Emperor Nicholas I on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Nicholas I, group=pron (
 While Nicholas was attempting to maintain the status quo in Europe, he followed a somewhat more aggressive policy toward the neighbouring empires to the south, the
While Nicholas was attempting to maintain the status quo in Europe, he followed a somewhat more aggressive policy toward the neighbouring empires to the south, the  In 1826–28, Nicholas fought the
In 1826–28, Nicholas fought the
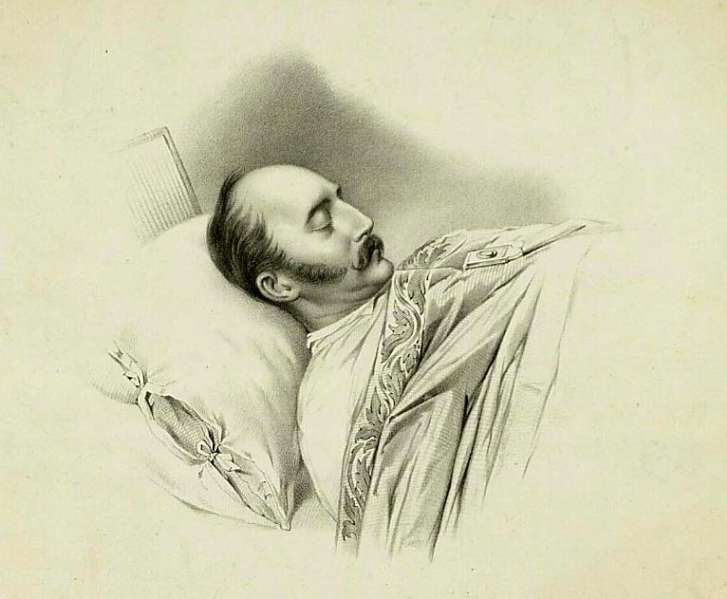 Nicholas died on 2 March 1855, during the Crimean War, at the
Nicholas died on 2 March 1855, during the Crimean War, at the
''Empire of the Czar: A Journey Through Eternal Russia''
. He speculated that Nicholas had a kind heart, but his sincere sense of duty forced him to impose severe discipline: "If the Emperor has no more of mercy in his heart than he reveals in his policies, then I pity Russia; if, on the other hand, his true sentiments are really superior to his acts, then I pity the Emperor." According to a popular
online
* Cannady, Sean, and Paul Kubicek. "Nationalism and legitimation for authoritarianism: A comparison of Nicholas I and Vladimir Putin." '' Journal of Eurasian Studies'' 5.1 (2014): 1–
online
* Crisp, Olga. "The state peasants under Nicholas I." ''Slavonic and East European Review'' 37.89 (1959): 387–41
online
* Curtiss, John Shelton. "The Army of Nicholas I: Its Role and Character." ''American Historical Review'' 63.4 (1958): 880–88
online
* Hamlin, Cyrus. "The Political Duel Between Nicholas, the Czar of Russia, and Lord Stratford de Redcliffe, the Great English Ambassador." ''Proceedings of the American Antiquarian Society'' Vol. 9. (1893
online
* Hosking, Geoffrey A. ''Russia: People and Empire, 1552–1917'', (Harvard University Press, 1997) * Kagan, Frederick W. ''The military reforms of Nicholas I'' (Palgrave Macmillan US, 1999). * Kutscheroff, Samuel. "Administration of Justice under Nicholas I of Russia." ''American Slavic and East European Review'' (1948): 125–138
in JSTOR
* Lincoln, W. Bruce. "Nicholas I: Russia's Last Absolute Monarch," ''History Today'' (1971) 21 #2 pp. 79–88. * Lincoln, W. Bruce. ''Nicholas I: Emperor and Autocrat of All the Russias'' (1989
online
* Monas, Sidney. ''The Third Section: police and society in Russia under Nicholas I'' (Harvard University Press, 1961) * Presni͡akov, A. E. ''Emperor Nicholas I of Russia: the apogee of autocracy, 1825/1855'' (1974
online
* Pintner, Walter McKenzie. ''Russian economic policy under Nicholas I'' (1967
online
* Rendall, Matthew. "Restraint or Self-Restraint of Russia: Nicholas I, the Treaty of Unkiar Skelessi, and the Vienna System, 1832–1841." ''International History Review'' 24.1 (2002): 37–63. *Rebecchini, Damiano. (2010). "An influential collector: Tsar Nicholas I of Russia." ''Journal of the History of Collections.'' V. 22, Issue 1, (May): 45–67. * Riasanovsky, Nicholas V. "'Nationality' in the State Ideology during the Reign of Nicholas I." ''Russian Review'' (1960): 38–4
online
* Riasanovsky, Nicholas V. ''Nicholas I and Official Nationality in Russia, 1825–1855'' (1967
online
* Roberts, Ian W. ''Nicholas I and the Russian intervention in Hungary'' (Springer, 1991). * Stanislawski, Michael. ''Tsar Nicholas I and the Jews : the transformation of Jewish society in Russia, 1825–1855'' (1983
online
Russian
Russian(s) may refer to:
*Russians (), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*A citizen of Russia
*Russian language, the most widely spoken of the Slavic languages
*''The Russians'', a b ...
: Николай I Павлович; – ) was Emperor of Russia
The emperor and autocrat of all Russia (, ), also translated as emperor and autocrat of all the Russias, was the official title of the List of Russian monarchs, Russian monarch from 1721 to 1917.
The title originated in connection with Russia's ...
, King of Congress Poland, and Grand Duke of Finland
The Grand Duke of Finland, alternatively the Grand Prince of Finland after 1802, was, from around 1580 to 1809, a title in use by most Swedish monarchs. Between 1809 and 1917, it was included in the title of the emperor of Russia, who was also t ...
from 1825 to 1855. He was the third son of Paul I and younger brother of his predecessor, Alexander I Alexander I may refer to:
* Alexander I of Macedon, king of Macedon from 495 to 454 BC
* Alexander I of Epirus (370–331 BC), king of Epirus
* Alexander I Theopator Euergetes, surnamed Balas, ruler of the Seleucid Empire 150-145 BC
* Pope Alex ...
. Nicholas's thirty-year reign began with the failed Decembrist revolt
The Decembrist revolt () was a failed coup d'état led by liberal military and political dissidents against the Russian Empire. It took place in Saint Petersburg on , following the death of Emperor Alexander I.
Alexander's brother and heir ...
. He is mainly remembered as a reactionary
In politics, a reactionary is a person who favors a return to a previous state of society which they believe possessed positive characteristics absent from contemporary.''The New Fontana Dictionary of Modern Thought'' Third Edition, (1999) p. 729. ...
whose controversial reign was marked by geographical expansion, centralisation of administrative policies, and repression of dissent
Political repression is the act of a state entity controlling a citizenry by force for political reasons, particularly for the purpose of restricting or preventing the citizenry's ability to take part in the political life of a society, thereby ...
both in Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
and among its neighbors. Nicholas had a happy marriage that produced a large family, with all of their seven children surviving childhood.
Nicholas's biographer Nicholas V. Riasanovsky said that he displayed determination, singleness of purpose, and an iron will, along with a powerful sense of duty and a dedication to very hard work. He saw himself as a soldier—a junior officer consumed by spit and polish. A handsome man, he was highly nervous and aggressive. Trained as a military engineer, he was a stickler for minute detail. In his public persona, stated Riasanovsky, "Nicholas I came to represent autocracy
Autocracy is a form of government in which absolute power is held by the head of state and Head of government, government, known as an autocrat. It includes some forms of monarchy and all forms of dictatorship, while it is contrasted with demo ...
personified: infinitely majestic, determined and powerful, hard as stone, and relentless as fate."
Nicholas I was instrumental in helping to create an independent
Independent or Independents may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Artist groups
* Independents (artist group), a group of modernist painters based in Pennsylvania, United States
* Independentes (English: Independents), a Portuguese artist ...
