emphysema on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Emphysema is any air-filled enlargement in the body's tissues. Most commonly emphysema refers to the permanent enlargement of air spaces ( alveoli) in the
 Emphysema is a respiratory disease of the
Emphysema is a respiratory disease of the
 Centrilobular emphysema, also called centriacinar emphysema, affects the centre of a
Centrilobular emphysema, also called centriacinar emphysema, affects the centre of a
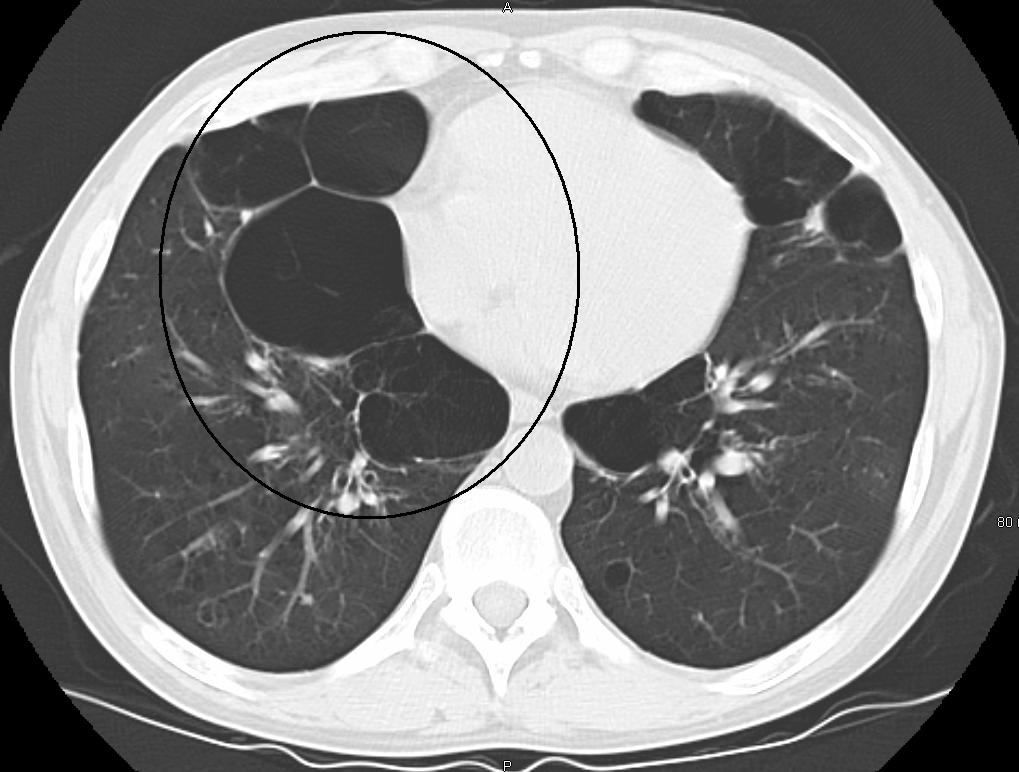 When the subpleural bullae are significant, the emphysema is called bullous emphysema. Bullae can become extensive and combine to form giant bullae. These can be large enough to take up a third of a hemithorax, compress the lung parenchyma, and cause displacement. The emphysema is now termed giant bullous emphysema, more commonly called vanishing lung syndrome due to the compressed parenchyma. A bleb or bulla may sometimes rupture and cause a
When the subpleural bullae are significant, the emphysema is called bullous emphysema. Bullae can become extensive and combine to form giant bullae. These can be large enough to take up a third of a hemithorax, compress the lung parenchyma, and cause displacement. The emphysema is now termed giant bullous emphysema, more commonly called vanishing lung syndrome due to the compressed parenchyma. A bleb or bulla may sometimes rupture and cause a
 Focal emphysema is a localized region of emphysema in the lung that is larger than alveoli, and often associated with
Focal emphysema is a localized region of emphysema in the lung that is larger than alveoli, and often associated with
 The terms ''emphysema'' and ''chronic bronchitis'' were formally defined in 1959 at the CIBA guest symposium, and in 1962 at the
The terms ''emphysema'' and ''chronic bronchitis'' were formally defined in 1959 at the CIBA guest symposium, and in 1962 at the
lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their ...
s, and is also known as pulmonary emphysema.
