historia Francorum''.
*
Excerpts here
*
The Dukes in the Regnum Francorum, A.D. 550–751.
''Speculum'', Vol. 51, No 3 (July 1976), pp 381–410. * * *Murray, Archibald C. and Walter A. Goffart, Goffart, Walter A. ''After Rome's Fall: Narrators and Sources of Early Medieval History''. 1999. *Nixon, C. E. V. and Rodgers, Barbara. ''In Praise of Later Roman Emperors''. Berkeley, 1994. * Laury Sarti, "Perceiving War and the Military in Early Christian Gaul (ca. 400–700 A.D.)" (= Brill's Series on the Early Middle Ages, 22), Leiden/Boston 2013, . *Herbert Schutz, Schutz, Herbert. ''The Germanic Realms in Pre-Carolingian Central Europe, 400–750''. American University Studies, Series IX: History, Vol. 196. New York: Peter Lang, 2000. *John Michael Wallace-Hadrill, Wallace-Hadrill, J. M. ''The Long-Haired Kings''. London: Butler & tanner Ltd, 1962. *John Michael Wallace-Hadrill, Wallace-Hadrill, J. M. ''The Barbarian West''. London: Hutchinson, 1970. *
Table. Capitals of the Frankish Kingdom according to the years, in 509–800.
{{Authority control Francia, Barbarian kingdoms Former monarchies of Europe States and territories established in the 500s States and territories disestablished in the 840s Former empires
barbarian kingdom
The barbarian kingdoms were states founded by various non-Roman, primarily Germanic, peoples in Western Europe and North Africa following the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century CE. The barbarian kingdoms were the princip ...
in Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's extent varies depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the Western half of the ancient Mediterranean ...
. It was ruled by the Frankish
Frankish may refer to:
* Franks, a Germanic tribe and their culture
** Frankish language or its modern descendants, Franconian languages, a group of Low Germanic languages also commonly referred to as "Frankish" varieties
* Francia, a post-Roman ...
Merovingian
The Merovingian dynasty () was the ruling family of the Franks from around the middle of the 5th century until Pepin the Short in 751. They first appear as "Kings of the Franks" in the Roman army of northern Gaul. By 509 they had united all the ...
and Carolingian
The Carolingian dynasty ( ; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Frankish noble family named after Charles Martel and his grandson Charlemagne, descendants of the Arnulfing and Pippinid c ...
dynasties during the Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages (historiography), Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th to the 10th century. They marked the start o ...
. Francia was among the last surviving Germanic kingdoms from the Migration Period
The Migration Period ( 300 to 600 AD), also known as the Barbarian Invasions, was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the fall of the Western Roman Empire and subsequent settlement of its former territories ...
era.
Originally, the core Frankish territories inside the former Western Roman Empire
In modern historiography, the Western Roman Empire was the western provinces of the Roman Empire, collectively, during any period in which they were administered separately from the eastern provinces by a separate, independent imperial court. ...
were located close to the Rhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the List of rivers of Europe, major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Austria–Swit ...
and Meuse
The Meuse or Maas is a major European river, rising in France and flowing through Belgium and the Netherlands before draining into the North Sea from the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta. It has a total length of .
History
From 1301, the upper ...
rivers in the north, but Frankish chiefs such as Chlodio
Chlodio (probably died after 450), also Clodio, Clodius, Clodion, Cloio or Chlogio, was a Frankish king who attacked and then apparently ruled Roman-inhabited lands around Cambrai and Tournai, near the modern border of Belgium and France. He is ...
would eventually expand their influence within Roman territory as far as the Somme river
The Somme ( , ; ) is a river in Picardy, northern France.
The river is in length, from its source in the high ground of the former at Fonsomme near Saint-Quentin, to the Bay of the Somme, in the English Channel. It lies in the geologica ...
in the 5th century.
Childeric I
Childeric I (died 481 AD) was a Frankish leader in the northern part of imperial Roman Gaul and a member of the Merovingian dynasty, described as a king (Latin ''rex''), both on his Roman-style seal ring, which was buried with him, and in fragm ...
, a Salian
The Salian dynasty or Salic dynasty () was a dynasty in the High Middle Ages. The dynasty provided four kings of Germany (1024–1125), all of whom went on to be crowned Holy Roman emperors (1027–1125).
After the death of the last Ottonian ...
Frankish king, was one of several military leaders commanding Roman forces of various ethnic affiliations in the northern part of what is now France. His son, Clovis I
Clovis (; reconstructed Old Frankish, Frankish: ; – 27 November 511) was the first List of Frankish kings, king of the Franks to unite all of the Franks under one ruler, changing the form of leadership from a group of petty kings to rule by a ...
, succeeded in unifying most of Gaul under his rule in the 6th century by notably conquering Soissons
Soissons () is a commune in the northern French department of Aisne, in the region of Hauts-de-France. Located on the river Aisne, about northeast of Paris, it is one of the most ancient towns of France, and is probably the ancient capital ...
in 486 and Aquitaine
Aquitaine (, ; ; ; ; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''Aguiéne''), archaic Guyenne or Guienne (), is a historical region of southwestern France and a former Regions of France, administrative region. Since 1 January 2016 it has been part of the administ ...
in 507 following the collapse of the Western Roman Empire, as well as establishing leadership over all the Frankish kingdoms on or near the Rhine frontier; thus founding what would come to be known as the Merovingian dynasty. The dynasty subsequently gained control over a significant part of what is now western and southern Germany. It was by building upon the basis of these Merovingian deeds that the subsequent Carolingian
The Carolingian dynasty ( ; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Frankish noble family named after Charles Martel and his grandson Charlemagne, descendants of the Arnulfing and Pippinid c ...
dynasty— through the nearly continuous campaigns of Pepin of Herstal
Pepin II (c. 635 – 16 December 714), commonly known as Pepin of Herstal, was a Franks, Frankish statesman and military leader who was the de facto ruler of Francia as the Mayor of the Palace from 680 until his death. He took the title Duke ...
, his son Charles Martel
Charles Martel (; – 22 October 741), ''Martel'' being a sobriquet in Old French for "The Hammer", was a Franks, Frankish political and military leader who, as Duke and Prince of the Franks and Mayor of the Palace, was the de facto ruler of ...
, grandson Pepin the Short
the Short (; ; ; – 24 September 768), was King of the Franks from 751 until his death in 768. He was the first Carolingian dynasty, Carolingian to become king.
Pepin was the son of the Frankish prince Charles Martel and his wife Rotrude of H ...
, and great-grandson Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( ; 2 April 748 – 28 January 814) was List of Frankish kings, King of the Franks from 768, List of kings of the Lombards, King of the Lombards from 774, and Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of what is now known as the Carolingian ...
— secured the greatest expansion of the Frankish state by the early 9th century. Charlemagne also received the Roman imperial crown in 800, thus creating the ''Frankish-Roman Empire'', which is also referred to as the Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–887) was a Franks, Frankish-dominated empire in Western and Central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as List of Frankish kings, kings of the Franks since ...
, or just the ''Frankish Empire'' ().
During the reign of the Merovingian and Carolingian dynasties, the Frankish realm was one large polity
A polity is a group of people with a collective identity, who are organized by some form of political Institutionalisation, institutionalized social relations, and have a capacity to mobilize resources.
A polity can be any group of people org ...
, generally subdivided into several smaller kingdoms ruled by different members of the ruling dynasties. Whilst these kingdoms coordinated, they also regularly came into conflict with one another. The old Frankish lands, for example, were initially contained within the kingdom of Austrasia
Austrasia was the northeastern kingdom within the core of the Francia, Frankish Empire during the Early Middle Ages, centring on the Meuse, Middle Rhine and the Moselle rivers. It included the original Frankish-ruled territories within what had ...
, centred on the Rhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the List of rivers of Europe, major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Austria–Swit ...
and Meuse
The Meuse or Maas is a major European river, rising in France and flowing through Belgium and the Netherlands before draining into the North Sea from the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta. It has a total length of .
History
From 1301, the upper ...
, roughly corresponding to later Lower Lotharingia
The Duchy of Lower Lotharingia, also called Northern Lotharingia, Lower Lorraine or Northern Lorraine (and also referred to as '' Lothier'' or '' Lottier''
. The bulk of the Gallo-Roman territory to its south and west was called Neustria
Neustria was the western part of the Kingdom of the Franks during the Early Middle Ages, in contrast to the eastern Frankish kingdom, Austrasia. It initially included land between the Loire and the Silva Carbonaria, in the north of present-day ...
. The exact borders and number of these subkingdoms varied over time, until a basic split between eastern and western domains became persistent.
After various treaties and conflicts in the late-9th and early-10th centuries, West Francia
In medieval historiography, West Francia (Medieval Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the West Franks () constitutes the initial stage of the Kingdom of France and extends from the year 843, from the Treaty of Verdun, to 987, the beginning of the Capet ...
came under control of the Capetian dynasty, becoming the Kingdom of France
The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the Middle Ages, medieval and Early modern France, early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe from th ...
, while East Francia
East Francia (Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the East Franks () was a successor state of Charlemagne's empire created in 843 and ruled by the Carolingian dynasty until 911. It was established through the Treaty of Verdun (843) which divided the for ...
and Lotharingia
Lotharingia was a historical region and an early medieval polity that existed during the late Carolingian and early Ottonian era, from the middle of the 9th to the middle of the 10th century. It was established in 855 by the Treaty of Prüm, a ...
came under the control of the non-Frankish Ottonian dynasty
The Ottonian dynasty () was a Saxons, Saxon dynasty of German monarchs (919–1024), named after three of its kings and Holy Roman emperors, especially Otto the Great. It is also known as the Saxon dynasty after the family's origin in the German ...
, becoming the Kingdom of Germany
The Kingdom of Germany or German Kingdom ( 'kingdom of the Germans', 'German kingdom', "kingdom of Germany", ) was the mostly Germanic language-speaking East Frankish kingdom, which was formed by the Treaty of Verdun in 843. The king was elec ...
(which would conquer Burgundy and Italy to then form the medieval Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
). Competing French and German nationalisms in later centuries would claim succession from Charlemagne and the original kingdom, but nowadays both have become seen by many as Pan-European
Pan-European can refer to:
* Pan-European identity
* Pan-European corridors
** Pan-European Corridor X
** Pan-European Corridor Xa
* Pan European Game Information
* Pan-European Institute
* Pan-European nationalism
* Pan-European Oil Pipeline
* ...
symbols.
Historical periods

Origins, the early Frankish period
The term "Franks" emerged in the 3rd century AD as a term for severalGermanic tribes
The Germanic peoples were tribal groups who lived in Northern Europe in Classical antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. In modern scholarship, they typically include not only the Roman-era ''Germani'' who lived in both ''Germania'' and parts ...
who settled on the northern Rhine frontier of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
, including the Bructeri
The Bructeri were a Germanic people, who lived in present-day North Rhine-Westphalia, just outside what was then the Roman Empire. The Romans originally reported them living east of the lower Rhine river, in a large area centred around present day ...
