electrical engineer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Electrical engineering is an
 In the 19th century, research into the subject started to intensify. Notable developments in this century include the work of
In the 19th century, research into the subject started to intensify. Notable developments in this century include the work of
 During the development of radio, many scientists and inventors contributed to
During the development of radio, many scientists and inventors contributed to
Antentop
', Vol. 2, No.3, pp. 87–96. when he patented the radio

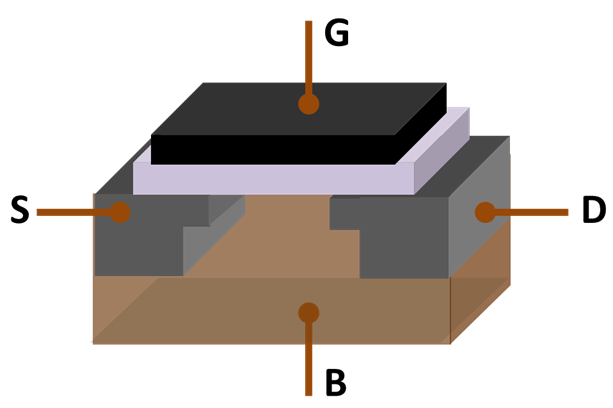 The first working
The first working
 Power & Energy engineering deals with the
Power & Energy engineering deals with the
 Telecommunications engineering focuses on the transmission of information across a
Telecommunications engineering focuses on the transmission of information across a

 Electronic engineering involves the design and testing of
Electronic engineering involves the design and testing of



 Computer engineering deals with the design of computers and
Computer engineering deals with the design of computers and


 Electrical engineers typically possess an
Electrical engineers typically possess an  At many schools, electronic engineering is included as part of an electrical award, sometimes explicitly, such as a Bachelor of Engineering (Electrical and Electronic), but in others, electrical and electronic engineering are both considered to be sufficiently broad and complex that separate degrees are offered.
Some electrical engineers choose to study for a postgraduate degree such as a
At many schools, electronic engineering is included as part of an electrical award, sometimes explicitly, such as a Bachelor of Engineering (Electrical and Electronic), but in others, electrical and electronic engineering are both considered to be sufficiently broad and complex that separate degrees are offered.
Some electrical engineers choose to study for a postgraduate degree such as a
 The advantages of licensure vary depending upon location. For example, in the United States and Canada "only a licensed engineer may seal engineering work for public and private clients". This requirement is enforced by state and provincial legislation such as
The advantages of licensure vary depending upon location. For example, in the United States and Canada "only a licensed engineer may seal engineering work for public and private clients". This requirement is enforced by state and provincial legislation such as
 Fundamental to the discipline are the sciences of
Fundamental to the discipline are the sciences of  Although most electrical engineers will understand basic
Although most electrical engineers will understand basic  A wide range of instrumentation is used by electrical engineers. For simple control circuits and alarms, a basic
A wide range of instrumentation is used by electrical engineers. For simple control circuits and alarms, a basic  For many engineers, technical work accounts for only a fraction of the work they do. A lot of time may also be spent on tasks such as discussing proposals with clients, preparing
For many engineers, technical work accounts for only a fraction of the work they do. A lot of time may also be spent on tasks such as discussing proposals with clients, preparing
International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC)
in-depth look at Electrical Engineering – online courses with video lectures.
IEEE Global History Network
A wiki-based site with many resources about the history of IEEE, its members, their professions and electrical and informational technologies and sciences. {{Authority control Electronic engineering Computer engineering Electrical and computer engineering Engineering disciplines
engineering
Engineering is the practice of using natural science, mathematics, and the engineering design process to Problem solving#Engineering, solve problems within technology, increase efficiency and productivity, and improve Systems engineering, s ...
discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems that use electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter possessing an electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwel ...
, electronics
Electronics is a scientific and engineering discipline that studies and applies the principles of physics to design, create, and operate devices that manipulate electrons and other Electric charge, electrically charged particles. It is a subfield ...
, and electromagnetism
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge via electromagnetic fields. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental forces of nature. It is the dominant force in the interacti ...
. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the latter half of the 19th century after the commercialization
Commercialisation or commercialization is the process of introducing a new product or production method into commerce—making it available on the market. The term often connotes especially entry into the mass market (as opposed to entry into e ...
of the electric telegraph
Electrical telegraphy is Point-to-point (telecommunications), point-to-point distance communicating via sending electric signals over wire, a system primarily used from the 1840s until the late 20th century. It was the first electrical telecom ...
, the telephone, and electrical power
Electric power is the rate of transfer of electrical energy within a electric circuit, circuit. Its SI unit is the watt, the general unit of power (physics), power, defined as one joule per second. Standard prefixes apply to watts as with oth ...
generation, distribution, and use.
Electrical engineering is divided into a wide range of different fields, including computer engineering
Computer engineering (CE, CoE, or CpE) is a branch of engineering specialized in developing computer hardware and software.
It integrates several fields of electrical engineering, electronics engineering and computer science.
Computer engi ...
, systems engineering
Systems engineering is an interdisciplinary field of engineering and engineering management that focuses on how to design, integrate, and manage complex systems over their Enterprise life cycle, life cycles. At its core, systems engineering uti ...
, power engineering
Power engineering, also called power systems engineering, is a subfield of electrical engineering that deals with the generation, transmission, distribution, and utilization of electric power, and the electrical apparatus connected to such sy ...
, telecommunications
Telecommunication, often used in its plural form or abbreviated as telecom, is the transmission of information over a distance using electronic means, typically through cables, radio waves, or other communication technologies. These means of ...
, radio-frequency engineering
Radio-frequency (RF) engineering is a subset of electrical engineering involving the application of transmission line, Waveguide (electromagnetism), waveguide, Antenna (radio), antenna, radar, and Electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic fiel ...
, signal processing
Signal processing is an electrical engineering subfield that focuses on analyzing, modifying and synthesizing ''signals'', such as audio signal processing, sound, image processing, images, Scalar potential, potential fields, Seismic tomograph ...
, instrumentation
Instrumentation is a collective term for measuring instruments, used for indicating, measuring, and recording physical quantities. It is also a field of study about the art and science about making measurement instruments, involving the related ...
, photovoltaic cell
A solar cell, also known as a photovoltaic cell (PV cell), is an electronic device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by means of the photovoltaic effect.
s, electronics
Electronics is a scientific and engineering discipline that studies and applies the principles of physics to design, create, and operate devices that manipulate electrons and other Electric charge, electrically charged particles. It is a subfield ...
, and optics
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of optical instruments, instruments that use or Photodetector, detect it. Optics usually describes t ...
and photonics
Photonics is a branch of optics that involves the application of generation, detection, and manipulation of light in the form of photons through emission, transmission, modulation, signal processing, switching, amplification, and sensing. E ...
. Many of these disciplines overlap with other engineering branches, spanning a huge number of specializations including hardware engineering, power electronics
Power electronics is the application of electronics to the control and conversion of electric power.
The first high-power electronic devices were made using mercury-arc valves. In modern systems, the conversion is performed with semiconduct ...
, electromagnetics
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge via electromagnetic fields. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental forces of nature. It is the dominant force in the interacti ...
and waves, microwave engineering, nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is the manipulation of matter with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometers (nm). At this scale, commonly known as the nanoscale, surface area and quantum mechanical effects become important in describing propertie ...
, electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry concerned with the relationship between Electric potential, electrical potential difference and identifiable chemical change. These reactions involve Electron, electrons moving via an electronic ...
, renewable energies, mechatronics/control, and electrical materials science.
Electrical engineers typically hold a degree in electrical engineering, electronic or electrical and electronic engineering. Practicing engineers may have professional certification
Professional certification, trade certification, or professional designation, often called simply ''certification'' or ''qualification'', is a designation earned by a person to assure qualification to perform a job or task. Not all certifications ...
and be members of a professional body
A professional association (also called a professional body, professional organization, or professional society) is a group that usually seeks to advocacy, further a particular profession, the interests of individuals and organisations engaged in ...
or an international standards organization. These include the International Electrotechnical Commission
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC; ) is an international standards organization that prepares and publishes international standards for all electrical, electronics, electronic and related technologies. IEC standards cover a va ...
(IEC), the National Society of Professional Engineers
The National Society of Professional Engineers (abbreviate as NSPE) is a professional association representing licensed professional engineers in the United States. NSPE is the recognized voice and advocate of licensed Professional Engineers repr ...
(NSPE), the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is an American 501(c)(3) public charity professional organization for electrical engineering, electronics engineering, and other related disciplines.
The IEEE has a corporate office ...
(IEEE) and the Institution of Engineering and Technology
The Institution of Engineering and Technology (IET) is a multidisciplinary professional engineering institution. The IET was formed in 2006 from two separate institutions: the Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE), dating back to 1871,Engin ...
(IET, formerly the IEE).
Electrical engineers work in a very wide range of industries and the skills required are likewise variable. These range from circuit theory
Circuit may refer to:
Science and technology
Electrical engineering
* Electrical circuit, a complete electrical network with a closed-loop giving a return path for current
** Analog circuit, uses continuous signal levels
** Balanced circu ...
to the management skills of a project manager
A project manager is a professional in the field of project management. Project managers have the responsibility of the Project planning, planning, procurement and execution of a project, in any undertaking that has a defined scope, defined star ...
. The tools and equipment that an individual engineer may need are similarly variable, ranging from a simple voltmeter
A voltmeter is an instrument used for measuring electric potential difference between two points in an electric circuit. It is connected in parallel. It usually has a high resistance so that it takes negligible current from the circuit.
A ...
to sophisticated design and manufacturing software.
History
Electricity has been a subject of scientific interest since at least the early 17th century. William Gilbert was a prominent early electrical scientist, and was the first to draw a clear distinction betweenmagnetism
Magnetism is the class of physical attributes that occur through a magnetic field, which allows objects to attract or repel each other. Because both electric currents and magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, ...
and static electricity
Static electricity is an imbalance of electric charges within or on the surface of a material. The charge remains until it can move away by an electric current or electrical discharge. The word "static" is used to differentiate it from electric ...
. He is credited with establishing the term "electricity". He also designed the versorium: a device that detects the presence of statically charged objects. In 1762 Swedish professor Johan Wilcke invented a device later named electrophorus
In electromagnetism, an electrophorus or electrophore is a simple, manual, Capacitor, capacitive, electrostatic generator used to produce Electric charge, charge via the process of electrostatic induction. A first version of it was invented in 1 ...
that produced a static electric charge. By 1800 Alessandro Volta
Alessandro Giuseppe Antonio Anastasio Volta (, ; ; 18 February 1745 – 5 March 1827) was an Italian chemist and physicist who was a pioneer of electricity and Power (physics), power, and is credited as the inventor of the electric battery a ...
had developed the voltaic pile
upright=1.2, Schematic diagram of a copper–zinc voltaic pile. Each copper–zinc pair had a spacer in the middle, made of cardboard or felt soaked in salt water (the electrolyte). Volta's original piles contained an additional zinc disk at the ...
, a forerunner of the electric battery.
19th century
 In the 19th century, research into the subject started to intensify. Notable developments in this century include the work of
In the 19th century, research into the subject started to intensify. Notable developments in this century include the work of Hans Christian Ørsted
Hans Christian Ørsted (; 14 August 1777 – 9 March 1851), sometimes Transliteration, transliterated as Oersted ( ), was a Danish chemist and physicist who discovered that electric currents create magnetic fields. This phenomenon is known as ...
