Erosive Esophagitis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Esophagitis, also spelled oesophagitis, is a disease characterized by inflammation of the
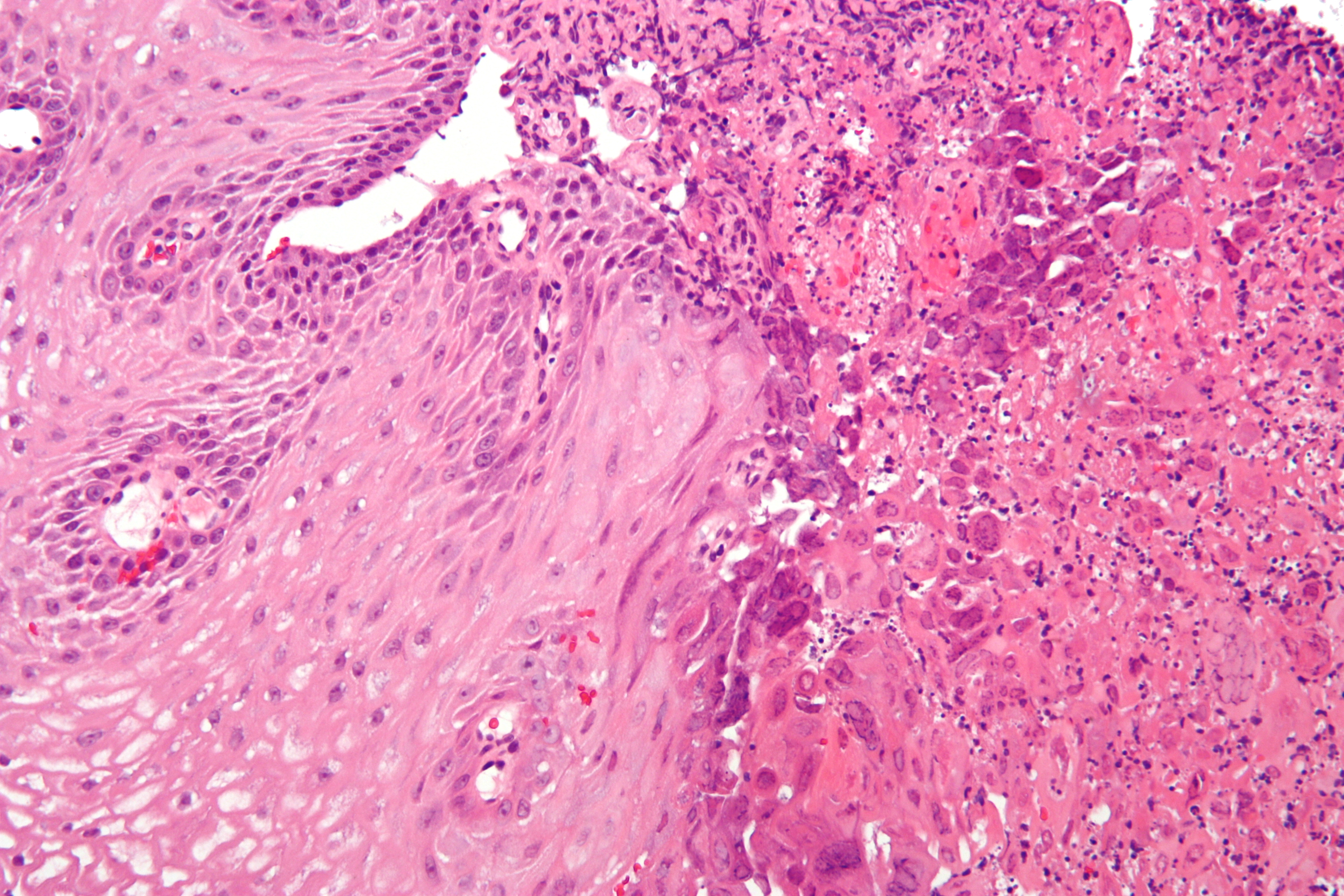 Infectious esophagitis
Esophagitis happens due to a viral, fungal, parasitic or bacterial infection. More likely to happen to people who have an immunodeficiency. Types include:
Fungal
*
Infectious esophagitis
Esophagitis happens due to a viral, fungal, parasitic or bacterial infection. More likely to happen to people who have an immunodeficiency. Types include:
Fungal
* 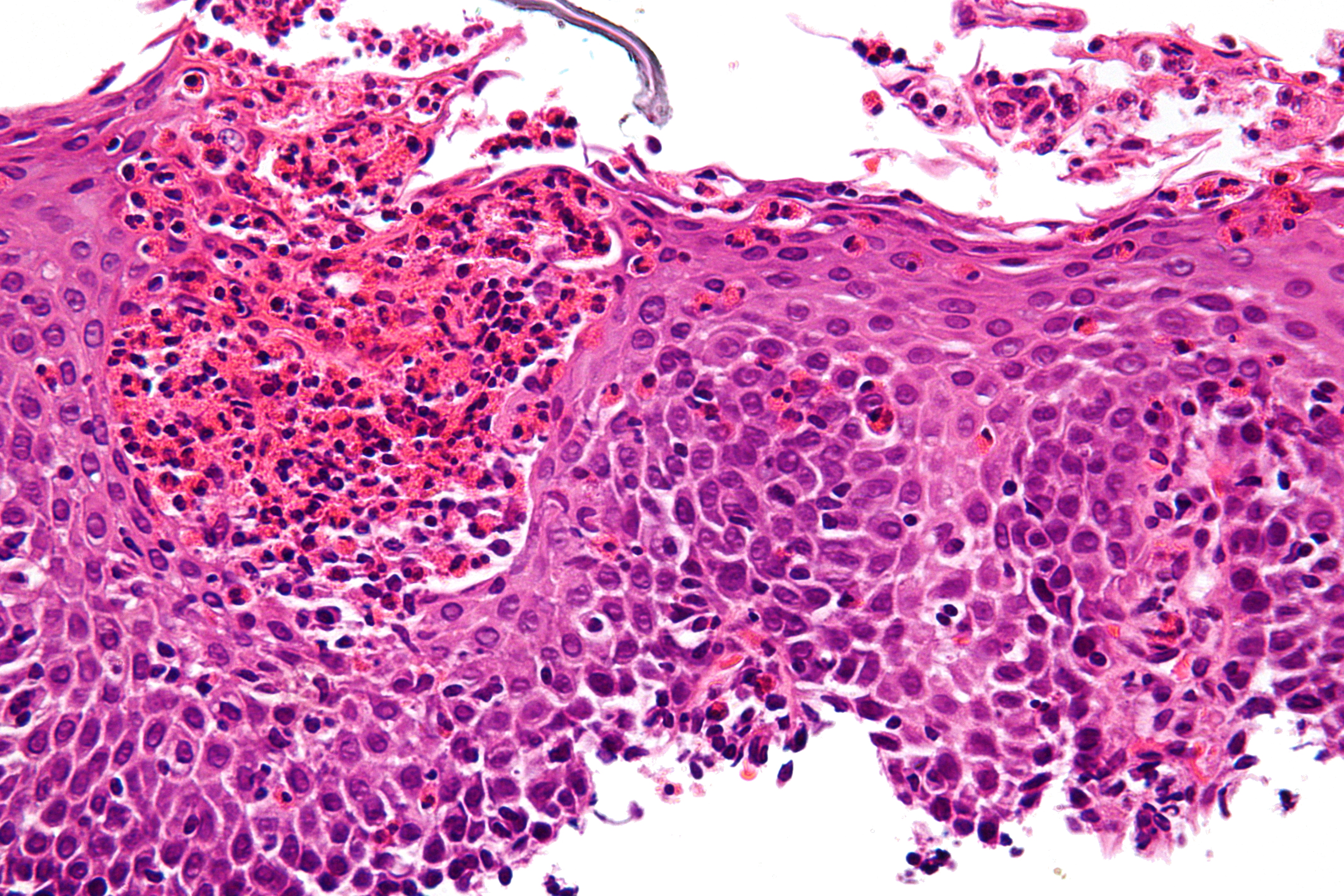 Eosinophilic esophagitis
Eosinophilic esophagitis
esophagus
The esophagus (American English), oesophagus (British English), or œsophagus (Œ, archaic spelling) (American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, see spelling difference) all ; : ((o)e)(œ)sophagi or ((o)e)(œ)sophaguses), c ...
. The esophagus is a tube composed of a mucosal
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is ...
lining, and longitudinal and circular smooth muscle
Smooth muscle is one of the three major types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being skeletal and cardiac muscle. It can also be found in invertebrates and is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. It is non- striated, so-called bec ...
fibers. It connects the pharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the human mouth, mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates ...
to the stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the upper gastrointestinal tract of Human, humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The Ancient Greek name for the stomach is ''gaster'' which is used as ''gastric'' in medical t ...
; swallowed food and liquids normally pass through it.
