English pattern on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
French-suited playing cards or French-suited cards are cards that use the French suits of (clovers or clubs ), (tiles or diamonds ), (hearts ), and (pikes or spades ). Each suit contains three or four face/court cards. In a 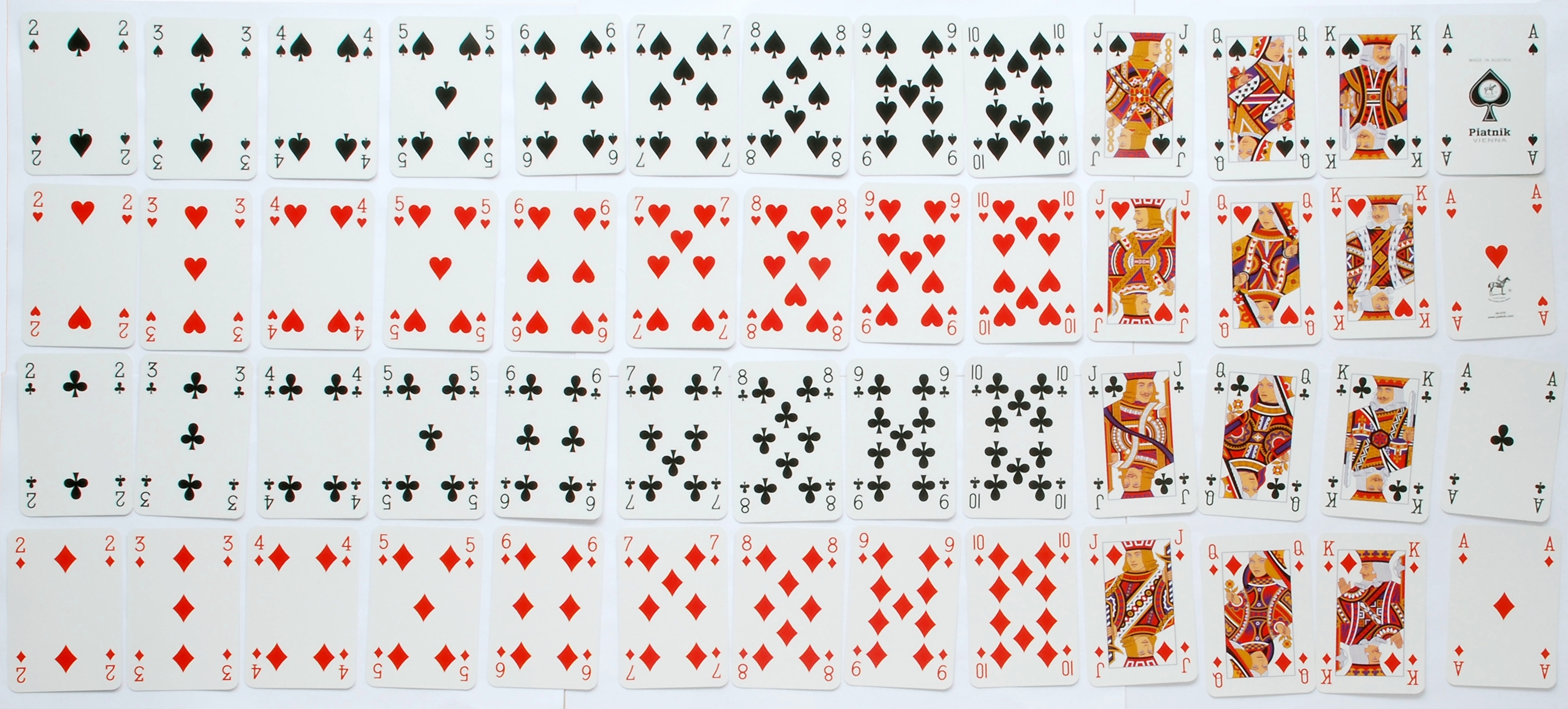
standard 52-card deck
The standard 52-card deck of French-suited playing cards is the most common pack of playing cards used today. The main feature of most playing card decks that empower their use in diverse games and other activities is their double-sided design, w ...
these are the ( knave or jack), the ( lady or queen), and the (king
King is a royal title given to a male monarch. A king is an Absolute monarchy, absolute monarch if he holds unrestricted Government, governmental power or exercises full sovereignty over a nation. Conversely, he is a Constitutional monarchy, ...
