Flooding (computer Networking) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
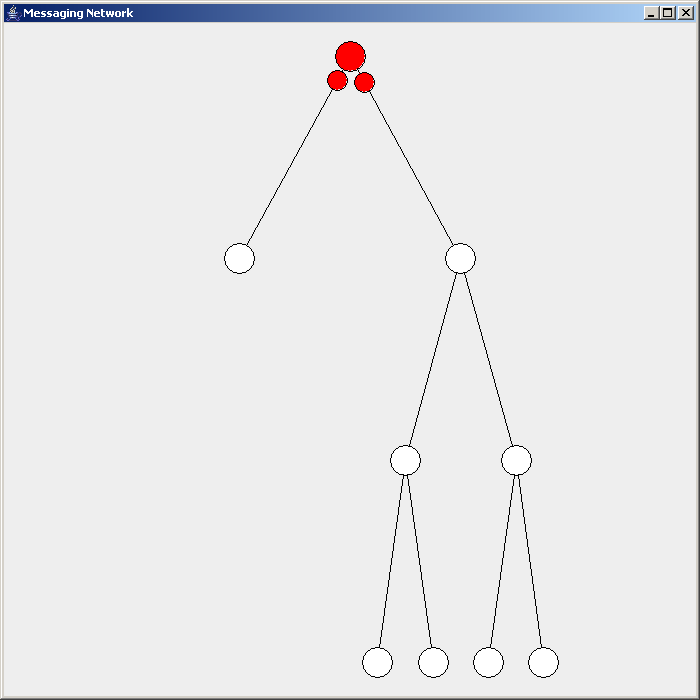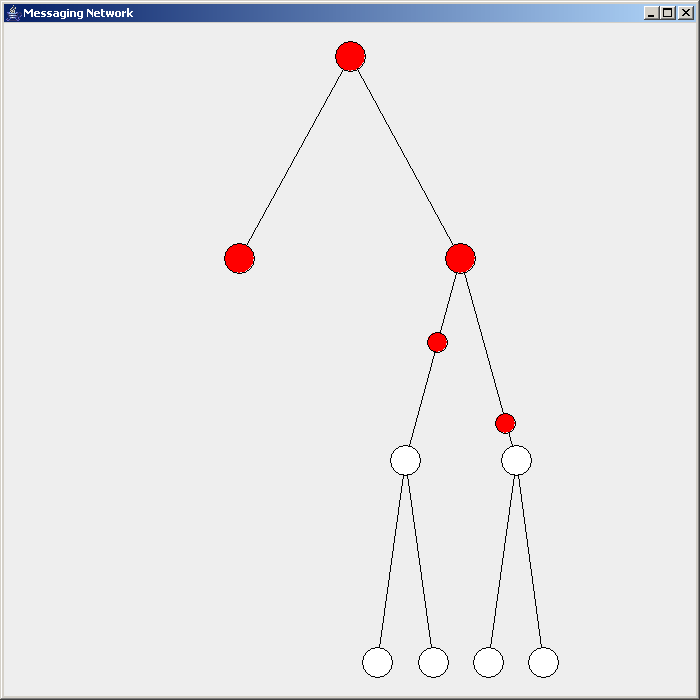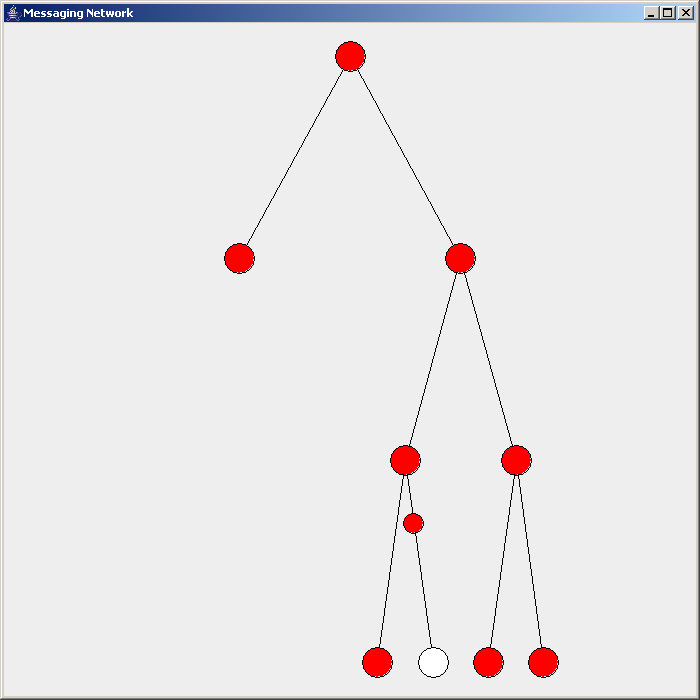