Emphysema is a lower respiratory tract
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of conducting air to the alveoli for the purposes of gas exchange in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respirator ...
disease, characterised by enlarged air-filled spaces in the lungs
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory syste ...
, that can vary in size and may be very large. The spaces are caused by the breakdown of the walls
Walls may refer to:
*The plural of wall, a structure
* Walls (surname), a list of notable people with the surname
Places
* Walls, Louisiana, United States
* Walls, Mississippi, United States
*Walls, Ontario
Perry is a township (Canada), ...
of the alveoli, which replace the spongy lung tissue. This reduces the total alveolar surface available for gas exchange
Gas exchange is the physical process by which gases move passively by diffusion across a surface. For example, this surface might be the air/water interface of a water body, the surface of a gas bubble in a liquid, a gas-permeable membrane, or a b ...
leading to a reduction in oxygen supply for the blood. Emphysema usually affects the middle age
Middle age (or middle adulthood) is the age range of the years halfway between childhood and old age. The exact range is subject to public debate, but the term is commonly used to denote the age range from 45 to 65 years.
Overall
This time span ...
d or older population because it takes time to develop with the effects of tobacco smoking
Tobacco smoking is the practice of burning tobacco and ingesting the resulting smoke. The smoke may be inhaled, as is done with cigarettes, or released from the mouth, as is generally done with pipes and cigars. The practice is believed to hav ...
and other risk factors. Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (A1AD or AATD) is a genetic disorder that may result in lung disease or liver disease. Onset of lung problems is typically between 20 and 50 years of age. This may result in shortness of breath, wheezing, or an inc ...
is a genetic risk factor that may lead to the condition presenting earlier.
When associated with significant airflow limitation, emphysema is a major subtype of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of progressive lung disease characterized by chronic respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. GOLD defines COPD as a heterogeneous lung condition characterized by chronic respiratory s ...
(COPD), a progressive lung disease characterized by long-term breathing problems and poor airflow. Without COPD, the finding of emphysema on a CT lung scan still confers a higher mortality risk in tobacco smokers. In 2016 in the United States there were 6,977 deaths from emphysema – 2.2 per 100,000 people. Globally it accounts for 5% of all deaths. A 2018 review of work on the effects of tobacco and cannabis smoking found that a possibly cumulative toxic effect could be a risk factor for developing emphysema and spontaneous pneumothorax.
There are four types of emphysema, three of which are related to the anatomy of the lobules of the lung – centrilobular or centriacinar, panlobular or panacinar, and paraseptal or distal acinar emphysema – and are not associated with fibrosis
Fibrosis, also known as fibrotic scarring, is the development of fibrous connective tissue in response to an injury. Fibrosis can be a normal connective tissue deposition or excessive tissue deposition caused by a disease.
Repeated injuries, ch ...
(scarring). The fourth type is known as paracicatricial emphysema or irregular emphysema that involves the acinus
An acinus (; : acini; adjective, acinar or acinous) refers to any cluster of cells that resembles a many-lobed "berry", such as a raspberry ('' acinus'' is Latin for "berry"). The berry-shaped termination of an exocrine gland, where the secr ...
irregularly and is associated with fibrosis. Though the different types can be seen on imaging
Imaging is the representation or reproduction of an object's form; especially a visual representation (i.e., the formation of an image).
Imaging technology is the application of materials and methods to create, preserve, or duplicate images.
...
they are not well-defined clinically. There are also a number of associated conditions, including bullous emphysema, focal emphysema, and Ritalin lung. Only the first two types of emphysema – centrilobular and panlobular – are associated with significant airflow obstruction, with that of centrilobular emphysema around 20 times more common than panlobular. Centrilobular emphysema is the only type associated with smoking
Smoking is a practice in which a substance is combusted, and the resulting smoke is typically inhaled to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream of a person. Most commonly, the substance used is the dried leaves of the tobacco plant, whi ...