). In addition, in Tarot packs, there is a (knight
A knight is a person granted an honorary title of a knighthood by a head of state (including the pope) or representative for service to the monarch, the church, or the country, especially in a military capacity.
The concept of a knighthood ...
) ranking between the queen and the jack. Aside from these aspects, decks can include a wide variety of regional and national patterns, which often have different deck sizes. In comparison to Spanish, Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, a Romance ethnic group related to or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance languag ...
, German, and Swiss playing cards, French cards are the most widespread due to the geopolitical, commercial, and cultural influence of France, the United Kingdom, and the United States in the 19th and 20th centuries. Other reasons for their popularity were the simplicity of the suit insignia, which simplifies mass production, and the popularity of whist and contract bridge
Contract bridge, or simply bridge, is a trick-taking game, trick-taking card game using a standard 52-card deck. In its basic format, it is played by four players in two Team game, competing partnerships, with partners sitting opposite each othe ...
. The English pattern of French-suited cards is so widespread that it is also known as the International or Anglo-American pattern.

History
Playing cards arrived in Europe from Mamluk Egypt around 1370 and were already reported inFrance
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
in 1377. The French suit insignia was derived from German suits around 1480. Between the transition from the suit of bells to tiles there was a suit of crescents.
One of the most distinguishing features of the French cards is the queen. Mamluk cards and their derivatives, the Latin-suited and German-suited cards, all have three male face cards. Queens began appearing in Italian tarot
Tarot (, first known as ''trionfi (cards), trionfi'' and later as ''tarocchi'' or ''tarocks'') is a set of playing cards used in tarot games and in fortune-telling or divination. From at least the mid-15th century, the tarot was used to play t ...
decks in the mid-15th century and some German decks replaced two kings with queens. While other decks abandoned the queen in non-tarot decks, the French kept them and dropped the knight
A knight is a person granted an honorary title of a knighthood by a head of state (including the pope) or representative for service to the monarch, the church, or the country, especially in a military capacity.
The concept of a knighthood ...
as the middle face card. Face card design was heavily influenced by Spanish cards that used to circulate in France. One of the most obvious traits inherited from Spain are the standing kings; kings from Italian, Portuguese, or Germanic cards are seated. Spanish-suited cards are still used in France, mostly in Northern Catalonia
Northern Catalonia, North Catalonia or French Catalonia is the Catalan language, Catalan-speaking and cultural territory ceded to France by Spain through the signing of the Treaty of the Pyrenees in 1659 in exchange for France's effective renu ...
, and Brittany
Brittany ( ) is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the north-west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica in Roman Gaul. It became an Kingdom of Brittany, independent kingdom and then a Duch ...
and the Vendée
Vendée () is a department in the Pays de la Loire region in Western France, on the Atlantic coast. In 2019, it had a population of 685,442.Aluette cards.
In the 19th century, corner indices and rounded corners were added and cards became reversible, relieving players from having to flip face cards right-side up. The index for aces and face cards usually follow the local language but most decks of the Paris pattern use the numeral "1" for aces.