Esophagitis can be asymptomatic
Asymptomatic (or clinically silent) is an adjective categorising the medical conditions (i.e., injuries or diseases) that patients carry but without experiencing their symptoms, despite an explicit diagnosis (e.g., a positive medical test).
P ...
; or can cause epigastric
In anatomy, the epigastrium (or epigastric region) is the upper central region of the abdomen. It is located between the costal margins and the subcostal plane. Pain may be referred to the epigastrium from damage to structures derived from the fo ...
and/or substernal burning pain, especially when lying down or straining; and can make swallowing difficult (dysphagia
Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under " symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, in some contexts it is classified as a condition in its own right.
It may be a sensation that suggests difficulty in the passage of solids or l ...
). The most common cause of esophagitis is the reverse flow of acid from the stomach into the lower esophagus: gastroesophageal reflux disease
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is a chronic upper gastrointestinal disease in which stomach content persistently and regularly flows up into the esophagus, resulting in symptoms and/or ...
(GERD).
__TOC__
Signs and symptoms
The symptoms of esophagitis include: *Heartburn
Heartburn is a burning sensation felt behind the breastbone. It is a symptom that is commonly linked to acid reflux and is often triggered by food, particularly fatty, sugary, spicy, chocolate, citrus, onion-based and tomato-based products. Ly ...
– a burning sensation in the lower mid-chest
* Nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. It can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the throat.
Over 30 d ...
* Dysphagia
Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under " symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, in some contexts it is classified as a condition in its own right.
It may be a sensation that suggests difficulty in the passage of solids or l ...
– swallowing is painful, with difficulty passing or inability to pass food through the esophagus
* Vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis, puking and throwing up) is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteritis, pre ...
(emesis)
* Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues. Since the abdomen contains most of the body's vital organs, it can be an indicator of a wide variety of diseases. Given th ...
* Cough
A cough is a sudden expulsion of air through the large breathing passages which can help clear them of fluids, irritants, foreign particles and Microorganism, microbes. As a protective reflex, coughing can be repetitive with the cough reflex fol ...
Complications
If the disease remains untreated, it can cause scarring and discomfort in the esophagus. If the irritation is not allowed to heal, esophagitis can result in esophageal ulcers. Esophagitis can develop intoBarrett's esophagus
Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal ( metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells that line the lower part of the esophagus. The cells change from stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium, intersper ...
and can increase the risk of esophageal cancer.
Causes
Infectious esophagitis cannot be spread. However, infections can be spread by those who have infectious esophagitis. Esophagitis can develop due to many causes.GERD
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is a chronic upper gastrointestinal disease in which stomach content persistently and regularly flows up into the esophagus, resulting in symptoms and/or ...
is the most common cause of esophagitis because of the backflow of acid from the stomach, which can irritate the lining of the esophagus.
Other causes include:
* Medicines – Can cause esophageal damage that can lead to esophageal ulcers
** Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a Indication (medicine), therapeutic drug class which Analgesic, reduces pain, Anti-inflammatory, decreases inflammation, Antipyretic, decreases fever, and Antithrombotic, prevents bl ...
s (NSAIDS) – aspirin, naproxen sodium, and ibuprofen. Known to irritate the GI tract.
** Antibiotics – doxycycline
Doxycycline is a Broad-spectrum antibiotic, broad-spectrum antibiotic of the Tetracycline antibiotics, tetracycline class used in the treatment of infections caused by bacteria and certain parasites. It is used to treat pneumonia, bacterial p ...
and tetracycline
Tetracycline, sold under various brand names, is an antibiotic in the tetracyclines family of medications, used to treat a number of infections, including acne, cholera, brucellosis, plague, malaria, and syphilis. It is available in oral an ...
** Quinidine
Quinidine is a class I antiarrhythmic agent, class IA antiarrhythmic agent used to treat heart rhythm disturbances. It is a diastereomer of Antimalarial medication, antimalarial agent quinine, originally derived from the bark of the cinchona tre ...
** Bisphosphonate
Bisphosphonates are a class of drugs that prevent the loss of bone density, used to treat osteoporosis and similar diseases. They are the most commonly prescribed to treat osteoporosis.
Evidence shows that they reduce the risk of fracture in ...
s – used to treat osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to more porous bone, and consequent increase in Bone fracture, fracture risk.
It is the most common reason f ...
** Steroids
** Potassium chloride
** Vitamins and supplements (iron, vitamin C
Vitamin C (also known as ascorbic acid and ascorbate) is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits, berries and vegetables. It is also a generic prescription medication and in some countries is sold as a non-prescription di ...