.
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to more porous bone, and consequent increase in Bone fracture, fracture risk.
It is the most common reason f ...
is often a comorbidity
In medicine, comorbidity refers to the simultaneous presence of two or more medical conditions in a patient; often co-occurring (that is, concomitant or concurrent) with a primary condition. It originates from the Latin term (meaning "sicknes ...
of emphysema. The use of systemic corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invol ...
for treating exacerbations is a significant risk factor for osteoporosis, and their repeated use is recommended against.
Signs and symptoms
 Emphysema is a respiratory disease of the
Emphysema is a respiratory disease of the lower respiratory tract
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of conducting air to the alveoli for the purposes of gas exchange in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respirator ...
. It is commonly caused by tobacco smoking
Tobacco smoking is the practice of burning tobacco and ingesting the resulting smoke. The smoke may be inhaled, as is done with cigarettes, or released from the mouth, as is generally done with pipes and cigars. The practice is believed to hav ...
but some people are affected who have never smoked. The presence of emphysema is a clear risk factor for lung cancer, made stronger in those who smoke.
Early symptoms of emphysema vary. They can include a cough (with or without sputum), wheezing, a fast breathing rate, breathlessness on exertion, and a feeling of tightness in the chest. There may be frequent cold or flu infections. Other symptoms may include anxiety, depression, fatigue, sleep problems and weight loss. These symptoms could also relate to other lung conditions or other health problems; therefore, emphysema is often underdiagnosed. The shortness of breath emphysema causes can increase over time and develop into chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of progressive lung disease characterized by chronic respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. GOLD defines COPD as a heterogeneous lung condition characterized by chronic respiratory s ...
.
A sign of emphysema in smokers is a higher number of alveolar macrophage
An alveolar macrophage, pulmonary macrophage, (or dust cell, or dust eater) is a type of macrophage, a phagocytosis#Professional phagocytic cells, professional phagocyte, found in the airways and at the level of the pulmonary alveolus, alveoli in ...
s sampled from the bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) in the lungs. The number can be four to six times greater in those who smoke than in non-smokers.
Emphysema is also associated with barrel chest.
Types
There are four main types of emphysema, three of which are related to the anatomy of the lobules of the lung – centrilobular or centriacinar, panlobular or panacinar, and paraseptal or distal acinar and are not associated withfibrosis
Fibrosis, also known as fibrotic scarring, is the development of fibrous connective tissue in response to an injury. Fibrosis can be a normal connective tissue deposition or excessive tissue deposition caused by a disease.
Repeated injuries, ch ...
(scarring). Although fibrosis is not a normal feature of these subtypes, repair strategies in end-stage emphysema may lead to pulmonary fibrosis
Pulmonary fibrosis is a condition in which the lungs become scarred over time. Symptoms include shortness of breath, a dry cough, feeling tired, weight loss, and nail clubbing. Complications may include pulmonary hypertension, respiratory ...
. The fourth subtype is known as paracicatricial emphysema or irregular emphysema, involves the acinus irregularly and is associated with fibrosis.
Only the first two types of emphysema – centrilobular and panlobular – are associated with significant airflow obstruction, with that of centrilobular emphysema around 20 times more common than panlobular. The subtypes can be seen on imaging
Imaging is the representation or reproduction of an object's form; especially a visual representation (i.e., the formation of an image).
Imaging technology is the application of materials and methods to create, preserve, or duplicate images.
...
but are not well-defined clinically.
There are also a number of associated conditions including bullous emphysema, focal emphysema, and Ritalin lung.
Centrilobular
 Centrilobular emphysema, also called centriacinar emphysema, affects the centre of a
Centrilobular emphysema, also called centriacinar emphysema, affects the centre of a pulmonary lobule
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory syste ...
(centrilobular) in the lung, the area around the terminal bronchiole and the first respiratory bronchiole, and can be seen on imaging as an area around the tip of the visible pulmonary artery. Centrilobular emphysema is the most common type usually associated with smoking, and with chronic bronchitis
Bronchitis is inflammation of the bronchi (large and medium-sized airways) in the lungs that causes coughing. Bronchitis usually begins as an infection in the nose, ears, throat, or sinuses. The infection then makes its way down to the bronchi. ...