, Ampsivarii
The Ampsivarii, sometimes referenced by modern writers as Ampsivari (a simplification not warranted by the sources), were a Germanic tribe mentioned by ancient authors.
Their homeland was originally around the middle of the river Ems, which f ...
, Chamavi
The Chamavi were a Germanic people of Roman imperial times who lived just north of the Roman border () along the Rhine river delta in what is now the Netherlands, and perhaps stretching into what is now Germany.
In the Roman records of the th ...
, Chattuarii and Salians
The Salian Franks, or Salians, sometimes referred to using the Latin word or , were a Frankish people who lived in what was is now the Netherlands in the fourth century. They are only mentioned under this name in historical records relating to ...
. While all of them had a tradition of participating in the Roman military, the Salians were allowed to settle within the Roman Empire. In 358, having already been living in the ''civitas'' of Batavia for some time, Emperor Julian
Julian (; ; 331 – 26 June 363) was the Caesar (title), Caesar of the West from 355 to 360 and Roman emperor from 361 to 363, as well as a notable philosopher and author in Ancient Greek, Greek. His rejection of Christianity, and his promoti ...
defeated the Chamavi and Salians, allowing the latter to settle further away from the border, in Toxandria
Texandria (also Toxiandria; later Toxandria, Taxandria), is a region mentioned in the 4th century AD and during the Middle Ages. It was situated in the southern part of the modern Netherlands and in the northern part of present-day Belgium, an area ...
.
Some of the early Frankish leaders, such as Flavius Bauto
Flavius Bauto (died c. 385) was a Romanised Frank who served as a ''magister militum'' of the Roman Empire and was a powerful figure in the court of emperor Valentinian II.
Biography
In 381, during the Gothic War (376-382), Bauto was sent by wes ...
and Arbogast, were committed to the cause of the Romans, but other Frankish rulers, such as Mallobaudes
Mallobaudes or Mellobaudes was a 4th-century Frankish king who also held the Roman title of ''comes domesticorum''.
In 354 he was a ''tribunus armaturarum'' in the Roman army in Gaul, where he served under Silvanus, who usurped power in 355. Mal ...
, were active on Roman soil for other reasons. After the fall of Arbogastes, his son Arigius succeeded in establishing a hereditary
Heredity, also called inheritance or biological inheritance, is the passing on of traits from parents to their offspring; either through asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction, the offspring cells or organisms acquire the genetic inform ...
countship at Trier
Trier ( , ; ), formerly and traditionally known in English as Trèves ( , ) and Triers (see also Names of Trier in different languages, names in other languages), is a city on the banks of the Moselle (river), Moselle in Germany. It lies in a v ...
and after the fall of the usurper Constantine III Constantine III may refer to:
* Constantine III (Western Roman emperor), self-proclaimed western Roman Emperor 407–411
* Heraclius Constantine, Byzantine Emperor in 641
* Constans II, Byzantine emperor 641–668, sometimes referred to under this ...
some Franks supported the usurper Jovinus
Jovinus was a Gallo-Roman senator and claimed to be Roman Emperor (411–413 AD).
Following the defeat of the usurper known as Constantine III, Jovinus was proclaimed emperor at Mainz in 411, a puppet supported by Gundahar, king of the Burgu ...
(411). Jovinus was dead by 413, but the Romans found it increasingly difficult to manage the Franks within their borders. The Frankish king Theudemer was executed by the sword, in c. 422.
Around 428, the king Chlodio
Chlodio (probably died after 450), also Clodio, Clodius, Clodion, Cloio or Chlogio, was a Frankish king who attacked and then apparently ruled Roman-inhabited lands around Cambrai and Tournai, near the modern border of Belgium and France. He is ...
, whose kingdom may have been in the ''civitas Tungrorum
The ''Civitas Tungrorum'' was a large Roman administrative district dominating what is now eastern Belgium and the southern Netherlands. In the early days of the Roman Empire it was in the province of Gallia Belgica, but it later joined the neighb ...
'' (with its capital in Tongeren
Tongeren (; ; ; ) is a city and former municipality located in the Belgian province of Limburg, in the southeastern corner of the Flemish region of Belgium. Tongeren is the oldest town in Belgium, as the only Roman administrative capital wit ...
), launched an attack on Roman territory and extended his realm as far as ''Camaracum'' (Cambrai
Cambrai (, ; ; ), formerly Cambray and historically in English Camerick or Camericke, is a city in the Nord department and in the Hauts-de-France region of France on the Scheldt river, which is known locally as the Escaut river.
A sub-pref ...
) and the Somme river
The Somme ( , ; ) is a river in Picardy, northern France.
The river is in length, from its source in the high ground of the former at Fonsomme near Saint-Quentin, to the Bay of the Somme, in the English Channel. It lies in the geologica ...
. Though Sidonius Apollinaris
Gaius Sollius Modestus Apollinaris Sidonius, better known as Sidonius Apollinaris (5 November, 430 – 481/490 AD), was a poet, diplomat, and bishop. Born into the Gallo-Roman aristocracy, he was son-in-law to Emperor Avitus and was appointed Urb ...
relates that Flavius Aetius
Flavius Aetius (also spelled Aëtius; ; 390 – 21 September 454) was a Roman Empire, Roman general and statesman of the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, closing period of the Western Roman Empire. He was a military commander and the most inf ...
defeated a wedding party of his people (c. 431), this period marks the beginning of a situation that would endure for many centuries: the Germanic Franks ruled over an increasing number of Gallo-Roman subjects.
The Merovingians
The Merovingian dynasty () was the ruling family of the Franks from around the middle of the 5th century until Pepin the Short in 751. They first appear as "Kings of the Franks" in the Roman army of northern Gaul. By 509 they had united all the ...
, believed by some in the latter half of the 6th century to be relatives of Chlodio as reported by Gregory of Tours
Gregory of Tours (born ; 30 November – 17 November 594 AD) was a Gallo-Roman historian and Bishop of Tours during the Merovingian period and is known as the "father of French history". He was a prelate in the Merovingian kingdom, encom ...
(although, he himself did not share this belief), arose from within the Gallo-Roman military, with Childeric and his son Clovis being called "King of the Franks" in the Gallo-Roman military, even before having any Frankish territorial kingdom. Once Clovis defeated his Roman competitor for power in northern Gaul, Syagrius
Syagrius (c. 430 – 486 or 487 or 493–4) was a Roman general and the last ruler of a Western Roman rump state in northern Gaul, now called the Kingdom of Soissons. Gregory of Tours referred to him as King of the Romans. Syagrius's defeat by K ...
, he turned to the kings of the Franks to the north and east, as well as other post-Roman kingdoms already existing in Gaul: Visigoths
The Visigoths (; ) were a Germanic people united under the rule of a king and living within the Roman Empire during late antiquity. The Visigoths first appeared in the Balkans, as a Roman-allied Barbarian kingdoms, barbarian military group unite ...
, Burgundians
The Burgundians were an early Germanic peoples, Germanic tribe or group of tribes. They appeared east in the middle Rhine region in the third century AD, and were later moved west into the Roman Empire, in Roman Gaul, Gaul. In the first and seco ...
, and Alemanni
The Alemanni or Alamanni were a confederation of Germanic peoples, Germanic tribes
*
*
*
on the Upper Rhine River during the first millennium. First mentioned by Cassius Dio in the context of the campaign of Roman emperor Caracalla of 213 CE ...
.
The original core territory of the Frankish kingdom later came to be known as Austrasia
Austrasia was the northeastern kingdom within the core of the Francia, Frankish Empire during the Early Middle Ages, centring on the Meuse, Middle Rhine and the Moselle rivers. It included the original Frankish-ruled territories within what had ...
(the "eastern lands"), while the large Romanised Frankish kingdom in the west came to be known as Neustria
Neustria was the western part of the Kingdom of the Franks during the Early Middle Ages, in contrast to the eastern Frankish kingdom, Austrasia. It initially included land between the Loire and the Silva Carbonaria, in the north of present-day ...
.
Merovingian period
Merovingian rise and decline, 481–687
Chlodio's successors are obscure figures, but what can be certain is thatChilderic I
Childeric I (died 481 AD) was a Frankish leader in the northern part of imperial Roman Gaul and a member of the Merovingian dynasty, described as a king (Latin ''rex''), both on his Roman-style seal ring, which was buried with him, and in fragm ...
, possibly his grandson, ruled a Salian kingdom from Tournai
Tournai ( , ; ; ; , sometimes Anglicisation (linguistics), anglicised in older sources as "Tournay") is a city and Municipalities in Belgium, municipality of Wallonia located in the Hainaut Province, Province of Hainaut, Belgium. It lies by ...
as a '' foederatus'' of the Romans. Childeric is chiefly important to history for bequeathing the Franks to his son Clovis
Clovis may refer to:
People
* Clovis (given name), the early medieval (Frankish) form of the name Louis
** Clovis I (c. 466 – 511), the first king of the Franks to unite all the Frankish tribes under one ruler
** Clovis II (c. 634 – c. 657), ...
, who began an effort to extend his authority over the other Frankish tribes and to expand their ''territorium'' south and west into Gaul
Gaul () was a region of Western Europe first clearly described by the Roman people, Romans, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, and parts of Switzerland, the Netherlands, Germany, and Northern Italy. It covered an area of . Ac ...
. Clovis converted to Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
and put himself on good terms with the powerful Church and with his Gallo-Roman subjects.
In a thirty-year reign (481–511) Clovis defeated the Roman general Syagrius
Syagrius (c. 430 – 486 or 487 or 493–4) was a Roman general and the last ruler of a Western Roman rump state in northern Gaul, now called the Kingdom of Soissons. Gregory of Tours referred to him as King of the Romans. Syagrius's defeat by K ...
and conquered the Kingdom of Soissons
The Kingdom or Domain of Soissons is the historiographical name for the de facto independent Roman remnant of the Diocese of Gaul, which existed during late antiquity as a rump state of the Western Roman Empire until its conquest by the Franks i ...
, defeated the Alemanni
The Alemanni or Alamanni were a confederation of Germanic peoples, Germanic tribes
*
*
*
on the Upper Rhine River during the first millennium. First mentioned by Cassius Dio in the context of the campaign of Roman emperor Caracalla of 213 CE ...
(Battle of Tolbiac
The Battle of Tolbiac was fought between the Franks, who were fighting under Clovis I, and the Alamanni, whose leader is not known. The date of the battle has traditionally been given as 496, though other accounts suggest it may either have been ...
in 496) and established Frankish hegemony over them. Clovis defeated the Visigoths (Battle of Vouillé
The Battle of Vouillé (from Latin ''Campus Vogladensis'') was fought in the northern marches of Visigothic territory, at Vouillé, near Poitiers (Gaul), around Spring 507 between the Franks, commanded by Clovis, and the Visigoths, commanded ...
in 507) and conquered all of their territory north of the Pyrenees save Septimania
Septimania is a historical region in modern-day southern France. It referred to the western part of the Roman province of '' Gallia Narbonensis'' that passed to the control of the Visigoths in 462, when Septimania was ceded to their king, Theod ...