File:15thCenturySpanishCardDeck.jpg, Deck celebrating the
 The North-German pattern was created in Stralsund from a Hamburg derivative. It is familiarly known as the Berlin pattern, although this name arose from a misunderstanding about the origin of the cards which were formerly labelled as ''Berliner Spielkarten'' based on a finishing process used by that company. The crownless queens' hairstyles reflect the Biedermeier fashions of the day. They are usually in decks of 32 cards with the twos to sixes missing since skat, Germany's most popular card game, does not require a full deck. Decks of 36 cards (with the sixes) are for jass and tapp, a game played in
The North-German pattern was created in Stralsund from a Hamburg derivative. It is familiarly known as the Berlin pattern, although this name arose from a misunderstanding about the origin of the cards which were formerly labelled as ''Berliner Spielkarten'' based on a finishing process used by that company. The crownless queens' hairstyles reflect the Biedermeier fashions of the day. They are usually in decks of 32 cards with the twos to sixes missing since skat, Germany's most popular card game, does not require a full deck. Decks of 36 cards (with the sixes) are for jass and tapp, a game played in
 Around 1870, Dondorf of
Around 1870, Dondorf of
''Rococo Playing Cards''
at wopc.co.uk. Retrieved 13 April 2022.
union of Brittany and France
The union of the Duchy of Brittany with the Crown of France was the culmination of a political process begun at the end of the 15th century in the wake of the Mad War. It resulted in the Edict of Union of 13 August 1532 and the incorporation of ...
with Spanish suits but has queens instead of knights (Antoine de Logiriera of Toulouse, ).
File:French playing cards with suit of crescents.jpg, A transitional deck with suits of hearts and crescents (François Clerc of Lyon, late 15th century)
File:Kings-comparison.jpg, French Rouen pattern on the left, Spanish Toledo pattern on the right
Current standard patterns
The French suited pack has spawned many regional variations known as standard patterns based on their artwork and deck size. The Paris pattern was heavily exported throughout continental Europe which is why most French-suited patterns share a similar appearance. The English pattern, based on the extinct Rouennais pattern, is the most well known pattern in the world. It is also called the International or Anglo-American pattern. Patterns do not factor in Jokers, which came about in the early 20th century. Almost all 52-card packs produced in the present will contain at least two jokers, sometimes more. In Germany, packs produced for the game of Zwicker have six jokers.Paris pattern
The Paris pattern came to dominate in France around 1780 and became known as the . From the 19th century to 1945, the appearance of the cards used for domestic consumption was regulated by the French government. All cards were produced on watermarked paper made by the state to show payment of thestamp tax
Stamp duty is a duty (tax), tax that is levied on single property purchases or documents (including, historically, the majority of legal documents such as cheques, receipts, military commissions, marriage licences and land transactions). Histo ...
. The most common deck sold in France is the 32-card deck with the 2 to 6 removed and 1s as the index for aces. 52-card packs are also popular. The French have a unique habit of associating their face cards with historical or mythical personages which survives only in the ''portrait officiel''.
Belgian-Genoese pattern
The Belgian-Genoese pattern is very similar to its Parisian parent and is basically an export version not subject to France's domestic stamp tax. Hence they lack the usual French court card names such as Alexander, Judith and Lancelot. Other differences from the ''portrait officiel'' are that: the jack of clubs has a triangular shield bearing the coat of arms of the formerSpanish Netherlands
The Spanish Netherlands (; ; ; ) (historically in Spanish: , the name "Flanders" was used as a '' pars pro toto'') was the Habsburg Netherlands ruled by the Spanish branch of the Habsburgs from 1556 to 1714. They were a collection of States of t ...
(this is the main distinguishing feature); blue is usually replaced with green in the portraits and the diagonal dividing line lacks the beads. When the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
relaxed the ban against playing cards, Belgian type cards flooded their territory and are now found throughout the Balkans, North Africa, and the Middle East. They are also commonly found in France's former colonies. Within Belgium, the Francophone Walloons
Walloons ( ; ; ) are a Gallo-Romance languages, Gallo-Romance ethnic group native to Wallonia and the immediate adjacent regions of Flanders, France, Germany, Luxembourg and the Netherlands. Walloons primarily speak ''langues d'oïl'' such as B ...
are the primary users of this pattern, while the Flemish prefer the Dutch pattern. This is the second most common pattern in the world after the English pattern. Belgian packs come in either 32 or 52 cards as they do in France. It was named the Belgian-Genoese pattern because of its popularity in both places and is the national pattern of Belgium.
Genoese type cards are identical to Belgian ones and often lack corner indices. They come in 36 (lacking 2s to 5s), 40 (lacking 8s to 10s) or 52-card packs.
Piedmontese pattern
The Piedmontese pattern is similar to the Genoese packs but its face cards have a horizontal instead of diagonal dividing line and the aces are found in a decorative garland. They also come in the same number of cards as Genoese ones. The Piedmontese pattern was once used in neighboringSavoy
Savoy (; ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps. Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south and west and to the Aosta Vall ...
as both were previously united until France annexed the latter in 1860. A 78-card tarot version of the Piedmontese pattern, complete with knights, the fool, a suit of trumps depicting flowers, and corner indices, was printed in 1902 for Savoyard players. It was discontinued some time after 1910 but reproductions have been in print since 1984. The Chambéry
Chambéry (, , ; Franco-Provençal, Arpitan: ''Chambèri'') is the Prefectures in France, prefecture and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of the Savoie Departments of France, department in the southeastern ...
rules that come with the deck are similar to Piedmontese tarot games but the ace ranked between the jack and the 10 like in Triomphe
Triomphe (French for triumph), once known as French ruff, is a card game dating from the late 15th century. It most likely originated in France or Spain (as triunfo) and later spread to the rest of Europe. When the game arrived in Italy, it shared ...
. Another playing card deck named after Piedmont is the Italian-suited Tarocco Piemontese, used in Tarot card games
Tarot games are card games played with tarot packs designed for card play and which have a permanent trump suit alongside the usual four card suits. The games and packs which English-speakers call by the French name tarot are called tarocchi ...
.
Bavarian derivatives
A Parisian variant appeared in Bavaria in the mid-18th century where the king of diamonds wore aturban
A turban (from Persian language, Persian دولبند, ''dolband''; via Middle French ''turbant'') is a type of headwear based on cloth winding. Featuring many variations, it is worn as customary headwear by people of various cultures. Commun ...
. This originates from the German-suited Old Bavarian pattern. The king of spades, who represents David in the older decks, does not hold a harp. This group is closely associated with animal tarots.
= Russian pattern
= The Russian pattern created during the early 19th-century is based on a Baltic version of a Bavarian derivative. The current appearance was finalized by Adolf Charlemagne. It usually contains 52 or 36 cards, the latter lacking ranks 2 to 5. The stripped deck is used to play Durak. They can be found in many countries that were once part of theRussian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
or Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
.
= Adler Cego
= Adler-Cego is the last remaining animal tarot and is used in Germany'sBlack Forest
The Black Forest ( ) is a large forested mountain range in the States of Germany, state of Baden-Württemberg in southwest Germany, bounded by the Rhine Valley to the west and south and close to the borders with France and Switzerland. It is th ...
to play Cego. The courts are based on a Frankfurt version of a Bavarian derivative. It is sold with 54 cards; the 5 to 10 of the red suits and the 1 to 6 of the black suits are removed. Real and fictional animals are displayed on the trump suit. Trumps have a pink panel in each end with an Arabic numeral to show its rank.
= Industrie und Glück
= The Industrie und Glück ("Diligence and Fortune") tarock deck of Central Europe uses Roman numerals for the trumps. It is organized in the same manner as the Adler-Cego decks. Its trumps feature a newer pattern of more mundane scenes, such as depictions of rural life, than the traditional allegorical motifs found in Italian tarocchi decks. The turban wearing king is now in the suit of spades.Hamburg pattern and derivatives
French-suited cards are popular in Central Europe and compete very well against local German-suited playing cards.Hamburg
Hamburg (, ; ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg,. is the List of cities in Germany by population, second-largest city in Germany after Berlin and List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, 7th-lar ...
was once a major card-producing hub where makers began revising the Paris pattern to create the Hamburg pattern. Early examples were made by Suhr (1814–28) in Hamburg itself, while other manufacturers of the pattern were based elsewhere in the German Empire, in Austria, Belgium, France, Sweden and Switzerland. The Hamburg cards generated a family of similar patterns, all of which have the King of Spades holding David's harp, with the other hand holding a sceptre.
 The North-German pattern was created in Stralsund from a Hamburg derivative. It is familiarly known as the Berlin pattern, although this name arose from a misunderstanding about the origin of the cards which were formerly labelled as ''Berliner Spielkarten'' based on a finishing process used by that company. The crownless queens' hairstyles reflect the Biedermeier fashions of the day. They are usually in decks of 32 cards with the twos to sixes missing since skat, Germany's most popular card game, does not require a full deck. Decks of 36 cards (with the sixes) are for jass and tapp, a game played in
The North-German pattern was created in Stralsund from a Hamburg derivative. It is familiarly known as the Berlin pattern, although this name arose from a misunderstanding about the origin of the cards which were formerly labelled as ''Berliner Spielkarten'' based on a finishing process used by that company. The crownless queens' hairstyles reflect the Biedermeier fashions of the day. They are usually in decks of 32 cards with the twos to sixes missing since skat, Germany's most popular card game, does not require a full deck. Decks of 36 cards (with the sixes) are for jass and tapp, a game played in Baden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg ( ; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a states of Germany, German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million i ...
. Decks of 52 cards usually include three jokers but Zwickern decks have six jokers.
The French-Swiss pattern shares the same descent from the North-German pattern's Hamburg parent but their most distinguishing characteristic is that instead of having corner indices, white Arabic numerals are found within the pips closest to the corner. French-Swiss cards comes only in decks of 36 with no ranks from two to five.
The Modern Portuguese pattern is a Parisian derivative from Germany. When it arrived in Portugal, the kings and jacks in hearts and diamonds swapped suits. The composition consists of 52 cards or until recently 40 cards. The latter had an unusual ranking (ace, king, jack, queen, eight, six–two). The jack ranking higher than the queen comes from the older Portuguese-suited games where a female knave was outranked by the knight
A knight is a person granted an honorary title of a knighthood by a head of state (including the pope) or representative for service to the monarch, the church, or the country, especially in a military capacity.
The concept of a knighthood ...
. They also use French-language indices.
The Dutch pattern originates from Germany and shares the same parent as the Modern Portuguese pattern but with different queens, and has been produced for the Netherlands by Belgian card makers since the 19th century. It has rarely been produced in the Netherlands itself. Its most distinguishing feature are scenic aces. Also found in Flanders
Flanders ( or ; ) is the Dutch language, Dutch-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, la ...
, they come in decks of 32 (no twos to sixes) or 52 cards.
The Trente et Quarante pattern is named after the game it is associated with. Unlike other patterns, it is usually found only in casinos. Although of German origin, this pattern is now produced only in Italy. They consist of 52 cards and no indices.
Dondorf Rhineland pattern
 Around 1870, Dondorf of
Around 1870, Dondorf of Frankfurt
Frankfurt am Main () is the most populous city in the States of Germany, German state of Hesse. Its 773,068 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the List of cities in Germany by population, fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located in the forela ...
produced the Rhineland
The Rhineland ( ; ; ; ) is a loosely defined area of Western Germany along the Rhine, chiefly Middle Rhine, its middle section. It is the main industrial heartland of Germany because of its many factories, and it has historic ties to the Holy ...
pattern. The kings have very thick beards. They have fallen out of popularity in Germany but are very common in Poland, Austria, the Netherlands, Denmark, and the Baltic states
The Baltic states or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term encompassing Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, and the OECD. The three sovereign states on the eastern co ...
. They come in decks of 24 (no 2s to 8s), 32 (no 2s to 6s), or 52 cards, the latter of which may have up to three jokers in some countries.
