Flyover Reconnaissance on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
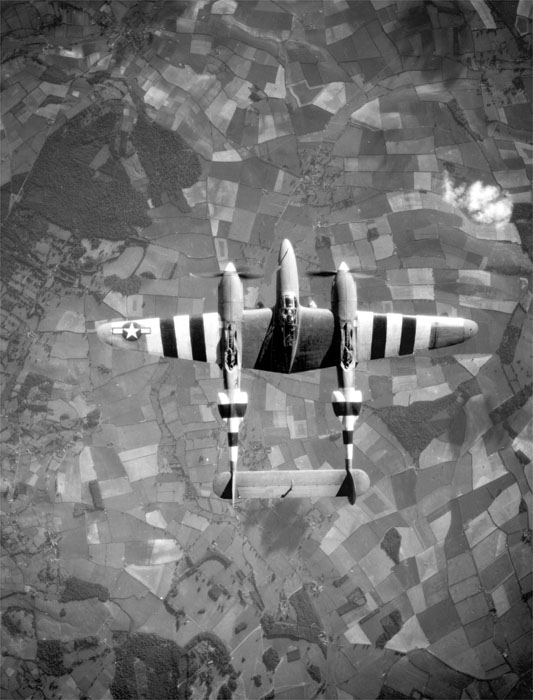 Aerial reconnaissance is
Aerial reconnaissance is
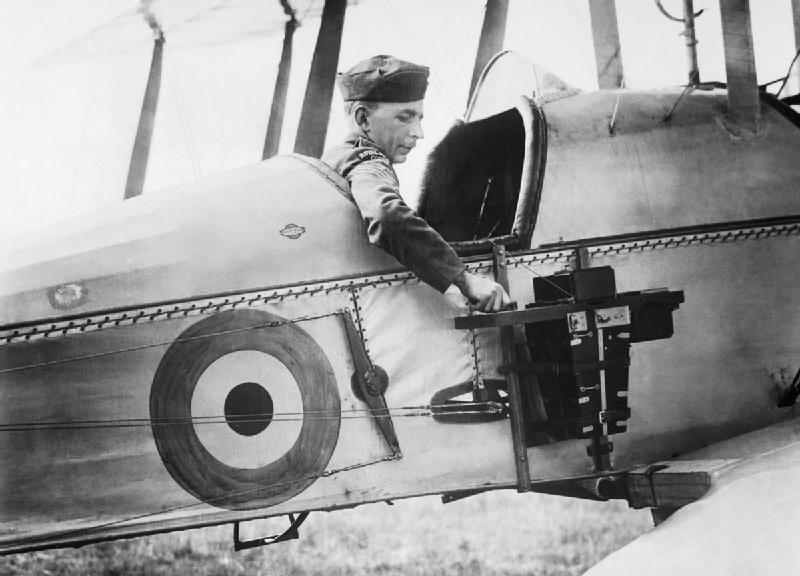 The use of aerial photography rapidly matured during the
The use of aerial photography rapidly matured during the  The
The
 During 1928, the
During 1928, the  Other fighters were also adapted for photo-reconnaissance, including the British
Other fighters were also adapted for photo-reconnaissance, including the British
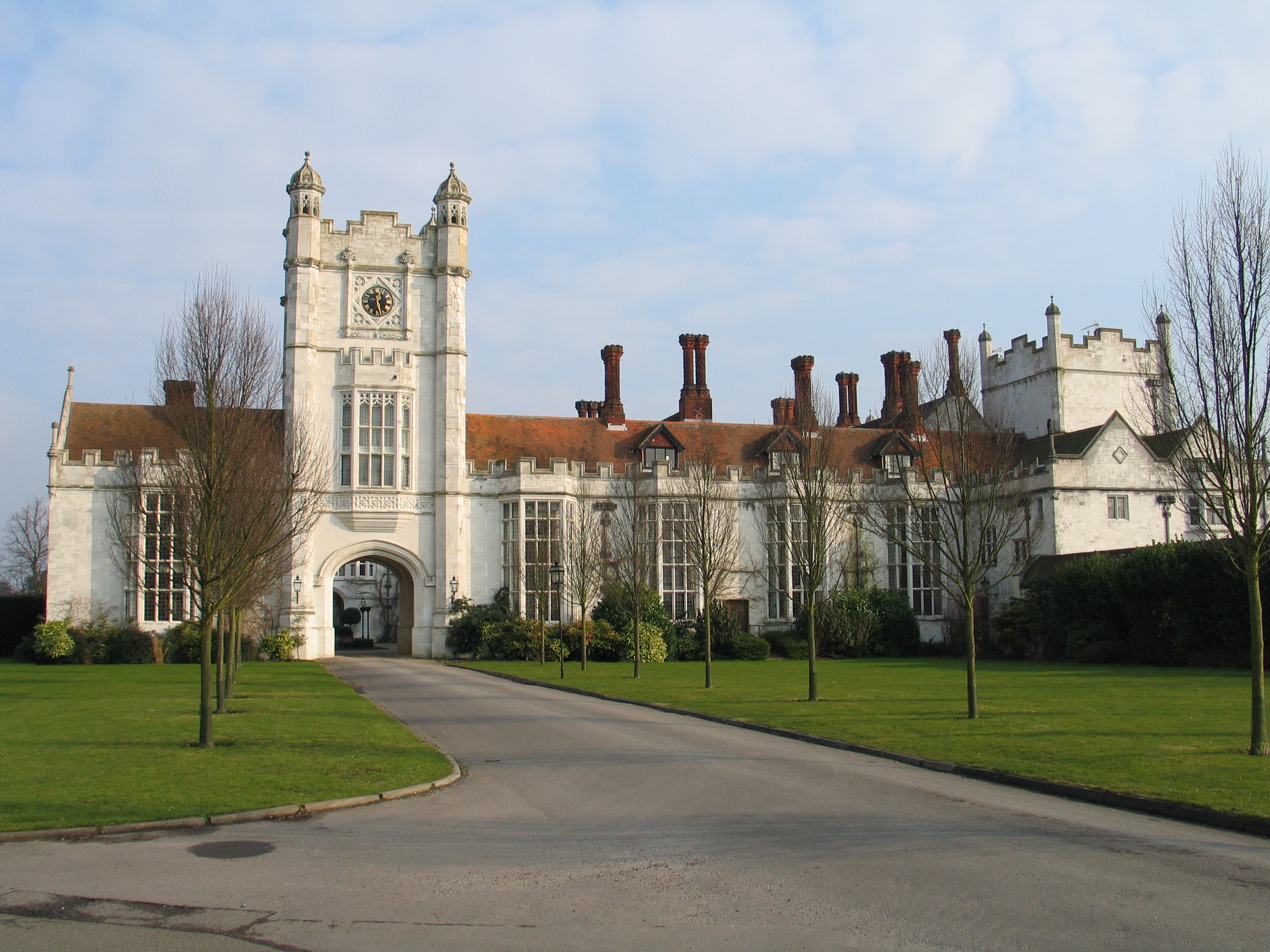 The collection and interpretation of aerial reconnaissance intelligence became a considerable enterprise during the war. Beginning in 1941,
The collection and interpretation of aerial reconnaissance intelligence became a considerable enterprise during the war. Beginning in 1941,
During 1942 and 1943, the CIU gradually expanded and was involved in the planning stages of practically every operation of the war, and in every aspect of intelligence. In 1945, daily intake of material averaged 25,000 negatives and 60,000 prints. Thirty-six million prints were made during the war. By
/ref> According to R.V. Jones, photographs were used to establish the size and the characteristic launching mechanisms for both the
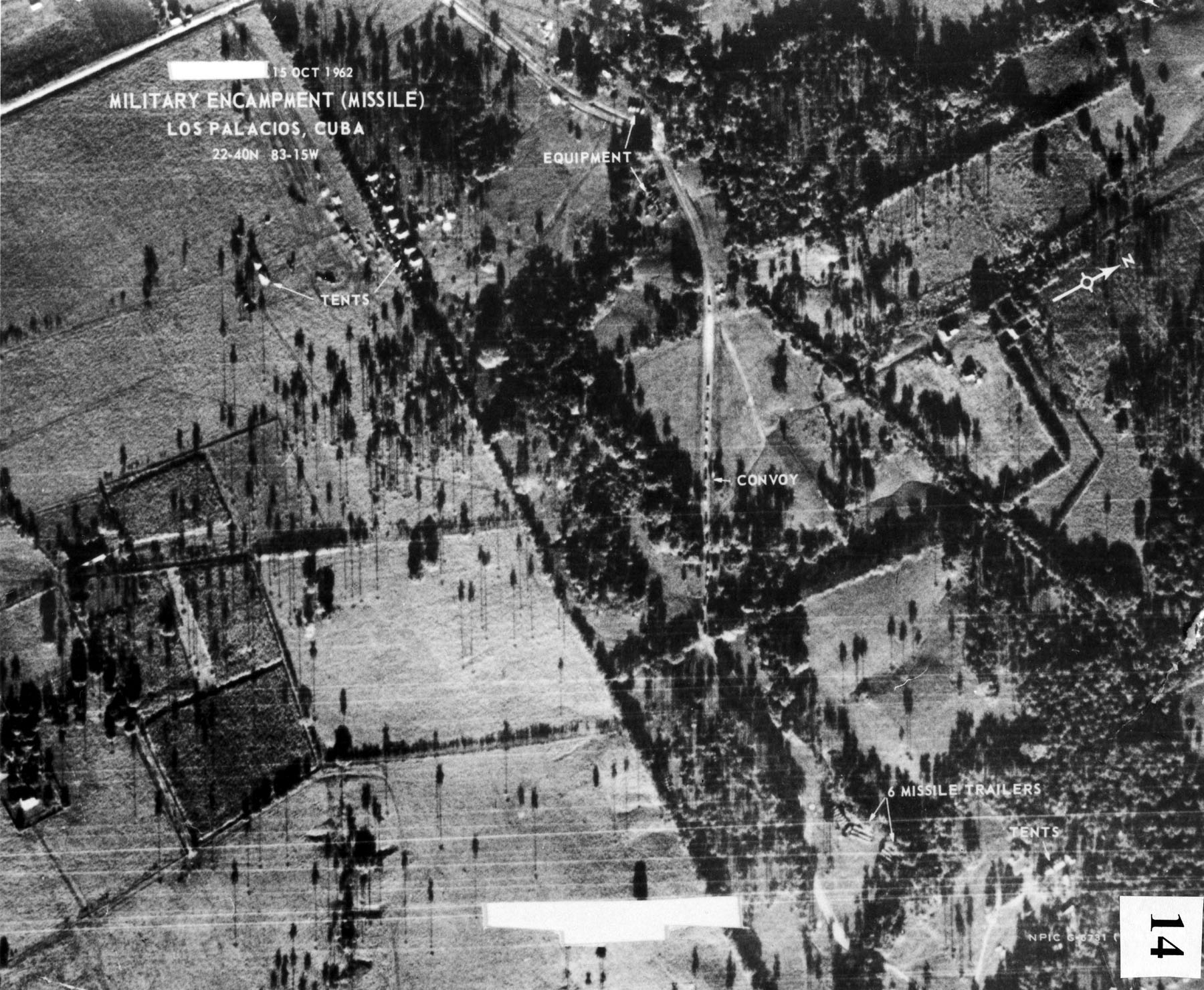 The onset of the
The onset of the
"Global Hawk to replace U-2 spy plane in 2015."
''Air Force Times,'' 10 August 2011. Retrieved: 22 August 2011. however, in January 2012, it was instead decided to extend the U-2's service life. Critics have pointed out that the RQ-4's cameras and sensors are less capable and lack all-weather operating capability; however, some of the U-2's sensors could be installed on the RQ-4. In late 2014, Lockheed Martin proposed converting the manned U-2 fleet into UAVs, which would substantially bolster its payload capability;Butler, Amy
"Lockheed updates unmanned U-2 concept."
''Aviation Week'', 24 November 2014. Retrieved: 7 December 2015. however, the USAF declined to provide funding for such an extensive conversion.Drew, James
"U-2 poised to receive radar upgrade, but not un-manned conversion."
''Flightglobal.com'', 31 July 2015. Retrieved: 7 December 2015. During the 2010s, American defense conglomerate Lockheed Martin promoted its proposal to develop a Hypersonic speed, hypersonic Unmanned aerial vehicle, UAV, which it referred to the Lockheed Martin SR-72, SR-72 in allusion to its function as a spiritual successor to the retired SR-71 Blackbird. The company has also developed several other reconnaissance UAVs, such as the Lockheed Martin RQ-170 Sentinel.
 * AeroVironment Wasp III (airplane – electric propulsion)
* Aeryon Scout/Aeryon SkyRanger (VTOL Rotorcraft) – Some UAVs are small enough to carry in a backpack with similar functionality to larger ones
* EMT Aladin (aircraft – electric – Made in Germany)
* Bramor C4EYE (aircraft – electric – Made in Slovenia)
* Bayraktar Mini UAV (aircraft – electric – Made in Turkey)
* RQ-84Z Areohawk (aircraft – electric – Made in New Zealand)
Low cost miniature UAVs demand increasingly miniature imaging payloads. Developments in miniature electronics have fueled the development of increasingly capable surveillance payloads, allowing miniature UAVs to provide high levels of capability in never before seen packages.