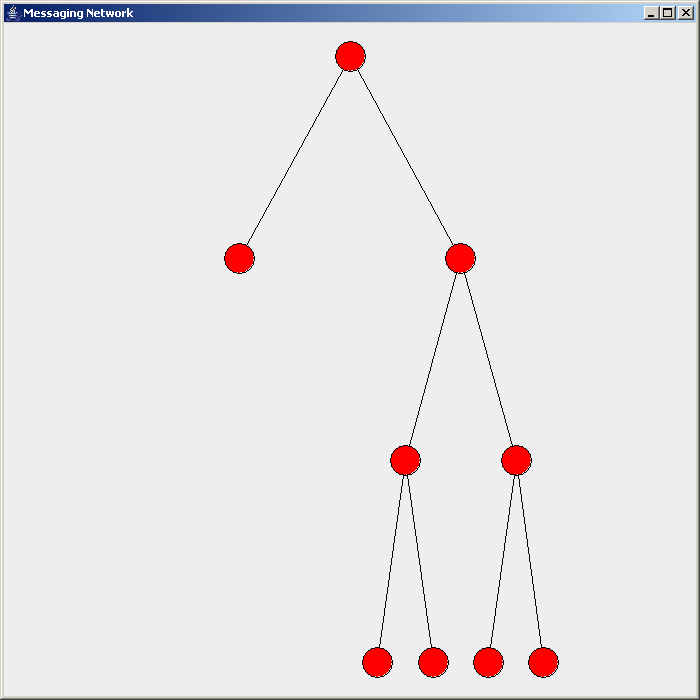
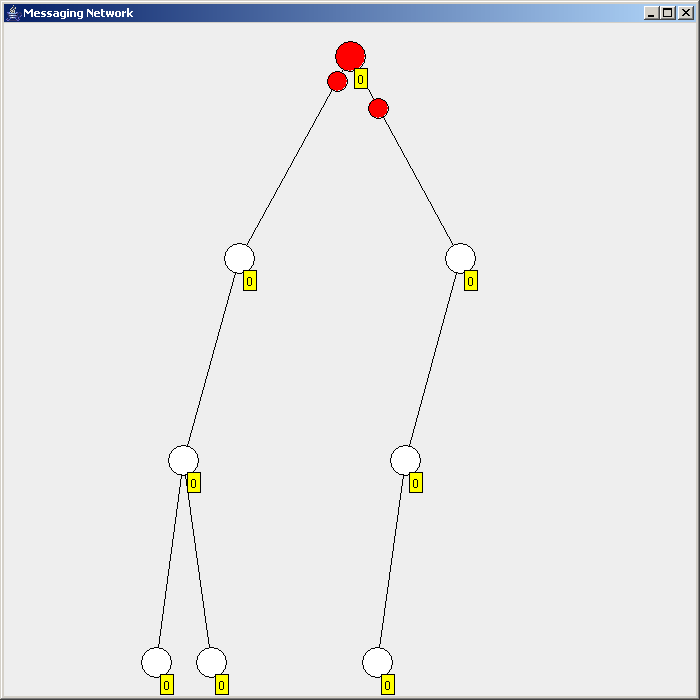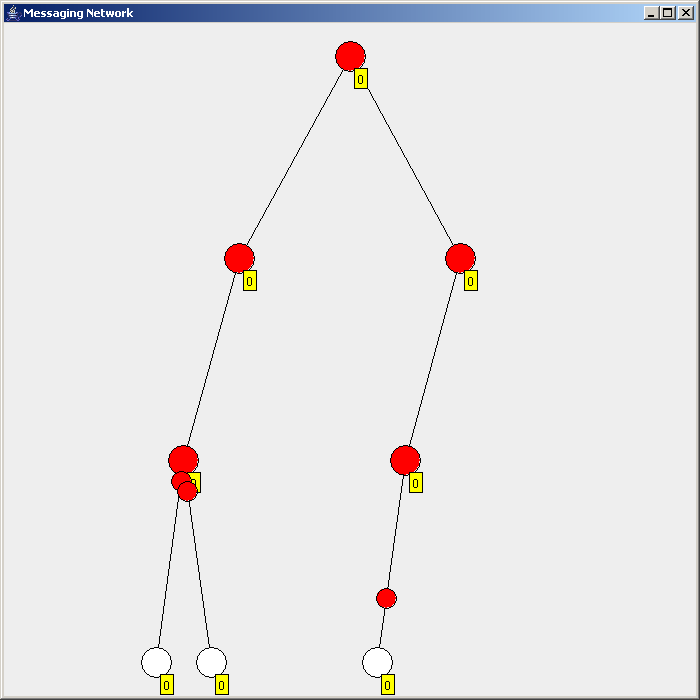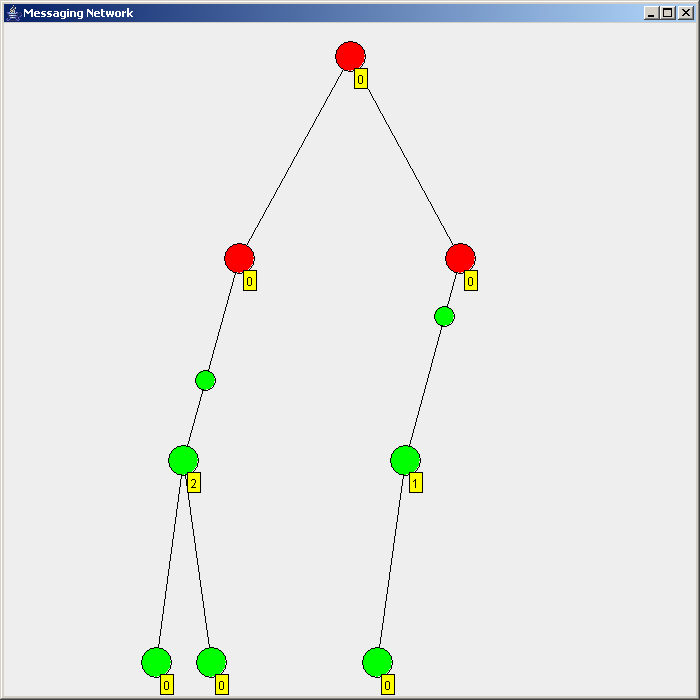