, who discovered in 1820 that an electric current produces a magnetic field that will deflect a compass needle; of William Sturgeon
William Sturgeon (; 22 May 1783 – 4 December 1850) was an English electrical engineer and inventor who made the first electromagnet and the first practical electric motor.
Early life
Sturgeon was born on 22 May 1783 in Whittington, near ...
, who in 1825 invented the electromagnet
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. Electromagnets usually consist of wire (likely copper) wound into a electromagnetic coil, coil. A current through the wire creates a magnetic ...
; of Joseph Henry
Joseph Henry (December 17, 1797– May 13, 1878) was an American physicist and inventor who served as the first secretary of the Smithsonian Institution. He was the secretary for the National Institute for the Promotion of Science, a precursor ...
and Edward Davy
Edward Davy (16 June 1806 – 26 January 1885) was an English physician, scientist, and inventor who played a prominent role in the development of telegraphy, and invented an electric relay.
Davy was born in Ottery St Mary, Devonshire, Engla ...
, who invented the electrical relay in 1835; of Georg Ohm
Georg Simon Ohm (; ; 16 March 1789 – 6 July 1854) was a German mathematician and physicist. As a school teacher, Ohm began his research with the new electrochemical cell, invented by Italian scientist Alessandro Volta. Using equipment of his o ...
, who in 1827 quantified the relationship between the electric current
An electric current is a flow of charged particles, such as electrons or ions, moving through an electrical conductor or space. It is defined as the net rate of flow of electric charge through a surface. The moving particles are called charge c ...
and potential difference
Voltage, also known as (electrical) potential difference, electric pressure, or electric tension, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a static electric field, it corresponds to the work needed per unit of charge ...
in a conductor; of Michael Faraday
Michael Faraday (; 22 September 1791 – 25 August 1867) was an English chemist and physicist who contributed to the study of electrochemistry and electromagnetism. His main discoveries include the principles underlying electromagnetic inducti ...
, the discoverer of electromagnetic induction
Electromagnetic or magnetic induction is the production of an electromotive force, electromotive force (emf) across an electrical conductor in a changing magnetic field.
Michael Faraday is generally credited with the discovery of induction in 1 ...
in 1831; and of James Clerk Maxwell
James Clerk Maxwell (13 June 1831 – 5 November 1879) was a Scottish physicist and mathematician who was responsible for the classical theory of electromagnetic radiation, which was the first theory to describe electricity, magnetism an ...
, who in 1873 published a unified theory
A theory is a systematic and rational form of abstract thinking about a phenomenon, or the conclusions derived from such thinking. It involves contemplative and logical reasoning, often supported by processes such as observation, experimentation, ...
of electricity and magnetism
Magnetism is the class of physical attributes that occur through a magnetic field, which allows objects to attract or repel each other. Because both electric currents and magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, ...
in his treatise ''Electricity and Magnetism''.
In 1782, Georges-Louis Le Sage developed and presented in Berlin
Berlin ( ; ) is the Capital of Germany, capital and largest city of Germany, by both area and List of cities in Germany by population, population. With 3.7 million inhabitants, it has the List of cities in the European Union by population withi ...
probably the world's first form of electric telegraphy, using 24 different wires, one for each letter of the alphabet. This telegraph connected two rooms. It was an electrostatic telegraph that moved gold leaf through electrical conduction.
In 1795, Francisco Salva Campillo proposed an electrostatic telegraph system. Between 1803 and 1804, he worked on electrical telegraphy, and in 1804, he presented his report at the Royal Academy of Natural Sciences and Arts of Barcelona. Salva's electrolyte telegraph system was very innovative though it was greatly influenced by and based upon two discoveries made in Europe in 1800—Alessandro Volta's electric battery for generating an electric current and William Nicholson and Anthony Carlyle's electrolysis of water. Electrical telegraph
Electrical telegraphy is point-to-point distance communicating via sending electric signals over wire, a system primarily used from the 1840s until the late 20th century. It was the first electrical telecommunications system and the most wid ...
y may be considered the first example of electrical engineering. Electrical engineering became a profession in the later 19th century. Practitioners had created a global electric telegraph
Electrical telegraphy is Point-to-point (telecommunications), point-to-point distance communicating via sending electric signals over wire, a system primarily used from the 1840s until the late 20th century. It was the first electrical telecom ...
network, and the first professional electrical engineering institutions were founded in the UK and the US to support the new discipline. Francis Ronalds
Sir Francis Ronalds Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS (21 February 17888 August 1873) was an English scientist and inventor, and arguably the first History of electrical engineering, electrical engineer. He was knighted for creating the first wo ...
created an electric telegraph system in 1816 and documented his vision of how the world could be transformed by electricity. Over 50 years later, he joined the new Society of Telegraph Engineers (soon to be renamed the Institution of Electrical Engineers
The Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE) was a British professional organisation of electronics, electrical, manufacturing, and information technology professionals, especially electrical engineers. It began in 1871 as the Society of Tel ...
) where he was regarded by other members as the first of their cohort. By the end of the 19th century, the world had been forever changed by the rapid communication made possible by the engineering development of land-lines, submarine cables, and, from about 1890, wireless telegraphy
Wireless telegraphy or radiotelegraphy is the transmission of text messages by radio waves, analogous to electrical telegraphy using electrical cable, cables. Before about 1910, the term ''wireless telegraphy'' was also used for other experimenta ...
.
Practical applications and advances in such fields created an increasing need for standardized units of measure. They led to the international standardization of the units volt
The volt (symbol: V) is the unit of electric potential, Voltage#Galvani potential vs. electrochemical potential, electric potential difference (voltage), and electromotive force in the International System of Units, International System of Uni ...
, ampere
The ampere ( , ; symbol: A), often shortened to amp,SI supports only the use of symbols and deprecates the use of abbreviations for units. is the unit of electric current in the International System of Units (SI). One ampere is equal to 1 c ...
, coulomb
The coulomb (symbol: C) is the unit of electric charge in the International System of Units (SI).
It is defined to be equal to the electric charge delivered by a 1 ampere current in 1 second, with the elementary charge ''e'' as a defining c ...
, ohm
Ohm (symbol Ω) is a unit of electrical resistance named after Georg Ohm.
Ohm or OHM may also refer to:
People
* Georg Ohm (1789–1854), German physicist and namesake of the term ''ohm''
* Germán Ohm (born 1936), Mexican boxer
* Jörg Ohm (1 ...
, farad
The farad (symbol: F) is the unit of electrical capacitance, the ability of a body to store an electrical charge, in the International System of Units, International System of Units (SI), equivalent to 1 coulomb per volt (C/V). It is named afte ...
, and henry
Henry may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Henry (given name), including lists of people and fictional characters
* Henry (surname)
* Henry, a stage name of François-Louis Henry (1786–1855), French baritone
Arts and entertainmen ...
. This was achieved at an international conference in Chicago
Chicago is the List of municipalities in Illinois, most populous city in the U.S. state of Illinois and in the Midwestern United States. With a population of 2,746,388, as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the List of Unite ...
in 1893. The publication of these standards formed the basis of future advances in standardization in various industries, and in many countries, the definitions were immediately recognized in relevant legislation.
During these years, the study of electricity was largely considered to be a subfield of physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge whi ...
since early electrical technology was considered electromechanical
Electromechanics combine processes and procedures drawn from electrical engineering and mechanical engineering. Electromechanics focus on the interaction of electrical and mechanical systems as a whole and how the two systems interact with each ...
in nature. The Technische Universität Darmstadt founded the world's first department of electrical engineering in 1882 and introduced the first-degree course in electrical engineering in 1883. The first electrical engineering degree program in the United States was started at Massachusetts Institute of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a Private university, private research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Established in 1861, MIT has played a significant role in the development of many areas of moder ...
(MIT) in the physics department under Professor Charles Cross, though it was Cornell University
Cornell University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university based in Ithaca, New York, United States. The university was co-founded by American philanthropist Ezra Cornell and historian and educator Andrew Dickson W ...
to produce the world's first electrical engineering graduates in 1885. The first course in electrical engineering was taught in 1883 in Cornell's Sibley College of Mechanical Engineering and Mechanic Arts.
In about 1885, Cornell President Andrew Dickson White
Andrew Dickson White (November 7, 1832 – November 4, 1918) was an American historian and educator who co-founded Cornell University, one of eight Ivy League universities in the United States, and served as its first president for nearly two de ...
established the first Department of Electrical Engineering in the United States. In the same year, University College London
University College London (Trade name, branded as UCL) is a Public university, public research university in London, England. It is a Member institutions of the University of London, member institution of the Federal university, federal Uni ...
founded the first chair of electrical engineering in Great Britain. Professor Mendell P. Weinbach at University of Missouri
The University of Missouri (Mizzou or MU) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Columbia, Missouri, United States. It is Missouri's largest university and the flagship of the four-campus Univers ...
established the electrical engineering department in 1886. Afterwards, universities and institutes of technology
An institute of technology (also referred to as technological university, technical university, university of technology, polytechnic university) is an institution of tertiary education that specializes in engineering, technology, applied science ...
gradually started to offer electrical engineering programs to their students all over the world.
During these decades the use of electrical engineering increased dramatically. In 1882, Thomas Edison
Thomas Alva Edison (February11, 1847October18, 1931) was an American inventor and businessman. He developed many devices in fields such as electric power generation, mass communication, sound recording, and motion pictures. These inventions, ...
switched on the world's first large-scale electric power network that provided 110 volts—direct current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional electric current, flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor (material), conductor such as a wire, but can also flow throug ...
(DC)—to 59 customers on Manhattan Island
Manhattan ( ) is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. Coextensive with New York County, Manhattan is the smallest county by area in the U.S. state of New York. Located almost entire ...
in New York City. In 1884, Sir Charles Parsons
Sir Charles Algernon Parsons (13 June 1854 – 11 February 1931) was an Anglo-Irish people, Anglo-Irish mechanical engineer and inventor who designed the modern steam turbine in 1884. His invention revolutionised marine propulsion, and he was al ...
invented the steam turbine
A steam turbine or steam turbine engine is a machine or heat engine that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam and uses it to do mechanical work utilising a rotating output shaft. Its modern manifestation was invented by Sir Charles Par ...
allowing for more efficient electric power generation. Alternating current
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current that periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time, in contrast to direct current (DC), which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in w ...
, with its ability to transmit power more efficiently over long distances via the use of transformer
In electrical engineering, a transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple Electrical network, circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces ...
s, developed rapidly in the 1880s and 1890s with transformer designs by Károly Zipernowsky, Ottó Bláthy
Ottó Titusz Bláthy (11 August 1860 – 26 September 1939) was a Hungarian electrical engineer. During his career he became the co-inventor of the modern electric transformer, the voltage regulator, the AC watt-hour meter, the turbo genera ...
and Miksa Déri (later called ZBD transformers), Lucien Gaulard
Lucien Gaulard (16 July 1850 – 26 November 1888) was a French engineer who invented devices for the transmission of alternating current electrical energy.
Biography
Gaulard was born in Paris, France in 1850.
A power transformer developed by G ...