, and conquered the Bretons
The Bretons (; or , ) are an ethnic group native to Brittany, north-western France. Originally, the demonym designated groups of Common Brittonic, Brittonic speakers who emigrated from Dumnonia, southwestern Great Britain, particularly Cornwal ...
(according to Gregory of Tours
Gregory of Tours (born ; 30 November – 17 November 594 AD) was a Gallo-Roman historian and Bishop of Tours during the Merovingian period and is known as the "father of French history". He was a prelate in the Merovingian kingdom, encom ...
) and made them vassals of the Franks. He also incorporated the various Roman military settlements (''laeti
(), the plural form of (), was a term used in the late Roman Empire to denote communities of ("barbarians"), i.e. foreigners, or people from outside the Empire, permitted to settle on, and granted land in, imperial territory on condition that ...
'') scattered over Gaul: the Saxons of Bessin
Bessin () is an area in Normandy
Normandy (; or ) is a geographical and cultural region in northwestern Europe, roughly coextensive with the historical Duchy of Normandy.
Normandy comprises Normandy (administrative region), mainland Norman ...
, the Britons
British people or Britons, also known colloquially as Brits, are the citizens of the United Kingdom, the British Overseas Territories, and the Crown dependencies.: British nationality law governs modern British citizenship and nationality, w ...
and the Alans
The Alans () were an ancient and medieval Iranian peoples, Iranic Eurasian nomads, nomadic pastoral people who migrated to what is today North Caucasus – while some continued on to Europe and later North Africa. They are generally regarded ...
of Armorica
In ancient times, Armorica or Aremorica (Gaulish: ; ; ) was a region of Gaul between the Seine and the Loire that includes the Brittany Peninsula, and much of historical Normandy.
Name
The name ''Armorica'' is a Latinized form of the Gauli ...
and Loire valley
The Loire Valley (, ), spanning , is a valley located in the middle stretch of the Loire river in central France, in both the administrative regions Pays de la Loire and Centre-Val de Loire. The area of the Loire Valley comprises about . It is r ...
or the Taifals
The Taifals or Tayfals ( or ''Theifali''; ) were a people of Germanic peoples, Germanic or Sarmatian origin, first documented north of the lower Danube in the mid third century AD. They experienced an unsettled and fragmented history, for the mo ...
of Poitou
Poitou ( , , ; ; Poitevin: ''Poetou'') was a province of west-central France whose capital city was Poitiers. Both Poitou and Poitiers are named after the Pictones Gallic tribe.
Geography
The main historical cities are Poitiers (historical ...
to name a few prominent ones. By the end of his life, Clovis ruled all of Gaul save the Gothic province of Septimania and the Burgundian kingdom
The Kingdom of the Burgundians, or First Kingdom of Burgundy, was established by Germanic Burgundians in the Rhineland and then in eastern Gaul in the 5th century.
History Background
The Burgundians, a Germanic tribe, may have migrated from the ...
in the southeast.
The exact date on which Clovis became "king of all Franks" is not known, but it happened sometime after the Battle of Vouillé
The Battle of Vouillé (from Latin ''Campus Vogladensis'') was fought in the northern marches of Visigothic territory, at Vouillé, near Poitiers (Gaul), around Spring 507 between the Franks, commanded by Clovis, and the Visigoths, commanded ...
, which is securely dated to 507. One year after this battle, Clovis made Paris his capital, and in the Christmas Day
Christmas is an annual festival commemorating the birth of Jesus Christ, observed primarily on December 25 as a religious and cultural celebration among billions of people around the world. A liturgical feast central to Christianity, Chri ...
of the same year he converted to Catholicism
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
, and some time later he orchestrated the murders of Frankish kings Sigobert and Ragnachar
Ragnachar or Ragnarius (died 509) was a Frankish petty king (''regulus'') who ruled from Cambrai. According to Gregory of Tours, Ragnachar "was so unrestrained in his wantonness that he scarcely had mercy for his own near relatives".Gregory, II, 4 ...
, uniting all Franks under his rule. The sole source for this early period is Gregory of Tours
Gregory of Tours (born ; 30 November – 17 November 594 AD) was a Gallo-Roman historian and Bishop of Tours during the Merovingian period and is known as the "father of French history". He was a prelate in the Merovingian kingdom, encom ...
, who wrote around the year 590. His chronology for the reigns of the early kings is almost certainly fabricated, often contradicting itself and other sources. Clovis' baptism, traditionally dated to 496, is now believed to have taken place in 508.
The Merovingians were a hereditary monarchy
A hereditary monarchy is a form of government and succession of power in which the throne passes from one member of a ruling family to another member of the same family. A series of rulers from the same family would constitute a dynasty. It is ...
. The Frankish kings adhered to the practice of partible inheritance
Partible inheritance, sometimes also called partitive, is a system of inheritance in which property is apportioned among heirs. It contrasts in particular with primogeniture, which was common in feudal society and requires that the whole or most ...
: dividing their lands among their sons. Even when multiple Merovingian kings ruled, the kingdom—not unlike the late Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
—was conceived of as a single realm ruled collectively by several kings and the turn of events could result in the reunification of the whole realm under a single king. The Merovingian kings ruled by divine right and their kingship was symbolised daily by their long hair and initially by their acclamation, which was carried out by raising the king on a shield in accordance with the ancient Germanic practice of electing a war-leader at an assembly of the warriors.
= Clovis's sons
= At the death of Clovis, his kingdom was divided territorially by his four adult sons in such a way that each son was granted a comparable portion of fiscal land, which was probably land once part of the Roman fisc, now seized by the Frankish government. Clovis's sons made their capitals near the Frankish heartland in northeastern Gaul.
Clovis's sons made their capitals near the Frankish heartland in northeastern Gaul. Theuderic I
__NOTOC__
Theuderic I ( 487 – 534) was the Merovingian king of Metz, Rheims, or Austrasia—as it is variously called—from 511 to 534.
He was the son of Clovis I and one of his earlier wives or concubines (possibly a Franco-Rhenish Pr ...
made his capital at Reims
Reims ( ; ; also spelled Rheims in English) is the most populous city in the French Departments of France, department of Marne (department), Marne, and the List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, 12th most populous city in Fran ...
, Chlodomer
Chlodomer, also spelled Clodomir or Clodomer (c. 495 - 524) was the second of the four sons of Clovis I, King of the Franks.
History
Clodomir was the eldest son of Clovis and his wife, Clotilde. On the death of his father, in 511, he divided ...
at Orléans
Orléans (,"Orleans"
(US) and Childebert I Childebert I ( 496 – 13 December 558) was a Frankish King of the Merovingian dynasty, as third of the four sons of Clovis I who shared the kingdom of the Franks upon their father's death in 511. He was one of the sons of Saint Clo ...
at (US) and Childebert I Childebert I ( 496 – 13 December 558) was a Frankish King of the Merovingian dynasty, as third of the four sons of Clovis I who shared the kingdom of the Franks upon their father's death in 511. He was one of the sons of Saint Clo ...
Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
, and Chlothar I
Chlothar I, sometime called "the Old" (French: le Vieux), (died December 561) also anglicised as Clotaire from the original French version, was a king of the Franks of the Merovingian dynasty and one of the four sons of Clovis I.
With his eldes ...
at Soissons
Soissons () is a commune in the northern French department of Aisne, in the region of Hauts-de-France. Located on the river Aisne, about northeast of Paris, it is one of the most ancient towns of France, and is probably the ancient capital ...
. During their reigns, the Thuringii
The Thuringii, or Thuringians were a Germanic people who lived in the kingdom of the Thuringians that appeared during the late Migration Period south of the Harz Mountains of central Germania, a region still known today as Thuringia. The Thuring ...
(532), Burgundes (534), and Saxons
The Saxons, sometimes called the Old Saxons or Continental Saxons, were a Germanic people of early medieval "Old" Saxony () which became a Carolingian " stem duchy" in 804, in what is now northern Germany. Many of their neighbours were, like th ...
and Frisians
The Frisians () are an ethnic group indigenous to the German Bight, coastal regions of the Netherlands, north-western Germany and southern Denmark. They inhabit an area known as Frisia and are concentrated in the Dutch provinces of Friesland an ...
(c. 560) were incorporated into the Frankish kingdom. The outlying trans-Rhenish tribes were loosely attached to Frankish sovereignty, and though they could be forced to contribute to Frankish military efforts, in times of weak kings they were uncontrollable and liable to attempt independence. The Romanised Burgundian kingdom, however, was preserved in its territoriality by the Franks and converted into one of their primary divisions, incorporating the central Gallic heartland of Chlodomer's realm with its capital at Orléans.
The fraternal kings showed only intermittent signs of friendship and were often in rivalry. On the early death of Chlodomer, his brother Chlothar had his young sons murdered in order to take a share of his kingdom, which was, in accordance with custom, divided between the surviving brothers. Theuderic died in 534, but his adult son Theudebert I
Theudebert I () (–548) was the Merovingian king of Austrasia from 533 to his death in 548. He was the son of Theuderic I and the father of Theudebald.
Sources
Most of what we know about Theudebert comes from the ''Histories'' or ''History of ...
was capable of defending his inheritance, which formed the largest of the Frankish subkingdoms and the kernel of the later kingdom of Austrasia
Austrasia was the northeastern kingdom within the core of the Francia, Frankish Empire during the Early Middle Ages, centring on the Meuse, Middle Rhine and the Moselle rivers. It included the original Frankish-ruled territories within what had ...
.
Theudebert was the first Frankish king to formally sever his ties to the Roman Emperor in Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
by striking gold coins with his own image on them and calling himself ''magnus rex'' (great king) because of his supposed suzerainty over peoples as far away as Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a Roman province, province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, on the west by Noricum and upper Roman Italy, Italy, and on the southward by Dalmatia (Roman province), Dalmatia and upper Moesia. It ...
. Theudebert interfered in the Gothic War on the side of the Gepids
The Gepids (; ) were an East Germanic tribes, East Germanic tribe who lived in the area of modern Romania, Hungary, and Serbia, roughly between the Tisza, Sava, and Carpathian Mountains. They were said to share the religion and language of the G ...
and Lombards
The Lombards () or Longobards () were a Germanic peoples, Germanic people who conquered most of the Italian Peninsula between 568 and 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the ''History of the Lombards'' (written betwee ...
against the Ostrogoths
The Ostrogoths () were a Roman-era Germanic peoples, Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Goths, Gothic kingdoms within the Western Roman Empire, drawing upon the large Gothic populatio ...
, receiving the provinces of Raetia
Raetia or Rhaetia ( , ) was a province of the Roman Empire named after the Rhaetian people. It bordered on the west with the country of the Helvetii, on the east with Noricum, on the north with Vindelicia, on the south-west with Transalpine ...
, Noricum
Noricum () is the Latin name for the kingdom or federation of tribes that included most of modern Austria and part of Slovenia. In the first century AD, it became a province of the Roman Empire. Its borders were the Danube to the north, R ...
