eye irritant on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The human eye is a  The eye can be considered as a living optical device. It is approximately spherical in shape, with its outer layers, such as the outermost, white part of the eye (the
The eye can be considered as a living optical device. It is approximately spherical in shape, with its outer layers, such as the outermost, white part of the eye (the

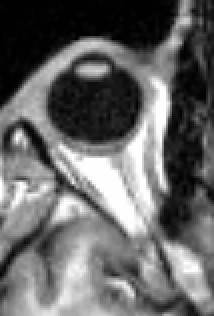 Humans have two eyes, situated on the left and the right of the
Humans have two eyes, situated on the left and the right of the
 The eye is made up of three coats, or layers, enclosing various anatomical structures. The outermost layer, known as the fibrous tunic, is composed of the
The eye is made up of three coats, or layers, enclosing various anatomical structures. The outermost layer, known as the fibrous tunic, is composed of the 
File:Eye orbit anterior.jpg, Eye and orbit anatomy with motor nerves
File:Lateral orbit nerves.jpg, Image showing orbita with eye and nerves visible (periocular fat removed)
File:Lateral orbit anatomy 2.jpg, Image showing orbita with eye and periocular fat
File:Eye orbit anatomy anterior2.jpg, Normal
 The approximate
The approximate
 The human eye can detect a luminance from 10−6 cd/m2, or one millionth (0.000001) of a
The human eye can detect a luminance from 10−6 cd/m2, or one millionth (0.000001) of a  The eye includes a
The eye includes a
 The visual system in the human brain is too slow to process information if images are slipping across the retina at more than a few degrees per second. Thus, to be able to see while moving, the brain must compensate for the motion of the head by turning the eyes. Frontal-eyed animals have a small area of the retina with very high visual acuity, the
The visual system in the human brain is too slow to process information if images are slipping across the retina at more than a few degrees per second. Thus, to be able to see while moving, the brain must compensate for the motion of the head by turning the eyes. Frontal-eyed animals have a small area of the retina with very high visual acuity, the
 When a creature with binocular vision looks at an object, the eyes must rotate around a vertical axis so that the projection of the image is in the centre of the retina in both eyes. To look at a nearby object, the eyes rotate 'towards each other' (
When a creature with binocular vision looks at an object, the eyes must rotate around a vertical axis so that the projection of the image is in the centre of the retina in both eyes. To look at a nearby object, the eyes rotate 'towards each other' (
 Almost all mammals have brown or darkly-pigmented irises. In humans, brown is by far the most common eye color, with approximately 79% of people in the world having it. Brown eyes result from a relatively high concentration of melanin in the stroma of the iris, which causes light of both shorter and longer wavelengths to be absorbed.
In many parts of the world, it is nearly the only iris color present. Brown eyes are common in
Almost all mammals have brown or darkly-pigmented irises. In humans, brown is by far the most common eye color, with approximately 79% of people in the world having it. Brown eyes result from a relatively high concentration of melanin in the stroma of the iris, which causes light of both shorter and longer wavelengths to be absorbed.
In many parts of the world, it is nearly the only iris color present. Brown eyes are common in
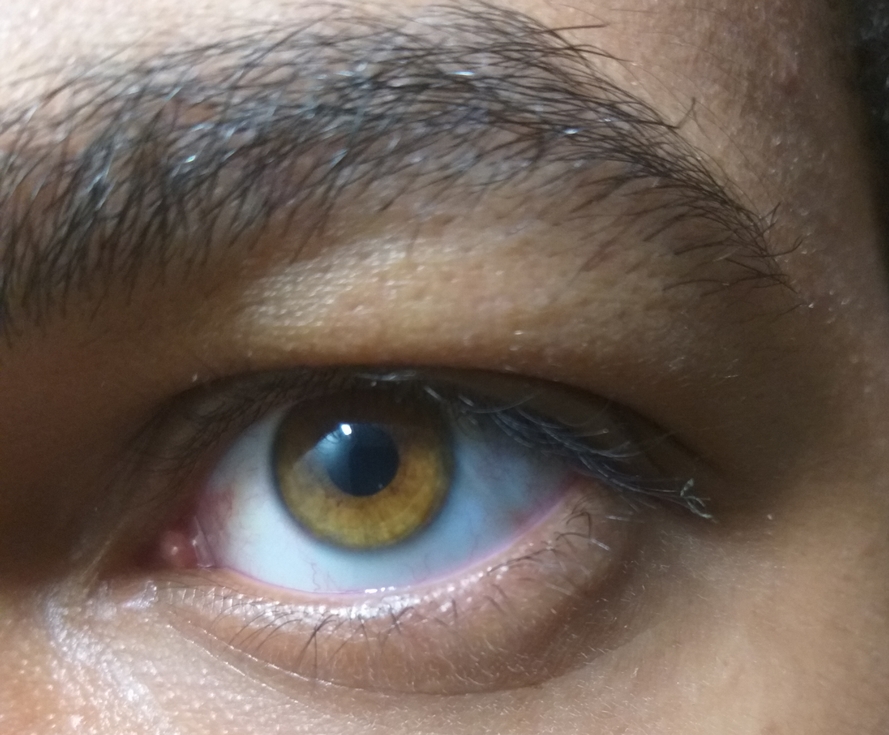 Amber eyes are a solid color with a strong yellowish/golden and russet/coppery tint, which may be due to the yellow pigment called lipochrome (also found in green eyes). Amber eyes should not be confused with hazel eyes. Although hazel eyes may contain specks of amber or gold, they usually tend to have many other colors, including green, brown and orange. Also, hazel eyes may appear to shift in color and consist of flecks and ripples, while amber eyes are of a solid gold hue. Even though amber is similar to gold, some people have russet or copper colored amber eyes that are mistaken for hazel, though hazel tends to be duller and contains green with red/gold flecks, as mentioned above. Amber eyes may also contain amounts of very light gold-ish gray. People with that eye color are common in northern
Amber eyes are a solid color with a strong yellowish/golden and russet/coppery tint, which may be due to the yellow pigment called lipochrome (also found in green eyes). Amber eyes should not be confused with hazel eyes. Although hazel eyes may contain specks of amber or gold, they usually tend to have many other colors, including green, brown and orange. Also, hazel eyes may appear to shift in color and consist of flecks and ripples, while amber eyes are of a solid gold hue. Even though amber is similar to gold, some people have russet or copper colored amber eyes that are mistaken for hazel, though hazel tends to be duller and contains green with red/gold flecks, as mentioned above. Amber eyes may also contain amounts of very light gold-ish gray. People with that eye color are common in northern
 Hazel eyes are due to a combination of
Hazel eyes are due to a combination of
File:Greeneyes.jpg, Green eyes
File:Hazel Eyes Ojos Avellana (Marron-Verde) Caracas Venezuela.jpg, Green-hazel eyes
 Eye irritation has been defined as "the magnitude of any stinging, scratching, burning, or other irritating sensation from the eye". It is a common problem experienced by people of all ages. Related eye symptoms and signs of irritation are discomfort, dryness, excess tearing, itchiness, grating, foreign body sensation, ocular fatigue, pain, soreness, redness, swollen eyelids, and tiredness, etc. These eye symptoms are reported with intensities from mild to severe. It has been suggested that these eye symptoms are related to different causal mechanisms, and symptoms are related to the particular ocular anatomy involved.
Several suspected causal factors in our environment have been studied so far. One hypothesis is that indoor air pollution may cause eye and airway irritation. Eye irritation depends somewhat on destabilization of the outer-eye tear film, i.e. the formation of dry spots on the cornea, resulting in ocular discomfort. Occupational factors are also likely to influence the perception of eye irritation. Some of these are lighting (glare and poor contrast), gaze position, reduced blink rate, limited number of breaks from visual tasking, and a constant combination of accommodation, musculoskeletal burden, and impairment of the visual nervous system. Another factor that may be related is work stress. In addition, psychological factors have been found in multivariate analyses to be associated with an increase in eye irritation among VDU users. Other risk factors, such as chemical toxins/irritants (e.g.
Eye irritation has been defined as "the magnitude of any stinging, scratching, burning, or other irritating sensation from the eye". It is a common problem experienced by people of all ages. Related eye symptoms and signs of irritation are discomfort, dryness, excess tearing, itchiness, grating, foreign body sensation, ocular fatigue, pain, soreness, redness, swollen eyelids, and tiredness, etc. These eye symptoms are reported with intensities from mild to severe. It has been suggested that these eye symptoms are related to different causal mechanisms, and symptoms are related to the particular ocular anatomy involved.
Several suspected causal factors in our environment have been studied so far. One hypothesis is that indoor air pollution may cause eye and airway irritation. Eye irritation depends somewhat on destabilization of the outer-eye tear film, i.e. the formation of dry spots on the cornea, resulting in ocular discomfort. Occupational factors are also likely to influence the perception of eye irritation. Some of these are lighting (glare and poor contrast), gaze position, reduced blink rate, limited number of breaks from visual tasking, and a constant combination of accommodation, musculoskeletal burden, and impairment of the visual nervous system. Another factor that may be related is work stress. In addition, psychological factors have been found in multivariate analyses to be associated with an increase in eye irritation among VDU users. Other risk factors, such as chemical toxins/irritants (e.g.
sensory organ
A sense is a biological system used by an organism for sensation, the process of gathering information about the surroundings through the detection of stimuli. Although, in some cultures, five human senses were traditionally identified as su ...
in the visual system
The visual system is the physiological basis of visual perception (the ability to perception, detect and process light). The system detects, phototransduction, transduces and interprets information concerning light within the visible range to ...
that reacts to visible light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm ...
allowing eyesight. Other functions include maintaining the circadian rhythm
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural oscillation that repeats roughly every 24 hours. Circadian rhythms can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., Endogeny (biology), endogenous) and responds to the env ...
, and keeping balance.
 The eye can be considered as a living optical device. It is approximately spherical in shape, with its outer layers, such as the outermost, white part of the eye (the
The eye can be considered as a living optical device. It is approximately spherical in shape, with its outer layers, such as the outermost, white part of the eye (the sclera
The sclera, also known as the white of the eye or, in older literature, as the tunica albuginea oculi, is the opaque, fibrous, protective outer layer of the eye containing mainly collagen and some crucial elastic fiber.
In the development of t ...
) and one of its inner layers (the pigmented choroid
The choroid, also known as the choroidea or choroid coat, is a part of the uvea, the vascular layer of the eye. It contains connective tissues, and lies between the retina and the sclera. The human choroid is thickest at the far extreme rear o ...
) keeping the eye essentially light tight except on the eye's optic axis. In order, along the optic axis, the optical components consist of a first lens (the cornea—the clear part of the eye) that accounts for most of the optical power of the eye and accomplishes most of the focusing of light from the outside world; then an aperture
In optics, the aperture of an optical system (including a system consisting of a single lens) is the hole or opening that primarily limits light propagated through the system. More specifically, the entrance pupil as the front side image o ...
(the pupil
The pupil is a hole located in the center of the iris of the eye that allows light to strike the retina.Cassin, B. and Solomon, S. (1990) ''Dictionary of Eye Terminology''. Gainesville, Florida: Triad Publishing Company. It appears black becau ...
) in a diaphragm (the iris—the coloured part of the eye) that controls the amount of light entering the interior of the eye; then another lens (the crystalline lens) that accomplishes the remaining focusing of light into images; and finally a light-sensitive part of the eye (the retina
The retina (; or retinas) is the innermost, photosensitivity, light-sensitive layer of tissue (biology), tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some Mollusca, molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focus (optics), focused two-dimensional ...
), where the images fall and are processed. The retina makes a connection to the brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
via the optic nerve
In neuroanatomy, the optic nerve, also known as the second cranial nerve, cranial nerve II, or simply CN II, is a paired cranial nerve that transmits visual system, visual information from the retina to the brain. In humans, the optic nerve i ...
. The remaining components of the eye keep it in its required shape, nourish and maintain it, and protect it.
Three types of cells in the retina convert light energy into electrical energy used by the nervous system
In biology, the nervous system is the complex system, highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its behavior, actions and sense, sensory information by transmitting action potential, signals to and from different parts of its body. Th ...
: rods respond to low intensity light and contribute to perception of low-resolution, black-and-white images; cones respond to high intensity light and contribute to perception of high-resolution, coloured images; and the recently discovered photosensitive ganglion cell
Intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (ipRGCs), also called photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (pRGC), or melanopsin-containing retinal ganglion cells (mRGCs), are a type of neuron in the retina of the mammalian eye. The presence ...
s respond to a full range of light intensities and contribute to adjusting the amount of light reaching the retina, to regulating and suppressing the hormone melatonin
Melatonin, an indoleamine, is a natural compound produced by various organisms, including bacteria and eukaryotes. Its discovery in 1958 by Aaron B. Lerner and colleagues stemmed from the isolation of a substance from the pineal gland of cow ...
, and to entraining circadian rhythm
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural oscillation that repeats roughly every 24 hours. Circadian rhythms can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., Endogeny (biology), endogenous) and responds to the env ...
.Structure

 Humans have two eyes, situated on the left and the right of the
Humans have two eyes, situated on the left and the right of the face
The face is the front of the head that features the eyes, nose and mouth, and through which animals express many of their emotions. The face is crucial for human identity, and damage such as scarring or developmental deformities may affect th ...
. The eyes sit in bony cavities called the orbits
In celestial mechanics, an orbit (also known as orbital revolution) is the curved trajectory of an physical body, object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an satellite, artificia ...
, in the skull
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate.
In the human, the skull comprises two prominent ...
. There are six extraocular muscles
The extraocular muscles, or extrinsic ocular muscles, are the seven extrinsic muscles of the eye in human eye, humans and other animals. Six of the extraocular muscles, the four recti muscles, and the superior oblique muscle, superior and inferior ...
that control eye movements. The front visible part of the eye is made up of the whitish sclera
The sclera, also known as the white of the eye or, in older literature, as the tunica albuginea oculi, is the opaque, fibrous, protective outer layer of the eye containing mainly collagen and some crucial elastic fiber.
In the development of t ...
, a coloured iris, and the pupil
The pupil is a hole located in the center of the iris of the eye that allows light to strike the retina.Cassin, B. and Solomon, S. (1990) ''Dictionary of Eye Terminology''. Gainesville, Florida: Triad Publishing Company. It appears black becau ...
. A thin layer called the conjunctiva
In the anatomy of the eye, the conjunctiva (: conjunctivae) is a thin mucous membrane that lines the inside of the eyelids and covers the sclera (the white of the eye). It is composed of non-keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium with gobl ...
sits on top of this. The front part is also called the anterior
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position pro ...
segment of the eye.
The eye is not shaped like a perfect sphere; rather it is a fused two-piece unit, composed of an anterior (front) segment and the posterior (back) segment. The anterior segment is made up of the cornea, iris and lens. The cornea is transparent and more curved and is linked to the larger posterior segment, composed of the vitreous, retina, choroid and the outer white shell called the sclera. The cornea is typically about in diameter, and 0.5 mm (500 μm) in thickness near its centre. The posterior chamber constitutes the remaining five-sixths; its diameter is typically about . An area termed the limbus connects the cornea and sclera. The iris is the pigmented circular structure concentrically surrounding the centre of the eye, the pupil, which appears to be black. The size of the pupil, which controls the amount of light entering the eye, is adjusted by the iris' dilator and sphincter muscles.
Light energy enters the eye through the cornea, through the pupil and then through the lens. The lens shape is changed for near focus (accommodation) and is controlled by the ciliary muscle. Between the two lenses (the cornea and the crystalline lens), there are four optical surfaces which each refract
In physics, refraction is the redirection of a wave as it passes from one medium to another. The redirection can be caused by the wave's change in speed or by a change in the medium. Refraction of light is the most commonly observed phenome ...
light as it travels along the optical path. One basic model describing the geometry of the optical system is the Arizona Eye Model. This model describes the accommodation of the eye geometrically. Photons of light falling on the light-sensitive cells of the retina ( photoreceptor cones and rods) are converted into electrical signals that are transmitted to the brain by the optic nerve and interpreted as sight and vision.
Development
The human eye primarily develops from theectoderm
The ectoderm is one of the three primary germ layers formed in early embryonic development. It is the outermost layer, and is superficial to the mesoderm (the middle layer) and endoderm (the innermost layer). It emerges and originates from the o ...
. The lens and the epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of man ...
of the cornea arise from the surface ectoderm directly; other structures come from either the neural ectoderm or the neural crest
The neural crest is a ridge-like structure that is formed transiently between the epidermal ectoderm and neural plate during vertebrate development. Neural crest cells originate from this structure through the epithelial-mesenchymal transition, ...
, which itself arises from the ectoderm. The mesoderm
The mesoderm is the middle layer of the three germ layers that develops during gastrulation in the very early development of the embryo of most animals. The outer layer is the ectoderm, and the inner layer is the endoderm.Langman's Medical ...
has limited contributions: it is the origin of the vitreous body
The vitreous body (''vitreous'' meaning "glass-like"; , ) is the clear gel that fills the space between the Lens (vision), lens and the retina of the eye, eyeball (the vitreous chamber) in humans and other vertebrates. It is often referred to as ...
, the blood vessels of the eye, and the extraocular muscles.
Size
The size of the eye differs among adults by only 1-2 mm. The eyeball is generally less tall than it is wide. The sagittal vertical (height) of a human adult eye is approximately , the transverse horizontal diameter (width) is and the axial anteroposterior size (depth) averages with no significant difference between sexes and age groups. Strong correlation has been found between the transverse diameter and the width of the orbit (r = 0.88). The typical adult eye has an anterior to posterior diameter of , and a volume of . The eyeball grows rapidly, increasing from about diameter at birth to by three years of age. By age 12, the eye attains its full size.Components
cornea
The cornea is the transparency (optics), transparent front part of the eyeball which covers the Iris (anatomy), iris, pupil, and Anterior chamber of eyeball, anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and Lens (anatomy), lens, the cornea ...
and sclera
The sclera, also known as the white of the eye or, in older literature, as the tunica albuginea oculi, is the opaque, fibrous, protective outer layer of the eye containing mainly collagen and some crucial elastic fiber.
In the development of t ...
, which provide shape to the eye and support the deeper structures. The middle layer, known as the vascular tunic or uvea, consists of the choroid
The choroid, also known as the choroidea or choroid coat, is a part of the uvea, the vascular layer of the eye. It contains connective tissues, and lies between the retina and the sclera. The human choroid is thickest at the far extreme rear o ...
, ciliary body
The ciliary body is a part of the eye that includes the ciliary muscle, which controls the shape of the lens, and the ciliary epithelium, which produces the aqueous humor. The aqueous humor is produced in the non-pigmented portion of the ciliary ...
, pigmented epithelium and iris. The innermost is the retina
The retina (; or retinas) is the innermost, photosensitivity, light-sensitive layer of tissue (biology), tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some Mollusca, molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focus (optics), focused two-dimensional ...
, which gets its oxygenation from the blood vessels of the choroid (posteriorly) as well as the retinal vessels (anteriorly).
The spaces of the eye are filled with the aqueous humour
The aqueous humour is a transparent water-like fluid similar to blood plasma, but containing low protein concentrations. It is secreted from the ciliary body, a structure supporting the lens of the eyeball. It fills both the anterior and the po ...
anteriorly, between the cornea and lens, and the vitreous body
The vitreous body (''vitreous'' meaning "glass-like"; , ) is the clear gel that fills the space between the Lens (vision), lens and the retina of the eye, eyeball (the vitreous chamber) in humans and other vertebrates. It is often referred to as ...
, a jelly-like substance, behind the lens, filling the entire posterior cavity. The aqueous humour is a clear watery fluid that is contained in two areas: the anterior chamber
The anterior chamber ( AC) is the aqueous humor-filled space inside the eye between the iris and the cornea's innermost surface, the endothelium. Hyphema, anterior uveitis and glaucoma are three main pathologies in this area. In hyphema, ...
between the cornea and the iris, and the posterior chamber
The posterior chamber is a narrow space behind the peripheral part of the iris, and in front of the suspensory ligament of the lens and the ciliary processes. The posterior chamber consists of small space directly posterior to the iris but ante ...
between the iris and the lens. The lens is suspended to the ciliary body by the suspensory ligament ( zonule of Zinn), made up of hundreds of fine transparent fibers which transmit muscular forces to change the shape of the lens for accommodation (focusing). The vitreous body is a clear substance composed of water and proteins, which give it a jelly-like and sticky composition.

Extraocular muscles
Each eye has sevenextraocular muscles
The extraocular muscles, or extrinsic ocular muscles, are the seven extrinsic muscles of the eye in human eye, humans and other animals. Six of the extraocular muscles, the four recti muscles, and the superior oblique muscle, superior and inferior ...
located in its orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit (also known as orbital revolution) is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an ...
. Six of these muscles control the eye movements, the seventh controls the movement of the upper eyelid
An eyelid ( ) is a thin fold of skin that covers and protects an eye. The levator palpebrae superioris muscle retracts the eyelid, exposing the cornea to the outside, giving vision. This can be either voluntarily or involuntarily. "Palpebral ...
. The six muscles are four recti muscles – the lateral rectus, the medial rectus, the inferior rectus, and the superior rectus
The superior rectus muscle is a muscle in the orbit (anatomy), orbit. It is one of the extraocular muscles. It is innervation, innervated by the superior division of the oculomotor nerve (III). In the primary position (looking straight ahead), its ...
, and two oblique muscles the inferior oblique, and the superior oblique. The seventh muscle is the levator palpebrae superioris muscle
The levator palpebrae superioris () is the muscle in the orbit that elevates the upper eyelid.
Structure
The levator palpebrae superioris originates from inferior surface of the lesser wing of the sphenoid bone, just above the optic foramen. It ...
. When the muscles exert different tensions, a torque is exerted on the globe that causes it to turn, in almost pure rotation, with only about one millimeter of translation. Thus, the eye can be considered as undergoing rotations about a single point in the centre of the eye.
anatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of morphology concerned with the study of the internal structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old scien ...
of the human eye and orbit, anterior view
Vision
Field of view
 The approximate
The approximate field of view
The field of view (FOV) is the angle, angular extent of the observable world that is visual perception, seen at any given moment. In the case of optical instruments or sensors, it is a solid angle through which a detector is sensitive to elec ...
of an individual human eye (measured from the fixation point, i.e., the point at which one's gaze is directed) varies by facial anatomy, but is typically 30° superior (up, limited by the brow), 45° nasal (limited by the nose), 70° inferior (down), and 100° temporal (towards the temple). For both eyes, combined (binocular vision Binocular vision is seeing with two eyes. The Field_of_view, field of view that can be surveyed with two eyes is greater than with one eye. To the extent that the visual fields of the two eyes overlap, #Depth, binocular depth can be perceived. Th ...
) visual field is approximately 100° vertical and a maximum 190° horizontal, approximately 120° of which makes up the binocular field of view (seen by both eyes) flanked by two uniocular fields (seen by only one eye) of approximately 40 degrees. It is an area of 4.17 steradian
The steradian (symbol: sr) or square radian is the unit of solid angle in the International System of Units (SI). It is used in three-dimensional geometry, and is analogous to the radian, which quantifies planar angles. A solid angle in the fo ...
s or 13700 square degrees for binocular vision. When viewed at large angles from the side, the iris and pupil may still be visible by the viewer, indicating the person has peripheral vision possible at that angle.
About 15° temporal and 1.5° below the horizontal is the blind spot created by the optic nerve nasally, which is roughly 7.5° high and 5.5° wide.
Dynamic range
The retina has a static contrast ratio of around 100:1 (about 6.5 f-stops). As soon as the eye moves rapidly to acquire a target (saccade
In vision science, a saccade ( ; ; ) is a quick, simultaneous movement of both Eye movement (sensory), eyes between two or more phases of focal points in the same direction. In contrast, in Smooth pursuit, smooth-pursuit movements, the eyes mov ...
s), it re-adjusts its exposure by adjusting the iris, which adjusts the size of the pupil. Initial dark adaptation takes place in approximately four seconds of profound, uninterrupted darkness; full adaptation through adjustments in retinal rod photoreceptors is 80% complete in thirty minutes. The process is nonlinear and multifaceted, so an interruption by light exposure requires restarting the dark adaptation process over again. The human eye can detect a luminance from 10−6 cd/m2, or one millionth (0.000001) of a
The human eye can detect a luminance from 10−6 cd/m2, or one millionth (0.000001) of a candela per square meter
The candela per square metre (symbol: cd/m2) is the unit of luminance in the International System of Units (SI). The unit is based on the candela, the SI unit of luminous intensity, and the square metre, the SI unit of area.
The nit (symbol: nt ...
to 108 cd/m2 or one hundred million (100,000,000) candelas per square meter. (that is it has a range of 1014, or one hundred trillion 100,000,000,000,000, about 46.5 f-stops). This range does not include looking at the midday sun (109 cd/m2) or lightning discharge.
At the low end of the range is the absolute threshold of vision for a steady light across a wide field of view, about 10−6 cd/m2 (0.000001 candela per square meter). The upper end of the range is given in terms of normal visual performance as 108 cd/m2 (100,000,000 or one hundred million candelas per square meter).
 The eye includes a
The eye includes a lens
A lens is a transmissive optical device that focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements'') ...
similar to lenses
A lens is a transmissive optical device that focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements''), ...
found in optical instruments such as cameras and the same physics principles can be applied. The pupil
The pupil is a hole located in the center of the iris of the eye that allows light to strike the retina.Cassin, B. and Solomon, S. (1990) ''Dictionary of Eye Terminology''. Gainesville, Florida: Triad Publishing Company. It appears black becau ...
of the human eye is its aperture
In optics, the aperture of an optical system (including a system consisting of a single lens) is the hole or opening that primarily limits light propagated through the system. More specifically, the entrance pupil as the front side image o ...
; the iris is the diaphragm that serves as the aperture stop. Refraction in the cornea
The cornea is the transparency (optics), transparent front part of the eyeball which covers the Iris (anatomy), iris, pupil, and Anterior chamber of eyeball, anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and Lens (anatomy), lens, the cornea ...
causes the effective aperture (the entrance pupil
In an optical system, the entrance pupil is the optical image of the physical aperture stop, as 'seen' through the optical elements in front of the stop. The corresponding image of the aperture stop as seen through the optical elements behin ...
) to differ slightly from the physical pupil diameter. The entrance pupil is typically about 4 mm in diameter, although it can range from 2 mm () in a brightly lit place to 8 mm () in the dark. The latter value decreases slowly with age; older people's eyes sometimes dilate to not more than 5–6mm in the dark, and may be as small as 1mm in the light.
Movement
 The visual system in the human brain is too slow to process information if images are slipping across the retina at more than a few degrees per second. Thus, to be able to see while moving, the brain must compensate for the motion of the head by turning the eyes. Frontal-eyed animals have a small area of the retina with very high visual acuity, the
The visual system in the human brain is too slow to process information if images are slipping across the retina at more than a few degrees per second. Thus, to be able to see while moving, the brain must compensate for the motion of the head by turning the eyes. Frontal-eyed animals have a small area of the retina with very high visual acuity, the fovea centralis
The ''fovea centralis'' is a small, central pit composed of closely packed Cone cell, cones in the eye. It is located in the center of the ''macula lutea'' of the retina.
The ''fovea'' is responsible for sharp central visual perception, vision ...
. It covers about 2 degrees of visual angle in people. To get a clear view of the world, the brain must turn the eyes so that the image of the object of regard falls on the fovea. Any failure to make eye movements correctly can lead to serious visual degradation.
Having two eyes allows the brain to determine the depth and distance of an object, called stereovision, and gives the sense of three-dimensionality to the vision. Both eyes must point accurately enough that the object of regard falls on corresponding points of the two retinas to stimulate stereovision; otherwise, double vision might occur. Some persons with congenitally crossed eyes tend to ignore one eye's vision, thus do not suffer double vision, and do not have stereovision. The movements of the eye are controlled by six muscles attached to each eye, and allow the eye to elevate, depress, converge, diverge and roll. These muscles are both controlled voluntarily and involuntarily to track objects and correct for simultaneous head movements.
Rapid
Rapid eye movement, REM, typically refers to thesleep
Sleep is a state of reduced mental and physical activity in which consciousness is altered and certain Sensory nervous system, sensory activity is inhibited. During sleep, there is a marked decrease in muscle activity and interactions with th ...
stage during which the most vivid dreams occur. During this stage, the eyes move rapidly.
Saccadian
Saccades are quick, simultaneous movements of both eyes in the same direction controlled by the frontal lobe of the brain.Fixational
Even when looking intently at a single spot, the eyes drift around. This ensures that individual photosensitive cells are continually stimulated in different degrees. Without changing input, these cells would otherwise stop generating output. Eye movements include drift,ocular tremor
Ocular tremor (ocular microtremor) is a constant, involuntary eye tremor of a low amplitude and high frequency. It is a type of fixational eye movement that occurs in all normal people, even when the eye appears still. The frequency of ocular m ...
, and microsaccades. Some irregular drifts, movements smaller than a saccade and larger than a microsaccade, subtend up to one tenth of a degree. Researchers vary in their definition of microsaccades by amplitude. Martin Rolfs states that 'the majority of microsaccades observed in a variety of tasks have amplitudes smaller than 30 min-arc'. However, others state that the "current consensus has largely consolidated around a definition of microsaccades that includes magnitudes up to 1°."
Vestibulo-ocular
Thevestibulo-ocular reflex
The vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR) is a reflex that acts to stabilize Gaze (physiology), gaze during head movement, with eye movement due to activation of the vestibular system, it is also known as the cervico-ocular reflex. The reflex acts to im ...
is a reflex
In biology, a reflex, or reflex action, is an involuntary, unplanned sequence or action and nearly instantaneous response to a stimulus.
Reflexes are found with varying levels of complexity in organisms with a nervous system. A reflex occurs ...
eye movement that stabilizes images on the retina
The retina (; or retinas) is the innermost, photosensitivity, light-sensitive layer of tissue (biology), tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some Mollusca, molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focus (optics), focused two-dimensional ...
during head movement by producing an eye movement in the direction opposite to head movement in response to neural input from the vestibular system of the inner ear, thus maintaining the image in the centre of the visual field. For example, when the head moves to the right, the eyes move to the left. This applies for head movements up and down, left and right, and tilt to the right and left, all of which give input to the ocular muscles to maintain visual stability.
Smooth pursuit
Eyes can also follow a moving object around. This tracking is less accurate than the vestibulo-ocular reflex, as it requires the brain to process incoming visual information and supplyfeedback
Feedback occurs when outputs of a system are routed back as inputs as part of a chain of cause and effect that forms a circuit or loop. The system can then be said to ''feed back'' into itself. The notion of cause-and-effect has to be handle ...
. Following an object moving at constant speed is relatively easy, though the eyes will often make saccades to keep up. The smooth pursuit movement can move the eye at up to 100°/s in adult humans.
It is more difficult to visually estimate speed in low light conditions or while moving, unless there is another point of reference for determining speed.
Optokinetic
The optokinetic reflex (or optokinetic nystagmus) stabilizes the image on the retina through visual feedback. It is induced when the entire visual scene drifts across the retina, eliciting eye rotation in the same direction and at a velocity that minimizes the motion of the image on the retina. When the gaze direction deviates too far from the forward heading, a compensatory saccade is induced to reset the gaze to the centre of the visual field. For example, when looking out of the window at a moving train, the eyes can focus on a moving train for a short moment (by stabilizing it on the retina), until the train moves out of the field of vision. At this point, the eye is moved back to the point where it first saw the train (through a saccade).Near response
The adjustment to close-range vision involves three processes to focus an image on the retina.Vergence movement
 When a creature with binocular vision looks at an object, the eyes must rotate around a vertical axis so that the projection of the image is in the centre of the retina in both eyes. To look at a nearby object, the eyes rotate 'towards each other' (
When a creature with binocular vision looks at an object, the eyes must rotate around a vertical axis so that the projection of the image is in the centre of the retina in both eyes. To look at a nearby object, the eyes rotate 'towards each other' (convergence
Convergence may refer to:
Arts and media Literature
*''Convergence'' (book series), edited by Ruth Nanda Anshen
*Convergence (comics), "Convergence" (comics), two separate story lines published by DC Comics:
**A four-part crossover storyline that ...
), while for an object farther away they rotate 'away from each other' (divergence
In vector calculus, divergence is a vector operator that operates on a vector field, producing a scalar field giving the rate that the vector field alters the volume in an infinitesimal neighborhood of each point. (In 2D this "volume" refers to ...
).
Pupil constriction
Lenses cannot refract light rays at their edges as well as closer to the centre. The image produced by any lens is therefore somewhat blurry around the edges ( spherical aberration). It can be minimized by screening out peripheral light rays and looking only at the better-focused centre. In the eye, the pupil serves this purpose by constricting while the eye is focused on nearby objects. Small apertures also give an increase indepth of field
The depth of field (DOF) is the distance between the nearest and the farthest objects that are in acceptably sharp focus (optics), focus in an image captured with a camera. See also the closely related depth of focus.
Factors affecting depth ...
, allowing a broader range of "in focus" vision. In this way the pupil has a dual purpose for near vision: to reduce spherical aberration and increase depth of field.
Lens accommodation
Changing the curvature of the lens is carried out by theciliary muscle
The ciliary muscle is an intrinsic muscle of the eye formed as a ring of smooth muscleSchachar, Ronald A. (2012). "Anatomy and Physiology." (Chapter 4) . in the eye's middle layer, the uvea ( vascular layer). It controls accommodation for vie ...
s surrounding the lens; this process is known as "accommodation". Accommodation narrows the inner diameter of the ciliary body, which actually relaxes the fibers of the suspensory ligament attached to the periphery of the lens, and also allows the lens to relax into a more convex, or globular, shape. A more convex lens refracts light more strongly and focuses divergent light rays from near objects onto the retina, allowing closer objects to be brought into better focus.
Medicine
The human eye contains enough complexity to warrant specialized attention and care beyond the duties of ageneral practitioner
A general practitioner (GP) is a doctor who is a Consultant (medicine), consultant in general practice.
GPs have distinct expertise and experience in providing whole person medical care, whilst managing the complexity, uncertainty and risk ass ...
. These specialists, or eye care professional
An eye care professional is an individual who provides a service related to the eyes or vision. It is any healthcare worker involved in eye care, from one with a small amount of post-secondary training to practitioners with a doctoral level of edu ...
s, serve different functions in different countries. Eye care professionals can have overlap in their patient care privileges. For example, both an ophthalmologist
Ophthalmology (, ) is the branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis, treatment, and surgery of eye diseases and disorders.
An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a ...
(M.D.) and optometrist
Optometry is the healthcare practice concerned with examining the eyes for visual defects, prescribing corrective lenses, and detecting eye abnormalities.
In the United States and Canada, optometrists are those that hold a post-baccalaureate f ...
(O.D.) are professionals who diagnose eye disease and can prescribe lenses to correct vision. Typically, only ophthalmologists are licensed to perform surgical procedures. Ophthalmologists may also specialize within a surgical area, such as cornea
The cornea is the transparency (optics), transparent front part of the eyeball which covers the Iris (anatomy), iris, pupil, and Anterior chamber of eyeball, anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and Lens (anatomy), lens, the cornea ...
, cataracts
A cataract is a cloudy area in the lens of the eye that leads to a decrease in vision of the eye. Cataracts often develop slowly and can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms may include faded colours, blurry or double vision, halos around ligh ...
, laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radi ...
, retina
The retina (; or retinas) is the innermost, photosensitivity, light-sensitive layer of tissue (biology), tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some Mollusca, molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focus (optics), focused two-dimensional ...
, or oculoplastics.
Eye care professionals include:
* Ocularist An ocularist specializes in the fabrication and fitting of ocular prostheses for people who have lost an eye or eyes due to trauma or illness.{{Cite journal , last1=Khandekar , first1=Rajiv , last2=Changal , first2=Nusrat , last3=AlRasheed , first3 ...
s
* Ophthalmologists
* Optometrists
* Opticians
* Orthoptists and vision therapists
Pigmentation
Brown
Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
, East Asia
East Asia is a geocultural region of Asia. It includes China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan, plus two special administrative regions of China, Hong Kong and Macau. The economies of Economy of China, China, Economy of Ja ...
, Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
, Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Pers ...
, South Asia
South Asia is the southern Subregion#Asia, subregion of Asia that is defined in both geographical and Ethnicity, ethnic-Culture, cultural terms. South Asia, with a population of 2.04 billion, contains a quarter (25%) of the world's populatio ...
, West Asia
West Asia (also called Western Asia or Southwest Asia) is the westernmost region of Asia. As defined by most academics, UN bodies and other institutions, the subregion consists of Anatolia, the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Mesopotamia, the Armenian ...
, Oceania
Oceania ( , ) is a region, geographical region including Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Outside of the English-speaking world, Oceania is generally considered a continent, while Mainland Australia is regarded as its co ...
, Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
and the Americas
The Americas, sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America and South America.''Webster's New World College Dictionary'', 2010 by Wiley Publishing, Inc., Cleveland, Ohio. When viewed as a sing ...
. Light or medium-pigmented brown eyes can also be commonly found in Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
, among the Americas
The Americas, sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America and South America.''Webster's New World College Dictionary'', 2010 by Wiley Publishing, Inc., Cleveland, Ohio. When viewed as a sing ...
, and parts of Central Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which ...
, West Asia
West Asia (also called Western Asia or Southwest Asia) is the westernmost region of Asia. As defined by most academics, UN bodies and other institutions, the subregion consists of Anatolia, the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Mesopotamia, the Armenian ...
and South Asia
South Asia is the southern Subregion#Asia, subregion of Asia that is defined in both geographical and Ethnicity, ethnic-Culture, cultural terms. South Asia, with a population of 2.04 billion, contains a quarter (25%) of the world's populatio ...
. Light brown eyes bordering amber and hazel coloration are common in Europe, but can also be observed in East Asia and Southeast Asia, though are uncommon in the region.
Amber
 Amber eyes are a solid color with a strong yellowish/golden and russet/coppery tint, which may be due to the yellow pigment called lipochrome (also found in green eyes). Amber eyes should not be confused with hazel eyes. Although hazel eyes may contain specks of amber or gold, they usually tend to have many other colors, including green, brown and orange. Also, hazel eyes may appear to shift in color and consist of flecks and ripples, while amber eyes are of a solid gold hue. Even though amber is similar to gold, some people have russet or copper colored amber eyes that are mistaken for hazel, though hazel tends to be duller and contains green with red/gold flecks, as mentioned above. Amber eyes may also contain amounts of very light gold-ish gray. People with that eye color are common in northern
Amber eyes are a solid color with a strong yellowish/golden and russet/coppery tint, which may be due to the yellow pigment called lipochrome (also found in green eyes). Amber eyes should not be confused with hazel eyes. Although hazel eyes may contain specks of amber or gold, they usually tend to have many other colors, including green, brown and orange. Also, hazel eyes may appear to shift in color and consist of flecks and ripples, while amber eyes are of a solid gold hue. Even though amber is similar to gold, some people have russet or copper colored amber eyes that are mistaken for hazel, though hazel tends to be duller and contains green with red/gold flecks, as mentioned above. Amber eyes may also contain amounts of very light gold-ish gray. People with that eye color are common in northern Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
, and in fewer numbers in southern Europe, the Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
, North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of t ...
, and South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
.
Hazel
Rayleigh scattering
Rayleigh scattering ( ) is the scattering or deflection of light, or other electromagnetic radiation, by particles with a size much smaller than the wavelength of the radiation. For light frequencies well below the resonance frequency of the scat ...
and a moderate amount of melanin in the iris' anterior border layer. Hazel eyes often appear to shift in color from a brown to a green. Although hazel mostly consists of brown and green, the dominant color in the eye can either be brown/gold or green. This is why hazel eyes can be mistaken as amber and vice versa. The combination can sometimes produce a multicolored iris, i.e., an eye that is light brown/amber near the pupil and charcoal or dark green on the outer part of the iris (or vice versa) when observed in sunlight.
Definitions of the eye color ''hazel'' vary: it is sometimes considered to be synonymous with light brown or gold, as in the color of a hazelnut
The hazelnut is the fruit of the hazel tree and therefore includes any of the nuts deriving from species of the genus '' Corylus'', especially the nuts of the species ''Corylus avellana''. They are also known as cobnuts or filberts according to ...
shell.
Around 18% of the US population and 5% of the world population have hazel eyes. Hazel eyes are found in Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
, most commonly in the Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
and the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, and have also been observed to be very common among the Low Saxon
Low Saxon (), also known as West Low German () are a group of Low German dialects spoken in parts of the Netherlands, northwestern Germany and southern Denmark (in North Schleswig by parts of the German-speaking minority). It is one of two di ...
speaking populations of northern Germany.
Green
Green eyes are most common in Northern,Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
and Central Europe
Central Europe is a geographical region of Europe between Eastern Europe, Eastern, Southern Europe, Southern, Western Europe, Western and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Central Europe is known for its cultural diversity; however, countries in ...
. Around 8–10% of men and 18–21% of women in Iceland
Iceland is a Nordic countries, Nordic island country between the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between North America and Europe. It is culturally and politically linked with Europe and is the regi ...
and 6% of men and 17% of women in the Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
have green eyes. Among European Americans
European Americans are Americans of European ancestry. This term includes both people who descend from the first European settlers in the area of the present-day United States and people who descend from more recent European arrivals. Since th ...
, green eyes are most common among those of recent Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
*Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Foot ...
and Germanic ancestry, with about 16%.
The green color is caused by the combination of: 1) an amber or light brown pigmentation in the stroma of the iris (which has a low or moderate concentration of melanin) with: 2) a blue shade created by the Rayleigh scattering of reflected light. Green eyes contain the yellowish pigment lipochrome.
Blue
The inheritance pattern followed by blue eyes was previously assumed to be a mendelian recessive trait, however, eye color inheritance is now recognized as a polygenic trait, meaning that it is controlled by the interactions of several genes. Blue eyes are predominant in northern and eastern Europe, particularly around theBaltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
. Blue eyes are also found in southern Europe, Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Pers ...
, South Asia
South Asia is the southern Subregion#Asia, subregion of Asia that is defined in both geographical and Ethnicity, ethnic-Culture, cultural terms. South Asia, with a population of 2.04 billion, contains a quarter (25%) of the world's populatio ...
, North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of t ...
and West Asia
West Asia (also called Western Asia or Southwest Asia) is the westernmost region of Asia. As defined by most academics, UN bodies and other institutions, the subregion consists of Anatolia, the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Mesopotamia, the Armenian ...
.
Approximately 8% to 10% of the global population have blue eyes. A 2002 study found that the prevalence of blue eye color among the white population in the United States to be 33.8% for those born from 1936 through 1951.
Gray
Like blue eyes, gray eyes have a dark epithelium at the back of the iris and a relatively clear stroma at the front. One possible explanation for the difference in the appearance of gray and blue eyes is that gray eyes have larger deposits ofcollagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix of the connective tissues of many animals. It is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up 25% to 35% of protein content. Amino acids are bound together to form a trip ...
in the stroma, so that the light that is reflected from the epithelium undergoes Mie scattering
In electromagnetism, the Mie solution to Maxwell's equations (also known as the Lorenz–Mie solution, the Lorenz–Mie–Debye solution or Mie scattering) describes the scattering of an electromagnetic plane wave by a homogeneous sphere. The sol ...
(which is not strongly frequency-dependent) rather than Rayleigh scattering (in which shorter wavelengths of light are scattered more). This would be analogous to the change in the color of the sky, from the blue given by the Rayleigh scattering of sunlight by small gas molecules when the sky is clear, to the gray caused by Mie scattering of large water droplets when the sky is cloudy. Alternatively, it has been suggested that gray and blue eyes might differ in the concentration of melanin at the front of the stroma.
Gray eyes can also be found among the Algeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Alger ...
n Shawia people of the Aurès Mountains in Northwest Africa, in the Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
/West Asia
West Asia (also called Western Asia or Southwest Asia) is the westernmost region of Asia. As defined by most academics, UN bodies and other institutions, the subregion consists of Anatolia, the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Mesopotamia, the Armenian ...
, Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Pers ...
, and South Asia
South Asia is the southern Subregion#Asia, subregion of Asia that is defined in both geographical and Ethnicity, ethnic-Culture, cultural terms. South Asia, with a population of 2.04 billion, contains a quarter (25%) of the world's populatio ...
. Under magnification, gray eyes exhibit small amounts of yellow and brown color in the iris.
Irritation
 Eye irritation has been defined as "the magnitude of any stinging, scratching, burning, or other irritating sensation from the eye". It is a common problem experienced by people of all ages. Related eye symptoms and signs of irritation are discomfort, dryness, excess tearing, itchiness, grating, foreign body sensation, ocular fatigue, pain, soreness, redness, swollen eyelids, and tiredness, etc. These eye symptoms are reported with intensities from mild to severe. It has been suggested that these eye symptoms are related to different causal mechanisms, and symptoms are related to the particular ocular anatomy involved.
Several suspected causal factors in our environment have been studied so far. One hypothesis is that indoor air pollution may cause eye and airway irritation. Eye irritation depends somewhat on destabilization of the outer-eye tear film, i.e. the formation of dry spots on the cornea, resulting in ocular discomfort. Occupational factors are also likely to influence the perception of eye irritation. Some of these are lighting (glare and poor contrast), gaze position, reduced blink rate, limited number of breaks from visual tasking, and a constant combination of accommodation, musculoskeletal burden, and impairment of the visual nervous system. Another factor that may be related is work stress. In addition, psychological factors have been found in multivariate analyses to be associated with an increase in eye irritation among VDU users. Other risk factors, such as chemical toxins/irritants (e.g.
Eye irritation has been defined as "the magnitude of any stinging, scratching, burning, or other irritating sensation from the eye". It is a common problem experienced by people of all ages. Related eye symptoms and signs of irritation are discomfort, dryness, excess tearing, itchiness, grating, foreign body sensation, ocular fatigue, pain, soreness, redness, swollen eyelids, and tiredness, etc. These eye symptoms are reported with intensities from mild to severe. It has been suggested that these eye symptoms are related to different causal mechanisms, and symptoms are related to the particular ocular anatomy involved.
Several suspected causal factors in our environment have been studied so far. One hypothesis is that indoor air pollution may cause eye and airway irritation. Eye irritation depends somewhat on destabilization of the outer-eye tear film, i.e. the formation of dry spots on the cornea, resulting in ocular discomfort. Occupational factors are also likely to influence the perception of eye irritation. Some of these are lighting (glare and poor contrast), gaze position, reduced blink rate, limited number of breaks from visual tasking, and a constant combination of accommodation, musculoskeletal burden, and impairment of the visual nervous system. Another factor that may be related is work stress. In addition, psychological factors have been found in multivariate analyses to be associated with an increase in eye irritation among VDU users. Other risk factors, such as chemical toxins/irritants (e.g. amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are organic compounds that contain carbon-nitrogen bonds. Amines are formed when one or more hydrogen atoms in ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups. The nitrogen atom in an amine possesses a lone pair of elec ...
s, formaldehyde
Formaldehyde ( , ) (systematic name methanal) is an organic compound with the chemical formula and structure , more precisely . The compound is a pungent, colourless gas that polymerises spontaneously into paraformaldehyde. It is stored as ...
, acetaldehyde
Acetaldehyde (IUPAC systematic name ethanal) is an organic compound, organic chemical compound with the chemical formula, formula , sometimes abbreviated as . It is a colorless liquid or gas, boiling near room temperature. It is one of the most ...
, acrolein, N-Decane, VOCs, ozone
Ozone () (or trioxygen) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , break ...
, pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are used to control pests. They include herbicides, insecticides, nematicides, fungicides, and many others (see table). The most common of these are herbicides, which account for approximately 50% of all p ...
s and preservative
A preservative is a substance or a chemical that is added to products such as food products, beverages, pharmaceutical drugs, paints, biological samples, cosmetics, wood, and many other products to prevent decomposition by microbial growth or ...
s, allergen
An allergen is an otherwise harmless substance that triggers an allergic reaction in sensitive individuals by stimulating an immune response.
In technical terms, an allergen is an antigen that is capable of stimulating a type-I hypersensitivi ...
s, etc.) might cause eye irritation as well.
Certain volatile organic compound
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are organic compounds that have a high vapor pressure at room temperature. They are common and exist in a variety of settings and products, not limited to Indoor mold, house mold, Upholstery, upholstered furnitur ...
s that are both chemically reactive and airway irritants may cause eye irritation. Personal factors (e.g. use of contact lenses, eye make-up, and certain medications) may also affect destabilization of the tear film and possibly result in more eye symptoms. Nevertheless, if airborne particles alone should destabilize the tear film and cause eye irritation, their content of surface-active compounds must be high. An integrated physiological risk model with blink frequency, destabilization, and break-up of the eye tear film as inseparable phenomena may explain eye irritation among office workers in terms of occupational, climate, and eye-related physiological risk factors.
There are two major measures of eye irritation. One is blink frequency, which can be observed by human behavior. The other measures are break up time, tear flow, hyperemia (redness, swelling), tear fluid cytology, and epithelial damage (vital stains) etc., which are human beings' physiological reactions. Blink frequency is defined as the number of blinks per minute and it is associated with eye irritation. Blink frequencies are individual with mean frequencies of < 2–3 to 20–30 blinks/minute, and they depend on environmental factors including the use of contact lens
Contact lenses, or simply contacts, are thin lenses placed directly on the surface of the eyes. Contact lenses are ocular prosthetic devices used by over 150 million people worldwide, and they can be worn to correct vision or for cosmetic ...
es. Dehydration, mental activities, work conditions, room temperature, relative humidity, and illumination all influence blink frequency. Break-up time (BUT) is another major measure of eye irritation and tear film stability. It is defined as the time interval (in seconds) between blinking and rupture. BUT is considered to reflect the stability of the tear film as well. In normal persons, the break-up time exceeds the interval between blinks, and, therefore, the tear film is maintained. Studies have shown that blink frequency is correlated negatively with break-up time. This phenomenon indicates that perceived eye irritation is associated with an increase in blink frequency since the cornea and conjunctiva both have sensitive nerve endings that belong to the first trigeminal branch.Sibony PA, Evinger C. "Anatomy and physiology of normal and abnormal eyelid position and movement". In: Miller NR, Newman NJ, editors. Walsh & Hoyt's ''Clinical Neuro-ophthalmology''. Baltimore, MD: Williams and Wilkins; 1998. pp. 1509–1592 Other evaluating methods, such as hyperemia, cytology etc. have increasingly been used to assess eye irritation.
There are other factors that are related to eye irritation as well. Three major factors that influence the most are indoor air pollution, contact lenses and gender differences. Field studies have found that the prevalence of objective eye signs is often significantly altered among office workers in comparisons with random samples of the general population. These research results might indicate that indoor air pollution has played an important role in causing eye irritation. There are more and more people wearing contact lens now and dry eyes appear to be the most common complaint among contact lens wearers. Although both contact lens wearers and spectacle wearers experience similar eye irritation symptoms, dryness, redness, and grittiness have been reported far more frequently among contact lens wearers and with greater severity than among spectacle wearers. Studies have shown that incidence of dry eyes increases with age,Seal, D. V., and Mackie, I. A. (1986). "The questionable dry eye as a clinical and biochemical entity". In F. J. Holly (Ed.) ''The preocular tear film – In health, disease, and contact lens wear''. Dry Eye Institute, Lubbock, TX, pp. 41–51. especially among women. Tear film stability (e.g. tear break-up time) is significantly lower among women than among men. In addition, women have a higher blink frequency while reading. Several factors may contribute to gender differences. One is the use of eye make-up. Another reason could be that the women in the reported studies have done more VDU work than the men, including lower grade work. A third often-quoted explanation is related to the age-dependent decrease of tear secretion, particularly among women after 40 years of age.
In a study conducted by UCLA
The University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) is a public land-grant research university in Los Angeles, California, United States. Its academic roots were established in 1881 as a normal school then known as the southern branch of the C ...
, the frequency of reported symptoms in industrial buildings was investigated. The study's results were that eye irritation was the most frequent symptom in industrial building spaces, at 81%. Modern office work with use of office equipment has raised concerns about possible adverse health effects. Since the 1970s, reports have linked mucosal, skin, and general symptoms to work with self-copying paper. Emission of various particulate and volatile substances has been suggested as specific causes. These symptoms have been related to sick building syndrome
Sick building syndrome (SBS) is a condition in which people develop symptoms of illness or become infected with chronic disease from the building in which they work or reside. In scientific literature, SBS is also known as building-related illn ...
(SBS), which involves symptoms such as irritation to the eyes, skin, and upper airways, headache and fatigue.
Many of the symptoms described in SBS and multiple chemical sensitivity
Multiple chemical sensitivity (MCS) is an unrecognized and controversial diagnosis characterized by chronic symptoms attributed to exposure to low levels of commonly used chemicals. Symptoms are typically vagueness, vague and non-specific sympt ...
(MCS) resemble the symptoms known to be elicited by airborne irritant chemicals. A repeated measurement design was employed in the study of acute symptoms of eye and respiratory tract irritation resulting from occupational exposure to sodium borate dusts. The symptom assessment of the 79 exposed and 27 unexposed subjects comprised interviews before the shift began and then at regular hourly intervals for the next six hours of the shift, four days in a row. Exposures were monitored concurrently with a personal real time aerosol monitor. Two different exposure profiles, a daily average and short term (15 minute) average, were used in the analysis. Exposure-response relations were evaluated by linking incidence rates for each symptom with categories of exposure.
Acute incidence rates for nasal, eye, and throat irritation, and coughing and breathlessness were found to be associated with increased exposure levels of both exposure indices. Steeper exposure-response slopes were seen when short term exposure concentrations were used. Results from multivariate logistic regression analysis suggest that current smokers tended to be less sensitive to the exposure to airborne sodium borate dust.
Several actions can be taken to prevent eye irritation—
* trying to maintain normal blinking by avoiding room temperatures that are too high; avoiding relative humidities that are too high or too low, because they reduce blink frequency or may increase water evaporation.
* trying to maintain an intact film of tears
Tears are a clear liquid secreted by the lacrimal glands (tear gland) found in the eyes of all land mammals. Tears are made up of water, electrolytes, proteins, lipids, and mucins that form layers on the surface of eyes. The different types of ...
by the following actions:
:# Blinking and short breaks may be beneficial for VDU users. Increasing these two actions might help maintain the tear film.
:# Downward gazing is recommended to reduce ocular surface area and water evaporation.
:# The distance between the VDU and keyboard should be kept as short as possible to minimize evaporation from the ocular surface area by a low direction of the gaze, and
:#Blink training can be beneficial.
In addition, other measures are proper lid hygiene, avoidance of eye rubbing, and proper use of personal products and medication. Eye make-up should be used with care.
Disease
There are manydiseases
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that adversely affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism and is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that are asso ...
, disorders, and age-related changes that may affect the eyes and surrounding structures.
As the eye ages, certain changes occur that can be attributed solely to the aging process. Most of these anatomic and physiologic processes follow a gradual decline. With aging, the quality of vision worsens due to reasons independent of diseases of the aging eye. While there are many changes of significance in the non-diseased eye, the most functionally important changes seem to be a reduction in pupil size and the loss of accommodation or focusing capability (presbyopia
Presbyopia is a physiological insufficiency of optical Accommodation (vertebrate eye), accommodation associated with the aging of the human eye, eye; it results in progressively worsening ability to focus clearly on close objects. Also known as ...
). The area of the pupil governs the amount of light that can reach the retina. The extent to which the pupil dilates decreases with age, leading to a substantial decrease in light received at the retina. In comparison to younger people, it is as though older persons are constantly wearing medium-density sunglasses. Therefore, for any detailed visually guided tasks on which performance varies with illumination, older persons require extra lighting. Certain ocular diseases can come from sexually transmitted infection
A sexually transmitted infection (STI), also referred to as a sexually transmitted disease (STD) and the older term venereal disease (VD), is an infection that is Transmission (medicine), spread by Human sexual activity, sexual activity, e ...
s such as herpes and genital warts. If contact between the eye and area of infection occurs, the STI can be transmitted to the eye.
With aging, a prominent white ring develops in the periphery of the cornea called arcus senilis
Arcus senilis (AS), also known as gerontoxon, arcus lipoides, arcus corneae, corneal arcus, arcus adiposus, or arcus cornealis, are rings in the peripheral cornea. It is usually caused by cholesterol deposits, so it may be a sign of high cholester ...
. Aging causes laxity, downward shift of eyelid tissues and atrophy of the orbital fat. These changes contribute to the etiology of several eyelid disorders such as ectropion, entropion, dermatochalasis, and ptosis. The vitreous gel undergoes liquefaction (posterior vitreous detachment
A posterior vitreous detachment (PVD) is a condition of the eye in which the vitreous membrane separates from the retina.
It refers to the separation of the posterior hyaloid membrane from the retina anywhere posterior to the vitreous base (a 3� ...
or PVD) and its opacities — visible as floater
Floaters or eye floaters are sometimes visible deposits (e.g., the shadows of tiny structures of protein or other cell debris projected onto the retina) within the eye's vitreous humour ("the vitreous"), which is normally transparent, or between ...
s — gradually increase in number.
Eye care professional
An eye care professional is an individual who provides a service related to the eyes or vision. It is any healthcare worker involved in eye care, from one with a small amount of post-secondary training to practitioners with a doctoral level of edu ...
s, including ophthalmologist
Ophthalmology (, ) is the branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis, treatment, and surgery of eye diseases and disorders.
An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a ...
s and optometrist
Optometry is the healthcare practice concerned with examining the eyes for visual defects, prescribing corrective lenses, and detecting eye abnormalities.
In the United States and Canada, optometrists are those that hold a post-baccalaureate f ...
s, are involved in the treatment and management of ocular and vision disorders. A Snellen chart
A Snellen chart is an eye chart that can be used to measure visual acuity. Snellen charts are named after the Dutch ophthalmologist Herman Snellen who developed the chart in 1862 as a measurement tool for the acuity formula developed by his profe ...
is one type of eye chart
__NOTOC__
An eye chart is a chart used to measure visual acuity comprising lines of optotypes in ranges of sizes. Optotypes are the letters or symbols shown on an eye chart. Eye charts are often used by health care professionals, such as optometr ...
used to measure visual acuity
Visual acuity (VA) commonly refers to the clarity of visual perception, vision, but technically rates an animal's ability to recognize small details with precision. Visual acuity depends on optical and neural factors. Optical factors of the eye ...
. At the conclusion of a complete eye examination
An eye examination, commonly known as an eye test, is a series of tests performed to assess Visual acuity, vision and ability to Focus (optics), focus on and discern objects. It also includes other tests and examinations of the human eye, eyes. ...
, the eye doctor might provide the patient with an eyeglass prescription for corrective lens
A corrective lens is a transmissive optical device that is worn on the eye to improve visual perception. The most common use is to treat refractive errors: myopia, hypermetropia, astigmatism, and presbyopia. Glasses or "spectacles" are w ...
es. Some disorders of the eyes for which corrective lenses are prescribed include myopia (near-sightedness
Myopia, also known as near-sightedness and short-sightedness, is an eye condition where light from distant objects focuses in front of, instead of on, the retina. As a result, distant objects appear blurred vision, blurry, while close objects ...
), hyperopia
Far-sightedness, also known as long-sightedness, hypermetropia, and hyperopia, is a condition of the eye where distant objects are seen clearly but near objects appear blurred. This blur is due to incoming light being focused behind, instead o ...
(far-sightedness), astigmatism
Astigmatism is a type of refractive error due to rotational asymmetry in the eye's refractive power. The lens and cornea of an eye without astigmatism are nearly spherical, with only a single radius of curvature, and any refractive errors ...
, and presbyopia
Presbyopia is a physiological insufficiency of optical Accommodation (vertebrate eye), accommodation associated with the aging of the human eye, eye; it results in progressively worsening ability to focus clearly on close objects. Also known as ...
(the loss of focusing range during aging).
Macular degeneration
Macular degeneration is especially prevalent in the U.S. and affects roughly 1.75 million Americans each year. Having lower levels of lutein and zeaxanthin within the macula may be associated with an increase in the risk of age-related macular degeneration. Lutein and zeaxanthin act asantioxidant
Antioxidants are Chemical compound, compounds that inhibit Redox, oxidation, a chemical reaction that can produce Radical (chemistry), free radicals. Autoxidation leads to degradation of organic compounds, including living matter. Antioxidants ...
s that protect the retina and macula from oxidative damage from high-energy light waves. As the light waves enter the eye, they excite electrons that can cause harm to the cells in the eye, but they can cause oxidative damage that may lead to macular degeneration or cataracts. Lutein and zeaxanthin bind to the electron free radical and are reduced rendering the electron safe. There are many ways to ensure a diet rich in lutein and zeaxanthin, the best of which is to eat dark green vegetables including kale, spinach, broccoli and turnip greens. Nutrition is an important aspect of the ability to achieve and maintain proper eye health. Lutein
Lutein (;"Lutein"
File:Human eyelashes.jpg, Long, thick, and dark eyelashes are considered an attractive facial feature as they draw attention to the eyes. Subject exhibits trichomegaly (exceptionally long lashes)
File:Human eye with limbal ring, anterior view.jpg, A thick, dark, limbal ring is seen as an attractive feature
File:Human eye in dim light.jpg, Pupils dilate in response to sexual arousal and larger pupils are perceived to be more attractive
File:Diagram of human eye without labels.svg, Right eye without labels (horizontal section)
File:Blausen 0388 EyeAnatomy 01.png
File:Blausen 0389 EyeAnatomy 02.png
File:Three Main Layers of the Eye.png, The structures of the eye labeled
File:Three Internal chambers of the Eye.svg, Another view of the eye and the structures of the eye labeled
Interactive Tool to explore the Human Eye
* * {{Authority control Facial features Sensory organs Ophthalmology Vision by taxon Visual system
zeaxanthin
Zeaxanthin is one of the most common carotenoids in nature, and is used in the xanthophyll cycle. Synthesized in plants and some micro-organisms, it is the pigment that gives paprika (made from bell peppers), corn, saffron, goji ( wolfberries) ...
are two major carotenoids, found in the macula of the eye, that are being researched to identify their role in the pathogenesis of eye disorders such as age-related macular degeneration
Macular degeneration, also known as age-related macular degeneration (AMD or ARMD), is a medical condition which may result in blurred vision, blurred or vision loss, no vision in the center of the visual field. Early on there are often no sym ...
and cataracts
A cataract is a cloudy area in the lens of the eye that leads to a decrease in vision of the eye. Cataracts often develop slowly and can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms may include faded colours, blurry or double vision, halos around ligh ...
.
Sexuality
Human eyes (particularly the iris and itscolor
Color (or colour in English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English; American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, see spelling differences) is the visual perception based on the electromagnetic spectrum. Though co ...
) and the area surrounding the eye ( lids, lashes, brows) have long been a key component of physical attractiveness
Physical attractiveness is the degree to which a person's physical features are considered aesthetics, aesthetically pleasing or beauty, beautiful. The term often implies sexual attraction, sexual attractiveness or desirability, but can also be d ...
. Eye contact plays a significant role in human nonverbal communication. A prominent limbal ring (dark ring around the iris of the eye) is considered attractive. Additionally, long and full eyelashes are coveted as a sign of beauty and are considered an attractive facial feature
The face is the front of the head that features the eyes, nose and mouth, and through which animals express many of their emotions. The face is crucial for human identity, and damage such as scarring or developmental deformities may affect ...
. Pupil size has also been shown to play an influential role in attraction and nonverbal communication, with dilated (larger) pupils perceived to be more attractive. It should also be noted that dilated pupils are a response to sexual arousal and stimuli. In the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
, women used the juice of the berries of the belladonna plant in eyedrops to dilate the pupils and make the eyes appear more seductive.Images
See also
* Eye colour * Eye development *Eye disease
This is a partial list of human eye diseases and disorders.
The World Health Organization (WHO) publishes a classification of known diseases and injuries, the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, or ...
* Eye strain
Eye strain, also medically termed as asthenopia (), is a common eye condition characterized by nonspecific symptom, non-specific symptoms such as fatigue, pain in or around the eyes, blurred vision, headache, and occasional diplopia, double vis ...
* Hyaloid canal
* Iris recognition
Iris recognition is an automated method of biometrics, biometric identification that uses mathematical pattern-recognition techniques on video images of one or both of the iris (anatomy), irises of an individual's Human eye, eyes, whose complex ...
* Knobloch syndrome
* Lacrimal caruncle
* Rheum
Rheum (; from Greek language, Greek: wikt:ῥεῦμα, ῥεῦμα ''rheuma'' 'a flowing, rheum') is a thin mucus naturally discharged from the eyes, nose, or mouth, often during sleep (contrast with mucopurulent discharge).Amodio, Aime"Where ...
* Spectral sensitivity
Spectral sensitivity is the relative efficiency of detection, of light or other signal, as a function of the frequency or wavelength of the signal.
In visual neuroscience, spectral sensitivity is used to describe the different characteristics ...
References
External links
* *Interactive Tool to explore the Human Eye
* * {{Authority control Facial features Sensory organs Ophthalmology Vision by taxon Visual system