Nordic pattern
In 1895, Dondorf produced a deck on behalf of Adolph Wulff of Denmark. The king of diamonds holds an orb while the other kings hold scepters. Many of the court designs were altered or swapped for the Swedish market. Presently, this pattern is printed only by Piatnik of Austria for export to Finland, which is why it is also known as the Finnish pattern. It is an amalgam of the original Dondorf and revised Swedish designs with the court indices numbered from 11 to 13. It comes in 52-card decks with three jokers.Bourgeois Tarot
The Bourgeois Tarot was designed by C.L. Wüst of Frankfurt in the mid-19th century. It is popular in Francophone Europe and Quebec and is also used in Denmark to play tarot games that require the full 78-card deck. Like theIndustrie und Glück
Industry may refer to:
Economics
* Industry (economics), a generally categorized branch of economic activity
* Industry (manufacturing), a specific branch of economic activity, typically in factories with machinery
* The wider industrial sector ...
, the trumps depict genre scenes but modern editions use Arabic numerals instead of Roman ones. A 54-card version with different trump designs is used in Baden
Baden (; ) is a historical territory in southern Germany. In earlier times it was considered to be on both sides of the Upper Rhine, but since the Napoleonic Wars, it has been considered only East of the Rhine.
History
The margraves of Ba ...
to play Cego.
Modern Swedish pattern
Swedes used to use Bavarian-derived patterns. In the early 20th century, the firm Öberg & Son invented a new pattern unrelated to the old ones. This pattern has spread to neighboring Finland. The clothing for the figures in the court cards are color coordinated; green for spades, red for hearts, purple for clubs, and blue for diamonds. They are used in the standard 52-card format.English pattern
Card makers fromRouen
Rouen (, ; or ) is a city on the River Seine, in northwestern France. It is in the prefecture of Regions of France, region of Normandy (administrative region), Normandy and the Departments of France, department of Seine-Maritime. Formerly one ...
began exporting to England around 1480. According to David Parlett
David Parlett (born 18 May 1939 in London) is a games scholar, historian, and translator from South London, who has studied both card games and board games. He is the president of the British Skat Association.
Life
David Sidney Parlett was bo ...
, Latin-suited cards must have already been circulating in England since there is evidence of playing cards there from at least the 1450s and French suits were invented sometime after 1470. This would then explain why the English renamed French suits to the Latin ones with which they were familiar. Hence the clovers were called clubs and pikes were named after the swords (''spade''). The English started producing their own cards a century later. In 1628, the importation of foreign playing cards was banned to protect local manufacturers. English cardmakers produced lower-quality cards than their continental counterparts, leading to the loss of detail from the Rouennais pattern. The English pattern is the result of Charles Goodall and Son's reworking of the old Rouen pattern during the 19th century. The majority of decks sold in this pattern is the 52-card deck. One deck invented in the United States but more commonly found in Australia and New Zealand contains 11s, 12s, and red 13s to play the six-handed version of the Euchre
Euchre or eucre ( ) is a trick-taking game, trick-taking card game played in Canada, Great Britain, New Zealand, Upstate New York, and the Midwestern United States. It is played with a deck of 24, 25, 28, or 32 standard playing cards. There are no ...
variant 500. In the late nineteenth century, they were also used for variants of draw poker
Draw poker is any poker variant in which each player is dealt a complete hand before the first betting round, and then develops the hand for later rounds by replacing, or "drawing", cards.
The descriptions below assume the reader is familiar w ...
and royal cassino. Decks marketed for Canasta
Canasta (; Spanish language, Spanish for "basket") is a card game of the rummy family of games believed to be a variant of 500 rum. Although many variations exist for two, three, five or six players, it is most commonly played by four in two par ...
often have card point values printed on the cards.
Vienna pattern
Lyon
Lyon (Franco-Provençal: ''Liyon'') is a city in France. It is located at the confluence of the rivers Rhône and Saône, to the northwest of the French Alps, southeast of Paris, north of Marseille, southwest of Geneva, Switzerland, north ...
was a major card exporter to German-speaking countries from the late 16th through the 18th centuries. While the Lyonnais pattern died out in most places, it survived in Austria and the Czech Republic and its modern incarnation is the Vienna pattern. Five types are recorded by the International Playing Card Society, all of them double-headed. Type A, also called the 'Large Crown' version of the pattern, emerged in the early 1800s and was based on the double-headed, Lyons export pattern, but with the crowns of the kings truncated by the frames of the cards and no discernible dividing line. The court figures are highly ornamented. Today's version by Piatnik is based on an 1885 Type A design by Neumayer.
Type C was the earliest of three Vienna pattern types that were around at the turn of the 19th century. It originated in Sopron
Sopron (; , ) is a city in Hungary on the Austrian border, near Lake Neusiedl/Lake Fertő.
History
Ancient times-13th century
In the Iron Age a hilltop settlement with a burial ground existed in the neighbourhood of Sopron-Várhely.
When ...
and Saxony
Saxony, officially the Free State of Saxony, is a landlocked state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, and Bavaria, as well as the countries of Poland and the Czech Republic. Its capital is Dresden, and ...
and went on to become the standard pattern in Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historic ...
before giving way in the mid-19th century to Type D, also called the 'Small Crown' version of the Vienna pattern, since the crowns of the kings are visible in their entirety within the card frame.
Type E appeared in the 1860s and, again, the crowns are partially cut off by the frames of the cards. It appears to have died out in the 1960s.
Today the Vienna pattern in Austria comes in pack of 24 (lacking the 2s to 8s), 32 (lacking 2s to 6s), or 52 cards, the last with corner indices and three jokers.
Lombard pattern
The Lombard or Milanese pattern come in 40-card decks that is missing the 8s, 9s, and 10s and lack corner indices. The Lombard decks exported toSwiss Italian
The Italian language in Italian Switzerland or Swiss Italian (, ) is the variety of the Italian language taught in the Italian-speaking area of Switzerland. While this variety is mainly spoken in the canton of Ticino and in the southern part ...
regions contain corner indices and also labels the ranks of the face cards. It is probably derived from the Lyonnais pattern and its offshoot, the extinct Provence pattern.
Tuscan pattern
The Tuscan or Florentine pattern, dating from the mid-19th century, is the only French-suited deck that is not reversible in the present. Cards measure 58 × 88 mm but the ''Toscane Grandi'' by Modiano are 67 × 101 mm large. It has the same composition of cards as the Lombard pattern. There was another pattern called "Tuscan" but it has ceased printing since the 1980s.Baronesse pattern
Dondorf of Frankfurt produced this pattern around 1900 and, today, it is used inPatience
or forbearance, is the ability to endure difficult or undesired long-term circumstances. Patience involves perseverance or tolerance in the face of delay, provocation, or stress without responding negatively, such as reacting with disrespect ...
decks by many companies worldwide. The court cards are dressed in rococo
Rococo, less commonly Roccoco ( , ; or ), also known as Late Baroque, is an exceptionally ornamental and dramatic style of architecture, art and decoration which combines asymmetry, scrolling curves, gilding, white and pastel colours, sculpte ...
period costumes and wear powdered wigs. The Kings are crowned and carry state regalia or, in the case of the King of Hearts, a pair of spectacles. The Queens, also crowned, sport jewellery; the Queen of Spades coquettishly brandishes a folding fan and the Queen of Diamonds a peacock feather fan. The Jacks are young gentlemen with tricorn hats. The Jack of Hearts carries a sword and the Jack of Spades a cane. The backs usually have ornate, often floral, designs. They were made by ASS Altenburger (as "Baronesse"), by VEB Altenburger (as "Rokoko") and Coeur in the past. The earliest examples had no corner indices; they appeared from about 1906 onwards.
Since 1914, Piatnik have produced a derivative pattern for several of their patience packs that are referred to as Rococo playing cards.at wopc.co.uk. Retrieved 13 April 2022.
See also
*Standard 52-card deck
The standard 52-card deck of French-suited playing cards is the most common pack of playing cards used today. The main feature of most playing card decks that empower their use in diverse games and other activities is their double-sided design, w ...
* Playing cards in Unicode
Play is a range of Motivation#Intrinsic and extrinsic, intrinsically motivated activities done for recreation. Play is commonly associated with children and juvenile-level activities, but may be engaged in at any life stage, and among other high ...
Notes
References
Sources
* * {{Playing card decks French card games Playing card suit systems