, and part of Veneto
Veneto, officially the Region of Veneto, is one of the 20 regions of Italy, located in the Northeast Italy, north-east of the country. It is the fourth most populous region in Italy, with a population of 4,851,851 as of 2025. Venice is t ...
.
= Chlothar
= His son and successor,Theudebald
Theudebald (in modern English, ''Theobald''; in French, ''Thibaut'' or ''Théodebald''; in German, ''Theudowald'') (534 – 555), son of Theudebert I and Deuteria, was the king of Metz, Rheims, or Austrasia—as it is variously called ...
, was unable to retain them and on his death all of his vast kingdom passed to Chlothar, under whom, with the death of Childebert in 558, the entire Frankish realm was reunited under the rule of one king.
 In 561 Chlothar died and his realm was divided, in a replay of the events of fifty years prior, between his four sons, with the chief cities remaining the same. The eldest son,
In 561 Chlothar died and his realm was divided, in a replay of the events of fifty years prior, between his four sons, with the chief cities remaining the same. The eldest son, Charibert I
Charibert I (; ; 517 – December 567) was the Merovingian King of Paris, the second-eldest son of Chlothar I and his first wife Ingund. His elder brother Gunthar died sometime before their father's death. He shared in the partition of the Fran ...
, inherited the kingdom with its capital at Paris and ruled all of western Gaul. The second eldest, Guntram
Saint Gontrand ( 532 in Soissons – 28 March 592 in Chalon-sur-Saône), also called Gontran, Gontram, Guntram, Gunthram, Gunthchramn, and Guntramnus, was the king of the Kingdom of Orléans from AD 561 to AD 592. He was the third-eldest and seco ...
, inherited the old kingdom of the Burgundians, augmented by the lands of central France around the old capital of Orléans, which became his chief city, and most of Provence
Provence is a geographical region and historical province of southeastern France, which stretches from the left bank of the lower Rhône to the west to the France–Italy border, Italian border to the east; it is bordered by the Mediterrane ...
.
The rest of Provence, the Auvergne
Auvergne (; ; or ) is a cultural region in central France.
As of 2016 Auvergne is no longer an administrative division of France. It is generally regarded as conterminous with the land area of the historical Province of Auvergne, which was dis ...
, and eastern Aquitaine were assigned to the third son, Sigebert I
Sigebert I ( 535 – 575) was a Frankish king of Austrasia from the death of his father in 561 to his own death. He was the third surviving son out of four of Clotaire I and Ingund. His reign found him mostly occupied with a successful civil ...
, who also inherited Austrasia with its chief cities of Reims and Metz
Metz ( , , , then ) is a city in northeast France located at the confluence of the Moselle (river), Moselle and the Seille (Moselle), Seille rivers. Metz is the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Moselle (department), Moselle Departments ...
. The smallest kingdom was that of Soissons, which went to the youngest son, Chilperic I
Chilperic I ( 539 – September 584) was the king of Neustria (or Soissons) from 561 to his death. He was one of the sons of the Franks, Frankish king Clotaire I and Queen Aregund.
Life
Immediately after the death of his father in 561, he ...
. The kingdom Chilperic ruled at his death (584) became the nucleus of later Neustria
Neustria was the western part of the Kingdom of the Franks during the Early Middle Ages, in contrast to the eastern Frankish kingdom, Austrasia. It initially included land between the Loire and the Silva Carbonaria, in the north of present-day ...
.
This second fourfold division was quickly ruined by fratricidal wars, waged largely over the murder of Galswintha
Galswintha (540–568) was a queen consort of Neustria. She was the daughter of Athanagild, Visigothic king of Hispania (the Iberian Peninsula, comprising modern Spain and Portugal), and Goiswintha. Galswintha was the sister of Brunhilda—queen ...
, the wife of Chilperic, allegedly by his mistress (and second wife) Fredegund
Fredegund or Fredegunda (Vulgar Latin, Latin: ''Fredegundis''; French language, French: ''Frédégonde''; died 8 December 597) was the queen consort of Chilperic I, the Merovingian Franks, Frankish king of Neustria. Fredegund served as regent ...
. Galswintha's sister, the wife of Sigebert, Brunhilda Brunhilda may refer to:
* Brunhild, a figure in Germanic heroic legend
* Brunhilda of Austrasia (c. 543–613), Frankish queen
* ''Brunhilda'' (bird), a genus of birds
See also
*
*
* Broom-Hilda, an American newspaper comic strip
* Broomhild ...
, incited her husband to war and the conflict between the two queens continued to plague relations until the next century. Guntram sought to keep the peace, though he also attempted twice (585 and 589) to conquer Septimania from the Goths, but was defeated both times.
All the surviving brothers benefited at the death of Charibert, but Chilperic was also able to extend his authority during the period of war by bringing the Bretons to heel again. After his death, Guntram had to again force the Bretons to submit. In 587, the Treaty of Andelot
The Treaty of Andelot (or Pact of Andelot) was signed at Andelot-Blancheville in 587 between King Guntram of Burgundy and Queen Brunhilda of Austrasia. Based on the terms of the accord, Brunhilda agreed that Guntram adopt her son Childebert II ...
— the text of which explicitly refers to the entire Frankish realm as ''Francia'' — between Brunhilda and Guntram secured his protection of her young son Childebert II
Childebert II ( – 596) was the Merovingian king of Austrasia (which included Provence at the time) from 575 until his death in March 596, and the king of Burgundy from 592 to his death, as the adopted son of his uncle Guntram.
Childh ...
, who had succeeded the assassinated Sigebert (575). Together the territory of Guntram and Childebert was well over thrice as large as the small realm of Chilperic's successor, Chlothar II
Chlothar II, sometimes called "the Young" ( French: le Jeune), (May/June 584 – 18 October 629) was king of the Franks, ruling Neustria (584–629), Burgundy (613–629) and Austrasia (613–623).
The son of Chilperic I and his third wife, Fred ...
. During this period Francia took on the tripartite character it was to have throughout the rest of its history, being composed of Neustria, Austrasia, and Burgundy.

= Francia split into Neustria, Austrasia, and Burgundy
= When Guntram died in 592, Burgundy went to Childebert in its entirety, but he died in 595. His two sons divided the kingdom, with the elderTheudebert II
Theudebert II () (c.585–612), King of Austrasia (595–612 AD), was the son and heir of Childebert II. He received the kingdom of Austrasia plus the cities (''civitates'') of Poitiers, Tours, Le Puy-en-Velay, Bordeaux, and Châteaudun, as ...
taking Austrasia plus Childebert's portion of Aquitaine, while his younger brother Theuderic II
Theuderic II (also spelled Theuderich, Theoderic or Theodoric; in French, ''Thierry'') ( 587–613), king of Burgundy (595–613) and Austrasia (612–613), was the second son of Childebert II. At his father's death in 595, he received Guntram's ...
inherited Burgundy and Guntram's Aquitaine. United, the brothers sought to remove their father's cousin Chlothar II from power and they did succeed in conquering most of his kingdom, reducing him to only a few cities, but they failed to capture him.
In 599 they routed his forces at Dormelles
Dormelles () is a commune in the Seine-et-Marne department in the Île-de-France region in north-central France.
History
Dormelles was the site of a battle circa 599 between rival Merovingian kings. Chlothar II, ruler of Neustria, faced his cou ...
and seized the Dentelin
Dentelin was a region of the Frankish Empire disputed between Austrasia and Neustria.
Mentioned in the Chronicle of Fredegar, the Duchy of Dentelin included far north-eastern parts of modern France and south-western parts of Belgium. The cities ...
, but they then fell foul of each other and the remainder of their time on the thrones was spent in infighting, often incited by their grandmother Brunhilda, who, angered over her expulsion from Theudebert's court, convinced Theuderic to unseat him and kill him. In 612 he did and the whole realm of his father Childebert was once again ruled by one man. This was short-lived, however, as he died on the eve of preparing an expedition against Chlothar in 613, leaving a young son named Sigebert II :''See Sigeberht II of Essex for the Saxon ruler by that name.''
Sigebert II (601–613) or Sigisbert II, was the illegitimate son of Theuderic II, from whom he inherited the kingdoms of Burgundy and Austrasia in 613. However, he fell under the i ...
.
During their reigns, Theudebert and Theuderic campaigned successfully in Gascony
Gascony (; ) was a province of the southwestern Kingdom of France that succeeded the Duchy of Gascony (602–1453). From the 17th century until the French Revolution (1789–1799), it was part of the combined Province of Guyenne and Gascon ...
, where they had established the Duchy of Gascony
The Duchy of Gascony or Duchy of Vasconia was a duchy located in present-day southwestern France and northeastern Spain, an area encompassing the modern region of Gascony. The Duchy of Gascony, then known as ''Wasconia'', was originally a Franki ...
and brought the Basques
The Basques ( or ; ; ; ) are a Southwestern European ethnic group, characterised by the Basque language, a Basque culture, common culture and shared genetic ancestry to the ancient Vascones and Aquitanians. Basques are indigenous peoples, ...
to submission (602). This original Gascon conquest included lands south of the Pyrenees
The Pyrenees are a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. They extend nearly from their union with the Cantabrian Mountains to Cap de Creus on the Mediterranean coast, reaching a maximum elevation of at the peak of Aneto. ...
, namely Biscay
Biscay ( ; ; ), is a province of the Basque Country (autonomous community), Basque Autonomous Community, heir of the ancient Lordship of Biscay, lying on the south shore of the Bay of Biscay, eponymous bay. The capital and largest city is Bilb ...
and Gipuzkoa
Gipuzkoa ( , ; ; ) is a province of Spain and a historical territory of the autonomous community of the Basque Country. Its capital city is Donostia-San Sebastián. Gipuzkoa shares borders with the French department of Pyrénées-Atlantiqu ...
, but these were lost to the Visigoths in 612.
On the opposite end of his realm, the Alemanni had defeated Theuderic in a rebellion and the Franks were losing their hold on the trans-Rhenish tribes. In 610 Theudebert had extorted the Duchy of Alsace
The Duchy of Alsace (, ''Ducatum Elisatium''; ) was a large political subdivision of the Frankish Empire during the last century and a half of Merovingian rule. It corresponded to the territory of Alsace and was carved out of southern Austrasia in ...
from Theuderic, beginning a long period of conflict over which kingdom was to have the region of Alsace, Burgundy or Austrasia, which was only terminated in the late seventh century.
During the brief minority of Sigebert II, the office of the Mayor of the Palace
Under the Merovingian dynasty, the mayor of the palace or majordomo,
( or ) was the manager of the household of the Frankish king. He was the head of the Merovingian administrative ladder and orchestrated the operation of the entire court. He ...
, which had for sometime been visible in the kingdoms of the Franks, came to the fore in its internal politics, with a faction of nobles coalescing around the persons of Warnachar II
Warnachar (sometimes numbered Warnachar II; in modern French, ''Warnachaire'' or ''Garnier'') was the mayor of the palace of Burgundy (617-626) and briefly Austrasia (612-617). He began his career as the regent during Theuderic II's minority (596- ...