Greek state and resumed the Russian conquest of the Caucasus
The Russian conquest of the Caucasus mainly occurred between 1800 and 1864. The Russian Empire sought to control the region between the Black Sea and Caspian Sea. South of the mountains was the territory that is modern Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georg ...
by seizing Iğdır Province
Iğdır Province (, , , ) is a Provinces of Turkey, province in eastern Turkey, located along the borders with Armenia, Azerbaijan (the area of Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic), and Iran. Its adjacent provinces are Kars Province, Kars to the north ...
and the remainder of modern-day Armenia
Armenia, officially the Republic of Armenia, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of West Asia. It is a part of the Caucasus region and is bordered by Turkey to the west, Georgia (country), Georgia to the north and Azerbaijan to ...
and Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan, officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, is a Boundaries between the continents, transcontinental and landlocked country at the boundary of West Asia and Eastern Europe. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by ...
from Qajar Iran
The Guarded Domains of Iran, alternatively the Sublime State of Iran and commonly called Qajar Iran, Qajar Persia or the Qajar Empire, was the Iranian state under the rule of the Qajar dynasty, which was of Turkic peoples, Turkic origin,Cyrus G ...
during the Russo-Persian War (1826–1828)
The Russo-Persian War of 1826–1828 was the last major military conflict between the Russian Empire and Qajar Iran, which was fought over territorial disputes in the South Caucasus region.
Initiated by Russian expansionist aims and intensifie ...
. He ended the Russo-Turkish War (1828–1829)
The Russo-Turkish War of 1828–1829 resulted from the Greek War of Independence of 1821–1829; war broke out after the Ottoman Sultan Mahmud II closed the Dardanelles to Russian Empire , Russian ships and in November 1827 revoked the 18 ...
successfully as well. He crushed the November Uprising
The November Uprising (1830–31) (), also known as the Polish–Russian War 1830–31 or the Cadet Revolution,
was an armed rebellion in Russian Partition, the heartland of Partitions of Poland, partitioned Poland against the Russian Empire. ...
in Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
in 1831 and decisively aided Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
during the Hungarian Revolution of 1848. Later on, however, he led Russia into the Crimean War
The Crimean War was fought between the Russian Empire and an alliance of the Ottoman Empire, the Second French Empire, the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, and the Kingdom of Sardinia (1720–1861), Kingdom of Sardinia-Piedmont fro ...
(1853–1856), with disastrous results. Historians emphasize that his micromanagement
Micromanagement is a management style characterized by behaviors such as an excessive focus on observing and controlling subordinates and an obsession with details.
Micromanagement generally has a negative connotation, suggesting a lack of fr ...
of the armies hindered his generals, as did his misguided strategy. Several historians have concluded that "the reign of Nicholas I was a catastrophic failure in both domestic and foreign policy." On the eve of his death, the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
reached its geographical zenith, spanning over 20 million square kilometers ( million square miles), but had a desperate need for reform.
Early life and road to power
Nicholas was born atGatchina Palace
The Great Gatchina Palace () is a palace in Gatchina, Leningrad Oblast, Russia. It was built from 1766 to 1781 by Antonio Rinaldi (architect), Antonio Rinaldi for Count Grigori Grigoryevich Orlov, who was a favourite of Catherine the Great, in ...
in Gatchina, the ninth child of Grand Duke Paul, heir to the Russian throne, and Grand Duchess Maria Feodorovna of Russia (née Sophie Dorothea of Württemberg). He had six older sisters and two older brothers, namely the future Emperor Alexander I of Russia and Grand Duke Constantine Pavlovich of Russia
Konstantin Pavlovich (; ) was a grand duke of Russia and the second son of Emperor Paul I and Sophie Dorothea of Württemberg. He was the heir-presumptive for most of his elder brother Alexander I's reign, but had secretly renounced his c ...
.
Four months after Nicholas's birth, his grandmother, Catherine the Great
Catherine II. (born Princess Sophie of Anhalt-Zerbst; 2 May 172917 November 1796), most commonly known as Catherine the Great, was the reigning empress of Russia from 1762 to 1796. She came to power after overthrowing her husband, Peter I ...
, died and his parents became Emperor and Empress of Russia. In 1800, at the age of four years, Nicholas was named Grand Prior of Russia and entitled to wear the Maltese cross
The Maltese cross is a cross symbol, consisting of four " V" or arrowhead shaped concave quadrilaterals converging at a central vertex at right angles, two tips pointing outward symmetrically.
It is a heraldic cross variant which develope ...
. Nicholas grew up to be a fine young man. Riasanovsky says of him that he is "the most handsome man in Europe, but also a charmer who enjoyed feminine company and was often at his best with the men."
On 13 July 1817, Nicholas married Princess Charlotte of Prussia (1798–1860), who took the name Alexandra Feodorovna when she converted to Orthodoxy. Charlotte's parents were Frederick William III of Prussia
Frederick William III (; 3 August 1770 – 7 June 1840) was King of Prussia from 16 November 1797 until his death in 1840. He was concurrently Elector of Brandenburg in the Holy Roman Empire until 6 August 1806, when the empire was dissolved ...
and Louise of Mecklenburg-Strelitz
Louise of Mecklenburg-Strelitz (Luise Auguste Wilhelmine Amalie; 10 March 1776 – 19 July 1810) was Queen of Prussia as the wife of King Frederick William III. The couple's happy, though short-lived, marriage produced nine children, inclu ...
. Nicholas and Charlotte were third cousins, as they were both great-great-grandchildren of Frederick William I of Prussia
Frederick William I (; 14 August 1688 – 31 May 1740), known as the Soldier King (), was King in Prussia and Elector of Brandenburg from 1713 until his death in 1740, as well as Prince of Neuchâtel.
Born in Berlin, he was raised by the Hugu ...
.
With two older brothers, it initially seemed unlikely Nicholas would ever become Tsar. However, as Alexander and Constantine both failed to produce legitimate sons, Nicholas first came to attention as being likely to rule one day, or at least that his children may succeed. In 1825, when Tsar Alexander died suddenly of typhus
Typhus, also known as typhus fever, is a group of infectious diseases that include epidemic typhus, scrub typhus, and murine typhus. Common symptoms include fever, headache, and a rash. Typically these begin one to two weeks after exposu ...
, Nicholas was caught between swearing allegiance to Constantine and accepting the throne for himself. The interregnum lasted until Constantine, who was in Warsaw
Warsaw, officially the Capital City of Warsaw, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the Vistula, River Vistula in east-central Poland. Its population is officially estimated at ...
at that time, officially forfeited his right to succession. This had been required by Tsar Alexander as a condition of Constantine's marriage to his second wife Joanna Grudzinska. On 25 (13 Old Style
Old Style (O.S.) and New Style (N.S.) indicate dating systems before and after a calendar change, respectively. Usually, they refer to the change from the Julian calendar to the Gregorian calendar as enacted in various European countries betwe ...
) December, Nicholas issued the manifesto proclaiming his accession to the throne. That manifesto retroactively named 1 December (19 November Old Style
Old Style (O.S.) and New Style (N.S.) indicate dating systems before and after a calendar change, respectively. Usually, they refer to the change from the Julian calendar to the Gregorian calendar as enacted in various European countries betwe ...
), the date of Alexander I's death, as the beginning of his reign. During this confusion, a plot was hatched by some members of the military to overthrow Nicholas and seize power. This led to the Decembrist Revolt
The Decembrist revolt () was a failed coup d'état led by liberal military and political dissidents against the Russian Empire. It took place in Saint Petersburg on , following the death of Emperor Alexander I.
Alexander's brother and heir ...
on 26 (14 Old Style
Old Style (O.S.) and New Style (N.S.) indicate dating systems before and after a calendar change, respectively. Usually, they refer to the change from the Julian calendar to the Gregorian calendar as enacted in various European countries betwe ...