, John Dixon Gibbs
John Dixon Gibbs (1834–1912) was a British engineer and financier who, together with Lucien Gaulard, is often credited as the co-inventor of the AC step-down transformer. The transformer was first demonstrated in 1883 at London's Royal Aquari ...
and William Stanley Jr. Practical AC motor
An AC motor is an electric motor driven by an alternating current (AC). The AC motor commonly consists of two basic parts, an outside stator having coils supplied with alternating current to produce a rotating magnetic field, and an inside roto ...
designs including induction motor
An induction motor or asynchronous motor is an AC motor, AC electric motor in which the electric current in the rotor (electric), rotor that produces torque is obtained by electromagnetic induction from the magnetic field of the stator winding ...
s were independently invented by Galileo Ferraris
Galileo Ferraris (31 October 1847 – 7 February 1897) was an Italian university professor, physicist and electrical engineer, one of the pioneers of AC power system and inventor of the induction motor although he never patented his work. Many ne ...
and Nikola Tesla
Nikola Tesla (;"Tesla"
. ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. ; 10 July 1856 – 7 ...
and further developed into a practical . ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. ; 10 July 1856 – 7 ...
three-phase
Three-phase electric power (abbreviated 3ϕ) is a common type of alternating current (AC) used in electricity generation, Electric power transmission, transmission, and Electric power distribution, distribution. It is a type of polyphase system ...
form by Mikhail Dolivo-Dobrovolsky
Mikhail Osipovich Dolivo-Dobrovolsky (; or ''Michail Ossipowitsch Doliwo-Dobrowolski''; – ) was a Russian-born engineer, electrician, and inventor of Polish-Russian origins, active in the German Empire and also in Switzerland.
After study ...
and Charles Eugene Lancelot Brown. Charles Steinmetz and Oliver Heaviside
Oliver Heaviside ( ; 18 May 1850 – 3 February 1925) was an English mathematician and physicist who invented a new technique for solving differential equations (equivalent to the Laplace transform), independently developed vector calculus, an ...
contributed to the theoretical basis of alternating current engineering. The spread in the use of AC set off in the United States what has been called the '' war of the currents'' between a George Westinghouse
George Westinghouse Jr. (October 6, 1846 – March 12, 1914) was a prolific American inventor, engineer, and entrepreneurial industrialist based in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. He is best known for his creation of the railway air brake and for bei ...
backed AC system and a Thomas Edison backed DC power system, with AC being adopted as the overall standard.
Early 20th century
 During the development of radio, many scientists and inventors contributed to
During the development of radio, many scientists and inventors contributed to radio technology
Radio is the technology of communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 3 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmitter connected to ...
and electronics. The mathematical work of James Clerk Maxwell
James Clerk Maxwell (13 June 1831 – 5 November 1879) was a Scottish physicist and mathematician who was responsible for the classical theory of electromagnetic radiation, which was the first theory to describe electricity, magnetism an ...
during the 1850s had shown the relationship of different forms of electromagnetic radiation
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) is a self-propagating wave of the electromagnetic field that carries momentum and radiant energy through space. It encompasses a broad spectrum, classified by frequency or its inverse, wavelength ...
including the possibility of invisible airborne waves (later called "radio waves"). In his classic physics experiments of 1888, Heinrich Hertz
Heinrich Rudolf Hertz (; ; 22 February 1857 – 1 January 1894) was a German physicist who first conclusively proved the existence of the electromagnetic waves predicted by James Clerk Maxwell's equations of electromagnetism.
Biography
Heinri ...
proved Maxwell's theory by transmitting radio wave
Radio waves (formerly called Hertzian waves) are a type of electromagnetic radiation with the lowest frequencies and the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, typically with frequencies below 300 gigahertz (GHz) and wavelengths g ...
s with a spark-gap transmitter
A spark-gap transmitter is an obsolete type of transmitter, radio transmitter which generates radio waves by means of an electric spark."Radio Transmitters, Early" in Spark-gap transmitters were the first type of radio transmitter, and were the m ...
, and detected them by using simple electrical devices. Other physicists experimented with these new waves and in the process developed devices for transmitting and detecting them. In 1895, Guglielmo Marconi
Guglielmo Giovanni Maria Marconi, 1st Marquess of Marconi ( ; ; 25 April 1874 – 20 July 1937) was an Italian electrical engineer, inventor, and politician known for his creation of a practical radio wave-based Wireless telegraphy, wireless tel ...
began work on a way to adapt the known methods of transmitting and detecting these "Hertzian waves" into a purpose-built commercial wireless telegraphic system. Early on, he sent wireless signals over a distance of one and a half miles. In December 1901, he sent wireless waves that were not affected by the curvature of the Earth. Marconi later transmitted the wireless signals across the Atlantic between Poldhu, Cornwall
Cornwall (; or ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South West England. It is also one of the Celtic nations and the homeland of the Cornish people. The county is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, ...
, and St. John's, Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region of Labrador, having a total size of . As of 2025 the population ...
, a distance of .
Millimetre wave
Extremely high frequency (EHF) is the International Telecommunication Union designation for the band of radio frequencies in the electromagnetic spectrum from 30 to 300 gigahertz (GHz). It is in the microwave part of the radio spectrum, between t ...
communication was first investigated by Jagadish Chandra Bose
Sir Jagadish Chandra Bose (; ; 30 November 1858 – 23 November 1937) was a polymath with interests in biology, physics and writing science fiction. He was a pioneer in the investigation of radio microwave optics, made significant contributions ...
during 18941896, when he reached an extremely high frequency
Extremely high frequency (EHF) is the International Telecommunication Union designation for the band of radio frequencies in the electromagnetic spectrum from 30 to 300 gigahertz (GHz). It is in the microwave part of the radio spectrum, between t ...
of up to 60GHz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), often described as being equivalent to one event (or Cycle per second, cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose formal expression in ter ...
in his experiments. He also introduced the use of semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator. Its conductivity can be modified by adding impurities (" doping") to its crystal structure. When two regions with different doping level ...
junctions to detect radio waves, reprinted in Igor Grigorov, Ed., Antentop
', Vol. 2, No.3, pp. 87–96. when he patented the radio
crystal detector
A crystal detector is an obsolete electronic component used in some early 20th century radio receivers. It consists of a piece of crystalline mineral that rectifies an alternating current radio signal. It was employed as a detector ( demod ...
in 1901.
In 1897, Karl Ferdinand Braun
Karl Ferdinand Braun (; ; 6 June 1850 – 20 April 1918) was a German physicist, electrical engineer, and inventor. Braun contributed significantly to the development of radio with his 2 circuit system, which made long range radio transmiss ...
introduced the cathode-ray tube
A cathode-ray tube (CRT) is a vacuum tube containing one or more electron guns, which emit electron beams that are manipulated to display images on a phosphorescent screen. The images may represent electrical waveforms on an oscilloscope, a ...
as part of an oscilloscope
An oscilloscope (formerly known as an oscillograph, informally scope or O-scope) is a type of electronic test instrument that graphically displays varying voltages of one or more signals as a function of time. Their main purpose is capturing i ...
, a crucial enabling technology for electronic television
Television (TV) is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. Additionally, the term can refer to a physical television set rather than the medium of transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, ...
. John Fleming invented the first radio tube, the diode
A diode is a two-Terminal (electronics), terminal electronic component that conducts electric current primarily in One-way traffic, one direction (asymmetric electrical conductance, conductance). It has low (ideally zero) Electrical resistance ...
, in 1904. Two years later, Robert von Lieben and Lee De Forest #REDIRECT Lee de Forest
{{redirect category shell, {{R from move{{R from other capitalisation ...
independently developed the amplifier tube, called the triode
A triode is an electronic amplifier, amplifying vacuum tube (or ''thermionic valve'' in British English) consisting of three electrodes inside an evacuated glass envelope: a heated Electrical filament, filament or cathode, a control grid, grid ...
.
In 1920, Albert Hull developed the magnetron
The cavity magnetron is a high-power vacuum tube used in early radar systems and subsequently in microwave oven, microwave ovens and in linear particle accelerators. A cavity magnetron generates microwaves using the interaction of a stream of ...
which would eventually lead to the development of the microwave oven
A microwave oven, or simply microwave, is an electric oven that heats and cooks food by exposing it to electromagnetic radiation in the microwave frequency range. This induces Dipole#Molecular dipoles, polar molecules in the food to rotate and ...
in 1946 by Percy Spencer. In 1934, the British military
The British Armed Forces are the unified military forces responsible for the defence of the United Kingdom, its Overseas Territories and the Crown Dependencies. They also promote the UK's wider interests, support international peacekeeping e ...
began to make strides toward radar
Radar is a system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), direction ( azimuth and elevation angles), and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It is a radiodetermination method used to detect and track ...
(which also uses the magnetron) under the direction of Dr Wimperis, culminating in the operation of the first radar station at Bawdsey in August 1936.
In 1941, Konrad Zuse
Konrad Ernst Otto Zuse (; ; 22 June 1910 – 18 December 1995) was a German civil engineer, List of pioneers in computer science, pioneering computer scientist, inventor and businessman. His greatest achievement was the world's first programm ...
presented the Z3, the world's first fully functional and programmable computer using electromechanical parts. In 1943, Tommy Flowers
Thomas Harold Flowers Order of the British Empire, MBE (22 December 1905 – 28 October 1998) was an English engineer with the British General Post Office. During World War II, Flowers designed and built Colossus computer, Colossus, the world's ...
designed and built the Colossus, the world's first fully functional, electronic, digital and programmable computer. In 1946, the ENIAC
ENIAC (; Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) was the first Computer programming, programmable, Electronics, electronic, general-purpose digital computer, completed in 1945. Other computers had some of these features, but ENIAC was ...
(Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) of John Presper Eckert
John Adam Presper "Pres" Eckert Jr. (April 9, 1919 – June 3, 1995) was an American electrical engineering, electrical engineer and computer pioneer. With John Mauchly, he designed the first general-purpose electronic digital computer (ENIAC), ...
and John Mauchly
John William Mauchly ( ; August 30, 1907 – January 8, 1980) was an American physicist who, along with J. Presper Eckert, designed ENIAC, the first general-purpose electronic digital computer, as well as EDVAC, BINAC and UNIVAC I, the f ...
followed, beginning the computing era. The arithmetic performance of these machines allowed engineers to develop completely new technologies and achieve new objectives.
In 1948, Claude Shannon
Claude Elwood Shannon (April 30, 1916 – February 24, 2001) was an American mathematician, electrical engineer, computer scientist, cryptographer and inventor known as the "father of information theory" and the man who laid the foundations of th ...
published "A Mathematical Theory of Communication" which mathematically describes the passage of information with uncertainty (electrical noise
In electronics, noise is an unwanted disturbance in an electrical signal.
Noise generated by electronic devices varies greatly as it is produced by several different effects.
In particular, noise is inherent in physics and central to therm ...
).
Solid-state electronics

 The first working
The first working transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electric power, power. It is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semicondu ...
was a point-contact transistor
The point-contact transistor was the first type of transistor to be successfully demonstrated. It was developed by research scientists John Bardeen and Walter Brattain at Bell Laboratories in December 1947. They worked in a group led by phys ...
invented by John Bardeen
John Bardeen (; May 23, 1908 – January 30, 1991) was an American solid-state physicist. He is the only person to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics twice: first in 1956 with William Shockley and Walter Houser Brattain for their inventio ...
and Walter Houser Brattain
Walter Houser Brattain (; February 10, 1902 – October 13, 1987) was an American solid-state physicist who shared the 1956 Nobel Prize in Physics with John Bardeen and William Shockley for their invention of the point-contact transistor. Bra ...
while working under William Shockley
William Bradford Shockley ( ; February 13, 1910 – August 12, 1989) was an American solid-state physicist, electrical engineer, and inventor. He was the manager of a research group at Bell Labs that included John Bardeen and Walter Houser Brat ...
at the Bell Telephone Laboratories
Nokia Bell Labs, commonly referred to as ''Bell Labs'', is an American industrial research and development company owned by Finnish technology company Nokia. With headquarters located in Murray Hill, New Jersey, Murray Hill, New Jersey, the compa ...