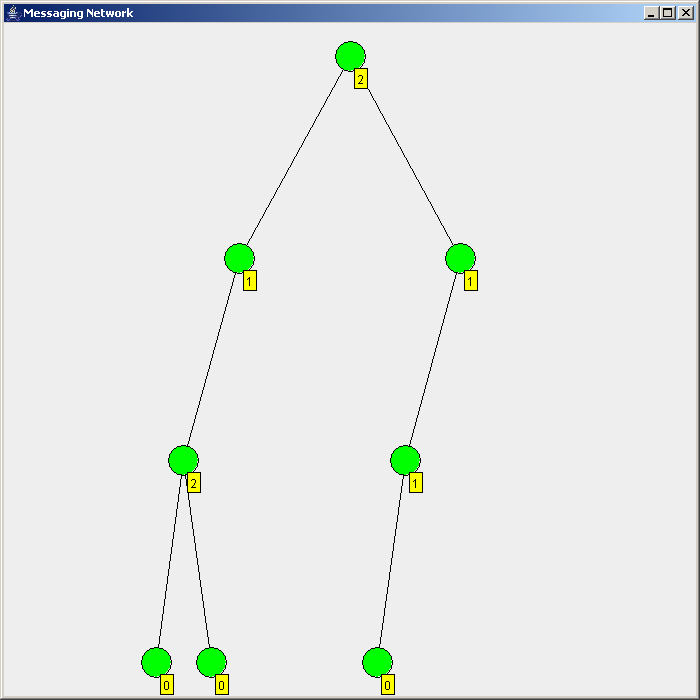 Flooding is used in computer networks routing algorithm in which every incoming packet is sent through every outgoing link except the one it arrived on.