* AeroVironment Wasp III (airplane – electric propulsion)
* Aeryon Scout/Aeryon SkyRanger (VTOL Rotorcraft) – Some UAVs are small enough to carry in a backpack with similar functionality to larger ones
* EMT Aladin (aircraft – electric – Made in Germany)
* Bramor C4EYE (aircraft – electric – Made in Slovenia)
* Bayraktar Mini UAV (aircraft – electric – Made in Turkey)
* RQ-84Z Areohawk (aircraft – electric – Made in New Zealand)
Low cost miniature UAVs demand increasingly miniature imaging payloads. Developments in miniature electronics have fueled the development of increasingly capable surveillance payloads, allowing miniature UAVs to provide high levels of capability in never before seen packages.
The Central Intelligence Agency and Overhead Reconnaissance: The U-2 and Oxcart Programs, 1954–1974
'. Washington, DC: Central Intelligence Agency, 1992. . * Polmar, Norman. ''Spyplane: The U-2 History Declassified''. London: Zenith Imprint, 2001. . * Stanley, Colonel Roy M. II, USAF (Ret). ''V-Weapons Hunt: Defeating German Secret Weapons.'' Barnsley, South Yorkshire, UK: Pen & Sword, 2010. .
National Collection of Aerial Photography
The official archive of British Government declassified aerial photography. {{DEFAULTSORT:Aerial Reconnaissance Aerial reconnaissance, Aerial warfare, Reconnaissance Espionage Military cartography
 Aerial reconnaissance is
Aerial reconnaissance is reconnaissance
In military operations, military reconnaissance () or scouting is the exploration of an area by military forces to obtain information about enemy forces, the terrain, and civil activities in the area of operations. In military jargon, reconnai ...
for a military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. Militaries are typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with their members identifiable by a d ...
or strategic
Strategy (from Greek στρατηγία ''stratēgia'', "troop leadership; office of general, command, generalship") is a general plan to achieve one or more long-term or overall goals under conditions of uncertainty. In the sense of the "art o ...
purpose that is conducted using reconnaissance aircraft
A reconnaissance aircraft (colloquially, a spy plane) is a military aircraft designed or adapted to perform aerial reconnaissance with roles including collection of imagery intelligence (including using Aerial photography, photography), signals ...
. The role of reconnaissance can fulfil a variety of requirements including artillery spotting
An artillery observer, artillery spotter, or forward observer (FO) is a soldier responsible for directing artillery and mortar fire support onto a target. An artillery observer usually accompanies a tank or infantry unit. Spotters ensure that ...
, the collection of imagery intelligence
Imagery intelligence (IMINT), pronounced as either as ''Im-Int'' or ''I-Mint'', is an intelligence gathering discipline wherein imagery is analyzed (or "exploited") to identify information of intelligence value. Imagery used for defense intell ...
, and the observation of enemy maneuvers.