, and potassium) – Supplements and minerals can be hard on the GI tract.
* Chemical injury by alkaline
In chemistry, an alkali (; from the Arabic word , ) is a basic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a soluble base has a pH greater than 7.0. The ...
or acidic
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis acid.
The first category of acids are the ...
solutions
* Physical injury resulting from nasogastric tube
Nasogastric intubation is a medical process involving the insertion of a plastic tube (nasogastric tube or NG tube) through the nose, down the esophagus, and down into the stomach. Orogastric intubation is a similar process involving the insertion ...
s.
* Alcohol use disorder
Alcoholism is the continued drinking of alcohol despite it causing problems. Some definitions require evidence of dependence and withdrawal. Problematic use of alcohol has been mentioned in the earliest historical records. The World Hea ...
– Can wear down the lining of the esophagus.
* Crohn's disease
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea, fever, abdominal distension, and weight loss. Complications outside of the ...
– a type of IBD that can cause esophagitis if it attacks the esophagus.
* Stress – Can cause higher levels of acid reflux
* Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy (RT, RTx, or XRT) is a therapy, treatment using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of treatment of cancer, cancer therapy to either kill or control the growth of malignancy, malignant cell (biology), ...
– Can affect the immune system.
* Allergies
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, are various conditions caused by hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include Allergic rhinitis, hay fever, Food allergy, food al ...
(food, inhalants) – Allergies can stimulate eosinophilic esophagitis.
* Infection – People with immunodeficiencies have a higher chance of developing esophagitis.
* Vomiting – Acid can irritate esophagus.
* Hernia
A hernia (: hernias or herniae, from Latin, meaning 'rupture') is the abnormal exit of tissue or an organ (anatomy), organ, such as the bowel, through the wall of the cavity in which it normally resides. The term is also used for the normal Devel ...
s – A hernia can poke through the diaphragm muscle and can inhibit stomach acid and food from draining quickly.
* Surgery
* Eosinophilic esophagitis
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is an allergic inflammatory condition of the esophagus that involves eosinophils, a type of white blood cell. In healthy individuals, the esophagus is typically devoid of eosinophils. In EoE, eosinophils migrate t ...
, a more chronic condition with a theorized autoimmune component
Mechanism
The esophagus is a muscular tube made of both voluntary and involuntary muscles. It is responsible forperistalsis
Peristalsis ( , ) is a type of intestinal motility, characterized by symmetry in biology#Radial symmetry, radially symmetrical contraction and relaxation of muscles that propagate in a wave down a tube, in an wikt:anterograde, anterograde dir ...
of food. It is about 8 inches long and passes through the diaphragm before entering the stomach. The esophagus is made up of three layers: from the inside out, they are the mucosa
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It ...
, submucosa
The submucosa (or tela submucosa) is a thin layer of tissue in various organs of the gastrointestinal, respiratory, and genitourinary tracts. It is the layer of dense irregular connective tissue that supports the mucosa (mucous membrane) an ...
, muscularis externa
The muscular layer (muscular coat, muscular fibers, muscularis propria, muscularis externa) is a region of muscle in many organs in the vertebrate body, adjacent to the submucosa. It is responsible for gut movement such as peristalsis. The Latin, ...
. The mucosa, the inner most layer and lining of the esophagus, is composed of stratified squamous epithelium
A stratified squamous epithelium consists of squamous (flattened) epithelial cells arranged in layers upon a basal membrane. Only one layer is in contact with the basement membrane; the other layers adhere to one another to maintain structural ...
, lamina propria
The lamina propria is a thin layer of connective tissue that forms part of the moist linings known as mucous membranes or mucosae, which line various tubes in the body, such as the respiratory tract, the gastrointestinal tract, and the urogenital ...
, and muscularis mucosae
The muscularis mucosae (or lamina muscularis mucosae) is a thin layer ( lamina) of muscle of the gastrointestinal tract, located outside the lamina propria, and separating it from the submucosa. It is present in a continuous fashion from the esop ...
. At the end of the esophagus is the lower esophageal sphincter, which normally prevents stomach acid from entering the esophagus.
If the sphincter is not sufficiently tight, it may allow acid to enter the esophagus, causing inflammation of one or more layers. Esophagitis may also occur if an infection is present, which may be due to bacteria, viruses, or fungi; or by diseases that affect the immune system.
Irritation can be caused by GERD, vomiting, surgery, medications, hernias, and radiation injury. Inflammation can cause the esophagus to narrow, which makes swallowing food difficult and may result in food bolus impaction.
Diagnosis
Esophagitis can be diagnosed by upper endoscopy, biopsy, upper GI series (or barium swallow), and laboratory tests. An upper endoscopy is a procedure to look at the esophagus by using an endoscope. While looking at the esophagus, the doctor is able to take a smallbiopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, an interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiology, interventional cardiologist. The process involves the extraction of sampling (medicine), sample ...
. The biopsy can be used to confirm inflammation of the esophagus.
An upper GI series uses a barium contrast, fluoroscopy
Fluoroscopy (), informally referred to as "fluoro", is an imaging technique that uses X-rays to obtain real-time moving images of the interior of an object. In its primary application of medical imaging, a fluoroscope () allows a surgeon to see t ...
, and an X-ray. During a barium X-ray, a solution with barium or pill is taken before getting an X-ray. The barium makes the organs more visible and can detect if there is any narrowing, inflammation, or other abnormalities that can be causing the disease. The upper GI series can be used to find the cause of GI symptoms. An esophagram is if only the throat and esophagus are looked at.
Laboratory tests can be done on biopsies removed from the esophagus and can help determine the cause of the esophagitis. Laboratory tests can help diagnose a fungal, viral, or bacterial infection. Scanning for white blood cells can help diagnose eosinophil esophagitis.
Some lifestyle indicators for this disease include stress, unhealthy eating, smoking, drinking, family history, allergies, and immunodeficiency.
Types
Reflux esophagitisGastroesophageal reflux disease
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is a chronic upper gastrointestinal disease in which stomach content persistently and regularly flows up into the esophagus, resulting in symptoms and/or ...
is usually assumed to be caused by inflammation from gastric acid
Gastric acid or stomach acid is the acidic component – hydrochloric acid – of gastric juice, produced by parietal cells in the gastric glands of the stomach lining. In humans, the pH is between one and three, much lower than most other a ...
reflux which irritates the mucosa
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It ...
. One study suggests that the pathogenesis of may be cytokine
Cytokines () are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling.
Cytokines are produced by a broad range of cells, including immune cells like macrophages, B cell, B lymphocytes, T cell, T lymphocytes ...
-mediated.
 Infectious esophagitis
Esophagitis happens due to a viral, fungal, parasitic or bacterial infection. More likely to happen to people who have an immunodeficiency. Types include:
Fungal
*
Infectious esophagitis
Esophagitis happens due to a viral, fungal, parasitic or bacterial infection. More likely to happen to people who have an immunodeficiency. Types include:
Fungal
* Candida
Candida, or Cándida (Spanish), may refer to:
Biology and medicine
* ''Candida'' (fungus), a genus of yeasts
** Candidiasis, an infection by ''Candida'' organisms
* Malvasia Candida, a variety of grape
Places
* Candida, Campania, a ''comu ...
( Esophageal candidiasis)
Viral
* Herpes simplex
Herpes simplex, often known simply as herpes, is a viral disease, viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus. Herpes infections are categorized by the area of the body that is infected. The two major types of herpes are Cold sore, ora ...
( Herpes esophagitis)
* Cytomegalovirus
''Cytomegalovirus'' (CMV) (from ''cyto-'' 'cell' via Greek - 'container' + 'big, megalo-' + -''virus'' via Latin 'poison') is a genus of viruses in the order '' Herpesvirales'', in the family '' Herpesviridae'', in the subfamily '' Betaherp ...
Drug-induced esophagitis
Damage to the esophagus due to medications. If the esophagus is not coated or if the medicine is not taken with enough liquid, it can damage the tissues.
 Eosinophilic esophagitis
Eosinophilic esophagitis
Eosinophilic esophagitis
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is an allergic inflammatory condition of the esophagus that involves eosinophils, a type of white blood cell. In healthy individuals, the esophagus is typically devoid of eosinophils. In EoE, eosinophils migrate t ...
is caused by a high concentration of eosinophils in the esophagus. The presence of eosinophils in the esophagus may be due to an allergen and is often correlated with GERD. The direction of cause and effect between inflammation and acid reflux is poorly established, with recent studies (in 2016) hinting that reflux does not cause inflammation. This esophagitis can be triggered by allergies to food or to inhaled allergens. This type is still poorly understood.
Lymphocytic esophagitis
Lymphocytic esophagitis is a rare and poorly understood entity associated with an increased amount of lymphocytes
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include T cells (for cell-mediated and cytotoxic adaptive immunity), B cells (for humoral, antibody-driven adaptive immunity), and ...
in the lining of the esophagus. It was first described in 2006. Disease associations may include Crohn's disease
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea, fever, abdominal distension, and weight loss. Complications outside of the ...
, gastroesophageal reflux disease
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is a chronic upper gastrointestinal disease in which stomach content persistently and regularly flows up into the esophagus, resulting in symptoms and/or ...
and coeliac disease
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine. Patients develop intolerance to gluten, which is present in foods such as wheat, rye, spelt ...
. It causes similar changes on endoscopy as eosinophilic esophagitis
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is an allergic inflammatory condition of the esophagus that involves eosinophils, a type of white blood cell. In healthy individuals, the esophagus is typically devoid of eosinophils. In EoE, eosinophils migrate t ...
including esophageal rings, narrow-lumen esophagus, and linear furrows.
Caustic esophagitis
Caustic esophagitis is the damage of tissue via chemical origin. This occasionally occurs through occupational exposure (via breathing of fumes that mix into the saliva which is then swallowed) or through pica.
By severity
The severity of reflux esophagitis is commonly classified into four grades according to the ''Los Angeles Classification'':Prevention
Since there can be many causes underlying esophagitis, it is important to try to find the cause to help to prevent esophagitis. To prevent reflux esophagitis, avoid acidic foods, caffeine, eating before going to bed, alcohol, fatty meals, and smoking. To prevent drug-induced esophagitis, drink plenty of liquids when taking medicines, take an alternative drug, and do not take medicines while lying down, before sleeping, or too many at one time. Esophagitis is more prevalent in adults and does not discriminate.Treatment
Lifestyle changes
Losing weight, stop smoking and alcohol, lowering stress, avoid sleeping/lying down after eating, raising the head of the bed, taking medicines correctly, avoiding certain medications, and avoiding foods that cause the reflux that might be causing the esophagitis.Medications
Antacids
To treat reflux esophagitis, over the counter antacids, medications that reduce acid production ( H-2 receptor blockers), andproton pump inhibitors
Proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs) are a class of medications that cause a profound and prolonged reduction of gastric acid, stomach acid production. They do so by irreversibly inhibiting the stomach's H+/K+ ATPase, H+/K+ ATPase proton pump. The body ...
are recommended to help block acid production and to let the esophagus heal. Some prescription medications to treat reflux esophagitis include higher dose H-2 receptor blockers, proton pump inhibitors, and prokinetics
A prokinetic agent (also prokineticin, gastroprokinetic agent, gastrokinetic agent or propulsive) is a type of drug which enhances gastrointestinal motility by increasing the frequency or strength of contractions, but without disrupting their rhyt ...
, which help with the emptying of the stomach. However prokinetics are no longer licensed for GERD because their evidence of efficacy is poor, and following a safety review, licensed use of domperidone and metoclopramide is now restricted to short-term use in nausea and vomiting only.
For subtypes
To treat eosinophilic esophagitis, avoiding any allergens that may be stimulating the eosinophils is recommended. As for medications, proton pump inhibitors and steroids can be prescribed. Steroids that are used to treat asthma can be swallowed to treat eosinophil esophagitis due to nonfood allergens. The removal of food allergens from the diet is included to help treat eosinophilic esophagitis. For infectious esophagitis, medicine is prescribed based on what type of infection is causing the esophagitis. These medicines are prescribed to treat bacterial, fungal, viral, and/or parasitic infections.Procedures
* Anendoscopy
An endoscopy is a procedure used in medicine to look inside the body. The endoscopy procedure uses an endoscope to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. Unlike many other medical imaging techniques, endoscopes are insert ...
can be used to remove ill fragments.
* Surgery can be done to remove the damaged part of the esophagus.
* For reflux esophagitis, a fundoplication can be done to help strengthen the lower esophageal sphincter from allowing backflow of the stomach into the esophagus.
* For esophageal stricture, a gastroenterologist can perform a dilation of the esophagus.
As of 2020 evidence for magnetic sphincter augmentation is poor.
Prognosis
The prognosis for a person with esophagitis depends on the underlying causes and conditions. If a patient has a more serious underlying cause such as a digestive system or immune system issue, it may be more difficult to treat. Normally, the prognosis would be good with no serious illnesses. If there are more causes than one, the prognosis could move to fair.Terminology
The term is from Greek οἰσοφάγος "gullet" and -itis "inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
".
References
External links
{{Authority control Inflammations Esophagus disorders Acute pain