(BTL) in 1947. They then invented the bipolar junction transistor
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and electron holes as charge carriers. In contrast, a unipolar transistor, such as a field-effect transistor (FET), uses only one kind of charge carrier. A ...
in 1948. While early junction transistors were relatively bulky devices that were difficult to manufacture on a mass-production basis, they opened the door for more compact devices.
The first integrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
s were the hybrid integrated circuit
A hybrid integrated circuit (HIC), hybrid microcircuit, hybrid circuit or simply hybrid is a miniaturized electronic circuit constructed of individual devices, such as semiconductor devices (e.g. transistors, diodes or Integrated circuits, mo ...
invented by Jack Kilby
Jack St. Clair Kilby (November 8, 1923 – June 20, 2005) was an American electrical engineer who took part, along with Robert Noyce of Fairchild Semiconductor, in the realization of the first integrated circuit while working at Texas Instrumen ...
at Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments Incorporated (TI) is an American multinational semiconductor company headquartered in Dallas, Texas. It is one of the top 10 semiconductor companies worldwide based on sales volume. The company's focus is on developing analog ...
in 1958 and the monolithic integrated circuit chip invented by Robert Noyce
Robert Norton Noyce (December 12, 1927 – June 3, 1990), nicknamed "the Mayor of Silicon Valley", was an American physicist and entrepreneur who co-founded Fairchild Semiconductor in 1957 and Intel Corporation in 1968. He was also credited w ...
at Fairchild Semiconductor
Fairchild Semiconductor International, Inc. was an American semiconductor company based in San Jose, California. It was founded in 1957 as a division of Fairchild Camera and Instrument by the " traitorous eight" who defected from Shockley Semi ...
in 1959.
The MOSFET
upright=1.3, Two power MOSFETs in amperes">A in the ''on'' state, dissipating up to about 100 watt">W and controlling a load of over 2000 W. A matchstick is pictured for scale.
In electronics, the metal–oxide–semiconductor field- ...
(metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor, or MOS transistor) was invented by Mohamed Atalla
Mohamed M. Atalla (; August 4, 1924 – December 30, 2009) was an Egyptian-American engineer, physicist, cryptographer, inventor and entrepreneur. He was a semiconductor pioneer who made important contributions to modern electronics. He is best ...
and Dawon Kahng
Dawon Kahng (; May 4, 1931 – May 13, 1992) was a Korean-American electrical engineer and inventor, known for his work in solid-state electronics. He is best known for inventing the MOSFET (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transisto ...
at BTL in 1959. It was the first truly compact transistor that could be miniaturised and mass-produced for a wide range of uses. It revolutionized the electronics industry
The electronics industry is the industry (economics), industry that produces electronic devices. It emerged in the 20th century and is today one of the largest global industries. Contemporary society uses a vast array of electronic devices that ar ...
, becoming the most widely used electronic device in the world.
The MOSFET made it possible to build high-density integrated circuit chips. The earliest experimental MOS IC chip to be fabricated was built by Fred Heiman and Steven Hofstein at RCA Laboratories
RCA Corporation was a major American electronics company, which was founded in 1919 as the Radio Corporation of America. It was initially a patent trust owned by General Electric (GE), Westinghouse, AT&T Corporation and United Fruit Company ...
in 1962. MOS technology enabled Moore's law
Moore's law is the observation that the Transistor count, number of transistors in an integrated circuit (IC) doubles about every two years. Moore's law is an observation and Forecasting, projection of a historical trend. Rather than a law of ...
, the doubling of transistors on an IC chip every two years, predicted by Gordon Moore
Gordon Earle Moore (January 3, 1929 – March 24, 2023) was an American businessman, engineer, and the co-founder and emeritus chairman of Intel Corporation. He proposed Moore's law which makes the observation that the number of transistors i ...
in 1965. Silicon-gate MOS technology was developed by Federico Faggin
Federico Faggin (, ; born 1 December 1941) is an Italian-American physicist, engineer, inventor and entrepreneur. He is best known for designing the first commercial microprocessor, the Intel 4004. He led the 4004 (MCS-4) project and the desig ...
at Fairchild in 1968. Since then, the MOSFET has been the basic building block of modern electronics. The mass-production of silicon MOSFETs and MOS integrated circuit chips, along with continuous MOSFET scaling
file:D2PAK.JPG, upright=1.3, Two power transistor, power MOSFETs in D2PAK surface-mount packages. Operating as switches, each of these components can sustain a blocking voltage of 120volts, V in the ''off'' state, and can conduct a conti ...
miniaturization at an exponential pace (as predicted by Moore's law
Moore's law is the observation that the Transistor count, number of transistors in an integrated circuit (IC) doubles about every two years. Moore's law is an observation and Forecasting, projection of a historical trend. Rather than a law of ...
), has since led to revolutionary changes in technology, economy, culture and thinking.
The Apollo program
The Apollo program, also known as Project Apollo, was the United States human spaceflight program led by NASA, which Moon landing, landed the first humans on the Moon in 1969. Apollo followed Project Mercury that put the first Americans in sp ...
which culminated in landing astronauts on the Moon with Apollo 11
Apollo 11 was a spaceflight conducted from July 16 to 24, 1969, by the United States and launched by NASA. It marked the first time that humans Moon landing, landed on the Moon. Commander Neil Armstrong and Lunar Module pilot Buzz Aldrin l ...
in 1969 was enabled by NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
's adoption of advances in semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator. Its conductivity can be modified by adding impurities (" doping") to its crystal structure. When two regions with different doping level ...
electronic technology, including MOSFETs in the Interplanetary Monitoring Platform
Interplanetary Monitoring Platform was a program managed by the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, as part of the Explorers program, with the primary objectives of investigation of interplanetary space, interplanetary plas ...
(IMP) and silicon integrated circuit chips in the Apollo Guidance Computer
The Apollo Guidance Computer (AGC) was a digital computer produced for the Apollo program that was installed on board each Apollo command module (CM) and Apollo Lunar Module (LM). The AGC provided computation and electronic interfaces for guidanc ...
(AGC).
The development of MOS integrated circuit technology in the 1960s led to the invention of the microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor (computing), processor for which the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit (IC), or a small number of ICs. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, a ...
in the early 1970s. The first single-chip microprocessor was the Intel 4004
The Intel 4004 was part of the 4 chip MCS-4 micro computer set, released by the Intel, Intel Corporation in November 1971; the 4004 being part of the first commercially marketed microprocessor chipset, and the first in a long line of List of I ...
, released in 1971. The Intel 4004 was designed and realized by Federico Faggin at Intel with his silicon-gate MOS technology, along with Intel's Marcian Hoff
Marcian Edward "Ted" Hoff Jr. (born October 28, 1937, in Rochester, New York) is one of the inventors of the microprocessor.
Education and work history
Hoff received a bachelor's degree in electrical engineering from the Rensselaer Polytechnic In ...
and Stanley Mazor and Busicom's Masatoshi Shima. The microprocessor led to the development of microcomputer
A microcomputer is a small, relatively inexpensive computer having a central processing unit (CPU) made out of a microprocessor. The computer also includes memory and input/output (I/O) circuitry together mounted on a printed circuit board (P ...
s and personal computers, and the microcomputer revolution
The history of the personal computer as a mass-market consumer electronic device began with the microcomputer revolution of the 1970s. A personal computer is one intended for interactive individual use, as opposed to a mainframe computer whe ...
.
Subfields
One of the properties of electricity is that it is very useful for energy transmission as well as for information transmission. These were also the first areas in which electrical engineering was developed. Today, electrical engineering has many subdisciplines, the most common of which are listed below. Although there are electrical engineers who focus exclusively on one of these subdisciplines, many deal with a combination of them. Sometimes, certain fields, such aselectronic engineering
Electronic engineering is a sub-discipline of electrical engineering that emerged in the early 20th century and is distinguished by the additional use of active components such as semiconductor devices to amplify and control electric current flo ...
and computer engineering
Computer engineering (CE, CoE, or CpE) is a branch of engineering specialized in developing computer hardware and software.
It integrates several fields of electrical engineering, electronics engineering and computer science.
Computer engi ...
, are considered disciplines in their own right.
Power and energy
 Power & Energy engineering deals with the
Power & Energy engineering deals with the generation
A generation is all of the people born and living at about the same time, regarded collectively. It also is "the average period, generally considered to be about 20–30 years, during which children are born and grow up, become adults, and b ...
, transmission, and distribution Distribution may refer to:
Mathematics
*Distribution (mathematics), generalized functions used to formulate solutions of partial differential equations
*Probability distribution, the probability of a particular value or value range of a varia ...
of electricity as well as the design of a range of related devices. These include transformer
In electrical engineering, a transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple Electrical network, circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces ...
s, electric generator
In electricity generation, a generator, also called an ''electric generator'', ''electrical generator'', and ''electromagnetic generator'' is an electromechanical device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy for use in an externa ...
s, electric motor
An electric motor is a machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a electromagnetic coil, wire winding to gene ...
s, high voltage engineering, and power electronics
Power electronics is the application of electronics to the control and conversion of electric power.
The first high-power electronic devices were made using mercury-arc valves. In modern systems, the conversion is performed with semiconduct ...
. In many regions of the world, governments maintain an electrical network called a power grid
''Power Grid'' is the English-language version of the second edition of the multiplayer German-style board game ''Funkenschlag'', designed by Friedemann Friese and first released in 2004. ''Power Grid'' was released by Rio Grande Games.
I ...
that connects a variety of generators together with users of their energy. Users purchase electrical energy from the grid, avoiding the costly exercise of having to generate their own. Power engineers may work on the design and maintenance of the power grid as well as the power systems that connect to it. Such systems are called ''on-grid'' power systems and may supply the grid with additional power, draw power from the grid, or do both. Power engineers may also work on systems that do not connect to the grid, called ''off-grid'' power systems, which in some cases are preferable to on-grid systems.
Telecommunications
 Telecommunications engineering focuses on the transmission of information across a
Telecommunications engineering focuses on the transmission of information across a communication channel
A communication channel refers either to a physical transmission medium such as a wire, or to a logical connection over a multiplexed medium such as a radio channel in telecommunications and computer networking. A channel is used for infor ...
such as a coax cable
Coaxial cable, or coax (pronounced ), is a type of electrical cable consisting of an inner conductor surrounded by a concentric conducting shield, with the two separated by a dielectric ( insulating material); many coaxial cables also have a ...
, optical fiber
An optical fiber, or optical fibre, is a flexible glass or plastic fiber that can transmit light from one end to the other. Such fibers find wide usage in fiber-optic communications, where they permit transmission over longer distances and at ...
or free space
A vacuum (: vacuums or vacua) is space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective (neuter ) meaning "vacant" or "void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressur ...
. Transmissions across free space require information to be encoded in a carrier signal
In telecommunications, a carrier wave, carrier signal, or just carrier, is a periodic waveform (usually sinusoidal) that conveys information through a process called ''modulation''. One or more of the wave's properties, such as amplitude or frequ ...
to shift the information to a carrier frequency suitable for transmission; this is known as modulation
Signal modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform in electronics and telecommunication for the purpose of transmitting information.
The process encodes information in form of the modulation or message ...
. Popular analog modulation techniques include amplitude modulation
Amplitude modulation (AM) is a signal modulation technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting messages with a radio wave. In amplitude modulation, the instantaneous amplitude of the wave is varied in proportion t ...
and frequency modulation
Frequency modulation (FM) is a signal modulation technique used in electronic communication, originally for transmitting messages with a radio wave. In frequency modulation a carrier wave is varied in its instantaneous frequency in proporti ...
. The choice of modulation affects the cost and performance of a system and these two factors must be balanced carefully by the engineer.
Once the transmission characteristics of a system are determined, telecommunication engineers design the transmitter
In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter (often abbreviated as XMTR or TX in technical documents) is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna (radio), antenna with the purpose of sig ...
s and receivers needed for such systems. These two are sometimes combined to form a two-way communication device known as a transceiver
In radio communication, a transceiver is an electronic device which is a combination of a radio ''trans''mitter and a re''ceiver'', hence the name. It can both transmit and receive radio waves using an antenna, for communication purposes. The ...
. A key consideration in the design of transmitters is their power consumption
Electric energy consumption is energy consumption in the form of electrical energy. About a fifth of global energy is consumed as electricity: for residential, industrial, commercial, transportation and other purposes.
The global electricity con ...
as this is closely related to their signal strength
In telecommunications, particularly in radio frequency engineering, signal strength is the transmitter power output as received by a reference antenna at a distance from the transmitting antenna. High-powered transmissions, such as those used i ...
. Typically, if the power of the transmitted signal is insufficient once the signal arrives at the receiver's antenna(s), the information contained in the signal will be corrupted by noise
Noise is sound, chiefly unwanted, unintentional, or harmful sound considered unpleasant, loud, or disruptive to mental or hearing faculties. From a physics standpoint, there is no distinction between noise and desired sound, as both are vibrat ...
, specifically static.
Control engineering

Control engineering
Control engineering, also known as control systems engineering and, in some European countries, automation engineering, is an engineering discipline that deals with control systems, applying control theory to design equipment and systems with d ...
focuses on the modeling of a diverse range of dynamic system
In mathematics, a dynamical system is a system in which a function describes the time dependence of a point in an ambient space, such as in a parametric curve. Examples include the mathematical models that describe the swinging of a clock ...
s and the design of controllers that will cause these systems to behave in the desired manner. To implement such controllers, electronics control engineers may use electronic circuit
An electronic circuit is composed of individual electronic components, such as resistors, transistors, capacitors, inductors and diodes, connected by conductive wires or Conductive trace, traces through which electric current can flow. It is a t ...
s, digital signal processor
A digital signal processor (DSP) is a specialized microprocessor chip, with its architecture optimized for the operational needs of digital signal processing. DSPs are fabricated on metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) integrated circuit chips. ...
s, microcontroller
A microcontroller (MC, uC, or μC) or microcontroller unit (MCU) is a small computer on a single integrated circuit. A microcontroller contains one or more CPUs (processor cores) along with memory and programmable input/output peripherals. Pro ...
s, and programmable logic controller
A programmable logic controller (PLC) or programmable controller is an industrial computer that has been ruggedized and adapted for the control of manufacturing processes, such as assembly lines, machines, robotic devices, or any activity that ...
s (PLCs). Control engineering
Control engineering, also known as control systems engineering and, in some European countries, automation engineering, is an engineering discipline that deals with control systems, applying control theory to design equipment and systems with d ...
has a wide range of applications from the flight and propulsion systems of commercial airliners to the cruise control
Cruise control (also known as speed control, cruise command, autocruise, or tempomat) is a system that automatically controls the speed of an automobile. The system is a servomechanism that takes over the car's throttle to maintain a steady sp ...
present in many modern automobile
A car, or an automobile, is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of cars state that they run primarily on roads, Car seat, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport private transport#Personal transport, peopl ...
s. It also plays an important role in industrial automation.
Control engineers often use feedback
Feedback occurs when outputs of a system are routed back as inputs as part of a chain of cause and effect that forms a circuit or loop. The system can then be said to ''feed back'' into itself. The notion of cause-and-effect has to be handle ...
when designing control system
A control system manages, commands, directs, or regulates the behavior of other devices or systems using control loops. It can range from a single home heating controller using a thermostat controlling a domestic boiler to large industrial ...
s. For example, in an automobile
A car, or an automobile, is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of cars state that they run primarily on roads, Car seat, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport private transport#Personal transport, peopl ...
with cruise control
Cruise control (also known as speed control, cruise command, autocruise, or tempomat) is a system that automatically controls the speed of an automobile. The system is a servomechanism that takes over the car's throttle to maintain a steady sp ...
the vehicle's speed
In kinematics, the speed (commonly referred to as ''v'') of an object is the magnitude of the change of its position over time or the magnitude of the change of its position per unit of time; it is thus a non-negative scalar quantity. Intro ...
is continuously monitored and fed back to the system which adjusts the motor's power output accordingly. Where there is regular feedback, control theory
Control theory is a field of control engineering and applied mathematics that deals with the control system, control of dynamical systems in engineered processes and machines. The objective is to develop a model or algorithm governing the applic ...
can be used to determine how the system responds to such feedback.
Control engineers also work in robotics
Robotics is the interdisciplinary study and practice of the design, construction, operation, and use of robots.
Within mechanical engineering, robotics is the design and construction of the physical structures of robots, while in computer s ...
to design autonomous systems using control algorithms which interpret sensory feedback to control actuators that move robots such as autonomous vehicles, autonomous drones and others used in a variety of industries.
Electronics
electronic circuit
An electronic circuit is composed of individual electronic components, such as resistors, transistors, capacitors, inductors and diodes, connected by conductive wires or Conductive trace, traces through which electric current can flow. It is a t ...
s that use the properties of component
Component may refer to:
In engineering, science, and technology Generic systems
*System components, an entity with discrete structure, such as an assembly or software module, within a system considered at a particular level of analysis
* Lumped e ...
s such as resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electronic component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active e ...
s, capacitor
In electrical engineering, a capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy by accumulating electric charges on two closely spaced surfaces that are insulated from each other. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term st ...
s, inductor
An inductor, also called a coil, choke, or reactor, is a Passivity (engineering), passive two-terminal electronic component, electrical component that stores energy in a magnetic field when an electric current flows through it. An inductor typic ...
s, diode
A diode is a two-Terminal (electronics), terminal electronic component that conducts electric current primarily in One-way traffic, one direction (asymmetric electrical conductance, conductance). It has low (ideally zero) Electrical resistance ...
s, and transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electric power, power. It is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semicondu ...
s to achieve a particular functionality. The tuned circuit
An LC circuit, also called a resonant circuit, tank circuit, or tuned circuit, is an electric circuit consisting of an inductor, represented by the letter L, and a capacitor, represented by the letter C, connected together. The circuit can act ...
, which allows the user of a radio to filter out all but a single station, is just one example of such a circuit. Another example to research is a pneumatic signal conditioner.
Prior to the Second World War, the subject was commonly known as ''radio engineering'' and basically was restricted to aspects of communications and radar
Radar is a system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), direction ( azimuth and elevation angles), and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It is a radiodetermination method used to detect and track ...
, commercial radio
Commercial broadcasting (also called private broadcasting) is the broadcasting of television programs and radio programming by privately owned corporate media, as opposed to state sponsorship, for example. It was the United States' first model ...
, and early television. Later, in post-war years, as consumer devices began to be developed, the field grew to include modern television, audio systems, computers, and microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor (computing), processor for which the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit (IC), or a small number of ICs. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, a ...
s. In the mid-to-late 1950s, the term ''radio engineering'' gradually gave way to the name ''electronic engineering''.
Before the invention of the integrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
in 1959, electronic circuits were constructed from discrete components that could be manipulated by humans. These discrete circuits consumed much space and power and were limited in speed, although they are still common in some applications. By contrast, integrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
s packed a large number—often millions—of tiny electrical components, mainly transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electric power, power. It is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semicondu ...
s, into a small chip around the size of a coin
A coin is a small object, usually round and flat, used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in order to facilitate trade. They are most often issued by ...
. This allowed for the powerful computers and other electronic devices we see today.
Microelectronics and nanoelectronics

Microelectronics
Microelectronics is a subfield of electronics. As the name suggests, microelectronics relates to the study and manufacture (or microfabrication) of very small electronic designs and components. Usually, but not always, this means micrometre ...
engineering deals with the design and microfabrication
Microfabrication is the process of fabricating miniature structures of micrometre scales and smaller. Historically, the earliest microfabrication processes were used for integrated circuit fabrication, also known as "semiconductor manufacturing" ...
of very small electronic circuit components for use in an integrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
or sometimes for use on their own as a general electronic component. The most common microelectronic components are semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator. Its conductivity can be modified by adding impurities (" doping") to its crystal structure. When two regions with different doping level ...
transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electric power, power. It is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semicondu ...
s, although all main electronic components (resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electronic component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active e ...
s, capacitor
In electrical engineering, a capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy by accumulating electric charges on two closely spaced surfaces that are insulated from each other. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term st ...
s etc.) can be created at a microscopic level.
Nanoelectronics
Nanoelectronics refers to the use of nanotechnology in electronic components. The term covers a diverse set of devices and materials, with the common characteristic that they are so small that inter-atomic interactions and quantum mechanical ...
is the further scaling of devices down to nanometer
330px, Different lengths as in respect to the Molecule">molecular scale.
The nanometre (international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: nm), or nanometer (American spelling
Despite the va ...
levels. Modern devices are already in the nanometer regime, with below 100 nm processing having been standard since around 2002.
Microelectronic components are created by chemically fabricating wafers of semiconductors such as silicon (at higher frequencies, compound semiconductor
Semiconductor materials are nominally small band gap insulators. The defining property of a semiconductor material is that it can be compromised by doping it with impurities that alter its electronic properties in a controllable way.
Because of ...
s like gallium arsenide and indium phosphide) to obtain the desired transport of electronic charge and control of current. The field of microelectronics involves a significant amount of chemistry and material science and requires the electronic engineer working in the field to have a very good working knowledge of the effects of quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics is the fundamental physical Scientific theory, theory that describes the behavior of matter and of light; its unusual characteristics typically occur at and below the scale of atoms. Reprinted, Addison-Wesley, 1989, It is ...
.
Signal processing
Signal processing
Signal processing is an electrical engineering subfield that focuses on analyzing, modifying and synthesizing ''signals'', such as audio signal processing, sound, image processing, images, Scalar potential, potential fields, Seismic tomograph ...
deals with the analysis and manipulation of signal
A signal is both the process and the result of transmission of data over some media accomplished by embedding some variation. Signals are important in multiple subject fields including signal processing, information theory and biology.
In ...
s. Signals can be either analog, in which case the signal varies continuously according to the information, or digital
Digital usually refers to something using discrete digits, often binary digits.
Businesses
*Digital bank, a form of financial institution
*Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) or Digital, a computer company
*Digital Research (DR or DRI), a software ...
, in which case the signal varies according to a series of discrete values representing the information. For analog signals, signal processing may involve the amplification and filtering of audio signals for audio equipment or the modulation
Signal modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform in electronics and telecommunication for the purpose of transmitting information.
The process encodes information in form of the modulation or message ...
and demodulation
Demodulation is the process of extracting the original information-bearing signal from a carrier wave. A demodulator is an electronic circuit (or computer program in a software-defined radio) that is used to recover the information content fro ...
of signals for telecommunications. For digital signals, signal processing may involve the compression, error detection
In information theory and coding theory with applications in computer science and telecommunications, error detection and correction (EDAC) or error control are techniques that enable reliable delivery of digital data over unreliable communi ...
and error correction
In information theory and coding theory with applications in computer science and telecommunications, error detection and correction (EDAC) or error control are techniques that enable reliable delivery of digital data over unreliable communi ...
of digitally sampled signals.
Signal processing is a very mathematically oriented and intensive area forming the core of digital signal processing
Digital signal processing (DSP) is the use of digital processing, such as by computers or more specialized digital signal processors, to perform a wide variety of signal processing operations. The digital signals processed in this manner are a ...
and it is rapidly expanding with new applications in every field of electrical engineering such as communications, control, radar, audio engineer
An audio engineer (also known as a sound engineer or recording engineer) helps to produce a recording or a live performance, balancing and adjusting sound sources using equalization, dynamics processing and audio effects, mixing, reproduc ...
ing, broadcast engineering
Broadcast engineering or radio engineering is the field of electrical engineering, and now to some extent computer engineering and information technology, which deals with radio and television broadcasting. Audio engineering and RF engineering a ...
, power electronics, and biomedical engineering
Biomedical engineering (BME) or medical engineering is the application of engineering principles and design concepts to medicine and biology for healthcare applications (e.g., diagnostic or therapeutic purposes). BME also integrates the logica ...
as many already existing analog systems are replaced with their digital counterparts. Analog signal processing is still important in the design of many control system
A control system manages, commands, directs, or regulates the behavior of other devices or systems using control loops. It can range from a single home heating controller using a thermostat controlling a domestic boiler to large industrial ...
s.
DSP processor ICs are found in many types of modern electronic devices, such as digital television set
A television set or television receiver (more commonly called TV, TV set, television, telly, or tele) is an electronic device for viewing and hearing television broadcasts, or as a computer monitor. It combines a tuner, display, and loudspeake ...
s, radios, hi-fi
High fidelity (hi-fi or, rarely, HiFi) is the high-quality reproduction of sound. It is popular with audiophiles and home audio enthusiasts. Ideally, high-fidelity equipment has inaudible noise and distortion, and a flat (neutral, uncolored) ...
audio equipment, mobile phones, multimedia players, camcorders and digital cameras, automobile control systems, noise cancelling headphones, digital spectrum analyzer
A spectrum analyzer measures the magnitude of an input signal versus frequency within the full frequency range of the instrument. The primary use is to measure the power of the spectrum of known and unknown signals. The input signal that most co ...
s, missile guidance systems, radar
Radar is a system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), direction ( azimuth and elevation angles), and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It is a radiodetermination method used to detect and track ...
systems, and telematics
Telematics is an interdisciplinary field encompassing telecommunications, vehicular technologies (road transport, road safety, etc.), electrical engineering (sensors, instrumentation, wireless communications, etc.), and computer science (multimedia ...
systems. In such products, DSP may be responsible for noise reduction
Noise reduction is the process of removing noise from a signal. Noise reduction techniques exist for audio and images. Noise reduction algorithms may distort the signal to some degree. Noise rejection is the ability of a circuit to isolate an u ...
, speech recognition
Speech recognition is an interdisciplinary subfield of computer science and computational linguistics that develops methodologies and technologies that enable the recognition and translation of spoken language into text by computers. It is also ...
or synthesis
Synthesis or synthesize may refer to:
Science Chemistry and biochemistry
*Chemical synthesis, the execution of chemical reactions to form a more complex molecule from chemical precursors
**Organic synthesis, the chemical synthesis of organi ...
, encoding or decoding digital media, wirelessly transmitting or receiving data, triangulating positions using GPS, and other kinds of image processing
An image or picture is a visual representation. An image can be two-dimensional, such as a drawing, painting, or photograph, or three-dimensional, such as a carving or sculpture. Images may be displayed through other media, including a pr ...
, video processing In electronics engineering, video processing is a particular case of signal processing, in particular image processing, which often employs filter (video), video filters and where the input and output Signal (electrical engineering), signals are vid ...
, audio processing, and speech processing
Speech processing is the study of speech signals and the processing methods of signals. The signals are usually processed in a digital representation, so speech processing can be regarded as a special case of digital signal processing, applied to ...
.
Instrumentation

Instrumentation engineering
Instrumentation is a collective term for measuring instruments, used for indicating, measuring, and recording physical quantities. It is also a field of study about the art and science about making measurement instruments, involving the related ...
deals with the design of devices to measure physical quantities such as pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and eve ...
, flow, and temperature. The design of such instruments requires a good understanding of physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge whi ...
that often extends beyond electromagnetic theory
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge via electromagnetic fields. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental forces of nature. It is the dominant force in the interact ...
. For example, flight instrument
Flight instruments are the instruments in the cockpit of an aircraft that provide the pilot with data about the flight situation of that aircraft, such as altitude, airspeed, Variometer, vertical speed, heading and much more other crucial inform ...
s measure variables such as wind speed
In meteorology, wind speed, or wind flow speed, is a fundamental atmospheric quantity caused by air moving from high to low pressure, usually due to changes in temperature. Wind speed is now commonly measured with an anemometer.
Wind spe ...
and altitude to enable pilots the control of aircraft analytically. Similarly, thermocouple
A thermocouple, also known as a "thermoelectrical thermometer", is an electrical device consisting of two dissimilar electrical conductors forming an electrical junction. A thermocouple produces a temperature-dependent voltage as a result of the ...
s use the Peltier-Seebeck effect
The thermoelectric effect is the direct conversion of temperature differences to electric voltage and vice versa via a thermocouple. A thermoelectric device creates a voltage when there is a different temperature on each side. Conversely, when ...
to measure the temperature difference between two points.
Often instrumentation is not used by itself, but instead as the sensor
A sensor is often defined as a device that receives and responds to a signal or stimulus. The stimulus is the quantity, property, or condition that is sensed and converted into electrical signal.
In the broadest definition, a sensor is a devi ...
s of larger electrical systems. For example, a thermocouple might be used to help ensure a furnace's temperature remains constant. For this reason, instrumentation engineering is often viewed as the counterpart of control.
Computers
 Computer engineering deals with the design of computers and
Computer engineering deals with the design of computers and computer system
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to automatically carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (''computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as ''programs'', wh ...
s. This may involve the design of new hardware. Computer engineers may also work on a system's software. However, the design of complex software systems is often the domain of software engineering, which is usually considered a separate discipline. Desktop computer
A desktop computer, often abbreviated as desktop, is a personal computer designed for regular use at a stationary location on or near a desk (as opposed to a portable computer) due to its size and power requirements. The most common configuratio ...
s represent a tiny fraction of the devices a computer engineer might work on, as computer-like architectures are now found in a range of embedded device
An embedded system is a specialized computer system—a combination of a computer processor, computer memory, and input/output peripheral devices—that has a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or Electronics, electronic syst ...
s including video game console
A video game console is an electronic device that Input/output, outputs a video signal or image to display a video game that can typically be played with a game controller. These may be home video game console, home consoles, which are generally ...
s and DVD player
A DVD player is a machine that plays DVDs produced under both the DVD-Video and DVD-Audio technical standards, two different and incompatible standards. Some DVD players will also play audio CDs. DVD players are connected to a television to ...
s. Computer engineers are involved in many hardware and software aspects of computing. Robot
A robot is a machine—especially one Computer program, programmable by a computer—capable of carrying out a complex series of actions Automation, automatically. A robot can be guided by an external control device, or the robot control, co ...
s are one of the applications of computer engineering.
Photonics and optics
Photonics
Photonics is a branch of optics that involves the application of generation, detection, and manipulation of light in the form of photons through emission, transmission, modulation, signal processing, switching, amplification, and sensing. E ...
and optics
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of optical instruments, instruments that use or Photodetector, detect it. Optics usually describes t ...
deals with the generation, transmission, amplification, modulation, detection, and analysis of electromagnetic radiation
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) is a self-propagating wave of the electromagnetic field that carries momentum and radiant energy through space. It encompasses a broad spectrum, classified by frequency or its inverse, wavelength ...
. The application of optics deals with design of optical instruments such as lens
A lens is a transmissive optical device that focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements'') ...
es, microscope
A microscope () is a laboratory equipment, laboratory instrument used to examine objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using a microscope. Microscopic ...
s, telescope
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption, or Reflection (physics), reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally, it was an optical instrument using len ...
s, and other equipment that uses the properties of electromagnetic radiation. Other prominent applications of optics include electro-optical sensor
Electro-optical sensors are electronic detectors that convert light, or a change in light, into an electronic signal. These sensors are able to detect electromagnetic radiation from the infrared down to the ultraviolet wavelengths. They are used i ...
s and measurement systems, laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radi ...
s, fiber-optic communication
Fiber-optic communication is a form of optical communication for transmitting information from one place to another by sending pulses of infrared or visible light through an optical fiber. The light is a form of carrier wave that is modul ...
systems, and optical disc systems (e.g. CD and DVD). Photonics builds heavily on optical technology, supplemented with modern developments such as optoelectronics
Optoelectronics (or optronics) is the study and application of electronic devices and systems that find, detect and control light, usually considered a sub-field of photonics. In this context, ''light'' often includes invisible forms of radi ...
(mostly involving semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator. Its conductivity can be modified by adding impurities (" doping") to its crystal structure. When two regions with different doping level ...
s), laser systems, optical amplifier
An optical amplifier is a device that amplifies an optical signal directly, without the need to first convert it to an electrical signal. An optical amplifier may be thought of as a laser without an optical cavity, or one in which feedback fro ...
s and novel materials (e.g. metamaterial
A metamaterial (from the Greek word μετά ''meta'', meaning "beyond" or "after", and the Latin word ''materia'', meaning "matter" or "material") is a type of material engineered to have a property, typically rarely observed in naturally occu ...
s).
Related disciplines

Mechatronics
Mechatronics engineering, also called mechatronics, is the synergistic integration of mechanical, electrical, and computer systems employing mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, electronic engineering and computer engineering, and also ...
is an engineering discipline that deals with the convergence of electrical and mechanical
Mechanical may refer to:
Machine
* Machine (mechanical), a system of mechanisms that shape the actuator input to achieve a specific application of output forces and movement
* Mechanical calculator, a device used to perform the basic operations o ...
systems. Such combined systems are known as electromechanical
Electromechanics combine processes and procedures drawn from electrical engineering and mechanical engineering. Electromechanics focus on the interaction of electrical and mechanical systems as a whole and how the two systems interact with each ...
systems and have widespread adoption. Examples include automated manufacturing systems, heating, ventilation and air-conditioning systems, and various subsystems of aircraft and automobile
A car, or an automobile, is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of cars state that they run primarily on roads, Car seat, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport private transport#Personal transport, peopl ...
s.
''Electronic systems design'' is the subject within electrical engineering that deals with the multi-disciplinary design issues of complex electrical and mechanical systems.
The term ''mechatronics'' is typically used to refer to macroscopic
The macroscopic scale is the length scale on which objects or phenomena are large enough to be visible with the naked eye, without magnifying optical instruments. It is the opposite of microscopic.
Overview
When applied to physical phenome ...
systems but futurist
Futurists (also known as futurologists, prospectivists, foresight practitioners and horizon scanners) are people whose specialty or interest is futures studies or futurology or the attempt to systematically explore predictions and possibilities ...
s have predicted the emergence of very small electromechanical devices. Already, such small devices, known as microelectromechanical system
MEMS (micro-electromechanical systems) is the technology of microscopic devices incorporating both electronic and moving parts. MEMS are made up of components between 1 and 100 micrometres in size (i.e., 0.001 to 0.1 mm), and MEMS devices ...
s (MEMS), are used in automobiles to tell airbag
An airbag is a vehicle occupant-restraint system using a bag designed to inflate in milliseconds during a collision and then deflate afterwards. It consists of an airbag cushion, a flexible fabric bag, an inflation module, and an impact sensor. ...
s when to deploy, in digital projector
A video projector is an image projector that receives a video signal and projects the corresponding image onto a projection screen using a lens (optics), lens system. Video projectors use a very bright ultra-high-performance lamp (a special me ...
s to create sharper images, and in inkjet printer
Inkjet printing is a type of printer (computing), computer printing that recreates a digital image by propelling droplets of ink onto paper or plastic substrates. Inkjet printers were the most commonly used type of printer in 2008, and range f ...
s to create nozzles for high definition printing. In the future it is hoped the devices will help build tiny implantable medical devices and improve optical communication
Optical communication, also known as optical telecommunication, is communication at a distance using light to carry information. It can be performed visually or by using electronic devices. The earliest basic forms of optical communication date ...
.
In aerospace engineering
Aerospace engineering is the primary field of engineering concerned with the development of aircraft and spacecraft. It has two major and overlapping branches: aeronautical engineering and astronautical engineering. Avionics engineering is s ...
and robotics
Robotics is the interdisciplinary study and practice of the design, construction, operation, and use of robots.
Within mechanical engineering, robotics is the design and construction of the physical structures of robots, while in computer s ...
, an example is the most recent electric propulsion
Spacecraft electric propulsion (or just electric propulsion) is a type of spacecraft propulsion technique that uses electrostatic or electromagnetic fields to accelerate mass to high speed and thus generating thrust to modify the velocity of a ...
and ion propulsion.
Education
 Electrical engineers typically possess an
Electrical engineers typically possess an academic degree
An academic degree is a qualification awarded to a student upon successful completion of a course of study in higher education, usually at a college or university. These institutions often offer degrees at various levels, usually divided into und ...
with a major in electrical engineering, electronics engineering
Electronic engineering is a sub-discipline of electrical engineering that emerged in the early 20th century and is distinguished by the additional use of active components such as semiconductor devices to amplify and control electric current flow ...
, electrical engineering technology, or electrical and electronic engineering. The same fundamental principles are taught in all programs, though emphasis may vary according to title. The length of study for such a degree is usually four or five years and the completed degree may be designated as a Bachelor of Science in Electrical/Electronics Engineering Technology, Bachelor of Engineering
A Bachelor of Engineering (BEng) or a Bachelor of Science in Engineering (BSE) is an undergraduate academic degree awarded to a college graduate majoring in an engineering discipline at a higher education institution.
In the United Kingdom, a Ba ...
, Bachelor of Science, Bachelor of Technology
A Bachelor of Technology (BTech) is an undergraduate degree that is awarded for a higher education program in engineering.
Countries
Australia
In Australia, the Bachelor of Technology degree is offered by RMIT University, Edith Cowan Univ ...
, or Bachelor of Applied Science
A Bachelor of Applied Science (BAS or BASc) is an undergraduate academic degree of applied sciences.
Usage
In Canada, the Netherlands and other places the Bachelor of Applied Science (BASc) is equivalent to the Bachelor of Engineering, and is cl ...
, depending on the university. The bachelor's degree
A bachelor's degree (from Medieval Latin ''baccalaureus'') or baccalaureate (from Modern Latin ''baccalaureatus'') is an undergraduate degree awarded by colleges and universities upon completion of a course of study lasting three to six years ...
generally includes units covering physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge whi ...
, mathematics, computer science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, ...
, project management
Project management is the process of supervising the work of a Project team, team to achieve all project goals within the given constraints. This information is usually described in project initiation documentation, project documentation, crea ...
, and a variety of topics in electrical engineering. Initially such topics cover most, if not all, of the subdisciplines of electrical engineering.
Master of Engineering
A Master of Engineering (abbreviated MEng, ME, M.E. or M.Eng.) is a Professional degree, professional master's degree in the field of engineering.
International variations
Australia
In Australia, the Master of Engineering degree is a research ...
/Master of Science (MEng/MSc), a Master of Engineering Management, a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) in Engineering, an Engineering Doctorate
Engineering is the practice of using natural science, mathematics, and the engineering design process to solve problems within technology, increase efficiency and productivity, and improve systems. Modern engineering comprises many subfiel ...
(Eng.D.), or an Engineer's degree
An engineer's degree is an advanced academic degree in engineering which is conferred in Europe, some countries of Asia and Latin America, North Africa and a few institutions in the United States. The degree may require a thesis but always require ...
. The master's and engineer's degrees may consist of either research, coursework
Coursework (also course work, especially British English) is work performed by students or trainees for the purpose of learning. Coursework may be specified and assigned by teachers, or by learning guides in self-taught courses. Coursework can e ...
or a mixture of the two. The Doctor of Philosophy and Engineering Doctorate degrees consist of a significant research component and are often viewed as the entry point to academia
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of tertiary education. The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, founded approximately 386 BC at Akademia, a sanctuary of Athena, the go ...
. In the United Kingdom and some other European countries, Master of Engineering is often considered to be an undergraduate degree of slightly longer duration than the Bachelor of Engineering rather than a standalone postgraduate degree.
Professional practice
In most countries, a bachelor's degree in engineering represents the first step towardsprofessional certification
Professional certification, trade certification, or professional designation, often called simply ''certification'' or ''qualification'', is a designation earned by a person to assure qualification to perform a job or task. Not all certifications ...
and the degree program itself is certified by a professional body
A professional association (also called a professional body, professional organization, or professional society) is a group that usually seeks to advocacy, further a particular profession, the interests of individuals and organisations engaged in ...
. After completing a certified degree program the engineer must satisfy a range of requirements (including work experience requirements) before being certified. Once certified the engineer is designated the title of Professional Engineer
A professional is a member of a profession or any person who works in a specified professional activity. The term also describes the standards of education and training that prepare members of the profession with the particular knowledge and ski ...
(in the United States, Canada and South Africa), Chartered engineer
Regulation and licensure in engineering is established by various jurisdictions of the world to encourage life, public welfare, safety, well-being, then environment and other interests of the general public and to define the licensure process thr ...
or Incorporated Engineer (in India, Pakistan, the United Kingdom, Ireland and Zimbabwe
file:Zimbabwe, relief map.jpg, upright=1.22, Zimbabwe, relief map
Zimbabwe, officially the Republic of Zimbabwe, is a landlocked country in Southeast Africa, between the Zambezi and Limpopo Rivers, bordered by South Africa to the south, Bots ...
), Chartered Professional Engineer (in Australia and New Zealand) or European Engineer
European Engineer (EUR ING) is an international professional qualification and title for highly qualified engineers used in over 32 European countries. Contemporary EUR ING engineers are degree-qualified and have gained the highest level of profes ...
(in much of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
).
Quebec
Quebec is Canada's List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, ...
's Engineers Act. In other countries, no such legislation exists. Practically all certifying bodies maintain a code of ethics that they expect all members to abide by or risk expulsion. In this way these organizations play an important role in maintaining ethical standards for the profession. Even in jurisdictions where certification has little or no legal bearing on work, engineers are subject to contract law
A contract is an agreement that specifies certain legally enforceable rights and obligations pertaining to two or more Party (law), parties. A contract typically involves consent to transfer of goods, Service (economics), services, money, or pr ...
. In cases where an engineer's work fails he or she may be subject to the tort of negligence and, in extreme cases, the charge of criminal negligence
In criminal law, criminal negligence is an offence that involves a breach of an objective standard of behaviour expected of a defendant. It may be contrasted with strictly liable offences, which do not consider states of mind in determining c ...
. An engineer's work must also comply with numerous other rules and regulations, such as building code
A building code (also building control or building regulations) is a set of rules that specify the standards for construction objects such as buildings and non-building structures. Buildings must conform to the code to obtain planning permis ...
s and legislation pertaining to environmental law
Environmental laws are laws that protect the environment. The term "environmental law" encompasses treaties, statutes, regulations, conventions, and policies designed to protect the natural environment and manage the impact of human activitie ...
.
Professional bodies of note for electrical engineers include the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is an American 501(c)(3) public charity professional organization for electrical engineering, electronics engineering, and other related disciplines.
The IEEE has a corporate office ...
(IEEE) and the Institution of Engineering and Technology
The Institution of Engineering and Technology (IET) is a multidisciplinary professional engineering institution. The IET was formed in 2006 from two separate institutions: the Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE), dating back to 1871,Engin ...
(IET). The IEEE claims to produce 30% of the world's literature in electrical engineering, has over 360,000 members worldwide and holds over 3,000 conferences annually. The IET publishes 21 journals, has a worldwide membership of over 150,000, and claims to be the largest professional engineering society in Europe. Obsolescence of technical skills is a serious concern for electrical engineers. Membership and participation in technical societies, regular reviews of periodicals in the field and a habit of continued learning are therefore essential to maintaining proficiency. An MIET(Member of the Institution of Engineering and Technology) is recognised in Europe as an Electrical and computer (technology) engineer.
In Australia, Canada, and the United States, electrical engineers make up around 0.25% of the labor force.
Tools and work
From theGlobal Positioning System
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite-based hyperbolic navigation system owned by the United States Space Force and operated by Mission Delta 31. It is one of the global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) that provide ge ...
to electric power generation
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric power from sources of primary energy. For utilities in the electric power industry, it is the stage prior to its delivery ( transmission, distribution, etc.) to end users or its stor ...
, electrical engineers have contributed to the development of a wide range of technologies. They design, develop, test, and supervise the deployment of electrical systems and electronic devices. For example, they may work on the design of telecommunications systems, the operation of electric power station
A power station, also referred to as a power plant and sometimes generating station or generating plant, is an industrial facility for the generation of electric power. Power stations are generally connected to an electrical grid.
Many power s ...
s, the lighting
Lighting or illumination is the deliberate use of light to achieve practical or aesthetic effects. Lighting includes the use of both artificial light sources like lamps and light fixtures, as well as natural illumination by capturing daylight. ...
and wiring of buildings, the design of household appliance
A home appliance, also referred to as a domestic appliance, an electric appliance or a household appliance, is a machine which assists in household functions such as cooking, cleaning and food preservation.
The domestic application attached to ...
s, or the electrical control of industrial machinery.
 Fundamental to the discipline are the sciences of
Fundamental to the discipline are the sciences of physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge whi ...
and mathematics as these help to obtain both a qualitative and quantitative
Quantitative may refer to:
* Quantitative research, scientific investigation of quantitative properties
* Quantitative analysis (disambiguation)
* Quantitative verse, a metrical system in poetry
* Statistics, also known as quantitative analysis
...
description of how such systems will work. Today most engineering work involves the use of computer
A computer is a machine that can be Computer programming, programmed to automatically Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (''computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic set ...
s and it is commonplace to use computer-aided design
Computer-aided design (CAD) is the use of computers (or ) to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. This software is used to increase the productivity of the designer, improve the quality of design, improve c ...
programs when designing electrical systems. Nevertheless, the ability to sketch ideas is still invaluable for quickly communicating with others.
 Although most electrical engineers will understand basic
Although most electrical engineers will understand basic circuit theory
Circuit may refer to:
Science and technology
Electrical engineering
* Electrical circuit, a complete electrical network with a closed-loop giving a return path for current
** Analog circuit, uses continuous signal levels
** Balanced circu ...
(that is, the interactions of elements such as resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electronic component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active e ...
s, capacitor
In electrical engineering, a capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy by accumulating electric charges on two closely spaced surfaces that are insulated from each other. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term st ...
s, diode
A diode is a two-Terminal (electronics), terminal electronic component that conducts electric current primarily in One-way traffic, one direction (asymmetric electrical conductance, conductance). It has low (ideally zero) Electrical resistance ...
s, transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electric power, power. It is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semicondu ...
s, and inductor
An inductor, also called a coil, choke, or reactor, is a Passivity (engineering), passive two-terminal electronic component, electrical component that stores energy in a magnetic field when an electric current flows through it. An inductor typic ...
s in a circuit), the theories employed by engineers generally depend upon the work they do. For example, quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics is the fundamental physical Scientific theory, theory that describes the behavior of matter and of light; its unusual characteristics typically occur at and below the scale of atoms. Reprinted, Addison-Wesley, 1989, It is ...
and solid state physics
Solid-state physics is the study of rigid matter, or solids, through methods such as solid-state chemistry, quantum mechanics, crystallography, electromagnetism, and metallurgy. It is the largest branch of condensed matter physics. Solid-state p ...
might be relevant to an engineer working on VLSI (the design of integrated circuits), but are largely irrelevant to engineers working with macroscopic electrical systems. Even circuit theory
Circuit may refer to:
Science and technology
Electrical engineering
* Electrical circuit, a complete electrical network with a closed-loop giving a return path for current
** Analog circuit, uses continuous signal levels
** Balanced circu ...
may not be relevant to a person designing telecommunications systems that use off-the-shelf components. Perhaps the most important technical skills for electrical engineers are reflected in university programs, which emphasize strong numerical skills, computer literacy
Computer literacy is defined as the knowledge and ability to use computers and related technology efficiently, with skill levels ranging from elementary use to computer programming and advanced problem solving. Computer literacy can also refer t ...
, and the ability to understand the technical language and concepts that relate to electrical engineering.
 A wide range of instrumentation is used by electrical engineers. For simple control circuits and alarms, a basic
A wide range of instrumentation is used by electrical engineers. For simple control circuits and alarms, a basic multimeter
A multimeter (also known as a multi-tester, volt-ohm-milliammeter, volt-ohmmeter or VOM, avometer or ampere-volt-ohmmeter) is a measuring instrument that can measure multiple electrical properties. A typical multimeter can measure voltage, elec ...
measuring voltage
Voltage, also known as (electrical) potential difference, electric pressure, or electric tension, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a Electrostatics, static electric field, it corresponds to the Work (electrical), ...
, current, and resistance may suffice. Where time-varying signals need to be studied, the oscilloscope
An oscilloscope (formerly known as an oscillograph, informally scope or O-scope) is a type of electronic test instrument that graphically displays varying voltages of one or more signals as a function of time. Their main purpose is capturing i ...
is also an ubiquitous instrument. In RF engineering
Radio-frequency (RF) engineering is a subset of electrical engineering involving the application of transmission line, Waveguide (electromagnetism), waveguide, Antenna (radio), antenna, radar, and Electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic fiel ...
and high-frequency telecommunications, spectrum analyzer
A spectrum analyzer measures the magnitude of an input signal versus frequency within the full frequency range of the instrument. The primary use is to measure the power of the spectrum of known and unknown signals. The input signal that most co ...
s and network analyzers are used. In some disciplines, safety can be a particular concern with instrumentation. For instance, medical electronics designers must take into account that much lower voltages than normal can be dangerous when electrodes are directly in contact with internal body fluids. Power transmission engineering also has great safety concerns due to the high voltages used; although voltmeter
A voltmeter is an instrument used for measuring electric potential difference between two points in an electric circuit. It is connected in parallel. It usually has a high resistance so that it takes negligible current from the circuit.
A ...
s may in principle be similar to their low voltage equivalents, safety and calibration issues make them very different. Many disciplines of electrical engineering use tests specific to their discipline. Audio electronics engineers use audio test sets consisting of a signal generator and a meter, principally to measure level but also other parameters such as harmonic distortion and noise
Noise is sound, chiefly unwanted, unintentional, or harmful sound considered unpleasant, loud, or disruptive to mental or hearing faculties. From a physics standpoint, there is no distinction between noise and desired sound, as both are vibrat ...
. Likewise, information technology have their own test sets, often specific to a particular data format, and the same is true of television broadcasting.
 For many engineers, technical work accounts for only a fraction of the work they do. A lot of time may also be spent on tasks such as discussing proposals with clients, preparing
For many engineers, technical work accounts for only a fraction of the work they do. A lot of time may also be spent on tasks such as discussing proposals with clients, preparing budget
A budget is a calculation plan, usually but not always financial plan, financial, for a defined accounting period, period, often one year or a month. A budget may include anticipated sales volumes and revenues, resource quantities including tim ...
s and determining project schedules. Many senior engineers manage a team of technician
A technician is a worker in a field of technology who is proficient in the relevant skill and technique, with a relatively practical understanding of the theoretical principles.
Specialisation
The term technician covers many different special ...
s or other engineers and for this reason project management
Project management is the process of supervising the work of a Project team, team to achieve all project goals within the given constraints. This information is usually described in project initiation documentation, project documentation, crea ...
skills are important. Most engineering projects involve some form of documentation and strong written communication skills are therefore very important.
The workplace
A workplace is a location where someone works, for their employer or themselves, a place of employment. Such a place can range from a home office to a large office building or factory. For industrialized societies, the workplace is one of the ...
s of engineers are just as varied as the types of work they do. Electrical engineers may be found in the pristine lab environment of a fabrication plant, on board a Naval ship
A naval ship (or naval vessel) is a military ship (or sometimes boat, depending on classification) that is used by a navy. Naval ships are differentiated from civilian ships by construction and purpose. Generally, naval ships are damage resili ...
, the offices of a consulting firm
A consulting firm or simply consultancy is a professional service firm that provides expertise and specialised labour for a fee, through the use of consultants. Consulting firms may have one employee or thousands; they may consult in a broad ra ...
or on site at a mine. During their working life, electrical engineers may find themselves supervising a wide range of individuals including scientists, electrician
An electrician is a tradesman, tradesperson specializing in electrical wiring of buildings, transmission lines, stationary machines, and related equipment. Electricians may be employed in the installation of new electrical components or the ...
s, computer programmer
A programmer, computer programmer or coder is an author of computer source code someone with skill in computer programming.
The professional titles ''software developer'' and ''software engineer'' are used for jobs that require a progr ...
s, and other engineers.
Electrical engineering has an intimate relationship with the physical sciences. For instance, the physicist Lord Kelvin
William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin (26 June 182417 December 1907), was a British mathematician, Mathematical physics, mathematical physicist and engineer. Born in Belfast, he was the Professor of Natural Philosophy (Glasgow), professor of Natur ...
played a major role in the engineering of the first transatlantic telegraph cable
Transatlantic telegraph cables were undersea cables running under the Atlantic Ocean for telegraph communications. Telegraphy is a largely obsolete form of communication, and the cables have long since been decommissioned, but telephone and dat ...
. Conversely, the engineer Oliver Heaviside
Oliver Heaviside ( ; 18 May 1850 – 3 February 1925) was an English mathematician and physicist who invented a new technique for solving differential equations (equivalent to the Laplace transform), independently developed vector calculus, an ...
produced major work on the mathematics of transmission on telegraph cables. Electrical engineers are often required on major science projects. For instance, large particle accelerator
A particle accelerator is a machine that uses electromagnetic fields to propel electric charge, charged particles to very high speeds and energies to contain them in well-defined particle beam, beams. Small accelerators are used for fundamental ...
s such as CERN
The European Organization for Nuclear Research, known as CERN (; ; ), is an intergovernmental organization that operates the largest particle physics laboratory in the world. Established in 1954, it is based in Meyrin, western suburb of Gene ...
need electrical engineers to deal with many aspects of the project including the power distribution, the instrumentation, and the manufacture and installation of the superconducting electromagnets.Martini, p. 179
See also
* Barnacle (slang) *Comparison of EDA software
This page is a comparison of electronic design automation (EDA) software which is used today to design the near totality of electronic devices. Modern electronic devices are too complex to be designed without the help of a computer. Electronic dev ...
* Electrical Technologist
*Electronic design automation
Electronic design automation (EDA), also referred to as electronic computer-aided design (ECAD), is a category of software tools for designing Electronics, electronic systems such as integrated circuits and printed circuit boards. The tools wo ...
*Glossary of electrical and electronics engineering
This glossary of electrical and electronics engineering is a list of definitions of terms and concepts related specifically to electrical engineering and electronics engineering. For terms related to engineering in general, see Glossary of engineer ...
* Index of electrical engineering articles
*Information engineering
Information engineering is the engineering discipline that deals with the generation, distribution, analysis, and use of information, data, and knowledge in electrical systems. The field first became identifiable in the early 21st century.
Th ...
*International Electrotechnical Commission
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC; ) is an international standards organization that prepares and publishes international standards for all electrical, electronics, electronic and related technologies. IEC standards cover a va ...
(IEC)
*List of electrical engineers
This is a list of electrical engineers (by no means exhaustive), people who have made notable contributions to electrical engineering or computer engineering.
{, class="wikitable sortable"
, -
! Name !! Contribution(s)
, -
!A
,
, -
, Norman Ab ...
*List of engineering branches
Engineering is the discipline and profession that applies scientific theories, mathematical methods, and empirical evidence to design, create, and analyze technological solutions, balancing technical requirements with concerns or constraints on ...
*List of mechanical, electrical and electronic equipment manufacturing companies by revenue
The following is a list of the world's largest manufacturing companies, ordered by revenue in millions of U.S. dollars according to the Fortune Global 500. Currently the 50 biggest companies by revenue are included.
2022
2020
*Revenue with aster ...
*List of Russian electrical engineers
A list is a set of discrete items of information collected and set forth in some format for utility, entertainment, or other purposes. A list may be memorialized in any number of ways, including existing only in the mind of the list-maker, but ...
* Occupations in electrical/electronics engineering
* Outline of electrical engineering
* Timeline of electrical and electronic engineering
Notes
References
;Bibliography * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Martini, L., "BSCCO-2233 multilayered conductors", in ''Superconducting Materials for High Energy Colliders'', pp. 173–181, World Scientific, 2001 . * * * * * * * *Schmidt, Rüdiger, "The LHC accelerator and its challenges", in Kramer M.; Soler, F.J.P. (eds), ''Large Hadron Collider Phenomenology'', pp. 217–250, CRC Press, 2004 . * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC)
in-depth look at Electrical Engineering – online courses with video lectures.
IEEE Global History Network
A wiki-based site with many resources about the history of IEEE, its members, their professions and electrical and informational technologies and sciences. {{Authority control Electronic engineering Computer engineering Electrical and computer engineering Engineering disciplines