History
Early developments
After the French Revolution, the new rulers became interested in using theballoon
A balloon is a flexible membrane bag that can be inflated with a gas, such as helium, hydrogen, nitrous oxide, oxygen, or air. For special purposes, balloons can be filled with smoke, liquid water, granular media (e.g. sand, flour or rice), ...
to observe enemy manoeuvres and appointed scientist Charles Coutelle to conduct studies using the balloon ''L'Entreprenant'', the first military reconnaissance aircraft. The balloon found its first use in the 1794 conflict with Austria, where in the Battle of Fleurus they gathered information. Moreover, the presence of the balloon had a demoralizing effect on the Austrian troops, which improved the likelihood of victory for the French troops. To operate such balloons, a new unit of the French military, the French Aerostatic Corps
The French Aerostatic Corps or Company of Aeronauts () was the world's first balloon unit, Jeremy Beadle and Ian Harrison, ''First, Lasts & Onlys: Military'', p. 42 founded in 1794 to use balloons, primarily for reconnaissance.
Experimentation
...
, was established; this organisation has been recognised as being the world's first air force
An air force in the broadest sense is the national military branch that primarily conducts aerial warfare. More specifically, it is the branch of a nation's armed services that is responsible for aerial warfare as distinct from an army aviati ...
.
After the invention of photography, primitive aerial photographs were made of the ground from manned and unmanned balloons, starting in the 1860s, and from tethered kites from the 1880s onwards. An example was Arthur Batut's kite-borne camera photographs of Labruguière
Labruguière (; Languedocien: ''La Bruguièira'') is a commune in the Tarn department in southern France.
The Thoré is a river that is part of the commune's eastern border, flows north-northwestward through the northern part of the commune, c ...
starting from 1889.
In the early 20th century, Julius Neubronner
Julius Gustav Neubronner (8 February 1852 – 17 April 1932) was a German apothecary, inventor, company founder, and a pioneer of amateur photography and film. He was part of a dynasty of apothecaries in Kronberg im Taunus. Neubronner was court ap ...
experimented with pigeon photography. These pigeons carried small cameras that incorporated timers. (photographs by Alfred Nobel's rocket and the Bavarian pigeon fleet)
Ludwig Rahrmann in 1891 patented a means of attaching a camera to a large calibre artillery projectile or rocket, and this inspired Alfred Maul to develop his Maul Camera Rockets starting in 1903. Alfred Nobel
Alfred Bernhard Nobel ( ; ; 21 October 1833 – 10 December 1896) was a Swedish chemist, inventor, engineer, and businessman. He is known for inventing dynamite, as well as having bequeathed his fortune to establish the Nobel Prizes. He also m ...
in 1896 had already built the first rocket carrying a camera, which took photographs of the Swedish landscape during its flights. Maul improved his camera rockets and the Austrian Army even tested them in the Turkish-Bulgarian War in 1912 and 1913, but by then and from that time on camera-carrying aircraft were found to be superior. (summary and photo)
The first use of airplanes in combat missions was by the Italian Air Force
The Italian Air Force (; AM, ) is the air force of the Italy, Italian Republic. The Italian Air Force was founded as an independent service arm on 28 March 1923 by Victor Emmanuel III of Italy, King Victor Emmanuel III as the ("Royal Air Force ...
during the Italo-Turkish War
The Italo-Turkish (, "Tripolitanian War", , "War of Libya"), also known as the Turco-Italian War, was fought between the Kingdom of Italy and the Ottoman Empire from 29 September 1911 to 18 October 1912. As a result of this conflict, Italy captur ...
of 1911–1912. On 23 October 1911, an Italian pilot, Capt. Carlo Piazza, flew over the Turkish lines in Libya
Libya, officially the State of Libya, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya border, the east, Sudan to Libya–Sudan border, the southeast, Chad to Chad–L ...
to conduct an aerial reconnaissance mission; Another aviation first occurred on November 1 with the first ever dropping of an aerial bomb
An aerial bomb is a type of Explosive weapon, explosive or Incendiary device, incendiary weapon intended to travel through the Atmosphere of Earth, air on a predictable trajectory. Engineers usually develop such bombs to be dropped from an aircra ...
, performed by '' Sottotenente'' Giulio Gavotti
Giulio Gavotti (17 October 1882 in Genoa – 6 October 1939) was an Italian lieutenant and pilot who fought in the Italo-Turkish War where he dropped the world's first aerial bomb from his Taube monoplane over the Ain Zara oasis in Libya.
Aeri ...
, on Turkish troops from an early model of Etrich Taube
The Etrich ''Taube'', also known by the names of the various later manufacturers who built versions of the type, such as the Rumpler ''Taube'', was a pre-World War I monoplane aircraft. It was the first military aeroplane to be mass-produced in ...
aircraft.
The first reconnaissance flight in Europe took place in Greece, over Thessaly, on 18 October 1912 (5 October by the Julian calendar) over the Ottoman army. The pilot also dropped some hand-grenades over the Turkish Army barracks, although without success. This was the first day of the Balkan wars, and during the same day a similar mission was flown by German mercenaries in Ottoman service in the Thrace front against the Bulgarians. The Greek and the Ottoman mission flown during the same day are the first military aviation combat missions in a conventional war. A few days later, on 16 October 1912, a Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
n Albatros aircraft performed one of Europe's first reconnaissance flight in combat conditions, against the Turkish lines on the Balkan peninsula
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
, during the Balkan Wars
The Balkan Wars were two conflicts that took place in the Balkans, Balkan states in 1912 and 1913. In the First Balkan War, the four Balkan states of Kingdom of Greece (Glücksburg), Greece, Kingdom of Serbia, Serbia, Kingdom of Montenegro, M ...
of 1912–1913.
Maturation during the First World War
 The use of aerial photography rapidly matured during the
The use of aerial photography rapidly matured during the First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, as aircraft used for reconnaissance purposes were outfitted with cameras to record enemy movements and defences. At the start of the conflict, the usefulness of aerial photography was not fully appreciated, with reconnaissance being accomplished with map sketching from the air.
Frederick Charles Victor Laws
Group Captain Frederick Charles Victor Laws (29 November 1887 – 27 October 1975), was an officer in the Royal Air Force, an aerial surveyor, and the founder and most prominent pioneer of British aerial reconnaissance.
Early military service
...
started experiments in aerial photography in 1912 with No. 1 Squadron RAF
Number 1 Squadron, also known as No. 1 (Fighter) Squadron, is a squadron of the Royal Air Force. It was the first squadron to fly a VTOL aircraft. It currently operates Eurofighter Typhoon aircraft from RAF Lossiemouth.
The squadron motto, ' ...
using the British dirigible ''Beta''. He discovered that vertical photos taken with 60% overlap could be used to create a stereoscopic
Stereoscopy, also called stereoscopics or stereo imaging, is a technique for creating or enhancing the illusion of depth in an image by means of stereopsis for binocular vision. The word ''stereoscopy'' derives . Any stereoscopic image is ...
effect when viewed in a stereoscope, thus creating a perception of depth that could aid in cartography and in intelligence derived from aerial images. The dirigibles were eventually allocated to the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom ...
, so Laws formed the first aerial reconnaissance unit of fixed-wing aircraft; this became No. 3 Squadron RAF
Number 3 Squadron, also known as No. 3 (Fighter) Squadron, of the Royal Air Force operates the Eurofighter Typhoon FGR4 from RAF Coningsby, Lincolnshire, since reforming on 1 April 2006. It was first formed on 13 May 1912 as one of the first sq ...
.
Germany was one of the first countries to adopt the use of a camera for aerial reconnaissance, opting for a Görz
Gorizia (; ; , ; ; ) is a town and (municipality) in northeastern Italy, in the autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia. It is located at the foot of the Julian Alps, bordering Slovenia. It is the capital of the Regional decentralization ...
, in 1913. French Military Aviation began the war with several squadrons of Bleriot observation planes, equipped with cameras for reconnaissance. The French Army developed procedures for getting prints into the hands of field commanders in record time.