, Rado, and Pepin of Landen
Pepin I (also Peppin, Pipin, or Pippin) of Landen (c. 580 – 27 February 640), also called the Elder or the Old, was the Mayor of the palace of Austrasia under the Merovingian King Dagobert I from 623 to 629. He was also the Mayor for Sige ...
, to give the kingdom over to Chlothar in order to remove Brunhilda, the young king's regent, from power. Warnachar was himself already the mayor of the palace of Austrasia, while Rado and Pepin were to find themselves rewarded with mayoral offices after Chlothar's coup succeeded and Brunhilda and the ten-year-old king were killed.
=Rule of Chlothar II
= Immediately after his victory, Chlothar II promulgated theEdict of Paris
The Edict of Paris (in Latin: Chlotarii II Edictum, in French: Édit de Clotaire II) was promulgated 18 October 614 in Paris by Chlothar II, the Merovingian king of the Franks. It is a body of legislation focused on administering justice and ensu ...
(614), which has generally been viewed as a concession to the nobility, though this view has come under recent criticism. The Edict primarily sought to guarantee justice and end corruption in government, but it also entrenched the regional differences between the three kingdoms of Francia and probably granted the nobles more control over judicial appointments.
By 623 the Austrasians had begun to clamour for a king of their own, since Chlothar was so often absent from the kingdom and, because of his upbringing and previous rule in the Seine basin, was more or less an outsider there. Chlothar thus granted that his son Dagobert I
Dagobert I (; 603/605 – 19 January 639) was King of the Franks. He ruled Austrasia (623–634) and Neustria and Burgundy (629–639). He has been described as the last king of the Merovingian dynasty to wield real royal power, after which the ...
would be their king and he was duly acclaimed by the Austrasian warriors in the traditional fashion. Nonetheless, though Dagobert exercised true authority in his realm, Chlothar maintained ultimate control over the whole Frankish kingdom.
 During the joint reign of Chlothar and Dagobert, who have been called "the last ruling Merovingians", the Saxons, who had been loosely attached to Francia since the late 550s, rebelled under
During the joint reign of Chlothar and Dagobert, who have been called "the last ruling Merovingians", the Saxons, who had been loosely attached to Francia since the late 550s, rebelled under Berthoald, Duke of Saxony Berthoald (died 622) was the Duke of the Saxons during the reign of the Frankish kings Chlothar II and his son Dagobert I, the last ruling Merovingians.Max Diesenberger (2003), "Hair, Sacrality and Symbolic Capital in the Frankish Kingdoms," ''The ...
, and were defeated and reincorporated into the kingdom by the joint action of father and son. When Chlothar died in 628, Dagobert, in accordance with his father's wishes, granted a subkingdom to his younger brother Charibert II
Charibert II (607/6178 April 632), a son of Clotaire II and his junior wife Sichilde, was briefly King of Aquitaine from 629 to his death, with his capital at Toulouse. There are no direct statements about when Charibert was born exactly, the on ...
. This subkingdom, commonly called Aquitaine, was a new creation.
= Dagobert I
= Dagobert, in his dealings with the Saxons, Alemans, and Thuringii, as well as the
Dagobert, in his dealings with the Saxons, Alemans, and Thuringii, as well as the Slavs
The Slavs or Slavic people are groups of people who speak Slavic languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout the northern parts of Eurasia; they predominantly inhabit Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, and ...
beyond the borders of Francia, upon whom he tried to force tribute but who instead defeated him under their king Samo
Samo (–) was the founder and sole ruler of the first recorded political union of Slavs, Slavic tribes, known as Samo's Empire ("realm", "kingdom", or "tribal union"), ruling from 623 until his death in 658. According to Fredegarius, the only ...
at the Battle of Wogastisburg
According to the contemporary ''Chronicle of Fredegar'', the Battle of Wogastisburg (also called the siege of Wogastisburg) took place between Slavs (''Sclav, cognomento Winidi'') under King Samo and Franks under King Dagobert I in 631 or 632. Th ...
in 631, made all the far eastern peoples subject to the court of Neustria and not of Austrasia. This, first and foremost, incited the Austrasians to request a king of their own from the royal household.
The subkingdom of Aquitaine corresponded to the southern half of the old Roman province of Aquitania and its capital was at Toulouse
Toulouse (, ; ; ) is a city in southern France, the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Haute-Garonne department and of the Occitania (administrative region), Occitania region. The city is on the banks of the Garonne, River Garonne, from ...
. The other cities of his kingdom were Cahors
Cahors (; ) is a Communes of France, commune in the western part of Southern France. It is the smallest prefecture among the 13 departments that constitute the Occitania (administrative region), Occitanie Region. The capital and main city of t ...
, Agen
Agen (, , ) is the prefecture of the Lot-et-Garonne department in Nouvelle-Aquitaine, Southwestern France. It lies on the river Garonne, southeast of Bordeaux. In 2021, the commune had a population of 32,485.
Geography
The city of Agen l ...
, Périgueux
Périgueux (, ; or ) is a commune in the Dordogne department, in the administrative region of Nouvelle-Aquitaine, southwestern France.
Périgueux is the prefecture of Dordogne, and the capital city of Périgord. It is also the seat of ...
, Bordeaux
Bordeaux ( ; ; Gascon language, Gascon ; ) is a city on the river Garonne in the Gironde Departments of France, department, southwestern France. A port city, it is the capital of the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region, as well as the Prefectures in F ...
, and Saintes; the duchy of Vasconia was also part of his allotment. Charibert campaigned successfully against the Basques, but after his death they revolted again (632). At the same time the Bretons rose up against Frankish suzerainty. In 635 an army sent by Dagobert subdued the Basques, while threats of military action induced the Breton leader Judicael to relent, make peace with the Franks, and pay tribute.
Meanwhile, Dagobert had Charibert's infant successor Chilperic assassinated and reunited the entire Frankish realm again (632), though he was forced by the strong Austrasian aristocracy to grant his own son Sigebert III
Sigebert III ( 630–656) was the Merovingian dynasty, Merovingian king of Austrasia from 633 to his death around 656. He was described as the first Merovingian ''roi fainéant'', or "do-nothing king", with the mayor of the palace in fact ruling ...
to them as a subking in 633. This act was precipitated largely by the Austrasians' desire to be self-governing at a time when Neustrians dominated at the royal court. Chlothar had been the king at Paris for decades before becoming the king at Metz as well and the Merovingian monarchy was ever after him to be a Neustrian monarchy first and foremost.
Indeed, it is in the 640s that "Neustria" first appears in writing, its late appearance relative to "Austrasia" probably due to the fact that Neustrians (who formed the bulk of the authors of the time) called their region simply "Francia". ''Burgundia'' too defined itself in opposition to Neustria at about this time. However, it was the Austrasians, who had been seen as a distinct people within the realm since the time of Gregory of Tours, who were to make the most strident moves for independence.
The young Sigebert was dominated during his minority by the mayor, Grimoald the Elder
Grimoald I (616–657), called the Elder (in French, ''Grimaud l'Ainé''), was the mayor of the palace of Austrasia from 643 to his death. He was the son of Pepin of Landen and Itta.
Biography
With the death of Pepin in 640, Grimoald became th ...
, who convinced the childless king to adopt his own Merovingian-named son Childebert as his son and heir. After Dagobert's death in 639, the duke of Thuringia
Thuringia is a historical and political region of Central Germany.
Kings of Thuringia
*500?–507 Bisinus
*507–529 Baderich
*507–525 Berthachar
*507–532 Herminafried
:''Conquered by the Franks.''
Frankish dukes of Th ...
, Radulf, rebelled and tried to make himself king. He defeated Sigebert in what was a serious reversal for the ruling dynasty (640).
The king lost the support of many magnates while on campaign and the weakness of the monarchic institutions by that time are evident in his inability to effectively make war without the support of the magnates; in fact, he could not even provide his own bodyguard without the loyal aid of Grimoald and Adalgisel
Adalgisel or Adalgis (''Adalgyselus ducis'' in contemporary Latin) was a Frankish duke and the mayor of the palace of Austrasia. He assumed that office in December 633 or January 634 at the same time that Sigebert III assumed the kingship. Along w ...
. He is often regarded as the first ''roi fainéant
''Roi fainéant'' ( "do-nothing king", "lazy king") is a French term primarily used to refer to the later kings of the Merovingian dynasty after they seemed to have lost their initial powers of dominion. It is usually applied to those Frankish rul ...
'': "do-nothing king", not insofar as he "did nothing", but insofar as he accomplished little.
Clovis II
Clovis II (633 – 657) was King of the Franks in Neustria and Burgundy, having succeeded his father Dagobert I in 639. His brother Sigebert III had been King of Austrasia since 634. He was initially under the regency of his mother Nanth ...
, Dagobert's successor in Neustria and Burgundy, which were thereafter attached yet ruled separately, was a minor for almost the whole of his reign. He was dominated by his mother Nanthild
Nanthild ( 610 – 642), also known as ''Nantéchilde'', ''Nanthechilde'', ''Nanthildis'', ''Nanthilde'', or ''Nantechildis'', was a Frankish queen consort and regent, the third of many consorts of Dagobert I, king of the Franks (629–639). She w ...
and the mayor of the Neustrian palace, Erchinoald
Erchinoald (also ''Erkinoald'' and, in French, ''Erchenout'') succeeded Aega as the mayor of the palace of Neustria in 641 and succeeded Flaochad in Burgundy in 642 and remained such until his death in 658.
Family
According to Fredegar, he was ...
. Erchinoald's successor, Ebroin
Ebroin (died 680 or 681) was the Frankish mayor of the palace of Neustria on two occasions; firstly from 658 to his deposition in 673 and secondly from 675 to his death in 680 or 681. In a violent and despotic career, he strove to impose the ...
, dominated the kingdom for the next fifteen years of near-constant civil war. On his death (656), Sigbert's son was shipped off to Ireland, while Grimoald's son Childebert reigned in Austrasia.
Ebroin eventually reunited the entire Frankish kingdom for Clovis's successor Chlothar III
Chlothar III (also spelled ''Chlotar'', ''Clothar'', ''Clotaire'', ''Chlotochar'', or ''Hlothar''; 652–673) was King of the Franks, ruling in
Neustria and Burgundy from 657 to his death. He also briefly ruled Austrasia.
He was the eldest son of ...
by killing Grimoald and removing Childebert in 661. However, the Austrasians demanded a king of their own again and Chlothar installed his younger brother Childeric II
Childeric II ( 653 – 675) was List of Frankish kings, King of the Franks in the 7th century. He ruled Austrasia from 662 and Neustria and Kingdom of Burgundy, Burgundy from 673 until his death, making him sole king for the final two years o ...
. During Chlothar's reign, the Franks had made an attack on northwestern Italy, but were driven off by Grimoald, King of the Lombards
Grimoald or Grimwald (†671) was a 7th-century King of Italy, ruling as Duke of Benevento from 647 to 662, and then as King of the Lombards from 662 until his death in 671.