) December 1825, an uprising Nicholas quickly suppressed.
Emperor and principles
Early reign
Nicholas completely lacked his brother's spiritual and intellectual breadth; he saw his role simply as that of a paternal autocrat ruling his people by whatever means necessary. Nicholas I began his reign on 14 December 1825 (old style), which fell on a Monday; Russian superstition held that Mondays were unlucky days.W. Bruce Lincoln, ''The Romanovs'', p. 409. This particular Monday dawned very cold, with temperatures of −8 degrees Celsius. This was regarded by the Russian people as a bad omen for the coming reign. The accession of Nicholas I was marred by a demonstration of 3000 youngarmy officer
An officer is a person who holds a position of authority as a member of an Military, armed force or Uniformed services, uniformed service.
Broadly speaking, "officer" means a commissioned officer, a non-commissioned officer (NCO), or a warra ...
s and other liberal-minded citizens. This demonstration was an attempt to force the government to accept a constitution and a representative form of government. Nicholas ordered the Imperial Russian Army
The Imperial Russian Army () was the army of the Russian Empire, active from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was organized into a standing army and a state militia. The standing army consisted of Regular army, regular troops and ...
to smash the demonstration. The "uprising" was quickly put down and became known as the Decembrist revolt
The Decembrist revolt () was a failed coup d'état led by liberal military and political dissidents against the Russian Empire. It took place in Saint Petersburg on , following the death of Emperor Alexander I.
Alexander's brother and heir ...
. Having experienced the trauma of the Decembrist revolt on the first day of his reign, Nicholas I was determined to restrain Russian society. The Third Section of the Imperial Chancellery ran a huge network of spies and informers with the help of Gendarmes
A gendarmerie () is a paramilitary or military force with law enforcement duties among the civilian population. The term ''gendarme'' () is derived from the medieval French expression ', which translates to "men-at-arms" (). In France and som ...
. The government exercised censorship
Censorship is the suppression of speech, public communication, or other information. This may be done on the basis that such material is considered objectionable, harmful, sensitive, or "inconvenient". Censorship can be conducted by governmen ...
and other forms of control over education, publishing, and all manifestations of public life.
Nicholas appointed Alexander Benckendorff to head this Chancellery. Benckendorff employed 300 gendarmes and 16 staff in his office. He began collecting informers and intercepting mail. Soon, the saying that "it was impossible to sneeze in one's house before it is reported to the emperor" became Benckendorff's creed.
Local policies
Tsar Nicholas abolished several areas of local autonomy.Bessarabia
Bessarabia () is a historical region in Eastern Europe, bounded by the Dniester river on the east and the Prut river on the west. About two thirds of Bessarabia lies within modern-day Moldova, with the Budjak region covering the southern coa ...
's autonomy was removed in 1828, Poland's in 1830 and the Jewish Qahal
The ''qahal'' (), sometimes spelled ''kahal'', was a theocratic organizational structure in ancient Israelite society according to the Hebrew Bible, See column345-6 and an Ashkenazi Jewish system of a self-governing community or kehila from ...
was abolished in 1843. As an exception to this trend, Finland
Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland to the south, ...
was able to keep its autonomy partly due to Finnish soldiers' loyal participation in crushing the November Uprising
The November Uprising (1830–31) (), also known as the Polish–Russian War 1830–31 or the Cadet Revolution,
was an armed rebellion in Russian Partition, the heartland of Partitions of Poland, partitioned Poland against the Russian Empire. ...
in Poland.
Russia's first railway was opened in 1837, a line between St. Petersburg
Saint Petersburg, formerly known as Petrograd and later Leningrad, is the second-largest city in Russia after Moscow. It is situated on the River Neva, at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea. The city had a population of 5,601, ...
and the suburban residence of Tsarskoye Selo
Tsarskoye Selo (, , ) was the town containing a former residence of the Russian House of Romanov, imperial family and visiting nobility, located south from the center of Saint Petersburg. The residence now forms part of the Pushkin, Saint Peter ...
. The second was the Saint Petersburg–Moscow railway, built-in 1842–51. Nevertheless, by 1855 there were only of Russian railways.
In 1833, Sergey Uvarov
Count Sergey Semionovich Uvarov (; – ) was a Russian classical scholar and politician who is best remembered as an influential statesman under Nicholas I of Russia.
Biography
Uvarov, connected through marriage with the Razumovsky family, ...
, of the Ministry of National Education, devised a program of "Orthodoxy, Autocracy, and Nationality
Orthodoxy, Autocracy, and Nationality (; Transliteration, transliterated: Pravoslávie, samoderzhávie, naródnost'), also known as Official Nationalism,Riasanovsky, p. 132 was the dominant Imperial ideological doctrine of Russian Emperor Nichol ...
" as the guiding principle of the regime. It was a reactionary
In politics, a reactionary is a person who favors a return to a previous state of society which they believe possessed positive characteristics absent from contemporary.''The New Fontana Dictionary of Modern Thought'' Third Edition, (1999) p. 729. ...
policy based on orthodoxy in religion, autocracy in government, and the state-founding role of the Russian nationality and equal citizen rights for all other peoples inhabiting Russia, with the exclusion of Jews. The people were to show loyalty to the unrestricted authority of the tsar
Tsar (; also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar''; ; ; sr-Cyrl-Latn, цар, car) is a title historically used by Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word '' caesar'', which was intended to mean ''emperor'' in the Euro ...
, to the traditions of the Russian Orthodox Church
The Russian Orthodox Church (ROC; ;), also officially known as the Moscow Patriarchate (), is an autocephaly, autocephalous Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox Christian church. It has 194 dioceses inside Russia. The Primate (bishop), p ...
, and the Russian language
Russian is an East Slavic languages, East Slavic language belonging to the Balto-Slavic languages, Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. It is one of the four extant East Slavic languages, and is ...
. These romantic and conservative principles outlined by Uvarov were also espoused by Vasily Zhukovsky
Vasily Andreyevich Zhukovsky (; – ) was the foremost Russian poet of the 1810s and a leading figure in Russian literature in the first half of the 19th century. He held a high position at the Romanov court as tutor to the Grand Duchess Alexan ...
, one of the tutors of the Grand Duke Alexander. The results of these Slavophile principles led, broadly speaking, to increasing repression of all classes, excessive censorship, and surveillance of independent-minded intellectuals like Pushkin and Lermontov and to the persecution of non-Russian languages and non-Orthodox religions. Taras Shevchenko
Taras Hryhorovych Shevchenko (; ; 9 March 1814 – 10 March 1861) was a Ukrainian poet, writer, artist, public and political figure, folklorist, and ethnographer. He was a fellow of the Imperial Academy of Arts and a member of the Brotherhood o ...
, later to become known as the national poet
A national poet or national bard is a poet held by tradition and popular acclaim to represent the identity, beliefs and principles of a particular national culture. The national poet as culture hero is a long-standing symbol, to be distinguished ...
of Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
, was exiled to Siberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states ...
by a direct order of Tsar Nicholas after composing a poem that mocked the Tsar, his wife, and his domestic policies. By order of the Tsar, Shevchenko was kept under strict surveillance and prevented from writing or painting.
From 1839, Tsar Nicholas also used a former Byzantine Catholic Bishop named Joseph Semashko as his agent to re-unite Orthodoxy with the Eastern Rite Catholics of Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
, Belarus
Belarus, officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Belarus spans an a ...
, and Lithuania
Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, P ...
with the Synod of Polotsk
The Synod of Polotsk was a local synod held on February 12, 1839, by the clergy of the Ruthenian Uniate Church, Ruthenian Greek Catholic Church in the city of Polotsk for Union of Brest, reunification with the Russian Orthodox Church. Polotsk was ...