 The
The Royal Flying Corps
The Royal Flying Corps (RFC) was the air arm of the British Army before and during the First World War until it merged with the Royal Naval Air Service on 1 April 1918 to form the Royal Air Force. During the early part of the war, the RFC sup ...
recon pilots began to use cameras for recording their observations in 1914 and by the Battle of Neuve Chapelle
The Battle of Neuve Chapelle (10–13 March 1915) took place in the First World War in the Artois region of France. The attack was intended to cause a rupture in the German lines, which would then be exploited with a rush to the Aubers Ridge an ...
in 1915 the entire system of German trenches was being photographed. The first purpose-built and practical aerial camera was invented by Captain John Moore-Brabazon
Lieutenant Colonel John Theodore Cuthbert Moore-Brabazon, 1st Baron Brabazon of Tara, , HonFRPS (8 February 1884 – 17 May 1964) was an English aviation pioneer and Conservative politician. He was the first Englishman to pilot a heavier-than- ...
in 1915 with the help of the Thornton-Pickard company, greatly enhancing the efficiency of aerial photography. The camera was inserted into the floor of the aircraft and could be triggered by the pilot at intervals.
Moore-Brabazon also pioneered the incorporation of stereoscopic techniques into aerial photography, allowing the height of objects on the landscape to be discerned by comparing photographs taken at different angles. In 1916, the Austro-Hungarian Empire
Austria-Hungary, also referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Dual Monarchy or the Habsburg Monarchy, was a multi-national constitutional monarchy in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. A military and diplomatic alliance, it consist ...
made vertical camera axis aerial photos above Italy for map-making.
By the end of the war, aerial cameras had dramatically increased in size and focal power
In optics, optical power (also referred to as dioptric power, refractive power, focal power, focusing power, or convergence power) is the degree to which a lens, mirror, or other optical system converges or diverges light. It is equal to the r ...
and were used increasingly frequently as they proved their pivotal military worth; by 1918 both sides were photographing the entire front twice a day and had taken over half a million photos since the beginning of the conflict.
In January 1918, General Allenby
Field Marshal Edmund Henry Hynman Allenby, 1st Viscount Allenby, (23 April 1861 – 14 May 1936) was a senior British Army officer and imperial governor. He fought in the Second Boer War and also in World War I, in which he led the Britis ...
used five Australian pilots from No. 1 Squadron AFC to photograph a area in Palestine
Palestine, officially the State of Palestine, is a country in West Asia. Recognized by International recognition of Palestine, 147 of the UN's 193 member states, it encompasses the Israeli-occupied West Bank, including East Jerusalem, and th ...
as an aid to correcting and improving maps of the Turkish front. This was a pioneering use of aerial photography as an aid for cartography
Cartography (; from , 'papyrus, sheet of paper, map'; and , 'write') is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an imagined reality) can ...
. Lieutenants Leonard Taplin, Allan Runciman Brown, H. L. Fraser, Edward Patrick Kenny, and L. W. Rogers photographed a block of land stretching from the Turkish front lines deep into their rear areas. Beginning 5 January, they flew with a fighter escort to ward off enemy fighters. Using Royal Aircraft Factory BE.12 and Martinsyde
Martinsyde was a British aircraft and motorcycle manufacturer between 1908 and 1922, when it was forced into liquidation by a factory fire.
History
The company was first formed in 1908 as a partnership between H.P. Martin and George Handasyde ...
airplanes, they not only overcame enemy air attacks, but also bucked 65 mile-per-hour winds, anti-aircraft fire, and malfunctioning equipment to complete their task circa 19 January 1918.
Second World War
High-speed reconnaissance aircraft
 During 1928, the
During 1928, the Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the Air force, air and space force of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies. It was formed towards the end of the World War I, First World War on 1 April 1918, on the merger of t ...
(RAF) developed an electric heating system for the aerial camera; this innovation allowed reconnaissance aircraft to take pictures from very high altitudes without the camera parts freezing. In 1939, Sidney Cotton
Frederick Sidney Cotton (17 June 1894 – 13 February 1969) was an Australian inventor, photographer and aviation and photography pioneer, responsible for developing and promoting an early colour film process, and largely responsible for the ...
and Flying Officer
Flying officer (Fg Offr or F/O) is a junior officer rank used by some air forces, with origins from the Royal Air Force. The rank is used by air forces of many countries that have historical British influence.
Flying officer is immediately ...
Maurice Longbottom of the RAF suggested that airborne reconnaissance may be a task better suited to fast, small aircraft which would use their speed and high service ceiling to avoid detection and interception. Although this may perhaps seem obvious today with modern reconnaissance tasks performed by fast, high flying aircraft, at the time it was radical thinking.
Cotton and Longbottom proposed the use of Spitfire
The Supermarine Spitfire is a British single-seat fighter aircraft that was used by the Royal Air Force and other Allied countries before, during, and after World War II. It was the only British fighter produced continuously throughout the ...
s with their armament and radio
Radio is the technology of communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 3 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmitter connec ...
s removed and replaced with extra fuel and cameras. This concept led to the development of the Spitfire PR variants. With their armaments removed, these planes could attain a maximum speed of 396 mph while flying at an altitude of 30,000 feet, and were used for photo-reconnaissance missions. The Spitfire PR was fitted with five cameras, which were heated to ensure good results (while the cockpit was not). In the reconnaissance role, the Spitfire proved to be extremely successful, resulting in numerous Spitfire variants being built specifically for that purpose. These served initially with what later became No. 1 Photographic Reconnaissance Unit (PRU).
 Other fighters were also adapted for photo-reconnaissance, including the British
Other fighters were also adapted for photo-reconnaissance, including the British Mosquito
Mosquitoes, the Culicidae, are a Family (biology), family of small Diptera, flies consisting of 3,600 species. The word ''mosquito'' (formed by ''Musca (fly), mosca'' and diminutive ''-ito'') is Spanish and Portuguese for ''little fly''. Mos ...
and the American P-38 Lightning
The Lockheed P-38 Lightning is an American single-seat, twin piston-engined fighter aircraft that was used during World War II. Developed for the United States Army Air Corps (USAAC) by the Lockheed Corporation, the P-38 incorporated a distinc ...
and P-51 Mustang
The North American Aviation P-51 Mustang is an American long-range, single-seat fighter aircraft, fighter and fighter-bomber used during World War II and the Korean War, among other conflicts. The Mustang was designed in 1940 by a team headed ...
. Such aircraft were painted in PRU Blue or Pink camouflage colours to make them difficult to spot in the air, and often were stripped of weapons or had engines modified for better performance at high altitude
Altitude is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum (geodesy), datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context (e.g., aviation, geometr ...
s (over ).
The American F-4, a factory modification of the Lockheed P-38 Lightning
The Lockheed P-38 Lightning is an American single-seat, twin piston-engined fighter aircraft that was used during World War II. Developed for the United States Army Air Corps (USAAC) by the Lockheed Corporation, the P-38 incorporated a distinc ...
, replaced the nose-mounted four machine guns and cannon with four high-quality K-17 cameras. Approximately 120 F-4 and F-4As were hurriedly made available by March 1942, reaching the 8th Photographic Squadron in Australia by April (the first P-38s to see action). The F-4 had an early advantage of long range and high speed combined with ability to fly at high altitude
Altitude is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum (geodesy), datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context (e.g., aviation, geometr ...
; a potent combination for reconnaissance. In the last half of 1942 Lockheed would produce 96 F-5As, based on the P-38G with all later P-38 photo-reconnaissance variants designated F-5. In its reconnaissance role, the Lightning was so effective that over 1,200 F-4 and F-5 variants were delivered by Lockheed, and it was the United States Army Air Forces
The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF or AAF) was the major land-based aerial warfare service component of the United States Army and ''de facto'' aerial warfare service branch of the United States during and immediately after World War II ...
's (USAAF) primary photo-reconnaissance type used throughout the war in all combat theatres. The Mustang F-6 arrived later in the conflict and, by spring 1945, became the dominant reconnaissance type flown by the USAAF in the European theatre
The European theatre of World War II was one of the two main theatres of combat during World War II, taking place from September 1939 to May 1945. The Allied powers (including the United Kingdom, the United States, the Soviet Union and Franc ...
. American photo-reconnaissance operations in Europe were centred at RAF Mount Farm, with the resulting photographs transferred to Medmenham for interpretation. Approximately 15,000 Fairchild K-20 aerial cameras were manufactured for use in Allied reconnaissance aircraft between 1941 and 1945.