Life
Grimoald was born as the youngest son of Duke Gisulf II of Friu ...
, near Rivoli.
Dominance of the mayors of the palace, 687–751
In 673, Chlothar III died and some Neustrian and Burgundian magnates invited Childeric to become king of the whole realm, but he soon upset some Neustrian magnates and he was assassinated (675). The reign ofTheuderic III
Theuderic III (also spelled Theuderich, Theoderic or Theodoric; , 651–691) was King of the Franks in the 7th century. He ruled Neustria and Burgundy on two occasions (in 673 and again from 675 to 691), as well as Austrasia from 679 until his ...
was to prove the end of the Merovingian dynasty's power.
Theuderic III succeeded his brother Chlothar III in Neustria in 673, but Childeric II of Austrasia displaced him soon thereafter—until he died in 675, and Theuderic III retook his throne. When Dagobert II died in 679, Theuderic received Austrasia as well and became king of the whole Frankish realm. Thoroughly Neustrian in outlook, he allied with his mayor Berchar
Berchar (also Berthar) was the mayor of the palace of Neustria and Burgundy from 686 to 688/689. He was the successor of Waratton, whose daughter Anstrude he had married.
Unlike Waratton, however, Berthar did not keep peace with Pepin of Herist ...
and made war on the Austrasian who had installed Dagobert II
Dagobert II (; ; died 679) was a Merovingian king of the Franks, ruling in Austrasia from 675 or 676 until his death. He is one of the more obscure Merovingians. He has been considered a martyr since at least the ninth century.
None of the narrati ...
, Sigebert III's son, in their kingdom (briefly in opposition to Clovis III).
In 687 he was defeated by Pepin of Herstal
Pepin II (c. 635 – 16 December 714), commonly known as Pepin of Herstal, was a Franks, Frankish statesman and military leader who was the de facto ruler of Francia as the Mayor of the Palace from 680 until his death. He took the title Duke ...
, the Arnulfing mayor of Austrasia and the real power in that kingdom, at the Battle of Tertry and was forced to accept Pepin as sole mayor and ''dux et princeps Francorum'': "Duke and Prince of the Franks", a title which signifies, to the author of the ''Liber Historiae Francorum'', the beginning of Pepin's "reign". Thereafter the Merovingian monarchs showed only sporadically, in our surviving records, any activities of a non-symbolic and self-willed nature.
During the period of confusion in the 670s and 680s, attempts had been made to re-assert Frankish suzerainty over the Frisians, but to no avail. In 689, however, Pepin launched a campaign of conquest in Western Frisia (''Frisia Citerior'') and defeated the Rulers of Frisia, Frisian king Radbod, King of the Frisians, Radbod near Dorestad, an important trading centre. All the land between the Scheldt and the Vlie was incorporated into Francia.
Then, circa 690, Pepin attacked central Frisia and took Utrecht (city), Utrecht. In 695 Pepin could even sponsor the foundation of the Archdiocese of Utrecht (695–1580), Archdiocese of Utrecht and the beginning of the conversion of the Frisians under Willibrord. However, Eastern Frisia (''Frisia Ulterior'') remained outside of Frankish suzerainty.
Having achieved great successes against the Frisians, Pepin turned towards the Alemanni. In 709 he launched a war against Willehari, duke of the Ortenau, probably in an effort to force the succession of the young sons of the deceased Gotfrid on the ducal throne. This outside interference led to another war in 712 and the Alemanni were, for the time being, restored to the Frankish fold.
However, in southern Gaul, which was not under Arnulfing influence, the regions were pulling away from the royal court under leaders such as Savaric of Auxerre, Antenor of Provence, and Odo the Great, Odo of Aquitaine. The reigns of Clovis IV and Childebert III from 691 until 711 have all the hallmarks of those of ''rois fainéants'', though Childebert is founding making royal judgements against the interests of his supposed masters, the Arnulfings.
= Death of Pepin
= When Pepin died in 714, however, the Frankish realm plunged into civil war and the dukes of the outlying provinces became ''de facto'' independent. Pepin's appointed successor, Theudoald, under his widow, Plectrude, initially opposed an attempt by the king, Dagobert III, to appoint Ragenfrid as mayor of the palace in all the realms, but soon there was a third candidate for the mayoralty of Austrasia in Pepin's illegitimate adult son,Charles Martel
Charles Martel (; – 22 October 741), ''Martel'' being a sobriquet in Old French for "The Hammer", was a Franks, Frankish political and military leader who, as Duke and Prince of the Franks and Mayor of the Palace, was the de facto ruler of ...
.
After the defeat of Plectrude and Theudoald by the king (now Chilperic II) and Ragenfrid, Charles briefly raised a king of his own, Chlothar IV, in opposition to Chilperic. Finally, at Battle of Soissons (718), a battle near Soisson, Charles definitively defeated his rivals and forced them into hiding, eventually accepting the king back on the condition that he receive his father's positions (718). There were no more active Merovingian kings after that point and Charles and his Carolingian
The Carolingian dynasty ( ; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Frankish noble family named after Charles Martel and his grandson Charlemagne, descendants of the Arnulfing and Pippinid c ...
heirs ruled the Franks.
After 718 Charles Martel embarked on a series of wars intended to strengthen the Franks' hegemony in western Europe. In 718 he defeated the rebellious Saxons, in 719 he overran Western Frisia, in 723 he suppressed the Saxons again, and in 724 he defeated Ragenfrid and the rebellious Neustrians, ending the civil war phase of his rule. In 720, when Chilperic II died, he had appointed Theuderic IV king, but this last was a mere puppet of his. In 724 he forced his choice of Hugbert of Bavaria, Hugbert for the ducal succession upon the Bavarians and forced the Alemanni to assist him in his campaigns in Bavaria (725 and 726), where laws were promulgated in Theuderic's name. In 730 Alemannia had to be subjugated by the sword and its duke, Lantfrid, was killed. In 734 Charles fought against Eastern Frisia and finally subdued it.
= Umayyad invasion
= In the 730s the Umayyad conquest of Hispania, Umayyad conquerors of Spain, who had also subjugatedSeptimania
Septimania is a historical region in modern-day southern France. It referred to the western part of the Roman province of '' Gallia Narbonensis'' that passed to the control of the Visigoths in 462, when Septimania was ceded to their king, Theod ...
, began advancing northwards into central Francia and the Loire valley
The Loire Valley (, ), spanning , is a valley located in the middle stretch of the Loire river in central France, in both the administrative regions Pays de la Loire and Centre-Val de Loire. The area of the Loire Valley comprises about . It is r ...
. It was at this time (circa 736) that Maurontus, the ''dux'' of Provence, called in the Umayyads to aid him in resisting the expanding influence of the Carolingians. However, Charles invaded the Rhône Valley with his brother Childebrand and a Lombard army and devastated the region. It was because of the alliance against the Arabs that Charles was unable to support Pope Gregory III against the Lombards.
In 732 or 737—modern scholars have debated over the date—Charles marched against an Arab army between Poitiers and Tours and defeated it in a Battle of Tours, watershed battle that turned back the tide of the Arab advance north of the Pyrenees
The Pyrenees are a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. They extend nearly from their union with the Cantabrian Mountains to Cap de Creus on the Mediterranean coast, reaching a maximum elevation of at the peak of Aneto. ...
. But Charles's real interests lay in the northeast, primarily with the Saxons, from whom he had to extort the tribute which for centuries they had paid to the Merovingians.
Shortly before his death in October 741, Charles divided the realm as if he were king between his two sons by his first wife, marginalising his younger son Grifo (noble), Grifo, who did receive a small portion (it is unknown exactly what). Though there had been no king since Theuderic's death in 737, Charles's sons Pepin the Younger and Carloman, son of Charles Martel, Carloman were still only mayors of the palaces. The Carolingians had assumed the regal status and practice, though not the regal title, of the Merovingians. The division of the kingdom gave Austrasia
Austrasia was the northeastern kingdom within the core of the Francia, Frankish Empire during the Early Middle Ages, centring on the Meuse, Middle Rhine and the Moselle rivers. It included the original Frankish-ruled territories within what had ...
, Alemannia, and Thuringia to Carloman and Neustria, Provence, and Burgundy to Pepin. It is indicative of the ''de facto'' autonomy of the duchies of Aquitaine (under Hunald I, Hunoald) and Bavaria (under Odilo of Bavaria, Odilo) that they were not included in the division of the ''regnum''.
After Charles Martel was buried, in the Abbey of Saint-Denis alongside the Merovingian kings, conflict immediately erupted between Pepin and Carloman on one side and Grifo their younger brother on the other. Though Carloman captured and imprisoned Grifo, it may have been enmity between the elder brothers that caused Pepin to release Grifo while Carloman was on a pilgrimage to Rome. Perhaps in an effort to neutralise his brother's ambitions, Carloman initiated the appointment of a new king, Childeric III, drawn from a monastery, in 743. Others have suggested that perhaps the position of the two brothers was weak or challenged, or perhaps there Carloman was merely acting for a loyalist or legitimist party in the kingdom.
In 743 Pepin campaigned against Odilo and forced him to submit to Frankish suzerainty. Carloman also campaigned against the Saxons and the two together defeated a rebellion led by Hunoald at the head of the Basques
The Basques ( or ; ; ; ) are a Southwestern European ethnic group, characterised by the Basque language, a Basque culture, common culture and shared genetic ancestry to the ancient Vascones and Aquitanians. Basques are indigenous peoples, ...
and another led by Alemanni, in which Liutfrid of Alsatia probably died, either fighting for or against the brothers. In 746, however, the Frankish armies were still, as Carloman was preparing to retire from politics and enter the monastery of Monte Soratte. Pepin's position was further stabilised and the path was laid for his assumption of the crown in 751.
Carolingian period
Carolingian Empire, 751–840
Pepin reigned as an elected king. Although such elections happened infrequently, a general rule in Germanic law stated that the king relied on the support of his leading men. These men reserved the right to choose a new "kingworthy" leader out of the ruling clan if they felt that the old one could not lead them in profitable battle. While in later France the kingdom became hereditary, the kings of the laterHoly Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
proved unable to abolish the Prince-elector, elective tradition and continued as elected rulers until the empire's formal end in 1806.
Pepin solidified his position in 754 by entering into an alliance with Pope Stephen II, who presented the king of the Franks a copy of the forged "Donation of Constantine" at Paris and in a magnificent ceremony at Saint Denis Basilica, Saint-Denis anointed the king and his family and declared him ''patricius Romanorum'' ("protector of the Romans"). The following year Pepin fulfilled his promise to the pope and retrieved the Exarchate of Ravenna, recently fallen to the Lombards
The Lombards () or Longobards () were a Germanic peoples, Germanic people who conquered most of the Italian Peninsula between 568 and 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the ''History of the Lombards'' (written betwee ...
, and returned it to the Papacy.