. The disease progresses from the centrilobular portion, leaving the lung parenchyma in the surrounding (perilobular) region preserved. Usually the upper lobes of the lungs are affected.
Panlobular
Panlobular emphysema, also called panacinar emphysema, affects all of the alveoli in a lobule, and can involve the whole lung or mainly the lower lobes. This type of emphysema is associated withalpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (A1AD or AATD) is a genetic disorder that may result in lung disease or liver disease. Onset of lung problems is typically between 20 and 50 years of age. This may result in shortness of breath, wheezing, or an inc ...
(A1AD or AATD), and Ritalin lung, and is not related to smoking.
Complications
Likely complications of centrilobular and panlobular emphysema, some of which are life-threatening, include:respiratory failure
Respiratory failure results from inadequate gas exchange by the respiratory system, meaning that the arterial oxygen, carbon dioxide, or both cannot be kept at normal levels. A drop in the oxygen carried in the blood is known as hypoxemia; a r ...
, pneumonia
Pneumonia is an Inflammation, inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as Pulmonary alveolus, alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of Cough#Classification, productive or dry cough, ches ...
, respiratory infections, pneumothorax
A pneumothorax is collection of air in the pleural space between the lung and the chest wall. Symptoms typically include sudden onset of sharp, one-sided chest pain and dyspnea, shortness of breath. In a minority of cases, a one-way valve is ...
, interstitial emphysema, pulmonary heart disease, and respiratory acidosis
The respiratory system (also respiratory apparatus, ventilatory system) is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies gr ...
.
Paraseptal
Paraseptal emphysema, also called distal acinar emphysema, relates to emphysematous change next to apleura
The pleurae (: pleura) are the two flattened closed sacs filled with pleural fluid, each ensheathing each lung and lining their surrounding tissues, locally appearing as two opposing layers of serous membrane separating the lungs from the med ...
l surface, or to a fissure
A fissure is a long, narrow crack opening along the surface of Earth. The term is derived from the Latin word , which means 'cleft' or 'crack'. Fissures emerge in Earth's crust, on ice sheets and glaciers, and on volcanoes.
Ground fissure
A ...
. The cystic spaces known as blebs or bullae that form in paraseptal emphysema typically occur in just one layer beneath the pleura. This distinguishes it from the honeycombing of small cystic spaces seen in fibrosis
Fibrosis, also known as fibrotic scarring, is the development of fibrous connective tissue in response to an injury. Fibrosis can be a normal connective tissue deposition or excessive tissue deposition caused by a disease.
Repeated injuries, ch ...
that typically occurs in layers. This type of emphysema is not associated with airflow obstruction.
Bullous
 When the subpleural bullae are significant, the emphysema is called bullous emphysema. Bullae can become extensive and combine to form giant bullae. These can be large enough to take up a third of a hemithorax, compress the lung parenchyma, and cause displacement. The emphysema is now termed giant bullous emphysema, more commonly called vanishing lung syndrome due to the compressed parenchyma. A bleb or bulla may sometimes rupture and cause a
When the subpleural bullae are significant, the emphysema is called bullous emphysema. Bullae can become extensive and combine to form giant bullae. These can be large enough to take up a third of a hemithorax, compress the lung parenchyma, and cause displacement. The emphysema is now termed giant bullous emphysema, more commonly called vanishing lung syndrome due to the compressed parenchyma. A bleb or bulla may sometimes rupture and cause a pneumothorax
A pneumothorax is collection of air in the pleural space between the lung and the chest wall. Symptoms typically include sudden onset of sharp, one-sided chest pain and dyspnea, shortness of breath. In a minority of cases, a one-way valve is ...
.
Paracicatricial
Paracicatricial emphysema, also known as irregular emphysema, is seen next to areas offibrosis
Fibrosis, also known as fibrotic scarring, is the development of fibrous connective tissue in response to an injury. Fibrosis can be a normal connective tissue deposition or excessive tissue deposition caused by a disease.