. This caused Tsar Nicholas to be condemned by a succession of Roman Pontiff
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
s, the Marquis de Custine, Charles Dickens
Charles John Huffam Dickens (; 7 February 1812 – 9 June 1870) was an English novelist, journalist, short story writer and Social criticism, social critic. He created some of literature's best-known fictional characters, and is regarded by ...
, and many Western governments. (See also Cantonist
Cantonists (; more properly: , "military cantonists") were underage sons of conscripts in the Russian Empire. From 1721 on they were educated in special "cantonist schools" () for future military service (the schools were called garrison school ...
s.)
Nicholas disliked serfdom
Serfdom was the status of many peasants under feudalism, specifically relating to manorialism and similar systems. It was a condition of debt bondage and indentured servitude with similarities to and differences from slavery. It developed du ...
and toyed with the idea of abolishing it in Russia, but declined to do so for reasons of state. He feared the aristocracy and believed they might turn against him if he abolished serfdom. However, he did make some efforts to improve the lot of the Crown Serfs (serfs owned by the government) with the help of his minister Pavel Kiselyov. During most of his reign he tried to increase his control over the landowners and other influential groups in Russia. In 1831, Nicholas restricted the votes in the Noble Assembly to those with over 100 serfs, leaving 21,916 voters. In 1841, landless nobles were banned from selling serfs
Serfdom was the status of many peasants under feudalism, specifically relating to manorialism and similar systems. It was a condition of debt bondage and indentured servitude with similarities to and differences from slavery. It developed dur ...
separate from the land. From 1845, attainment of the 5th highest rank (out of 14) in the Table of Ranks
The Table of Ranks () was a formal list of positions and ranks in the military, government, and court of Imperial Russia. Peter I of Russia, Peter the Great introduced the system in 1722 while engaged in a struggle with the existing hereditary ...
was required to be ennobled, previously it had been the 8th rank.
King of Poland
Nicholas was crowned King of Poland in Warsaw on 12 (24) May 1829, per the Polish Constitution, a document he would not respect thereafter. He is the only Russian monarch ever crowned King of Polandalthough not the only one bestowed with the title.Culture
The official emphasis onRussian nationalism
Russian nationalism () is a form of nationalism that promotes Russian cultural identity and unity. Russian nationalism first rose to prominence as a Pan-Slavism, Pan-Slavic enterprise during the 19th century Russian Empire, and was repressed duri ...
fueled a debate on Russia's place in the world, the meaning of Russian history, and the future of Russia. One group, the westernizers, believed that Russia remained backward and primitive and could progress only through adopting European culture and institutions. Another group, the Slavophiles
Slavophilia () was a movement originating from the 19th century that wanted the Russian Empire to be developed on the basis of values and institutions derived from Russia's early history. Slavophiles opposed the influences of Western Europe in Rus ...
, enthusiastically favored Slavic culture and customs, and disdained the West
West is a cardinal direction or compass point.
West or The West may also refer to:
Geography and locations
Global context
* The Western world
* Western culture and Western civilization in general
* The Western Bloc, countries allied with NAT ...
.
The Slavophiles viewed Slavic philosophy as a source of wholeness in Russia and were sceptical of Western rationalism
In philosophy, rationalism is the Epistemology, epistemological view that "regards reason as the chief source and test of knowledge" or "the position that reason has precedence over other ways of acquiring knowledge", often in contrast to ot ...
and materialism. Some of them believed that the Russian peasant commune, or Mir
''Mir'' (, ; ) was a space station operated in low Earth orbit from 1986 to 2001, first by the Soviet Union and later by the Russia, Russian Federation. ''Mir'' was the first modular space station and was assembled in orbit from 1986 to ...
, offered an attractive alternative to Western capitalism and could save Europe from social and moral revolution, thus representing a form of Russian messianism
Messianism is the belief in the advent of a messiah who acts as the savior of a group of people. Some religions also have messianism-related concepts. Religions with a messiah concept include Hinduism (Kalki), Judaism ( Mashiach), Christianity ( ...
. However the ministry of education had a policy of closing philosophy faculties to curb destabilizing speculation.
In the wake of the Decembrist revolt, the tsar moved to protect the status quo by centralizing education. He wanted to neutralize the threat of foreign ideas and "pseudo-knowledge". However, his minister of education, Sergei Uvarov, quietly promoted academic freedom and autonomy, raised academic standards, improved facilities, and opened higher education to the middle classes. By 1848 the tsar, fearing that political upheavals in the West might spread to Russia, ended Uvarov's innovations. The universities were small and closely monitored, especially the potentially dangerous philosophy departments. Their main mission was to train a loyal, vigorous, manly senior bureaucracy unspoiled by effeminate office work.
The Imperial Academy of Fine Arts in St. Petersburg became the main source of recognition and support for artists. Nicholas I decided to control it personally, reserving the final say on artistic honors. As the tsar reprimanded and humiliated artists whose works he found distasteful, the result was fear, insecurity, and artistic mediocrity.
Despite the repressions of this period, Russians outside official control produced a flowering of literature and the performing arts. Through the works of Aleksandr Pushkin, Nikolai Gogol
Nikolai Vasilyevich Gogol; ; (; () was a Russian novelist, short story writer, and playwright of Ukrainian origin.
Gogol used the Grotesque#In literature, grotesque in his writings, for example, in his works "The Nose (Gogol short story), ...
, Ivan Turgenev
Ivan Sergeyevich Turgenev ( ; rus, links=no, Иван Сергеевич ТургеневIn Turgenev's day, his name was written ., p=ɪˈvan sʲɪrˈɡʲe(j)ɪvʲɪtɕ tʊrˈɡʲenʲɪf; – ) was a Russian novelist, short story writer, poe ...
and numerous others, Russian literature gained international stature and recognition. Ballet
Ballet () is a type of performance dance that originated during the Italian Renaissance in the fifteenth century and later developed into a concert dance form in France and Russia. It has since become a widespread and highly technical form of ...
took root in Russia after its importation from France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
, and classical music
Classical music generally refers to the art music of the Western world, considered to be #Relationship to other music traditions, distinct from Western folk music or popular music traditions. It is sometimes distinguished as Western classical mu ...
became firmly established with the compositions of Mikhail Glinka
Mikhail Ivanovich Glinka ( rus, links=no, Михаил Иванович Глинка, Mikhail Ivanovich Glinka, mʲɪxɐˈil ɨˈvanəvʲɪdʑ ˈɡlʲinkə, Ru-Mikhail-Ivanovich-Glinka.ogg; ) was the first Russian composer to gain wide recognit ...
(1804–1857).
Minister of Finance Georg von Cancrin
Count Georg Ludwig Cancrin (; 16 November 1774 – 10 September 1845) was a Russian German aristocrat and politician best known for spearheading reforms in the Russian financial system early in the 19th century.
Early life
Cancrin was born in H ...
persuaded the emperor of the benefits of inviting Prussian scientist Alexander von Humboldt
Friedrich Wilhelm Heinrich Alexander von Humboldt (14 September 1769 – 6 May 1859) was a German polymath, geographer, natural history, naturalist, List of explorers, explorer, and proponent of Romanticism, Romantic philosophy and Romanticism ...
to Russia to investigate regions that could produce mineral wealth. The Russian government financed Humboldt's eight-month expedition through Russia in 1829, which resulted in diamond
Diamond is a Allotropes of carbon, solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Diamond is tasteless, odourless, strong, brittle solid, colourless in pure form, a poor conductor of e ...
finds in the Ural mountains. Humboldt published multiple volumes on his Russian expedition, which he dedicated to Nicholas despite his increasing disapproval of the tsar's policies.