Pepin donated the re-conquered areas around Rome to the Pope, laying the foundation for the Papal States in the "Donation of Pepin" which he laid on the tomb of St Peter. The papacy had good cause to expect that the remade Frankish monarchy would provide a deferential power base (''potestas'') in the creation of a new world order, centred on the Pope.
Upon Pepin's death in 768, his sons, Charles and Carloman, son of Pippin III, Carloman, once again divided the kingdom between themselves. However, Carloman withdrew to a monastery and died shortly thereafter, leaving sole rule to his brother, who would later become known as Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( ; 2 April 748 – 28 January 814) was List of Frankish kings, King of the Franks from 768, List of kings of the Lombards, King of the Lombards from 774, and Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of what is now known as the Carolingian ...
or Charles the Great, a powerful, intelligent, and modestly literate figure who became a legend for the later history of both France and Germany. Charlemagne restored an equal balance between emperor and pope.
From 772 onwards, Charles conquered and eventually defeated the Saxons
The Saxons, sometimes called the Old Saxons or Continental Saxons, were a Germanic people of early medieval "Old" Saxony () which became a Carolingian " stem duchy" in 804, in what is now northern Germany. Many of their neighbours were, like th ...
to incorporate their realm into the Frankish kingdom. This campaign expanded the practice of non-Roman Christian rulers undertaking the conversion of their neighbours by armed force; Frankish Catholic missionaries, along with others from Ireland and Anglo-Saxon England, had entered Saxon lands since the mid-8th century, resulting in increasing conflict with the Saxons, who resisted the missionary efforts and parallel military incursions.
Charles's main Saxon opponent, Widukind, accepted baptism in 785 as part of a peace agreement, but other Saxon leaders continued to fight. Upon his victory in 787 at Verden (Aller), Verden, Charles ordered the wholesale Massacre of Verden, killing of thousands of Paganism, pagan Saxon prisoners. After several more uprisings, the Saxons suffered definitive defeat in 804. This expanded the Frankish kingdom eastwards as far as the Elbe river, something the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
had only attempted once, and at which it failed in the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest (9 AD). In order to more effectively Christianize the Saxons, Charles founded several Diocese, bishoprics, among them Archbishopric of Bremen, Bremen, Münster, Paderborn, and Osnabrück.
At the same time (773–774), Charles conquered the Lombards
The Lombards () or Longobards () were a Germanic peoples, Germanic people who conquered most of the Italian Peninsula between 568 and 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the ''History of the Lombards'' (written betwee ...
and thus included northern Italy in his sphere of influence. He renewed the Vatican donation and the promise to the papacy of continued Frankish protection.
In 788, Tassilo III, Duke of Bavaria rebelled against Charles. Crushing the rebellion incorporated Bavaria into Charles's kingdom. This not only added to the royal ''fisc'', but also drastically reduced the power and influence of the Agilolfings (Tassilo's family), another leading family among the Franks and potential rivals. Until 796, Charles continued to expand the kingdom even farther southeast, into today's Austria and parts of Croatia.
Charles thus created a realm that reached from the Pyrenees
The Pyrenees are a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. They extend nearly from their union with the Cantabrian Mountains to Cap de Creus on the Mediterranean coast, reaching a maximum elevation of at the peak of Aneto. ...
in the southwest (actually, including an area in Northern Spain (''Marca Hispanica'') after 795) over almost all of today's France (except Brittany, which the Franks never conquered) eastwards to most of today's Germany, including northern Italy and today's Austria. In the hierarchy of the church, bishops and abbots looked to the patronage of the king's palace, where the sources of patronage and security lay. Charles had fully emerged as the leader of Western Christendom, and his patronage of monastic centres of learning gave rise to the "Carolingian Renaissance" of literate culture. Charles also created a large palace at Aachen, a series of roads, and a canal.
On Christmas Day, 800, Pope Leo III crowned Charles as "Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of the Romans" in Rome in a Charlemagne#Coronation, ceremony presented as a surprise (Charlemagne did not wish to be indebted to the bishop of Rome), a further papal move in the series of symbolic gestures that had been defining the mutual roles of papal ''auctoritas'' and imperial ''potestas.'' Though Charlemagne preferred the title "Emperor, king of the Franks and Lombards", the ceremony formally acknowledged the ruler of the Franks as the Roman Emperor, triggering disputes with the Byzantine Empire, which had maintained the title since the division of the Roman Empire into East and West. The pope's right to proclaim successors was based on the Donation of Constantine, a forged Roman imperial decree. After an initial protest at the usurpation, the Byzantine Emperor Michael I Rhangabes acknowledged in 812 Charlemagne as co-emperor, according to some. According to others, Michael I Rangabe, Michael I reopened negotiations with the Franks in 812 and recognized Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( ; 2 April 748 – 28 January 814) was List of Frankish kings, King of the Franks from 768, List of kings of the Lombards, King of the Lombards from 774, and Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of what is now known as the Carolingian ...
as ''basileus'' (emperor), but not as emperor of the Romans. The coronation gave permanent legitimacy to Carolingian primacy among the Franks. The Ottonians later resurrected this connection in 962.
Upon Charlemagne's death on 28 January 814 in Aachen, he was buried in his own Aachen Cathedral, Palace Chapel at Aachen.
Divided empire, after 840
Charlemagne had several sons, but only one survived him. This son, Louis the Pious, followed his father as the ruler of a united empire. But sole inheritance remained a matter of chance, rather than intent. When Louis died in 840, the Carolingians adhered to the custom ofpartible inheritance
Partible inheritance, sometimes also called partitive, is a system of inheritance in which property is apportioned among heirs. It contrasts in particular with primogeniture, which was common in feudal society and requires that the whole or most ...
, and after a brief civil war between the three sons, they made an agreement in 843, the Treaty of Verdun, which divided the empire in three:
# Louis's eldest surviving son Lothair I became Emperor in name but ''de facto'' only the ruler of the Middle Francia, Middle Frankish Kingdom, or Middle Francia, known as King of the Central or Middle Franks. His three sons in turn divided this kingdom between them into Lotharingia
Lotharingia was a historical region and an early medieval polity that existed during the late Carolingian and early Ottonian era, from the middle of the 9th to the middle of the 10th century. It was established in 855 by the Treaty of Prüm, a ...
(centered on Lorraine (province), Lorraine), Burgundy (region), Burgundy, and Lombardy. These areas with different cultures, peoples and traditions would later vanish as separate kingdoms, which would eventually become Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg, Lorraine (province), Lorraine, Switzerland, Savoyard state, Northern Italy and the various departments of France along the Rhône drainage basin and Jura massif.
# Louis's second son, Louis the German, became King of the East Frankish Kingdom or East Francia. This area formed the kernel of the later Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
by way of the Kingdom of Germany
The Kingdom of Germany or German Kingdom ( 'kingdom of the Germans', 'German kingdom', "kingdom of Germany", ) was the mostly Germanic language-speaking East Frankish kingdom, which was formed by the Treaty of Verdun in 843. The king was elec ...
enlarged with some additional territories from Lothair's Middle Frankish Realm: much of these territories eventually evolved into modern Austria, Switzerland and Germany. For a list of successors, see the List of German monarchs.
# His third son Charles the Bald became King of the West Franks, of the West Frankish Kingdom or West Francia. This area, most of today's southern and western France, became the foundation for the later Kingdom of France under the House of Capet. For his successors, see the List of French monarchs.
Subsequently, at the Treaty of Mersen (870) the partitions were recast, to the detriment of Lotharingia. On 12 December 884, Charles the Fat (son of Louis the German) reunited most of the Carolingian Empire, aside from Burgundy (region), Burgundy. In late 887, his nephew Arnulf of Carinthia revolted and assumed the title as King of the East Franks. Charles retired and soon died on 13 January 888.
Odo, Count of Paris was chosen to rule in the west, and was crowned the next month. At this point, West Francia was composed of Neustria in the west and in the east by Francia proper, the region between the Meuse
The Meuse or Maas is a major European river, rising in France and flowing through Belgium and the Netherlands before draining into the North Sea from the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta. It has a total length of .
History
From 1301, the upper ...
and the Seine. The Carolingians were restored ten years later in West Francia, and ruled until 987, when the last Frankish King, Louis V of France, Louis V, died.
West Francia
In medieval historiography, West Francia (Medieval Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the West Franks () constitutes the initial stage of the Kingdom of France and extends from the year 843, from the Treaty of Verdun, to 987, the beginning of the Capet ...
was the land under the control of Charles the Bald. It is the precursor of modern France. It was divided into the following great fiefs: Aquitaine, Brittany, Burgundy, Catalonia, Flanders, Gascony
Gascony (; ) was a province of the southwestern Kingdom of France that succeeded the Duchy of Gascony (602–1453). From the 17th century until the French Revolution (1789–1799), it was part of the combined Province of Guyenne and Gascon ...
, Septimania, Gothia, Paris & Blois, and Toulouse
Toulouse (, ; ; ) is a city in southern France, the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Haute-Garonne department and of the Occitania (administrative region), Occitania region. The city is on the banks of the Garonne, River Garonne, from ...
. After 1180 and Philip II of France, Phillip II, the kingdom came to be known as France, because the new ruling dynasty (the House of Capet, Capetians) were originally Counts of Paris.
Middle Francia was the territory ruled by Lothair I, wedged between East and West Francia. The kingdom, which included the Kingdom of Italy (medieval), Kingdom of Italy, Burgundy, the Provence
Provence is a geographical region and historical province of southeastern France, which stretches from the left bank of the lower Rhône to the west to the France–Italy border, Italian border to the east; it is bordered by the Mediterrane ...
, and the west of Austrasia
Austrasia was the northeastern kingdom within the core of the Francia, Frankish Empire during the Early Middle Ages, centring on the Meuse, Middle Rhine and the Moselle rivers. It included the original Frankish-ruled territories within what had ...
, was an unnatural creation of the Treaty of Verdun, with no historical or ethnic identity. The kingdom was split on the death of Lothair II of Lotharingia, Lothair II in 869 into those of Lotharingia
Lotharingia was a historical region and an early medieval polity that existed during the late Carolingian and early Ottonian era, from the middle of the 9th to the middle of the 10th century. It was established in 855 by the Treaty of Prüm, a ...
, Provence (with Burgundy divided between it and Lotharingia), and north Italy.
East Francia
East Francia (Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the East Franks () was a successor state of Charlemagne's empire created in 843 and ruled by the Carolingian dynasty until 911. It was established through the Treaty of Verdun (843) which divided the for ...
was the land of Louis the German. It was divided into four duchies: Duke of Swabia, Swabia (Alamannia), Duchy of Franconia, Franconia, Duchy of Saxony, Saxony and List of rulers of Bavaria, Bavaria; to which after the death of Lothair II were added the eastern parts of Lotharingia
Lotharingia was a historical region and an early medieval polity that existed during the late Carolingian and early Ottonian era, from the middle of the 9th to the middle of the 10th century. It was established in 855 by the Treaty of Prüm, a ...