Flooding is used in bridging and in systems such as
Flooding is used in computer networks routing algorithm in which every incoming packet is sent through every outgoing link except the one it arrived on.
Flooding is used in bridging and in systems such as

 Flooding is used in computer networks routing algorithm in which every incoming packet is sent through every outgoing link except the one it arrived on.
Flooding is used in bridging and in systems such as
Flooding is used in computer networks routing algorithm in which every incoming packet is sent through every outgoing link except the one it arrived on.
Flooding is used in bridging and in systems such as Usenet
Usenet () is a worldwide distributed discussion system available on computers. It was developed from the general-purpose Unix-to-Unix Copy (UUCP) dial-up network architecture. Tom Truscott and Jim Ellis conceived the idea in 1979, and it was ...
and peer-to-peer file sharing
Peer-to-peer file sharing is the distribution and sharing of digital media using peer-to-peer (P2P) networking technology. P2P file sharing allows users to access media files such as books, music, movies, and games using a P2P software program th ...
and as part of some routing protocol
A routing protocol specifies how routers communicate with each other to distribute information that enables them to select routes between nodes on a computer network. Routers perform the traffic directing functions on the Internet; data packet ...
s, including OSPF
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) is a routing protocol for Internet Protocol (IP) networks. It uses a link state routing (LSR) algorithm and falls into the group of interior gateway protocols (IGPs), operating within a single autonomous syste ...
, DVMRP The Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol (DVMRP), defined in , is a routing protocol used to share information between routers to facilitate the transportation of IP multicast packets among networks. It formed the basis of the Internet's hist ...
, and those used in ad-hoc wireless networks (WANETs).
Types
There are generally two types of flooding available, uncontrolled flooding and controlled flooding. In ''uncontrolled flooding'' each node unconditionally distributes packets to each of its neighbors. Without conditional logic to prevent indefinite recirculation of the same packet, broadcast storms are a hazard. ''Controlled flooding'' has its own two algorithms to make it reliable, SNCF (Sequence Number Controlled Flooding
Flooding is used in computer networks routing algorithm in which every incoming packet is sent through every outgoing link except the one it arrived on.
Flooding is used in bridging and in systems such as Usenet and peer-to-peer file shar ...
) and RPF ( reverse-path forwarding). In SNCF, the node attaches its own address and sequence number to the packet, since every node has a memory of addresses and sequence numbers. If it receives a packet in memory, it drops it immediately while in RPF, the node will only send the packet forward. If it is received from the next node, it sends it back to the sender.
Algorithms
There are several variants of flooding algorithms. Most work roughly as follows: #Each node acts as both a transmitter and a receiver. #Each node tries to forward every message to every one of its neighbors except the source node. This results in every message eventually being delivered to all reachable parts of the network. Algorithms may need to be more complex than this, since, in some case, precautions have to be taken to avoid wasted duplicate deliveries and infinite loops, and to allow messages to eventually expire from the system.Selective flooding
A variant of flooding called selective flooding partially addresses these issues by only sending packets to routers in the same direction. In selective flooding, the routers don't send every incoming packet on every line but only on those lines which are going approximately in the right direction.Advantages
The advantages of this method are that it is very simple to implement, if a packet can be delivered then it will (probably multiple times), and since flooding naturally utilizes every path through the network it will also use the shortest path.Disadvantages
Flooding can be costly in terms of wasted bandwidth. While a message may only have one destination it has to be sent to every host. In the case of a ping flood or a denial of service attack, it can be harmful to the reliability of acomputer network
A computer network is a set of computers sharing resources located on or provided by network nodes. The computers use common communication protocols over digital interconnections to communicate with each other. These interconnections ar ...
