|
Arado Ar 234
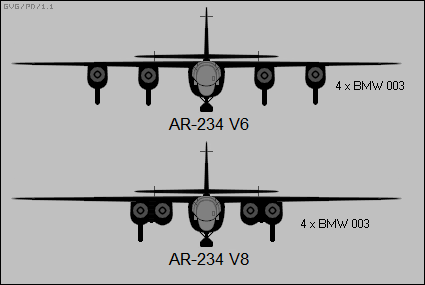
The Arado Ar 234 ''Blitz'' (English: lightning) is a jet-powered bomber designed and produced by the German aircraft manufacturer Arado. It was the world's first operational turbojet-powered bomber, seeing service during the final years of the Second World War. Development of the Ar 234 can be traced back to the latter half of 1940 and the request to tender from the Ministry of Aviation to produce a jet-powered high-speed reconnaissance aircraft. Arado was the only respondent with their ''E.370'' design. While its range was beneath that of the Ministry's specification, an initial order for two prototypes was promptly issued to the company, designated ''Ar 234''. While both of the prototypes had been mostly completed prior to the end of 1941, the Junkers Jumo 004 turbojet engines were not available prior to February 1943. Due to engine unreliability, the maiden flight of the Ar 234 V1 was delayed until 30 July 1943. In addition to the original reconnaissance-orientated ''Ar 234 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
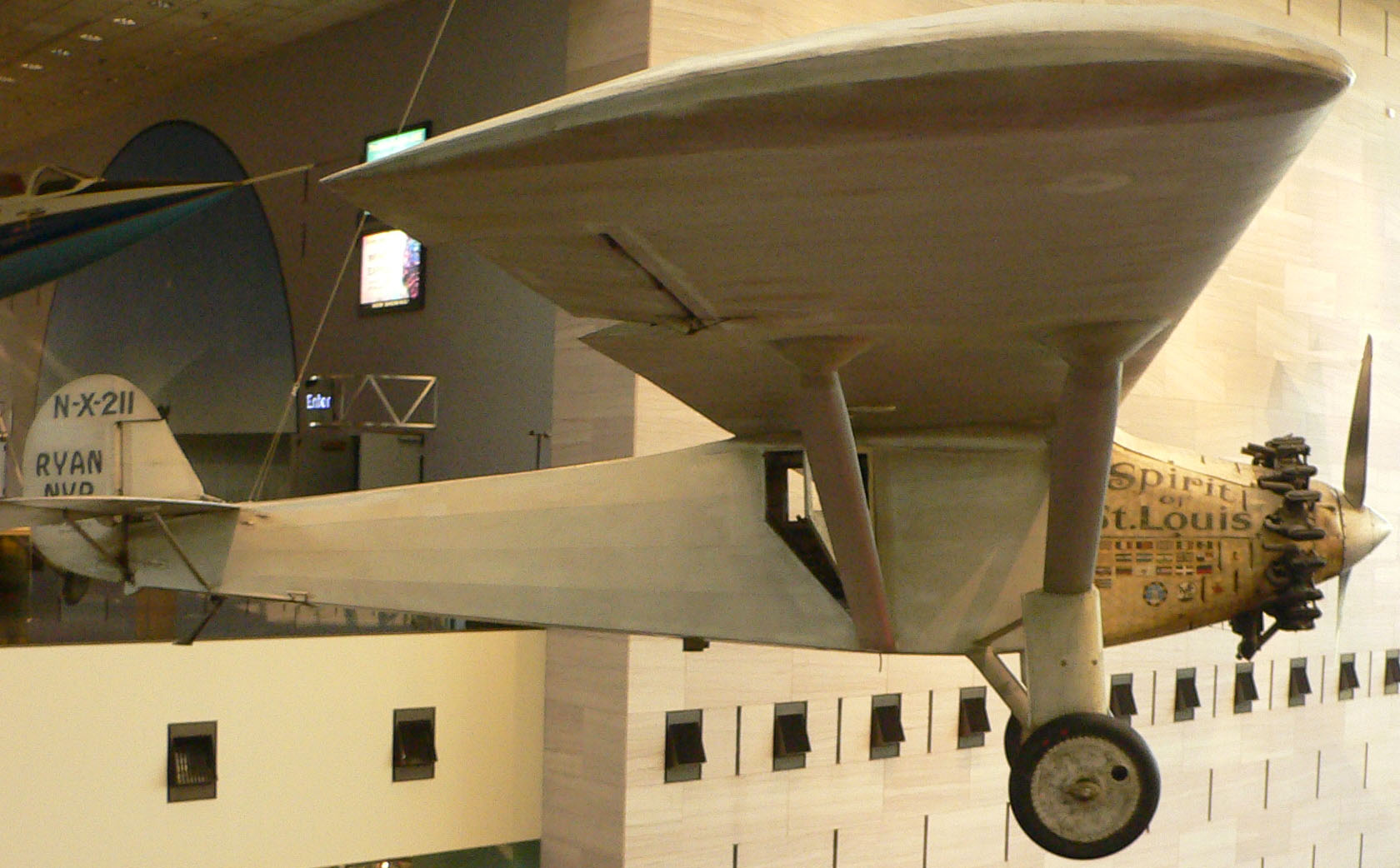
National Air And Space Museum
The National Air and Space Museum (NASM) of the Smithsonian Institution is a museum in Washington, D.C., in the United States, dedicated to history of aviation, human flight and space exploration. Established in 1946 as the National Air Museum, its main building opened on the National Mall near L'Enfant Plaza in 1976. In 2023, the museum welcomed 3.1 million visitors, making it the list of most-visited museums in the United States, fourth-most visited museum in the United States and List of most-visited museums, eleventh-most in the world. The museum is a center for research into the history and science of aviation and spaceflight, as well as planetary science and terrestrial geology and geophysics. Almost all of its spacecraft and aircraft on display are original primary or backup craft (rather than facsimiles). Its collection includes the Apollo 11 Command module Columbia, Command Module ''Columbia'', the Mercury-Atlas 6, ''Friendship 7'' capsule which was flown by John Glenn, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messerschmitt Me 262
The Messerschmitt Me 262, nicknamed (German for "Swallow") in fighter versions, or ("Storm Bird") in fighter-bomber versions, is a fighter aircraft and fighter-bomber that was designed and produced by the German aircraft manufacturer Messerschmitt. It was the world's first operational jet-powered fighter aircraft and one of two jet fighter aircraft types to see air-to-air combat in World War Two, the other being the Heinkel He 162. The design of what would become the Me 262 started in April 1939, before World War II. It made its maiden flight on 18 April 1941 with a piston engine, and its first jet-powered flight on 18 July 1942. Progress was delayed by problems with engines, metallurgy Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys. Metallurgy encompasses both the ..., and interference from Luftwaffe chie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BMW 003