The British de Havilland Mosquito
The de Havilland DH.98 Mosquito is a British twin-engined, multirole combat aircraft, introduced during the World War II, Second World War. Unusual in that its airframe was constructed mostly of wood, it was nicknamed the "Wooden Wonder", or " ...
excelled in the photo-reconnaissance role; the converted bomber was fitted with three cameras installed in what had been the bomb bay. It had a cruising speed of 255 mph, maximum speed of 362 mph and a maximum altitude of 35,000 feet. The first converted PRU (Photo-Reconnaissance Unit) Mosquito was delivered to RAF Benson
Royal Air Force Benson or RAF Benson is a Royal Air Force (RAF) List of Royal Air Force stations, station located at Benson, Oxfordshire, Benson, near Wallingford, Oxfordshire, Wallingford, in South Oxfordshire, England. It is a front-line st ...
in July 1941 by Geoffrey de Havilland
Captain (British Army and Royal Marines), Captain Sir Geoffrey de Havilland, (27 July 1882 – 21 May 1965) was an English aviation pioneer and aerospace engineer. De Havilland, The aircraft company he founded produced the de Havilland Mosquit ...
himself. The PR Mk XVI and later variants had pressurized
Pressurization or pressurisation is the application of pressure in a given situation or environment.
Examples Industrial
Industrial equipment is often maintained at pressures above or below atmospheric.
Atmospheric
This is the process by which a ...
cockpit
A cockpit or flight deck is the area, on the front part of an aircraft, spacecraft, or submersible, from which a pilot controls the vehicle.
The cockpit of an aircraft contains flight instruments on an instrument panel, and the controls th ...
s and also pressurized central and inner wing tanks to reduce fuel vaporization at high altitude
Altitude is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum (geodesy), datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context (e.g., aviation, geometr ...
. The Mosquito was faster than most enemy
An enemy or a foe is an individual or a group that is considered as forcefully adverse or threatening. The concept of an enemy has been observed to be "basic for both individuals and communities". The term "enemy" serves the social function of d ...
fighters at 35,000 ft,Bowman 2005, p. 21. and could roam almost anywhere. Colonel Roy M. Stanley II of United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the Air force, air service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is one of the six United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Tracing its ori ...
(USAF) stated of the aircraft: "I consider the Mosquito the best photo-reconnaissance aircraft of the war".Stanley 2010, p. 35. The United States Army Air Forces
The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF or AAF) was the major land-based aerial warfare service component of the United States Army and ''de facto'' aerial warfare service branch of the United States during and immediately after World War II ...
(USAAF) designation for the photo-reconnaissance Mosquito was F-8.
Apart from (for example) the Mosquito, most World War II bomber
A bomber is a military combat aircraft that utilizes
air-to-ground weaponry to drop bombs, launch aerial torpedo, torpedoes, or deploy air-launched cruise missiles.
There are two major classifications of bomber: strategic and tactical. Strateg ...
s were not as fast as fighters, although they were effective for aerial reconnaissance due to their long range, inherent stability in flight and capacity to carry large camera payloads. American bombers with top speeds of less than 300 mph used for reconnaissance include the B-24 Liberator
The Consolidated B-24 Liberator is an American heavy bomber, designed by Consolidated Aircraft of San Diego, California. It was known within the company as the Model 32, and some initial production aircraft were laid down as export models desi ...
(photo-reconnaissance variant designated F-7), B-25 Mitchell
The North American B-25 Mitchell is an American medium bomber that was introduced in 1941 and named in honor of Brigadier General William "Billy" Mitchell, a pioneer of U.S. military aviation. Used by many Allied air forces, the B-25 served ...
(F-10) and B-17 Flying Fortress
The Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress is an American four-engined heavy bomber aircraft developed in the 1930s for the United States Army Air Corps (USAAC). A fast and high-flying bomber, the B-17 dropped more bombs than any other aircraft during ...
(F-9). The revolutionary B-29 Superfortress
The Boeing B-29 Superfortress is a retired American four-engined Propeller (aeronautics), propeller-driven heavy bomber, designed by Boeing and flown primarily by the United States during World War II and the Korean War. Named in allusion to ...
was the world's largest combat-operational bomber when it appeared in 1944, with a top speed of over 350 mph which at that time was outstanding for such a large and heavy aircraft; the B-29 also had a pressurized cabin
Cabin pressurization is a process in which conditioned air is pumped into the cabin of an aircraft or spacecraft in order to create a safe and comfortable environment for humans flying at high altitudes. For aircraft, this air is usually bled ...
for high altitude flight. The photographic reconnaissance version of the B-29 was designated F-13 and carried a camera suite of three K-17B, two K-22 and one K-18 with provisions for others; it also retained the standard B-29 defensive armament of a dozen .50 caliber machine guns. In November 1944 an F-13 conducted the first flight by an Allied aircraft over Tokyo since the Doolittle Raid of April 1942. The Consolidated B-32 Dominator
The Consolidated B-32 Dominator (Consolidated Model 34) was an American heavy strategic bomber built for the United States Army Air Forces during World War II. A B-32 was involved in the last air combat engagement of the war, resulting in the ...
was also used for reconnaissance over Japan in August 1945.
The Japanese Army
An army, ground force or land force is an armed force that fights primarily on land. In the broadest sense, it is the land-based military branch, service branch or armed service of a nation or country. It may also include aviation assets by ...
Mitsubishi Ki-46
The Mitsubishi Ki-46 was a twin-engine reconnaissance aircraft that was used by the Imperial Japanese Army in World War II. Its Army ''Shiki'' designation was Type 100 Command Reconnaissance Aircraft (); the Allied brevity code World War II Alli ...
, a twin-engined aircraft designed expressly for the reconnaissance role with defensive armament of 1 light machine gun, entered service in 1941. Codename
A code name, codename, call sign, or cryptonym is a code word or name used, sometimes clandestinely, to refer to another name, word, project, or person. Code names are often used for military purposes, or in espionage. They may also be used in ...
d "Dinah" this aircraft was fast, elusive and proved difficult for Allied fighters to destroy. More than 1,500 Ki-46s were built and its performance was upgraded later in the war with the Ki-46-III variant. Another purpose-designed reconnaissance aircraft for the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service
The (IJNAS) was the air arm of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN). The organization was responsible for the operation of naval aircraft and the conduct of aerial warfare in the Pacific War.
The Japanese military acquired its first aircraft in ...
was the carrier-based
A carrier-based aircraft (also known as carrier-capable aircraft, carrier-borne aircraft, carrier aircraft or aeronaval aircraft) is a naval aircraft designed for operations from aircraft carriers. Carrier-based aircraft must be able to launch ...
, single-engine Nakajima C6N ''Saiun'' ("Iridescent Cloud"). Codename
A code name, codename, call sign, or cryptonym is a code word or name used, sometimes clandestinely, to refer to another name, word, project, or person. Code names are often used for military purposes, or in espionage. They may also be used in ...
d "Myrt" by the Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not an explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are calle ...
, the Nakajima C6N first flew in 1943 and was also highly elusive to American aircraft due to its excellent performance and speed of almost 400 mph. As fate would have it on 15 August 1945, a C6N1 was the last aircraft to be shot down in World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
. Japan also developed the high-altitude Tachikawa Ki-74
The Tachikawa Ki-74 (World War II Allied names for Japanese aircraft, Allied reporting name Patsy) was a Empire of Japan, Japanese experimental, long-Range (aeronautics), range reconnaissance bomber of World War II. A twin-engine, mid-wing monop ...
reconnaissance bomber, which was in a similar class of performance as the Mosquito
Mosquitoes, the Culicidae, are a Family (biology), family of small Diptera, flies consisting of 3,600 species. The word ''mosquito'' (formed by ''Musca (fly), mosca'' and diminutive ''-ito'') is Spanish and Portuguese for ''little fly''. Mos ...
, but only 16 were built and did not see operational service.
The Luftwaffe
The Luftwaffe () was the aerial warfare, aerial-warfare branch of the before and during World War II. German Empire, Germany's military air arms during World War I, the of the Imperial German Army, Imperial Army and the of the Imperial Ge ...
began deploying jet aircraft
A jet aircraft (or simply jet) is an aircraft (nearly always a fixed-wing aircraft) propelled by one or more jet engines.
Whereas the engines in Propeller (aircraft), propeller-powered aircraft generally achieve their maximum efficiency at much ...
in combat in 1944, and the twin- jet Arado Ar 234
The Arado Ar 234 ''Blitz'' (English: lightning) is a jet-powered bomber designed and produced by the German aircraft manufacturer Arado. It was the world's first operational turbojet-powered bomber, seeing service during the final years of the ...
''Blitz'' ("Lightning") reconnaissance bomber was the world's first operational jet-powered bomber. The Ar 234B-1 was equipped with two Rb 50/30 or Rb 75/30 cameras, and its top speed of 460 mph allowed it to outrun the fastest non-jet Allied fighters of the time. The twin piston
A piston is a component of reciprocating engines, reciprocating pumps, gas compressors, hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic cylinders, among other similar mechanisms. It is the moving component that is contained by a cylinder (engine), cylinder a ...
-engined Junkers Ju 388
The Junkers Ju 388 ''Klaus Störtebeker, Störtebeker'' is a World War II German ''Luftwaffe'' Multirole combat aircraft, multi-role aircraft based on the Junkers Ju 88, Ju 88 airframe by way of the Junkers Ju 188, Ju 188. It differed from its pr ...
high-altitude bomber was an ultimate evolution of the Ju 88
The Junkers Ju 88 is a twin-engined multirole combat aircraft designed and produced by the German aircraft manufacturer Junkers Aircraft and Motor Works. It was used extensively during the Second World War by the ''Luftwaffe'' and became one of ...
by way of the Ju 188
The Junkers Ju 188 "''Rächer''" ("Avenger") was a German ''Luftwaffe'' high-performance medium bomber built during World War II, the planned follow-up to the Ju 88 with better performance and payload. It was produced only in limited numbers, d ...
. The photographic reconnaissance Ju 388L variant had a pressurized
Pressurization or pressurisation is the application of pressure in a given situation or environment.
Examples Industrial
Industrial equipment is often maintained at pressures above or below atmospheric.
Atmospheric
This is the process by which a ...
cockpit
A cockpit or flight deck is the area, on the front part of an aircraft, spacecraft, or submersible, from which a pilot controls the vehicle.
The cockpit of an aircraft contains flight instruments on an instrument panel, and the controls th ...
from the Ju 388's original multi-role conception as not only a bomber but also a night fighter and bomber destroyer
Bomber destroyers were World War II interceptor aircraft intended to destroy enemy bomber aircraft. Bomber destroyers were typically larger and heavier than general interceptors, designed to mount more powerful armament, and often having twin en ...
, due to RLM's perceived threat of the U.S.
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguous ...
's high-altitude B-29
The Boeing B-29 Superfortress is a retired American four-engined Propeller (aeronautics), propeller-driven heavy bomber, designed by Boeing and flown primarily by the United States during World War II and the Korean War. Named in allusion to ...
(which ended up not being deployed in Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
). Approximately 50 Ju 388Ls were produced under rapidly deteriorating conditions at the end of the war. As with other high performance weapons introduced by Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
, too many circumstances in the war's logistics had changed by late 1944 for such aircraft to have any impact.
The DFS 228
The DFS 228 was a rocket-powered, high-altitude reconnaissance aircraft designed by the '' Deutsche Forschungsanstalt für Segelflug'' (DFS - "German Research Institute for Sailplane Flight") during World War II. By the end of the war, the aircr ...
was a rocket
A rocket (from , and so named for its shape) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using any surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely ...
-powered high-altitude reconnaissance aircraft under development in the latter part of World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
. It was designed by Felix Kracht
Felix Kracht (born 13 May 1912 in Krefeld; died 3 October 2002 in Weyhe) was a German engineer.
After graduating from the Technical University of Aachen, he put his theoretical knowledge into practice at the aeronautical association Flugwissensch ...
at the Deutsche Forschungsanstalt für Segelflug
The , or DFS , was formed in 1933 to centralise all gliding activity in Germany, under the directorship of Professor Walter Georgii. It was formed by the nationalisation of the Rhön-Rossitten Gesellschaft (RRG) at Darmstadt.Reitsch, H., 1955, ...
(German Institute for Sailplane Flight) and in concept is an interesting precursor to the post-war American
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, p ...
U-2, being essentially a powered long-wingspan
The wingspan (or just span) of a bird or an airplane is the distance from one wingtip to the opposite wingtip. For example, the Boeing 777–200 has a wingspan of , and a wandering albatross (''Diomedea exulans'') caught in 1965 had a wingsp ...
glider intended solely for the high-altitude aerial reconnaissance role. Advanced features of the DFS 228 design included a pressurized
Pressurization or pressurisation is the application of pressure in a given situation or environment.
Examples Industrial
Industrial equipment is often maintained at pressures above or below atmospheric.
Atmospheric
This is the process by which a ...
escape capsule for the pilot. The aircraft never flew under rocket power with only unpowered glider prototype
A prototype is an early sample, model, or release of a product built to test a concept or process. It is a term used in a variety of contexts, including semantics, design, electronics, and Software prototyping, software programming. A prototype ...
s flown prior to May 1945.
Imagery analysis
 The collection and interpretation of aerial reconnaissance intelligence became a considerable enterprise during the war. Beginning in 1941,
The collection and interpretation of aerial reconnaissance intelligence became a considerable enterprise during the war. Beginning in 1941, RAF Medmenham
RAF Medmenham is a former Royal Air Force station based at Danesfield House near Medmenham, in Buckinghamshire, England. Activities there specialised in photographic intelligence, and it was once the home of the RAF Intelligence Branch. Durin ...
was the main interpretation centre for photographic reconnaissance operations in the European
European, or Europeans, may refer to:
In general
* ''European'', an adjective referring to something of, from, or related to Europe
** Ethnic groups in Europe
** Demographics of Europe
** European cuisine, the cuisines of Europe and other West ...
and Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
theatres. The Central Interpretation Unit
MI4 was established in 1915 as a section of the Directorate of Military Intelligence (United Kingdom), Directorate of Military Intelligence (DMI). Section 4 was the designation for the Topographic Section, General Staff, later the Geographical ...
(CIU) was later amalgamated with the Bomber Command Damage Assessment Section and the Night Photographic Interpretation Section of No 3 Photographic Reconnaissance Unit, RAF Oakington
Royal Air Force Oakington or more simply RAF Oakington was a Royal Air Force station located north of Oakington, Cambridgeshire, England and northwest of Cambridge.
History Second World War
Construction was started in 1939, but was affected ...
, in 1942.Allied Central Interpretation Unit (ACIU)During 1942 and 1943, the CIU gradually expanded and was involved in the planning stages of practically every operation of the war, and in every aspect of intelligence. In 1945, daily intake of material averaged 25,000 negatives and 60,000 prints. Thirty-six million prints were made during the war. By
VE-day
Victory in Europe Day is the day celebrating the formal acceptance by the Allies of World War II of German Instrument of Surrender, Germany's unconditional surrender of Wehrmacht, its armed forces on Tuesday, 8 May 1945; it marked the official su ...
, the print library, which documented and stored worldwide cover, held 5,000,000 prints from which 40,000 reports had been produced.
American personnel had for some time formed an increasing part of the CIU and on 1 May 1944 this was finally recognised by changing the title of the unit to the Allied Central Interpretation Unit (ACIU). There were then over 1,700 personnel on the unit's strength. A large number of photographic interpreters were recruited from the Hollywood Film Studios including Xavier Atencio
Francis Xavier Atencio, also known as X Atencio (September 4, 1919 – September 10, 2017) was an American animator and Imagineer for The Walt Disney Company. He is perhaps best known for writing the scripts and song lyrics of the Disney theme p ...
. Two renowned archaeologists also worked there as interpreters: Dorothy Garrod
Dorothy Annie Elizabeth Garrod, CBE, FBA (5 May 1892 – 18 December 1968) was an English archaeologist who specialised in the Palaeolithic period. She held the position of Disney Professor of Archaeology at the University of Cambridge from 1 ...
, the first woman to hold an Oxbridge Chair, and Glyn Daniel
Glyn Edmund Daniel (23 April 1914 – 13 December 1986) was a Welsh scientist and archaeologist who taught at Cambridge University, where he specialised in the European Neolithic period. He was appointed Disney Professor of Archaeology in ...
, who went on to gain popular acclaim as the host of the television game show ''Animal, Vegetable or Mineral?
''Animal, Vegetable, Mineral?'' was a British television panel show which originally ran from 23 October 1952 to 18 March 1959. In the show, a panel of archaeologists, art historians, and natural history experts were asked to identify interest ...
''.
Sidney Cotton
Frederick Sidney Cotton (17 June 1894 – 13 February 1969) was an Australian inventor, photographer and aviation and photography pioneer, responsible for developing and promoting an early colour film process, and largely responsible for the ...
's aerial photographs were far ahead of their time. Together with other members of his reconnaissance squadron, he pioneered the technique of high-altitude, high-speed photography that was instrumental in revealing the locations of many crucial military and intelligence targets. Cotton also worked on ideas such as a prototype specialist reconnaissance aircraft and further refinements of photographic equipment. At its peak, British reconnaissance flights yielded 50,000 images per day to interpret.
Of particular significance in the success of the work of Medmenham was the use of stereoscopic
Stereoscopy, also called stereoscopics or stereo imaging, is a technique for creating or enhancing the illusion of depth in an image by means of stereopsis for binocular vision. The word ''stereoscopy'' derives . Any stereoscopic image is ...
images, using a between plate overlap of exactly 60%. Despite initial scepticism about the possibility of German rocket development, stereoscopic analysis proved its existence and major operations, including the 1943 offensives against the V-2 rocket
The V2 (), with the technical name ''Aggregat (rocket family), Aggregat-4'' (A4), was the world's first long-range missile guidance, guided ballistic missile. The missile, powered by a liquid-propellant rocket engine, was developed during the S ...
development plant at Peenemünde
Peenemünde (, ) is a municipality on the Baltic Sea island of Usedom in the Vorpommern-Greifswald district in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern in north-eastern Germany. It is part of the ''Amt (country subdivision), Amt'' (collective municipality) of Used ...
, were made possible by work carried out at Medmenham. Later offensives were also made against potential launch sites at Wizernes
Wizernes (; ) is a Communes of France, commune in the Pas-de-Calais department, northern France. It lies southwest of Saint-Omer on the banks of the river Aa (France), Aa at the D928 and D211 road junction. The commune is twinned with Ensdorf, ...
and 96 other launch sites in northern France.
Particularly important sites were measured, from the images, using Swiss stereoautograph
The stereoautograph is a complex opto-mechanical measurement instrument for the evaluation of analog or digital photograms. It is based on the stereoscopy effect by using two aero photos or two photograms of the topography or of buildings from d ...
machines made by Wild (Heerbrugg) and physical models made to facilitate understanding of what was there or what it was for.
It is claimed that Medmanham's greatest operational success was Operation Crossbow
''Crossbow'' was the code name in World War II for Anglo-American operations against the German V-weapons, long range reprisal weapons (V-weapons) programme. The primary V-weapons were the V-1 flying bomb and V-2 rocket, which were launched agai ...
which, from 23 December 1943, destroyed the V-1 infrastructure in northern France."Operation Crossbow", BBC2, broadcast 15 May 2011/ref> According to R.V. Jones, photographs were used to establish the size and the characteristic launching mechanisms for both the
V-1 flying bomb
The V-1 flying bomb ( "Vengeance Weapon 1") was an early cruise missile. Its official Reich Aviation Ministry () name was Fieseler Fi 103 and its suggestive name was (hellhound). It was also known to the Allies as the buzz bomb or doodlebug a ...
and the V-2 rocket
The V2 (), with the technical name ''Aggregat (rocket family), Aggregat-4'' (A4), was the world's first long-range missile guidance, guided ballistic missile. The missile, powered by a liquid-propellant rocket engine, was developed during the S ...
.
Cold War
Immediately after the Second World War, the long range aerial reconnaissance role was quickly taken up by adapted jetbomber
A bomber is a military combat aircraft that utilizes
air-to-ground weaponry to drop bombs, launch aerial torpedo, torpedoes, or deploy air-launched cruise missiles.
There are two major classifications of bomber: strategic and tactical. Strateg ...
s, such as the English Electric Canberra
The English Electric Canberra is a British first-generation, jet-powered medium bomber. It was developed by English Electric during the mid- to late 1940s in response to a 1944 Air Ministry requirement for a successor to the wartime de Havilla ...
and its American development the Martin B-57, that were capable of flying higher or faster than enemy aircraft
An aircraft ( aircraft) is a vehicle that is able to flight, fly by gaining support from the Atmosphere of Earth, air. It counters the force of gravity by using either Buoyancy, static lift or the Lift (force), dynamic lift of an airfoil, or, i ...
or defense
Defense or defence may refer to:
Tactical, martial, and political acts or groups
* Defense (military), forces primarily intended for warfare
* Civil defense, the organizing of civilians to deal with emergencies or enemy attacks
* Defense industr ...
s.Polmar 2001, p. 11.Lewis 1970, p. 371. Shortly after the Korean War
The Korean War (25 June 1950 – 27 July 1953) was an armed conflict on the Korean Peninsula fought between North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea; DPRK) and South Korea (Republic of Korea; ROK) and their allies. North Korea was s ...
, the United States begun to use RB-47
The Boeing B-47 Stratojet (Boeing company designation Model 450) is a retired American long-range, six-engined, turbojet-powered strategic bomber designed to fly at high subsonic speed and at high altitude to avoid enemy interceptor aircraft. ...
aircraft; these were at first were converted B-47 bombers, but later purposely built as RB-47 reconnaissance aircraft that had no bombing capability. Large cameras were mounted in the plane's belly and a truncated bomb bay
The bomb bay or weapons bay on some military aircraft is a compartment to carry bombs, usually in the aircraft's fuselage, with "bomb bay doors" which open at the bottom. The bomb bay doors are opened and the bombs are dropped when over the ...
was used for carrying photoflash bomb
Flashbombs are loaded into a photo-reconnaissance Melsbroek, Belgium. c.1944
A photoflash bomb, or flash bomb, is bomb">explosive ordnance dropped by aircraft, usually military surveillance aircraft, designed to detonate Air burst">above grou ...
s. Later versions of the RB-47, such as the RB-47H, were extensively modified for signals intelligence
Signals intelligence (SIGINT) is the act and field of intelligence-gathering by interception of ''signals'', whether communications between people (communications intelligence—abbreviated to COMINT) or from electronic signals not directly u ...
(ELINT), with additional equipment operator crew stations in the bomb bay; unarmed weather reconnaissance
Weather reconnaissance is the acquisition of weather data used for research and planning. Typically the term reconnaissance refers to observing weather from the air, as opposed to the ground.
Methods
Aircraft
Helicopters are not built to ...
WB-47s with cameras and meteorological instruments also served the United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the Air force, air service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is one of the six United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Tracing its ori ...
(USAF) during the 1960s.Natola 2002, pp. 179–181.
 The onset of the
The onset of the Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
led to development of several highly specialized and clandestine strategic reconnaissance aircraft
A reconnaissance aircraft (colloquially, a spy plane) is a military aircraft designed or adapted to perform aerial reconnaissance with roles including collection of imagery intelligence (including using Aerial photography, photography), signals ...
, or spy planes, such as the Lockheed U-2
The Lockheed U-2, nicknamed the "''Dragon Lady''", is an American single-engine, high–altitude reconnaissance aircraft operated by the United States Air Force (USAF) and the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) since the 1950s. Designed for all- ...
and its successor the SR-71 Blackbird
The Lockheed SR-71 "Blackbird" is a retired long-range, high-altitude, Mach 3+ strategic reconnaissance aircraft developed and manufactured by the American aerospace company Lockheed Corporation. Its nicknames include " Blackbird" and ...
(both from the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
). Flying these aircraft became an exceptionally demanding task, with crew
A crew is a body or a group of people who work at a common activity, generally in a structured or hierarchy, hierarchical organization. A location in which a crew works is called a crewyard or a workyard. The word has nautical resonances: the ta ...
s specially selected and trained due to the aircraft's extreme performance characteristics in addition to risk of being captured as spies
Spies most commonly refers to people who engage in spying, espionage or clandestine operations.
Spies or The Spies may also refer to:
Arts and media Films
* ''Spies'' (1928 film), English title for ''Spione'', a 1928 German film by Fritz Lan ...
. The American U-2 shot down in Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
airspace
Airspace is the portion of the atmosphere controlled by a country above its territory, including its territorial waters or, more generally, any specific three-dimensional portion of the atmosphere. It is not the same as outer space which is t ...
and capture of its pilot caused political turmoil at the height of the Cold War.
Beginning in the early 1960s, United States aerial and satellite reconnaissance was coordinated by the National Reconnaissance Office
The National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) is a member of the United States Intelligence Community and an agency of the United States Department of Defense which designs, builds, launches, and operates the reconnaissance satellites of the U.S. f ...
(NRO). Risks such as loss or capture of reconnaissance aircraft crewmembers also contributed to U.S.
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguous ...
development of the Ryan Model 147
The Ryan Model 147 Lightning Bug is a jet-powered drone, or unmanned aerial vehicle, produced and developed by Ryan Aeronautical from the earlier Ryan Firebee target drone series.
Beginning in 1962, the Model 147 was introduced as a reconn ...
RPV (Remotely Piloted Vehicle) unmanned drone aircraft which were partly funded by the NRO during the 1960s.
During the 1960s, the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the naval warfare, maritime military branch, service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is the world's most powerful navy with the largest Displacement (ship), displacement, at 4.5 millio ...
opted to convert many of its supersonic
Supersonic speed is the speed of an object that exceeds the speed of sound (Mach 1). For objects traveling in dry air of a temperature of 20 °C (68 °F) at sea level, this speed is approximately . Speeds greater than five times ...
carrier-based
A carrier-based aircraft (also known as carrier-capable aircraft, carrier-borne aircraft, carrier aircraft or aeronaval aircraft) is a naval aircraft designed for operations from aircraft carriers. Carrier-based aircraft must be able to launch ...
Nuclear weapon, nuclear bomber, the North American A-5 Vigilante, into the capable RA-5C Vigilante reconnaissance aircraft. Beginning in the early 1980s, the U.S. Navy outfitted and deployed Grumman F-14 Tomcat aircraft in one squadron aboard an aircraft carrier with a system called Tactical Airborne Reconnaissance Pod System (TARPS), which provided naval aerial reconnaissance capability until the Tomcat's retirement in 2006.Donald, David. "Northrop Grumman F-14 Tomcat, U.S. Navy today". ''Warplanes of the Fleet''. London: AIRtime Publishing Inc, 2004. .
Post Cold War
Since the 1980s, there has been an increasing tendency for militaries to rely upon assets other than manned aircraft to perform aerial reconnaissance. Alternative platforms include the use of surveillance satellites and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), such as the armed MQ-9 Reaper. By 2005, such UAVs could reportedly be equipped with compact cameras capable of identifying an object the size of a milk carton from altitudes of 60,000 feet. The U-2 has repeatedly been considered for retirement in favour of drones. In 2011, the USAF revealed plans to replace the U-2 with the RQ-4 Global Hawk, a UAV, within four years;Majumdar, Dave"Global Hawk to replace U-2 spy plane in 2015."
''Air Force Times,'' 10 August 2011. Retrieved: 22 August 2011. however, in January 2012, it was instead decided to extend the U-2's service life. Critics have pointed out that the RQ-4's cameras and sensors are less capable and lack all-weather operating capability; however, some of the U-2's sensors could be installed on the RQ-4. In late 2014, Lockheed Martin proposed converting the manned U-2 fleet into UAVs, which would substantially bolster its payload capability;Butler, Amy
"Lockheed updates unmanned U-2 concept."
''Aviation Week'', 24 November 2014. Retrieved: 7 December 2015. however, the USAF declined to provide funding for such an extensive conversion.Drew, James
"U-2 poised to receive radar upgrade, but not un-manned conversion."
''Flightglobal.com'', 31 July 2015. Retrieved: 7 December 2015. During the 2010s, American defense conglomerate Lockheed Martin promoted its proposal to develop a Hypersonic speed, hypersonic Unmanned aerial vehicle, UAV, which it referred to the Lockheed Martin SR-72, SR-72 in allusion to its function as a spiritual successor to the retired SR-71 Blackbird. The company has also developed several other reconnaissance UAVs, such as the Lockheed Martin RQ-170 Sentinel.
Technologies
Miniature UAVs
Due to the low cost of miniature UAVs, this technology brings aerial reconnaissance into the hands of soldiers on the ground. The soldier on the ground can both control the UAV and see its output, yielding great benefit over a disconnected approach. With small systems being man packable, operators are now able to deploy air assets quickly and directly. The low cost and ease of operation of these miniature UAVs has enabled forces such as the Libyan Rebels to use miniature UAVs. * AeroVironment Wasp III (airplane – electric propulsion)
* Aeryon Scout/Aeryon SkyRanger (VTOL Rotorcraft) – Some UAVs are small enough to carry in a backpack with similar functionality to larger ones
* EMT Aladin (aircraft – electric – Made in Germany)
* Bramor C4EYE (aircraft – electric – Made in Slovenia)
* Bayraktar Mini UAV (aircraft – electric – Made in Turkey)
* RQ-84Z Areohawk (aircraft – electric – Made in New Zealand)
Low cost miniature UAVs demand increasingly miniature imaging payloads. Developments in miniature electronics have fueled the development of increasingly capable surveillance payloads, allowing miniature UAVs to provide high levels of capability in never before seen packages.
* AeroVironment Wasp III (airplane – electric propulsion)
* Aeryon Scout/Aeryon SkyRanger (VTOL Rotorcraft) – Some UAVs are small enough to carry in a backpack with similar functionality to larger ones
* EMT Aladin (aircraft – electric – Made in Germany)
* Bramor C4EYE (aircraft – electric – Made in Slovenia)
* Bayraktar Mini UAV (aircraft – electric – Made in Turkey)
* RQ-84Z Areohawk (aircraft – electric – Made in New Zealand)
Low cost miniature UAVs demand increasingly miniature imaging payloads. Developments in miniature electronics have fueled the development of increasingly capable surveillance payloads, allowing miniature UAVs to provide high levels of capability in never before seen packages.
Reconnaissance pods
Reconnaissance pods can be carried by fighter-bomber aircraft. Examples include the British Digital Joint Reconnaissance Pod (DJRP); Chinese KZ900; UK RAPTOR; and the US Navy's F-14 Tomcat Tactical Airborne Reconnaissance Pod System (TARPS). Some aircraft made for non-military applications also have reconnaissance pods, i.e. the Qinetiq Mercator.See also
* Aerial photography * Aerorozvidka * Air observation post * Forward air control * Imagery intelligence * National Collection of Aerial Photography * Surveillance aircraft * United States aerial reconnaissance of the Soviet Union * List of United States Air Force reconnaissance aircraftReferences
Citations
Bibliography
* Bowman, Martin. ''de Havilland Mosquito'' (Crowood Aviation series). Ramsbury, Marlborough, Wiltshire, UK: The Crowood Press, 2005. . * Lewis, Peter. ''British Racing and Record Breaking Aircraft''. London: Putnam, 1970. . * Natola, Mark. "Boeing B-47 Stratojet." ''Schiffer Publishing Ltd'', 2002. . * Pedlow, Gregory W. & Donald E Welzenbach.The Central Intelligence Agency and Overhead Reconnaissance: The U-2 and Oxcart Programs, 1954–1974
'. Washington, DC: Central Intelligence Agency, 1992. . * Polmar, Norman. ''Spyplane: The U-2 History Declassified''. London: Zenith Imprint, 2001. . * Stanley, Colonel Roy M. II, USAF (Ret). ''V-Weapons Hunt: Defeating German Secret Weapons.'' Barnsley, South Yorkshire, UK: Pen & Sword, 2010. .
External links
National Collection of Aerial Photography
The official archive of British Government declassified aerial photography. {{DEFAULTSORT:Aerial Reconnaissance Aerial reconnaissance, Aerial warfare, Reconnaissance Espionage Military cartography