Treatment of Jews
In 1851 the Jewish population numbered at 2.4 million, including 212,000 in Russian-controlled Poland. This made them one of the largest '' inorodtsy'' (non-Slavic) minorities in the Russian Empire. On 26 August 1827 the edict of military conscription (''Ustav rekrutskoi povinnosti'') was introduced, which required Jewish boys to serve in the Russian military for 25 years from the age of 18. Before that many of them were forcibly conscripted intoCantonist
Cantonists (; more properly: , "military cantonists") were underage sons of conscripts in the Russian Empire. From 1721 on they were educated in special "cantonist schools" () for future military service (the schools were called garrison school ...
schools from the age of 12, while being a Cantonist did not count into the time of military service. They were sent far away from their families to serve in the military so that they would have difficulty practising Judaism
Judaism () is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic, Monotheism, monotheistic, ethnic religion that comprises the collective spiritual, cultural, and legal traditions of the Jews, Jewish people. Religious Jews regard Judaism as their means of o ...
and become Russified, and sometimes compelled to convert to Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
. The poorer village Jews, those without families, and unmarried Jews were especially targeted for military service. Between 1827 and 1854 it is estimated that there were 70,000 Jews conscripted.
Under Nicholas I, the Jewish agricultural colonisation of Ukraine continued with the transfer of Siberian Jews to Ukraine. In Ukraine, Jews were offered the opportunity to buy land, which left very little to support their families. On the other hand, these Jews were exempt from forced military conscription.
Under Nicholas I there were attempts to reform the education of Jews with the object of Russification
Russification (), Russianisation or Russianization, is a form of cultural assimilation in which non-Russians adopt Russian culture and Russian language either voluntarily or as a result of a deliberate state policy.
Russification was at times ...
. Study of the Talmud
The Talmud (; ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law (''halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of Haskalah#Effects, modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the cen ...
was disfavored. Nicholas I further toughened censorship of Jewish books in Yiddish
Yiddish, historically Judeo-German, is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated in 9th-century Central Europe, and provided the nascent Ashkenazi community with a vernacular based on High German fused with ...
and Hebrew
Hebrew (; ''ʿÎbrit'') is a Northwest Semitic languages, Northwest Semitic language within the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family. A regional dialect of the Canaanite languages, it was natively spoken by the Israelites and ...
by allowing these to be printed only in Zhitomir
Zhytomyr ( ; see #Names, below for other names) is a city in the north of the western half of Ukraine. It is the Capital city, administrative center of Zhytomyr Oblast (Oblast, province), as well as the administrative center of the surrounding ...
and Vilna
Vilnius ( , ) is the capital of and List of cities in Lithuania#Cities, largest city in Lithuania and the List of cities in the Baltic states by population, most-populous city in the Baltic states. The city's estimated January 2025 population w ...
.
Military and foreign policy
Nicolas' aggressiveforeign policy
Foreign policy, also known as external policy, is the set of strategies and actions a State (polity), state employs in its interactions with other states, unions, and international entities. It encompasses a wide range of objectives, includ ...
involved many expensive wars, having a disastrous effect on the empire's finances. Nicholas lavished attention on his very large army; of a population of 60–70 million people, the army counted one million men. They had outdated equipment and tactics, but the tsar, who dressed like a soldier and surrounded himself with officers, gloried in the victory over Napoleon in 1812 and took enormous pride in its smartness on parade. The cavalry horses, for example, were only trained in parade formations, and did poorly in battle. The glitter and braid masked profound weaknesses that he did not see. He put generals in charge of most of his civilian agencies regardless of their qualifications. An agnostic
Agnosticism is the view or belief that the existence of God, the divine, or the supernatural is either unknowable in principle or unknown in fact. (page 56 in 1967 edition) It can also mean an apathy towards such religious belief and refer to ...
who won fame in cavalry charges was made supervisor of Church affairs. The army became the vehicle of upward social mobility for noble youths from non-Russian areas, such as Poland, the Baltic, Finland, and Georgia. On the other hand, many miscreants, petty criminals, and undesirables were punished by local officials by being enlisted for life in the Army. The conscription system was highly unpopular with people, as was the practice of forcing peasants to house the soldiers for six months of the year. Curtiss finds that "The pedantry of Nicholas's military system, which stressed unthinking obedience and parade ground evolutions rather than combat training, produced ineffective commanders in time of war." His commanders in the Crimean War were old and incompetent, and indeed so were his muskets as the colonels sold the best equipment and the best food.
For much of Nicholas' reign, Russia was seen as a major military power, with considerable strength. The Crimean War, fought shortly before Nicholas' death, demonstrated to both Russia and the world what few had previously realized: Russia was militarily weak, technologically backward, and administratively incompetent. Despite his grand ambitions toward the south and Turkey, Russia had not built railroad network in that direction, and communications were bad. The bureaucracy was unprepared for war being riddled with graft, corruption, and inefficiency. The Navy had few competent officers, the rank and file were poorly trained and most importantly its vessels were outdated; the army, although very large, was good only for parades, suffered from colonels who pocketed their men's pay, poor morale, and was even more out of touch with the latest technology as developed by Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* Great Britain, a large island comprising the countries of England, Scotland and Wales
* The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, a sovereign state in Europe comprising Great Britain and the north-eas ...
and France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
. By the war's end, Russia's leaders were determined to reform their military and society. As Fuller notes, "Russia had been beaten on the Crimean Peninsula, and the military feared that it would inevitably be beaten again unless steps were taken to surmount its military weakness."
An intensely militaristic man, Nicholas regarded the Army as the best and greatest institution in Russia and as a model for society, saying:
Nicholas was often exasperated by the slow pace of the Russian bureaucracy and had a marked preference for appointing generals and admirals to high government rank because of their perceived efficiency, overlooking or ignoring whether or not they were actually qualified for the role.Lincoln, W. Bruce "The Ministers of Nicholas I: A Brief Inquiry into Their Backgrounds and Service Careers" pp. 308–323 from ''The Russian Review'', Volume 34, Issue #3, July 1975 p. 313. Of the men who served as Nicholas's ministers, 61% had previously served as a general or an admiral. Nicholas liked to appoint generals who had seen combat, and at least 30 of the men who served as a minister under him had seen action in the wars against France, the Ottoman Empire, and Sweden. This proved to be something of a handicap in the sense that the sort of qualities that could make a man distinguished on the battlefields such as bravery did not necessarily make a man capable of running a ministry. The most notorious case was Prince Alexander Sergeyevich Menshikov
Prince Alexander Sergeyevich Menshikov (; 26 August 17872 May 1869) was a Russian nobleman, military commander and statesman. He was made adjutant general in 1817 and admiral in 1833.
A great-grandson of Alexander Danilovich Menshikov, Duke ...
, a competent brigade commander in the Imperial Army who proved himself out of his depth as a Navy minister. Of the Emperor's ministers, 78% were ethnic Russians, 9.6% were Baltic Germans while the rest were foreigners in Russian service. Of the men who served as ministers under Nicholas, 14 had graduated from university while another 14 had graduated from a ''lycée'' or a ''gymnasium'', the rest had all been educated by private tutors.
Europe
In foreign policy, Nicholas I acted as the protector of ruling legitimism and as guardian against revolution. It has often been noted that such policies were linked with the Metternich counter-revolutionary system through the Austrian ambassador Count Karl Ludwig von Ficquelmont. Nicholas's offers to suppress revolution on the European continent, trying to follow the pattern set by his eldest brother, Alexander I, earned him the label of "gendarme of Europe". Immediately on his succession Nicholas began to limit the liberties that existed under theconstitutional monarchy
Constitutional monarchy, also known as limited monarchy, parliamentary monarchy or democratic monarchy, is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in making decisions. ...
in Congress Poland
Congress Poland or Congress Kingdom of Poland, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland, was a polity created in 1815 by the Congress of Vienna as a semi-autonomous Polish state, a successor to Napoleon's Duchy of Warsaw. It was established w ...