.
Messages can become duplicated in the network further increasing the load on the network as well as requiring an increase in processing complexity to disregard duplicate messages. Duplicate packets may circulate forever, unless certain precautions are taken:
* Use a hop count or a time to live (TTL) count and include it with each packet. This value should take into account the number of nodes that a packet may have to pass through on the way to its destination.
* Have each node keep track of every packet seen and only forward each packet once.
* Enforce a network topology
Network topology is the arrangement of the elements ( links, nodes, etc.) of a communication network. Network topology can be used to define or describe the arrangement of various types of telecommunication networks, including command and contr ...
without loop
Loop or LOOP may refer to:
Brands and enterprises
* Loop (mobile), a Bulgarian virtual network operator and co-founder of Loop Live
* Loop, clothing, a company founded by Carlos Vasquez in the 1990s and worn by Digable Planets
* Loop Mobile, ...
s.
Examples
InOpen Shortest Path First
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) is a routing protocol for Internet Protocol (IP) networks. It uses a link state routing (LSR) algorithm and falls into the group of interior gateway protocols (IGPs), operating within a single autonomous syste ...
(OSPF), flooding is used for transferring updates to the topology ( LSAs).
In low data rate communications, flooding can achieve fast and robust data communications in dedicated protocols such as VEmesh,virtual-extension.com which operates in the Sub-1 GHz frequency band and Bluetooth mesh networking, which operates in the 2.4 GHz frequency band. Both these protocols serve as underlying technologies in the Digital Addressable Lighting Interface in use in professional and commercial lighting control.
See also
*Broadcasting (networking)
In computer networking, telecommunication and information theory, broadcasting is a method of transferring a message to all recipients simultaneously. Broadcasting can be performed as a high-level operation in a program, for example, broadcas ...
* Flood search routing
*Multicast
In computer networking, multicast is group communication where data transmission is addressed to a group of destination computers simultaneously. Multicast can be one-to-many or many-to-many distribution. Multicast should not be confused wit ...
* Spanning Tree Protocol
References
{{reflist, refs= {{cite book , author-first1=Andrew S. , author-last1=Tanenbaum , author-link1=Andrew S. Tanenbaum , author-first2=David J. , author-last2=Wetherall , title=Computer Networks , edition=5th , date=2010-03-23 , publisher=Pearson Education
Pearson Education is a British-owned education publishing and assessment service to schools and corporations, as well for students directly. Pearson owns educational media brands including Addison–Wesley, Peachpit, Prentice Hall, eColleg ...
, isbn=978-0-13-212695-3 , pages=368–370
{{cite web , title=Controlled Flooding in Wireless Ad-hoc Networks , author-first1=Ashikur , author-last1=Rahman , author-first2=Wlodek , author-last2=Olesinski , author-first3=Pawel , author-last3=Gburzynski , publisher=University of Alberta
The University of Alberta, also known as U of A or UAlberta, is a public research university located in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. It was founded in 1908 by Alexander Cameron Rutherford,"A Gentleman of Strathcona – Alexander Cameron Ruth ...
, Department of Computing Science , location=Edmonton, Alberta, Canada , date=2004 , work=International Workshop on Wireless Ad-Hoc Networks , url=http://www.senserf.com/pg/PAPERS/tarp1.pdf , access-date=2015-10-15 , url-status=live , archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170210205207/http://www.senserf.com/pg/PAPERS/tarp1.pdf , archive-date=2017-02-10
Routing algorithms
Flooding algorithms