The BMW 003 (full RLM designation 109-003) is an early axial turbojet engine produced by BMW AG in Germany during World War II. The 003 and the Junkers Jumo 004 were the only German turbojet engines to reach production during World War II. Work had begun on the design of the BMW 003 before its contemporary, the Jumo 004, but prolonged developmental problems meant that the BMW 003 entered production much later, and the aircraft projects that had been designed with it in mind were re-engined with the Jumo powerplant instead. The most famous case of this was the Messerschmitt Me 262, which used the 003 in two of the V-series prototypes and in the two experimental A-1b aircraft. The only production aircraft to use the BMW 003 were the Heinkel He 162 and the later C-series, four-engined versions of the Arado Ar 234. About 3,500 BMW 003 engines were built in Germany, but very few were ever installed in aircraft. The engine also formed the basis for turbojet development in Japan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arado Ar 234V6 And Ar 234V8 Front-view Silhouettes
Arado may refer to: * Arado Flugzeugwerke, a German aircraft company * Arwad Arwad (; ), the classical antiquity, classical Aradus, is a town in Syria on an eponymous List of islands of Syria, island in the Mediterranean Sea. It is the administrative center of the Arwad nahiyah, Subdistrict (''nahiyah''), of which it is ..., an ancient city in Syria {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (20 April 1889 – 30 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his suicide in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the leader of the Nazi Party, becoming Chancellor of Germany#Nazi Germany (1933–1945), the chancellor in 1933 and then taking the title of in 1934. His invasion of Poland on 1 September 1939 marked the start of the Second World War. He was closely involved in military operations throughout the war and was central to the perpetration of the Holocaust: the genocide of Holocaust victims, about six million Jews and millions of other victims. Hitler was born in Braunau am Inn in Austria-Hungary and moved to German Empire, Germany in 1913. He was decorated during his service in the German Army in the First World War, receiving the Iron Cross. In 1919 he joined the German Workers' Party (DAP), the precursor of the Nazi Party, and in 1921 was app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Münster
Münster (; ) is an independent city#Germany, independent city (''Kreisfreie Stadt'') in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is in the northern part of the state and is considered to be the cultural centre of the Westphalia region. It is also a Münster (region), state district capital. Münster was the location of the Münster Rebellion, Anabaptist rebellion during the Protestant Reformation and the site of the signing of the Treaty of Westphalia ending the Thirty Years' War in 1648. Today, it is known as the bicycle capital of Germany. Münster gained the status of a ''Großstadt'' (major city) with more than 100,000 inhabitants in 1915. , there are 300,000 people living in the city, with about 61,500 students, only some of whom are recorded in the official population statistics as having their primary residence in Münster. Münster is a part of the international EUREGIO, Euregio region with more than 1,000,000 inhabitants (Enschede, Hengelo, Gronau, North Rhine-Westphalia, G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheine
Rheine () is a city in the district of Steinfurt (district), Steinfurt in Westphalia, Germany. It is the largest city in the district and the location of Rheine Air Base. Geography Rheine is on the river Ems (river), Ems, about north of Münster, west of Osnabrück and east of Hengelo (Netherlands). History Early history Although the region around the city has been populated since prehistoric times, Rheine was first mentioned in a document signed by Louis the Pious in 838. On 15 August 1327, it received its town charter from Louis II, Bishop of Münster. The settlement was near to the crossing of two old merchant roads and a ford over the river Ems. Frankish soldiers initially secured this strategic point with a barrack yard. Later a church and more buildings were added to this outpost. 17th – 19th centuries At the end of the Thirty Years' War the city was burned down almost completely. Swedish and Hessian troops besieged imperial soldiers who had entrenched themselves in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheine-Bentlage Air Base
Rheine-Bentlage Air Base () was an air base of the German Armed Forces and located near the village of Bentlage, 2 km northwest of the city of Rheine, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. History In 1939 work to build an air base for the Luftwaffe began. These preparations were completed in 1940. During World War II extensive use was made of the air base, particularly by night and day fighter squadrons. After the war the air base was abandoned. In 1960, following the founding of the Bundeswehr in 1955 and the establishing of a new branch within the German Army, the Aviation Corps, completely new military installations, hangars and a small runway made of asphalt, were constructed on the grounds of the former German Air Force base. Since 1960 various units of the German Army Aviation Corps have been stationed at Rheine Air Base. Initially, these units flew Sikorsky H-34 helicopters, which were used extensively during relief operations following the disastrous North Sea flood ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junkers
Junkers Flugzeug- und Motorenwerke AG (JFM, earlier JCO or JKO in World War I, English language, English: Junkers Aircraft and Motor Works) more commonly Junkers , was a major German aircraft manufacturer, aircraft and aircraft engine manufacturer. It was founded in Dessau, Germany, in 1895 by Hugo Junkers, initially manufacturing boilers and radiator (heating), radiators. During World War I and following the war, the company became famous for its pioneering all-metal aircraft. During World War II the company produced the Luftwaffe, German air force's planes, as well as piston engine, piston and jet engine, jet aircraft engines, albeit in the absence of its founder who had been removed by the Nazis in 1934. History Early inter-war period In the immediate post-war era, Junkers used their J8 layout as the basis for the F-13, first flown on 25 June 1919 and certified airworthy in July of the same year. This four passenger monoplane was the world's first all-metal airliner. Of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazi German