Repeated injuries, ch ...
(scarring) as large spaces. The scarring is most often a result of silicosis
Silicosis is a form of occupational lung disease caused by inhalation of crystalline silica dust. It is marked by inflammation and scarring in the form of Nodule (medicine), nodular lesions in the upper lobes of the lungs. It is a type of pneum ...
, granuloma
A granuloma is an aggregation of macrophages (along with other cells) that forms in response to chronic inflammation. This occurs when the immune system attempts to isolate foreign substances that it is otherwise unable to eliminate. Such sub ...
tous infection, tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can al ...
, or pulmonary infarction. It can be difficult to differentiate from the honeycombing of pulmonary fibrosis
Pulmonary fibrosis is a condition in which the lungs become scarred over time. Symptoms include shortness of breath, a dry cough, feeling tired, weight loss, and nail clubbing. Complications may include pulmonary hypertension, respiratory ...
.
HIV associated
Classic lung diseases are a complication ofHIV/AIDS
The HIV, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a retrovirus that attacks the immune system. Without treatment, it can lead to a spectrum of conditions including acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). It is a Preventive healthcare, pr ...
with emphysema being a source of disease. HIV is cited as a risk factor for the development of emphysema and COPD regardless of smoking status. Around 20 percent of those with HIV have increased emphysematous changes. This has suggested that an underlying mechanism related to HIV is a contributory factor in the development of emphysema. HIV associated emphysema occurs over a much shorter time than that associated with smoking; an earlier presentation is also seen in emphysema caused by alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (A1AD or AATD) is a genetic disorder that may result in lung disease or liver disease. Onset of lung problems is typically between 20 and 50 years of age. This may result in shortness of breath, wheezing, or an inc ...
. Both of these conditions predominantly show damage in the lower lungs, which suggests a similarity between the two mechanisms.
Alpha-1 related
Emphysema may develop in some people withalpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (A1AD or AATD) is a genetic disorder that may result in lung disease or liver disease. Onset of lung problems is typically between 20 and 50 years of age. This may result in shortness of breath, wheezing, or an inc ...
, the only genotype of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. This usually occurs a lot earlier (as does HIV associated emphysema) than other types.
Ritalin lung
The intravenous use ofmethylphenidate
Methylphenidate, sold under the brand names Ritalin ( ) and Concerta ( ) among others, is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. It may be taken Oral adm ...
, commonly marketed as ''Ritalin'' and widely used as a stimulant drug in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised by symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, impulsivity, and emotional dysregulation that are excessive and pervasive, impairing in multiple con ...
, can lead to emphysematous changes known as Ritalin lung. The mechanism underlying this link is not clearly understood. Ritalin tablets are not intended to be injected. They contain talc
Talc, or talcum, is a clay mineral composed of hydrated magnesium silicate, with the chemical formula . Talc in powdered form, often combined with corn starch, is used as baby powder. This mineral is used as a thickening agent and lubricant ...
as a filler, and it has been suggested that talc exposure causes granuloma
A granuloma is an aggregation of macrophages (along with other cells) that forms in response to chronic inflammation. This occurs when the immune system attempts to isolate foreign substances that it is otherwise unable to eliminate. Such sub ...
tosis leading to alveolar destruction. However, other intravenous drugs also contain talc, and no emphysematous change is associated with those. High resolution CT scanning shows the emphysema to be panlobular.
CPFE
Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema (CPFE) is a rare syndrome that shows upper-lobe emphysema, together with lower-lobe interstitial fibrosis. This is diagnosed byCT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
. This syndrome presents a marked susceptibility for the development of pulmonary hypertension
Pulmonary hypertension (PH or PHTN) is a condition of increased blood pressure in the pulmonary artery, arteries of the lungs. Symptoms include dypsnea, shortness of breath, Syncope (medicine), fainting, tiredness, chest pain, pedal edema, swell ...
.
SRIF
Smoking-related interstitial fibrosis (SRIF) is another type of fibrosis that occurs in emphysematous lungs and can be identified by pathologists. Unlike CPFE, this type of fibrosis is usually clinically occult (i.e., does not cause symptoms or imaging abnormalities). Occasionally, however, some patients with SRIF present with symptoms and radiologic findings of interstitial lung disease.Congenital lobar
Congenital lobar emphysema (CLE), also known as congenital lobar overinflation and infantile lobar emphysema, is a neonatal condition associated with enlarged air spaces in the lungs of newborn infants. It is diagnosed around the time of birth or in the first 6 months of life, occurring more often in boys than girls. CLE affects the upper lung lobes more than the lower lobes, and the left lung more often than the right lung. CLE is defined as thehyperinflation
In economics, hyperinflation is a very high and typically accelerating inflation. It quickly erodes the real versus nominal value (economics), real value of the local currency, as the prices of all goods increase. This causes people to minimiz ...
of one or more lobes of the lung due to the partial obstruction of the bronchus. This causes symptoms of pressure on the nearby organs. It is associated with several cardiac abnormalities such as patent ductus arteriosus
Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is a medical condition in which the ''ductus arteriosus'' fails to close after childbirth, birth: this allows a portion of oxygenated blood from the left heart to flow back to the lungs from the aorta, which has a h ...
, atrial septal defect
Atrial septal defect (ASD) is a congenital heart defect in which blood flows between the atrium (heart), atria (upper chambers) of the heart. Some flow is a normal condition both pre-birth and immediately post-birth via the Foramen ovale (heart) ...
, ventricular septal defect
A ventricular septal defect (VSD) is a defect in the ventricular septum, the wall dividing the left and right ventricles of the heart. It's a common heart problem present at birth ( congenital heart defect). The extent of the opening may vary ...
, and tetralogy of Fallot
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF), formerly known as Steno-Fallot tetralogy, is a congenital heart defect characterized by four specific cardiac defects. Classically, the four defects are:
* Pulmonary stenosis, which is narrowing of the exit from the r ...
. Although CLE may be caused by the abnormal development of bronchi
A bronchus ( ; : bronchi, ) is a passage or airway in the lower respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. The first or primary bronchi to branch from the trachea at the carina are the right main bronchus and the left main bronchus. Thes ...
, or compression of airways by nearby tissues, no cause is identified in half of cases. CT scan of the lungs is useful in assessing the anatomy of the lung lobes and status of the neighbouring lobes on whether they are hypoplastic or not. Contrast-enhanced CT is useful in assessing vascular abnormalities and mediastinal masses.
Focal
coalworker's pneumoconiosis
Black lung disease (BLD), also known as coal workers' pneumoconiosis, or simply black lung, is an occupational disease, occupational type of pneumoconiosis caused by long-term inhalation and deposition of coal dust in the lungs and the consequent ...
. This is also known as ''localized pulmonary emphysema''. Blebs and bullae may also be included as focal emphysema. These can be differentiated from the other type of enclosed air space known as a lung cyst by their size and wall thickness. A bleb or bulla has a wall thickness of less than 1 mm, and are smaller.
Occupational
A number of occupations are associated with the development of emphysema due to the inhalation of varied gases and particles. In the USuranium mining
Uranium mining is the process of extraction of uranium ore from the earth. Over 50,000 tons of uranium were produced in 2019. Kazakhstan, Canada, and Australia were the top three uranium producers, respectively, and together account for 68% of w ...
that releases radon gas
Radon is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Rn and atomic number 86. It is a radioactive decay, radioactive noble gas and is colorless and odorless. Of the three naturally occurring radon Isotope, isotopes, only radon-222, Rn ha ...
and particles has been shown to be a cause of emphysema deaths; the figures in the study included some miners who also smoked. Uranium mining and milling was found to create environmental pollution.
The inhalation of coal mine dust that can result in coalworker's pneumoconiosis
Black lung disease (BLD), also known as coal workers' pneumoconiosis, or simply black lung, is an occupational disease, occupational type of pneumoconiosis caused by long-term inhalation and deposition of coal dust in the lungs and the consequent ...
is an independent risk factor for the development of emphysema. Focal emphysema is associated with the coal macule, and this extends into progressive centrilobular emphysema. Less commonly a variant of panlobular emphysema develops.
Silicosis
Silicosis is a form of occupational lung disease caused by inhalation of crystalline silica dust. It is marked by inflammation and scarring in the form of Nodule (medicine), nodular lesions in the upper lobes of the lungs. It is a type of pneum ...
results from the inhalation of silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , commonly found in nature as quartz. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one of the most complex and abundant f ...
particles, and the formation of large silica nodules is associated with paracicatricial emphysema, with or without bullae.
Ozone-induced emphysema
Ozone
Ozone () (or trioxygen) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , break ...
is another pollutant
A pollutant or novel entity is a substance or energy introduced into the environment that has undesired effect, or adversely affects the usefulness of a resource. These can be both naturally forming (i.e. minerals or extracted compounds like oi ...
that can affect the respiratory system. Long-term exposure to ozone can result in emphysema.
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to more porous bone, and consequent increase in Bone fracture, fracture risk.
It is the most common reason f ...
is a major comorbidity
In medicine, comorbidity refers to the simultaneous presence of two or more medical conditions in a patient; often co-occurring (that is, concomitant or concurrent) with a primary condition. It originates from the Latin term (meaning "sicknes ...
of emphysema. Both conditions are associated with a low body mass index
Body mass index (BMI) is a value derived from the mass (Mass versus weight, weight) and height of a person. The BMI is defined as the human body weight, body mass divided by the square (algebra), square of the human height, body height, and is ...
. There is an association between treating emphysema and osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to more porous bone, and consequent increase in Bone fracture, fracture risk.
It is the most common reason f ...
; the use of systemic corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invol ...
for treating exacerbations is a significant risk factor for osteoporosis, and their repeated use is not recommended.
Other terms
Compensatory emphysema is overinflation of part of a lung in response to either removal by surgery of another part of the lung or decreased size of another part of the lung. Pulmonary interstitial emphysema (PIE) is a collection of air inside the lungs but outside the normal air space of the alveoli, found as pneumatoses inside theconnective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, a group of cells that are similar in structure, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops mostly from the mesenchyme, derived from the mesod ...
of the peribronchovascular sheaths, interlobular septa, and visceral pleura
The pleurae (: pleura) are the two flattened closed sacs filled with pleural fluid, each ensheathing each lung and lining their surrounding tissues, locally appearing as two opposing layers of serous membrane separating the lungs from the media ...
.
Lung volume reduction
Lung volume reduction may be offered to those with advanced emphysema. When other treatments fail, and the emphysema is in the upper lobes, a surgical option may be possible. A number of minimally invasive bronchoscopic procedures are increasingly used to reduce lung volume.Surgical
Where there is severe emphysema with significant hyperinflation that has proved unresponsive to other therapies, lung volume reduction surgery (LVRS) may be an option. LVRS involves the removal of tissue from the lobe most damaged by emphysema, which allows the other lobes to expand and give improved function. The procedure appears to be particularly effective if the emphysema primarily involves the upper lobes; however, the procedure increases the risk of adverse events and early death in people who have diffuse emphysema.Bronchoscopic
Minimally invasive bronchoscopic procedures may be carried out to reduce lung volume. These include the use of valves, coils, or thermal ablation. Endobronchial valves are one-way valves that may be used in those with severe hyperinflation resulting from advanced emphysema; a suitable target lobe and no collateral ventilation are required for this procedure. The placement of one or more valves in the lobe induces a partial collapse of the lobe that ensures a reduction in residual volume that improves lung function, the capacity for exercise, and quality of life. The placement of endobronchial coils made ofnitinol
Nickel titanium, also known as nitinol, is a metal alloy of nickel and titanium, where the two elements are present in roughly equal atomic percentages. Different alloys are named according to the weight percentage of nickel; e.g., nitinol 55 and ...
, instead of valves is recommended where there is collateral ventilation that would prevent the use of valves. Nitinol is a biocompatible shape-memory alloy
In metallurgy, a shape-memory alloy (SMA) is an alloy that can be deformed when cold but returns to its pre-deformed ("remembered") shape when heated. It is also known in other names such as memory metal, memory alloy, smart metal, smart alloy, ...
.
Both of these techniques are associated with adverse effects, including persistent air leaks and cardiovascular complications. Bronchoscopic thermal vapor ablation has an improved profile. Heated water vapor is used to target affected lobe regions, which leads to permanent fibrosis and volume reduction. The procedure is able to target individual lobe segments, can be carried out regardless of collateral ventilation, and can be repeated with the natural advance of emphysema.
Other surgeries
Lung transplantation
Lung transplantation, or pulmonary transplantation, is a surgical procedure in which one or both lungs are replaced by lungs from a donor. Donor lungs can be retrieved from a living or deceased donor. A living donor can only donate one lung lobe ...
– the replacement of either a single lung or both (bilateral) – may be considered in end-stage disease. A bilateral transplant is the preferred choice as complications can arise in a remaining single native lung; complications can include hyperinflation, pneumonia, and the development of lung cancer. Careful selection as recommended by the ''National Emphysema Treatment Trial'' (NETT) for transplant surgeries is needed as in some cases there will be an increased risk of mortality. Several factors, including age and exercise tolerance using the BODE index need to be taken into account. A transplant is considered only when there are no serious comorbidites. A CT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
or a ventilation/perfusion scan may be useful to evaluate cases for surgical interventions and to evaluate post-surgery responses. A bullectomy may be carried out when a giant bulla occupies more than a third of a hemithorax.
In other tissues
Trapped air can also develop in other tissues such as under the skin, known as subcutaneous emphysema. Orbital emphysema is the trapping of air in theorbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit (also known as orbital revolution) is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an ...
; a type of this is palpebral emphysema that affects just the eyelids. Emphysematous gastritis
Gastritis is the inflammation of the lining of the stomach. It may occur as a short episode or may be of a long duration. There may be no symptoms but, when symptoms are present, the most common is upper abdominal pain (see dyspepsia). Othe ...
is the presence of air in the stomach wall, usually caused by a bacterial infection. This is rare but has a high mortality rate.
History
 The terms ''emphysema'' and ''chronic bronchitis'' were formally defined in 1959 at the CIBA guest symposium, and in 1962 at the
The terms ''emphysema'' and ''chronic bronchitis'' were formally defined in 1959 at the CIBA guest symposium, and in 1962 at the American Thoracic Society The American Thoracic Society (ATS) is a nonprofit organization focused on improving care for pulmonary diseases, critical illnesses and sleep-related breathing disorders. It was established in 1905 as the
American Sanatorium Association, and ...
Committee meeting on Diagnostic Standards. The word ''emphysema'' is derived from Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
ἐμφύσημα 'inflation, swelling' (referring to a lung inflated by air-filled spaces), itself from ''emphysao'' 'to blow in, to inflate', composed of ἐν ''en'', meaning "''in''", and φυσᾶ ''physa'', meaning "''wind, blast''.
René Laennec
René-Théophile-Hyacinthe Laennec (; 17 February 1781 – 13 August 1826) was a French physician and musician. His skill at carving his own wooden flutes led him to invent the stethoscope in 1816, while working at the Hôpital Necker. ...
, the physician who invented the stethoscope
The stethoscope is a medicine, medical device for auscultation, or listening to internal sounds of an animal or human body. It typically has a small disc-shaped resonator that is placed against the skin, with either one or two tubes connected t ...
, used the term ''emphysema'' in his book ''A Treatise on the Diseases of the Chest and of Mediate Auscultation'' (1837) to describe lungs that did not collapse when he opened the chest during an autopsy. He noted that they did not collapse as usual because they were full of air and the airways were filled with mucus. Early descriptions of probable emphysema include: in 1679 by T. Bonet of a condition of "voluminous lungs" and in 1769 by Giovanni Morgagni of lungs which were "turgid particularly from air". In 1721 the first drawings of emphysema were made by Ruysh. These were followed the illustrations of Matthew Baillie in 1789 and descriptions of the destructive nature of the condition.
References
Bibliography
* * * *External links
* {{Authority control Chronic lower respiratory diseases Health effects of tobacco Occupational diseases