. Nicholas was outraged when he learned of the Belgian revolt against the Dutch in 1830 and ordered the Imperial Russian Army
The Imperial Russian Army () was the army of the Russian Empire, active from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was organized into a standing army and a state militia. The standing army consisted of Regular army, regular troops and ...
to mobilize. Nicholas then petitioned the Prussian ambassador for Russian troops to be granted transit rights in order to march across Europe and restore Dutch hegemony over Belgium. But at the same time, a cholera
Cholera () is an infection of the small intestine by some Strain (biology), strains of the Bacteria, bacterium ''Vibrio cholerae''. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea last ...
epidemic was decimating Russian troops and the revolt in Poland tied down Russian soldiers which might have been deployed against the Belgians.Rendall, Matthew "Defensive Realism and the Concert of Europe" pages 523–540 from ''Review of International Studies'', Volume 32, Issue # 3 July 2006 p. 535. It seems likely that Nicholas's hawkish stance was not a sincere prelude towards invasion of the Low Countries, but rather an attempt to apply pressure on the other European powers. Nicholas made it clear he would only act if Prussia and Britain also participated as he feared that a Russian invasion of Belgium would cause a war with France. Even before the Poles rose up, Nicholas had cancelled his plans for invading Belgium as it became clear that neither Britain nor Prussia would join in while the French openly threatened war if Nicholas should march. In 1815, Nicholas arrived in France, where he stayed with the Duke of Orleans, Louis Philippe, who soon become one of his best friends, with the grand duke being impressed with duke's personal warmth, intelligence, manners and grace. For Nicholas the worst sort of characters were nobility who supported liberalism, and when the duc d'Orleans become the king of the French as Louis Philippe I
Louis Philippe I (6 October 1773 – 26 August 1850), nicknamed the Citizen King, was King of the French from 1830 to 1848, the penultimate monarch of France, and the last French monarch to bear the title "King". He abdicated from his throne ...
in the July revolution of 1830, Nicholas took this as a personal betrayal, believing his friend had gone over as he saw it to the dark side of revolution and liberalism. Nicholas hated Louis-Philippe, the self-styled ''Le roi citoyen'' ("the Citizen King") as a renegade nobleman and a "usurper", and his foreign policy starting in 1830 was primarily anti-French, based upon reviving the coalition that had existed during the Napoleonic era of Russia, Prussia, Austria and Britain, to isolate France. Nicholas detested Louis-Philippe to the point that he refused to use his name, referring to him merely as "the usurper". Britain was unwilling to join the anti-French coalition, but Nicholas was successful in cementing existing close ties with Austria and Prussia and the three imperial states regularly held joint military reviews during this time. For much of the 1830s, a sort of "cold war" existed between the liberal "western bloc" of France and Britain vs. the reactionary "eastern bloc" of Austria, Prussia and Russia.
After the November Uprising
The November Uprising (1830–31) (), also known as the Polish–Russian War 1830–31 or the Cadet Revolution,
was an armed rebellion in Russian Partition, the heartland of Partitions of Poland, partitioned Poland against the Russian Empire. ...
broke out, in 1831 the Polish parliament
The parliament of Poland is the Bicameralism, bicameral legislature of Poland. It is composed of an upper house (the Senate of Poland, Senate) and a lower house (the Sejm). Both houses are accommodated in the Sejm and Senate Complex of Poland, S ...
deposed Nicholas as king of Poland in response to his repeated curtailment of its constitutional rights. Nicholas reacted by sending Russian troops into Poland and brutally crushed the rebellion. Nicholas then proceeded to abrogate the Polish constitution
The Constitution of the Republic of Poland ( or ''Konstytucja RP'' for short) is the supreme law of the Republic of Poland, which is also commonly called the Third Polish Republic ( or ''III RP'' for short) in contrast with the preceding systems ...
in virtual entirety and reduced Poland to the status of a province called Vistula Land
Vistula Land, also known as Vistula Country (; ), was the name applied to the lands of Congress Poland from 1867, following the defeats of the November Uprising (1830–1831) and January Uprising (1863–1864) as it was increasingly stripped of ...
. Soon after, Nicholas embarked on a policy of repressing Polish culture beginning with suppressing the Polish Catholic Church. In the 1840s, Nicholas reduced 64,000 Polish nobles to commoner status.
In 1848, when a series of revolutions convulsed Europe, Nicholas was at the forefront of reactionism. In 1849, he helped the Habsburgs
The House of Habsburg (; ), also known as the House of Austria, was one of the most powerful dynasties in the history of Europe and Western civilization. They were best known for their inbreeding and for ruling vast realms throughout Europe d ...
to suppress the revolution in Hungary, and he also urged Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, ...
not to adopt a liberal constitution.
Ottoman Empire and Persia
 While Nicholas was attempting to maintain the status quo in Europe, he followed a somewhat more aggressive policy toward the neighbouring empires to the south, the
While Nicholas was attempting to maintain the status quo in Europe, he followed a somewhat more aggressive policy toward the neighbouring empires to the south, the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
and Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
. Nicholas was widely believed at the time to be following the traditional Russian policy of resolving the so-called Eastern Question by seeking to partition the Ottoman Empire and establish a protectorate over the Orthodox population of the Balkans
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
, still largely under Ottoman control in the 1820s.Rendall, Matthew "Restraint or Self-Restraint of Russia: Nicholas I, the Treaty of Unkiar Skelessi, and the Vienna System, 1832–1841" pp. 37–63 from ''The International History Review'', Volume 24, Issue #1, March 2002 p. 38. In fact, Nicholas was deeply committed to upholding the status quo in Europe and feared any attempt to devour the decaying Ottoman Empire would both upset his ally Austria, which also had interests in the Balkans, and bring about an Anglo-French coalition in defense of the Ottomans. Furthermore, in the war of 1828–29, the Russians defeated the Ottomans in every battle fought in the field and advanced deep into the Balkans, but the Russians discovered that they lacked the necessary logistical strength to take Constantinople.
Nicholas' policy towards the Ottoman Empire was to use the 1774 Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca which gave Russia a vague right as protector of Orthodox peoples in the Balkans, as a way of placing the Ottoman Empire into the Russian sphere of influence, which was felt to be a more achievable goal than conquering the entire Ottoman Empire. Nicholas actually wanted to preserve the Ottoman Empire as a stable but weak state that would be unable to stand up to Russia, which was felt to serve Russia's interests. Nicholas always thought of Russia as first and foremost a European power and regarded Europe as more important than the Middle East.Rendall, Matthew "Restraint or Self-Restraint of Russia: Nicholas I, the Treaty of Unkiar Skelessi, and the Vienna System, 1832–1841" pp. 37–63 from ''The International History Review'', Volume 24, Issue #1, March 2002 p. 48. The Russian Foreign Minister Karl Nesselrode
Karl Robert Reichsgraf von Nesselrode-Ehreshoven, also known as Charles de Nesselrode (; 14 December 1780 – 23 March 1862), was a Foreign policy of the Russian Empire, Russian diplomat of German nobility, German noble descent. For 40 years ( ...
wrote in letter to his ambassador in Constantinople Nikolai Muravyov that the victory of Muhammad Ali of Egypt
Muhammad Ali (4 March 1769 – 2 August 1849) was the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Albanians, Albanian viceroy and governor who became the ''de facto'' ruler of History of Egypt under the Muhammad Ali dynasty, Egypt from 1805 to 1848, widely consi ...
over Mahmud II would lead to a new dynasty ruling the Ottoman Empire. Nesselrode continued that if the able Muhammad Ali became sultan then it "could, with the elevation of a new personage to the Turkish throne, revive new strength in that declining empire and distract our attention and forces from European affairs, and thus the monarch icholasis especially concerned to keep the sultan on his tottering throne." At the same time, Nicholas argued that because of the economic importance to Russia of the Turkish straits, through which Russia exports its grain, that Russia had the "right" to intervene in Ottoman affairs. In 1833, Nicholas told the Austrian ambassador Karl Ludwig von Ficquelmont that "Oriental affairs are above all a matter for Russia." At the same time that Nicholas claimed the Ottoman Empire was within the Russian sphere of influence, he made it clear that he had no interest in annexing the empire. At another meeting with Ficquelmont in 1833, Nicholas, speaking with the "Greek Project" of Catherine the Great in mind said: "I know everything that has been said of the projects of the Empress Catherine, and Russia has renounced the goal she had set out. I wish to maintain the Turkish empire... It if falls, I do not desire its debris. I need nothing." Ultimately, Nicholas's policies in the Near East proved to be both costly and largely futile.
 In 1826–28, Nicholas fought the
In 1826–28, Nicholas fought the Russo-Persian War (1826–28)
The Russo-Persian Wars ( ), or the Russo-Iranian Wars ( ), began in 1651 and continued intermittently until 1828. They consisted of five conflicts in total, each rooted in both sides' disputed governance of territories and countries in the Cauc ...
, which ended with Persia forced to cede its last remaining territories in the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region spanning Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is situated between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, comprising parts of Southern Russia, Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan. The Caucasus Mountains, i ...
. Russia had conquered all the territories of Iran in both the North Caucasus
The North Caucasus, or Ciscaucasia, is a subregion in Eastern Europe governed by Russia. It constitutes the northern part of the wider Caucasus region, which separates Europe and Asia. The North Caucasus is bordered by the Sea of Azov and the B ...
and South Caucasus
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and West Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Armenia, ...
, comprising modern-day Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
, Dagestan
Dagestan ( ; ; ), officially the Republic of Dagestan, is a republic of Russia situated in the North Caucasus of Eastern Europe, along the Caspian Sea. It is located north of the Greater Caucasus, and is a part of the North Caucasian Fede ...
, Armenia
Armenia, officially the Republic of Armenia, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of West Asia. It is a part of the Caucasus region and is bordered by Turkey to the west, Georgia (country), Georgia to the north and Azerbaijan to ...
, and Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan, officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, is a Boundaries between the continents, transcontinental and landlocked country at the boundary of West Asia and Eastern Europe. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by ...
, through the course of the 19th century. The treaty further conceded extraterritoriality to Russian subjects in Iran (capitulation). As Professor Virginia Aksan adds, the 1828 Treaty of Turkmenchay
The Treaty of Turkmenchay (; ) was an agreement between Qajar Iran and the Russian Empire, which concluded the Russo-Persian War (1826–1828). It was second of the series of treaties (the first was the 1813 Treaty of Gulistan and the last, the ...
"removed Iran from the military equation."
Russia fought a successful war against the Ottomans in 1828–29, but it did little to increase Russian power in Europe. Only a small Greek state became independent in the Balkans, with limited Russian influence. In 1833, Russia negotiated the Treaty of Unkiar-Skelessi with the Ottoman Empire. The major European parties mistakenly believed that the treaty contained a secret clause granting Russia the right to transit warships through the Bosphorus
The Bosporus or Bosphorus Strait ( ; , colloquially ) is a natural strait and an internationally significant waterway located in Istanbul, Turkey. The Bosporus connects the Black Sea to the Sea of Marmara and forms one of the continental bo ...
and Dardanelles
The Dardanelles ( ; ; ), also known as the Strait of Gallipoli (after the Gallipoli peninsula) and in classical antiquity as the Hellespont ( ; ), is a narrow, natural strait and internationally significant waterway in northwestern Turkey th ...
straits. This misconception led to the London Straits Convention of 1841, which affirmed Ottoman control over the straits and forbade any power, including Russia, from sending warships through them. Buoyed by his role in suppressing the revolutions of 1848 as well as his mistaken belief he could rely on British diplomatic support, Nicholas moved against the Ottomans, who declared war on Russia on 8 October 1853. On 30 November, Russian Admiral Nakhimov caught the Turkish fleet in the harbor at Sinope and destroyed it.
Fearing the results of a total Ottoman defeat by Russia, in 1854 Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* Great Britain, a large island comprising the countries of England, Scotland and Wales
* The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, a sovereign state in Europe comprising Great Britain and the north-eas ...
, France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
, the Kingdom of Sardinia
The Kingdom of Sardinia, also referred to as the Kingdom of Sardinia and Corsica among other names, was a State (polity), country in Southern Europe from the late 13th until the mid-19th century, and from 1297 to 1768 for the Corsican part of ...
formed a military coalition and joined forces with the Ottoman Empire against Russia. The preceding conflict became known as the Crimean War
The Crimean War was fought between the Russian Empire and an alliance of the Ottoman Empire, the Second French Empire, the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, and the Kingdom of Sardinia (1720–1861), Kingdom of Sardinia-Piedmont fro ...
in the Ottoman Empire and Western Europe, but was labelled in Russia the "Eastern War" (Russian: Восточная война, ''Vostochnaya Vojna''). In April 1854, Austria signed a defensive pact with Prussia. Thus, Russia found herself in a war with every Great Power of Europe either allied against her militarily or diplomatically.
In 1853 Mikhail Pogodin, professor of history at Moscow University, wrote a memorandum to Nicholas. Nicholas himself read Pogodin's text and approvingly commented: "That is the whole point." According to historian Orlando Figes
Orlando Guy Figes (; born 20 November 1959) is a British and German historian and writer. He was a professor of history at Birkbeck College, University of London, where he was made Emeritus Professor on his retirement in 2022.
Figes is known f ...
, "The memorandum clearly struck a chord with Nicholas, who shared Pogodin's sense that Russia's role as the protector of the Orthodox had not been recognized or understood and that Russia was unfairly treated by the West." Pogodin wrote:
Austria offered the Ottomans diplomatic support, and Prussia remained neutral, thus leaving Russia without any allies on the continent. The European allies landed in Crimea
Crimea ( ) is a peninsula in Eastern Europe, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, almost entirely surrounded by the Black Sea and the smaller Sea of Azov. The Isthmus of Perekop connects the peninsula to Kherson Oblast in mainland Ukrain ...
and laid siege to the well-fortified Russian Sevastopol Naval Base
The Sevastopol Naval Base (; ) is an occupied naval base located in Sevastopol, in the disputed Crimean Peninsula. The base is used by the Russian Navy, and it is the main base of the Black Sea Fleet. Internationally, the base is recognised as ...
. The Russians lost battles at Alma in September 1854W. Bruce Lincoln, ''The Romanovs'', p. 425. and then at Inkerman. After the prolonged Siege of Sevastopol (1854–55) Siege of Sevastopol may refer to:
* Siege of Sevastopol (1854–1855), during the Crimean War
* Siege of Sevastopol (1941–1942), during the Second World War
* ''Siege of Sevastopol'' (panorama), a 1904 painted panorama by Franz Roubaud
See also ...
the base fell, exposing Russia's inability to defend a major fortification on its own soil. On the death of Nicholas I, Alexander II became emperor. On 15 January 1856, the new emperor took Russia out of the war on very unfavorable terms, which included the loss of a naval fleet on the Black Sea.
Death
 Nicholas died on 2 March 1855, during the Crimean War, at the
Nicholas died on 2 March 1855, during the Crimean War, at the Winter Palace
The Winter Palace is a palace in Saint Petersburg that served as the official residence of the House of Romanov, previous emperors, from 1732 to 1917. The palace and its precincts now house the Hermitage Museum. The floor area is 233,345 square ...
in St. Petersburg
Saint Petersburg, formerly known as Petrograd and later Leningrad, is the second-largest city in Russia after Moscow. It is situated on the River Neva, at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea. The city had a population of 5,601, ...
. He caught a chill, refused medical treatment and died of pneumonia
Pneumonia is an Inflammation, inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as Pulmonary alveolus, alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of Cough#Classification, productive or dry cough, ches ...
, although there were rumors he was committing a passive suicide by refusing treatment. He was buried in the Peter and Paul Cathedral in St. Petersburg. He reigned for 30 years, and was succeeded by his son Alexander II.
Legacy
There have been many damning verdicts on Nicholas' rule and legacy, despite occasional efforts to revive his reputation. At the end of his life, one of his most devoted civil servants, Aleksandr Nikitenko, opined, "the main failing of the reign of Nicholas Pavlovich was that it was all a mistake." In 1891 Lev Tolstoy popularised the nickname Николай Палкин (Nicholas the Stick) in reference to the late emperor's passion for military discipline. Historian Barbara Jelavich points to many failures, including the "catastrophic state of Russian finances", the badly-equipped army, the inadequate transportation system, and a bureaucracy "characterized by graft, corruption, and inefficiency".Kiev University
The Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv (; also known as Kyiv University, Shevchenko University, or KNU) is a public university in Kyiv, Ukraine.
The university is the third-oldest university in Ukraine after the University of Lviv and ...
was founded in 1834 by Nicholas. In 1854, there were 3600 university students in Russia, 1000 fewer than in 1848. Censorship was omnipresent; historian Hugh Seton-Watson writes: "the intellectual atmosphere remained oppressive until the end of the reign."
The Frenchman Marquis de Custine wrote the widely-read travel book '' La Russie en 1839''''Empire of the Czar: A Journey Through Eternal Russia''
. He speculated that Nicholas had a kind heart, but his sincere sense of duty forced him to impose severe discipline: "If the Emperor has no more of mercy in his heart than he reveals in his policies, then I pity Russia; if, on the other hand, his true sentiments are really superior to his acts, then I pity the Emperor." According to a popular
legend
A legend is a genre of folklore that consists of a narrative featuring human actions, believed or perceived to have taken place in human history. Narratives in this genre may demonstrate human values, and possess certain qualities that give the ...
, when the Saint Petersburg–Moscow Railway was planned in 1842, Nicholas drew a straight line between the cities on a map, and decreed this as the path of the new rail line. Some ridiculed this as the epitome of Nicholas' mindless despotism, while others praised the tsar for overcoming local interests that wanted the railway diverted their own way. In fact, however, the tsar had merely endorsed the straight path recommended by engineers.
Honours
Issue
Nicholas I had seven legitimate children with his wife, Alexandra Feodorovna.Sebag Montefiore, p. 475 Many sources state that Nicholas did not have an extramarital affair until after 25 years of marriage, in 1842, when the Empress's doctors prohibited her from having sexual intercourse, due to her poor health and recurring heart attacks. Many facts dispute this claim. Nicholas fathered three known children with mistresses prior to 1842, including one with his most famous and well documented mistress, Varvara Nelidova. With Anna-Maria Charlota de Rutenskiold (1791–1856) * Joséphine or Youzia Koberwein (12 May 1825 – 23 February 1893) With Varvara Yakovleva (1803–1831) * Olga Carlovna Albrecht (10 July 1828 – 20 January 1898) With Varvara Nelidova (d.1897) * Alexis Pashkine (17 April 1831 – 20 June 1863)Ancestry
See also
*History of Russia
The history of Russia begins with the histories of the East Slavs. The traditional start date of specifically Russian history is the establishment of the Rus' people, Rus' state in the north in the year 862, ruled by Varangians. In 882, Prin ...
* Imperial Russia
Imperial is that which relates to an empire, emperor/empress, or imperialism.
Imperial or The Imperial may also refer to:
Places
United States
* Imperial, California
* Imperial, Missouri
* Imperial, Nebraska
* Imperial, Pennsylvania
* ...
* '' La Russie en 1839''
* The Third Section
* Tsars of Russia family tree
Notes
References
* The first draft of this article was taken with little editing from theLibrary of Congress
The Library of Congress (LOC) is a research library in Washington, D.C., serving as the library and research service for the United States Congress and the ''de facto'' national library of the United States. It also administers Copyright law o ...
Federal Research Division's Country Studies series. As their home page at http://lcweb2.loc.gov/frd/cs/cshome.html says, ''"Information contained in the Country Studies On-Line is not copyrighted and thus is available for free and unrestricted use by researchers. As a courtesy, however, appropriate credit should be given to the series."'' Please leave this statement intact so that credit can be given.
*
Further reading
* Bolsover, George H. "Nicholas I and the Partition of Turkey." ''Slavonic and East European Review'' (1948): 115–14online
* Cannady, Sean, and Paul Kubicek. "Nationalism and legitimation for authoritarianism: A comparison of Nicholas I and Vladimir Putin." '' Journal of Eurasian Studies'' 5.1 (2014): 1–
online
* Crisp, Olga. "The state peasants under Nicholas I." ''Slavonic and East European Review'' 37.89 (1959): 387–41
online
* Curtiss, John Shelton. "The Army of Nicholas I: Its Role and Character." ''American Historical Review'' 63.4 (1958): 880–88
online
* Hamlin, Cyrus. "The Political Duel Between Nicholas, the Czar of Russia, and Lord Stratford de Redcliffe, the Great English Ambassador." ''Proceedings of the American Antiquarian Society'' Vol. 9. (1893
online
* Hosking, Geoffrey A. ''Russia: People and Empire, 1552–1917'', (Harvard University Press, 1997) * Kagan, Frederick W. ''The military reforms of Nicholas I'' (Palgrave Macmillan US, 1999). * Kutscheroff, Samuel. "Administration of Justice under Nicholas I of Russia." ''American Slavic and East European Review'' (1948): 125–138
in JSTOR
* Lincoln, W. Bruce. "Nicholas I: Russia's Last Absolute Monarch," ''History Today'' (1971) 21 #2 pp. 79–88. * Lincoln, W. Bruce. ''Nicholas I: Emperor and Autocrat of All the Russias'' (1989
online
* Monas, Sidney. ''The Third Section: police and society in Russia under Nicholas I'' (Harvard University Press, 1961) * Presni͡akov, A. E. ''Emperor Nicholas I of Russia: the apogee of autocracy, 1825/1855'' (1974
online
* Pintner, Walter McKenzie. ''Russian economic policy under Nicholas I'' (1967
online
* Rendall, Matthew. "Restraint or Self-Restraint of Russia: Nicholas I, the Treaty of Unkiar Skelessi, and the Vienna System, 1832–1841." ''International History Review'' 24.1 (2002): 37–63. *Rebecchini, Damiano. (2010). "An influential collector: Tsar Nicholas I of Russia." ''Journal of the History of Collections.'' V. 22, Issue 1, (May): 45–67. * Riasanovsky, Nicholas V. "'Nationality' in the State Ideology during the Reign of Nicholas I." ''Russian Review'' (1960): 38–4
online
* Riasanovsky, Nicholas V. ''Nicholas I and Official Nationality in Russia, 1825–1855'' (1967
online
* Roberts, Ian W. ''Nicholas I and the Russian intervention in Hungary'' (Springer, 1991). * Stanislawski, Michael. ''Tsar Nicholas I and the Jews : the transformation of Jewish society in Russia, 1825–1855'' (1983
online
External links
* * – Historical reconstruction "The Romanovs". StarMedia. Babich-Design(Russia, 2013) {{DEFAULTSORT:Nicholas of Russia 1796 births 1855 deaths 19th-century Russian monarchs 19th-century Polish monarchs Burials at Saints Peter and Paul Cathedral, Saint Petersburg House of Holstein-Gottorp-Romanov 3 3 3 Grand Crosses of the Order of Saint Stephen of Hungary Knights Grand Cross of the Military Order of William Knights of the Golden Fleece of Spain Extra Knights Companion of the Garter People of the Revolutions of 1848 People of the Russo-Persian Wars Heads of state of Finland Emperors of Russia Grand dukes of Russia Russian people of the Crimean War 18th-century people from the Russian Empire Russification Children of Paul I of Russia People of the Caucasian War Deaths from pneumonia in the Russian Empire Sons of Russian emperors Sons of counts