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a totalitarian dictatorship. The Third Reich, meaning "Third Realm" or "Third Empire", referred to the Nazi claim that Nazi Germany was the successor to the earlier Holy Roman Empire (800–1806) and German Empire (1871–1918). The Third Reich, which the Nazis referred to as the Thousand-Year Reich, ended in May 1945, after 12 years, when the Allies defeated Germany and entered the capital, Berlin, ending World War II in Europe. After Hitler was appointed Chancellor of Germany in 1933, the Nazi Party began to eliminate political opposition and consolidate power. A 1934 German referendum confirmed Hitler as sole '' Führer'' (leader). Power was centralised in Hitler's person, and his word became the highest law. The government was not a coordinated, coopera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remagen
Remagen () is a town in Germany in the state of Rhineland-Palatinate, in the district of Ahrweiler (district), Ahrweiler. It is about a one-hour drive from Cologne, just south of Bonn, the former West Germany, West German seat of government. It is situated on the left (western) bank of the river Rhine. There is a ferry across the Rhine from Remagen every 10–15 minutes in the summer. Remagen has many notable and well-maintained buildings, churches, castles and monuments. It also has a sizeable pedestrian zone with plenty of shops. Overlooking the west bank of the Rhine just north of the city centre is the Apollinariskirche. It has an observation deck that is only open to parishioners on Sundays. Pedestrians reach the church via a dirt trail that passes a series of roadside monuments representing each of the fourteen Stations of the Cross. The church grounds contain an outdoor crypt and an abbey. Further down the river is one of the many castles along the Rhine, perched even highe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
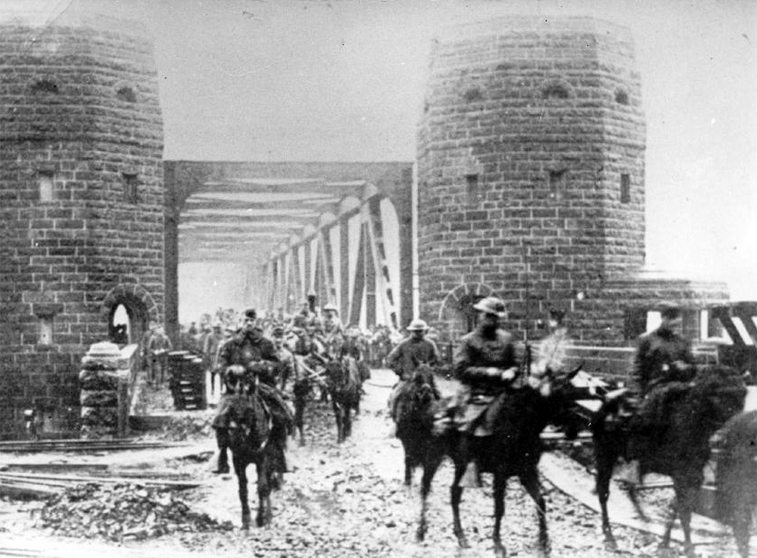
Ludendorff Bridge
The Ludendorff Bridge, also known as the Bridge at Remagen, was a bridge across the river Rhine in Germany which was captured by United States Army forces in early March 1945 during the Battle of Remagen, in the closing weeks of World War II, when it was one of the few remaining bridges in the region and therefore a critical strategic point. Built during World War I to help deliver reinforcements and supplies to German troops on the Western Front, it connected Remagen on the west bank and the village of Erpel on the east bank between two hills flanking the river. Midway through Operation Lumberjack, on 7 March 1945, the troops of the 1st U.S. Army approached Remagen and were surprised to find that the bridge was still standing. Its capture, two weeks before Field Marshal Bernard Montgomery's planned Operation Plunder, enabled the U.S. Army to establish a bridgehead on the eastern side of the Rhine. After the U.S. forces captured the bridge, German forces tried to destr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |