Erzerum Province on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Erzurum Province () is a
province
A province is an administrative division within a country or sovereign state, state. The term derives from the ancient Roman , which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire, Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
and metropolitan municipality
A metropolitan municipality is a municipality established to serve a metropolitan area.
Canada
In generic terms and in practical application within Canada, a metropolitan municipality is an urban local government with partial or complete consol ...
in the Eastern Anatolia Region
The Eastern Anatolia region () is a geographical region of Turkey. The most populous province in the region is Van Province. Other populous provinces are Malatya, Erzurum and Elazığ.
It is bordered by the Black Sea Region and Georgia in th ...
of Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
. Its area is 25,006 km2, and its population is 749,754 (2022). The capital of the province is the city of Erzurum
Erzurum (; ) is a List of cities in Turkey, city in eastern Anatolia, Turkey. It is the largest city and capital of Erzurum Province and is 1,900 meters (6,233 feet) above sea level. Erzurum had a population of 367,250 in 2010. It is the site of an ...
. It is the fourth largest province in all of Turkey. It is bordered by the provinces of Kars
Kars ( or ; ; ) is a city in northeast Turkey. It is the seat of Kars Province and Kars District.� ...
and Ağrı
Ağrı (; ) is a city in eastern Turkey, near the border with Iran. It is the seat of Ağrı Province and Ağrı District.
to the east, Muş
Muş (; ; ) is a city in eastern Turkey. It is the seat of Muş Province and Muş District.İl Beled ...
and Bingöl
Bingöl (; ; ), known as Çapakçur before 1944, is a city in Turkey. It is the seat of Bingöl Province and Bingöl District,Erzincan
Erzincan (; ), historically Yerznka (), is the capital of Erzincan Province in eastern Turkey. Nearby cities include Erzurum, Sivas, Tunceli, Bingöl, Elazığ, Malatya, Gümüşhane, Bayburt, and Giresun. The city is majority Turkish Sunni w ...
and Bayburt
Bayburt () is a city in northeast Turkey lying on the Çoruh River. It is the seat of Bayburt Province and Bayburt District.Rize
Rize (; ; ; ka, რიზე}; ) is a coastal city in the eastern part of the Black Sea Region of Turkey. It is the seat of Rize Province and Rize District.Artvin
Artvin (Laz language, Laz and ; ; ) is a List of cities in Turkey, city in northeastern Turkey about inland from the Black Sea. It is the seat of Artvin Province and Artvin District.Ardahan
Ardahan ( ka, არტაანი, tr; ; Russian: Ардаган) is a city in northeastern Turkey, near the Georgian border. It is the seat of Ardahan Province and Ardahan District.Turkish
Turkish may refer to:
* Something related to Turkey
** Turkish language
*** Turkish alphabet
** Turkish people, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
*** Turkish citizen, a citizen of Turkey
*** Turkish communities in the former Ottoman Empire
* The w ...
majority.
Geography
The surface area of the province of Erzurum is the fourth biggest in Turkey. The majority of the province iselevated
An elevated railway or elevated train (also known as an el train or el for short) is a railway with the Track (rail transport), tracks above street level on a viaduct or other elevated structure (usually constructed from steel, cast iron, concre ...
. Most plateaus are about above sea level, and the mountainous regions beyond the plateaus are and higher. Depression plains are located between the mountains and plateaus. The southern mountain range
A mountain range or hill range is a series of mountains or hills arranged in a line and connected by high ground. A mountain system or mountain belt is a group of mountain ranges with similarity in form, structure, and alignment that have aris ...
s include the Palandöken Mountains (highest peak Büyük Ejder high) and the Şahveled Mountains (highest peak Çakmak Mountain high). The northern mountain ranges are the second row elevations of the North Anatolian Mountains, i.e. Mescit Mountains (highest peak high), Kargapazarı Mountains (highest peak high) and Allahuekber Mountains
Allahuekber Mountains (, which means "Allahu akbar Mountains"), is a mountain range in northeastern Turkey. It is located on the border of Erzurum, Kars and Ardahan provinces. It is part of the Pontic Mountains.
When World War I began in 1914, ...
. The two depression plains between these mountainous areas are Erzurum Plains and Hasankale Plains. Aras Mountains
Aras Mountains (), is a mountain range in northeastern Turkey. Also known as Haykakan Par (). It is located on the border of Erzurum, Kars, Ağrı and Iğdır provinces. It is a ridge at the middle of the Armenian highlands. It starts near sourc ...
starts first in Erzurum. Then it extends towards the borders of Ağrı
Ağrı (; ) is a city in eastern Turkey, near the border with Iran. It is the seat of Ağrı Province and Ağrı District.
and Kars
Kars ( or ; ; ) is a city in northeast Turkey. It is the seat of Kars Province and Kars District.� ...
. Erzurum province is surrounded by Bingöl
Bingöl (; ; ), known as Çapakçur before 1944, is a city in Turkey. It is the seat of Bingöl Province and Bingöl District,Akdoğan Mountains from the south.
 Greater Erzurum
Area: 1,612 sq km, Population: 370,000 (2022)
Rest of Erzurum Province
Greater Erzurum
Area: 1,612 sq km, Population: 370,000 (2022)
Rest of Erzurum Province
 Known as ''Karanitis'' (),Smith, William (1852).
Known as ''Karanitis'' (),Smith, William (1852).
Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography (Abacaenum – Hytanis)
p. 514. Boston: Little, Brown. ''Arzen'', ''Erzen'', and (
Official Website of the Municipality
Armenian History and Presence in Erzurum
{{coord, 40, 03, 47, N, 41, 34, 01, E, region:TR-25_type:adm1st, display = title Provinces of Turkey Western Armenia
Continental climate
Continental climates often have a significant annual variation in temperature (warm to hot summers and cold winters). They tend to occur in central and eastern parts of the three northern-tier continents (North America, Europe, and Asia), typi ...
rules in the province with long and harsh winters, and short and mild summers.
Steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without closed forests except near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the tropical and subtropica ...
formations are prevalent geographic features of this province, occupying about 60% of the surface area, much of it fertile. Forested areas are small, mainly consisting of scots pine
''Pinus sylvestris'', the Scots pine (UK), Scotch pine (US), Baltic pine, or European red pine is a species of tree in the pine family Pinaceae that is native to Eurasia. It can readily be identified by its combination of fairly short, blue-gr ...
s and oak
An oak is a hardwood tree or shrub in the genus ''Quercus'' of the beech family. They have spirally arranged leaves, often with lobed edges, and a nut called an acorn, borne within a cup. The genus is widely distributed in the Northern Hemisp ...
s.
The eastern part of the province lies in the basin of the Aras river
The Aras is a transboundary river in the Caucasus. It rises in eastern Turkey and flows along the borders between Turkey and Armenia, between Turkey and the Nakhchivan exclave of Azerbaijan, between Iran and both Azerbaijan and Armenia, and, fin ...
, the western part in the Karasu (Euphrates)
The Karasu ( Turkish for 'black water') or Western Euphrates is a long river in eastern Turkey, one of the two sources of the Euphrates. It has a length of about 450 km. To the ancient Greeks the river was known as the ().
Course
The ri ...
basin, and the northern part in the Çoruh
The Chorokh ( ka, ჭოროხი ''Ch'orokhi'' , , ''Chorokh'', , , ''Akampsis'') is a river that rises in the Mescit Mountains in north-eastern Turkey, flows through the cities of Bayburt, İspir, Yusufeli, and Artvin, along the Kelkit-� ...
basin.
There are few natural lakes in the province, the major one being Lake Tortum (approximately 8 km2) fed by the Tortum (Uzundere) Falls. The Tortum hydroelectric power plant built in 1963 is situated on the inlet of this lake. There are three artificial lakes in the province.
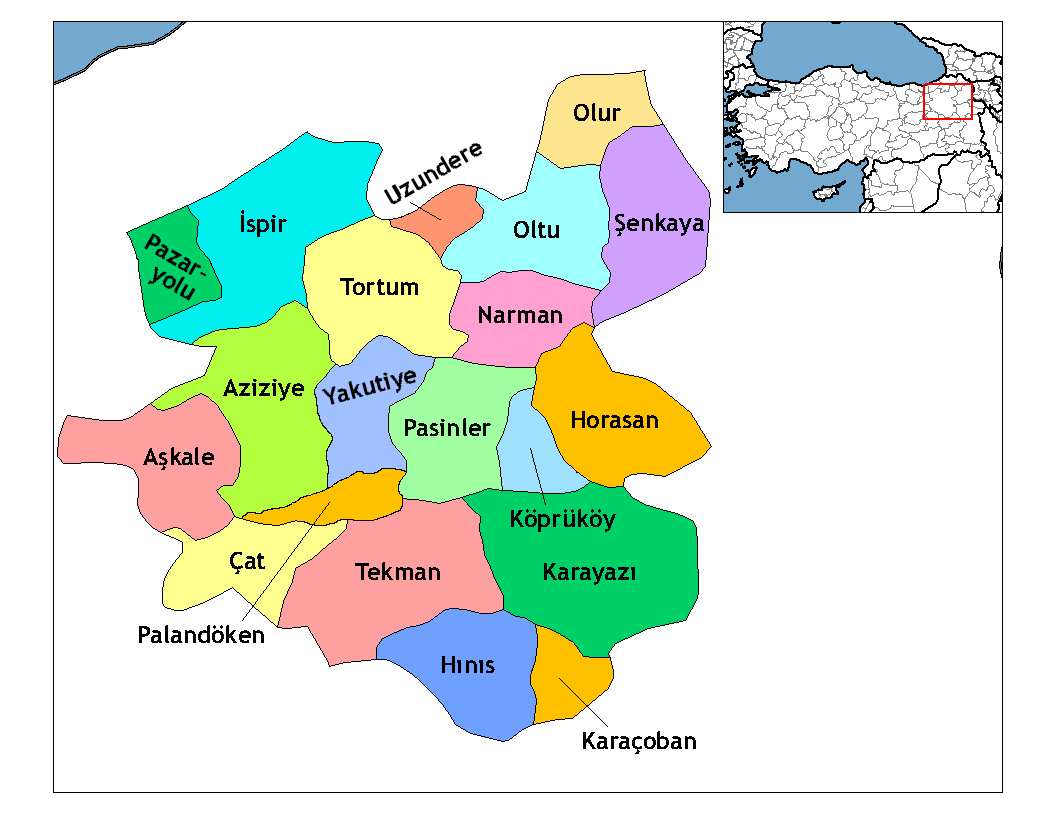
Districts

 Greater Erzurum
Area: 1,612 sq km, Population: 370,000 (2022)
Rest of Erzurum Province
Greater Erzurum
Area: 1,612 sq km, Population: 370,000 (2022)
Rest of Erzurum Province
History
 Known as ''Karanitis'' (),Smith, William (1852).
Known as ''Karanitis'' (),Smith, William (1852).Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography (Abacaenum – Hytanis)
p. 514. Boston: Little, Brown. ''Arzen'', ''Erzen'', and (
Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian diaspora, Armenian communities around the ...
:''Էրզրում նահանգ, Կարին'' ) ''Karin'' or ''Garin'', most of the province was incorporated into the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
in the 4th century (after the first split of Kingdom of Armenia in 387 between Romans and Iran), and a small mountain city called ''Karin ('') or ''Carana'' () was fortified. It became an important border fortress. This city was later (A.D. 415) renamed to Theodosiopolis (), in honour of Emperor Theodosius I
Theodosius I ( ; 11 January 347 – 17 January 395), also known as Theodosius the Great, was Roman emperor from 379 to 395. He won two civil wars and was instrumental in establishing the Nicene Creed as the orthodox doctrine for Nicene C ...
. Standing on the crossroads of main trade routes in Asia Minor
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
, the area was a centre of importance for Greeks, with Armenian majority and minorities like Syriac Christians, Jews, Assyrians
Assyrians (, ) are an ethnic group indigenous to Mesopotamia, a geographical region in West Asia. Modern Assyrians share descent directly from the ancient Assyrians, one of the key civilizations of Mesopotamia. While they are distinct from ot ...
and other. From the mid 3rd century AD and afterwards, the territory was dominated by and incorporated into the Sasanian Empire
The Sasanian Empire (), officially Eranshahr ( , "Empire of the Iranian peoples, Iranians"), was an List of monarchs of Iran, Iranian empire that was founded and ruled by the House of Sasan from 224 to 651. Enduring for over four centuries, th ...
, although it occasionally briefly fell under the rule of the neighboring Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
as well. From the mid 7th century AD, the Arabs
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of yea ...
frequently clashed with the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
, including over the region. Between the seventh and eighth centuries, Arabs and Byzantines alternately held the region in their power, local Armenian rulers played a significant role in these events. The city (present day Erzurum
Erzurum (; ) is a List of cities in Turkey, city in eastern Anatolia, Turkey. It is the largest city and capital of Erzurum Province and is 1,900 meters (6,233 feet) above sea level. Erzurum had a population of 367,250 in 2010. It is the site of an ...
) was alternatively held by the Arabs and Byzantines during the 7-10th centuries it was also part of the Georgian kingdom of Tao-Klarjeti Tao-Klarjeti may refer to:
* Tao-Klarjeti, part of Georgian historical region of Upper Kartli
* Kingdom of Tao-Klarjeti, AD 888 to 1008
{{set index article
Kingdom of Iberia
Historical regions of Georgia (country) ...
in the 10th century. Threatened and later devastated and looted by the Seljuk Turks
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; , ''Saljuqian'',) alternatively spelled as Saljuqids or Seljuk Turks, was an Oghuz Turks, Oghuz Turkic, Sunni Muslim dynasty that gradually became Persianate society, Persianate and contributed to Turco-Persi ...
in 1049, the old city of Erzen was conquered, but Theodosiopolis survived the invasion until it was captured some time later. From the year 1101 onward it is documented that the ruling dynasty of the Saltukids
The Saltukids or Saltuqids ( Modern Turkish: ''Saltuklu Beyliği'') were a dynasty ruling one of the Anatolian beyliks of the Seljuk Empire, founded after the Battle of Manzikert (1071) and centered on Erzurum. The Saltukids ruled between 1071 ...
held the town and much of the surrounding area in their power. Theodosiopolis repelled many attacks and military campaigns by the Seljuks of Rum and Georgians (the latter knew the city as Karnu-Kalaki)Rapp, Stephen H. (2003), ''Studies in Medieval Georgian Historiography: Early Texts And Eurasian Contexts'', p. 414. Peeters Publishers, until 1201 when the city and province were conquered by the Seljuk sultan Süleiman II of Rüm
Suleiman II, also known as Rukn ad-Din Suleiman Shah (Arabic: رکن الدین سلیمان شاه), was the Seljuk Sultan of Rûm between 1196 and 1204.
Son of Kilij Arslan II, Suleiman overthrew his brother, Sultan Kaykhusraw I, and became su ...
. Erzen-Erzurum fell to the Mongol
Mongols are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, China (Inner Mongolia and other 11 autonomous territories), as well as the republics of Buryatia and Kalmykia in Russia. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family of M ...
siege in 1242, and the city was looted and devastated. After the fall of the Seljuk Sultanate of Anatolia (Rum) in the early 14th century, it became an administrative province of the Ilkhanate
The Ilkhanate or Il-khanate was a Mongol khanate founded in the southwestern territories of the Mongol Empire. It was ruled by the Il-Khans or Ilkhanids (), and known to the Mongols as ''Hülegü Ulus'' (). The Ilkhanid realm was officially known ...
, and after their fall, became part of the Çoban beylik, Black Sheep Turkmen
The Qara Qoyunlu or Kara Koyunlu (, ; ), also known as the Black Sheep Turkomans, were a culturally Persianate, Muslim Turkoman "Kara Koyunlu, also spelled Qara Qoyunlu, Turkish Karakoyunlular, English Black Sheep, Turkmen tribal federation tha ...
, Mongols led by Timur Lenk
Timur, also known as Tamerlane (1320s17/18 February 1405), was a Turco-Mongol conqueror who founded the Timurid Empire in and around modern-day Afghanistan, Iran, and Central Asia, becoming the first ruler of the Timurid dynasty. An undefeated ...
, the White Sheep Turkmen and the rising Iranian Safavids
The Guarded Domains of Iran, commonly called Safavid Iran, Safavid Persia or the Safavid Empire, was one of the largest and longest-lasting Iranian empires. It was ruled from 1501 to 1736 by the Safavid dynasty. It is often considered the begi ...
captured the town in 1502 from the Aq Qoyunlu
The Aq Qoyunlu or the White Sheep Turkomans (, ; ) was a culturally Persianate society, Persianate,Kaushik Roy, ''Military Transition in Early Modern Asia, 1400–1750'', (Bloomsbury, 2014), 38; "Post-Mongol Persia and Iraq were ruled by two trib ...
.
In the Ottoman Empire
In 1514, the region was conquered by the Ottoman SultanSelim I
Selim I (; ; 10 October 1470 – 22 September 1520), known as Selim the Grim or Selim the Resolute (), was the List of sultans of the Ottoman Empire, sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1512 to 1520. Despite lasting only eight years, his reign is ...
following the Battle of Chaldiran
The Battle of Chaldiran (; ) took place on 23 August 1514 and ended with a decisive victory for the Ottoman Empire over the Safavid Empire. As a result, the Ottomans annexed Eastern Anatolia and Upper Mesopotamia from Safavid Iran. It marked ...
. During the Ottoman reign, the city Erzurum served as the main base of Ottoman military power in the region and as the capital of the province. Early in the 17th century, the province was threatened again and taken by Safavid Iran while enduring also a revolt by the province governor Abaza Mehmed Pasha
Abaza Mehmed Pasha (, ); 1576 – August 23, 1634) was a statesman and military commander of the Ottoman Empire, the namesake of the Abaza rebellion. He was the beylerbey of the Bosnia Eyalet in 1628–1631. He was executed by sultan Murat IV in ...
. This revolt was combined with Jelali Revolts
The Celali rebellions () were a series of rebellions in Anatolia of irregular troops led by bandit chiefs and provincial officials known as ''celalî'', ''celâli'', or ''jelālī'', against the authority of the Ottoman Empire in the late 16th and ...
(the uprising of the provincial musketeers called the ''Celali''), backed by Safavid Iran and lasted until 1628. However, Iran would reconquer it again, only this time under Nader Shah
Nader Shah Afshar (; 6 August 1698 or 22 October 1688 – 20 June 1747) was the founder of the Afsharid dynasty of Iran and one of the most powerful rulers in Iranian history, ruling as shah of Iran (Persia) from 1736 to 1747, when he was a ...
in the first half of the 18th century.
The Ottomans were routed by the Iranian Qajars in the 1821 battle at the city of Erzurum. The city was conquered by the Russian army in 1829, given back to the Ottoman Empire with the Treaty of Adrianople (Edirne). The poet Alexander Pushkin
Alexander Sergeyevich Pushkin () was a Russian poet, playwright, and novelist of the Romantic era.Basker, Michael. Pushkin and Romanticism. In Ferber, Michael, ed., ''A Companion to European Romanticism''. Oxford: Blackwell, 2005. He is consid ...
accompanied the Russian commander-in-chief, Ivan Paskevich
Count Ivan Fyodorovich Paskevich-Erevansky, Serene Prince of Warsaw ( – ) was a Russian military leader who was the ''namiestnik'' of Poland.
Paskevich is known for leading Russian forces in Poland during the November Uprising and for a s ...
, during that expedition and penned a brief account of the campaign. The city was again assaulted by the Russian army in the last Russo-Turkish War in 1877.
Beginning in late 1914 and picking up in the summer of 1915, the province saw the wholesale extermination of the Armenian population by state-sponsored forces as part of the Armenian genocide
The Armenian genocide was the systematic destruction of the Armenians, Armenian people and identity in the Ottoman Empire during World War I. Spearheaded by the ruling Committee of Union and Progress (CUP), it was implemented primarily t ...
.
The province was the site of the major fighting during Caucasus Campaign
The Caucasus campaign comprised armed conflicts between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire, later including Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, the Mountainous Republic of the Northern Caucasus, the German Empire, the Central Caspian Dict ...
of World War I between Russian and Ottoman forces including the key confrontation of the campaign, Battle of Erzurum which resulted in capture of Erzurum by Russian army under the command of Grand Duke Nicholas Nikolaevich on 16 February 1916. It was returned to the Ottomans with the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk was a separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Soviet Russia and the Central Powers (Germany, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and Bulgaria), by which Russia withdrew from World War I. The treaty, whi ...
in 1918. Erzurum was also a main Turkish
Turkish may refer to:
* Something related to Turkey
** Turkish language
*** Turkish alphabet
** Turkish people, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
*** Turkish citizen, a citizen of Turkey
*** Turkish communities in the former Ottoman Empire
* The w ...
base during the Turkish War of Independence
, strength1 = May 1919: 35,000November 1920: 86,000Turkish General Staff, ''Türk İstiklal Harbinde Batı Cephesi'', Edition II, Part 2, Ankara 1999, p. 225August 1922: 271,000Celâl Erikan, Rıdvan Akın: ''Kurtuluş Savaşı tarih ...
and the Erzurum congress
Erzurum Congress () was an assembly of Turkish Revolutionaries held from 23 July to 4 August 1919 in the city of Erzurum, in eastern Turkey, in accordance with the previously issued Amasya Circular. The congress united delegates from six easter ...
of Turkish nationalists was held here in 1919. It was declared a province of Turkey in 1924.
In Turkey
In September 1935 the third Inspectorate General (''Umumi Müfettişlik,'' UM) was created. The third UM span over the provinces of Erzurum,Artvin
Artvin (Laz language, Laz and ; ; ) is a List of cities in Turkey, city in northeastern Turkey about inland from the Black Sea. It is the seat of Artvin Province and Artvin District.Rize
Rize (; ; ; ka, რიზე}; ) is a coastal city in the eastern part of the Black Sea Region of Turkey. It is the seat of Rize Province and Rize District.Trabzon
Trabzon, historically known as Trebizond, is a city on the Black Sea coast of northeastern Turkey and the capital of Trabzon Province. The city was founded in 756 BC as "Trapezous" by colonists from Miletus. It was added into the Achaemenid E ...
, Kars
Kars ( or ; ; ) is a city in northeast Turkey. It is the seat of Kars Province and Kars District.� ...
Gümüşhane
Gümüşhane () is a city in the Black Sea Region of Turkey. It is the seat of Gümüşhane Province and Gümüşhane District.Erzincan
Erzincan (; ), historically Yerznka (), is the capital of Erzincan Province in eastern Turkey. Nearby cities include Erzurum, Sivas, Tunceli, Bingöl, Elazığ, Malatya, Gümüşhane, Bayburt, and Giresun. The city is majority Turkish Sunni w ...
and Ağrı
Ağrı (; ) is a city in eastern Turkey, near the border with Iran. It is the seat of Ağrı Province and Ağrı District.
. Its capital was to be in the city of Erzurum
Erzurum (; ) is a List of cities in Turkey, city in eastern Anatolia, Turkey. It is the largest city and capital of Erzurum Province and is 1,900 meters (6,233 feet) above sea level. Erzurum had a population of 367,250 in 2010. It is the site of an ...
and it was governed by an Inspector General. The Inspectorate General was dissolved in 1952 during the Government of the Democrat Party.
Economy
Historically, Erzurum producedwheat
Wheat is a group of wild and crop domestication, domesticated Poaceae, grasses of the genus ''Triticum'' (). They are Agriculture, cultivated for their cereal grains, which are staple foods around the world. Well-known Taxonomy of wheat, whe ...
and linseed
Flax, also known as common flax or linseed, is a flowering plant, ''Linum usitatissimum'', in the family Linaceae. It is cultivated as a food and fiber crop in regions of the world with temperate climates. In 2022, France produced 75% of the ...
; as of 1920, annual production of linseed grossed between 1,000 and 1,500 tons. Honey
Honey is a sweet and viscous substance made by several species of bees, the best-known of which are honey bees. Honey is made and stored to nourish bee colonies. Bees produce honey by gathering and then refining the sugary secretions of pl ...
was also produced for local use.
Approximately 18.5% of the total surface area is arable land
Arable land (from the , "able to be ploughed") is any land capable of being ploughed and used to grow crops.''Oxford English Dictionary'', "arable, ''adj''. and ''n.''" Oxford University Press (Oxford), 2013. Alternatively, for the purposes of a ...
, of which about 75% has permanent crops. A large portion of the agricultural produce comprises cereal
A cereal is a grass cultivated for its edible grain. Cereals are the world's largest crops, and are therefore staple foods. They include rice, wheat, rye, oats, barley, millet, and maize ( Corn). Edible grains from other plant families, ...
s. Forested areas occupy 8.8% of the total surface area, with forestry a local industry. Industries largely consist of manufacturing of forestry, agriculture, husbandry, chemistry, textile and mining products. There are 81 active industrial plants
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with cyanobacteria to produce sugars f ...
in the province, most of them located at the central district of Erzurum, and are small and medium enterprises. Due to their relatively small sizes, these industries mainly serve local markets causing lower capacity usage, low productivity and unemployment. About 40 plants are currently out of use, mostly due to high operating costs.
The province of Erzurum has the highest ratio of meadows and pastures in Turkey, ideal for livestock. However, once the main occupation, animal husbandry
Animal husbandry is the branch of agriculture concerned with animals that are raised for meat, animal fiber, fibre, milk, or other products. It includes day-to-day care, management, production, nutrition, selective breeding, and the raising ...
lost its importance in the 1980s with the introduction of a liberal economy
Economic liberalism is a political and economic ideology that supports a market economy based on individualism and private property in the means of production. Adam Smith is considered one of the primary initial writers on economic liberalism, ...
and the importation of animal products. A large organized industrial park concentrating on processing meat is being built with the hope of reviving this sector. Food industries include beekeeping
Beekeeping (or apiculture, from ) is the maintenance of bee colonies, commonly in artificial beehives. Honey bees in the genus '' Apis'' are the most commonly kept species but other honey producing bees such as '' Melipona'' stingless bees are ...
and trout farming.
Mining resources include lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleabl ...
, copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
, chromium
Chromium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in Group 6 element, group 6. It is a steely-grey, Luster (mineralogy), lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.
Chromium ...
, and zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
, the reserves of which are almost exhausted. There is a considerable amount of lignite
Lignite (derived from Latin ''lignum'' meaning 'wood'), often referred to as brown coal, is a soft, brown, combustible sedimentary rock formed from naturally compressed peat. It has a carbon content around 25–35% and is considered the lowest ...
, however because its ash
Ash is the solid remnants of fires. Specifically, ''ash'' refers to all non-aqueous, non- gaseous residues that remain after something burns. In analytical chemistry, to analyse the mineral and metal content of chemical samples, ash is the ...
and sulfur
Sulfur ( American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphur ( Commonwealth spelling) is a chemical element; it has symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms ...
ratios are high, it suitable only for industrial use. Magnesite
Magnesite is a mineral with the chemical formula ( magnesium carbonate). Iron, manganese, cobalt, and nickel may occur as admixtures, but only in small amounts.
Occurrence
Magnesite occurs as veins in and an alteration product of ultramafic r ...
, fire clay
Fire clay is a range of refractory clays used in the manufacture of ceramics, especially fire brick. The United States Environmental Protection Agency defines fire clay very generally as a "mineral aggregate composed of hydrous silicates of alumi ...
, gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate Hydrate, dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, drywall and blackboard or sidewalk ...
, manganese
Manganese is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese was first isolated in the 1770s. It is a transition m ...
, diatomite
Diatomaceous earth ( ), also known as diatomite ( ), celite, or kieselguhr, is a naturally occurring, soft, siliceous sedimentary rock that can be crumbled into a fine white to off-white powder. It has a particle size ranging from more than 3 ...
, marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock consisting of carbonate minerals (most commonly calcite (CaCO3) or Dolomite (mineral), dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2) that have recrystallized under the influence of heat and pressure. It has a crystalline texture, and is ty ...
, rock salt
In common usage, salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl). When used in food, especially in granulated form, it is more formally called table salt. In the form of a natural crystalline mineral, salt is also known as r ...
and perlite
Perlite is an amorphous volcanic glass that has a relatively high water content, typically formed by the Hydrate, hydration of obsidian. It occurs naturally and has the unusual property of greatly expanding when heated sufficiently. It is an indu ...
are also present. The few natural geothermal Geothermal is related to energy and may refer to:
* Geothermal energy, useful energy generated and stored in the Earth
* Geothermal activity, the range of natural phenomena at or near the surface, associated with release of the Earth's internal he ...
resources, except one, are not suitable for economic investments, and they are used as natural springs.
The gross domestic product GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the total market value of all the final goods and services produced and rendered in a specific time period by a country or countries. GDP is often used to measure the economic performance o ...
of Erzurum is US$1.16 billion, constituting less than 1% of the total and ranking 40th among Turkish provinces (1997 values).
Transportation is possible via paved and unpaved highways. The Erzurum international airport is open for commercial flights and is also used by the Turkish Air Force. The runways of this airport are the second longest in Turkey. Erzurum is also the main railroad hub in the Eastern Anatolia Region.
The largest contributor to the provincial economy, in recent years, has been Atatürk University
Atatürk University () is a public land-grant research university established in 1957 in Erzurum, Turkey, in collaboration with the University of Nebraska. The university comprises 23 faculties, 18 colleges, 8 institutes, and 30 research cente ...
, which is also one of the largest universities in Turkey, having more than forty thousand students. Tourist activities, which include skiing, rafting, and mountaineering, also provide a substantial proportion of the province's income. Skiing is centered on Palandöken Mountain.
Places of interest
* Öşvank ( Oshk Vank) Historical Georgian Monastery church,Uzundere
Uzundere () is a municipality and district of Erzurum Province, Turkey. Its area is 505 km2, and its population is 7,625 (2022). The mayor is Muhammet Halis Özsoy ( BBP).
Visitor attraction
Oshki, a historic Georgian Orthodox monastery from ...
.
* Bana cathedral
Bana ( ka, ბანა; ; ) is a ruined early medieval cathedral in present-day Erzurum Province, eastern Turkey, in what had formerly been a historical marchland known to Armenians as Tayk and to Georgians as Tao.
It is a large tetraconch design ...
, also known as the Penek cathedral
* Oltu
Oltu (; ) is a municipality and district of Erzurum Province, Turkey. Its area is 1,441 km2, and its population is 30,075 (2022). The mayor is Adem Çelebi, from the AKP.
History
An inscription found in Oltu's castle has been dated to the 7t ...
Russian cathedral, also known as Oltu Rus Kilisesi
* Haho Khakhuli Monastery
Khakhuli Monastery ( ka, ხახულის მონასტერი , ) was a Georgian Orthodox monastery in historical Medieval Georgian Kingdom of Tao (modern-day Turkey), in one of the gorges of the Tortum river. The main church is now u ...
, also known as Haho Bağbaşı Kilisesi, is a Georgian Orthodox monastery in historical Medieval Georgian Kingdom of Tao, located in Tortum
Tortum (; ; ) is a municipality and district of Erzurum Province, Turkey. Its area is 1,463 km2, and its population is 15,259 (2022). The current mayor is Muammer Yiğider from the Justice and Development Party (AKP).
History
Tortum was pa ...
.
Notable people
*İbrahim Hakkı Erzurumi
Ibrahim Hakki Erzurumi (18 May 1703 – 22 June 1780), a popular Turkish Sufi saint of the Ottoman Empire from Erzurum in eastern Anatolia who was a polymath, mystic, poet, author, astronomer, physicist, physician, psychologist, sociologist, ph ...
, Ottoman poet
A poet is a person who studies and creates poetry. Poets may describe themselves as such or be described as such by others. A poet may simply be the creator (thought, thinker, songwriter, writer, or author) who creates (composes) poems (oral t ...
and writer
A writer is a person who uses written words in different writing styles, genres and techniques to communicate ideas, to inspire feelings and emotions, or to entertain. Writers may develop different forms of writing such as novels, short sto ...
of the Marifetname poetry
Poetry (from the Greek language, Greek word ''poiesis'', "making") is a form of literature, literary art that uses aesthetics, aesthetic and often rhythmic qualities of language to evoke meaning (linguistics), meanings in addition to, or in ...
book
A book is a structured presentation of recorded information, primarily verbal and graphical, through a medium. Originally physical, electronic books and audiobooks are now existent. Physical books are objects that contain printed material, ...
* Erzurumlu Emrah, ashik
An ashik (; ) or ashugh (; ka, :ka:აშუღი, აშუღი) is traditionally a List of oral repositories, singer-poet and bard who accompanies his song—be it a dastan (traditional epic story, also known as ''Azeri hikaye, hikaye' ...
and poet
A poet is a person who studies and creates poetry. Poets may describe themselves as such or be described as such by others. A poet may simply be the creator (thought, thinker, songwriter, writer, or author) who creates (composes) poems (oral t ...
* Mehmed Kırkıncı, student
A student is a person enrolled in a school or other educational institution, or more generally, a person who takes a special interest in a subject.
In the United Kingdom and most The Commonwealth, commonwealth countries, a "student" attends ...
of Said Nursi
Said Nursi (1877Şükran Vahide, Islam in Modern Turkey: An Intellectual Biography of Bediuzzaman Said Nursi, p 3. – 23 March 1960) was a Kurdish scholar of Islam who wrote the Risale-i Nur Collection, a body of Qur'anic commentary exceedin ...
and leader
Leadership, is defined as the ability of an individual, group, or organization to "", influence, or guide other individuals, teams, or organizations.
"Leadership" is a contested term. Specialist literature debates various viewpoints on the co ...
of the Nur movement
Nurism () is an Islamic movement that was founded in Turkey in the early 20th century and based on the writings of Said Nursi (1877–1960).Svante E. Cornell ''Azerbaijan Since Independence'' M.E. Sharpe p. 283 His movement is based on Hanafi l ...
* İbrahim Erkal
İbrahim Erkal (10 October 1966 – 11 May 2017) was a Turkish singer, songwriter, composer and actor. Under the name İbrahim Güzelses, he released his first album in 1984. İbrahim Erkal released his first album under his own name in 1986 wit ...
, bestselling
A bestseller is a book or other media noted for its top selling status, with bestseller lists published by newspapers, magazines, and book store chains. Some lists are broken down into classifications and specialties (novel, nonfiction book, coo ...
Turkish
Turkish may refer to:
* Something related to Turkey
** Turkish language
*** Turkish alphabet
** Turkish people, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
*** Turkish citizen, a citizen of Turkey
*** Turkish communities in the former Ottoman Empire
* The w ...
classical music
Classical music generally refers to the art music of the Western world, considered to be #Relationship to other music traditions, distinct from Western folk music or popular music traditions. It is sometimes distinguished as Western classical mu ...
and Fantezi
Fantezi is a Turkish classical music genre composed in Turkish pop music in accordance with the tradition of the Turkish people. Also called folk song or urban folk music, in its plural form is a Turkish music genre which has taken many forms ove ...
music
Music is the arrangement of sound to create some combination of Musical form, form, harmony, melody, rhythm, or otherwise Musical expression, expressive content. Music is generally agreed to be a cultural universal that is present in all hum ...
artist
An artist is a person engaged in an activity related to creating art, practicing the arts, or demonstrating the work of art. The most common usage (in both everyday speech and academic discourse) refers to a practitioner in the visual arts o ...
, composer
A composer is a person who writes music. The term is especially used to indicate composers of Western classical music, or those who are composers by occupation. Many composers are, or were, also skilled performers of music.
Etymology and def ...
, songwriter
A songwriter is a person who creates musical compositions or writes lyrics for songs, or both. The writer of the music for a song can be called a composer, although this term tends to be used mainly in the classical music genre and film scoring. ...
and oud
The oud ( ; , ) is a Middle Eastern short-neck lute-type, pear-shaped, fretless stringed instrument (a chordophone in the Hornbostel–Sachs classification of instruments), usually with 11 strings grouped in six courses, but some models have ...
player
References
External links
*Official Website of the Municipality
Armenian History and Presence in Erzurum
{{coord, 40, 03, 47, N, 41, 34, 01, E, region:TR-25_type:adm1st, display = title Provinces of Turkey Western Armenia