. This division persisted until 1268, the end of the Hohenstaufen dynasty. Otto I, Holy Roman Emperor, Otto I was crowned on 2 February 962, marking the beginning of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
(''translatio imperii''). From the 10th century, East Francia became also known as ''regnum Teutonicum'' ("Teutons, Teutonic kingdom" or "Kingdom of Germany
The Kingdom of Germany or German Kingdom ( 'kingdom of the Germans', 'German kingdom', "kingdom of Germany", ) was the mostly Germanic language-speaking East Frankish kingdom, which was formed by the Treaty of Verdun in 843. The king was elec ...
"), a term that became prevalent in Salian times. The title of Holy Roman Emperor was used from that time, beginning with Conrad II, Holy Roman Emperor, Conrad II.
Life in Francia
Law
The different Frankish tribes, such as the Salii, Ripuarian Franks, Ripuarii, and Chamavi, had different legal traditions, which were only later codified, largely under Charlemagne. The ''Lex Salica, Leges Salica'', ''Lex Ribuaria, Ribuaria'', and ''Lex Chamavorum, Chamavorum'' were Carolingian creations, their basis in earlier Frankish reality being difficult for scholars to discern at the present distance. Under Charlemagne codifications were also made of Lex Saxonum, the Saxon law and Lex Frisionum, the Frisian law. It was also under Frankish hegemony that the other Germanic societies east of the Rhine began to codify their tribal law, in such compilations as the ''Lex Alamannorum'' and ''Lex Baiuvariorum'' for the Alemanni and Bavarii respectively. Throughout the Frankish kingdoms there continued to be Gallo-Romans subject to Roman law and clergy subject to canon law. After the Frankish conquest ofSeptimania
Septimania is a historical region in modern-day southern France. It referred to the western part of the Roman province of '' Gallia Narbonensis'' that passed to the control of the Visigoths in 462, when Septimania was ceded to their king, Theod ...
and Catalonia, those regions which had formerly been under Gothic control continued to utilise the Lex Visigothorum, Visigothic law code.
During the early period, Frankish law was preserved by the ''rachimburgs'', officials trained to remember it and pass it on. The Merovingians adopted the ''capitulary'' as a tool for the promulgation and preservation of royal ordinances. Its usage was to continue under the Carolingians and even the later Dukes of Spoleto, Spoletan emperors Guy III of Spoleto, Guy and Lambert II of Spoleto, Lambert under a programme of ''renovation regni Francorum'' ("renewal of the Frankish kingdom").
The last Merovingian capitulary was one of the most significant: the edict of Paris, issued by Chlothar II in 614 in the presence of his magnates, had been likened to a Frankish Magna Carta entrenching the rights of the nobility, but in actuality it sought to remove corruption from the judiciary and protect local and regional interests. Even after the last Merovingian capitulary, kings of the dynasty continued to independently exercise some legal powers. Childebert III even found cases against the powerful Arnulfings and became renowned among the people for his justness. But law in Francia was to experience a Carolingian Renaissance, renaissance under the Carolingians.
Among the legal reforms adopted by Charlemagne were the codifications of traditional law mentioned above. He also sought to place checks on the power of local and regional judiciaries by the method of appointing ''missi dominici'' in pairs to oversee specific regions for short periods of time. Usually ''missi'' were selected from outside their respective regions in order to prevent conflicts of interest. A capitulary of 802 gives insight into their duties. They were to execute justice, enforce respect for the royal rights, control the administration of the counts and dukes (then still royal appointees), receive the oath of allegiance, and supervise the clergy.
Church
The Frankish Church grew out of the Christianity in Gaul, Church in Gaul in the Merovingian period, which was given a particularly Germanic Christianity, Germanic development in a number of List of Frankish synods, "Frankish synods" throughout the 6th and 7th centuries, and with the Carolingian Renaissance, the Frankish Church became a substantial influence of the medieval Western Church. In the 7th century, the territory of the Frankish realm was (re-)Christianized with the help of Hiberno-Scottish mission, Irish and Scottish missionaries. The result was the establishment of numerous monasteries, which would become the nucleus of Old High German literacy in theCarolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–887) was a Franks, Frankish-dominated empire in Western and Central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as List of Frankish kings, kings of the Franks since ...
.
Columbanus was active in Frankish lands from 590, establishing monasteries until his death at Bobbio in 615. He arrived on the continent with twelve companions and founded Annegray, Luxeuil, and Fontaines in France and Bobbio in Italy. During the 7th century the disciples of Columbanus and other Scottish and Irish missionaries founded several monasteries or ''Schottenklöster'' in what are now France, Germany, Belgium, and Switzerland.
The Irish influence in these monasteries is reflected in the adoption of Insular art, Insular style in book production, visible in 8th-century works such as the Gelasian Sacramentary. The Insular script, Insular influence on the uncial script of the later Merovingian period eventually gave way to the development of the Carolingian minuscule in the 9th century.
Society
Immediately after the fall of Rome and through the Merovingian dynasty, trading towns were re-established in the ruins of ancient cities. These specialised in exchange of goods, craft and agriculture, and were mostly independent of aristocratic control. Carolingian Francia saw royal sponsorship for the construction of monastic cities, built to showcase a revival of the architecture of ancient Rome. Administration was conducted by bishops. The old Gallo-Roman aristocrats had survived in prestige and as an institution by taking up the episcopal offices, and they were now put in charge of fields such as justice, infrastructure, education and social services. Kings were legitimized by their links with the religious institutions. Episcopal elections became supervised by the kings, and royal confirmation helped to strengthen the bishops' authority as well. There were improvements in agriculture, notably the adoption of a new heavy plough and the growing use of the three-field system.Currency
Byzantine coinage was in use in Francia beforeTheudebert I
Theudebert I () (–548) was the Merovingian king of Austrasia from 533 to his death in 548. He was the son of Theuderic I and the father of Theudebald.
Sources
Most of what we know about Theudebert comes from the ''Histories'' or ''History of ...
began minting his own money at the start of his reign. Theudebert's successor restored the Byzantine Emperor's image on the coinage, and the Byzantine emperors continued to be depicted on some Frankish coins until the reign of Heraclius, Emperor Heraclius, before disappearing in 613. The solidus (coin), solidus and triens were minted in Francia between 534 and 679. The denarius (or French denier, denier) appeared later, in the name of Childeric II
Childeric II ( 653 – 675) was List of Frankish kings, King of the Franks in the 7th century. He ruled Austrasia from 662 and Neustria and Kingdom of Burgundy, Burgundy from 673 until his death, making him sole king for the final two years o ...
and various non-royals around 673–675. A Carolingian denarius replaced the Merovingian one, and the Frisian Pfennig, penning, in Gaul from 755 to the eleventh century.
The denarius subsequently appeared in Italy issued in the name of Carolingian monarchs after 794, later by so-called "native" kings in the tenth century, and later still by the Holy Roman Empire, German Emperors from Otto I, Holy Roman Emperor, Otto I (962). Finally, denarii were issued in Rome in the names of pope and emperor from Pope Leo III, Leo III and Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( ; 2 April 748 – 28 January 814) was List of Frankish kings, King of the Franks from 768, List of kings of the Lombards, King of the Lombards from 774, and Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of what is now known as the Carolingian ...
onwards to the late tenth century.
See also
*Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–887) was a Franks, Frankish-dominated empire in Western and Central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as List of Frankish kings, kings of the Franks since ...
* List of Frankish kings
Notes
References
Citations
Sources
; Primary sources *Ammianus Marcellinus.Roman History
'. trans. by Roger Pearse. London: Bohn, 1862. *Procopius. ''s:Author:Procopius, History of the Wars''. trans. by H. B. Dewing. *Fredegar.
The Fourth Book of the Chronicle of Fredegar with its Continuations
'. trans. by John Michael Wallace-Hadrill. Connecticut: Greenwood Press, 1960. *Fredegar.
Historia Epitomata
'. Woodruff, Jane Ellen. PhD Dissertation, University of Nebraska–Lincoln, 1987. *
Gregory of Tours
Gregory of Tours (born ; 30 November – 17 November 594 AD) was a Gallo-Roman historian and Bishop of Tours during the Merovingian period and is known as the "father of French history". He was a prelate in the Merovingian kingdom, encom ...
''Historia Francorum''.
*
Gregory of Tours
Gregory of Tours (born ; 30 November – 17 November 594 AD) was a Gallo-Roman historian and Bishop of Tours during the Merovingian period and is known as the "father of French history". He was a prelate in the Merovingian kingdom, encom ...
. ''The History of the Franks''. trans. by Ernest Brehaut. 1916Excerpts here
*
Gregory of Tours
Gregory of Tours (born ; 30 November – 17 November 594 AD) was a Gallo-Roman historian and Bishop of Tours during the Merovingian period and is known as the "father of French history". He was a prelate in the Merovingian kingdom, encom ...
. ''The History of the Franks''. 2 vol. trans. Ormonde Maddock Dalton, O. M. Dalton. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1967.
*Bernard Bachrach, Bachrach, Bernard S. (trans.) ''Liber Historiae Francorum''. 1973.
;Secondary sources
*Bernard Bachrach, Bachrach, Bernard S. ''Merovingian Military Organization, 481–751''. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press, 1971.
*Collins, Roger. ''Early Medieval Europe 300–1000''. London: MacMillan, 1991.
*Fouracre, Paul. "The Origins of the Nobility in Francia." ''Nobles and Nobility in Medieval Europe: Concepts, Origins, Transformations'', ed. Anne J. Duggan. Woodbridge: The Boydell Press, 2000. .
*Geary, Patrick J. ''Before France and Germany: the Creation and Transformation of the Merovingian World.'' New York: Oxford University Press, 1988.
*Edward James (historian), James, Edward. ''The Franks''. (Peoples of Europe series) Basil Blackwell, 1988.
*Lewis, Archibald R.The Dukes in the Regnum Francorum, A.D. 550–751.
''Speculum'', Vol. 51, No 3 (July 1976), pp 381–410. * * *Murray, Archibald C. and Walter A. Goffart, Goffart, Walter A. ''After Rome's Fall: Narrators and Sources of Early Medieval History''. 1999. *Nixon, C. E. V. and Rodgers, Barbara. ''In Praise of Later Roman Emperors''. Berkeley, 1994. * Laury Sarti, "Perceiving War and the Military in Early Christian Gaul (ca. 400–700 A.D.)" (= Brill's Series on the Early Middle Ages, 22), Leiden/Boston 2013, . *Herbert Schutz, Schutz, Herbert. ''The Germanic Realms in Pre-Carolingian Central Europe, 400–750''. American University Studies, Series IX: History, Vol. 196. New York: Peter Lang, 2000. *John Michael Wallace-Hadrill, Wallace-Hadrill, J. M. ''The Long-Haired Kings''. London: Butler & tanner Ltd, 1962. *John Michael Wallace-Hadrill, Wallace-Hadrill, J. M. ''The Barbarian West''. London: Hutchinson, 1970. *
External links
Table. Capitals of the Frankish Kingdom according to the years, in 509–800.
{{Authority control Francia, Barbarian kingdoms Former monarchies of Europe States and territories established in the 500s States and territories disestablished in the 840s Former empires